strategic direction
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
what is strategy
long term plan of how a business sets out to achieve its aims and objectives
strategic direction
determines the products it sells and the markets the business operates in
will need to be constantly assessed and changes when necessary to keep up with dynamic markets
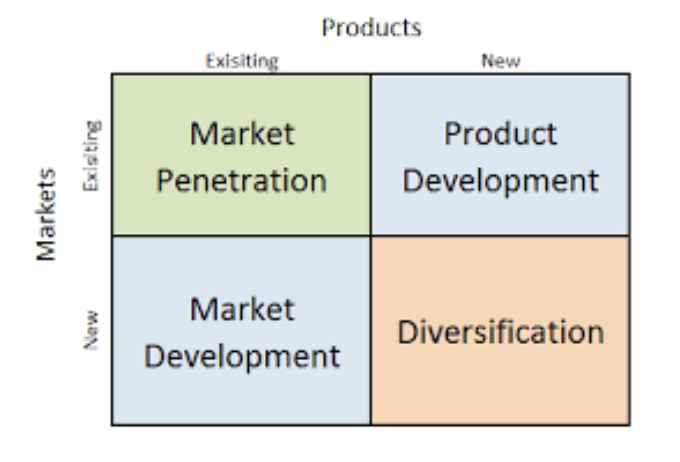
what is this
ansoff matrix
what is only way in which the strategic direction of a business can be analysed?
using ansoff matrix
what are the four sections of ansoff matrix
market penetration
product development
market development
diversification
what is market penetration
selling products into existing markets
reason for market penetration
boost sales
aim to boost market share
might invest more in promotional activity or change its pricing to sell more
little risk
may have little growth potential
in reality wouldn’t just focus solely on market penetration
what is market development
selling their existing products in new markets
features of market development
new geographical markets or distribution channels, different demographic feature
benefit of market development
already know the products
risk of market development
need to understand the conditions of new market, competitors, distribution systems which can be dangerous
what is product development
selling new products in an existing market
features of product development
investment in R+D
responding to changes in customer requirement
anticipating future change
new products take time
what is diversification
selling new product in a new market
features of diversification
high risk
typically works with a brand which has high levels of brand loyalty
can be the most suitable option as business may be less vulnerable to changes in one of its market segments
critique of ansoff martix
simple and easy to use
in reality there is a continuum
a new product could mean a slight modification
a new product to the business but not to the market
several strategies can be pursued at the same time
factors affecting which strategy is chosen
expected cost
expected return
opportunity cost
risk
fit with the resources and strengths of the business
impact on other stakeholders
ethical issues being involved
Business objectives
Profit maximisation, growth, survival, market share
Core competencies
What the business is good at (skills, technology, brand)
Resources available
Finance, workforce skills, technology, time
Risk appetite
Some strategies are riskier (e.g. diversification)
Market conditions
Size, growth rate, competition, customer demand
External environment (PESTLE)
Economic growth, technology, regulation, social trends
Competition
Strength of rivals, barriers to entry
Stakeholders
Shareholders (risk vs return), employees, customers
factors affecting which markets and products to choose
Business objectives
Profit maximisation, growth, survival, market share
Core competencies
What the business is good at (skills, technology, brand)
Resources available
Finance, workforce skills, technology, time
Risk appetite
Some strategies are riskier (e.g. diversification)
Market conditions
Size, growth rate, competition, customer demand
External environment (PESTLE)
Economic growth, technology, regulation, social trends
Competition
Strength of rivals, barriers to entry
Stakeholders
Shareholders (risk vs return), employees, customers