Art History Midterm 1
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms

Hall of Bulls - prehistory
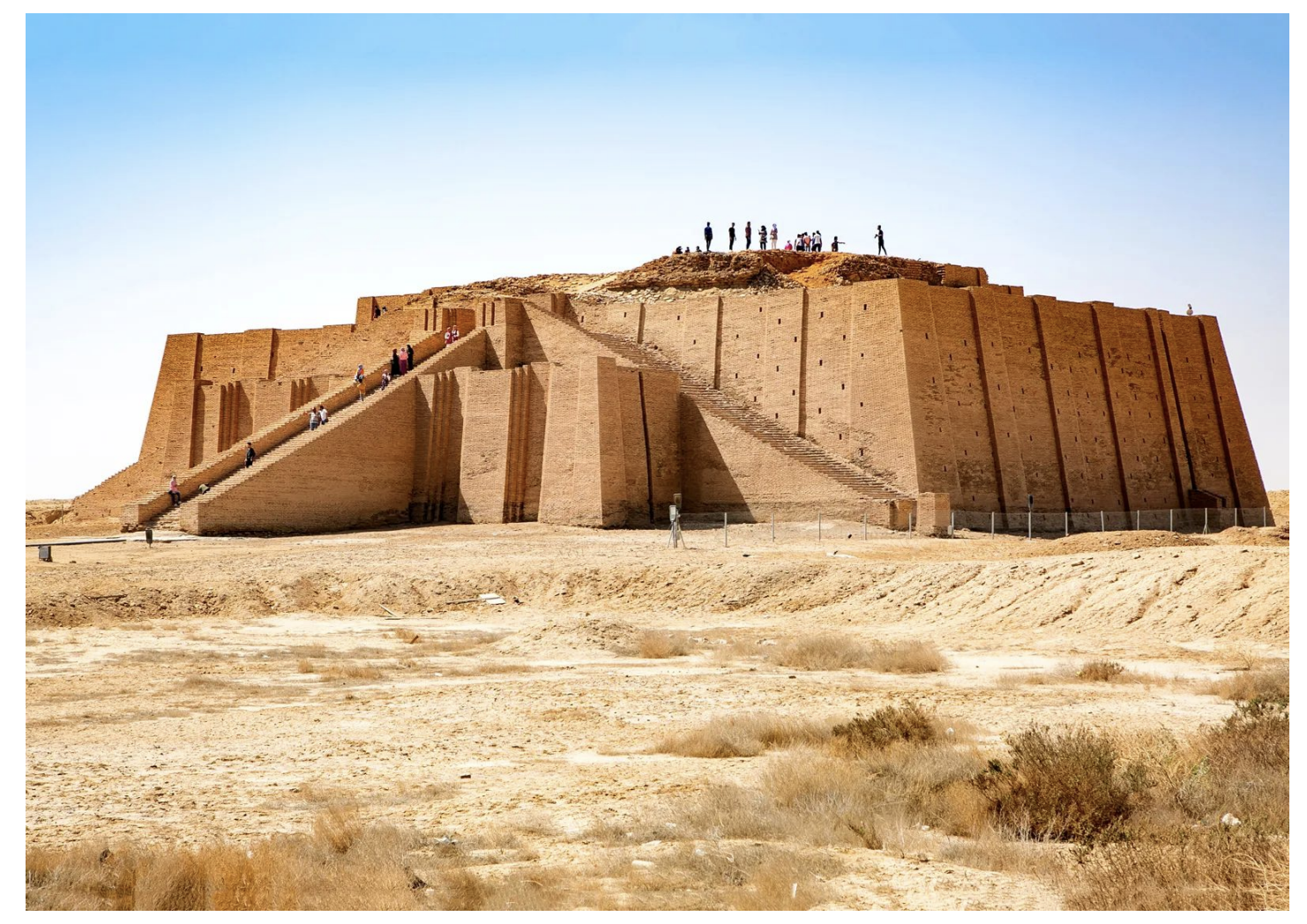

Ziggurat, Ur - Ancient Near East, Sumer
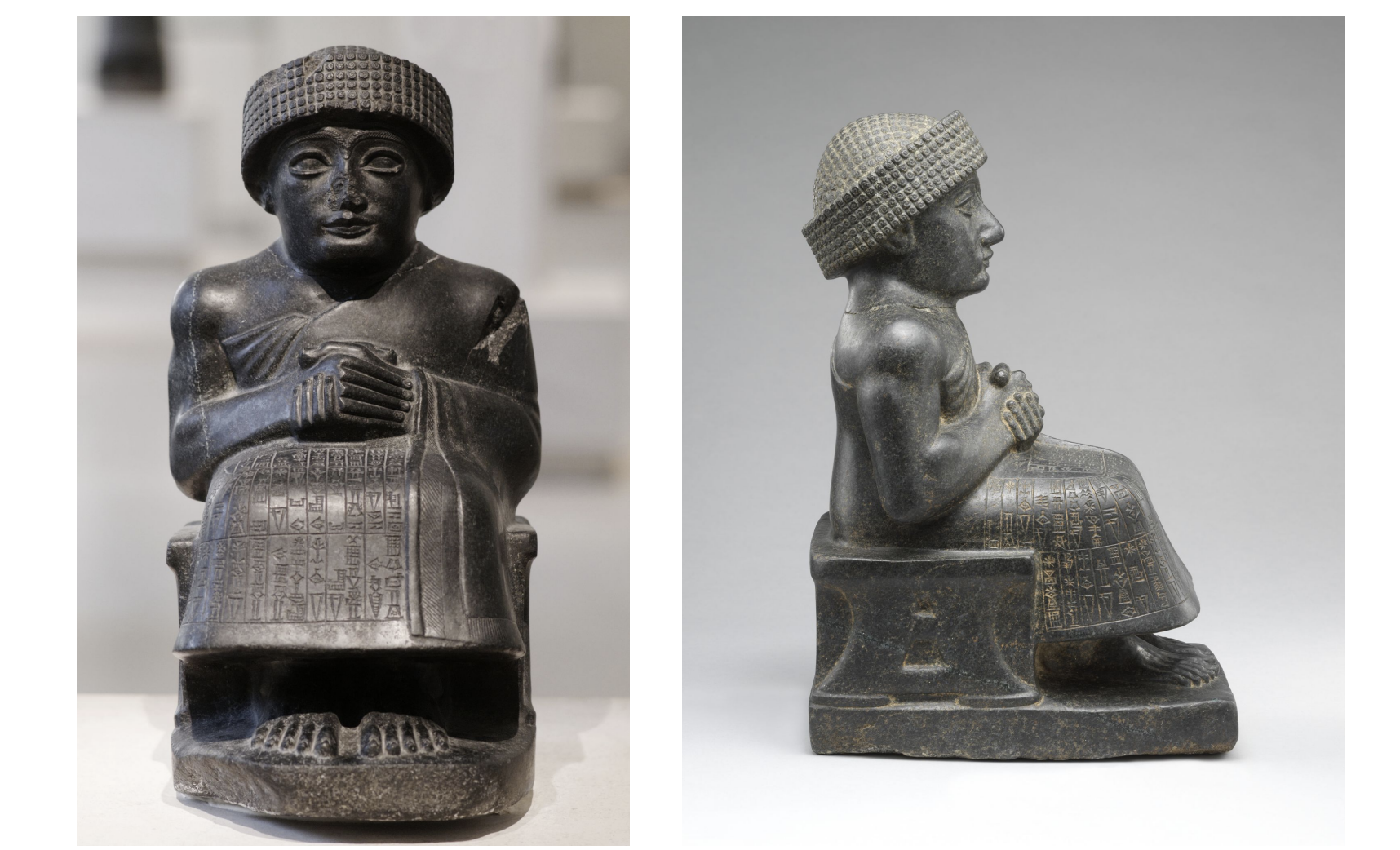

Statues of Gudea - Ancient Near East, Sumer

Victory Stele of Eannatum (Stele of Vultures) - Ancient Near East, Sumer
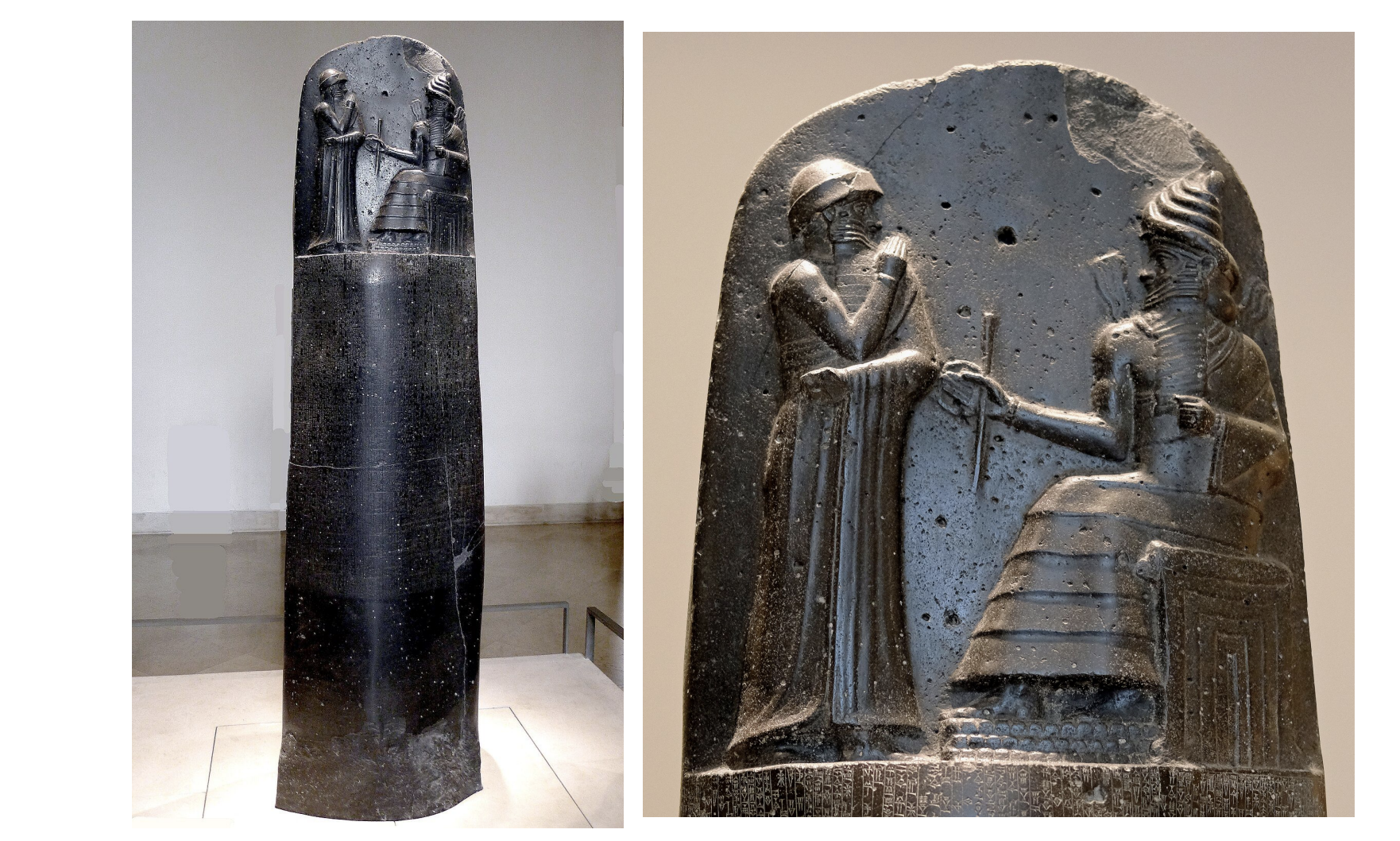

Stele with law code of Hammurabi - Ancient Near East, Babylon
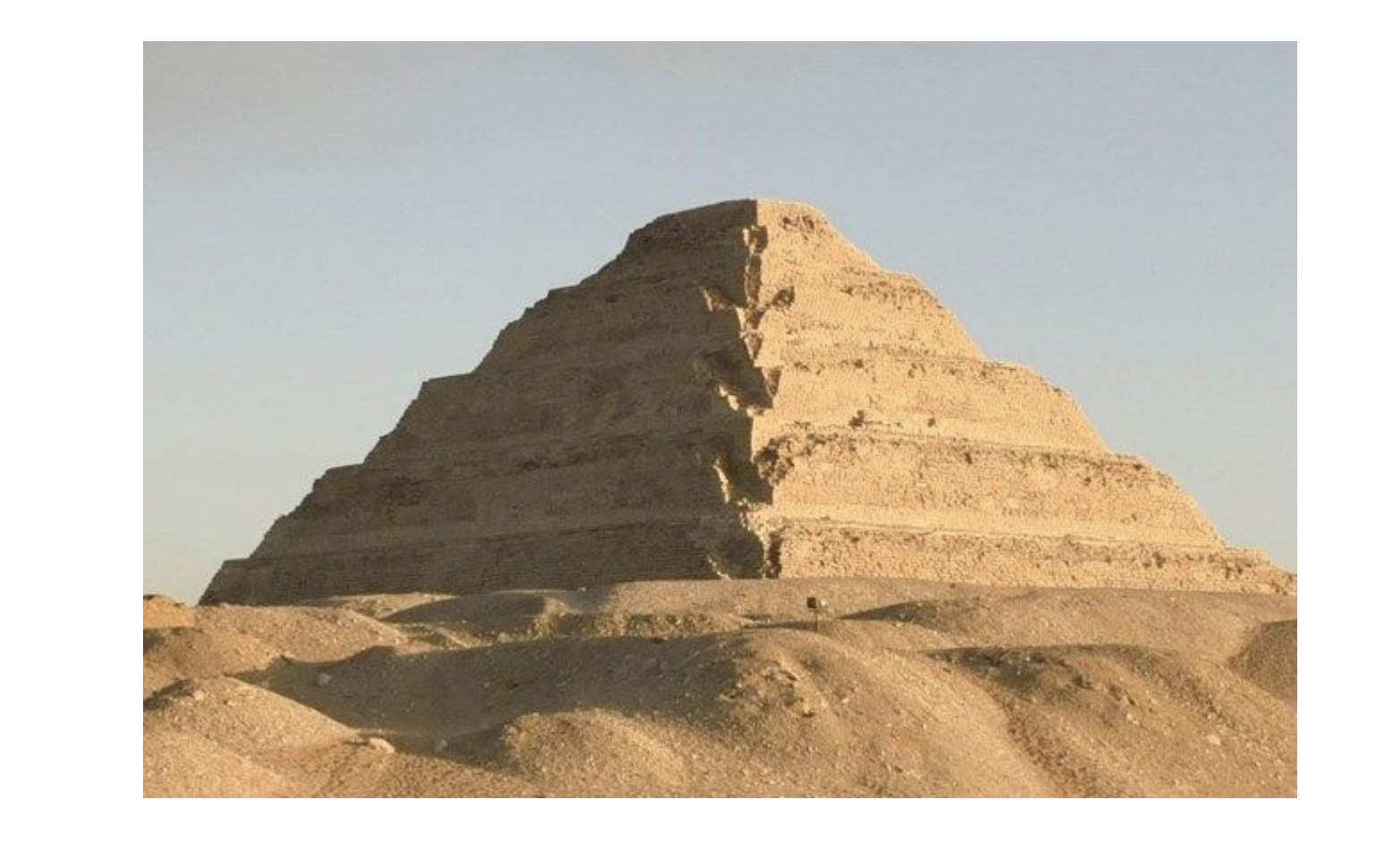

stepped pyramid - funerary complex of Djoser, by Imhotep, Egypt, Saqqara
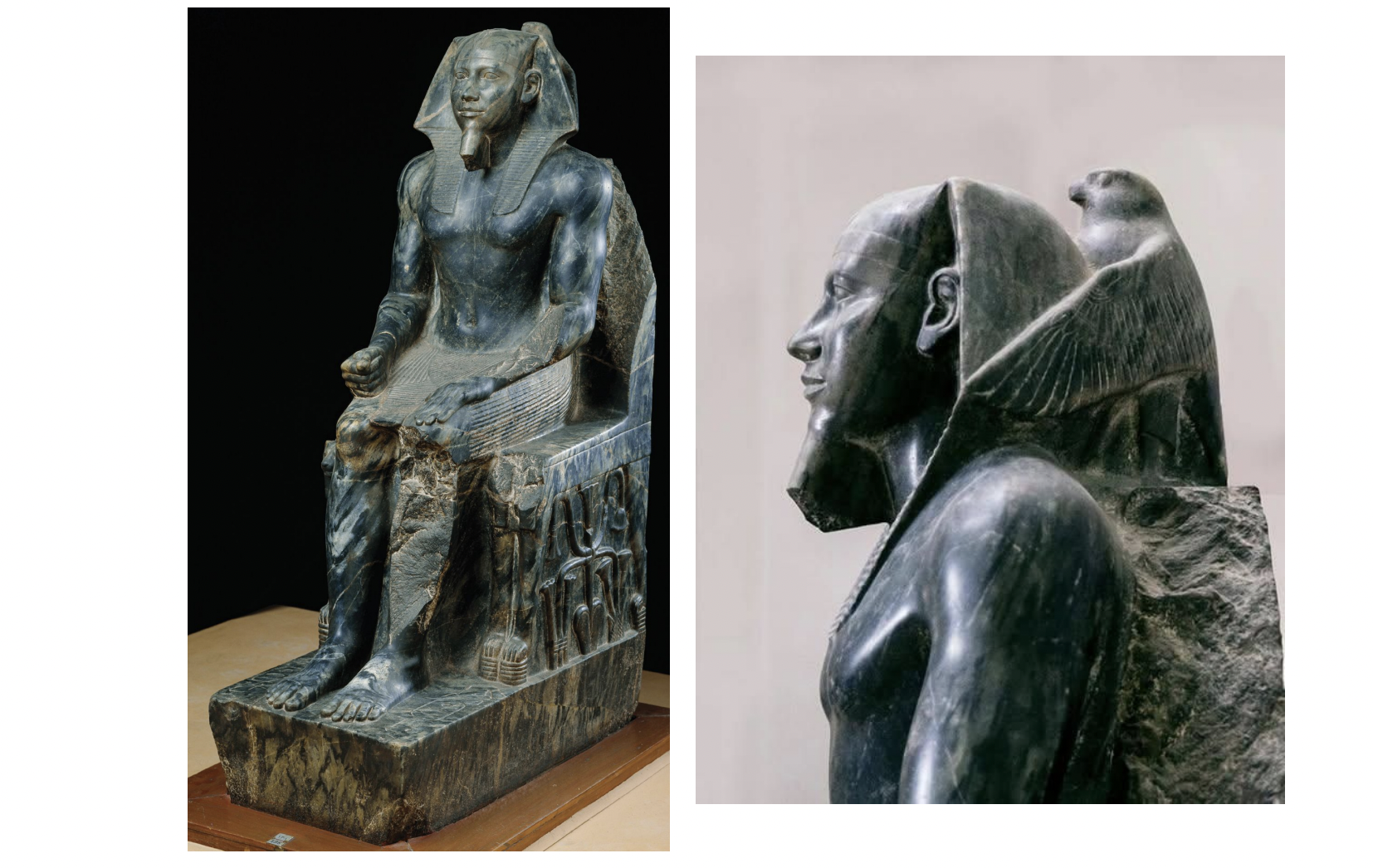

khafre enthroned, gizeh, egypt
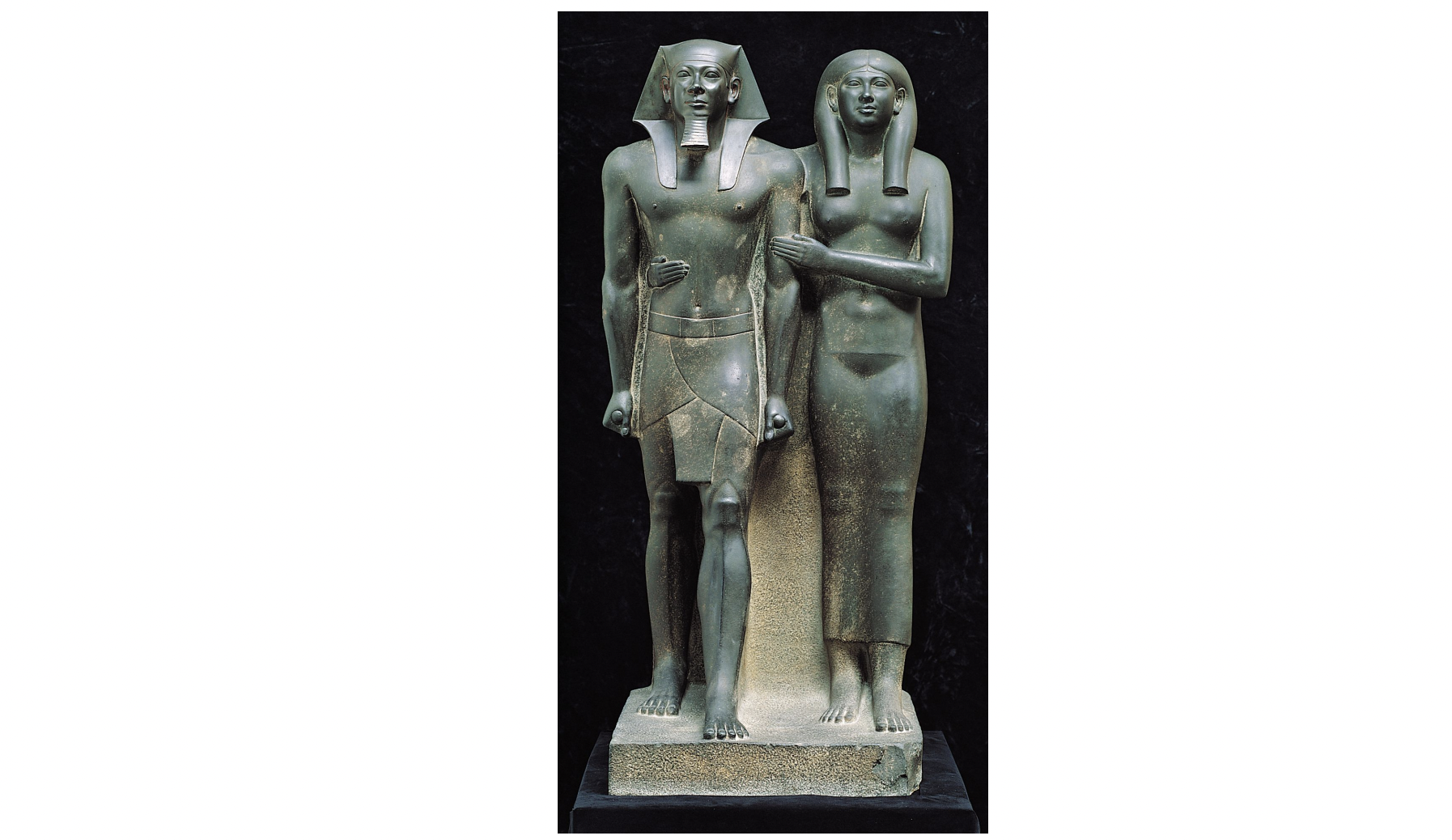

menkaure and khamerernebty, gizeh, egypt

ti watching a hippopotamus hunt, saqqara, egypt

akhenaton, karnak, egypt

akhenaton, nefertiti, and three daughters, tell el-amarna, egypt

last judgement of hu-nefer, egypt
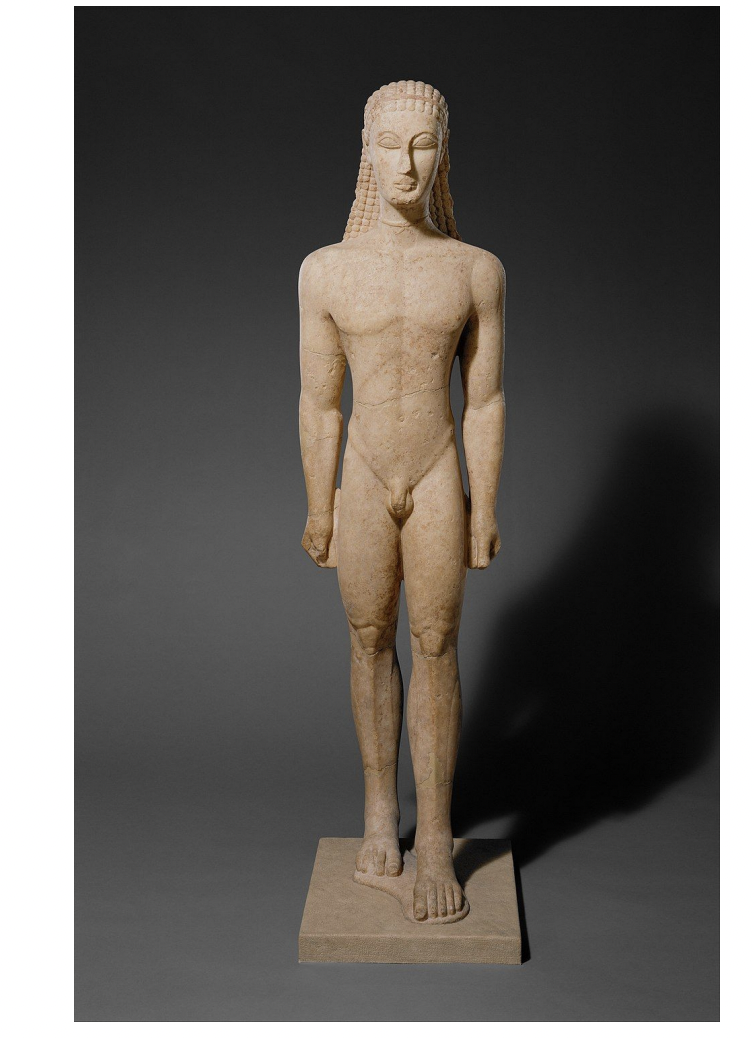

kouros, greece, archaic period
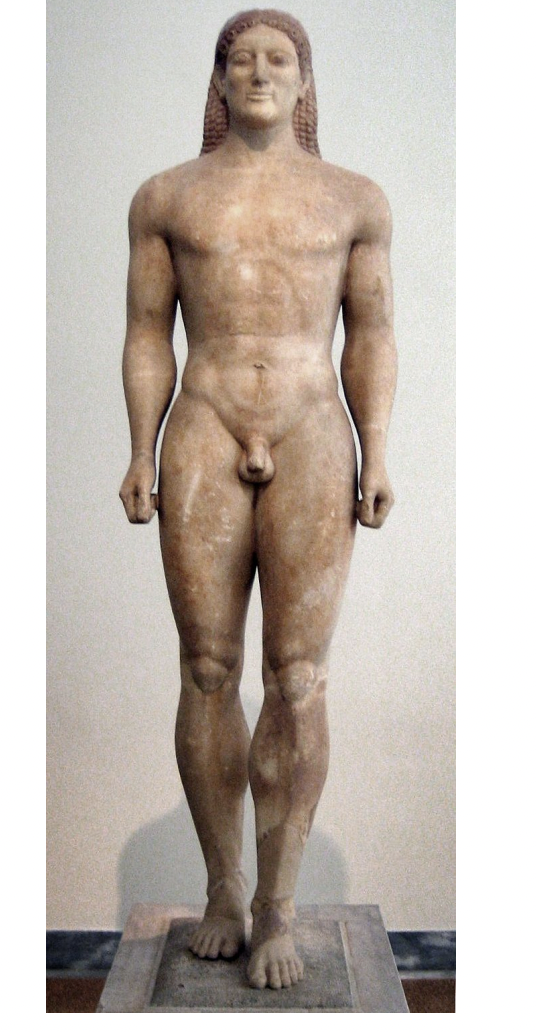
kouros, from anavysos, greece, archaic period

kore, from acropolis, greece, archaic period
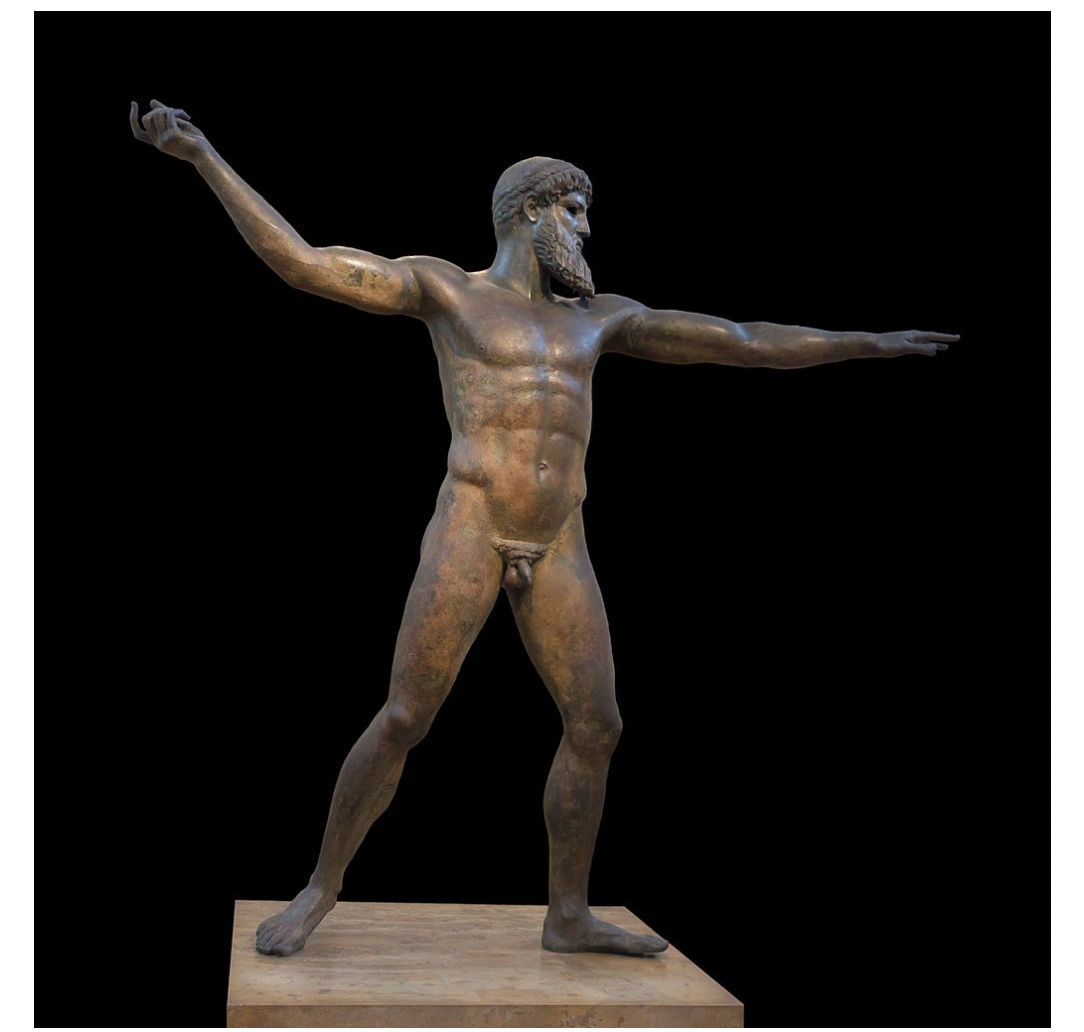

zeus (or poseidon?) from the sea off Cape Artemision, greece classical period
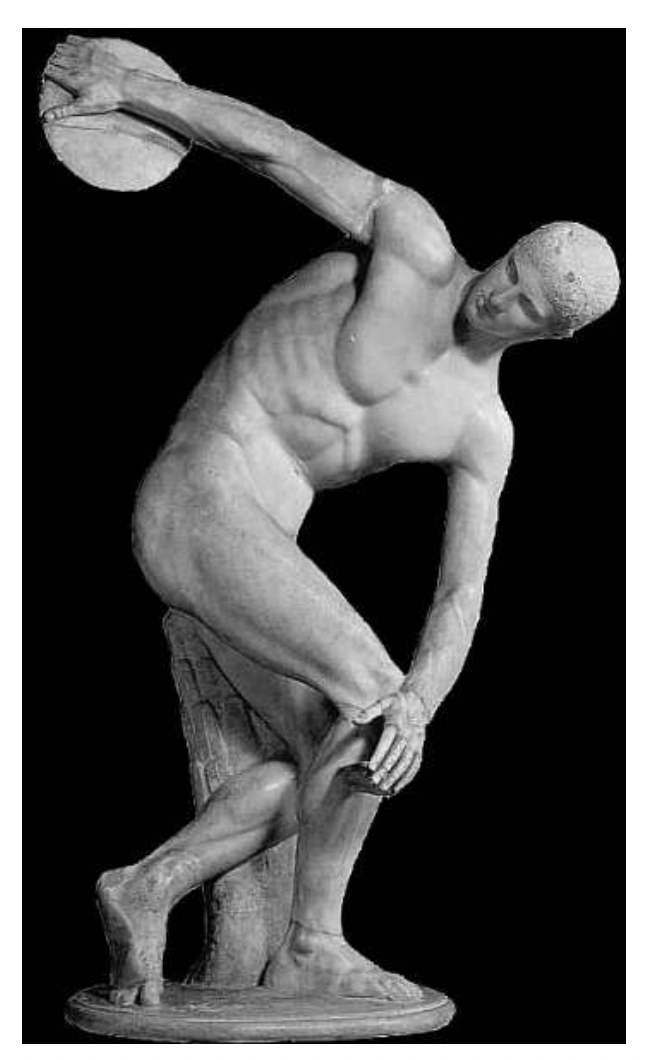

discobolos by myron, greece classical period
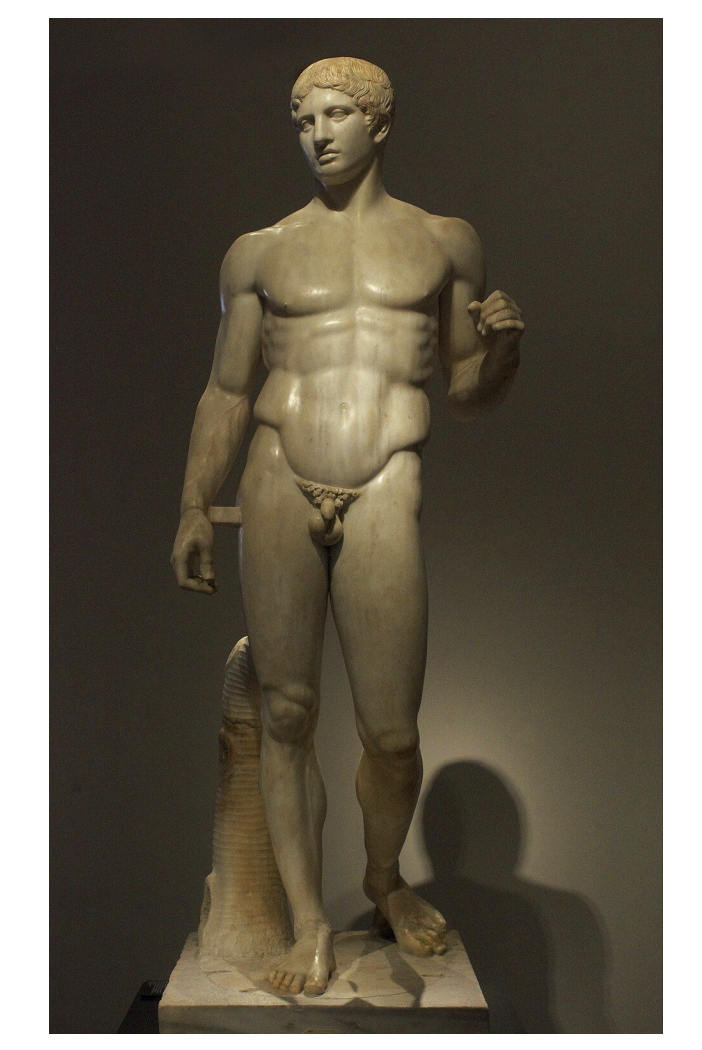

doryphoros (spear bearer) by polykleitos, greece classical period
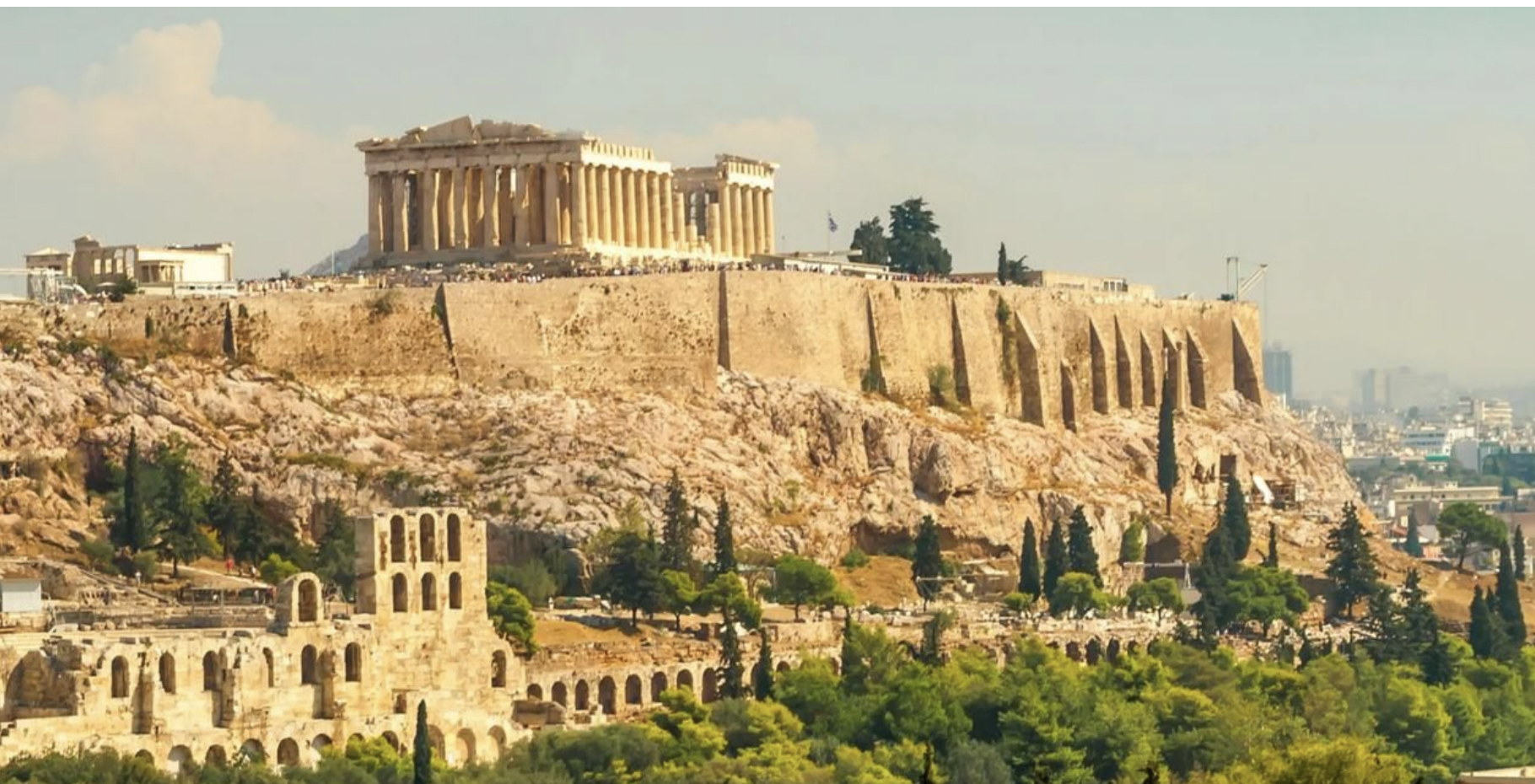

athenian acropolis, rebuilt after persian sack of 480 BCE, greece classical period
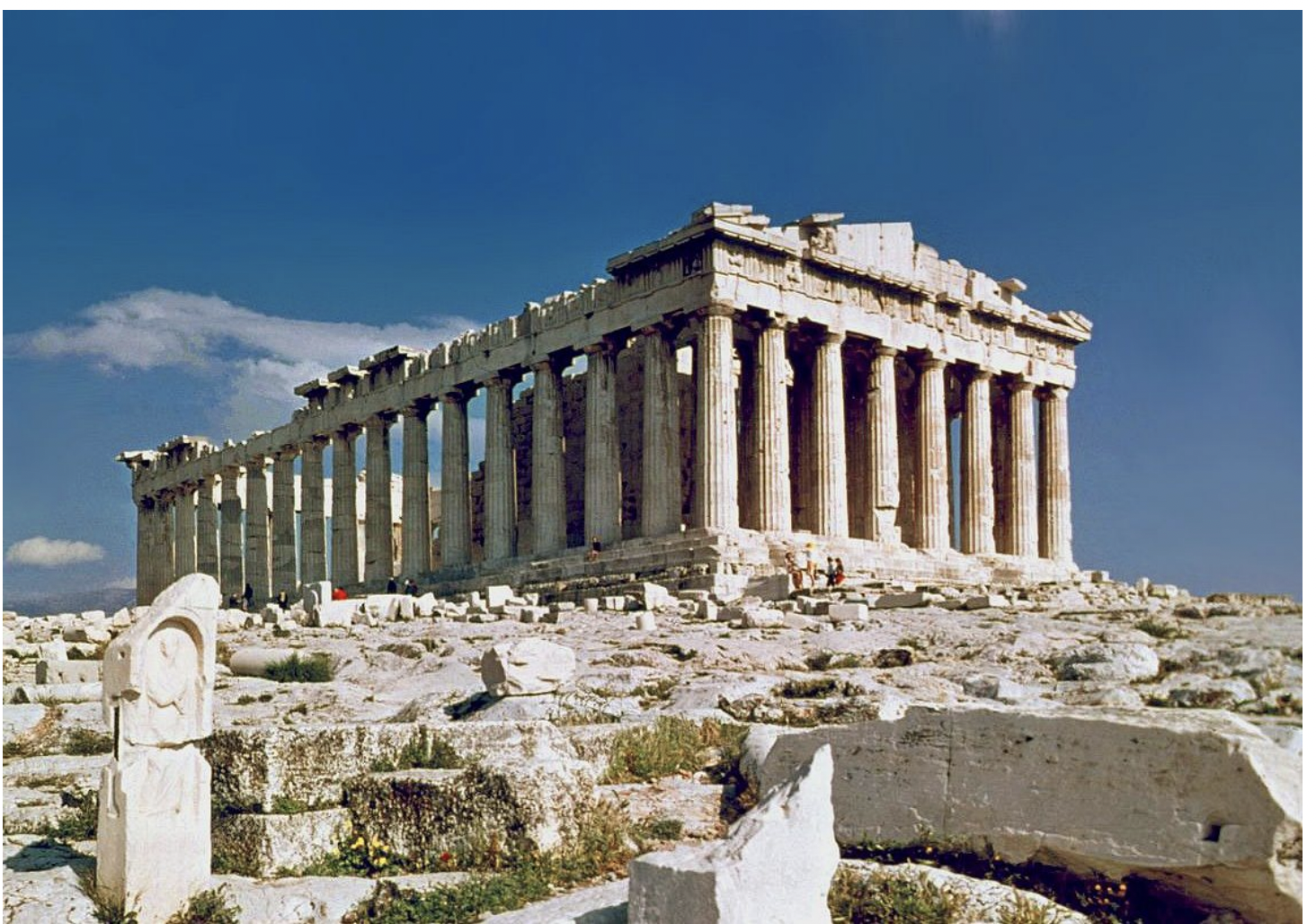

parthenon, greece classical period
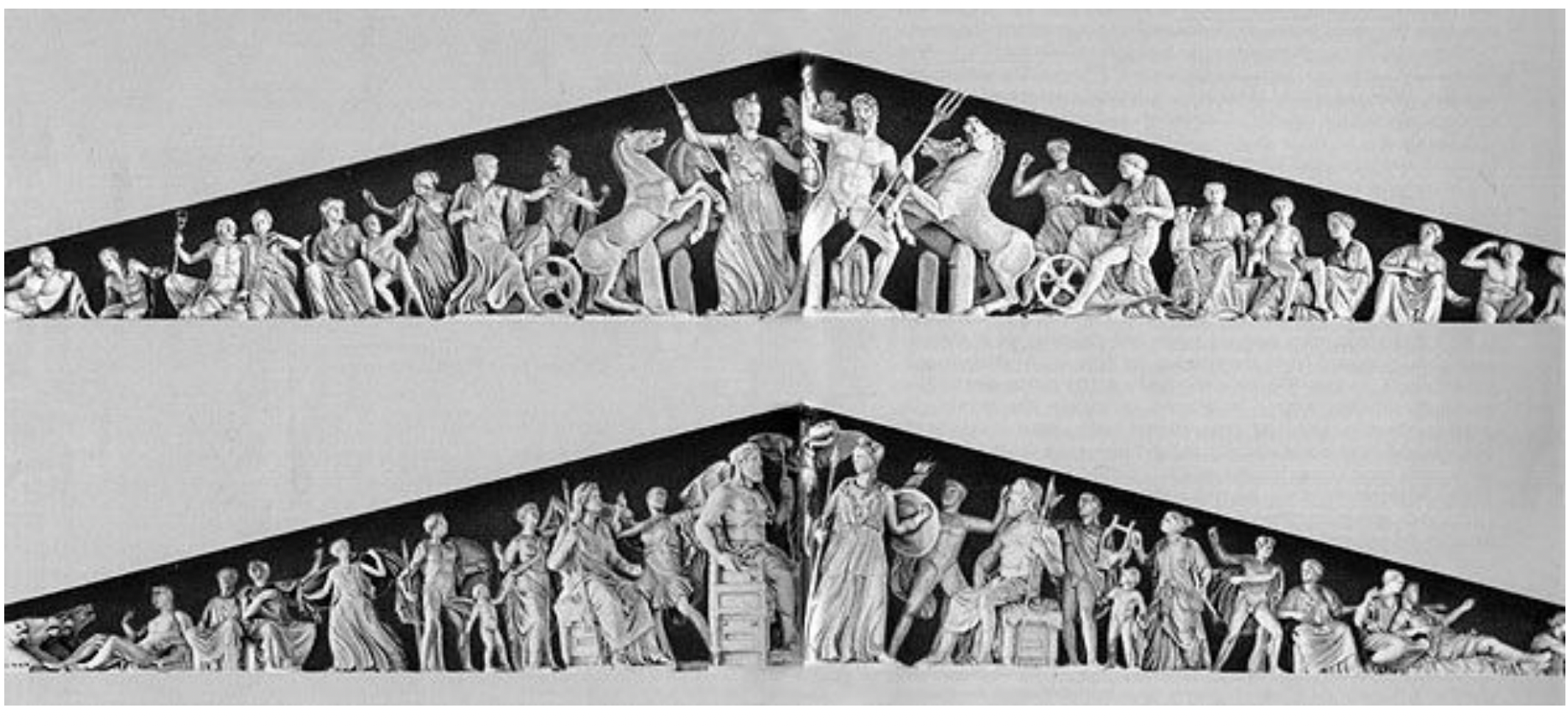

sculptures: pediments of the parthenon, greece classical period
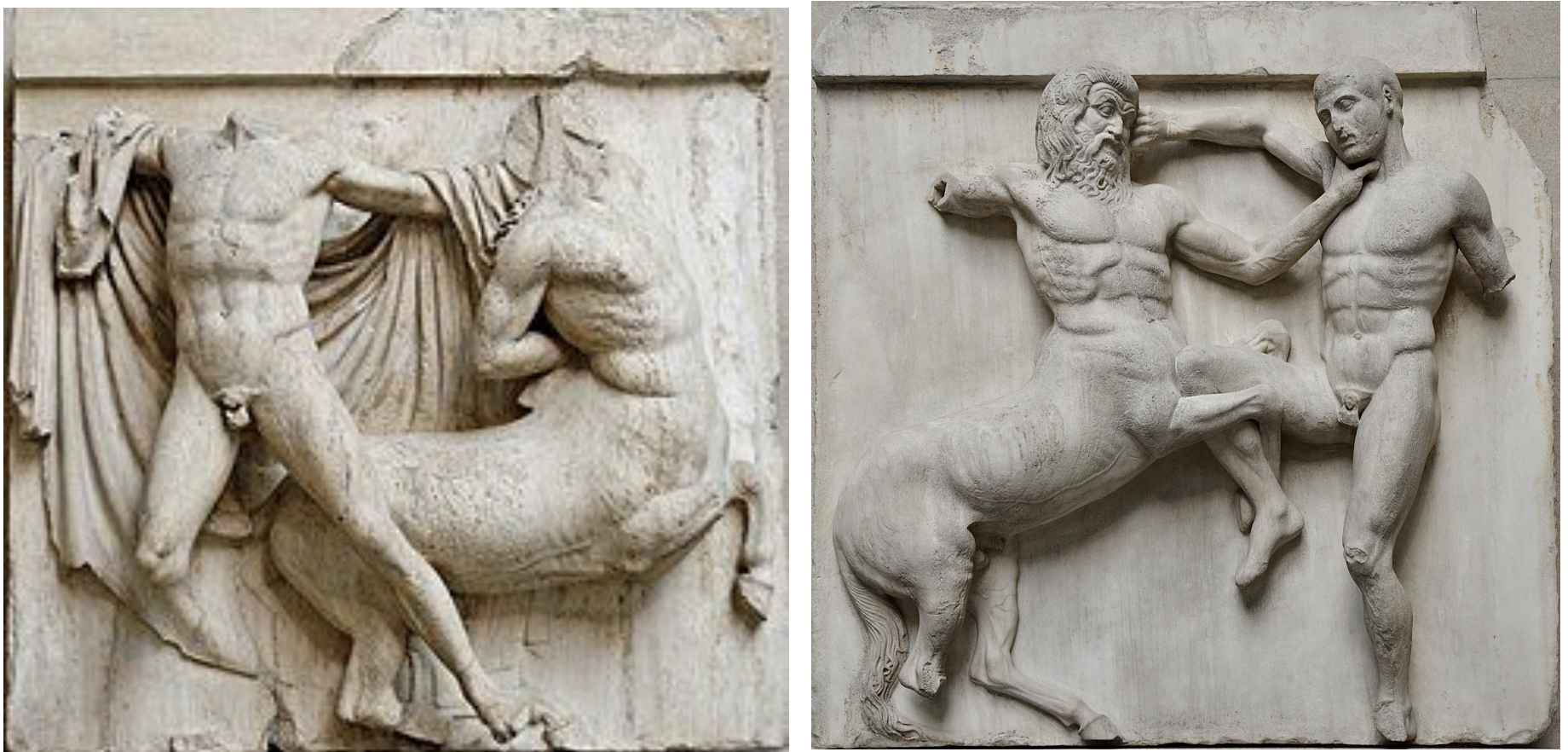
metopes: lapiths vs centaurs (on the parthenon), greece classical period
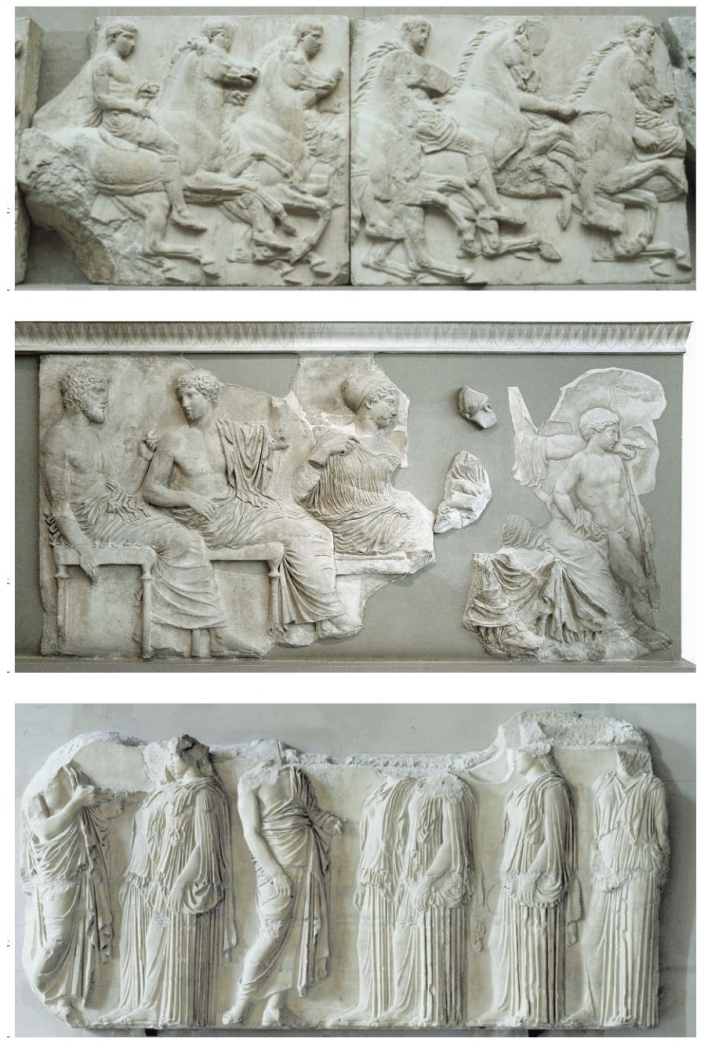

frieze: panathenaic festival procession (on the parthenon), greece classical period
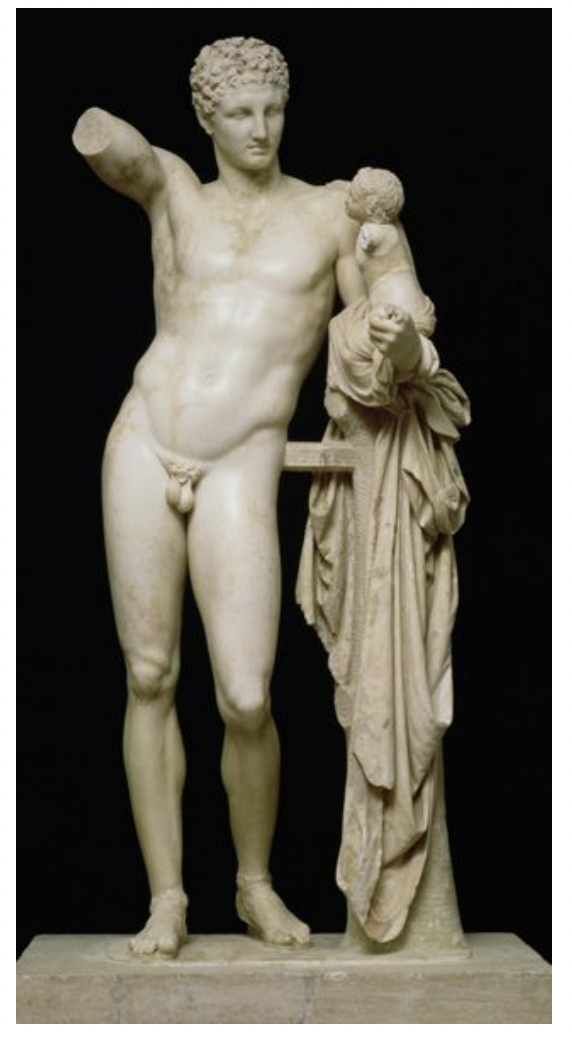

hermes and the infant dionysos, praxiteles, greece late classical period
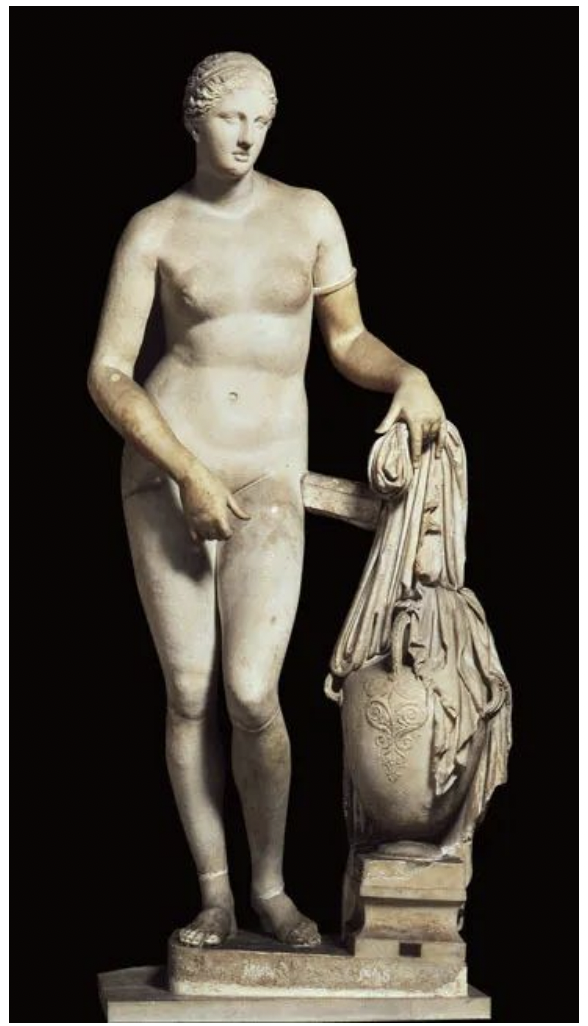

aphrodite of knidos by praxiteles, greece late classical period
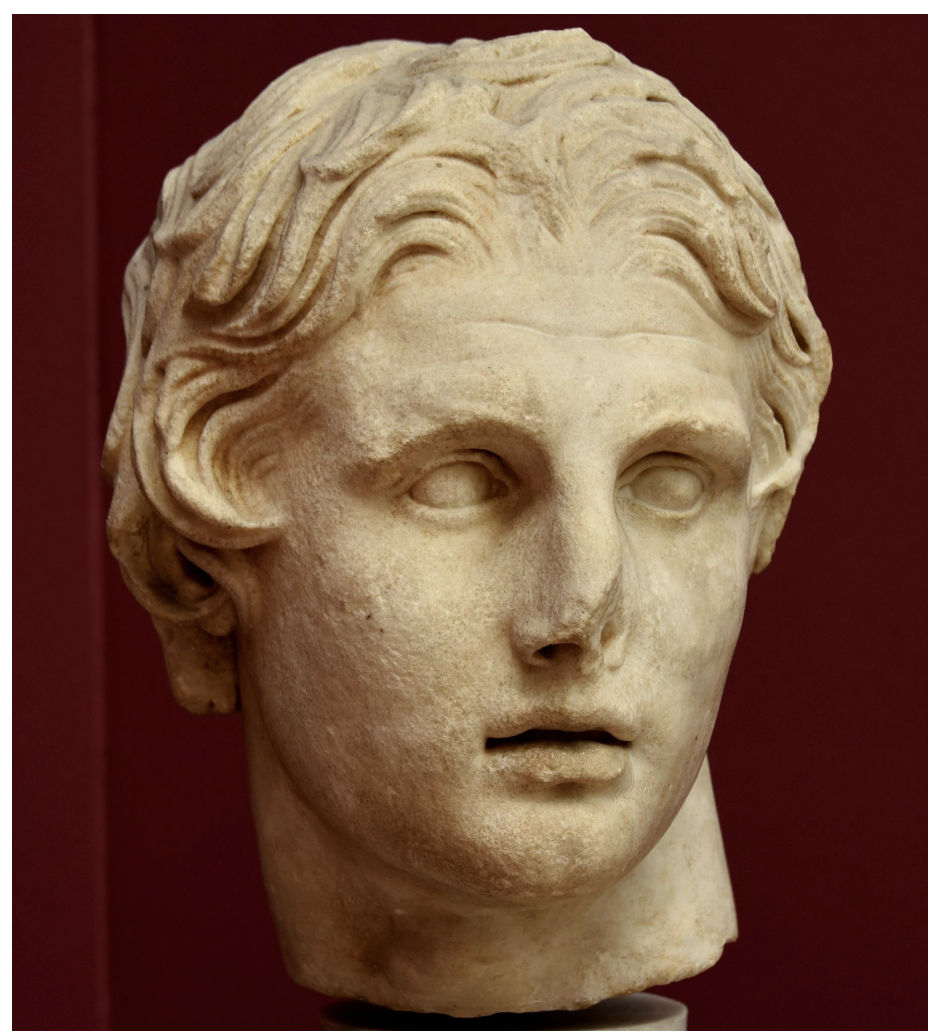

portrait of alexander the great, greece late classical period
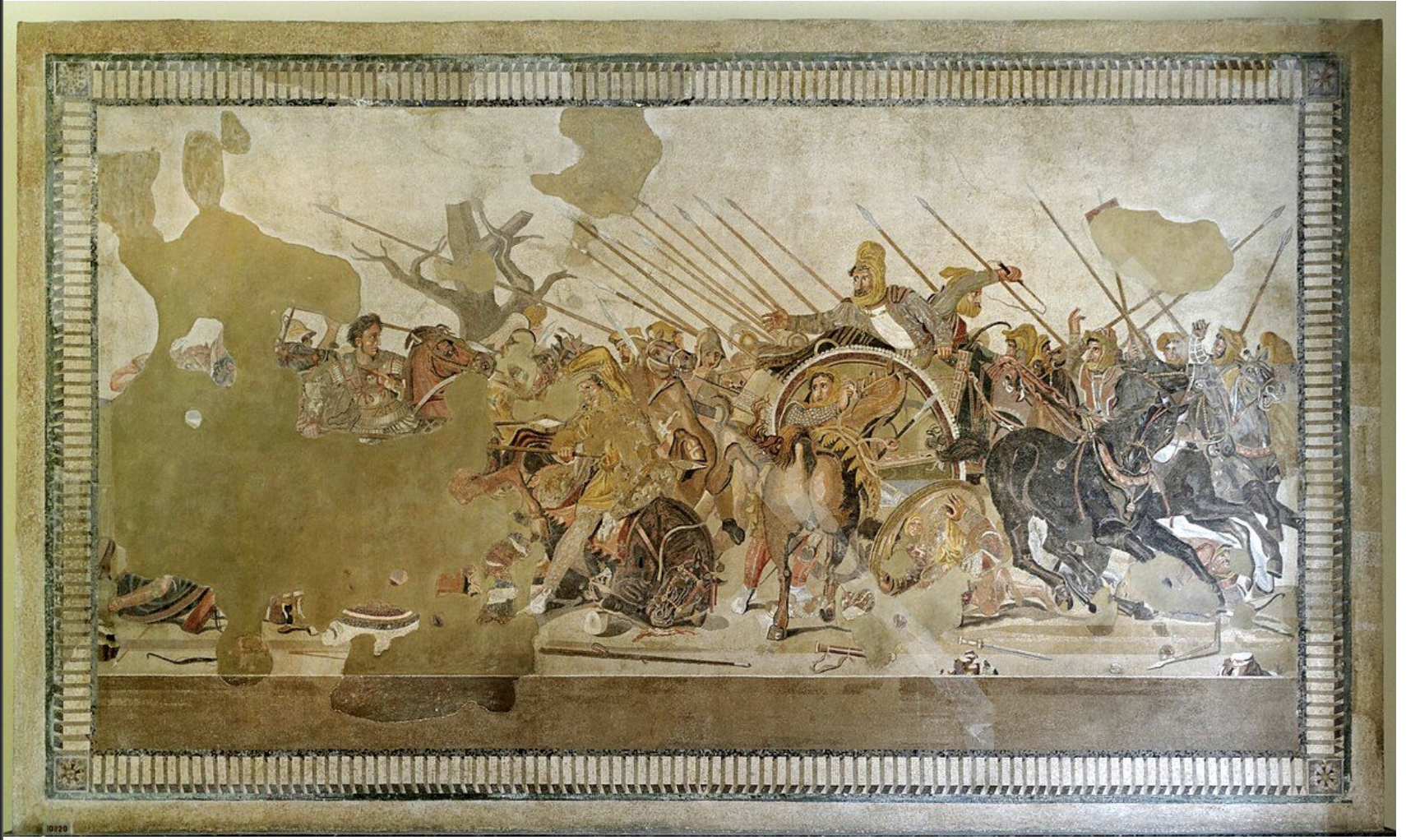

battle of issus (alexander mosaic), pompeii, greece late classical period
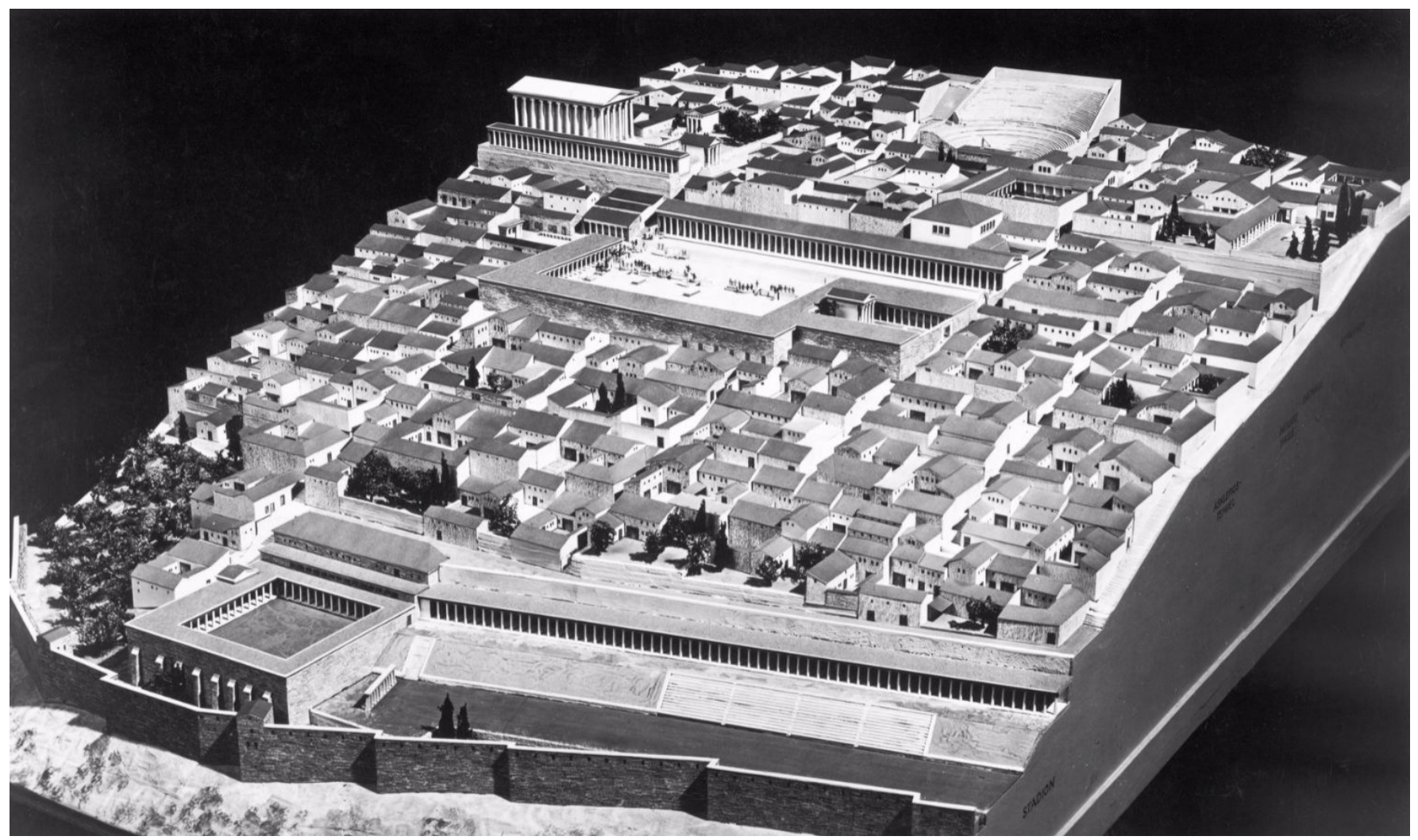

priene, 4th BCE restored view, greece the hellenistic period
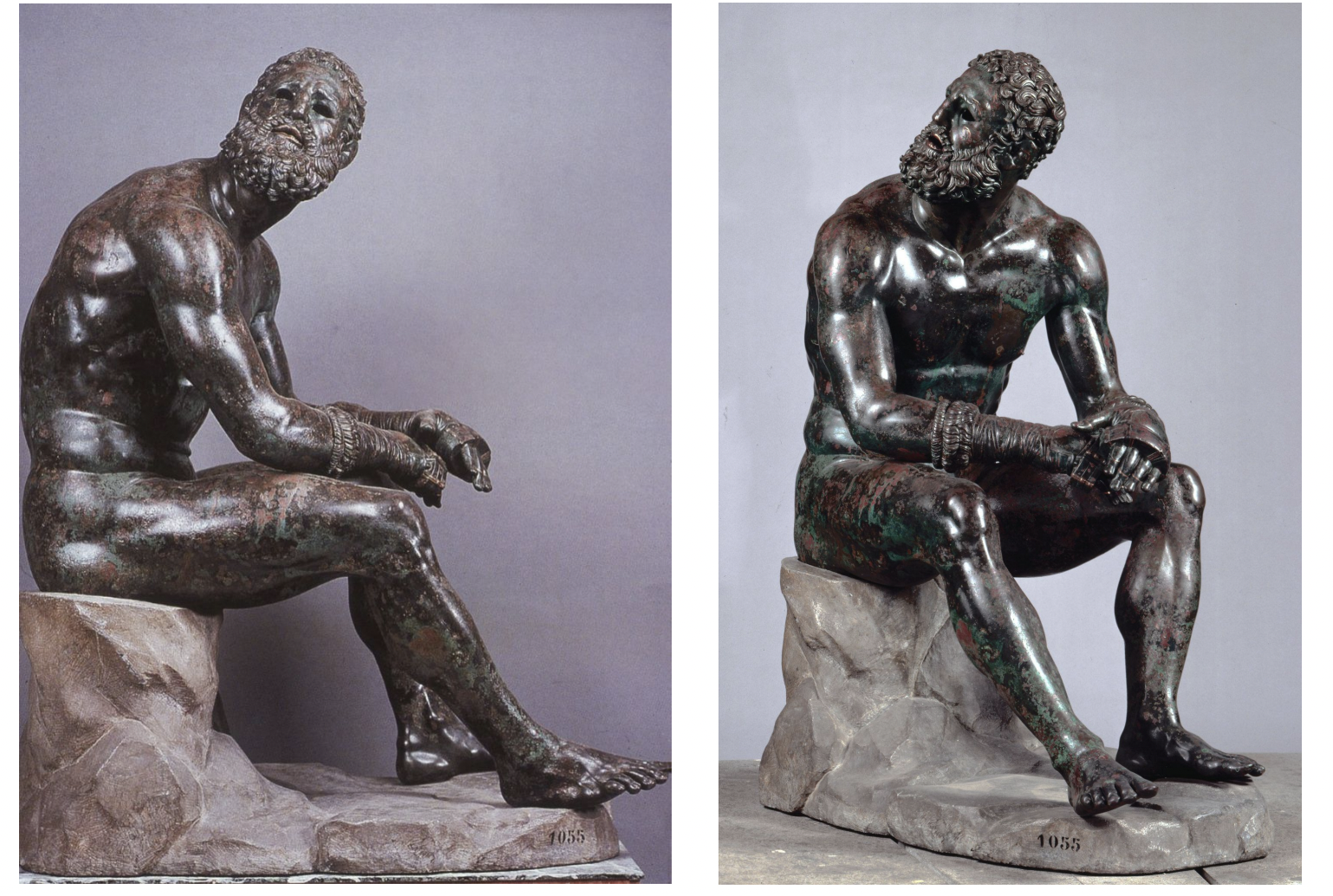

seated boxer, greece the hellenistic period
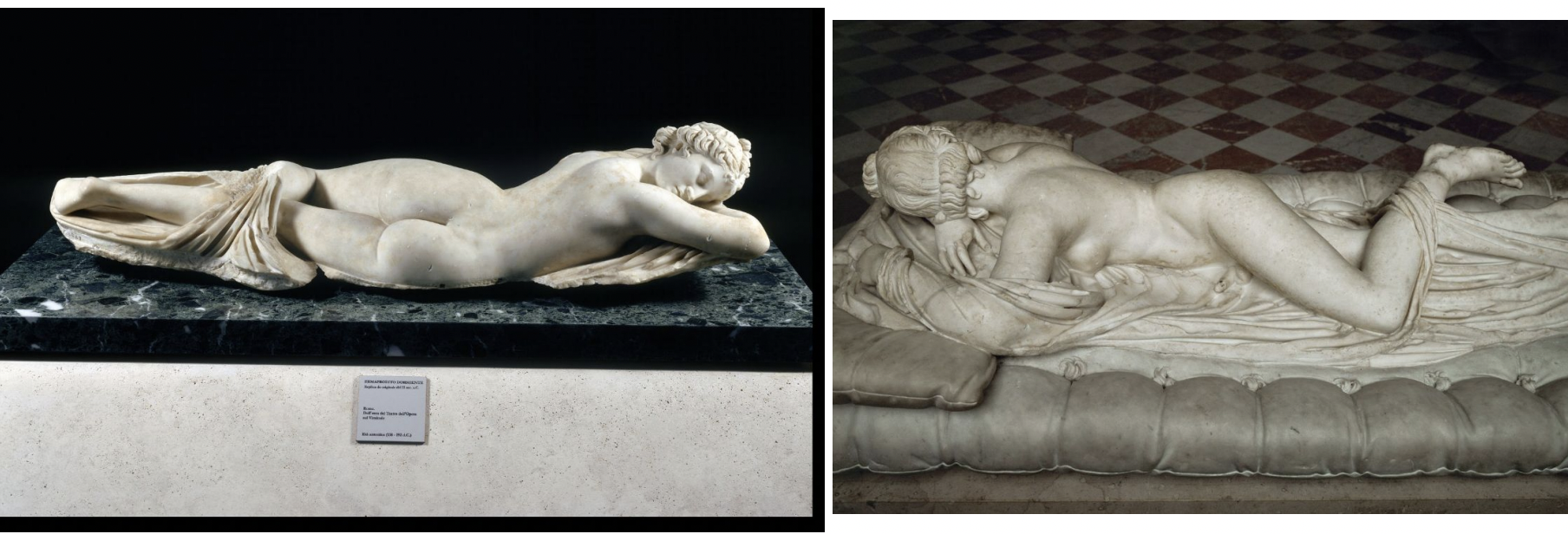

sleeping hermaphrodite, roman copy of original, greece the hellenistic period
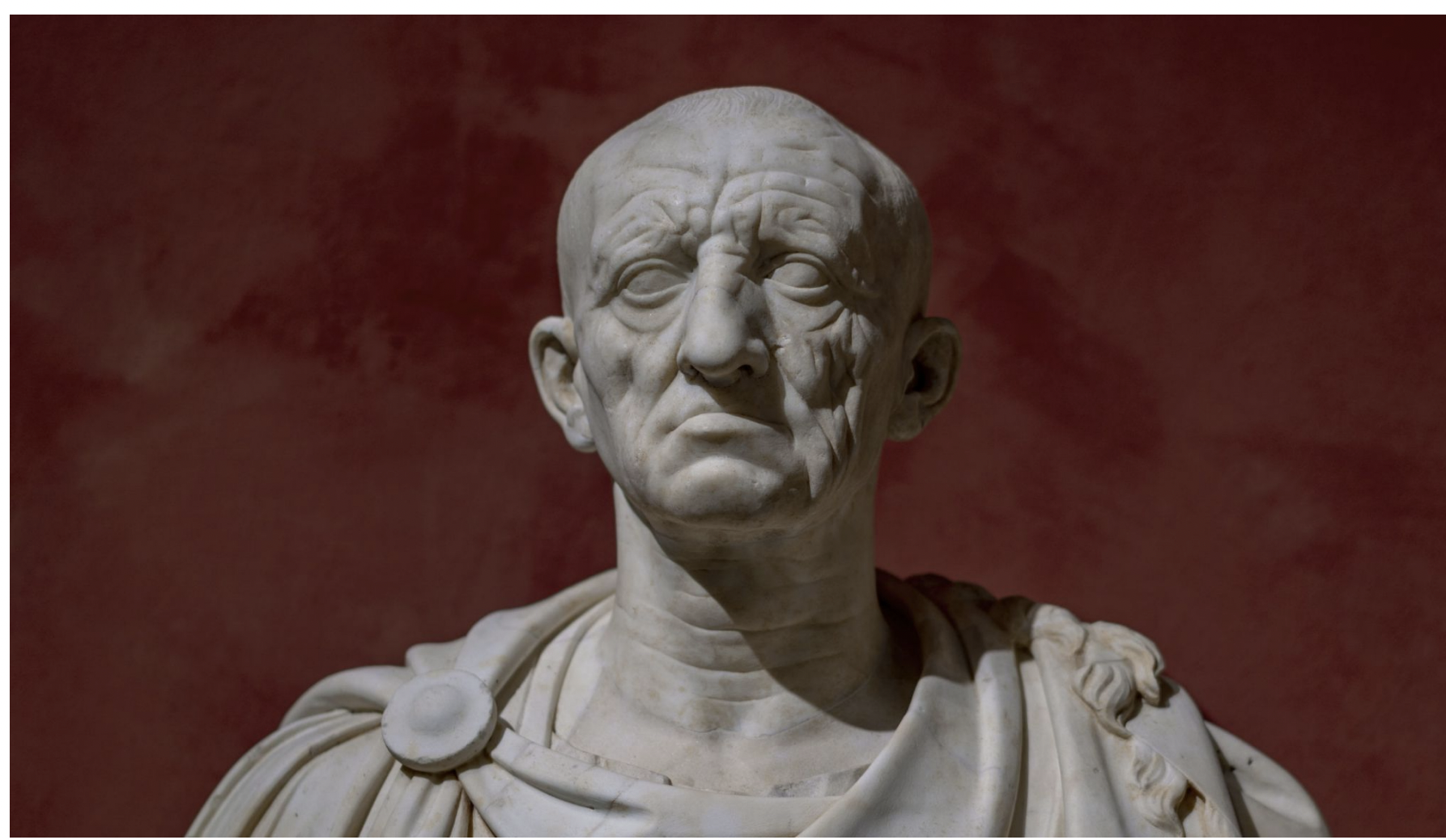

head of an elderly patrician, rome
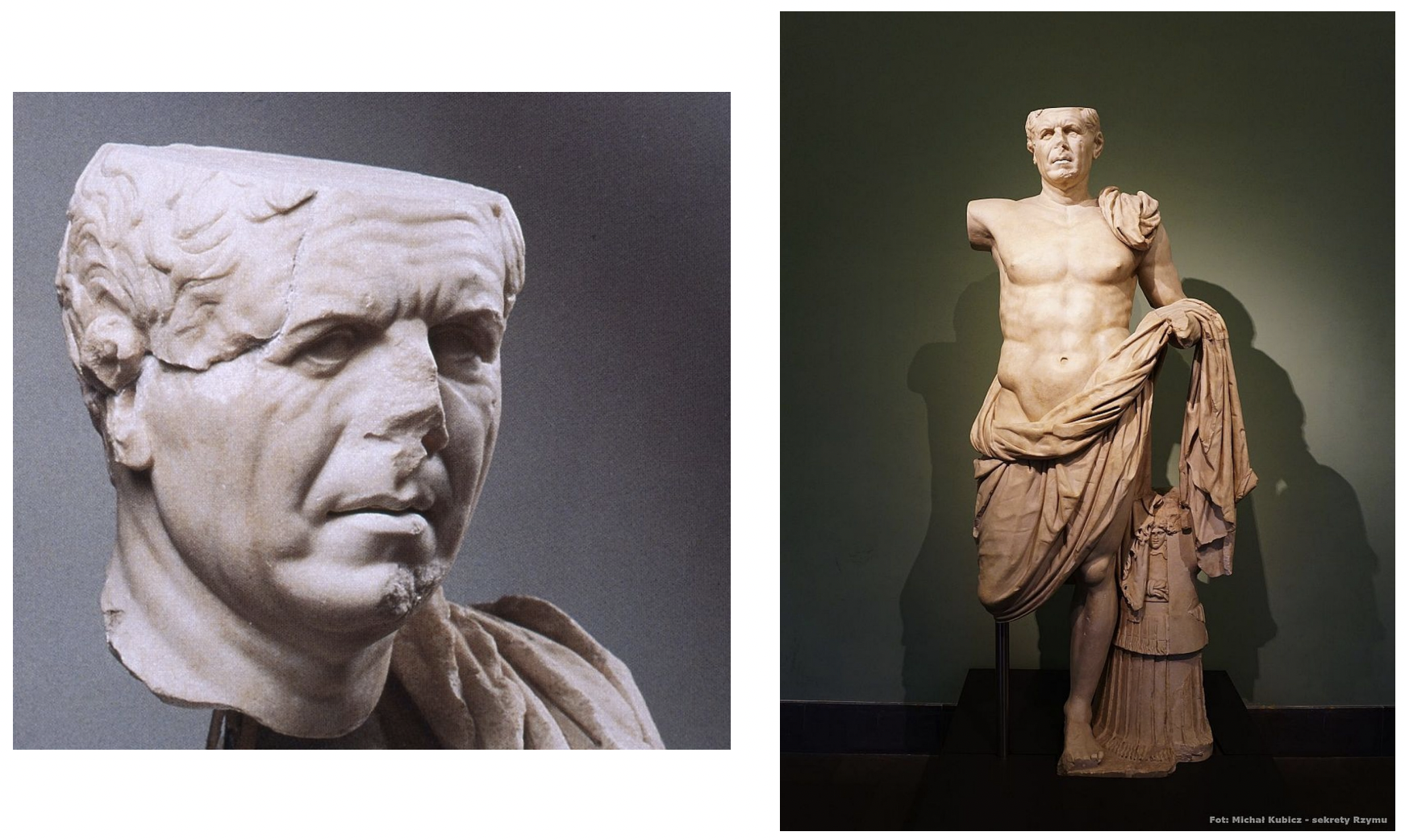

portrait of a roman general, rome
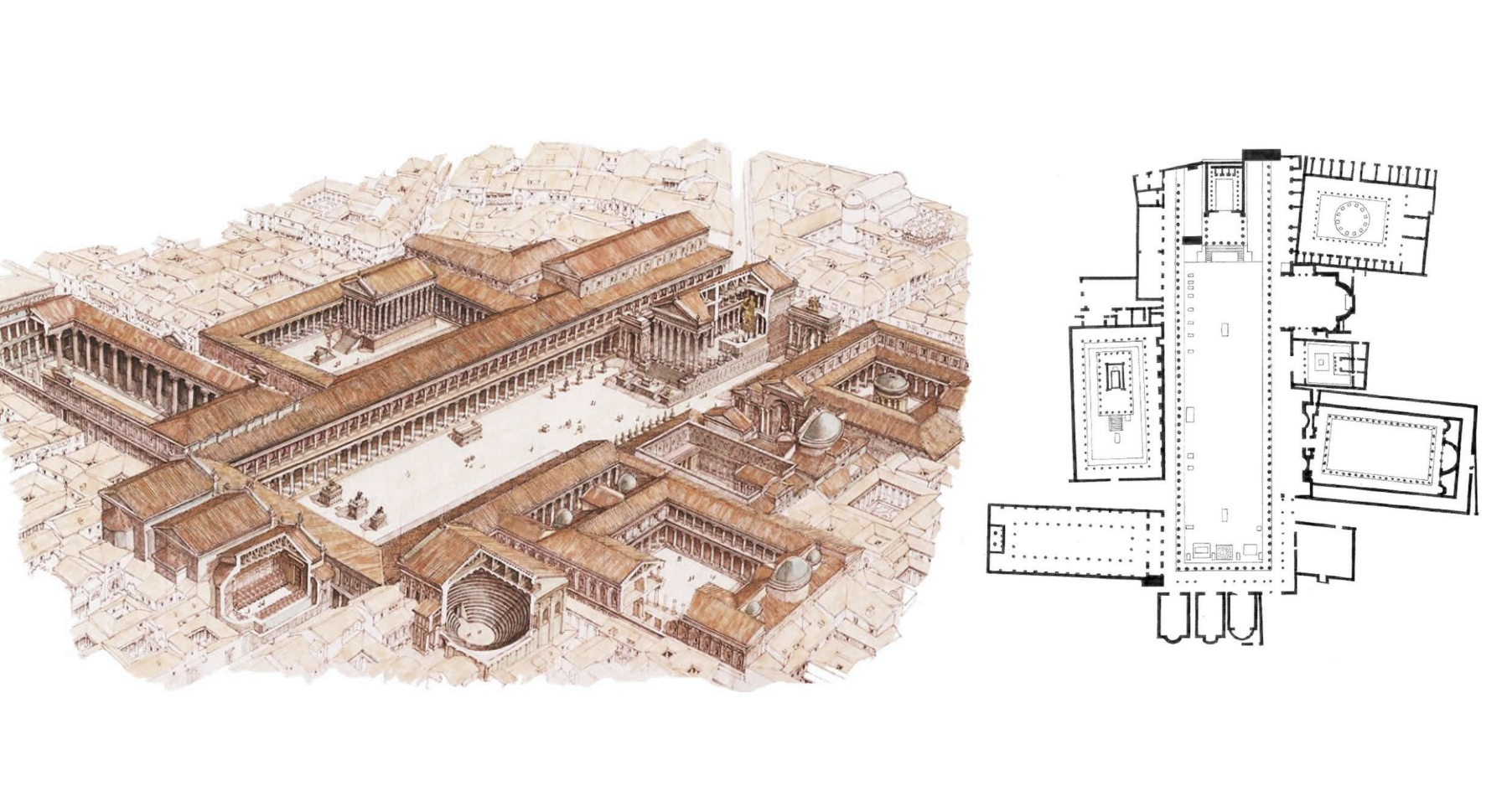
pompeii: forum, rome
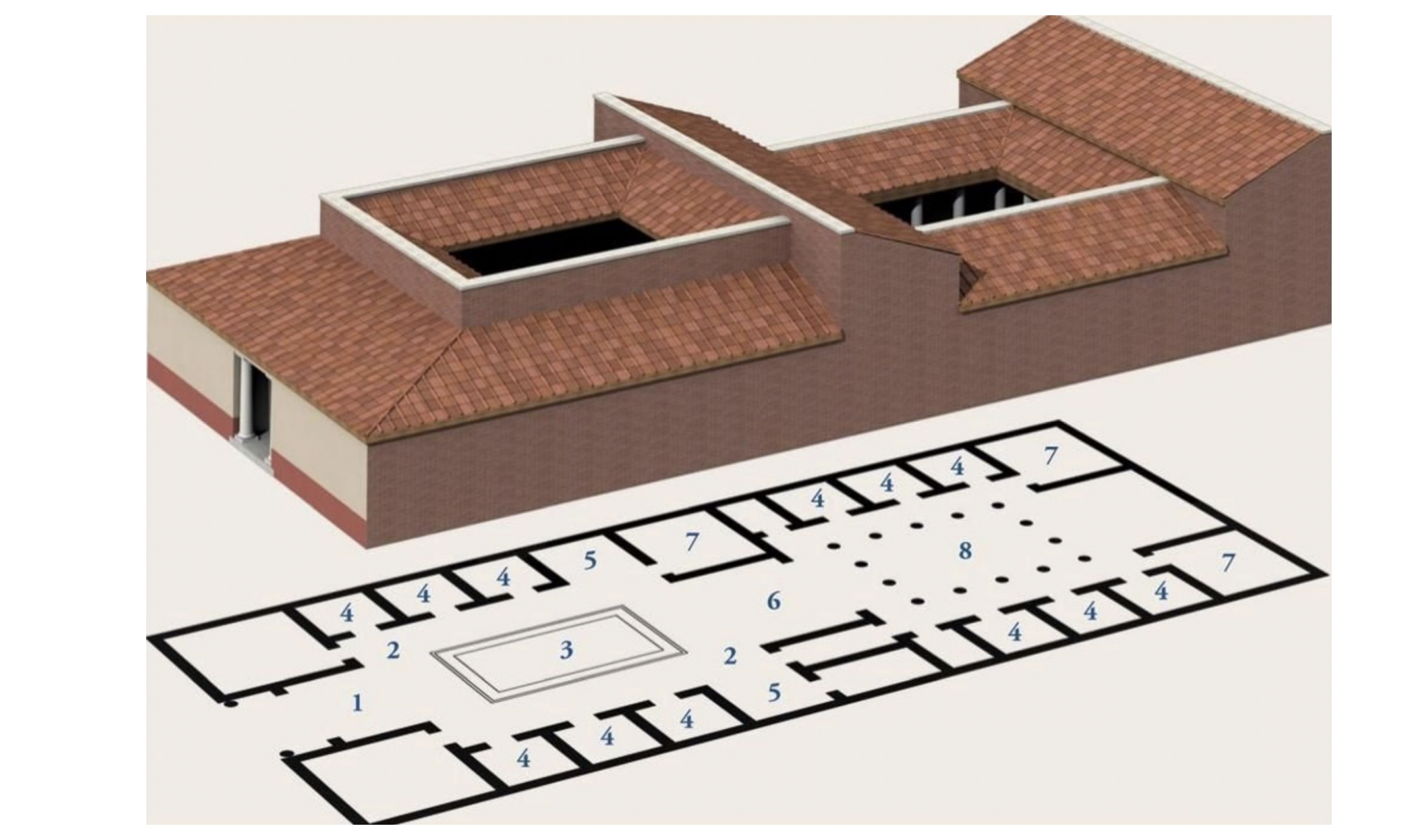
reconstruction of typical roman house with atrium, peristyle, rome
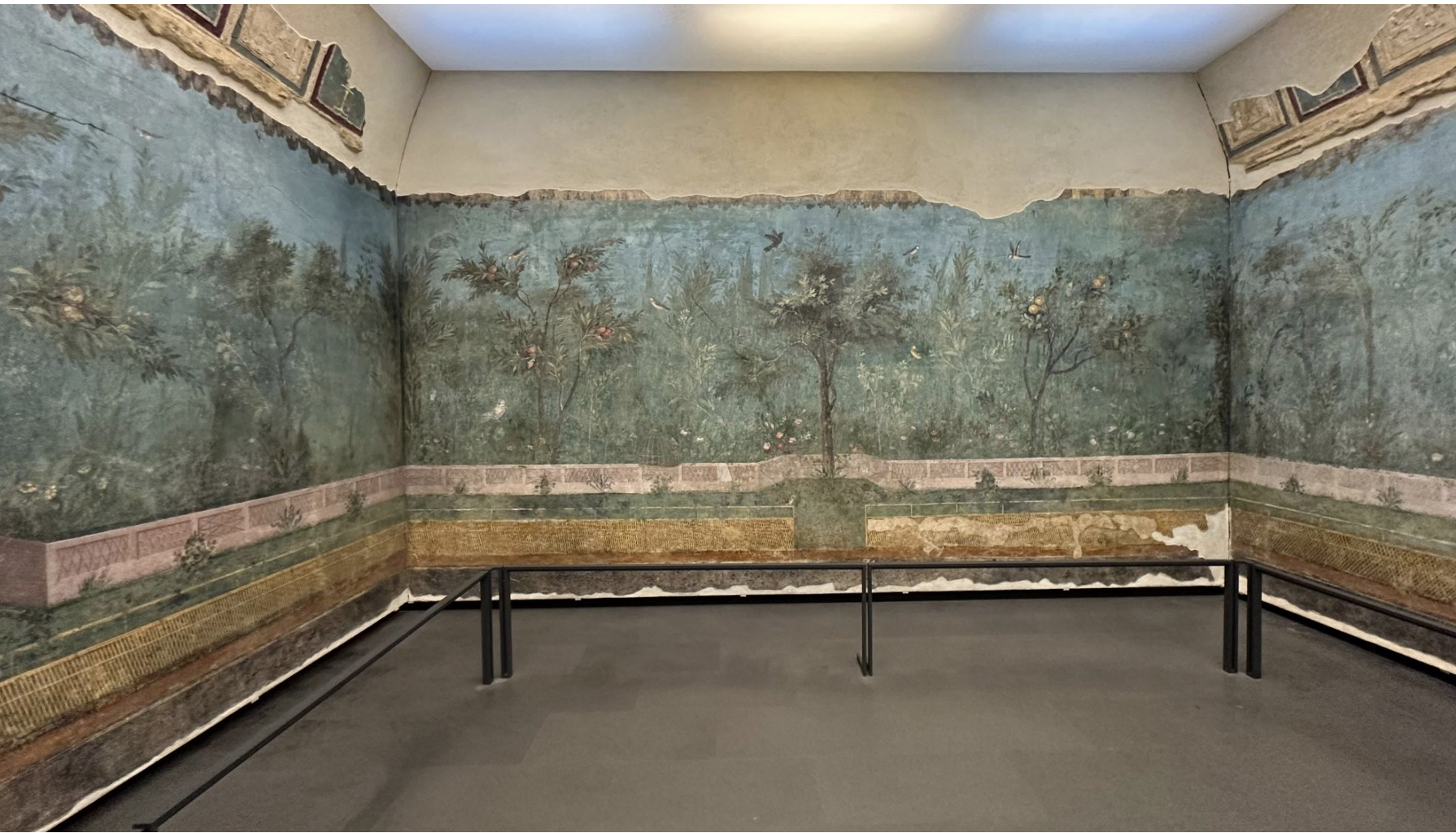

gardenscape, villa of livia, rome
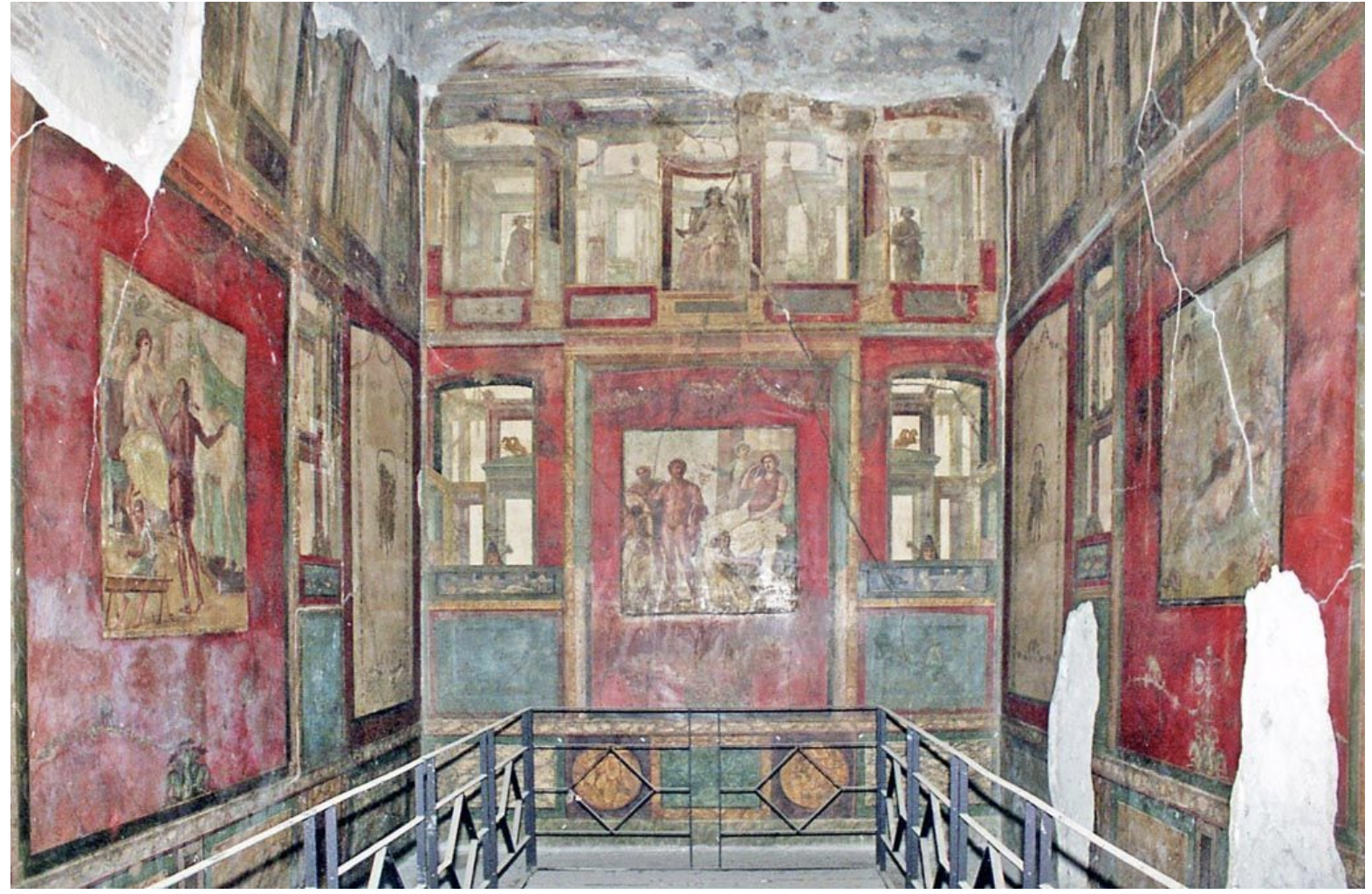

ixion room, house of vettii, pompeii, rome
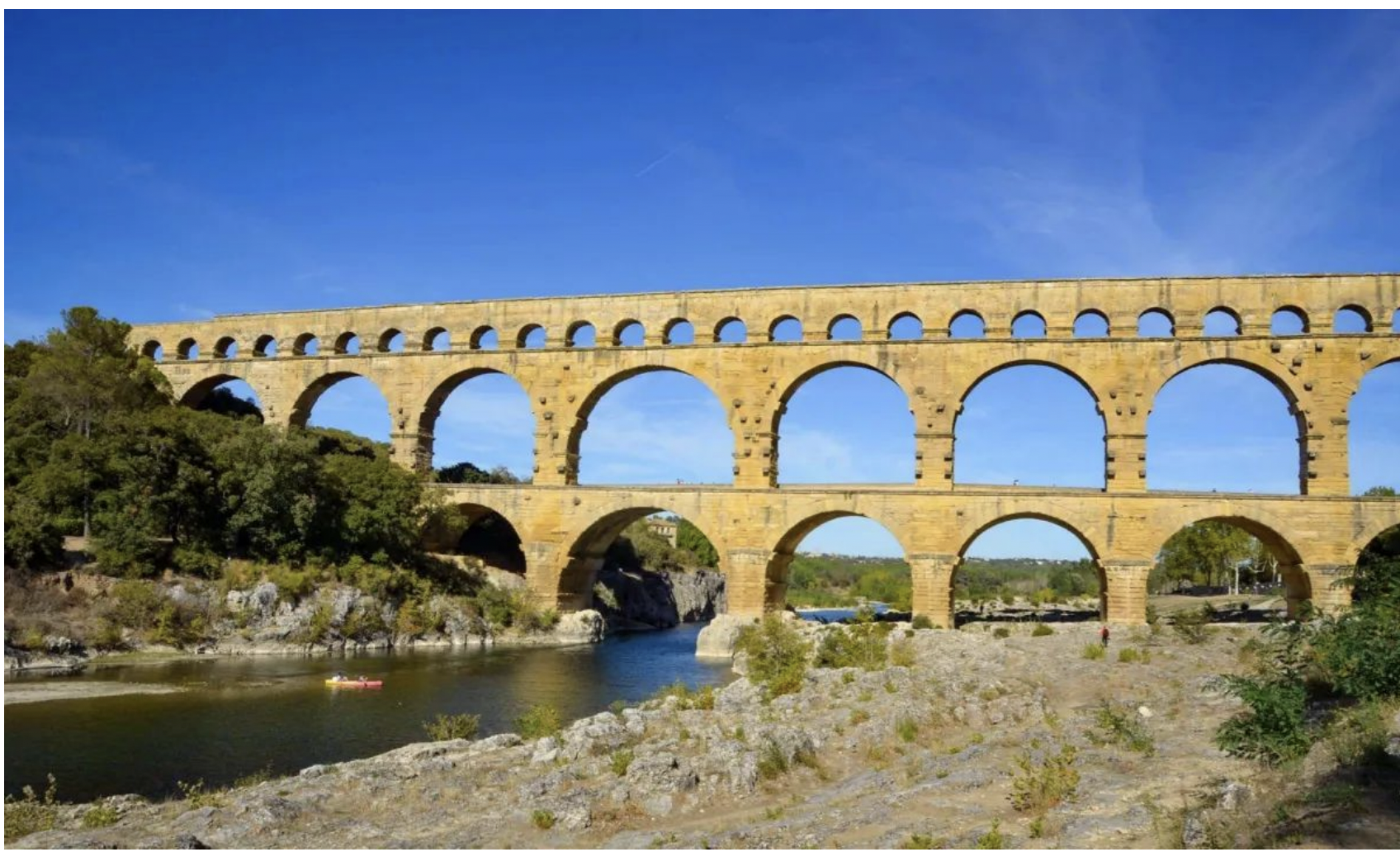

pont du gard, nimes france, rome
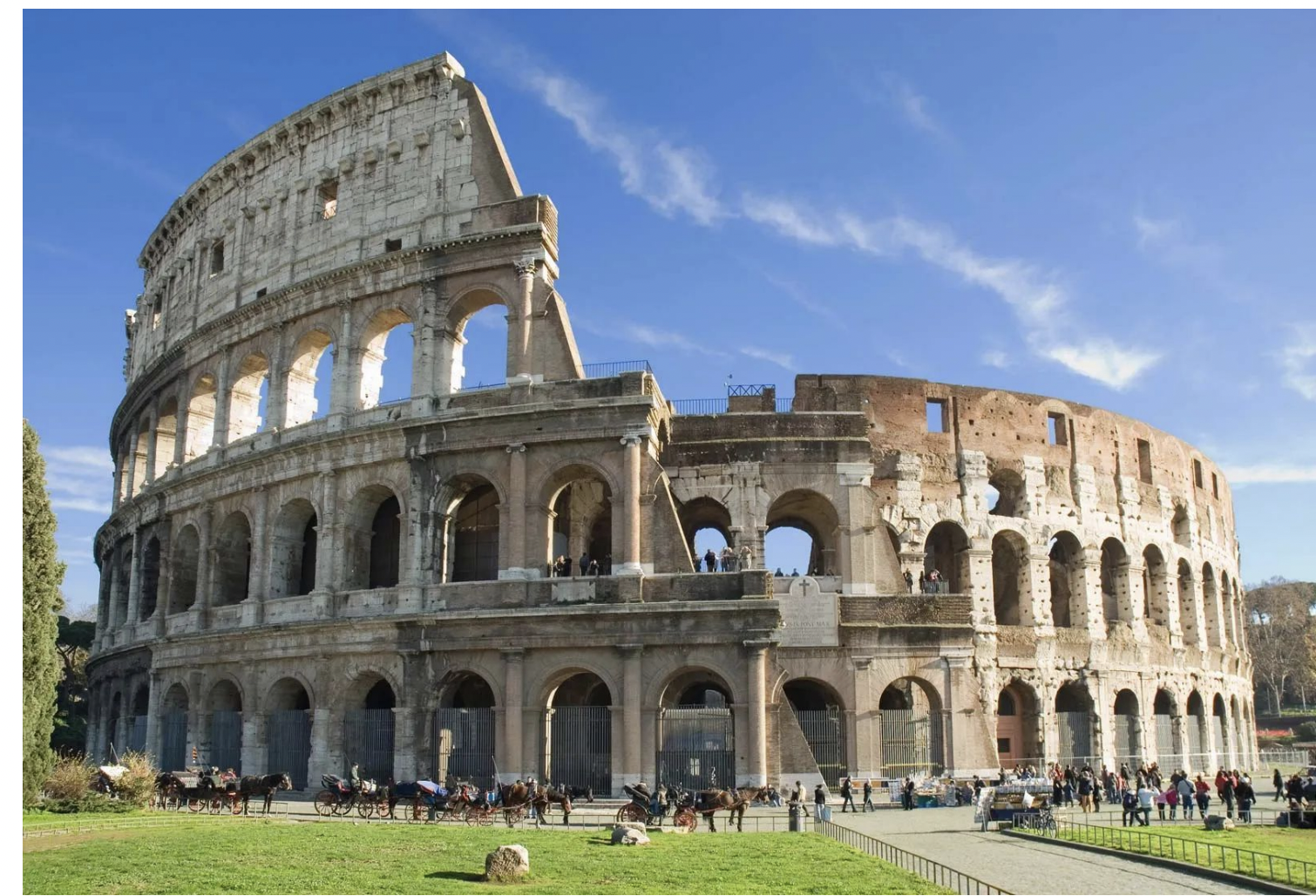

colosseum (flavian ampitheater), rome
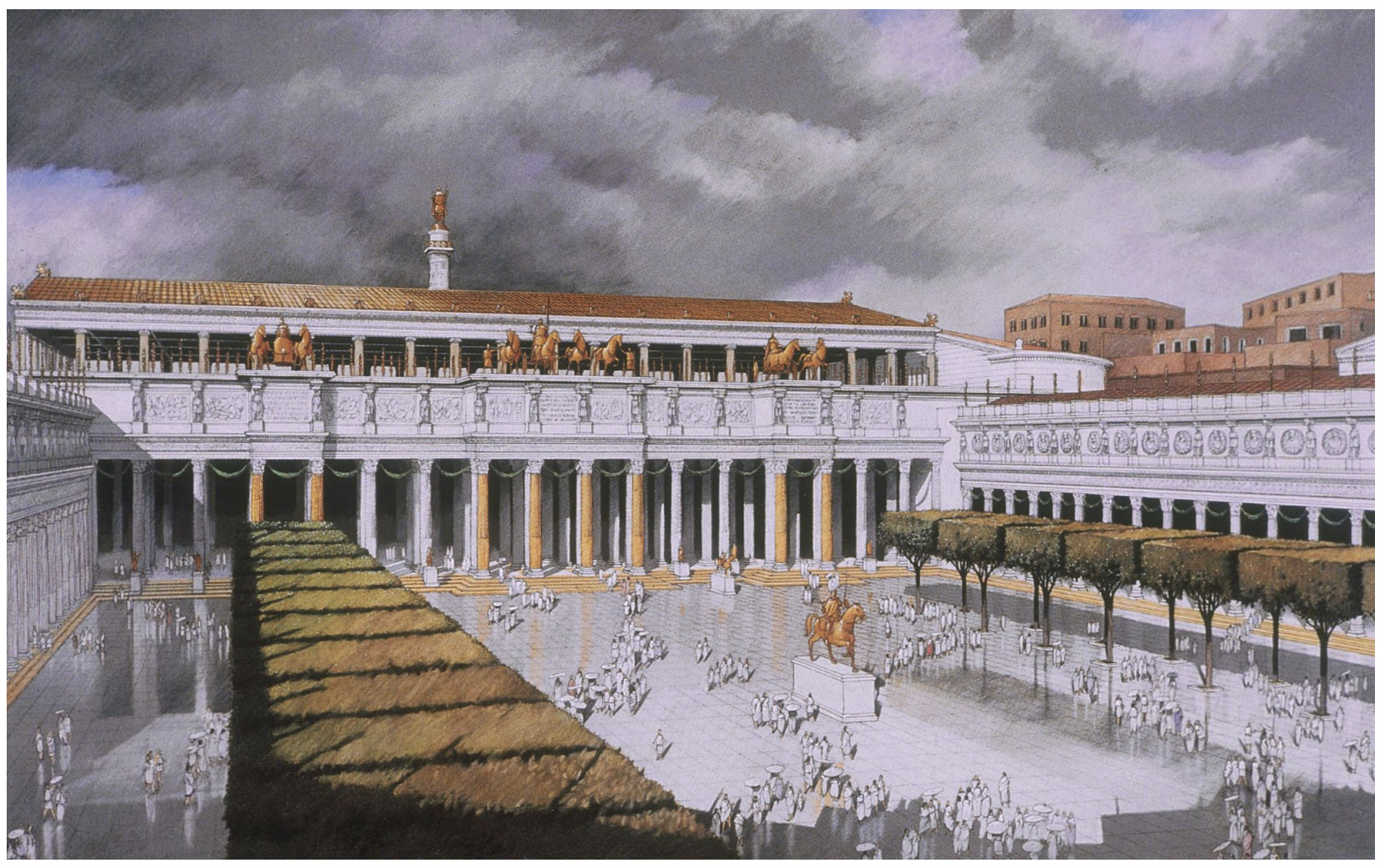

forum of trajan, by apollodorus of damascus, rome
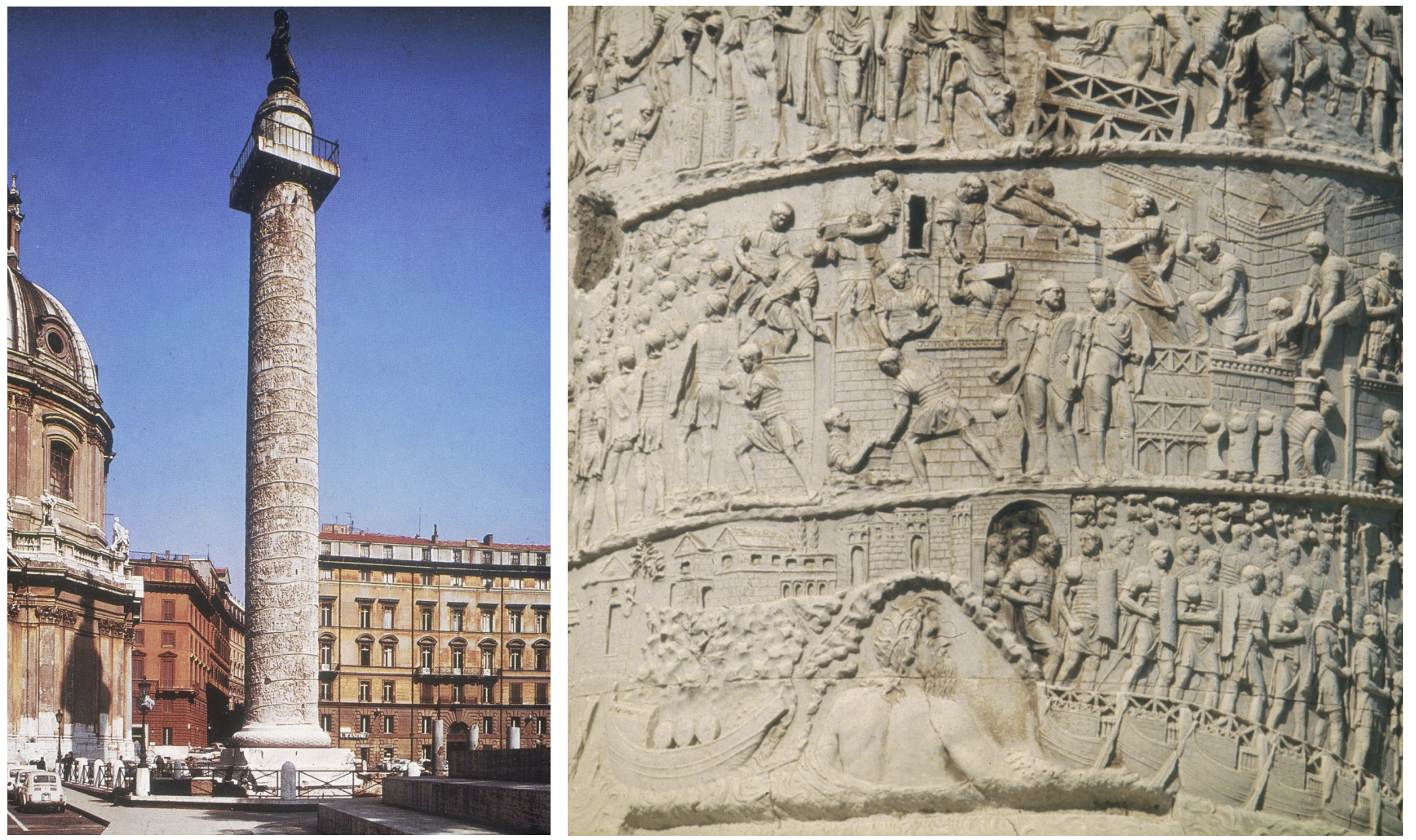

column of trajan, with scenes from dacian wars, rome
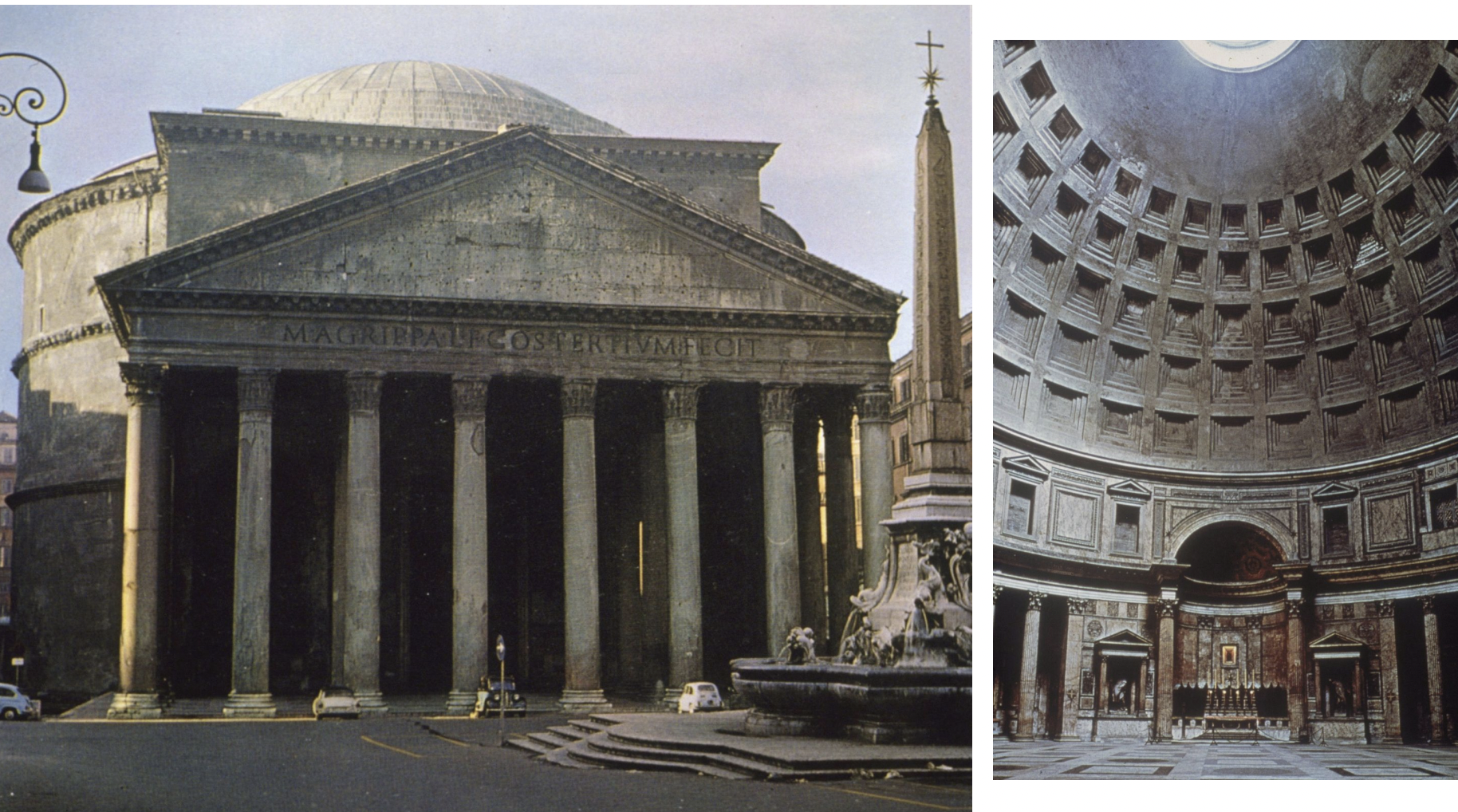

pantheon, rome
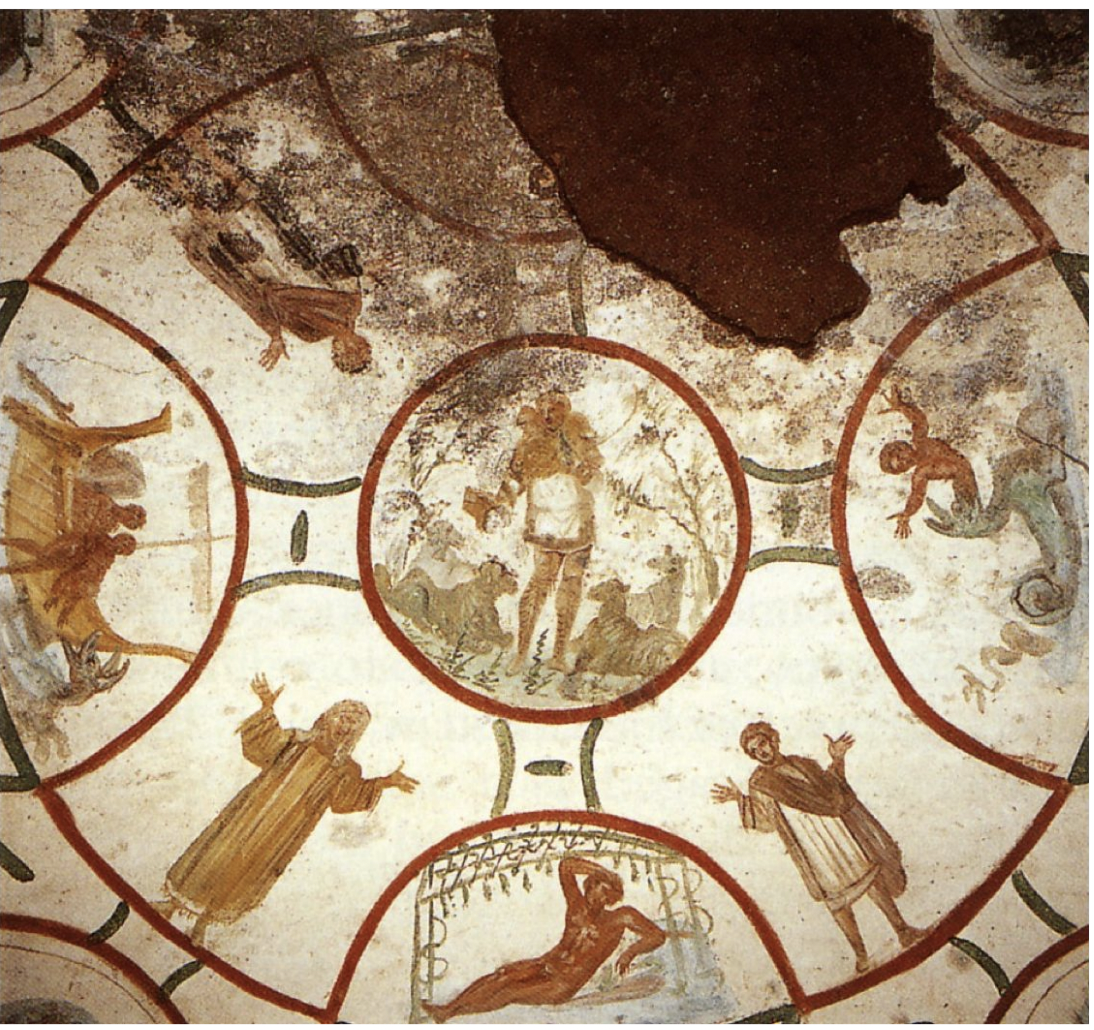

the good sheperd, jonah, orants, catacomb of saints peter and marcellinus - early christianity
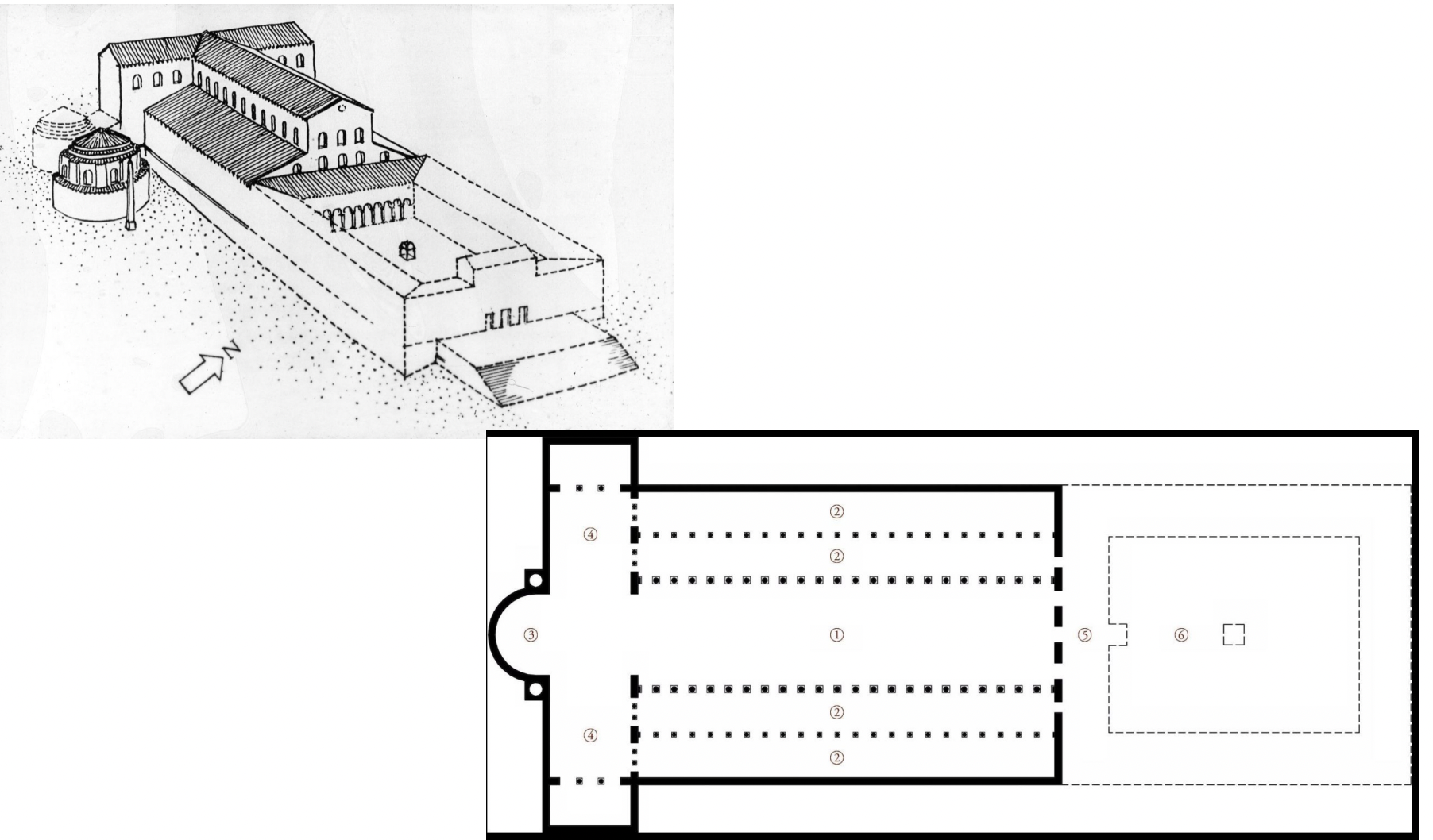
old st. peter’s, rome - early christianity
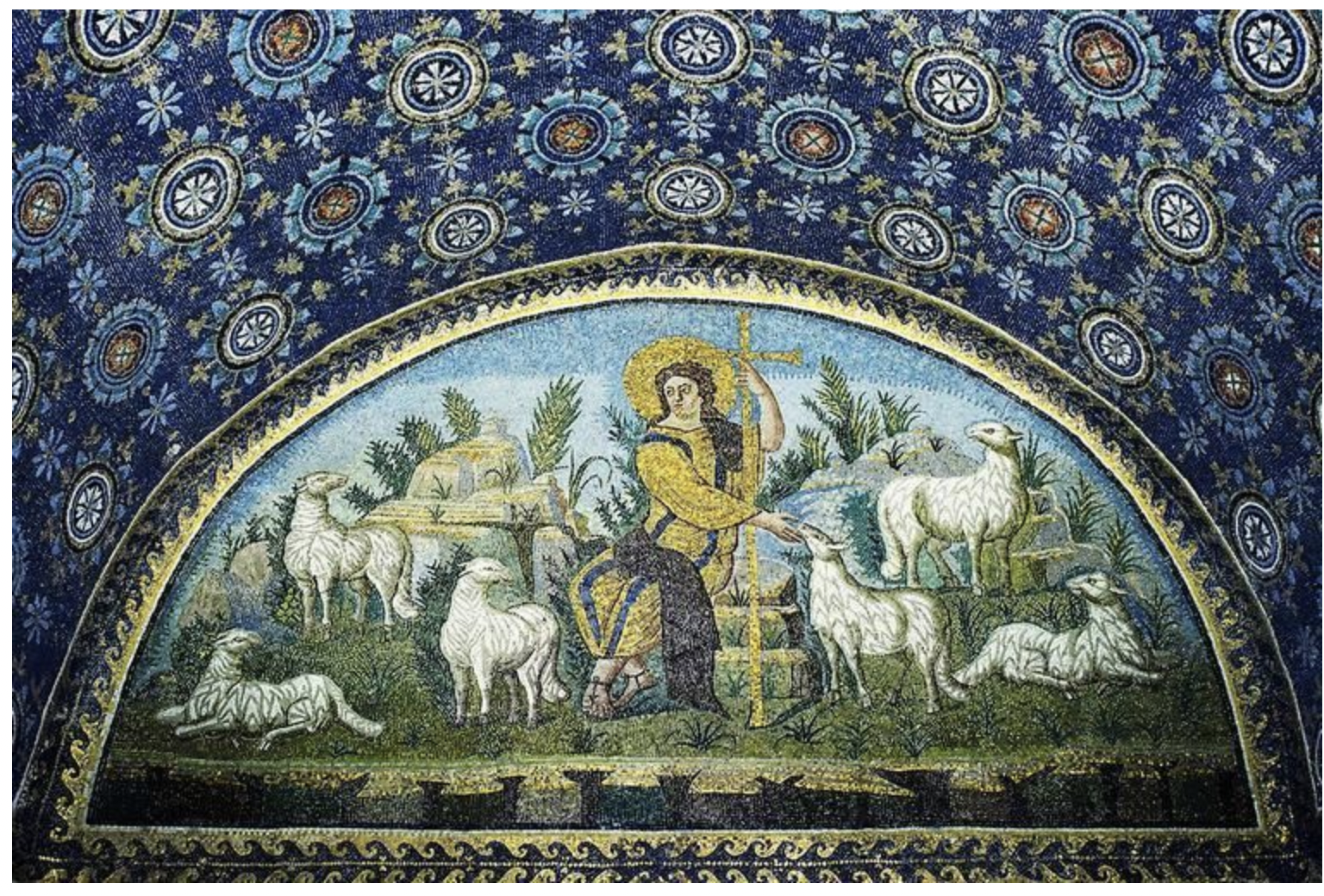

christ as good shepherd, mausoleum of galla placidia, ravenna - early christianity
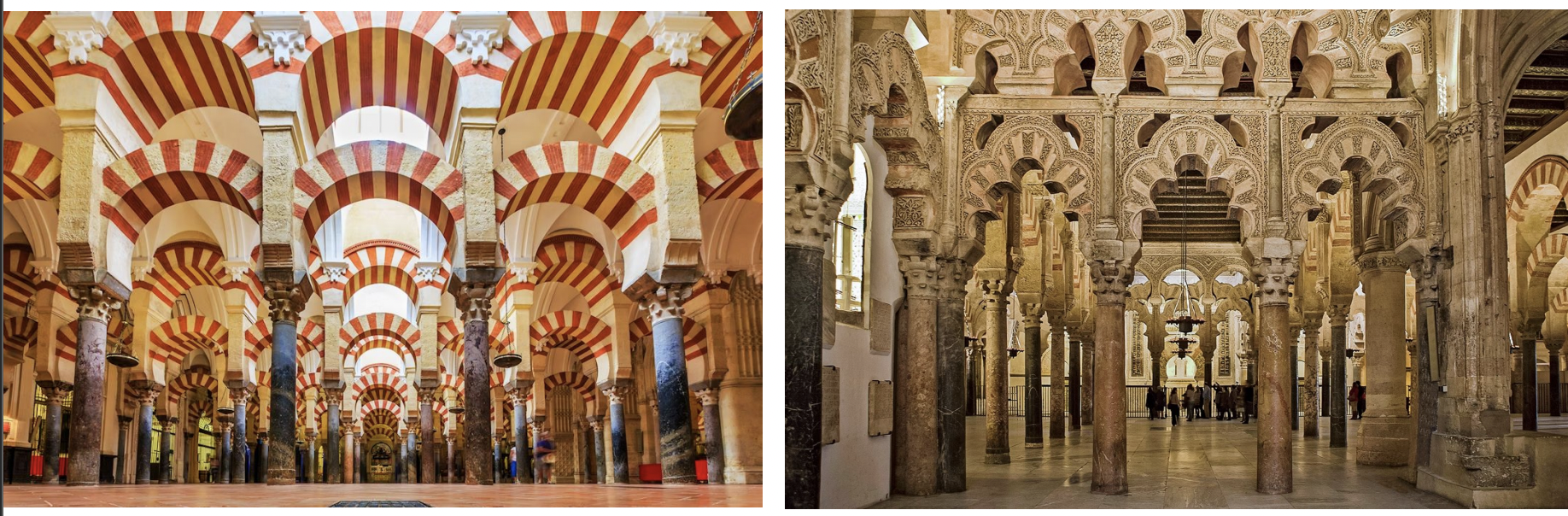

Mezquita (Great Mosque), Cordoba - Islamic Spain, early christianity
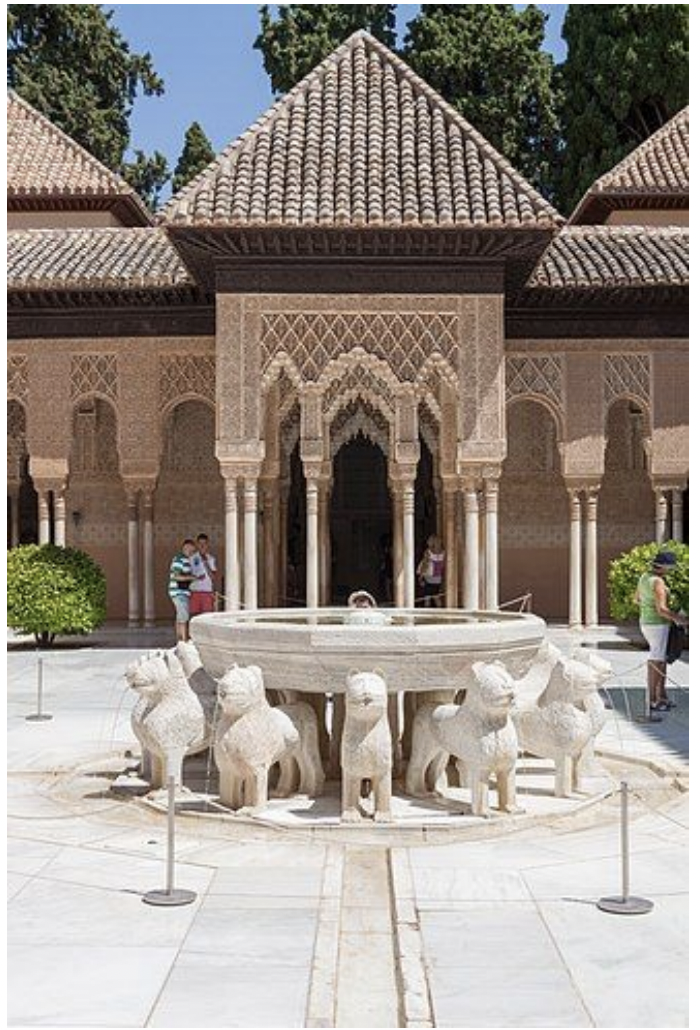

court of lions, alhambra, granada - islamic spain: early christianity
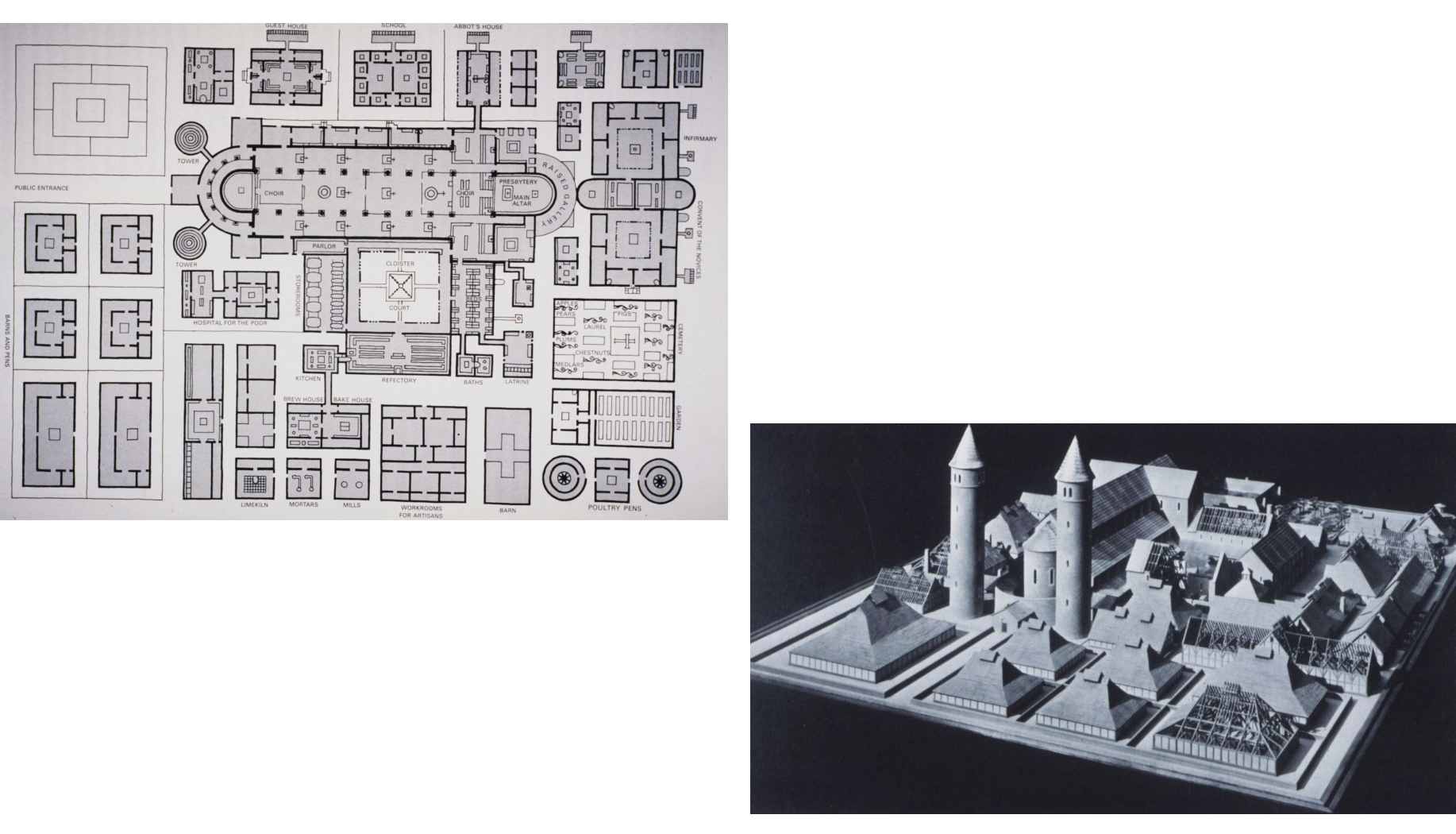
plan for a monastery, from Saint Gall - Early Medieval Art, early christianity
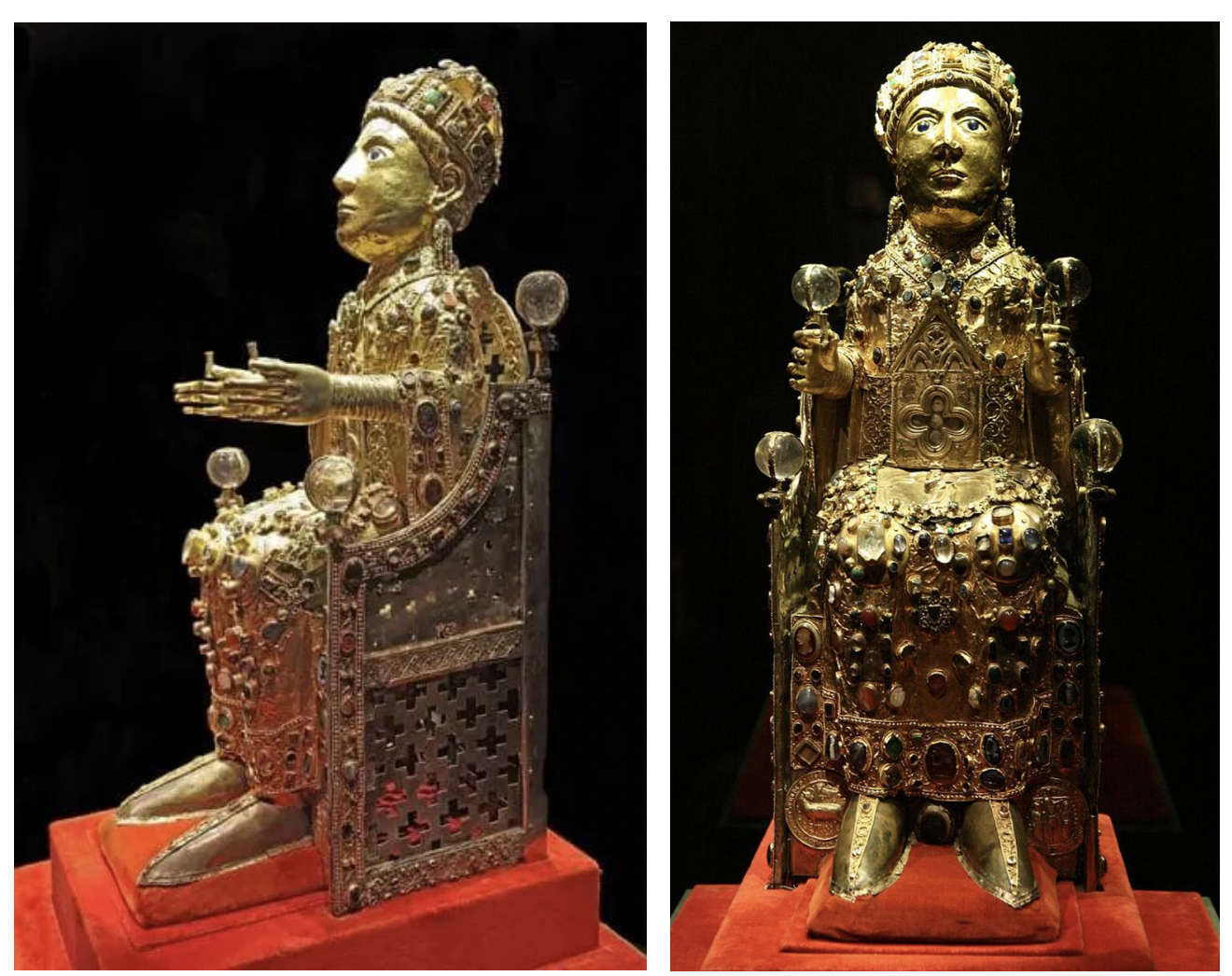

reliquary of sainte foy - romanesque art
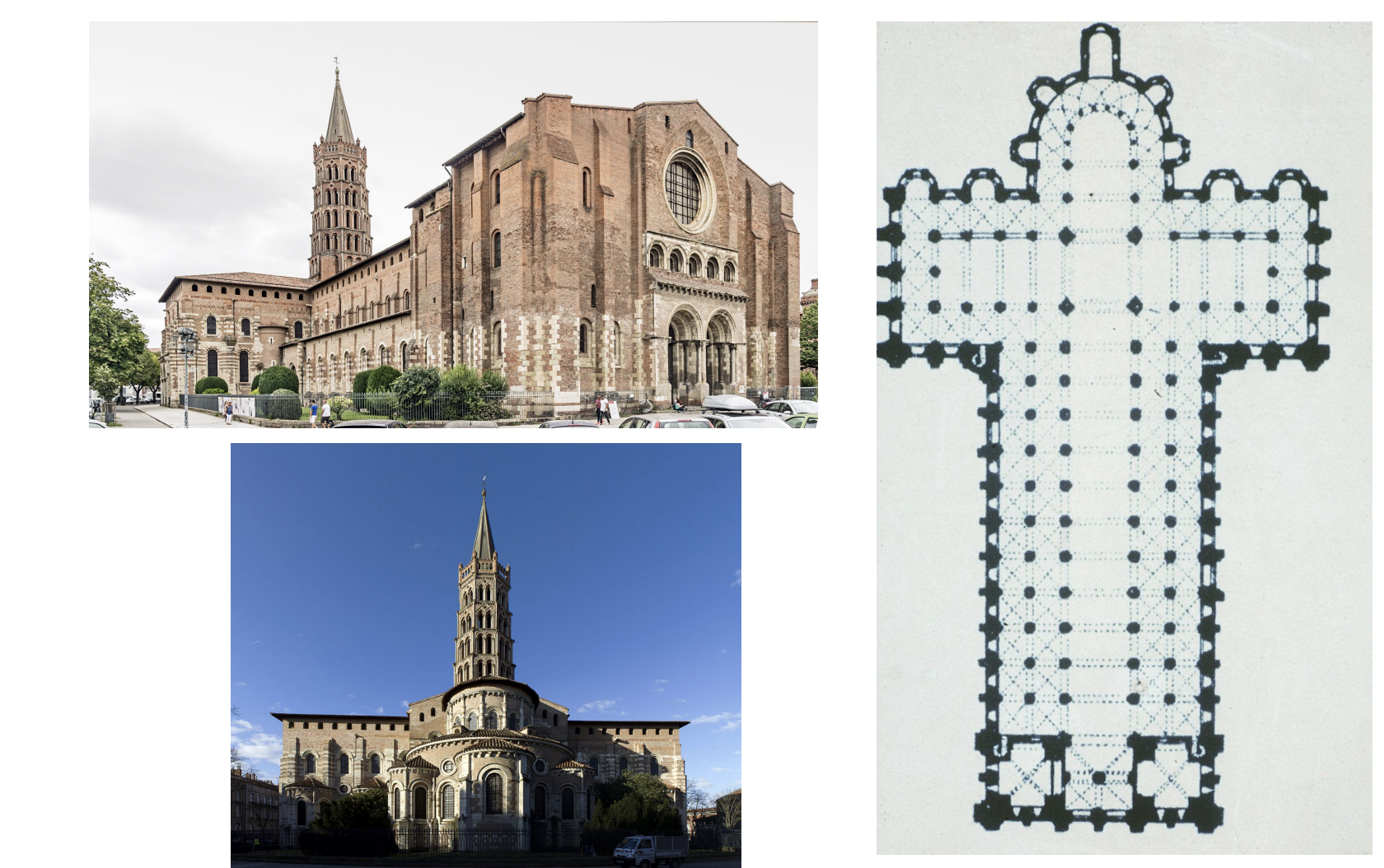

saint sernin, toulouse - romanesque art
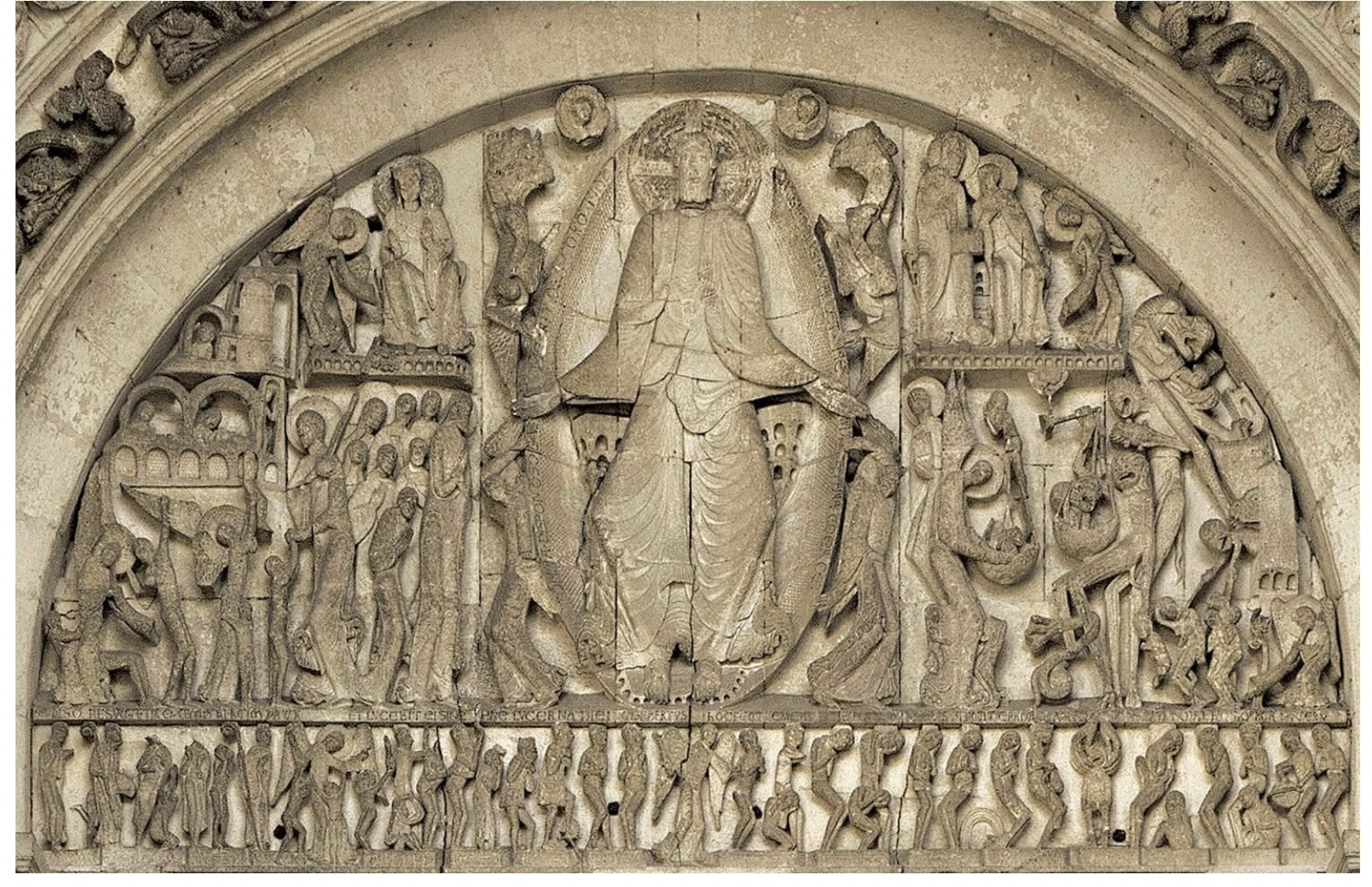

last judgement, by gislebertus, tympanum saint-lazare, autun - romanesque art
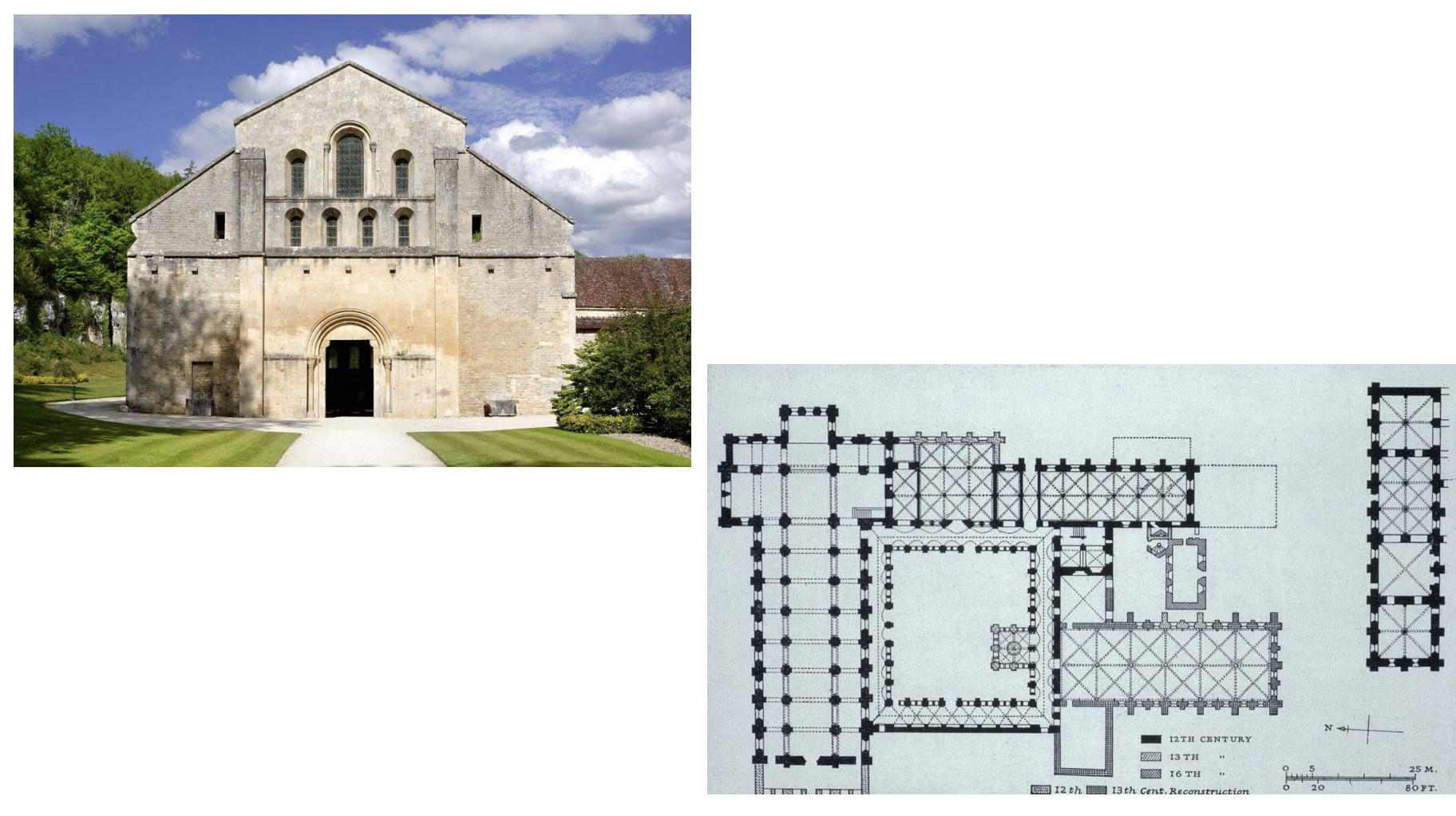
abbey church, fontenay - romanesque art

bayeux tapestry - romanesque art
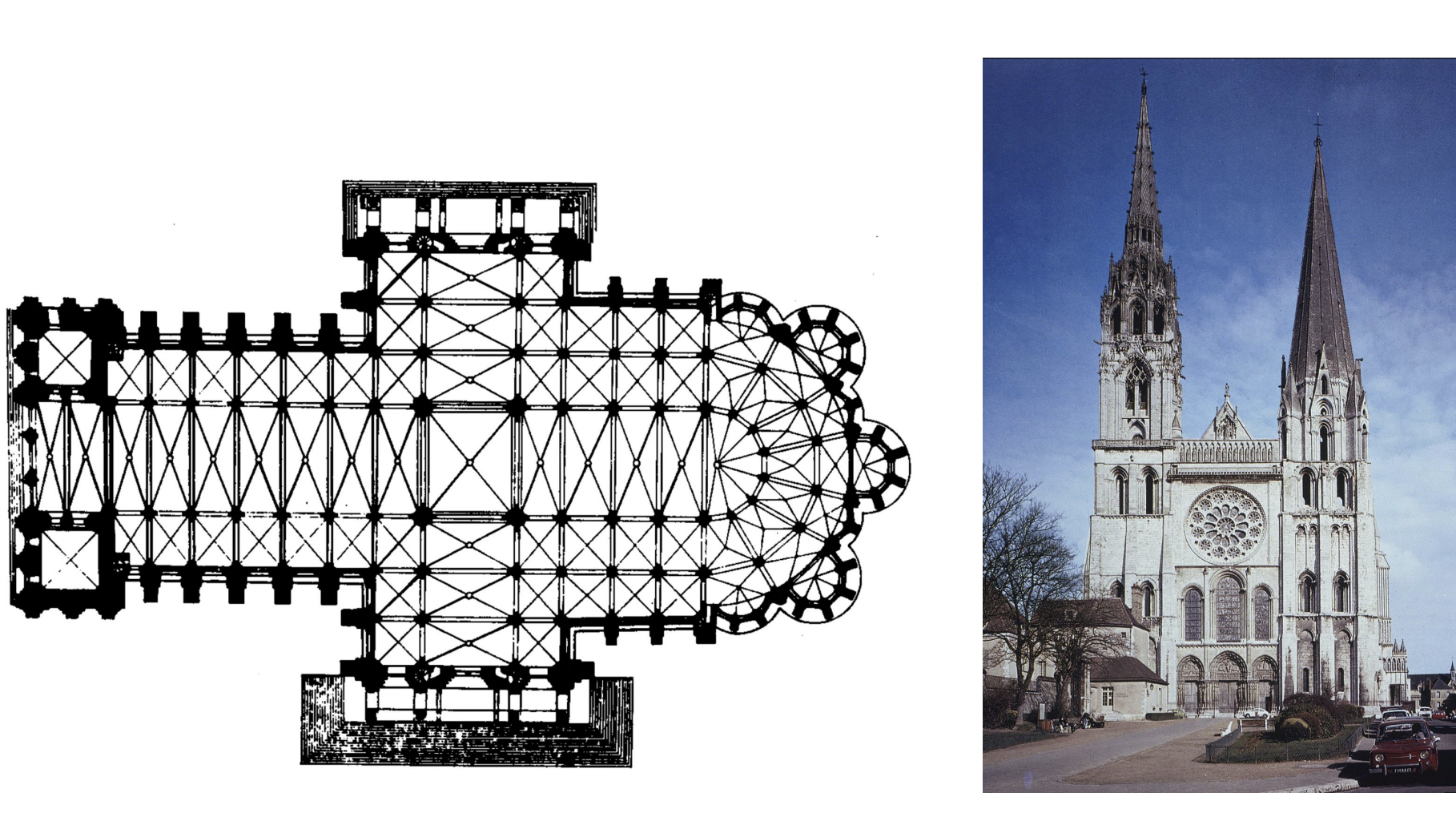
chartres cathedral - gothic art
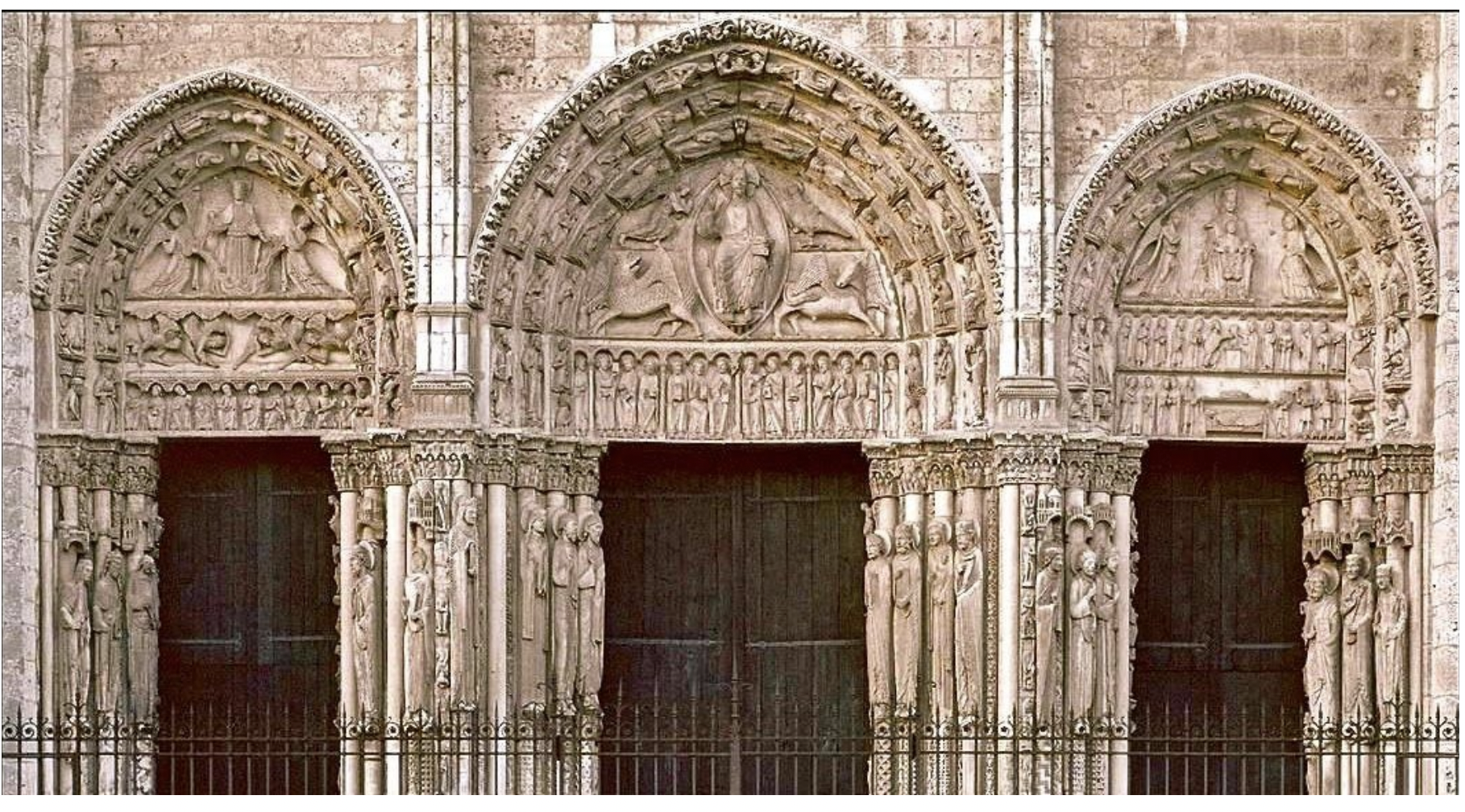

royal portal with jamb statues - gothic art
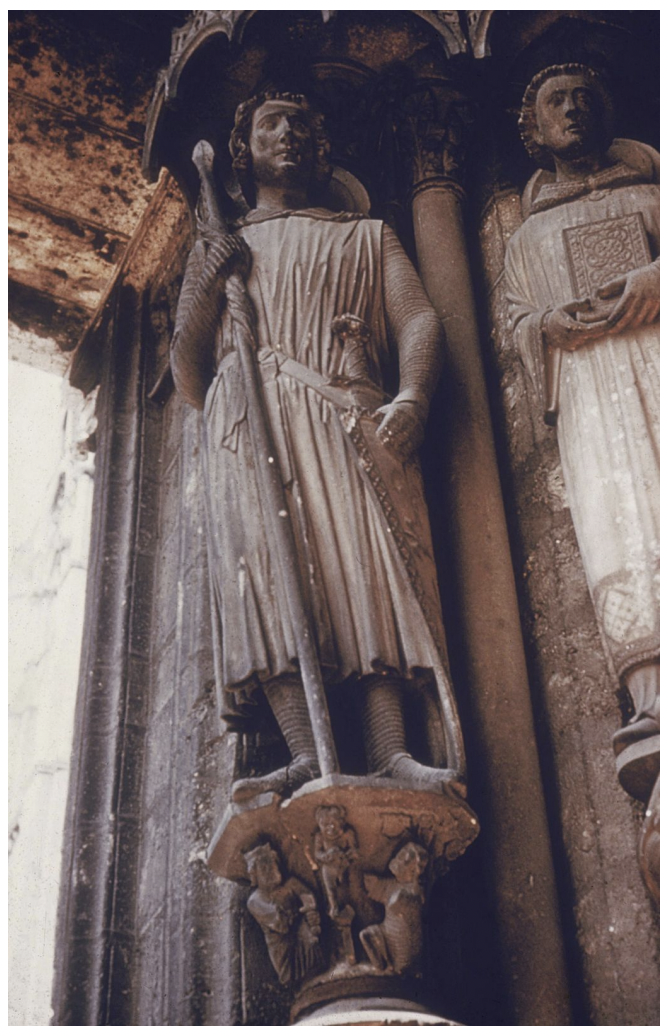

saint theodore - gothic art
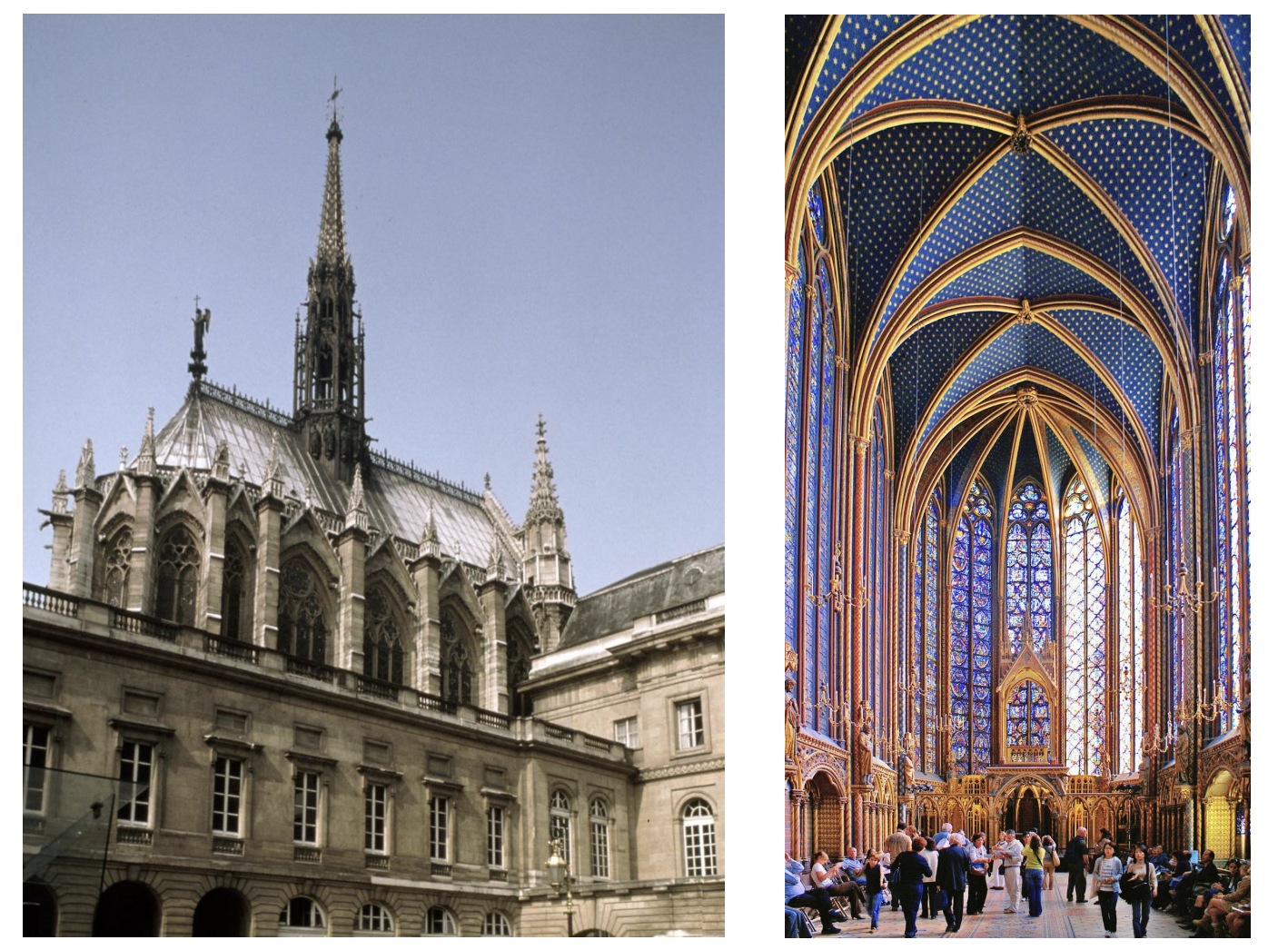

saint chapelle, paris - gothic art

hours of jeanne d’evreux, by pucelle - gothic art
What is the main difference between gothic art and romanesque art?
Romanesque architecture uses heavy, thick walls, rounded arches, and barrel vaults, resulting in dark, fortress-like interiors. In contrast, Gothic architecture uses pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses, which allows for taller, lighter structures with thinner walls and large, stained-glass windows. This innovation in Gothic architecture allowed for more open spaces and natural light.
cuneiform
a system of wedge-shaped marks created with a stylus on clay tablets that served as one of the earliest writing systems in ancient Mesopotamia
relief
a sculptural technique where figures and designs project from a flat background
register
a horizontal band or level within a work of art used to separate different scenes or narrative elements
hierarchic scale
a technique where the size of figures or objects is manipulated to represent their importance, not their physical reality
composite view
a convention where a single figure is drawn from multiple viewpoints at once, combining profile and frontal views. This technique was famously used in ancient Egyptian art to show the most recognizable features of a subject, such as a profile head and legs with a frontal torso and eye, to convey a complete and clear representation
divine kingship
the political-religious concept where a ruler is believed to have a sacred connection to the divine, often seen as a god or a god-like figure appointed by higher powers to govern
hieroglyphs
a system of writing that uses pictorial symbols, most famously in ancient Egypt, and served as both a means of communication and a form of artistic expression
papyrus
a paper-like material made from the stems of the Cyperus papyrus plant, used in ancient Egypt for both writing and art
archaic smile
a characteristic facial expression in early ancient Greek sculpture, defined by a slight, often enigmatic upturn of the lips. Used to convey a sense of vitality and serenity, bridging the gap between idealism and the emerging realism in Greek art
persian wars
a pivotal period from 499–449 BCE that directly preceded the Classical Period of Ancient Greek art. The wars fostered a newfound sense of Greek unity and confidence, which led to a cultural renaissance and the rise of Athens as a dominant power. This era is characterized by the rebuilding of the Athenian Acropolis and the construction of iconic structures like the Parthenon, which showcased a new style of harmony, proportion, and idealized human form in sculpture.
lost wax method
an ancient metal casting technique that creates a duplicate of an original wax model
contrapposto
a natural, asymmetrical human stance in art where the figure's weight is shifted onto one leg, causing the hips and shoulders to rest on slightly different axes. This pose creates a sense of dynamism and lifelikeness, moving away from the stiff, rigid figures of earlier eras
doric and ionic temples
Doric temples are defined by their sturdy, simple columns that lack a base and have a plain capital, representing strength and austerity. Ionic temples are characterized by more slender columns with scroll-like ornaments (volutes) on the capital and a base, symbolizing elegance and sophistication
Peloponnesian Wars 431- 404 BCE
Between Athens and Sparta. The war led to a new focus on themes of military victory and the afterlife in art
corinthian column
a classical architectural column defined by its ornate capital, which is decorated with carvings of acanthus leaves and scrolls. It is the most decorative of the three classical Greek orders, characterized by a slender and fluted shaft, and is known for its elegance and grandeur
veristic portraiture”
an ancient Roman art style characterized by extreme realism, depicting subjects with an emphasis on age, flaws, and imperfections like wrinkles and scars
fresco
a mural painting technique where water-based pigments are applied to freshly laid wet plaster
aqueduct
a man-made structure, often a monumental bridge with arches, designed to transport water over long distances to a city. They represent a major feat of ancient engineering, particularly from civilizations like the Romans, and are significant for their scale, impact on public health and agriculture, and their contribution to urban development
arch
a curved structural element that spans an opening and supports weight from above by distributing it outwards
barrel vault
a continuous, semicircular arch that forms a tunnel-like ceiling or roof
concrete
a form of mortar and aggregate used to construct large-scale structures like the Pantheon
basilica
a type of rectangular building with a long central hall (nave), flanked by aisles, and a semicircular apse at one end, which was originally used as a public and legal building in ancient Rome. Early Christians adopted this architectural style for churches, using it for its spacious layout to gather congregations, which became the standard for Christian church design
nave
the central and longest part of a church or other religious building, extending from the main entrance to the transept or chancel. It is the area designated for the laity (the congregation) to gather for worship
aisles
a passageway in a church or basilica that runs parallel to the nave and is separated from it by a row of columns or piers
gallery
an upper story or balcony that typically overlooks the main body of the church, or nave
clerestory
a row of windows in the upper part of a wall, typically in a basilica or church, that allows natural light to illuminate the interior
apse
a semi-circular or polygonal recess in a building, particularly common in art history at the eastern end of a church, often featuring the altar and clergy seating
dome
a rounded, convex roof or ceiling that forms the upper part of a building, known for its structural integrity and symbolic weight
oculus
a circular or oval opening, typically a window, located at the apex of a dome or roof. Its primary functions are to allow natural light to enter, illuminate the interior, and provide ventilation, while also serving as a significant decorative and symbolic element that draws attention upward
coffers
a recessed square or rectangular panel, often found on a ceiling, dome, or vault. These coffers are part of a coffered ceiling or coffered vault, which can be both decorative and structural. They serve to lighten the weight of a dome, hide structural elements for a more pleasing appearance, and create a grander or more regal feel to a room
basilica church
a large, rectangular building with a central nave and side aisles, originating from Roman public buildings and adapted for early Christian worship
transcept
a transept is the part of a cruciform (cross-shaped) church that crosses the main body (nave) at a right angle, forming the arms of the cross. This architectural feature creates a distinctive floor plan and provides additional space for chapels, altars, or choir stalls
mihrab
an architectural niche in the qibla wall of a mosque that indicates the direction of Mecca for prayer
muqarnas
a form of ornamental and three-dimensional architectural vaulting found in Islamic architecture, characterized by its intricate, honeycomb-like structure of superimposed niches. It was used to decorate domes, vaults, arches, and niches, serving both an aesthetic and a structural purpose to provide a decorative transition between architectural elements.
cloister
a covered walkway, usually in a monastic or religious building, that surrounds a central, open-air courtyard (garth) and provides access to other parts of the institution
relics
an object or a physical fragment, such as a piece of a saint's body or an item they used, that is venerated in a religious context
pilgrimage roads
the designated paths taken by pilgrims to reach a sacred site, which significantly influenced the development of art, architecture, and culture. These routes facilitated the movement of people, ideas, and artistic styles across Europe, leading to the construction of specialized churches, monasteries, and inns along the way to accommodate and inspire pilgrims
choir
the specific architectural area in a church located between the nave and the sanctuary, where the clergy and singers sit
ambulatory
a covered walkway or passageway, most often found in a church, that encircles the apse, the area behind the altar
radiating chapels
small, semi-circular or polygonal chapels that extend outwards from the apse of a large church, typically arranged in a radial pattern around the ambulatory
compound piers
an architectural support, often seen in Romanesque and Gothic cathedrals, composed of a central mass with attached columns, half-columns, or pilasters
cistercians
the aesthetic and architectural style of the Cistercian monastic order, known for its rejection of elaborate ornamentation in favor of simplicity and functionality. Influenced by St. Bernard of Clairvaux