AP Micro unit 4
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Price discrimination
when a firm sells the same unit of output at different prices [diff price w diff costumers/conditions]
DWL is eliminated or very close to if Perfect P.D
For price discrimination to be possible, three conditions must exist:
The firm must have market power (it can set prices).
It must be able to segregate markets — meaning it can separate consumers into groups with different demand elasticities.
Consumers must not be able to resell the product, because resale would undo the price differences.
Why do firms price discriminate?
To increase profit and output by creating more producer surplus/profit
Elastic Consumer
Very sensitive to price changes
Inelastic costumer
Not sensitive to price changes
3rd degree P.D
charges different groups of people different prices [bc diff groups have more sensitivity]
→ lores in groups who would other wise not come w/out a discount making profit 100 instead of zero
2nd degree P.D
Different prices based on different quantities [bulk buy is cheaper]
1st degree P.D : perfect price discrimination
charge each person the price theyre willing to pay
[uni tuition goes up or down at what they can charge an individuals]
Why does the MR curve fall faster than the price
As they lower the price of the next unit of output → price must be lowered on all previous units → MR falls faster
What happens to MR as perfect P.D is in place
it will be equal to price [every consumer pays full price of what they can,,,5k is all u will then all 5k it is]
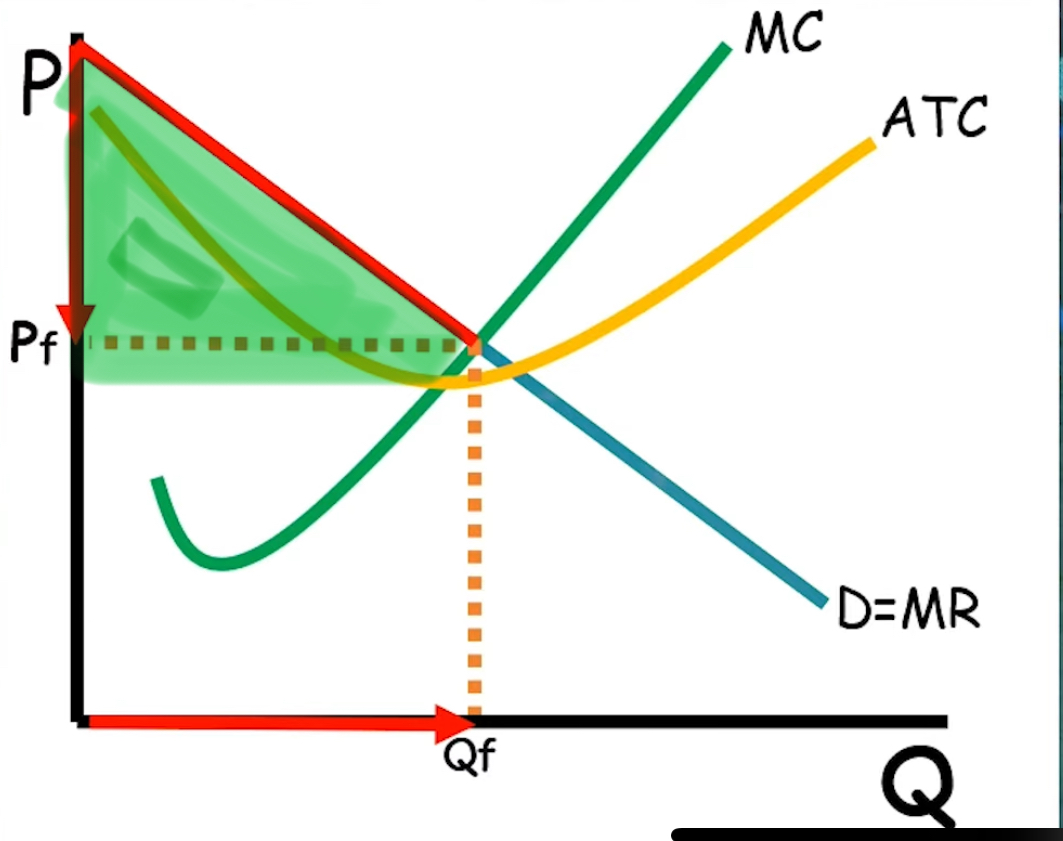
Perfect p.d
graph
max profit is mr =mc
firm charges every price on the demand curve downwards till the max quantity is charged
pf is the max price of product for just the last unit of output
Allocatively efficient
Turn c.s into all profit + (p - atc) x Q
Monopolistic competition
Many sellers
Low barriers to entry [Highly competitive]
Zero long-run profit
Different goods
some impact on prices
price goes up when less is made
What does differentiation of product allow?
Market power
Market structures in comparison
What the demand curve is
Perfect competition: perfectly elastic
Monopoly: entire market demand of an item
Monopolistic competition: only a portion of market demand [1 pizza firm vs entire market for pizza]
Oligopoly: Depends on rivals
Monopolistic Competition
Increase in price
more substitutes are bought
Monopolistic Competition
Increase in output
price must fall
Profit Maximization
MR=MC → for all firms
Monopolistic Competition
Short run Economic profit/loss
profit → p>ATC
loss but operate → p<ATC but p>AVC
loss → p< ATC and AVC
Monopolistic Competition
Short run graph
find maximization q to find price by going upwards to the demand curve
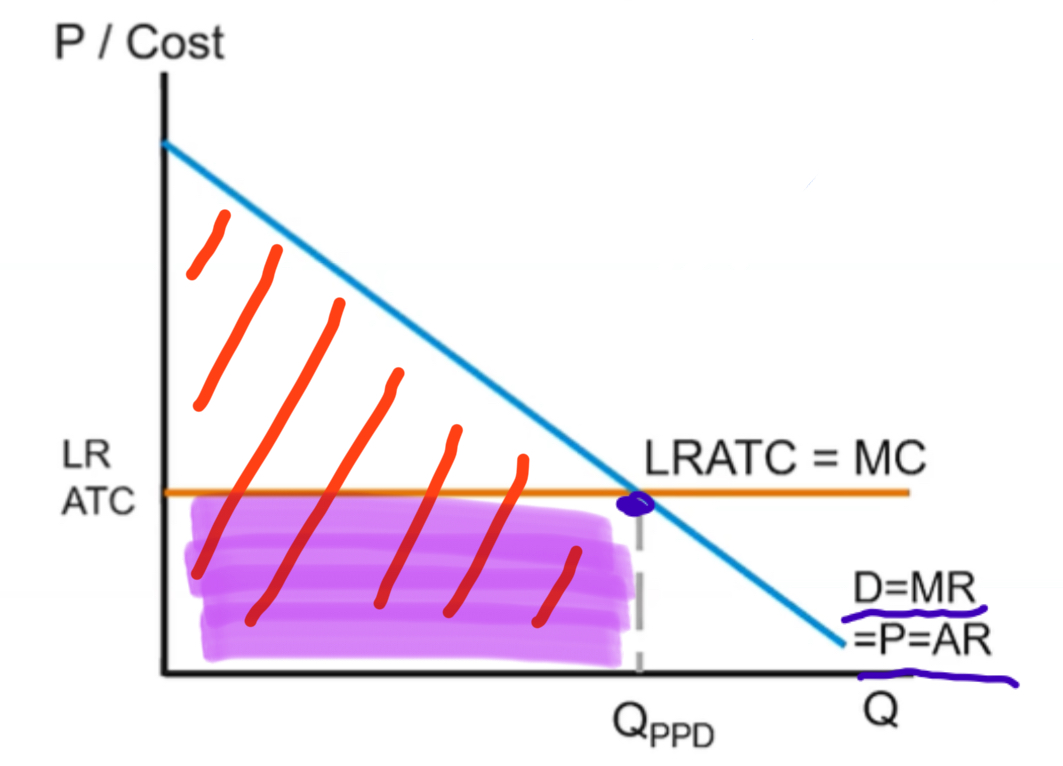
Monopolistic Competition
Long run graph
Will hit zero economic profit at ATC = Demand
ATC cannot fall below demand curve at any point in this graph
DWL is found at mc=p, mr=mc and Pf
Monopolistic Competition
short to long run
Profit edition
when making profit→ more firms enter the market = more competition → MR and Demand shift to the left = breaking even → demand is more elastic = more substitutes are available
Monopolistic Competition
short to long run
Loss edition
firms exit the market → each firm has more of the market demand = more consumers → Demand increases = breaks even → demand is less elastic
Firms’ efficiency
Perfect competition: Productively efficient
Allocatively efficient
Monopolistic Competition: not productively efficent not allocatively efficient [P ≠ minATC] [P ≠ MC]
Monopoly: not allocatively efficient [P ≠ MC]
The benefit of monopolistic competition is
Variety: product differences might negate inefficiencies
Monopolistic Competition
Changes in fixed cost
In short run only
lump sum tax
lump sum subsidy
change in rent
advertising
→ point is to shift demand right = less elastic D
Monopolistic Competition
Changes in fixed cost
Graph
Increase in fixed cost: ATC shifts up = loss
Decrease in fixed cost: ATC shifts down =profit
Monopolistic Competition
Changes in variable cost
Types
also only in short run
per unit tax
per unit subsidy
changes in wages
→ will shift ATC and MC
Monopolistic Competition
Changes in variable cost
Graph
increase in variable cost: MC n ATC shift up → so new mr=mc → higher price lower Q → economic loss
decrease in variable cost: MC n ATC shift down → new mr=mc → lower price higher Q → economic profit
Imperfect competition
Types
monopoly
oligopoly
monopolistic competition
Which of the following characteristics determines whether or not a firm will earn long-run economic profit?
barriers to entry
low= zero
high= positive profit
Oligopoly
Few sellers
High barriers to entry
High start-up cost
Government regulations
Established costumer loyalty
identical or differentiated products
long run profit can be positive
Monopoly
Only seller
High barriers [almost impossible]
unique good [no subsititutes]
Pricing power 100% [due to 2&3]
Firm demand curve
Perfect comp. vs Imperfect comp.
horizontal demand
price takers
→ inc price = sell zero output
→ dec price = sell same Q but at a profit loss
Downward sloping curve
→ inc = less output sold + vice verse\
Demand curve
Imperfect comp. Firms
MR is below demand
D=P=AR
Allocatively efficient
P=MC
Perfect Competition
millions of competitors
Identical products
no barriers
no price control
zero economic profit
Most competitive firms to least
perfect comp. → monopolistic → oligopoly → monopoly
a firm’s demand curve is the market demand curve
firm is a price maker