Chemistry quest intermolecular forces
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Goodluck , if you prefer quizlet --> https://quizlet.com/_d6229n?x=1qqt&i=3yyuve
Last updated 10:07 PM on 4/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
If a molecule has an electronegativity difference of 0-0.4, what type of compound is it
nonpolar covalent
2
New cards
If a molecule has a electronegativity difference of 0.4-1.7, what type of compound is it
polar covalent
3
New cards
If a molecule has a electronegativity difference of 1.7-4, what type of compound is it
ionic
4
New cards
N2F4 lewis dot diagram
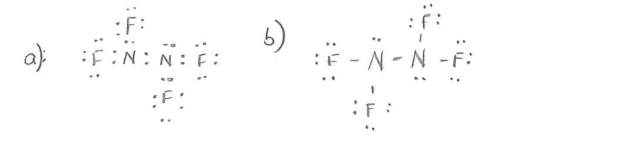
5
New cards
C2H5OH lewis dot diagram
\
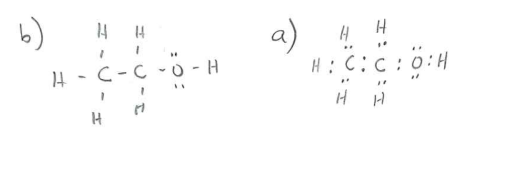
6
New cards
What happens to electrons in a covalent bond
* Electrons are shared between two atoms
\
\
7
New cards
What happens to electrons in a ionic bond
they are transferred
8
New cards
What type of elements is a covalent bond formed betweem
A covalent bond is formed between nonmetal elements.
9
New cards
How do you know which atom should be in the center when drawing lewis diagrams
the least electronegative
10
New cards
Which compound is most liekly to form a compound between each other A.aluminum and oxygen
B. magnesium and iodine
C. sulfur and fluoride
D. potasium and lithium
E. barium and bromine
B. magnesium and iodine
C. sulfur and fluoride
D. potasium and lithium
E. barium and bromine
C.
11
New cards
Which bonds would be considered covalent
1. H-S
2. Al-S
3. N-F
1. H-S
2. Al-S
3. N-F
1 and 3
12
New cards
A double bond consists of how many pairs of shared electrons
2
13
New cards
How can you use electronegativity to predict the bond type?
The greater the difference in electronegativity, the more polar the bond.
14
New cards
Why does a greater difference in electronegativity cause a more polar bond?
A bigger difference in electronegativity means that one atom is able to hog electrons for longer, creating a charge imbalance (partial-charge). The more electronegative atom would be slightly negative and less would be slightly positive
15
New cards
Are inter or intra moleculer forces stronger
Intramolecular forces like ionic and covalent bonds are stronger then intermolecular forces.
16
New cards
What is the order of bond strength
ionic bonds, covalent bonds, hydrogen, dipole-dipole, london dispersion
17
New cards
How strong is a london dispersion force
Weak
18
New cards
What type of molecules use London Dispersion forces?
all molecules
19
New cards
What happens to electrons in a london dispersion force
due to the constant motion of electrons they occasionally end up all on one side of the molecule creating a temporary dipole.
20
New cards
How does size of a molecule relate to the strengh of london forces
Bigger mass= stronger forces
21
New cards
are london dispersion forces temporary or permanent.
\
Temporary. They are caused by the movement of electrons, which creates temporary dipoles in molecules.
Temporary. They are caused by the movement of electrons, which creates temporary dipoles in molecules.
22
New cards
are dipole-dipole forces temporary or permanent
permanent
23
New cards
What causes dipole-dipole forces
A molecule being unbalances. There could be a pair of lone electrons, or the difference in electronegativity is very high between atoms in the molecule.
24
New cards
How does a dipole-dipole affect the interactions between molecules?
A charge inbalnece means that one side of the molecule is slightly positive while the other side is slightly negative. Thus two different molecules are attracted to each other so that the positive side of one molecule is attracted to the negative side of the other.
25
New cards
What are the four elements can be involved in a hydrogen bond
* Nitrogen (N)
* Oxygen (O)
* Fluorine (F)
* Hydrogen (H)
* Oxygen (O)
* Fluorine (F)
* Hydrogen (H)
26
New cards
What is the trend for boiling point
Stronger intermolecular force=higher boiling point
27
New cards
What is the order of boiling point trends between the different bonds, highest to lowest
Ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole, london dispersion.
28
New cards
What do weak dipole-dipole forces result in?
a lower melting point
29
New cards
A hydrogen bond is _________ (stronger/weaker) than a London Dispersion force and (stronger/weaker) than an ionic bond
stronger, stronger
30
New cards
Without London Dispersion Forces most nonpolar compounds would be a_______ at room temperature
gas
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
CRISC - Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control term definition - Part 53
20Updated 1207d ago0.0(0)
CRISC - Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control term definition - Part 53
20Updated 1207d ago0.0(0)