BAP - Beef
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
what is beef
meat from cattle
what is a cow
bovine female that has given birth
what is a heifer
female bovine not given birth
what is a bull
intact male bovid
what is a calf
young immature bovid
what is a steer
castrated male bovid
what is a bovid
mammal of the calf family
what is culling
removing from the herd
when were cattle imported to the US
1493 by Columbus
why were cattle needed in the 1840s
used for hides and tallow, much of the animal went to waste
when was the refridgerated rail car made
1880
describe the current beef inventory
beef production remains constant while cattle inventory decreases, and consumption of beef decreases
feeder operations
cattle graze grass for 3-4 months before feedlot
backgrounding operations
cattle fed dry forage, silage, and grain 90-120 days before feedlot
feedlots
TMR diet, put on weight
beef cattle inventory per farm
most under 50 animals
Missouri Ag and Beef
$93.7 bil industry
3rd in cattle farms
3rd in number of beef cattle
3rd in cow calf operations
biggest beef imports
austrailia, canada, brazil
biggest beef exports
Japan, South Korea, China
products from cattle
beef, leather, gelatin, tallow
species
group of organisms of similar individuals capable of exchanging genes
breed
group of organisms within a species having a distinct appearance
bos taurus
most common cattle species / north america
bos indicus
cattle species found in warmer climates
traits of a british bos taurus species
from britain, UK, and irelend
-smaller mature size
-mature faster
-less growth potential
-fertility and calving ease
-attain higher quality grades
-lower carcass yields
traits of a continental bos taurus species
from continental europe
-larger mature size
-later maturing
-carcass with less fat
-lower quality grades
-produce more calving difficulty
Aberdeen Angus
british breed
originated in scotland
noted by black color
most common breed in US
CAB
Certified Angus Beef (CAB)
modest or higher marbling
medium of fine marbling texture
cattle harvested 30 month of age or younger
10 to 16 square inch ribeye area
1100 pound hot carcass weight or less
less than 1” fat thickness
superior muscling
practically free of capillary ruptures
no dark cutters
no neck hump exceeding 2”
Charolais
continental breed
france
medium to large frame size
white with pink muzzle
demonstrate efficient growth
more pounds = more profit
Hereford
british breed
red with white face
longevity
cows 15+
bulls 12+
early maturity
Simmental
continental
switzerland
originally selected for
milk
meat
draft animals
Red Angus
british breed
same origin as Aberdeen angus
1917 only black allowed to register
1954 new herd book - red angus
black coloring dominant
Texas longhorn
iconic breed
eat wilder range of grasses, plants, weeds
produce very lean beef
longevity
docility
Gelbvieh
continental
“yellow cattle” in german
came to US in 1970s - clay center,NE
triple purpose breed
redish gold, russet or black in color
fine hair
medium to large body size
fast pre-weaning growth
Holstein
dairy breed
after lactating = sent to beef production
Limousin
continental breed
central and southwest france
breed of sturdiness, health, and adaptability
work and meat
Highland
british breed
from british highlands
high fat milk
horns help forage during heavy winters
Shorthorn
british breed
dual purpose
oldest recognized breed
roan coloring
how are cattle converters
they convert low quality foods into nutrient dense food for us
forages
by-products
major management components of cow calf operations
herd nutrition
pasture and range management
herd health
financial management
marketing
reproduction
genetics
Assessing profitability (cow calf operations)
calf crop percentage weaned (7mo of age)
average age at weaning
annual cow cost
compare market price with break-even price
why spring or fall calving
cows are not seasonal animals
280 day gestation length
some operations will utilize both calving seasons
larger farms
some bull both seasons
gives flexibility with heifers
spread out marketing risk
more labor requirements
more pasture management
spring calving
advantages and disadvantages
most common in US
feb-april
heifers calf before cows
advantages
increasing temp
growth of grasses
disadvantages
rain, snow, mud
fall calving
advantages and disadvantages
august-october
advantages
weaned calves marketing in spring
breeding for fall
weather and fescue toxicity
disadvantages
must get calves through winter
manage lactating cow
lower calf weight
three stages of parturition in cattle
prep stage: calf getting into position
delivery; 2-4 hours, dystocia
clean up: placenta passes in 8-12 hours
causes of calf loss
peri-natal calf mortality 3.5-5%
44% had dystocia
large calves to first calf heifers
majority lost during first 1-3 days
scours
pneumonia
Colostrum
immunoglobulins
passive immunity transfer
fat soluable vitamins
vitamin b12
iron
vigorously nursing in first 24 hours
care for neonatal calf
colostrum
weigh
tag
castrate
rumen development
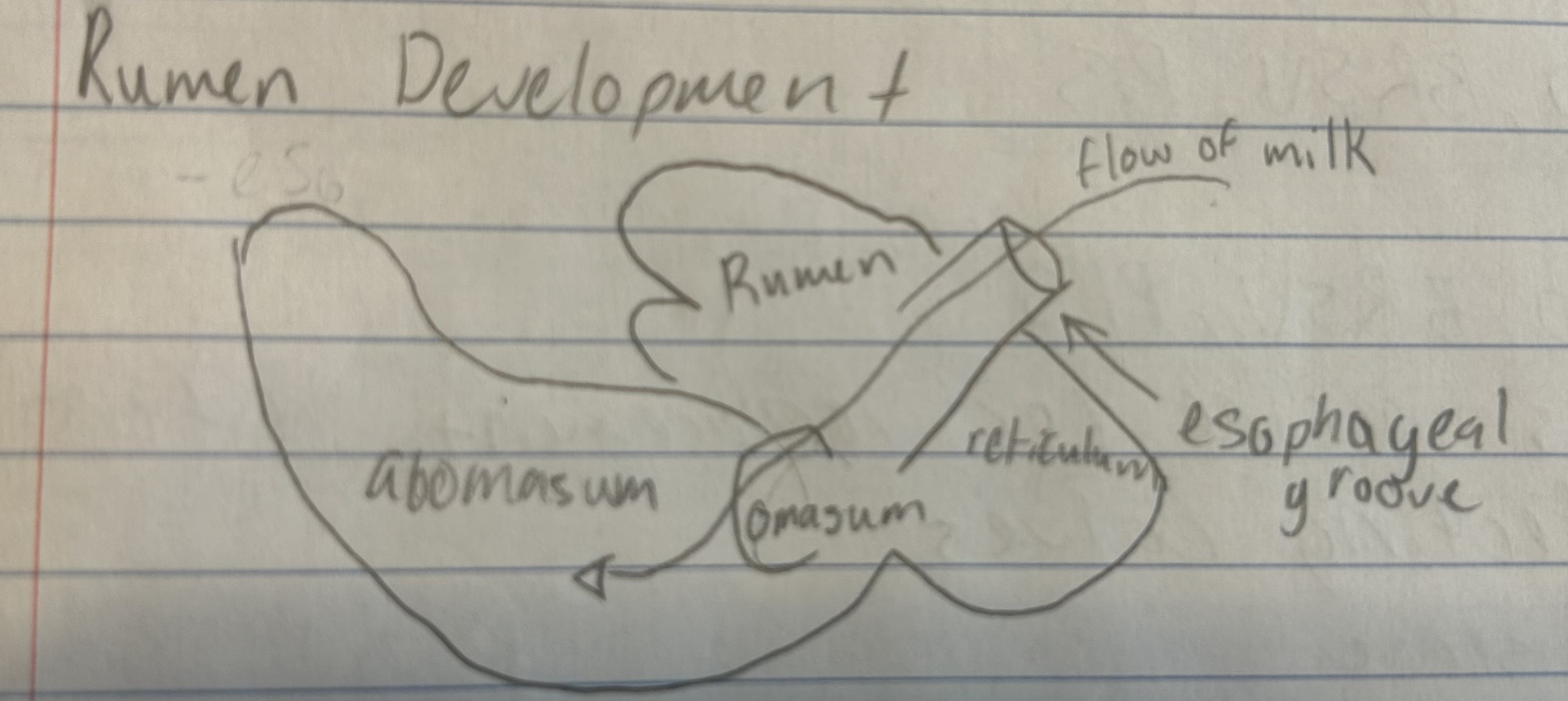
why dry out the umbilical cord
prevent bacteria from getting into calf
types of identification
ear tag
hot branding
freeze branding
castration
asap to reduce stress
easier housing (can keep heifers and steers together)
even distribution of fat
bloodless or surgical
dehorning
asap to reduce stress
safer for humans
done with hot iron to bud of the horn
vaccinations for calves and when to give them
60-90 days of age
clostridial diseases (7-way)
2-4 weeks before weaning
7-way
IBR,BVD,BRSV,PI3
brucellosis vaccine for replacement heifers
weaning
IBR,BVD,BRSV,PI3
brucellosis vaccine for replacement heifers
clostridial disease symptoms
Sudden Death: Often the first and only sign observed in a healthy animal.
Fever and Depression: Rapid onset of high temperature, listlessness, and loss of appetite.
Lameness and Swelling: Hardening or painful swellings that may crackle (crepitation) when touched due to gas under the skin.
blackleg symptoms
Gas bubbles under the skin that feel/sound like bubble wrap when pressed. Acute lameness and hot, painful swelling in heavy muscles (hips, shoulders) that later becomes cold and insensitive.
malignant edema
Soft, doughy swelling around a wound (e.g., from castration or difficult calving) that lacks the gas crackling typical of blackleg.
Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR)
commonly known as "Red Nose," is a highly contagious respiratory and reproductive disease in cattle caused by Bovine Herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1).
Bovine Viral Diarrhea (BVD)
a complex and costly viral disease in cattle. Its presentation is highly variable, often categorized into acute infections, reproductive issues, and the specialized "mucosal disease" syndrome
Bovine Respitory Syncytial Virus (BRSV)
It is particularly dangerous because it destroys the "cleaning cells" (ciliated epithelium) of the lungs, opening the door for severe secondary bacterial pneumonia.
when to wean
typically around 7 months of age
depends on BCS of calf
what is uterine torsion
uterine twist in cow
retained placenta
when placenta doesn’t pass within 8-12 hours after giving birth
best to provide antibiotics and not manipulate
5-15% occurrence in healthy herd
more frequent in bull calves
prolapse
inversion of vagina or uterus
could result in death of cow
encourage cow to stand after birth
high chance of reoccurrence
gestation length
280 days
calving interval
365 days
estrous cycle length
21 days
signs of estrus
standing heat
stand to be mounted
average duration 15-18 hours
mounting other cows
mucus discharge
swelling and reddening of the vulva
bellowing restlessness
reproductive diseases
brucellosis, leptospirosis,vibriosis, IBR, BVD, trichmoniasis
brucellosis
reproductive disease also known as bangs disease, non existent in missouri, can be transmitted from wild to domestic species, no cure
Leptospirosis
reproductive disease, wide spread problem in the south because of unvaccinated herds, a low grade uterine infection and the infected urine can pass it to other cows, can cause mastitus
vibriosis
venereal disease that causes infertility and occasionally abortions, causes raspatory infections and spreads from bull to cow during breeding
trichomoniasis
venereal disease that can cause abortions and includes symptoms of pyometra
vaginal discharge
pus in uterine lumen
infection in CL
what trait in cattle is of highest economic importance
reproductive performance
requirements for cows to be able to rebreed
appropriate BCS
lower than 4 causes longer post partum interval
PPI (post partum interval)
45-50 days
first calf cows have longer interval
at least 10 days longer
dystocia leads to longer interval
which areas are evaluated in BCSs
backbone
ribs
hips
pin bones
tail head
brisket
ideal time to check BCS
late summer/early fall
weaning
45 days after weaning
90 days before calving
calving time
beginning of breeding season
When to do a BSE
30 days before breeding season
components of a BSE
BCS
physical exam
scrotum and testes
semen evaluation
components of a semen evaluation
volume
concentration
motility
morphology
types of assisted reproductive tech
AI
CIDR (controlled internal drug release(typically progesterone))
embryo transfer
in vitro fertilization
goals for replacement heifers
puberty 12-14 months
conceive early in breeding season
large enough
rebreed quickly
calving at 2 years: pros and cons
pros:
make money sooner
more calves
see potential sooner
cons:
smaller pelvis
higher chance of dystocia
calving at 3 years: pros and cons
pros:
reduce dystocia
physically mature at time for breeding
cons:
money made later fewer calves
see potential later
puberty
period of adolescents reaching sexual maturity