Science 2023
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Please take all of these definitions with a grain of salt. Genetics: 1 to 3
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
Allele
Alternate forms of a gene. In most humans, we have two alleles of each gene (one inherened from each paren) which occupy the same relative position on homologous chromosomes
2
New cards
Autosomal chromosomes
Chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes
3
New cards
Base pair
Two complementary DNA nucleotide bases (A,T,C,G) that pair together to form a step of the DNA ladder
4
New cards
Chromosomes
A thread like structure made of DNA. We have 46 chromosomes and 23 pairs of chromosomes
5
New cards
Cloning
A process of asexually reproducing genetically identical genes, cells or organisms from a single parent
6
New cards
Co-dominance
An inheritance pattern where both alleles present are expressed
7
New cards
Diploid
Having two sets of chromosomes (2N)
8
New cards
DNA replication
The process where the DNA makes an identical copy of itself in preparation for cell division
9
New cards
Dominant allele
The gene which is expressed over the recessive gene in a heterozygous condition
10
New cards
Gene
a unit of heredity which is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring. Each gene is a nucleotide sequence on the DNA that codes for a polypedtide
11
New cards
Gene therapy
A new technology where genetic engineering techiques are used in the treatment of a genetic disorder or chronic disease
12
New cards
Genotoype
The genetic make up of cells in an organism
13
New cards
Haploid
Having one set of chromosomes which are unpaired (n). Gamates are haploid
14
New cards
Hereditary
Also called inheritance, its the passing on of traits from the parents to their offspring
15
New cards
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a particle gene in a diploid cell
16
New cards
Homologous
Two similar chromosomes, one paternal and one maternal in origin. It is the chromosome pairs that are matching.
17
New cards
Homozygous
Having identical alleles of a particular gene in a diploid cell
18
New cards
Independent assortment
random seperation of pairs of chromosomes during meiosis, giving different traits an equal opportunity of passing into a gamete. (during meiosis 4 different daughter cells are produced)
19
New cards
Karyotype
An organised, visual representation of the profile of an organisms chromosomes organised from biggest to smallest
20
New cards
Mitosis
a form of cell division that occurs during the growth and repair of cells, and also during asexual reproduction, when identical copies of cells need to be made. The parent cell divides into 2 identical daughter cells with diploid (2n) chromosomes
21
New cards
Meiosis
the process by which animals and plants produce gametes (sex cells) for sexual reproduction. The parent cell divides into 4 different daughter cells with haploid (n) chromosomes in each. The daughter cells produced are gametes. The different daughter cells allow for genetic variety
22
New cards
mRNA
It is a messanger made in the nucleus that carries instructions to make proteins.
23
New cards
Mutagen
A permanent change in the genetic information of an organism
24
New cards
Mutation
A permanent change in the genetic information of an organism
25
New cards
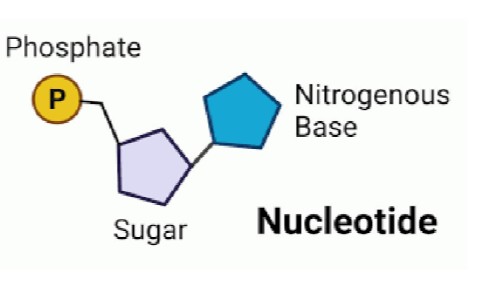
Nucleotide
A building block of DNA. This includes sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous base
26
New cards
Nucleotide/nitrogenous bases
Include Thymine, Adenine, Cytosine and Guanine
27
New cards
RNA
ribonucleic acid, a nucleic acid present in all living cells. Its principal role is to act as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins, although in some viruses RNA rather than DNA carries the genetic information. It is different to DNA as RNA’s sugar ring is made of ribose while DNA’s is made of deoxyribose
28
New cards
Selective breeding
involves selecting parents that have characteristics of interest in the hope that their offspring inherit those desirable characteristics.
29
New cards
Traits
a specific characteristic of an individual. Traits can be determined by genes, environmental factors or by a combination of both. Traits can be qualitative (such as eye color) or quantitative (such as height or blood pressure).
30
New cards
Phenotype
The physical make up of an organism. The geneotype that is expressed.
31
New cards
Polypeptide
A single chain of animo acids joined together by peptide bonds
32
New cards
Proteins
A molecule consisting of one or more polypetide chain bounded together
33
New cards
Recessive allele
A form of a gene that is only expressed in the homozyous condition
34
New cards
tRNA
is a small RNA molecule that plays a key role in protein synthesis. Transfer RNA serves as a link (or adaptor) between the messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule and the growing chain of amino acids that make up a protein.
35
New cards
Variation
Genetic variation is the presence of differences in sequences of genes between individual organisms of a species. It enables natural selection, one of the primary forces driving the evolution of life.