Lecture 21 Eyes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
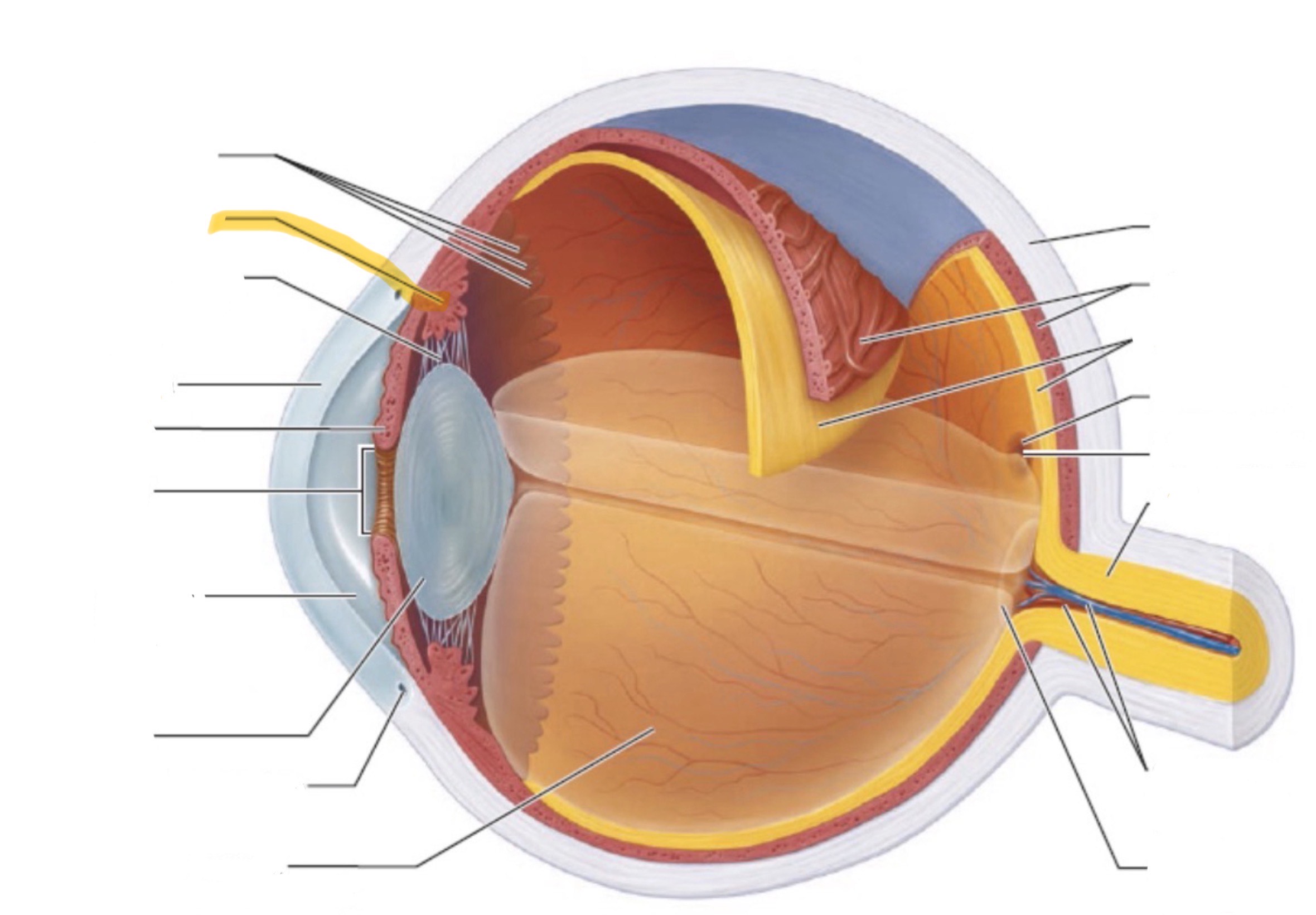
What is the highlighted part of the eye?
Cillary body
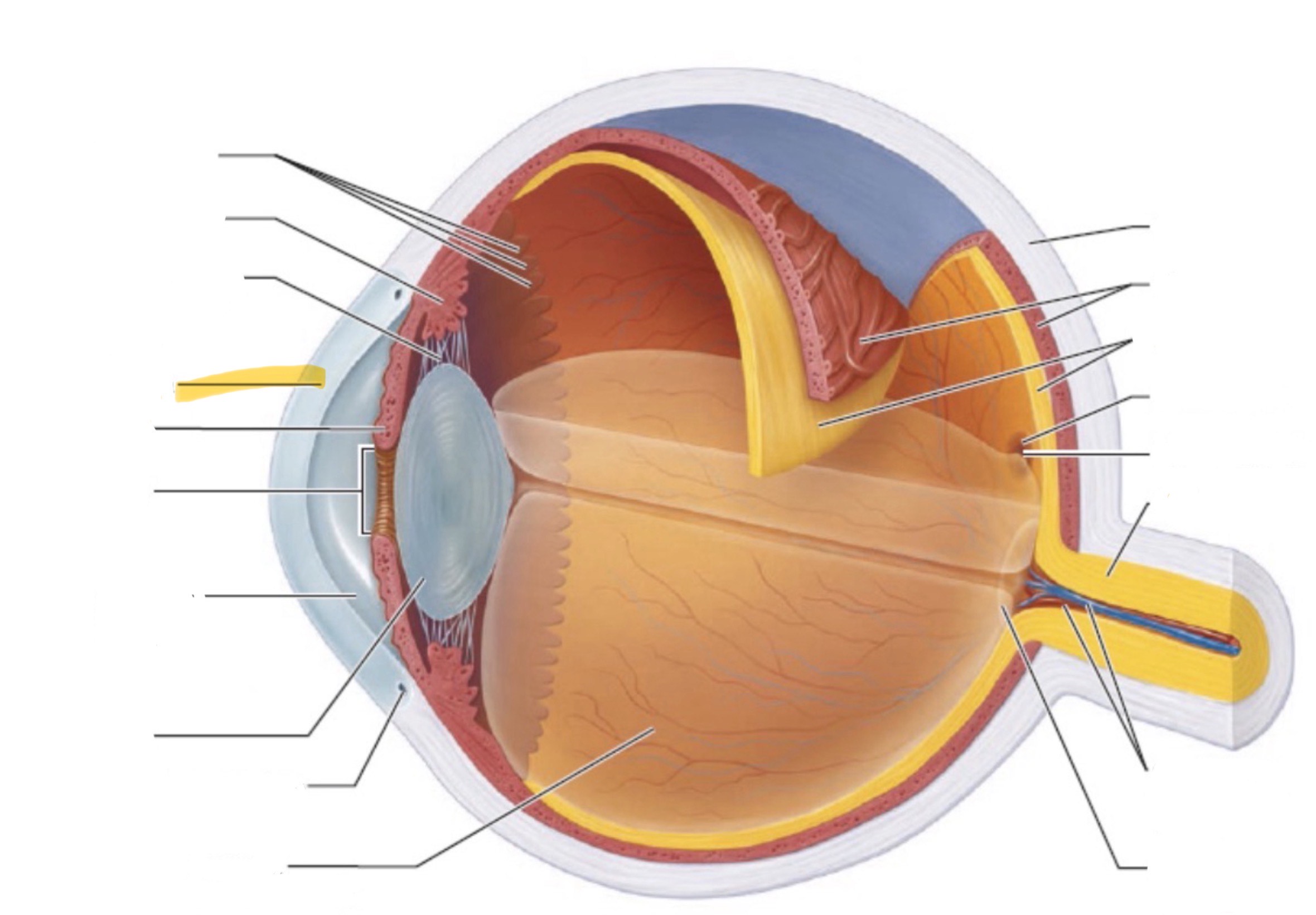
What is the highlighted part of the eye?
Cornea
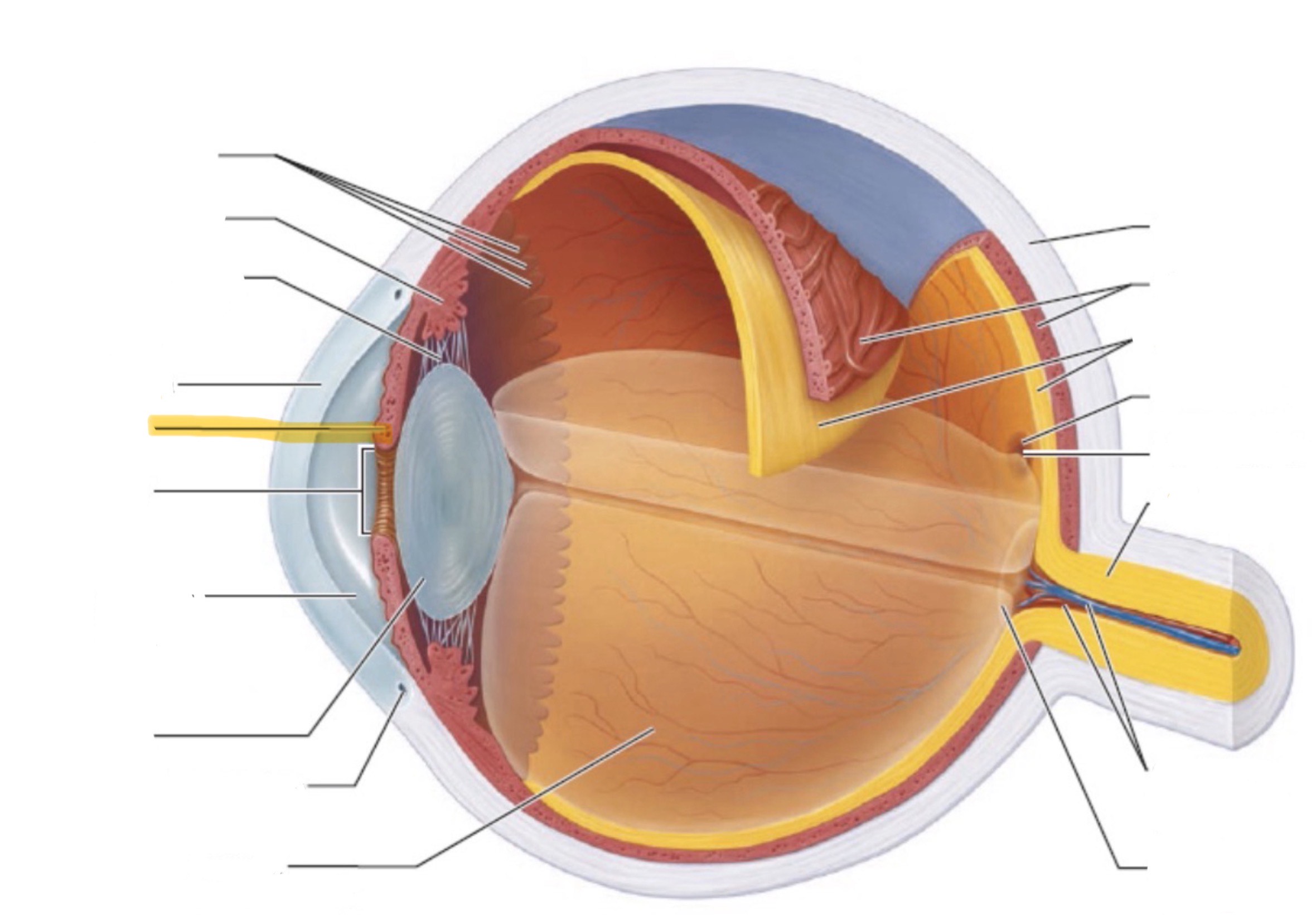
What is the highlighted part of the eye?
Iris
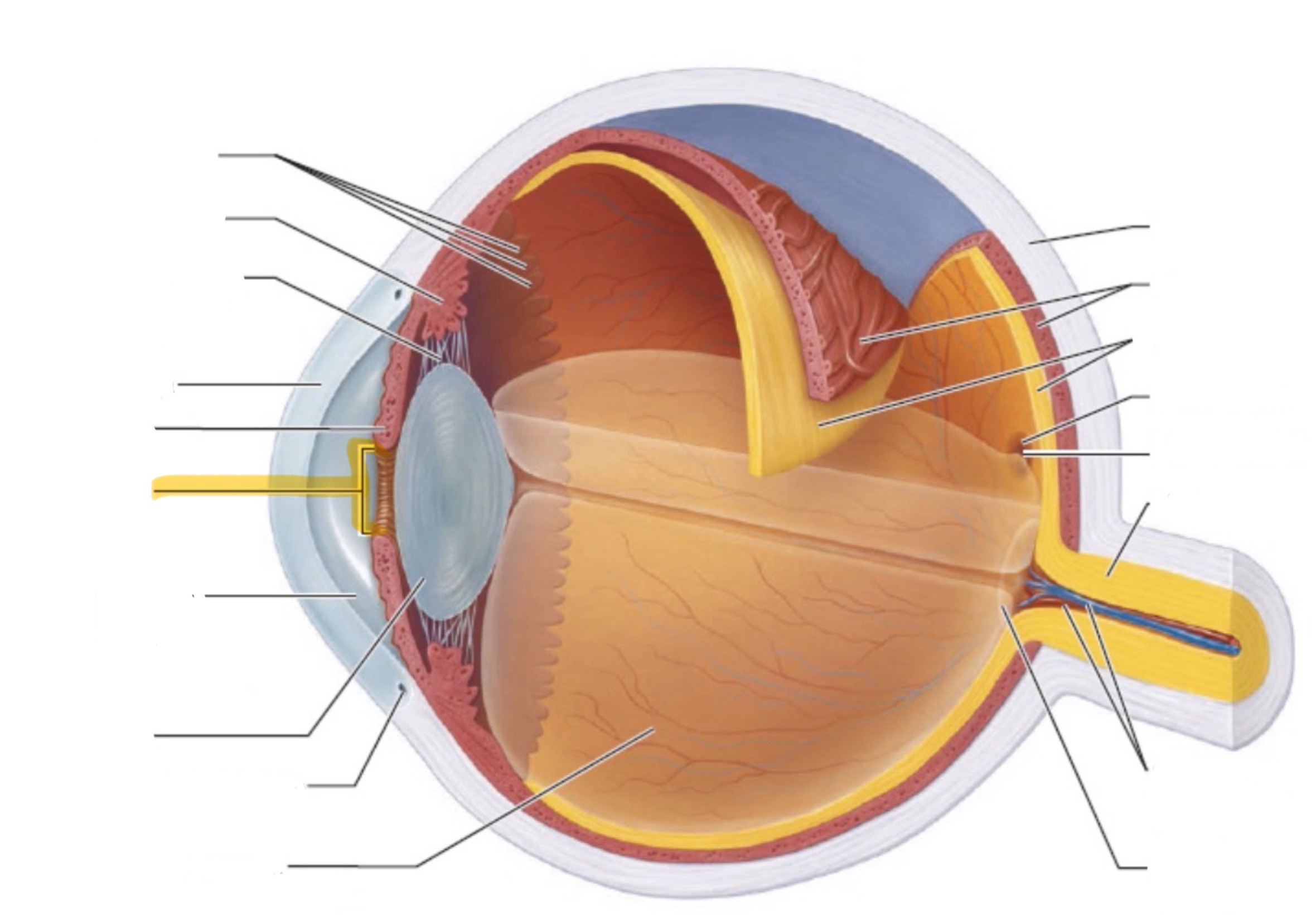
What is the highlighted part of the eye?
Pupil
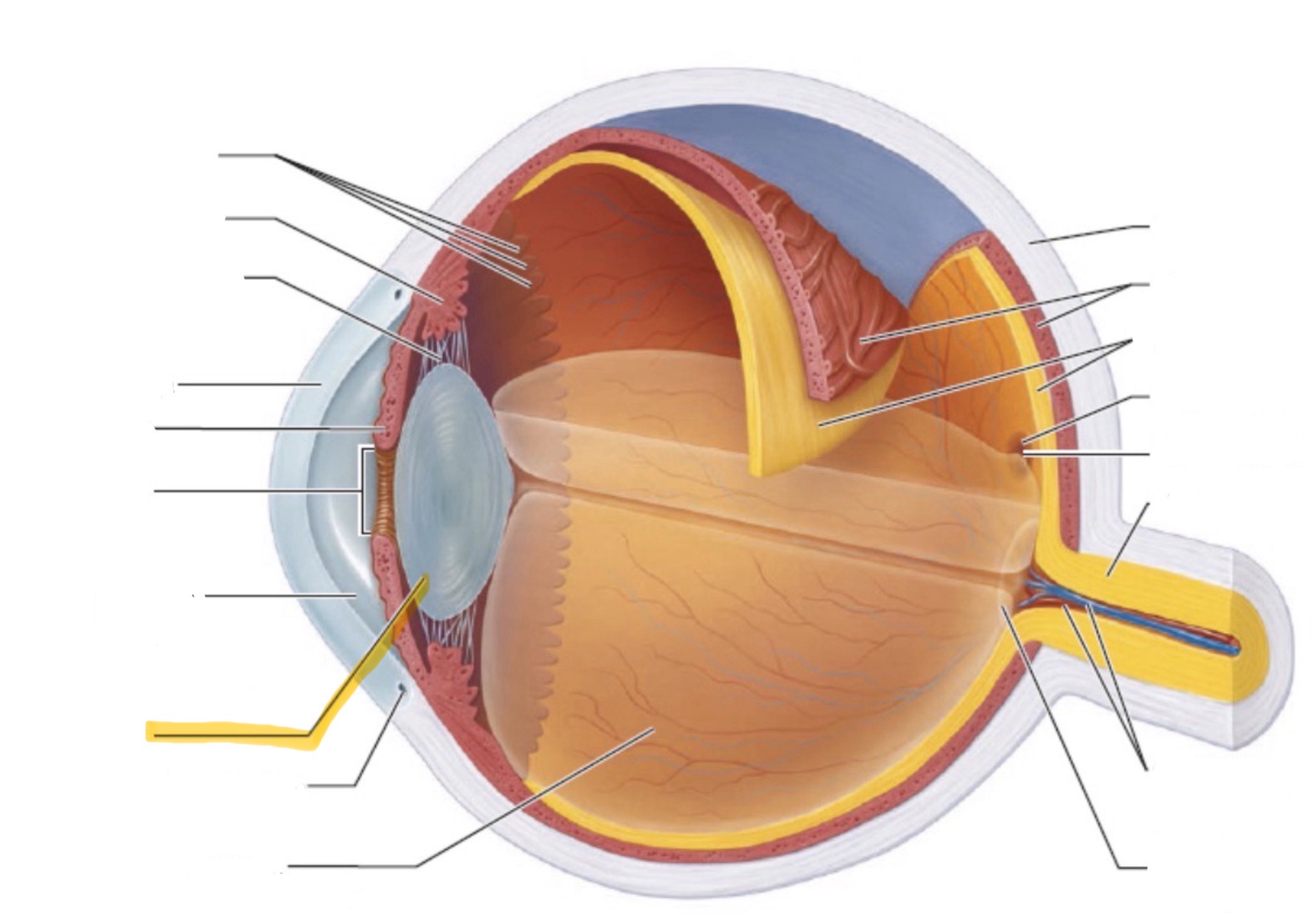
What is the highlighted part of the eye?
Lens
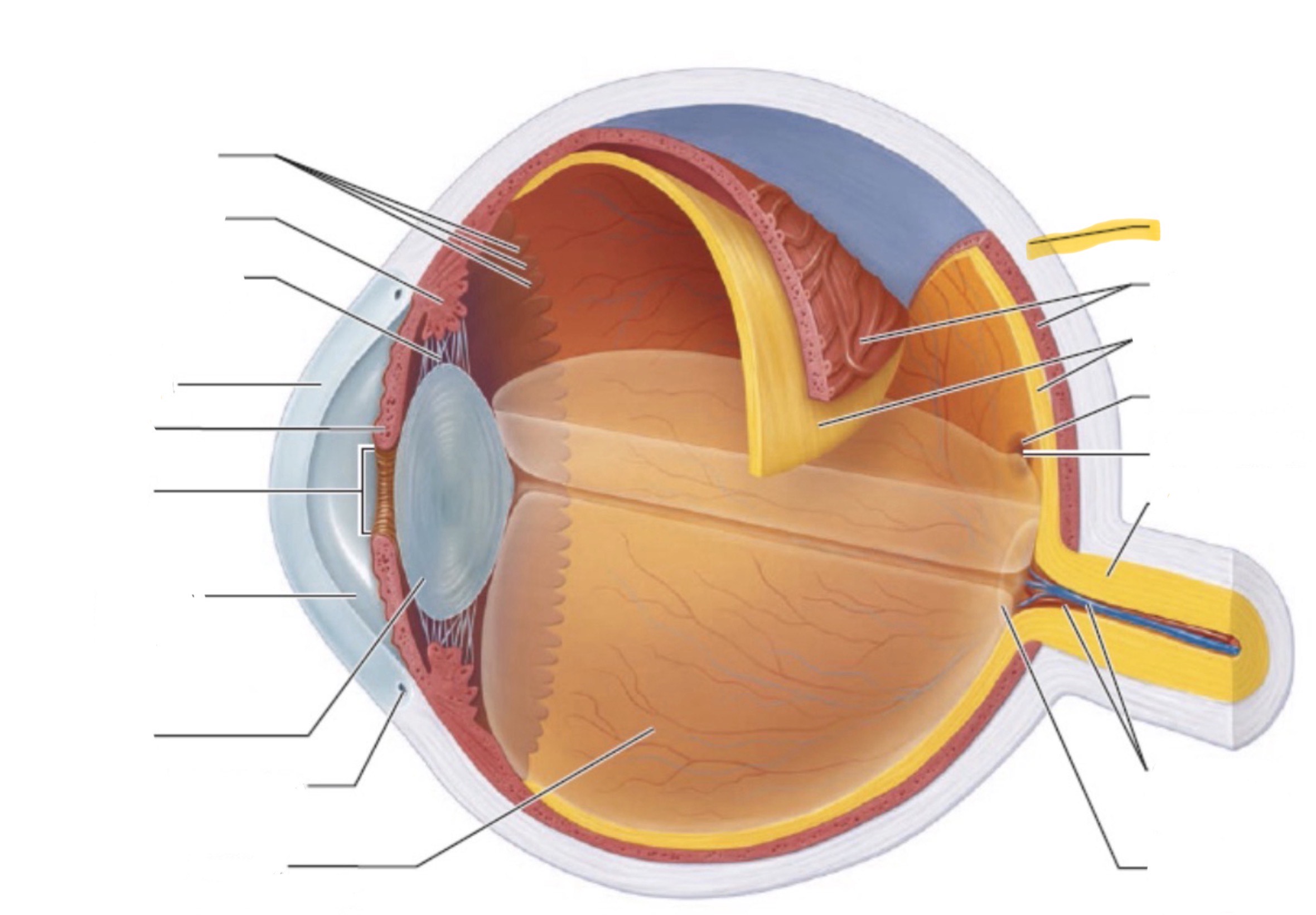
What is the highlighted part of the eye?
Sclera
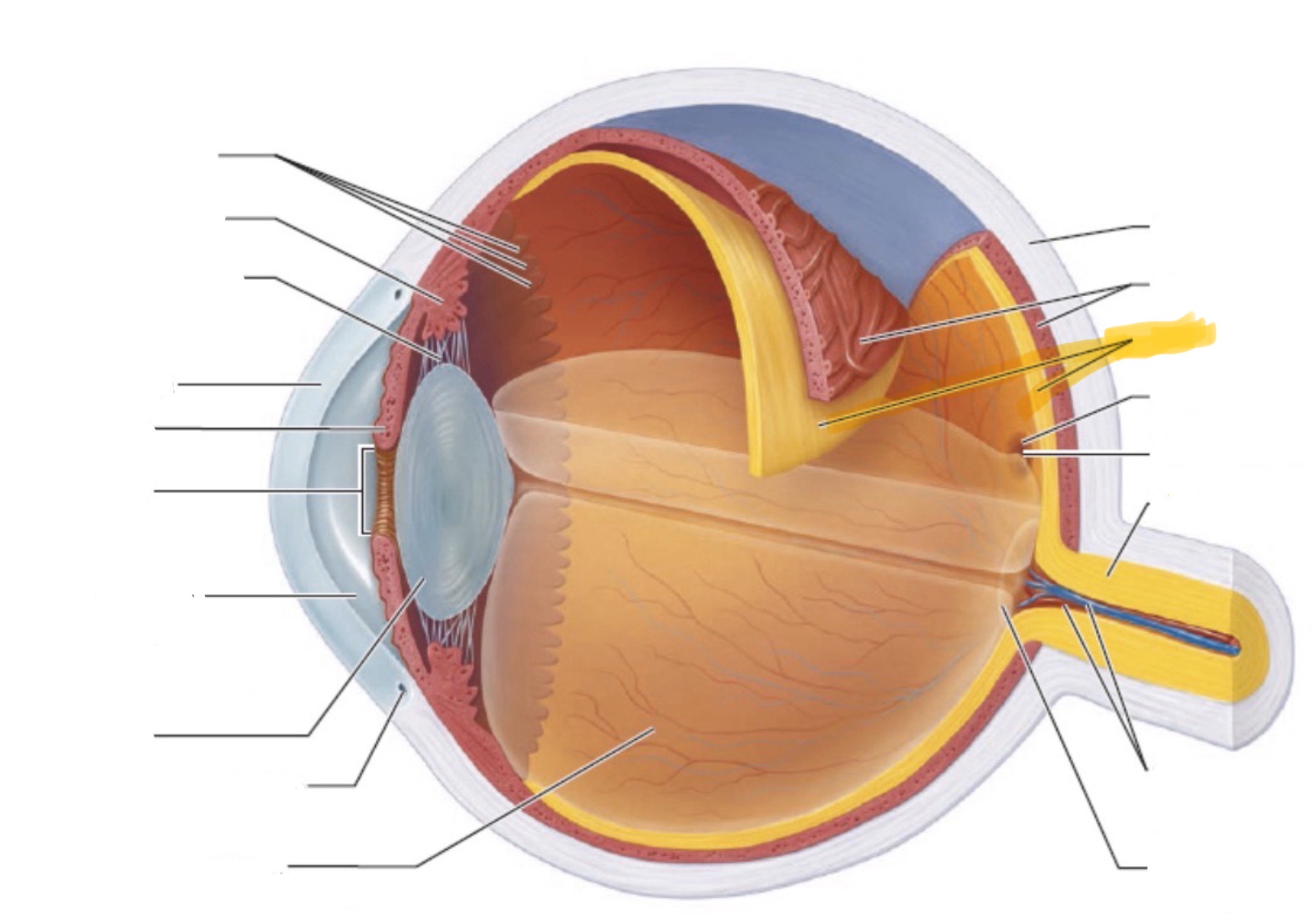
What is the highlighted part of the eye?
Retina
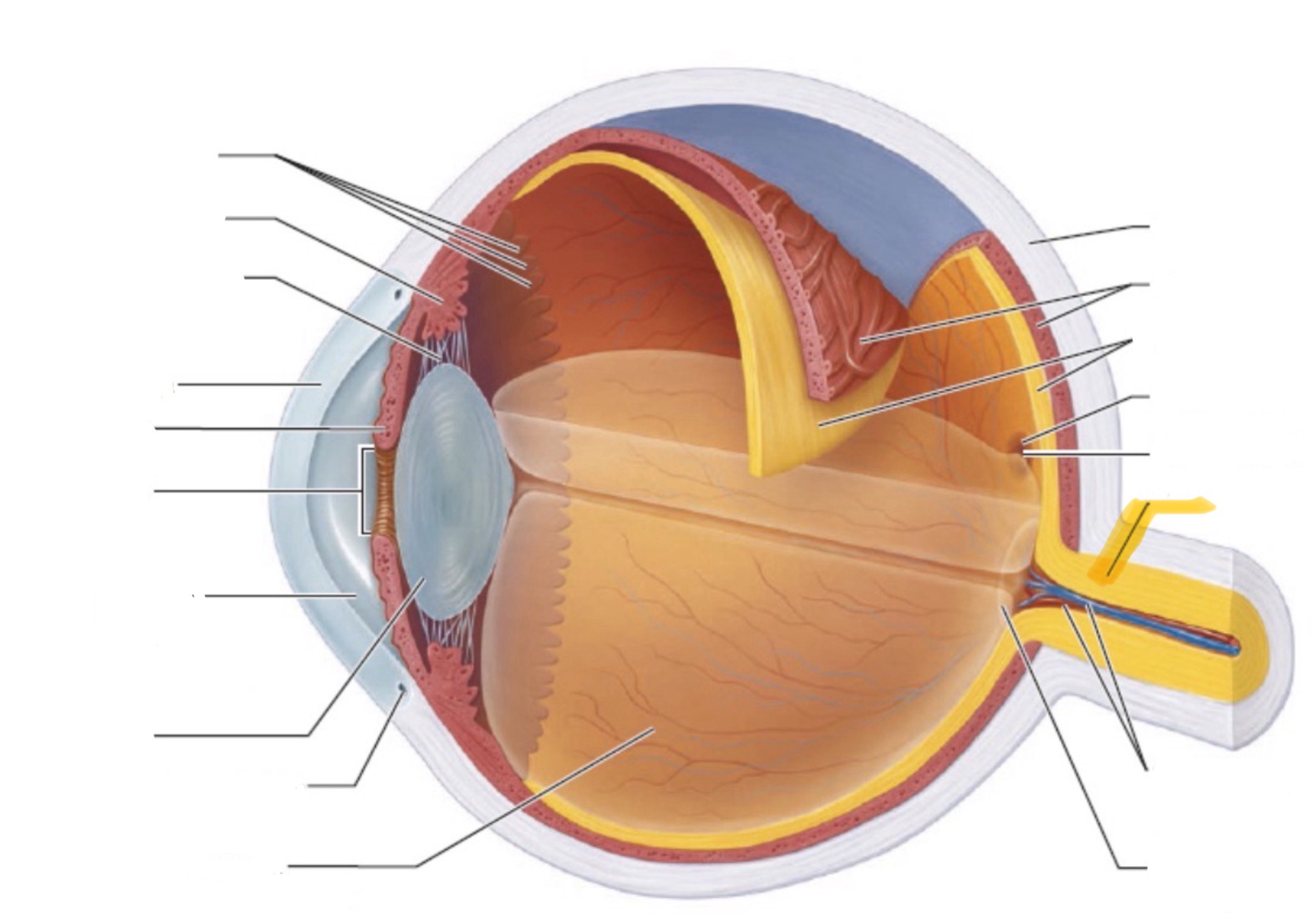
What is the highlighted part of the eye?
Optic nerve
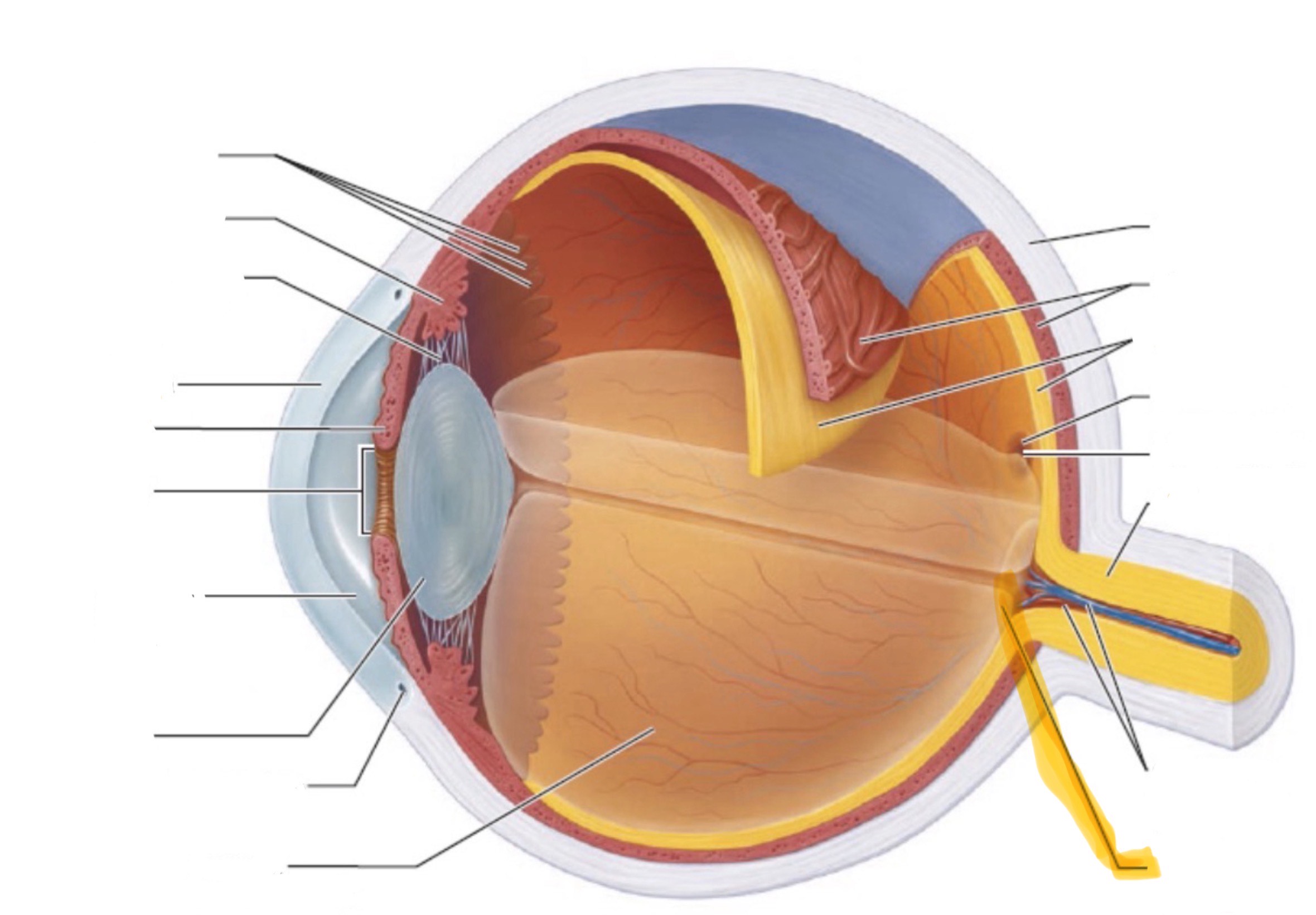
What is the highlighted part of the eye?
Optic disc
What is the accessory anatomical structure of the eye?
Eyebrows
Eyelids
Conjuctiva
Lacrimal Apparatus
Extrinsic eye muscle
What is the function of the Cornea?
Focus light onto the retina
Protects against dirt, germs, and UV ray
What is the function of the sclere?
Provides structure and protection
What is the function of the optic nerve?
Carries visual information from the retina to the brain
What is the function of the lens?
Focuses light rays onto the retina
What is the function of the retina?
Converts light into electrical signals to perceive images
What is the function of the ciliary body?
Produces aqueous humor which nourishes the eye and helps focus light
What is the function of the iris?
Controls the amount of light entering the eye
What is the function of the pupil?
Regulates the amount of light entering the eye
What is the function of the optic disc?
The optic nerve exits containing photoreceptors
What is the function of the fatty cushion?
Provides support and protection
Understand how light travels to the back of the retina and is processed through the rods and cones. (15.3)
Light enters the eye- Through the cornea and pupil then light is focused onto the retina
Photoreceptor activation- Light hit the photoreceptor in the retina which causes them to convert light into electrical signals
Phototransduction- initiate a biochemical process that converts light into electrical signals that then get sent to the brain
Signal transmission- The electrical signals travel through the optic nerve to the brain where they are interpreted as images
Visual Perception- The brain processes these signals to create the perception of visual images
What is the visual perception of cones?
Sensitive to low light levels and are primarily responsible for night vision and peripheral vision.
They do not perceive color only black and white
What is the visual perception of rods?
Sensitive to bright light levels and are responsible for color vision
Provide high spatial acuity and can differentiate different colors
What is the retinal Localization of rods?
Located in the periphery of the retina
What is the retinal Localization of cones?
Located in the central fovea (crucial for high acuity vision)
Describe the visual pathway from light passing through cornea to occipital lobe (15.4)
Light enters the eye- Through the corneas, pupil, and lens which focus light onto the retina
Photoreceptors convert light into signals- the retina contains rods and cones which detect light and convert into electrical signals
Signals are transmitted- the optic never carries these signals from the retina to the brain
Information is processed- the brain visual cortex interprets the visual information to form images and perception