APES - Unit 5: Land and Water Uses Modules 26-28
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Plowing
-A regular disturbance of soils that occurs in order to turn soil over (A horizon)
-Form of tilling --> includes other activities such as stirring, digging, and cultivation.
-^Tilling doesn't modify soil to same extent (plowing = extreme tilling)
Positive effects of plowing and tilling:
-Turning over the top horizons of soil
-Aerating soil
-Exposing nutrients to the surface
-Increasing the cation exchange capacity (CEC) of the soil
-Removing weeds
Negative effects of plowing and tilling:
-Higher rates of wind erosion
-Increased sediments in water
-Increased decomposition, leading to higher greenhouse gases
-Long-term soil compaction
Why do rainforests have nutrient poor soil?
-Nutrients exist in plants/vegetation
Slash-and-burn agriculture
-Clears the land by burning the existing vegetation to release nutrients into the soil.
-Only effective for a few years before the soil becomes completely depleted of nutrients
-Increases CO2 emissions + contributes to deforestation --> When rainforests that process carbon dioxide are removed, more is released into the atmosphere and less can be stored in the forest short-term and long-term.
-Farmers then need to practice shifting agriculture
Shifting agriculture
-Moving on to another area because of the nutrient-depleted soil
Irrigation
-Groundwater and surface waters are used
-Agriculture is the largest use of water worldwide, with 70% of water used for irrigation.
Aquifer
-Where groundwater is stored in pore spaces within permeable layers of rock and sediment, similar to a sponge
-Negative = cant see how much water is remaining (vs reservoir)
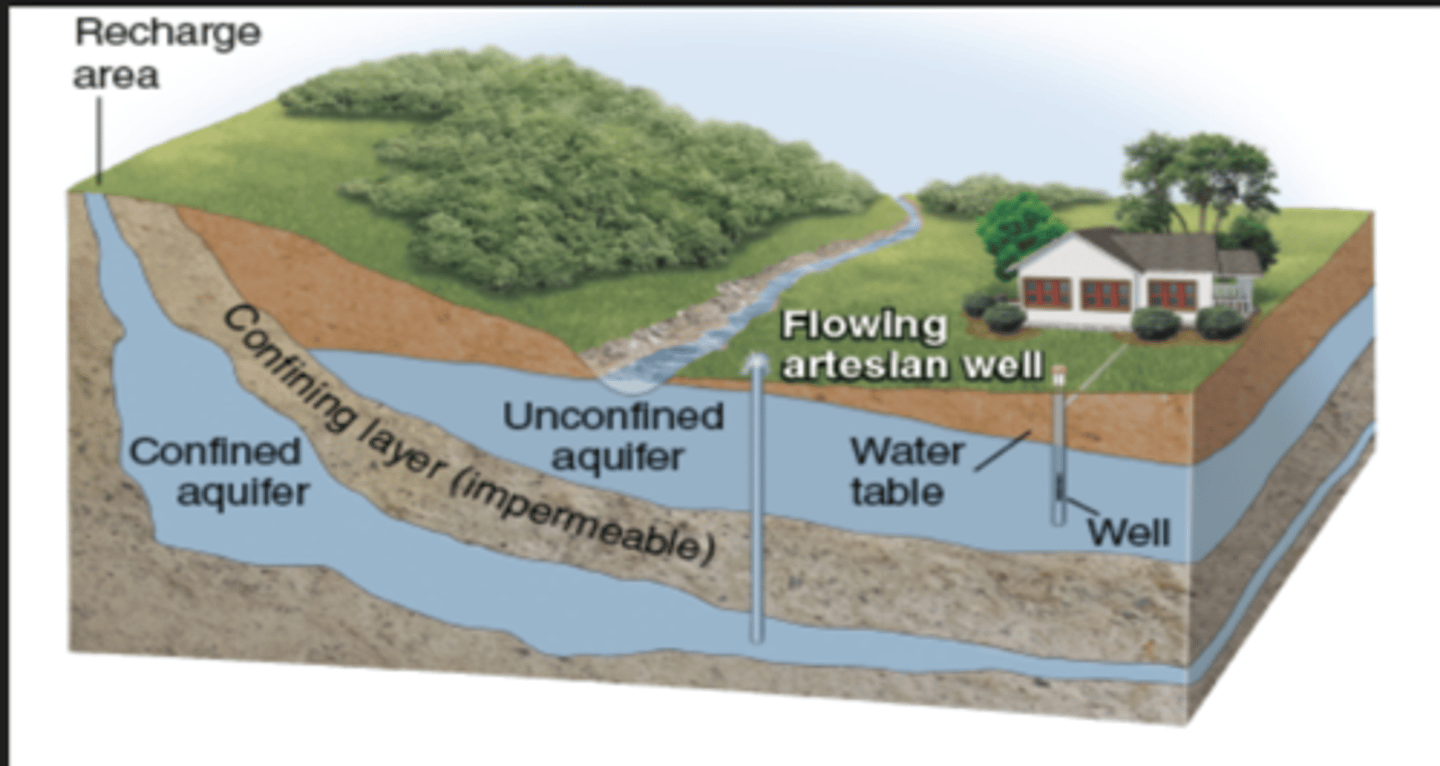
Unconfined vs Confined aquifers
-Aquifers that allow water to easily flow vs aquifers that are surrounded by impermeable rock or clay
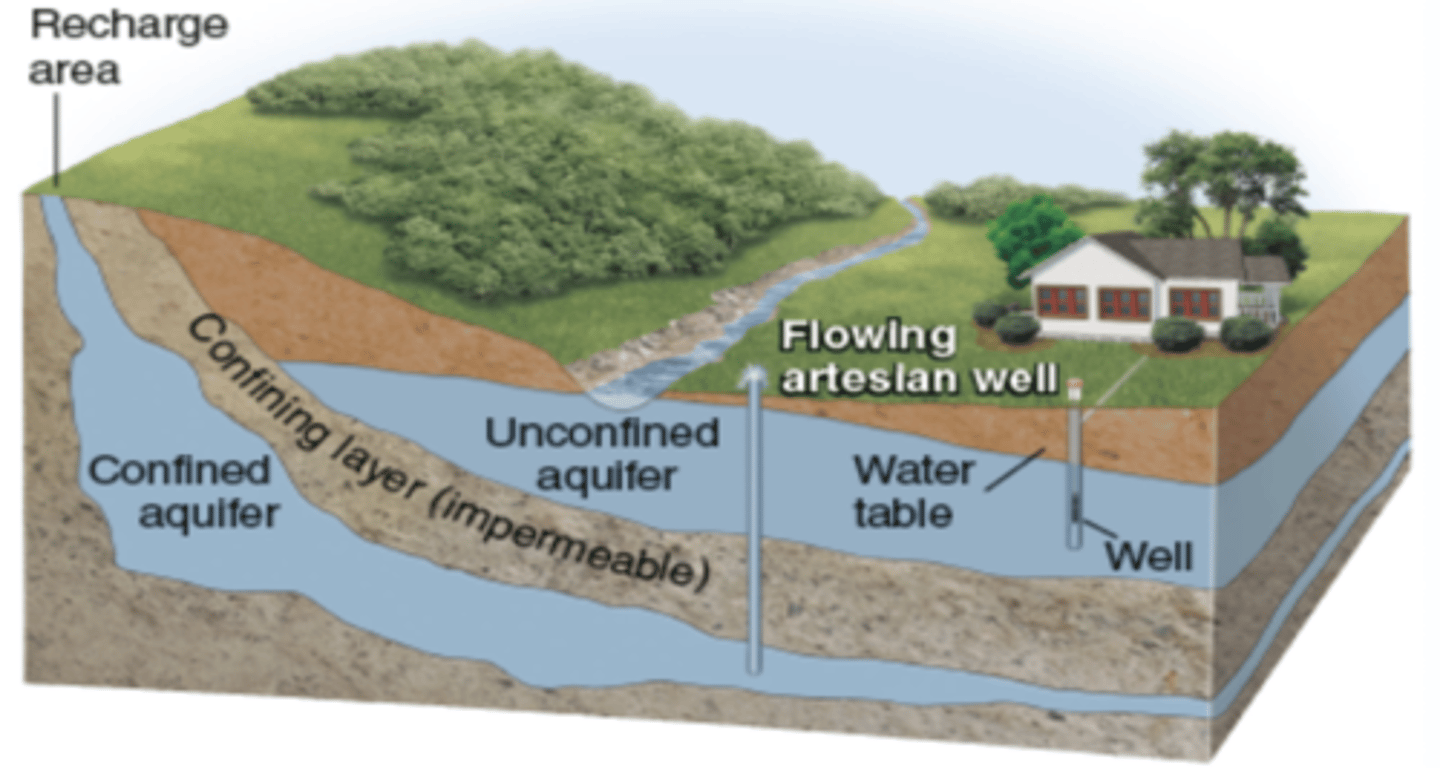
Water table
-The uppermost level at which the groundwater in a given area fully saturates the rock or soil.
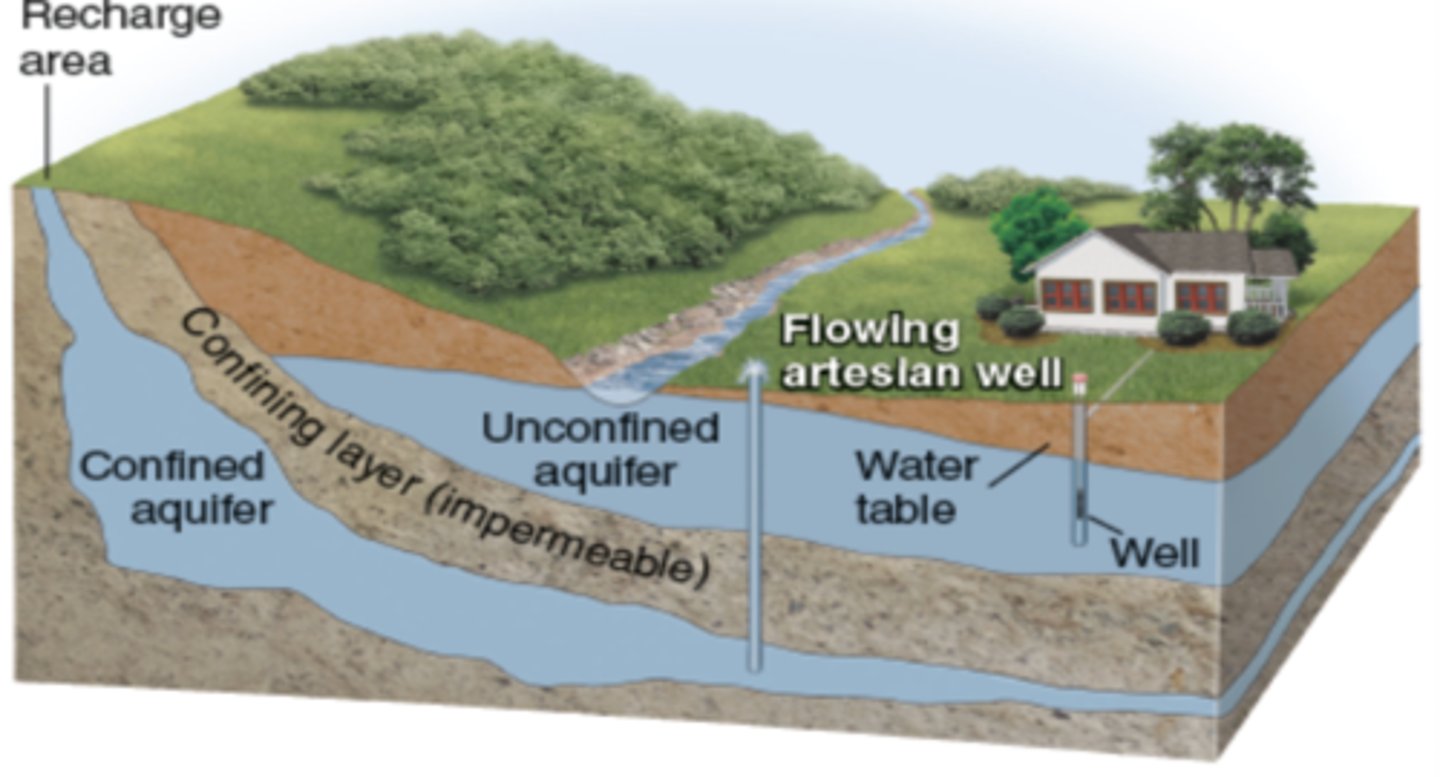
Groundwater recharge
-The process by which water from precipitation percolates through the soil into groundwater.
Springs
-Water that naturally percolates up to the surface.
Artesian well
-A well created by drilling a hole into a confined aquifer.
-Water in wells can take 10,000-20,000 years to recharge.
Water footprint
-The total daily per capita use of freshwater for a country or the
world
-Water is a resource that is limited, but does cycle through.
-^Overuse prevents water from recycling fast enough to replenish.
-In the US, 1/3 of freshwater use is irrigation
-^Other large uses of water = livestock.
Virtual Water Trade
-The concept of "virtual water" refers to the water embedded in products traded internationally.
-How does virtual water trade affect global water resources, especially in regions facing water scarcity? Should countries with abundant water resources reconsider exporting water-intensive products?
Ethics and Equity in Water Usage
-Given the varying availability of water resources, is it ethical for countries or corporations in water-rich regions to maintain high water footprints while many other areas face severe water scarcity? How should water equity be addressed in the context of global development and climate change?
Furrow irrigation
-Trenches or furrows filled with water next to crops (33% water loss)
Spray irrigation
-Water is pumped and sprayed over crops through nozzles (25% water loss)
Flood irrigation
-The entire field is flooded with water (20% water loss)
Drip irrigation
-Slowly dripping water through hoses directly near a plants roots (5% water loss)
Waterlogging
-A form of soil degradation that occurs when soil remains under water for prolonged periods.
Salinization
-Occurs when crops are waterlogged
-Large amounts of water evaporate and leave behind salts, which can be toxic and impede plant growth.
-Aquifers can become depleted due to overuse from different sources.
Aquifer depletion
-As the water table drops farther from the ground surface, springs that once bubbled up to the surface no longer emerge, and spring-fed streams dry up
Cone of depression
-An area lacking groundwater due to rapid withdrawal by a well
-If multiple users of an aquifer do not regulate use, a cone of depression expands, lowering the water source for all.
Types of pesticides
Fungicide – meant to target fungi
Rodenticide – specifically meant to target rodents
Persistent pesticides – pesticides that remain in the environment for years to decades (DDT)
Nonpersistent pesticides – pesticides the are meant to break down rapidly (weeks to months), but may have to be applied more often
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
-An agricultural practice that uses a variety of techniques designed to minimize pesticide inputs
Pesticide Resistance
-A trait that certain individual pests develop when they are exposed to a pesticide and survive, passing on traits aiding in surviving the pesticide.
-Stems from overuse of pesticides
-This leads to application of more and stronger pesticides – known as the pesticide treadmill.
Reduce use of pesticides: GMO
-Strains of crops can be modified to release toxins to pests so they can't eat the crop.
-Other methods could include making crops herbicide tolerant, so that crops can continue to be sprayed without being affected by the herbicide.
-^ This won't reduce use of pesticides, but can save more crops.
Monocropping
-Growing one crop in the same field to maximize yield
-Most common method of agriculture
Downsides:
-Pests are able to infest areas quickly
-Low genetic diversity = difficult to resist predators/disease + difficulty rebounding after population loss
Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations (CAFOs)
-Large indoor and outdoor structures to create maximum occupancy of animals for maximum output of meat. These are also known as "factory farms."
-Due to high demand of meat --> Beef cattle, dairy cows, hogs, and poultry
Benefits of CAFOS
-Minimize land costs
-Improve feeding efficiency
-Increase fraction of food energy that goes into production of animal body mass
Risks of using a manure lagoon
-The possibility of developing a leak in the liner that would allow the waste to seep into and contaminate the underlying groundwater and an overflow into adjacent water bodies
Negatives of CAFOS
-Ethical concerns of confinement of animals
-Animals fed grains, instead of natural grasses
-High use of antibiotics and nutrient supplements
-Hormone treatments provided to increase body mass
-Manure lagoons used
Other methods of producing meat:
-Free-range grazing: allowing animals to graze outdoors on grass for most or all of their lifecycle
-Nomadic grazing: the feeding of herds of animals by moving them to seasonally productive feeding grounds, often over long distances
Overgrazing and desertification
-Overgrazing = result of allowing cattle to graze in one location for too long
-Desertification = The transformation of arable, productive, low-precipitation land to desert or unproductive land due to climate change or destructive land use such as overgrazing and logging
Fishery
-A commercially harvestable population of fish within a particular ecological region.
Fishery collapse
-The decline of a fish population by 90 percent or more
Purse-seine nets
Nets surround a school of fish
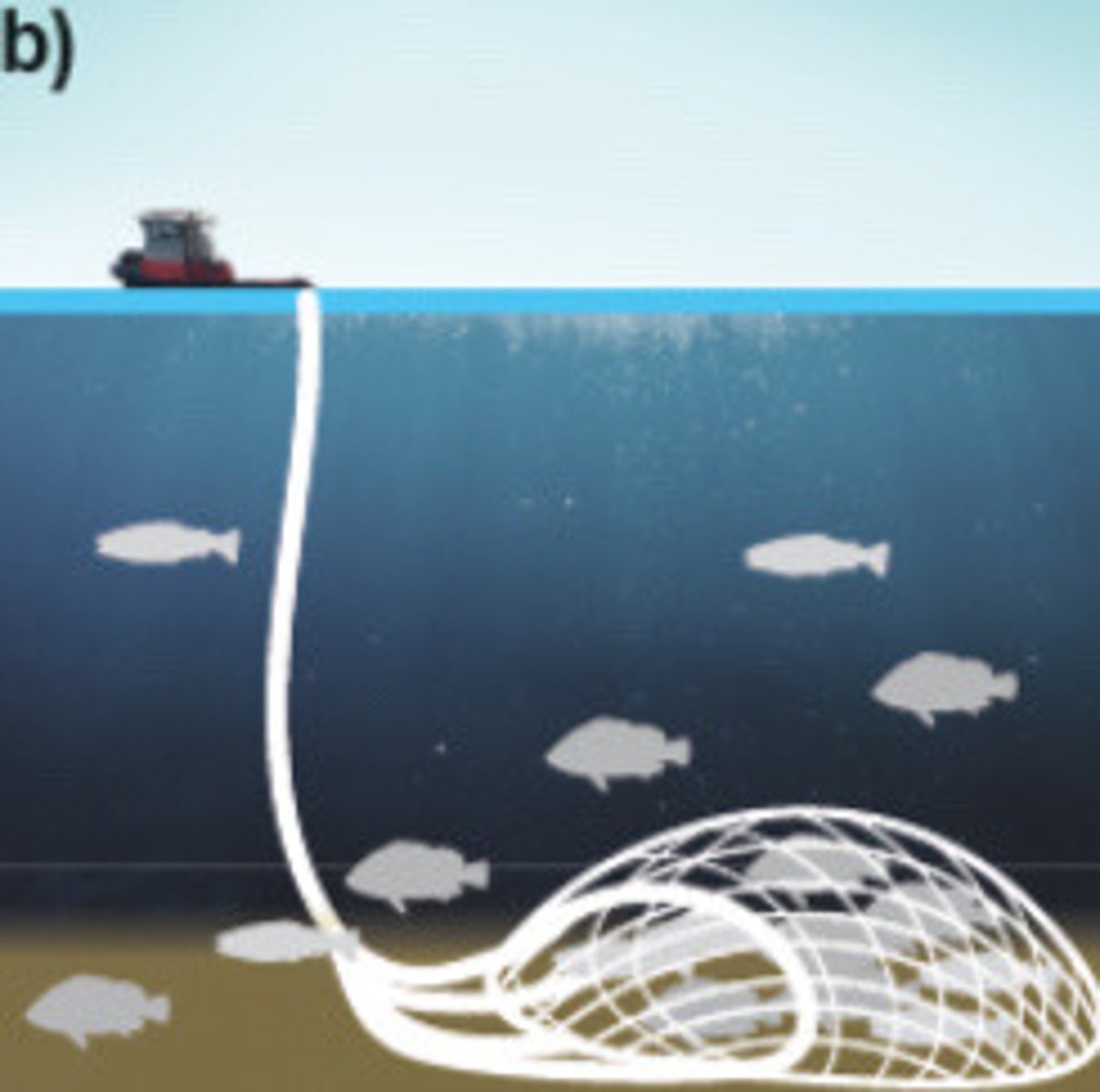
Bottom trawl nets
Nets run along the ocean bottom
Midwater trawl nets
Nets are pulled through the water above the ocean bottom
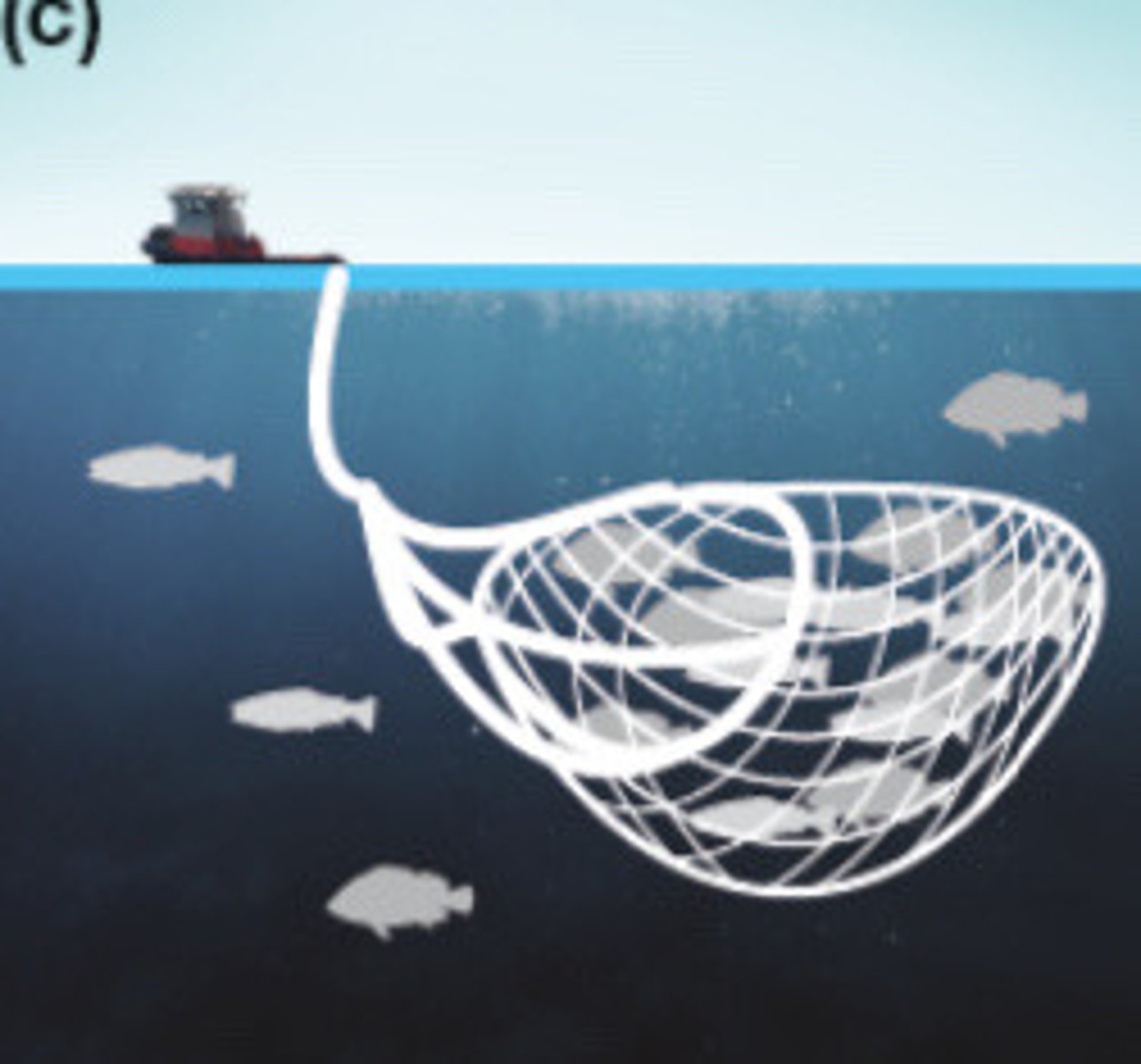
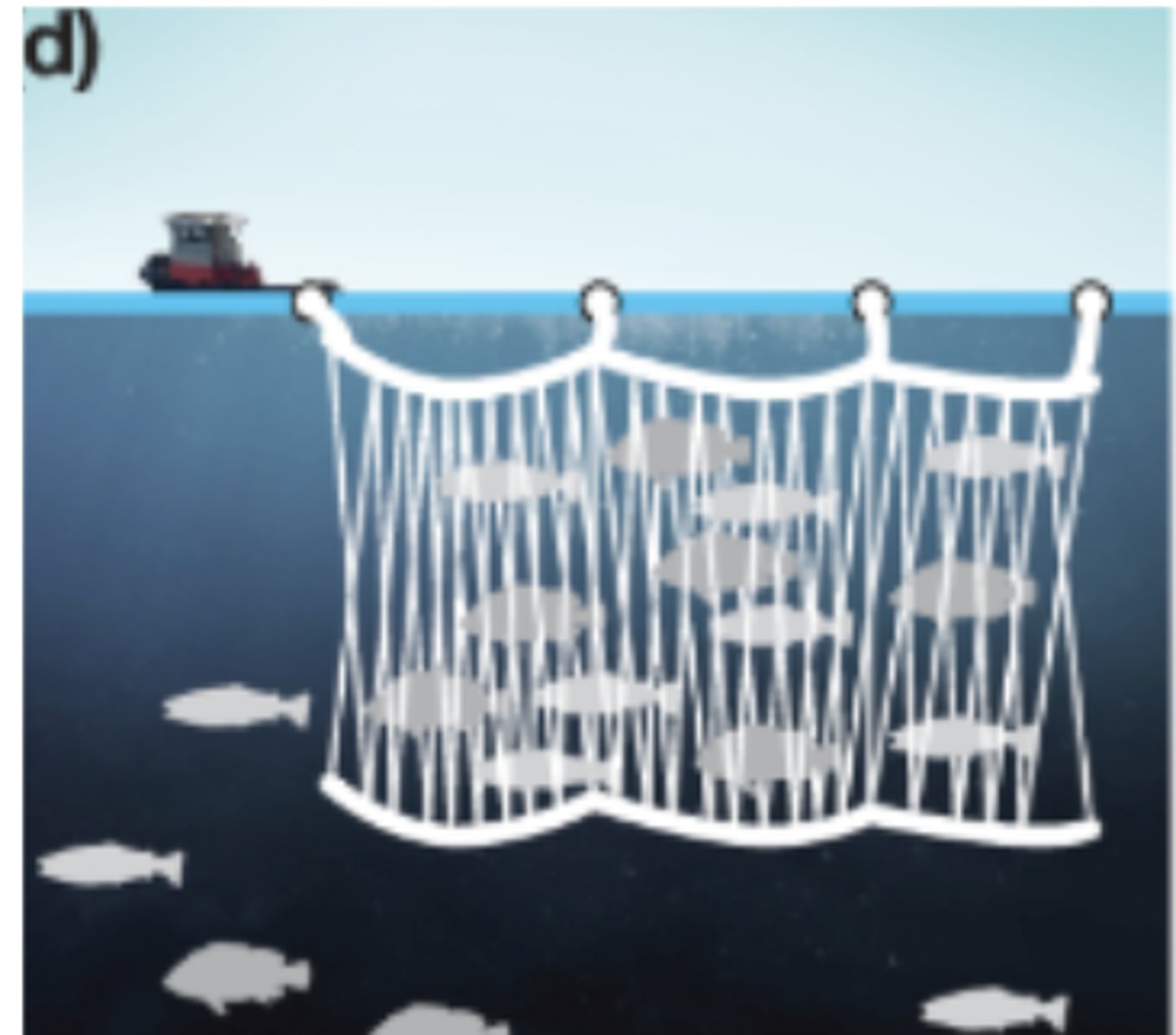
Gill nets
Nets have larger holes in them and are set up like a wall and fish swim into the holes, become caught, and can't escape

Longline trolling
Lines more than a mile long and have baited hooks every meter or so.
Bycatch
-An effect of attempting to catch as much fish as possible leads to unintentional catch of non-target species
Sustainable fishing
-Laws have been enacted to protect fisheries by setting maximum catch limits and shortening harvesting seasons.
-Movements by individuals to reduce consumption of fish, or to consume only farmed fish, can also reduce these issues.