Reproduction Ch. 2
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
In all domestic species, the reproductive tract lies directly beneath the rectum and is separated from it by the _____________
Rectogenital pouch
The female tract is a series of tubes. Each tube is organized in concentric layers as follows: (there are 4). All tubular components of the female reproductive tract has these four layers.
Serosa (outer), muscularis, submucosa, mucosa (inner)
Which layer of the female tract is a single-cell layer of squamous cells?
Serosa
Which layer of the female repro tract is made up of two layers of smooth muscle?
Muscularis
The outer layer of the muscularis is _______, the inner layer is _______.
Longitudinal, circular
The purpose of the muscularis is _______. This aides in the transport of secretory products, gametes, and early embryos. It is also important in the expulsion of the fetus and fetal membranes during parturition
contraction
This layer of the female repro tract houses the blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics.
Submucosa
This layer of the female repro tract is the inner most layer that is secretory.
mucosa
(T or F) Structures on the ovary undergo constant change
True
Outer connective tissue covering the ovaries
Tunica Albuginea
The ______ houses the vasculature, nerves, and lymphatics of the ovary. It is relatively dense. The ____ houses the oocytes and eventually the CL.
Medulla, cortex
Another name for the female gonads
Ovaries
What are the three sections of the oviducts?
Infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus
(T or F) The infundibulum connects to the ovary to catch the oocytes
False, they are not connected.
The muscularis is also known as the ________
Myometrium
What is the role of the myometrium?
The myometrium is important for contractility. This allows for transport of secretory products, gametes (ova and sperm), early embryos, and the explusion of fetus and fetal membranes during parturition
The ________ fuses to form the broad ligament, which is a connective sheet that suspends the female reproductive tract.
Peritoneum
Lining of the abdominal cavity
Peritoneum
The uterus produces ________, which lyses or kills the CL. Therefore, _______ production stops and cycling starts again.
Prostaglandin, progesterone
Describe ovary structure in the mare
The medulla is on the outside, and the cortex is on the inside. The follicles push inward rather than protruding.
Where does ovulation occur in the mare?
Ovulation fossa
Follicular growth is called…
Folliculogenesis
Describe the primordial follicle
This is the most immature follicle and is housed in the follicle. It is surrounded by a single layer of squamous cells.
The cortex is the outer portion of the ovary and contains the _____.
Follicles
The medulla is the inner portion of the ovary and contains the ______.
Blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics
Describe the primary follicle
These follicles have a single layer of cuboidal cells and are producing low levels of estradiol. They will either develop into secondary follicles or die.
Describe the secondary follicle
This follicle has 2 or more layers of follicle cells. The oocyte is surrounded by the Zona Pellucida
Describe the Antral follicle
Contains fluid filled antrum, produces more estradiol, and has 3 cell layers.
What are the three cell layers of the pre-ovulatory follicle
Granulosa, theca interna, and theca externa
The dominant preovulatory follicle is called the _______.
Graafin follicle
Order the three cell layers of the pre-ovulatory follicle from outermost to innermost
Theca externa, theca interna, granulosal
The cells produce androgens
Theca interna
These cells produce estrogen, inhibin, and follicular fluid. They also have FSH receptors and control oocyte maturation.
Granulosal
Structure on the ovary immediately after ovulation
Corpus hemorrhagicum
After the formation of the CH, theca interna cells and granulosal cells differentiate into luteal cells to form the…. These luteal cells will them produce progesterone
corpus luteum
Funnel shaped structure to catch oocyte
Infundibulum
Velvety, finger-like projections that increase surface area and chance of catching oocyte.
Fimbriae
Site of fertilization
Ampullary-isthmic junction
Point of juncture between the isthmus and uterus
Uterotubal junction
When ________ is high, the UTJ kinks like a garden hose to block embryos from dropping into the uterine horn. Once _______ decreases the UTJ straightens out and embryos can move into the uterine horn. (Cow)
Estradiol
The _____ of the oviduct secretes substances that nurture floating oocytes, help sustain spermatozoa function, and may also facilitate fertilization.
Mucosa
Primary functions of the Uterus (5)
Sperm transport, luteolysis and control of cyclicity, environment for preattachment of embryo, maternal contribution to the placenta, expulsion of the fetus and fetal placenta.
This type of uterus has 2 cervixes, each horn is a separate compartment, and there is one vaginal opening. (Marsupials and rabbits have these)
Duplex
This type of uterus has 2 uterine horns, a small uterine body, and a single cervical canal. (Mare, cow, bitch, queen, sow)
Bicornuate uterus
The muscularis is also known as the …
Myometrium
The uterus has 4 layers, what are they?
Serosa, muscularis, mucosa, and submucosa
Describe the muscularis
Two layers of smooth muscle, the inner is circular and the outer is longitudinal. These smooth muscle layers help with contraction. It is important for sperm transport, and expulsion of the fetus.
When progesterone is high, the muscularis is (less/more) active. When estrogen is high, the muscularis is (less/more) active. Except in mares.
less, more
Why would you want the muscularis to be inactive when progesterone is high?
Progesterone is high when there is a CL, meaning a follicle has ovulated, and there could be an embryo. Therefore, you don’t want contractions when there is an embryo.
Mucosa + submucosa = ??
Endometrium
Describe the function of the mucosa and submucosa
They form temporary glands that secrete substances which enhance embryonic development, sperm viability, sperm storage in the bitch, and provide nutrients for the embryo.
Do the glands in the endometrium grow under the control or progesterone or estradiol?
Progesterone
What is the serosa/perimetrium?
Thin and almost transparent layer covering the uterus.
The endometrium also produces __________ which causes regression of the CL if the animal is not pregnant.
Prostaglandin F2Alpha
______ are protuberances on the surface of the endometrium which will give rise to the maternal portion of the placenta if attachment of the embryo occurs. (List the two species that have this as well)
Caruncles, cow and ewe
These two species have many endometrial folds.
sow and mare
What does a queen have that will notify you she has had babies before?
Placental scars, which are where placental attachment has occurred.
The uterus is the organ of ______.
pregnancy
What are the three main functions of the cervix?
Lubrication, acts as a flushing system, and as a barrier during pregnancy.
Mucus in the cervix _______ when estradiol is high. (Increases/decreases)
Increases
The only part of the female reproductive tract that is not smooth muscle but rather cartilage.
Cervix
The _____ and the _____ have distinct, well-developed cervical rings.
Cow, ewe
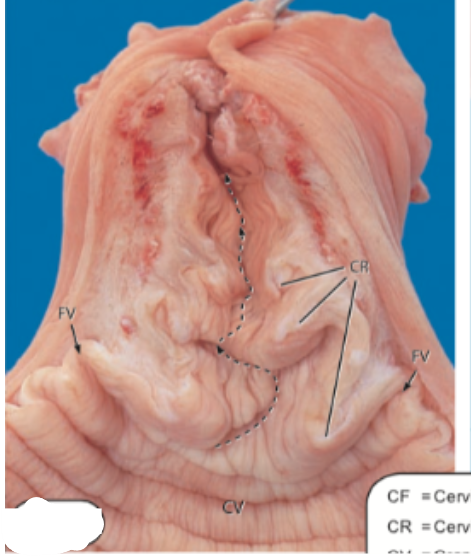
This image is of the _____ cervix.
Cow
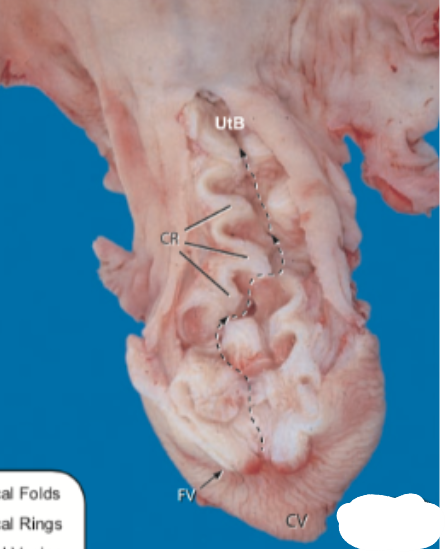
This image is of the _____ cervix.
ewe
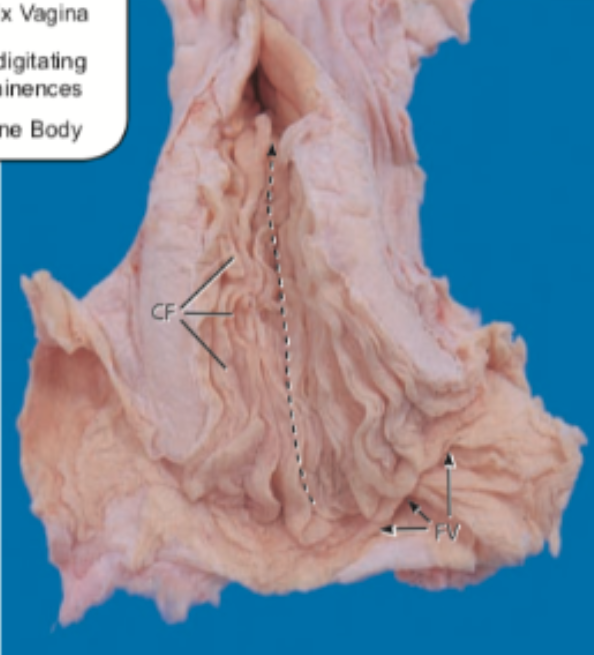
This image is of the ____ cervix.
Sow. Only species in this class where the penis is locked into the cervix and ejaculates into the cervix.
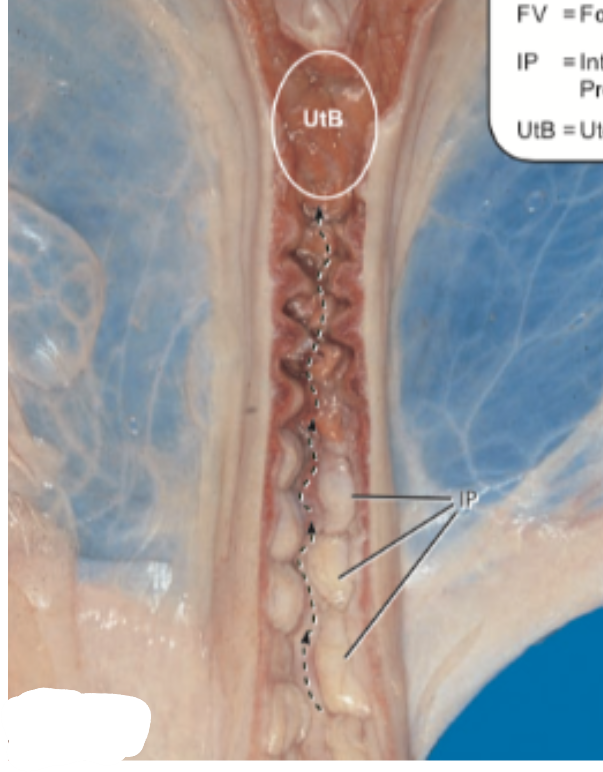
This image is of the _____ cervix.
Mare. Has longitudinal folds
Compare Different types of mucus, during different times, what hormone is controlling them, what they do
Cervical mucus during gestation serves to isolate and protect the pregnancy. It is very viscous and under progesterone’s control.
Cervical mucus during estrus is long and stringy and is used to lubricate the vagina and flush foreign materials out. It is under the control of Estradiol.
The copulatory organ. Also the site of expulsion of urine.
vagina
What is the order of the female repro tract starting at vulva and ending at oviduct?
Vulva, vagina, cervix, uterus, oviduct
There are two regions of the mucosal epithelium in the vagina. Describe them
The cranial region has columnar cells and is highly secretive. The caudual region is stratified squamous epithelium and has secretions that change with hormones.
External portion of the female repro tract
Vulva
Area surrounding anus and vulva
Perineum