Hepatic Pathologies - Bacterial, Fungal, and Parasitic Infections (Lecture 3)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are pyogenic abscess?
pus-forming bacteria (E.coli is m/c)
What are causes of pyogenic abscess? (HINT: 4)
- Direct extension from infection in biliary tract in pts w/ suppurative cholangitis, cholecystitis (m/c)
- Enters PV system due to appendicitis/diverticulitis (infection in intestine → PV → liver)
- Hepatic artery route (systemic infection)
- Trauma (blunt or penetrating)
Name 3 clinical presentations of pyogenic abscess
- Fever (FUO/PUO - fever/pyrexia of unknown origin);
- Increased WBC
- Malaise
- Anorexia
- RUQ pain
- Jaundice
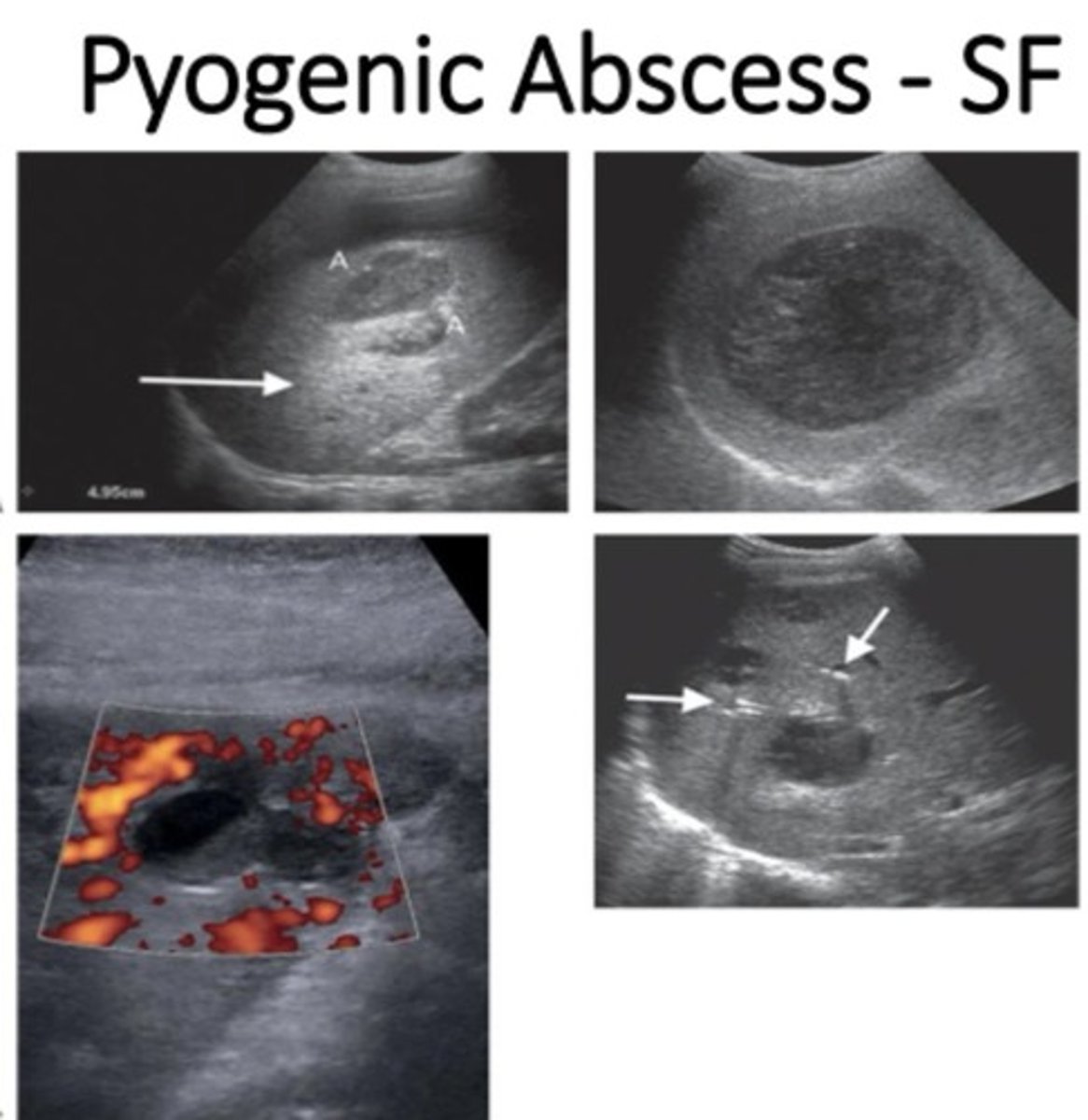
What are the sonographic features of pyogenic abscess?
- Fluid filled with posterior enhancement
- Pus: can be echofree or highly echogenic (variable appearance)
- Internal septations, debris
- Gas forming bacteria make hyperechoic foci
- Increased flow surrounding abscess (not within abscess)
What are treatments of pyogenic abscess? (HINT: 3)
if left untreated = 100% mortality
- Antibiotics
- Percutaneous drainage
- Surgery (last resort)
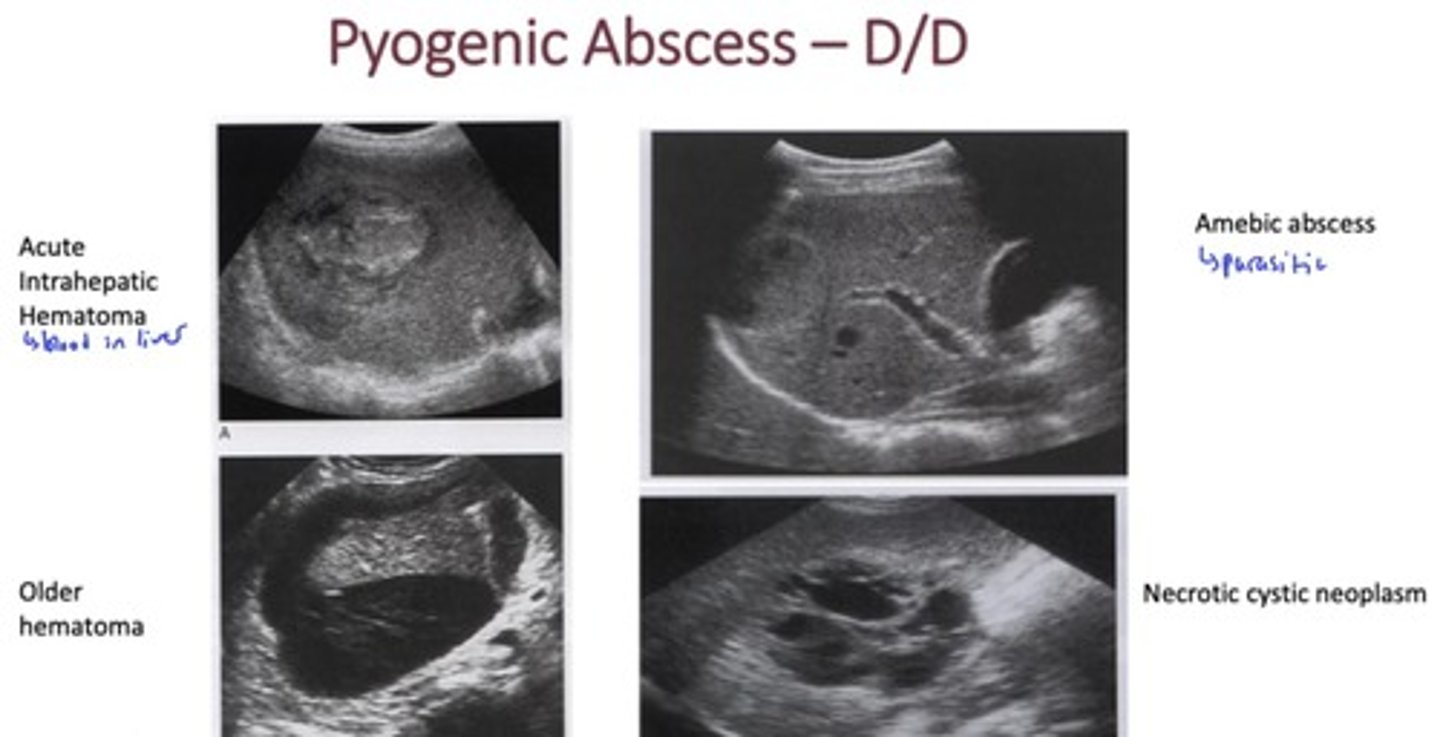
What are differential diagnoses of pyogenic abscess? (HINT: 3)
- hematoma
- other abscesses (amebic)
- necrotic cystic neoplasm
What is candidiasis?
- infection by fungi of genus Candida
- Part of normal flora of mouth, vagina, skin, and intestinal tract
How is candida spread?
spread through blood of myotic infection to solid organs (lungs - m/c, liver), to produce opportunistic infections in pts w/ decreased immunity
Name one clinical Presentation of candidiasis
- Persistent fever in neutropenic (decreased neutrophils) pt
- Pain, in area of involvement
What is the biochemical marker for candidiasis?
candidiasis in blood
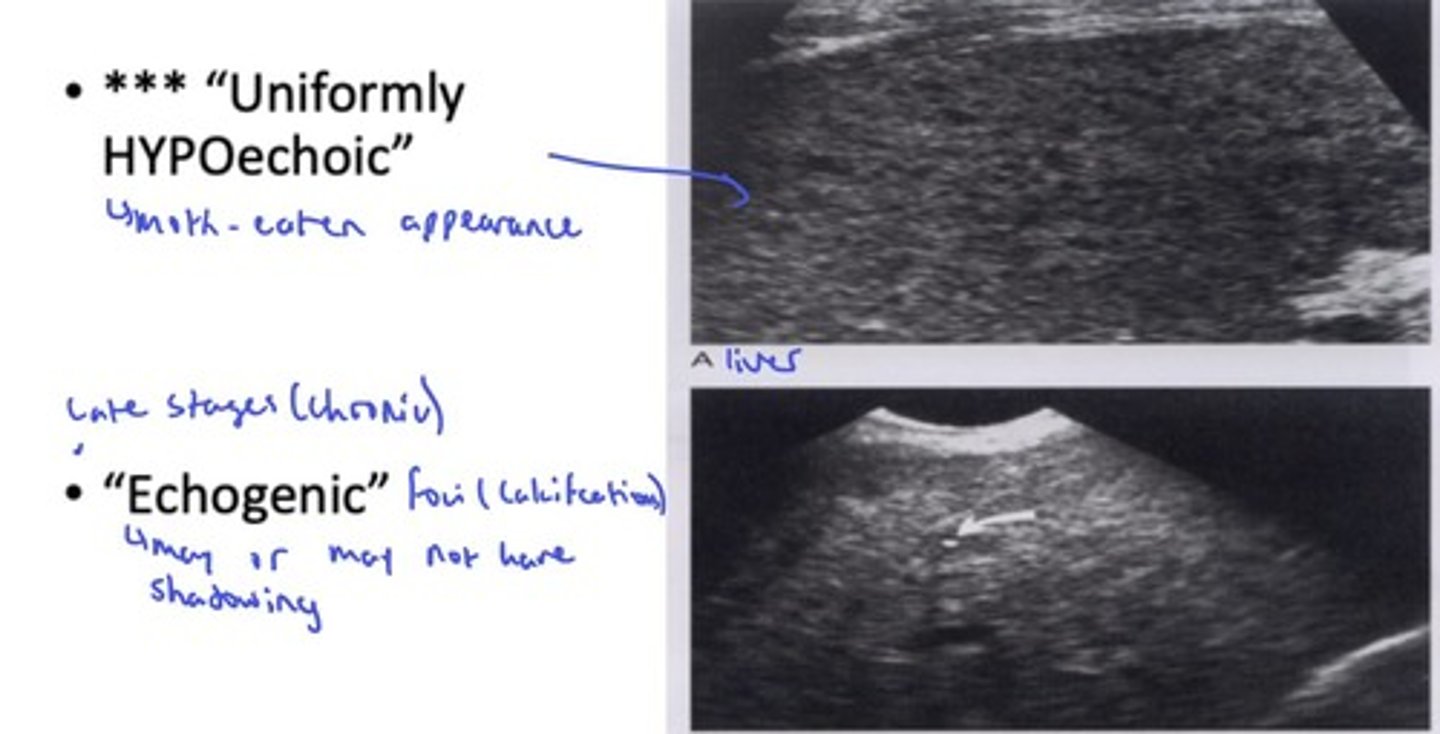
What are the sonographic features of candidiasis? (HINT: 4)
- Early stages: wheel within a wheel, bull's eye (1-4cm); Hyperechoic centre, hypoechoic rim
- Uniformly hypoechoic (moth-eaten appearance)
- Late/chronic: echogenic foci (calcifications w/ or w/o shadowing)
- Microabscesses: multiple small hypoechoic
What are differential diagnoses of candidiasis? (HINT: 2)
mets, cirrhosis
What is the treatment for candidiasis?
antifungals
What is the most common opportunistic infection in AIDs patients?
pneumocystis carinii (P. jiroveci)
What is the mode of transmission of pneumocystis carinii?
inhalation (therefore infection primarily infects lungs)
Name 3 clinical presentations of pneumocystis carinii
- CD4/ T-helper cell count under 200
- Breathing difficulty
- Fever
- Dry cough
- Weight loss
What are the sonographic features of pneumocystis carinii? (HINT: 2)
- Diffuse, tiny, non-shadowing echogenic foci (m/c)
- Echogenic clumps (dense calcification)
What is amebiasis?
parasitic infection caused by entamoeba histolytica from a fecal-oral route
A patient presents with dysentery and RUQ pain. Sonographically, there is a hypoechoic oval shaped lesion in the right liver lobe. What condition is the patient most likely to have?
Amebiasis (amebic abscess)
Name 3 clinical presentations of amebiasis
- RUQ pain (m/c)
- Fever
- Amebic dysentery (blood filled diarrhea)
- Hepatomegaly
What is the biochemical marker for amebiasis?
positive indirect hemagglutination test in more than 94% of pts
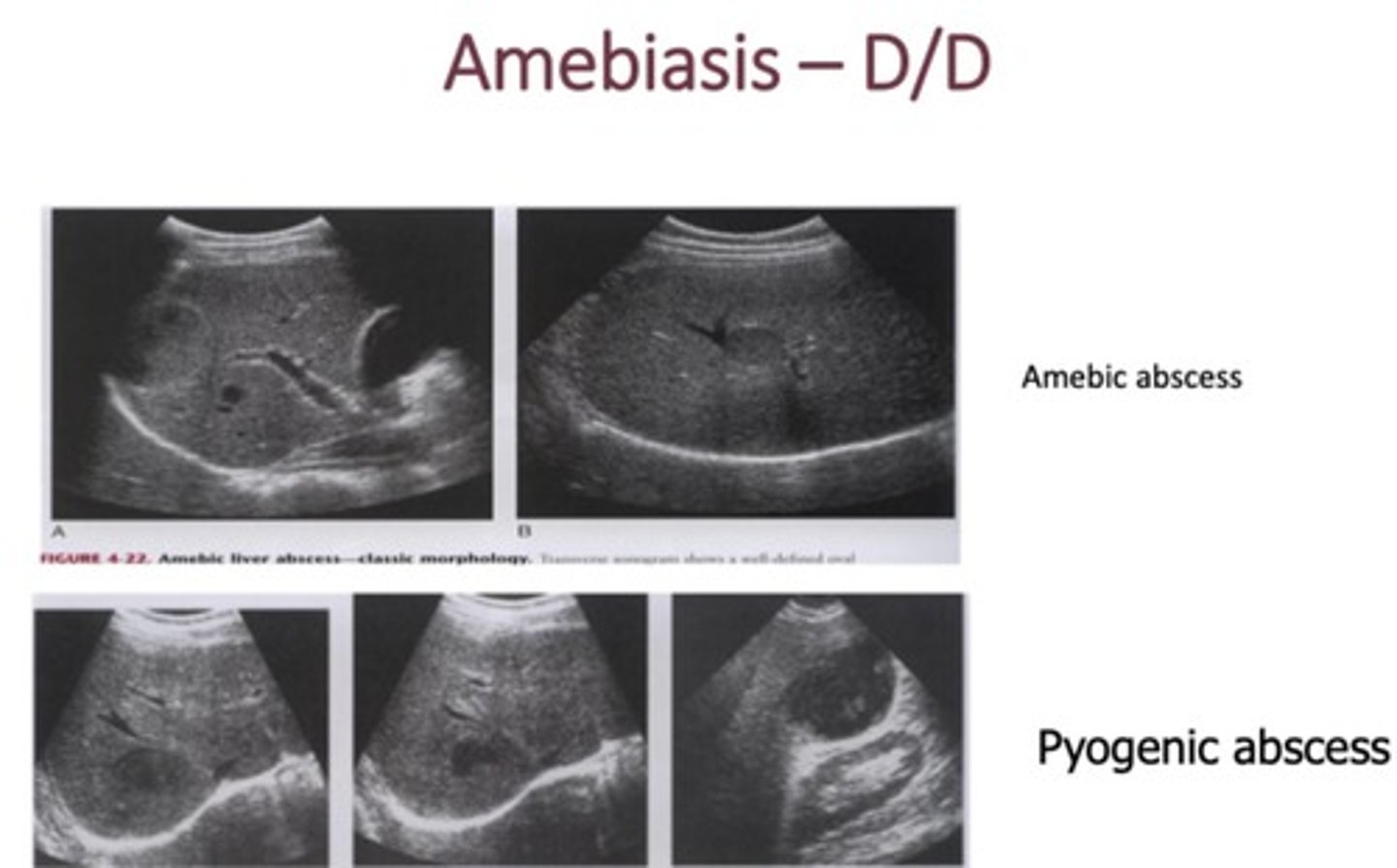
What are sonographic features of amebiasis? (HINT: 4)
- Round/oval shaped lesion
- Initially echogenic, later becomes uniformly hypoechoic
- Posterior enhancement
-Tends to be in rt liver lobe near diaphragm/hepatic flexure
What is echinococcosis (Hydatid Disease)?
tapeworm that lives in intestines of definitive host (canine animals), creating slow growing cysts in intermediate hosts (humans)
What is the clinical presentation of hydatid disease?
- Can be asymptomatic for 5-10 yrs
- Symptomatic when cyst compromises something (pressure, obstruction)
- Fever
- Pain, if infected
- Anaphylaxis (rare, happens if cyst ruptures)
Which parasitic condition is associated w/ anaphylaxis?
Echinococcosis (hydatid disease)
What is the biochemical marker for hydatid disease?
CFT (complement fixation test)
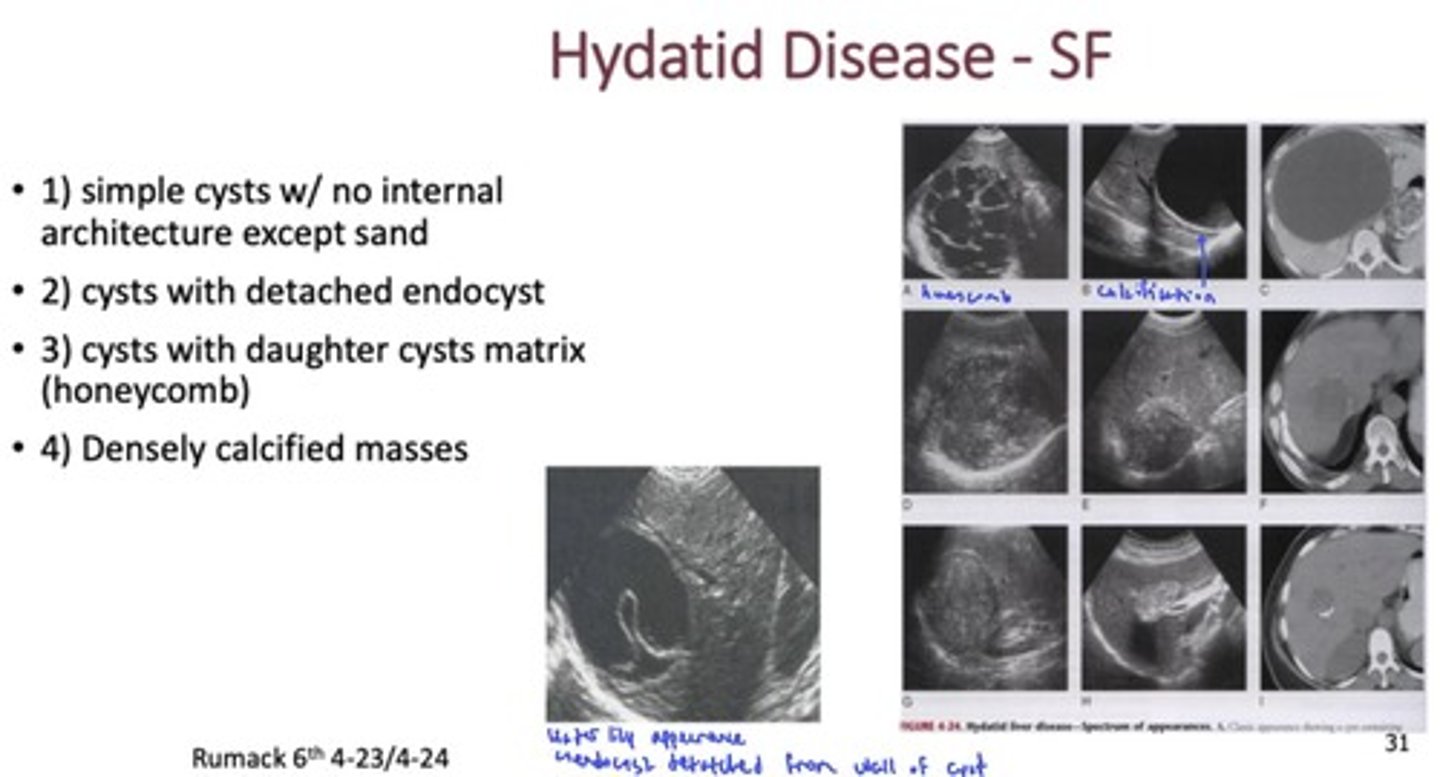
What are sonographic appearances of hydatid cysts?
- Simple cysts w/ no internal architecture except sand
- Cysts w/ detached endocyst
- Cysts w/ daughter cysts matrix (honeycomb)
- Densely calcified masses
What is schistosomiasis (biliharziasis)?
common parasitic infection from swimming in contaminated water, with infection entering intact skin
What are the clinical presentations of schistosomiasis?
- symptoms of portal hypertension (fibrosis compromising PV lumen)
- Late stage: jaundice
What are the sonographic features of schistosomiasis?
- Widened echogenic portal tracts at porta hepatis (most commonly)
- Features of PH: Early = increased liver size; Late = decreased liver size; Splenomegaly; Varices