Orgo 2 reagents and other quizlets
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
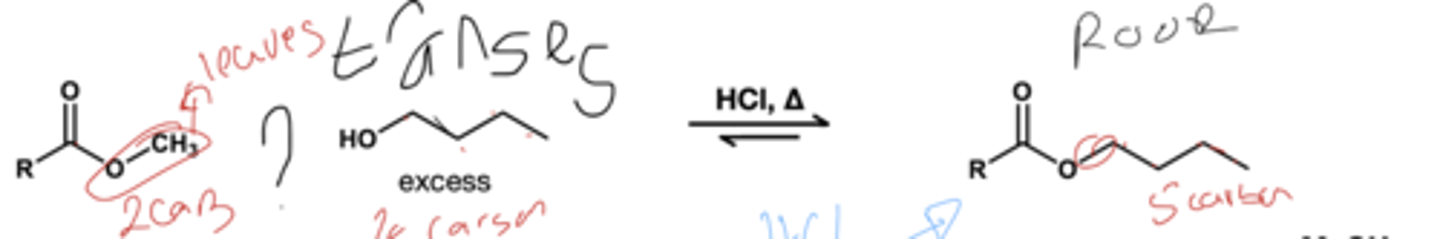
transestrification( acid) reagent? ester to another ester
ROH(xs)/ HCl, heat
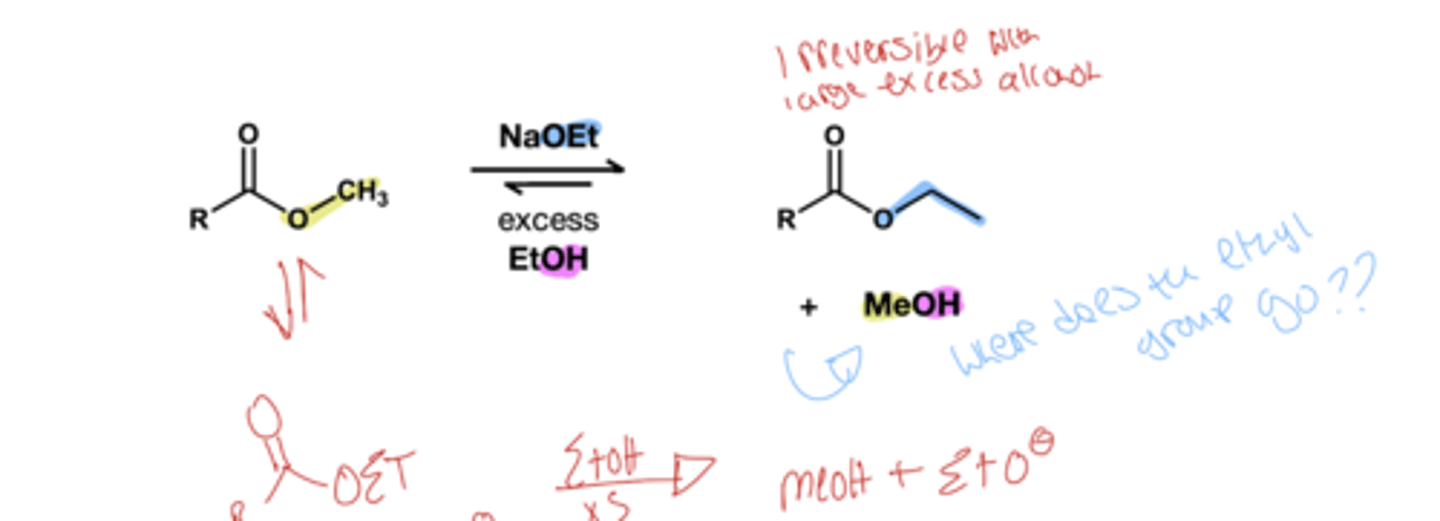
Transesterification( base) reagent?
ROH(xs)/ NAOR which can be NaOEt or NaOME
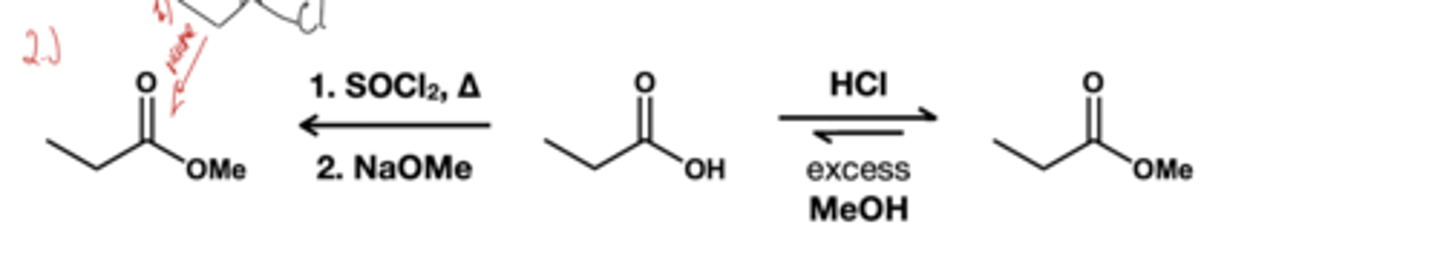
Fischer esterification reagent? going from carboxylic acid to ester
ROH(xs), HCl ; basically same reagent as acid transesterification except the starting material is a carboxylic acid
Ester hydrolysis acid reagent? *ester to carboxylic acid?
HCl, H2O
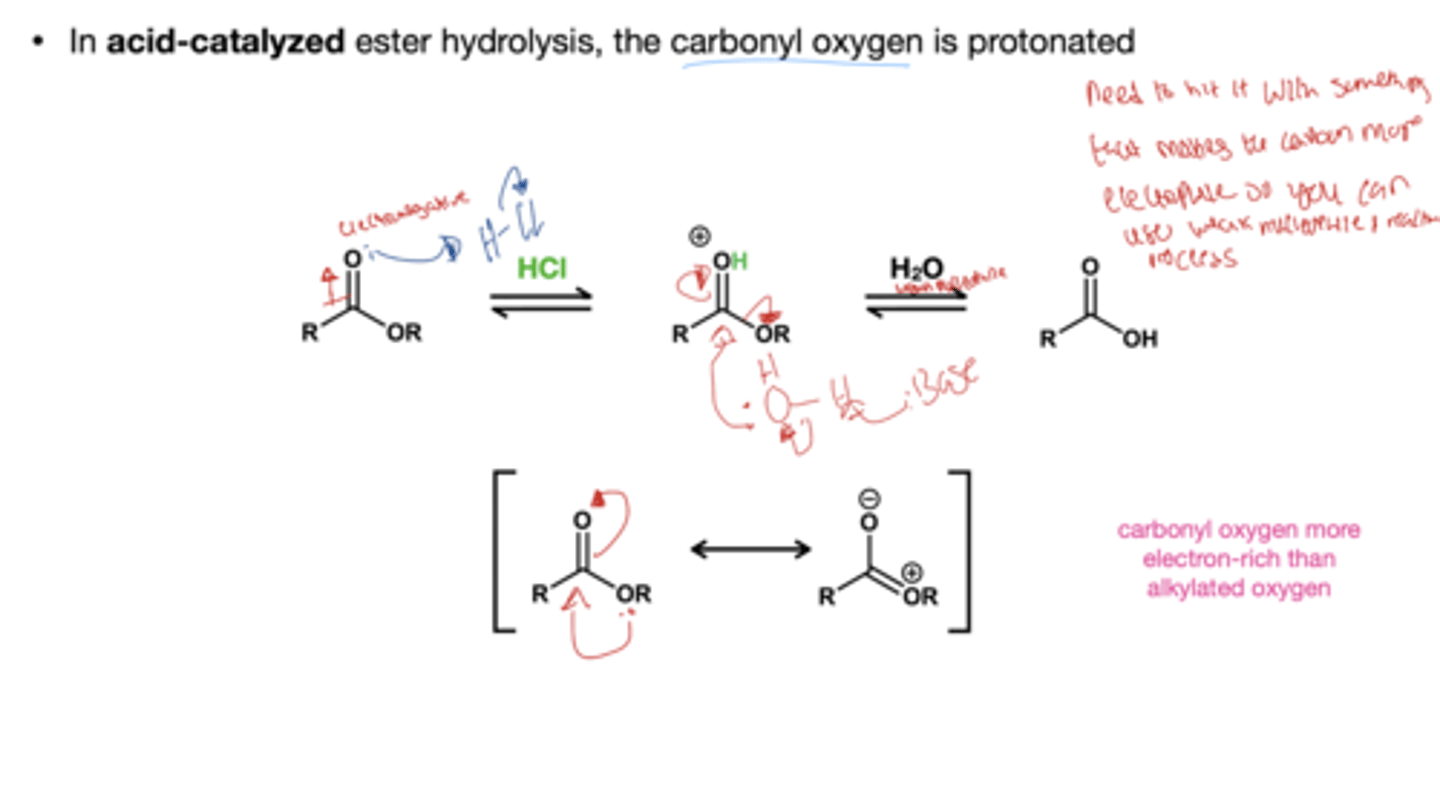
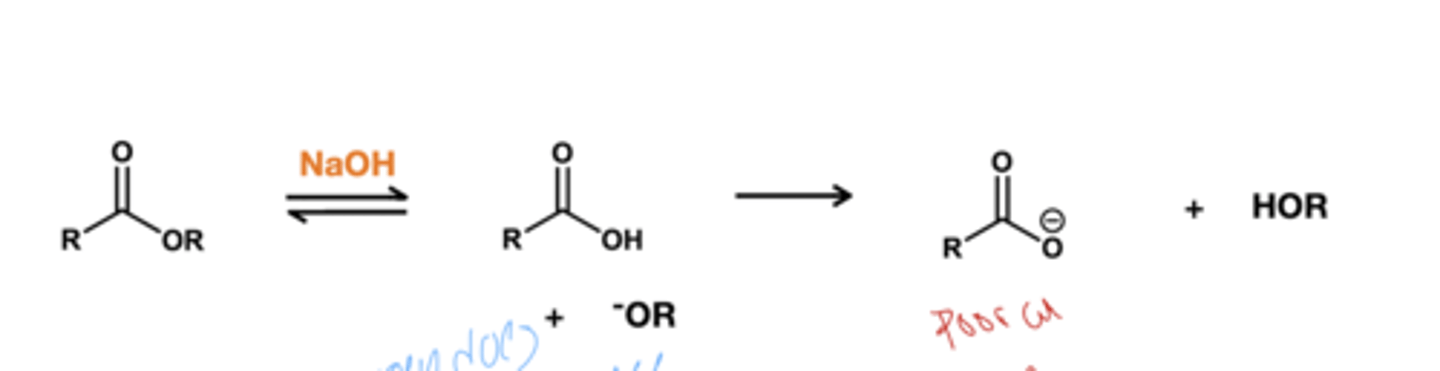
Ester hydrolysis acid reagent? *ester to carboxylate?
NaOH
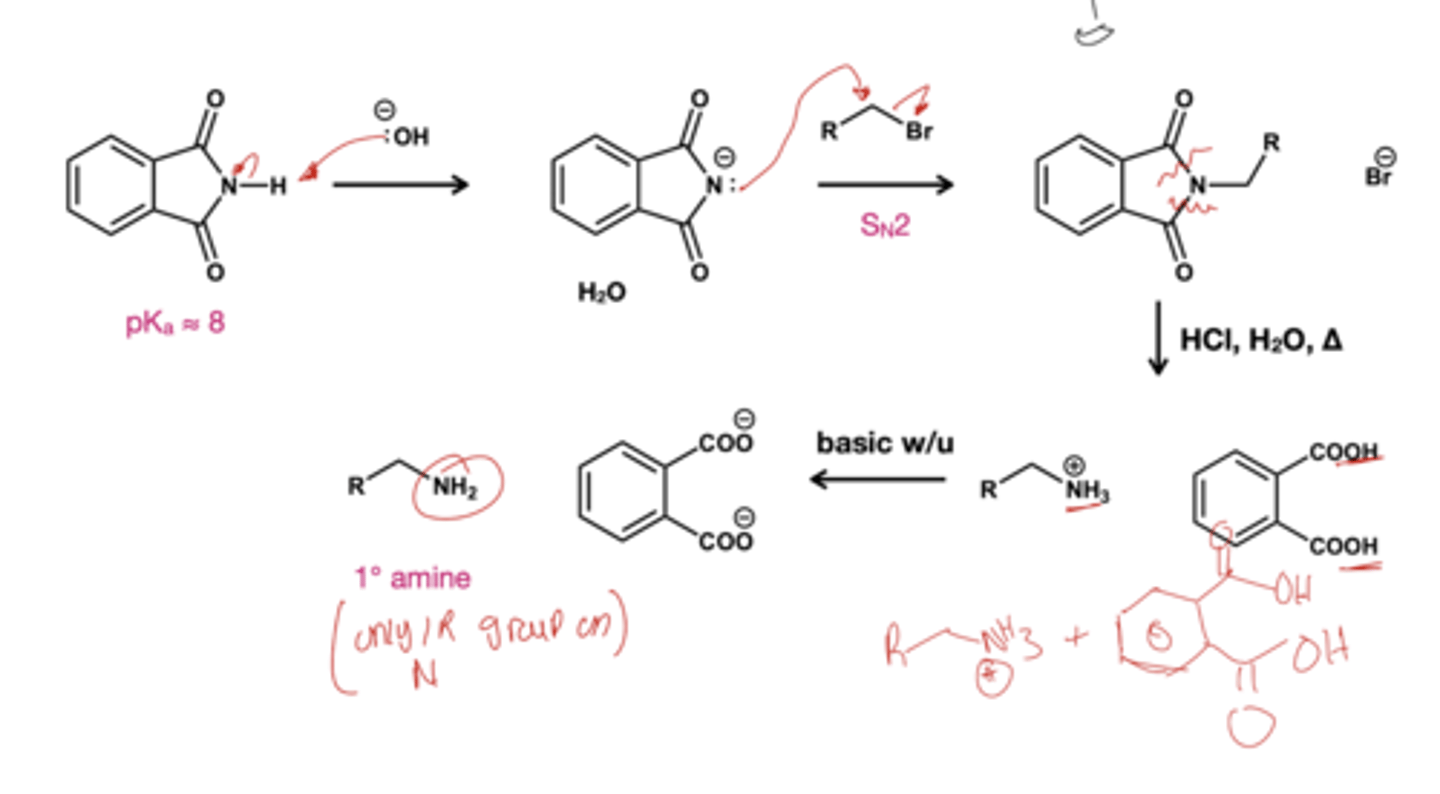
Gabriel synthesis reagent? makes primary amines from primary alkyl halide
1.) NaOH; base to deprotonate the cyclic structure
2.) R-Br( alkyl halide)
3.) HCl, H2O, and heat
4.) basic work-up
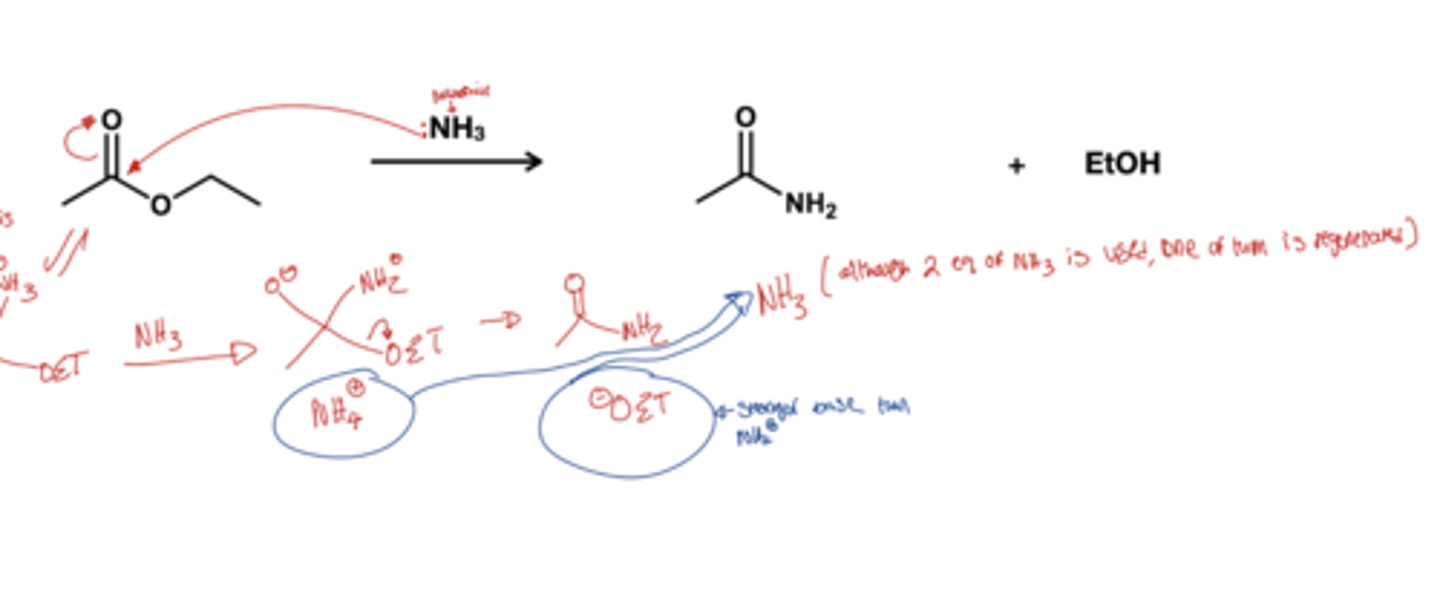
Ester to amide reagent?
1 HNR'2 or HNET2 or NH3; just 1 equivalence of amine without a base
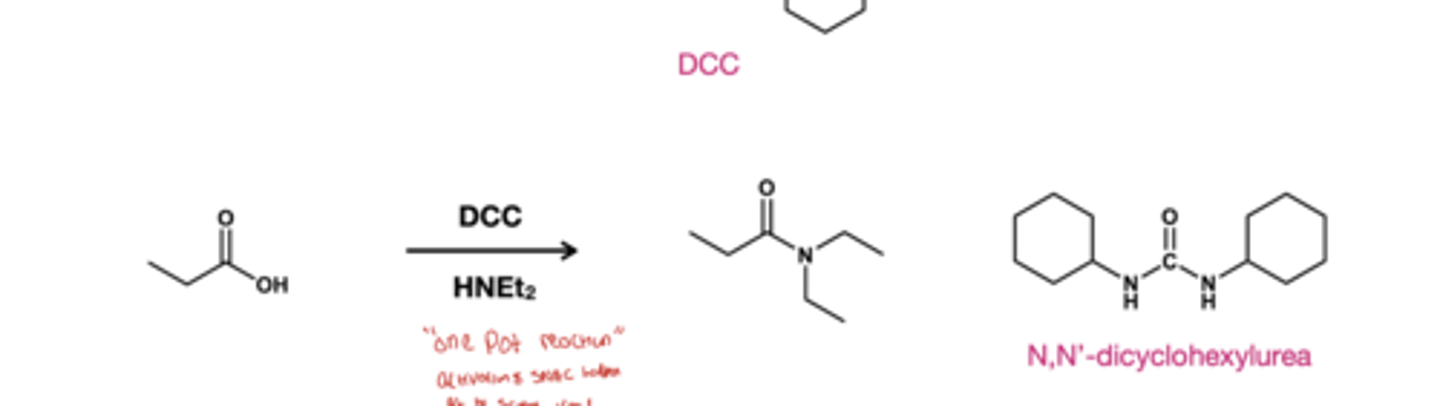
carboxylic acid to amide reagents?
DCC/ HNR2(HNEt2); using just the amine makes salt so we activate the carboxylic acid using DCC.
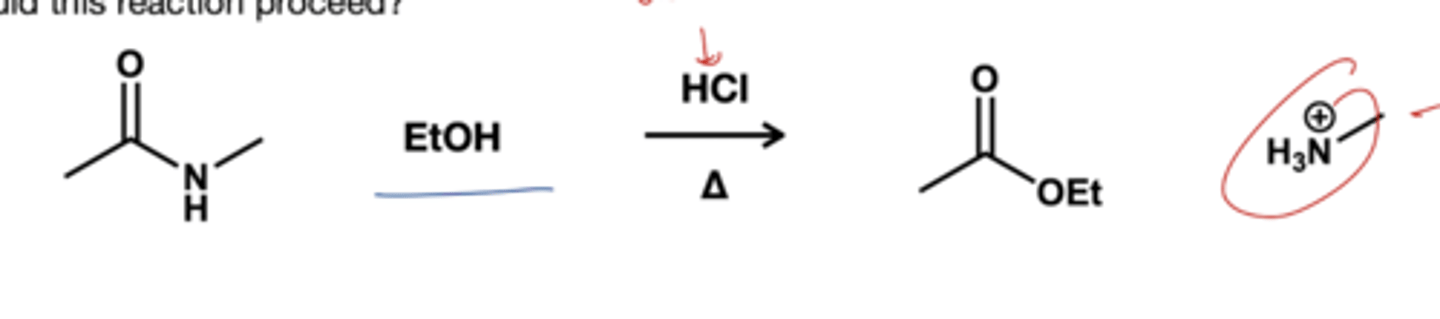
Amide to ester reagent?
ROH( ETOH, MEOH)/ HCL, heat. Amides will react with alcohol only in presence of acid catalyst to form esters
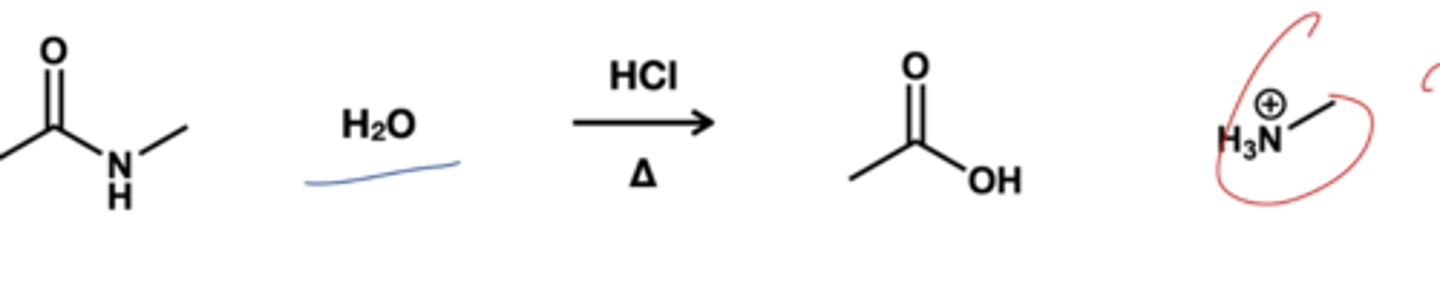
Amide to carboxylic acid reagent?
H2O/ HCl, heat; Amides will react with water in the presence of acid catalyst to form carboxylic acid.
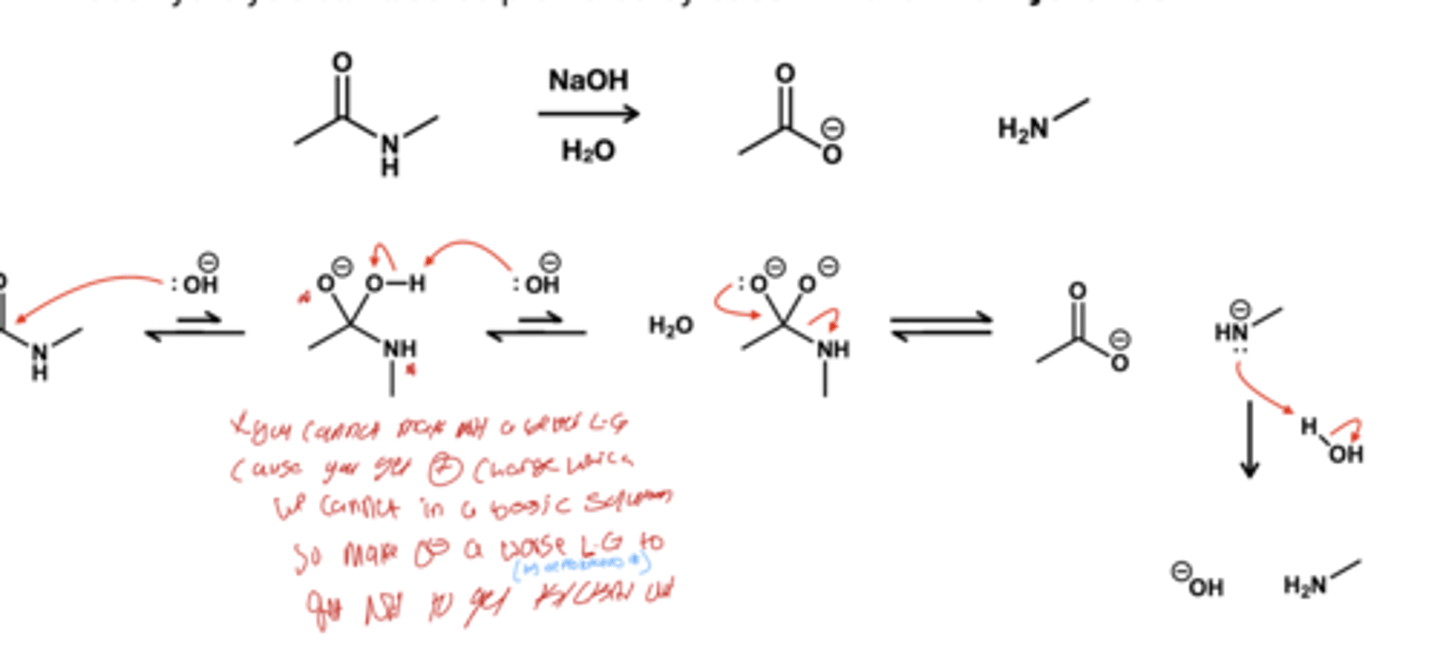
Amide to Carboxylate
NaOH, H2O
Amide to Nitrile reagent?
P4O10 or P2O5
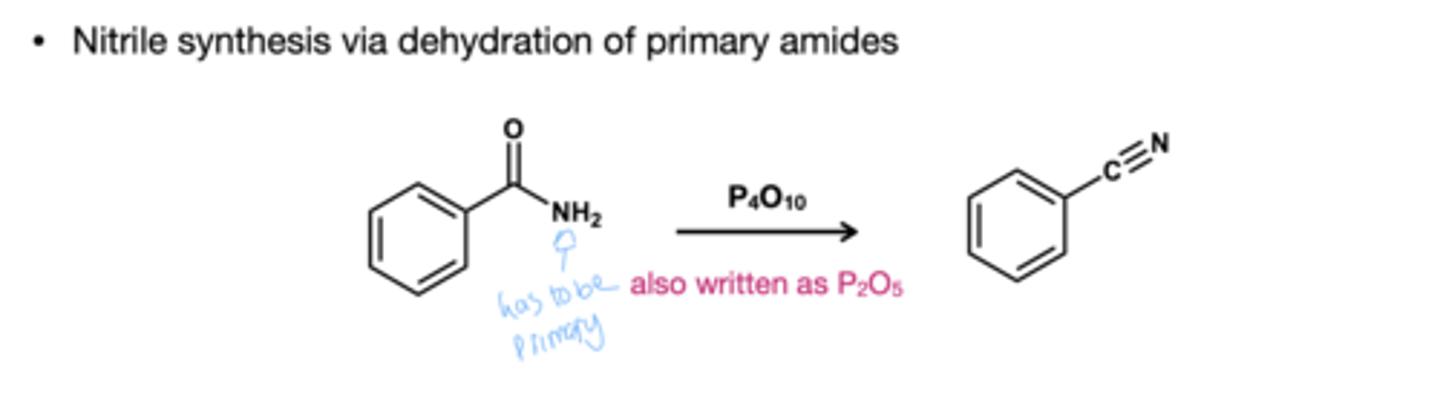
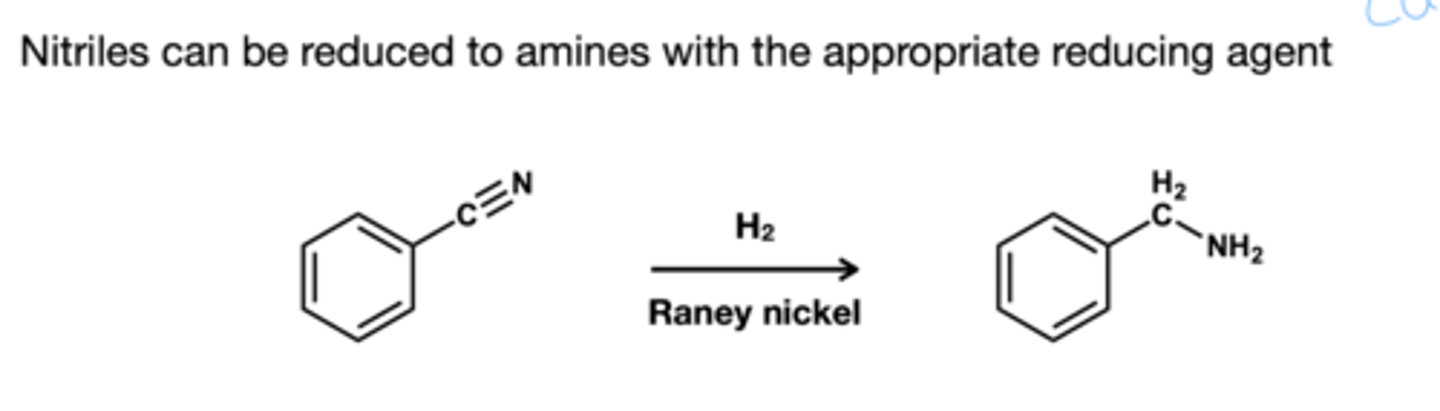
Nitrile to amine reducing agent?
H2, Raney Nickel
reactivity ranking for carbonyls?
acyl chloride > acid anhydride > aldehyde > ketone> ester = Carboxylic acid > amide > carboxylate ion.
Nitrile to ketone reagent?
1.) R'MgBr
2.) HCl, H2O
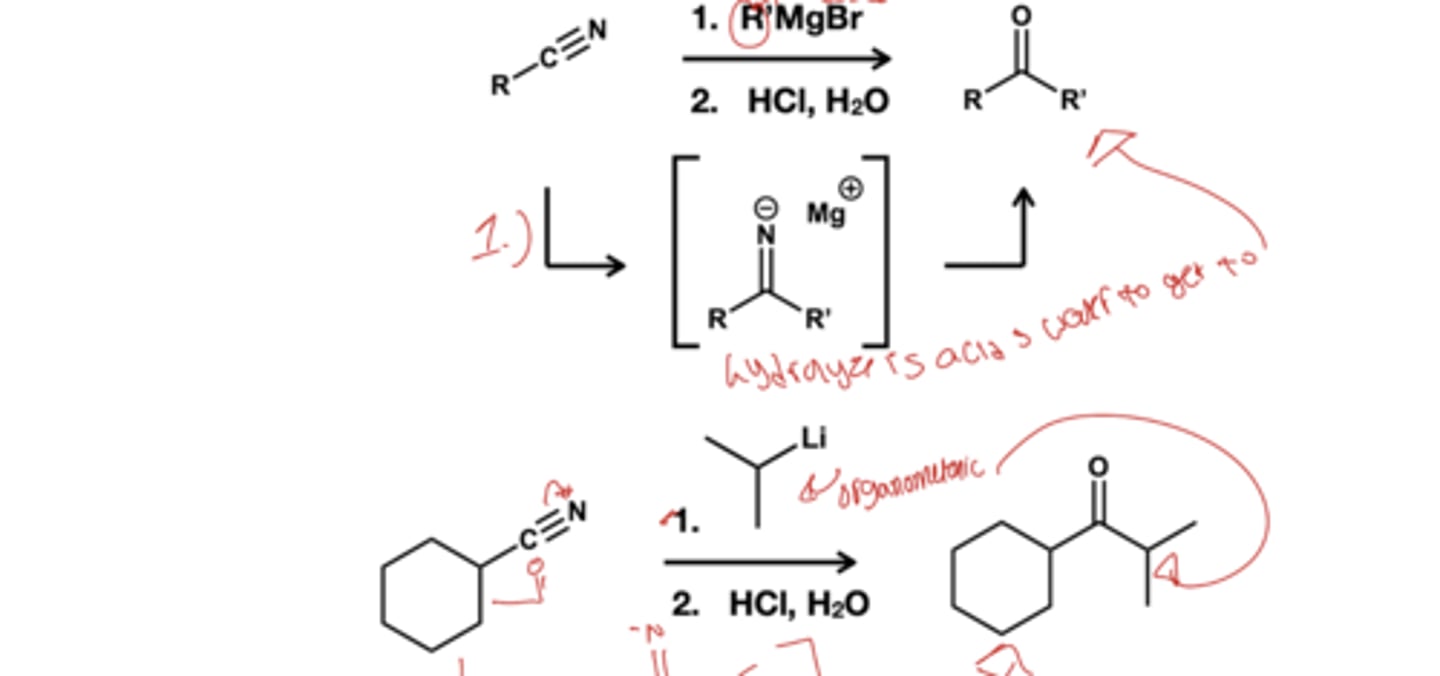
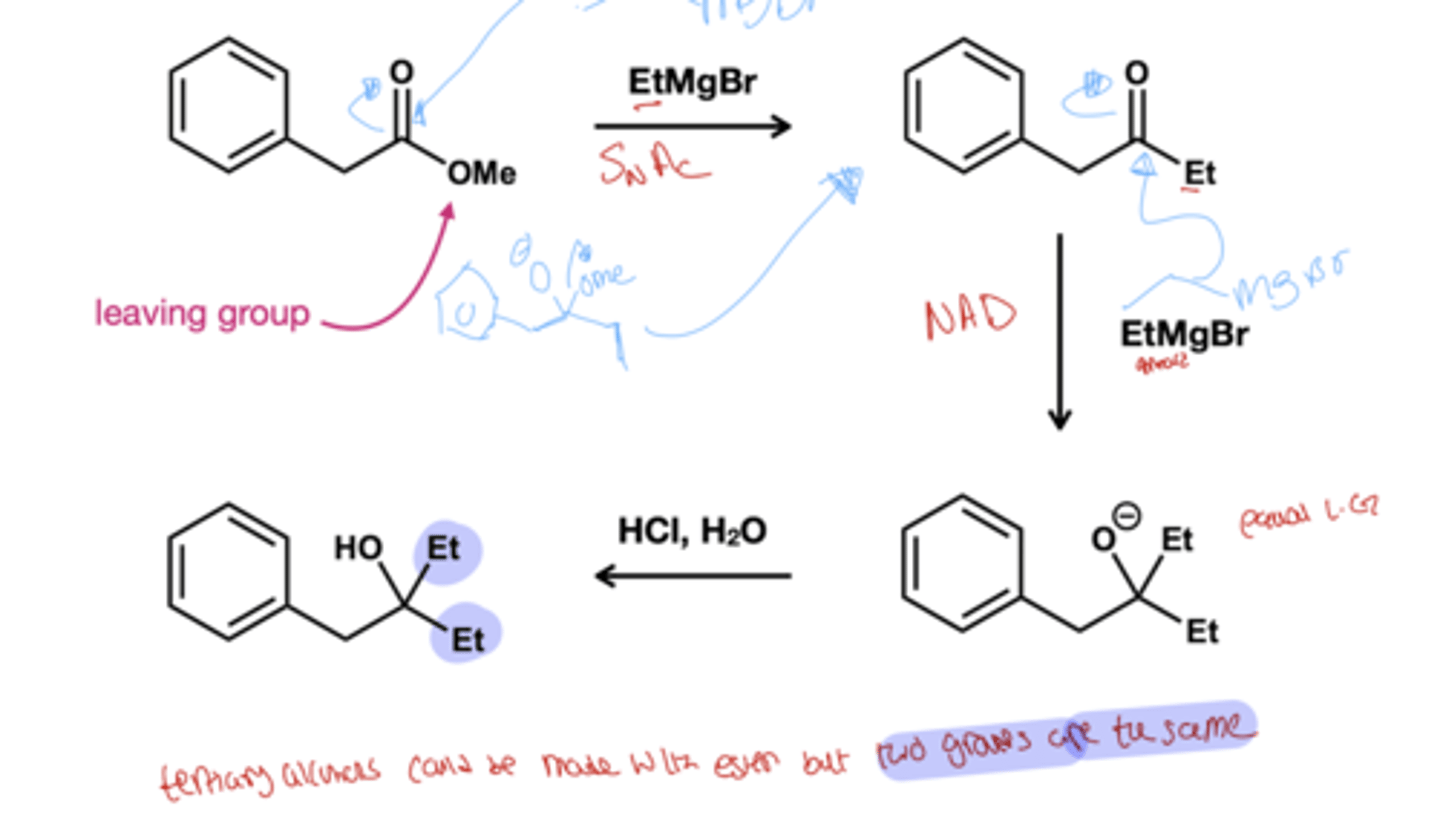
Grinards-> alcohol?
Grinard react with aldehyde(secondary alcohol) and ketone( tertiary) to form alcohol. They react twice with ester and acyl chloride to form alcohol( first is SnAc then NAD)
organocuprate with ketone, aldehyde, ester gives ?
No reaction
organocuprate with acyl chloride gives?
A ketone
cyanohydride reagents? only forms with aldehyde and ketones in slightly acidic conditions
NaCN, HCN
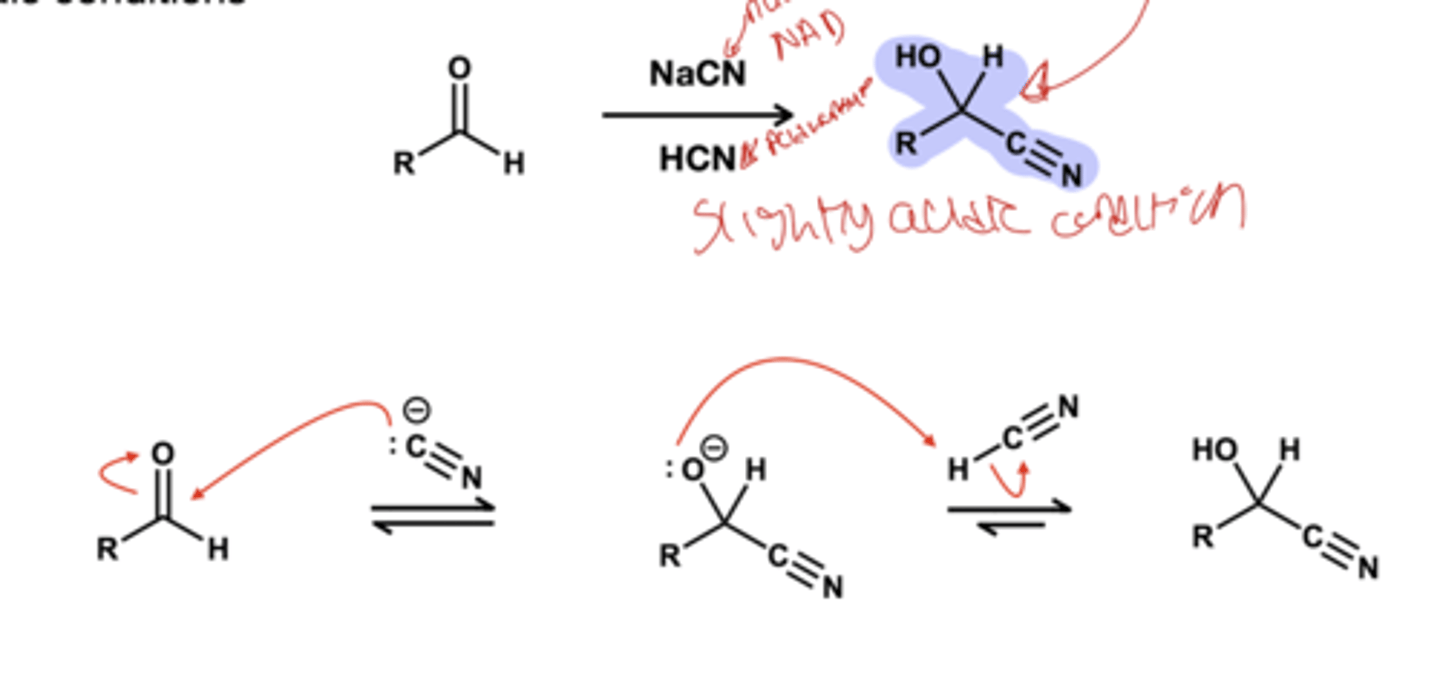
NaBH4, H2O and LiALH4, H2O reduces what?
they reduces ketones and aldehydes to alcohols
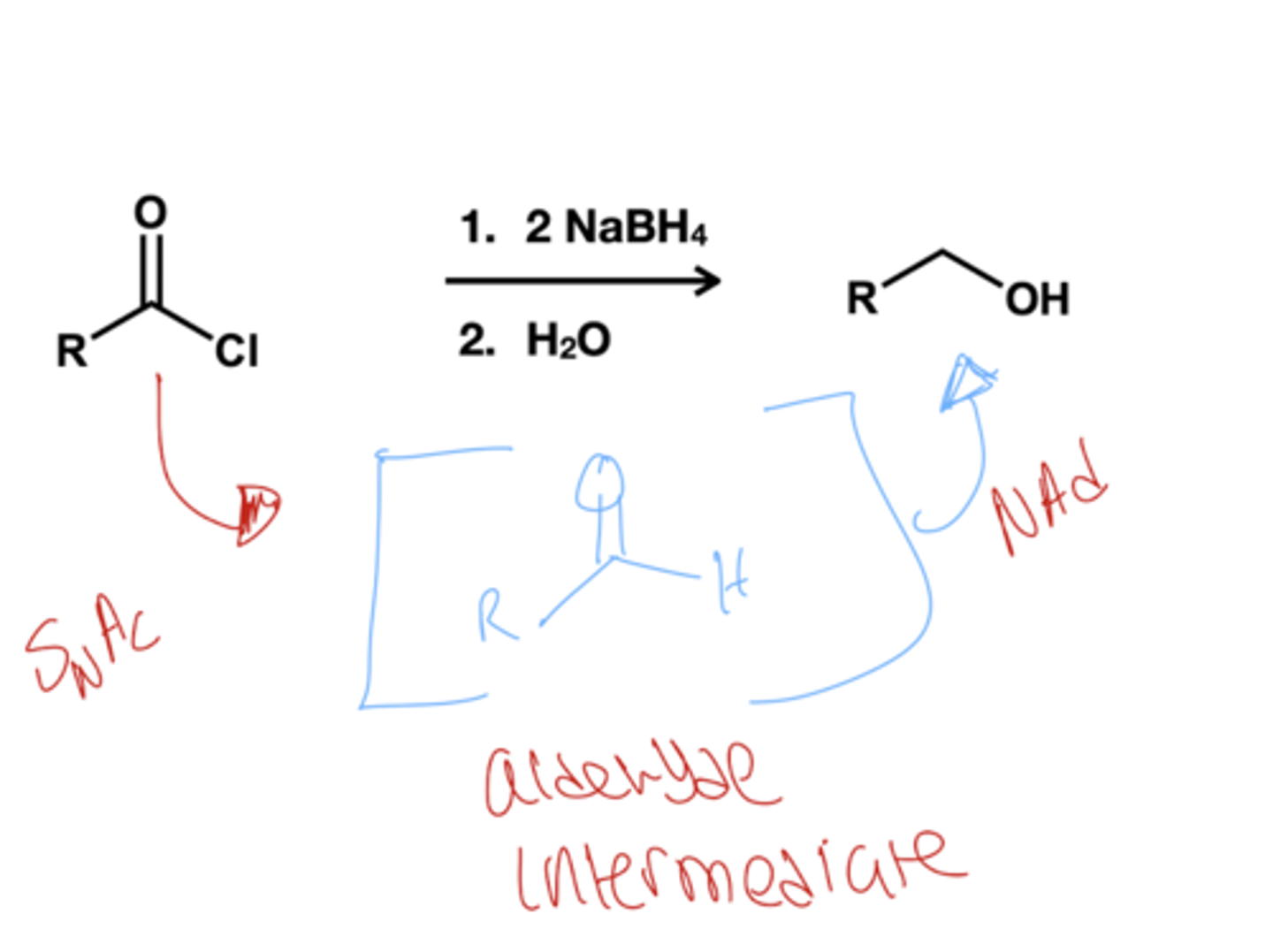
what reducing hydride donor reduces acyl chloride to alcohol?
1.) NaBH4( excess)
2.) H2O
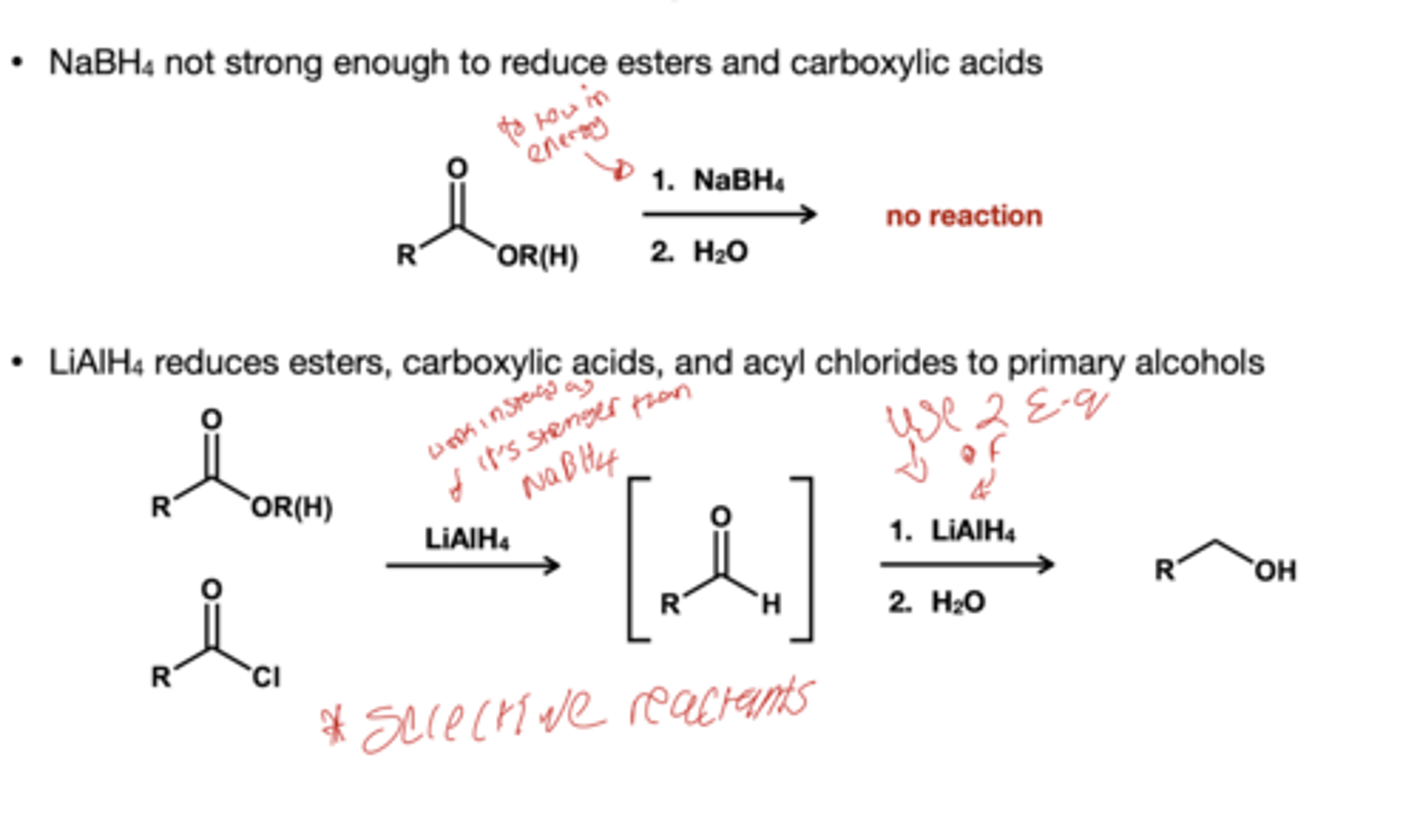
What reducing hydride reduces ester, carboxylic acid, and acyl chloride to primary alcohols?
1.) LiALH4( excess)
2.) H2O
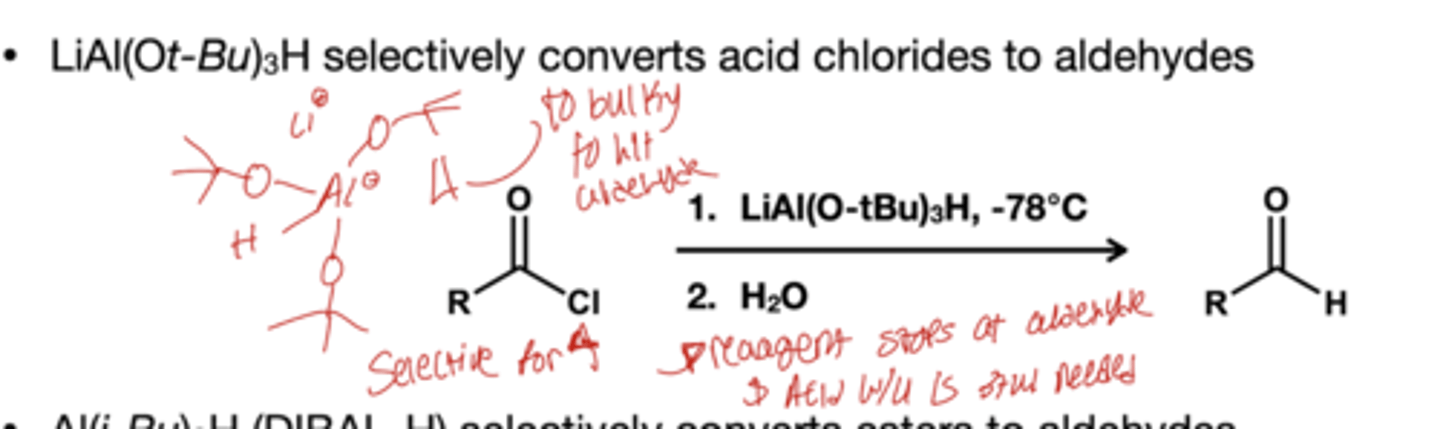
what stops the reduction of acyl chlorides to aldehydes?
1.) LiAl(O-tBU)3H, -78 degree celcius
2.) H2O
what stops the reduction of esters to aldehydes?
1.) DIBAl-H, -78 degree celcius
2.) H2O
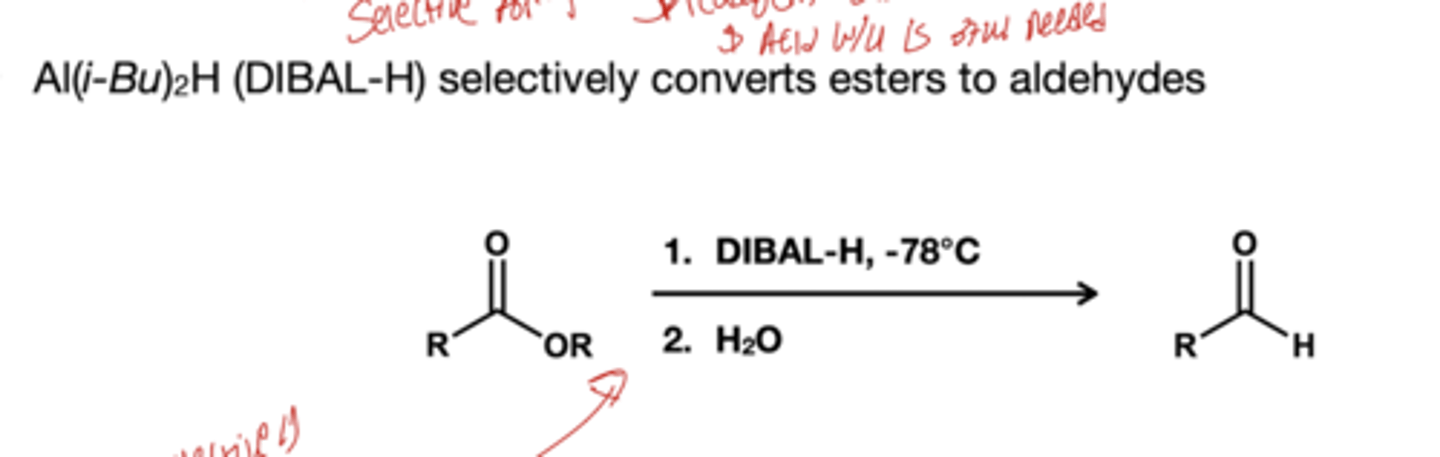
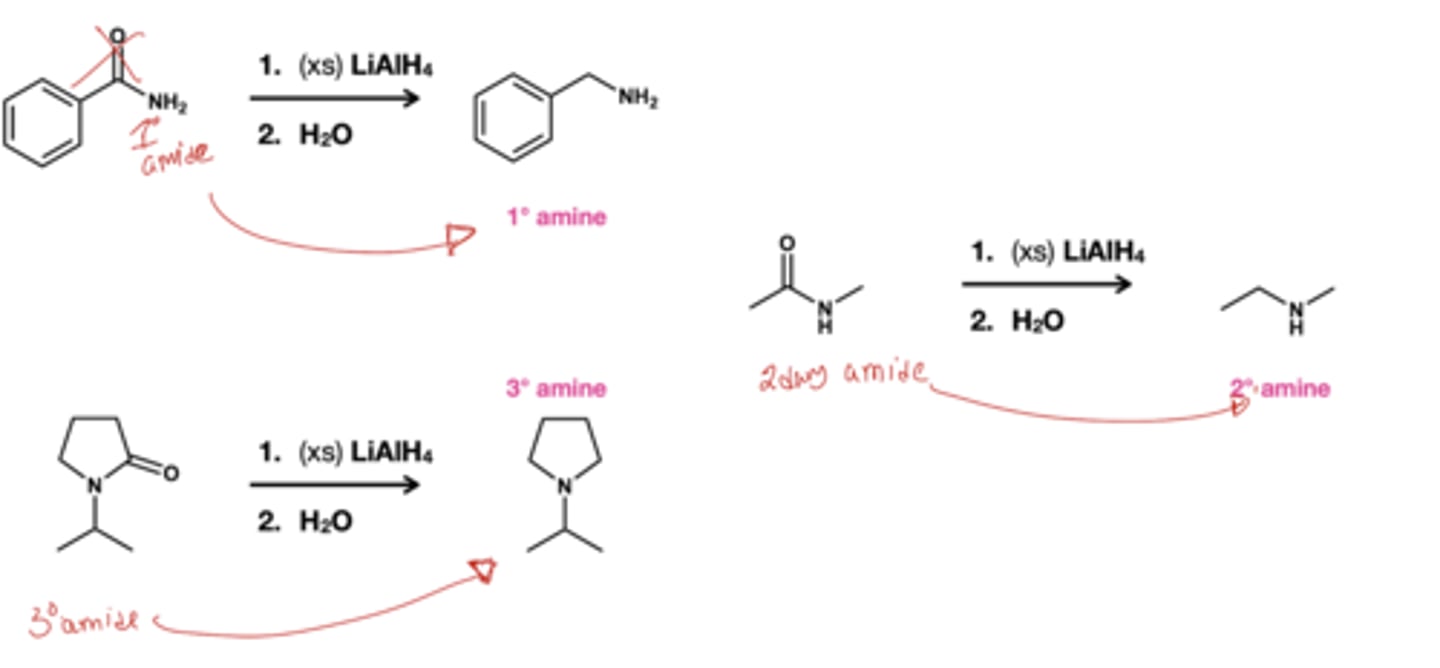
what does LiALH4 do to amides?
Reduces amides to their respectives amines; basically the structurw without the carbonyl
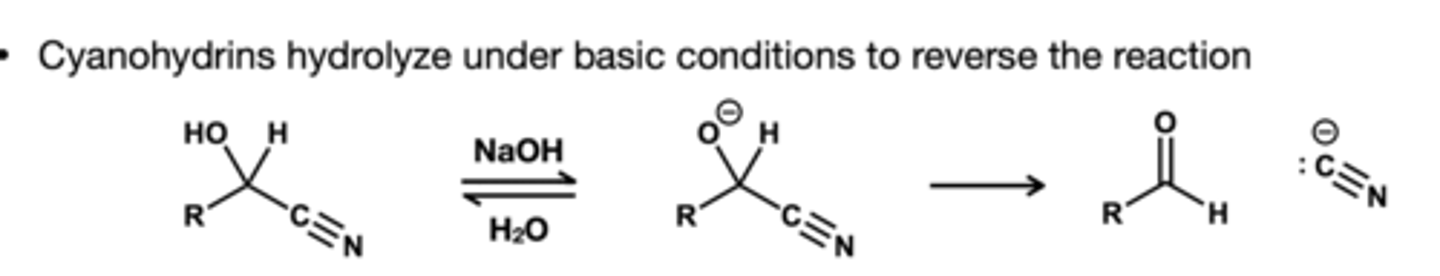
Cyanohydrins in basic conditions reagent and hwhat is does ?
reagnet: NaOH, H2O. this turns cyanohydrins back to their aldehyde or ketones
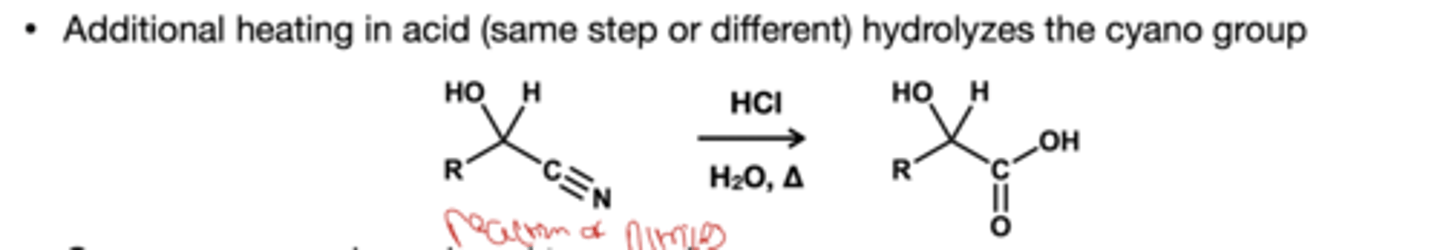
Cyanohydrins hydrolyzation reagents?
HCl, H2O, and heat which turns just the nitrile group to carboxylic acid
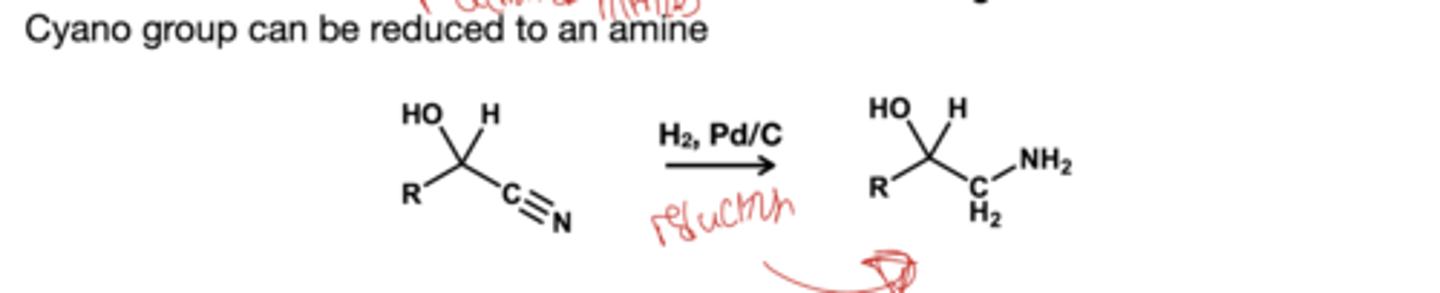
what reduces cyano group in a cyanohydrine to an amine?
H2, Pd/C
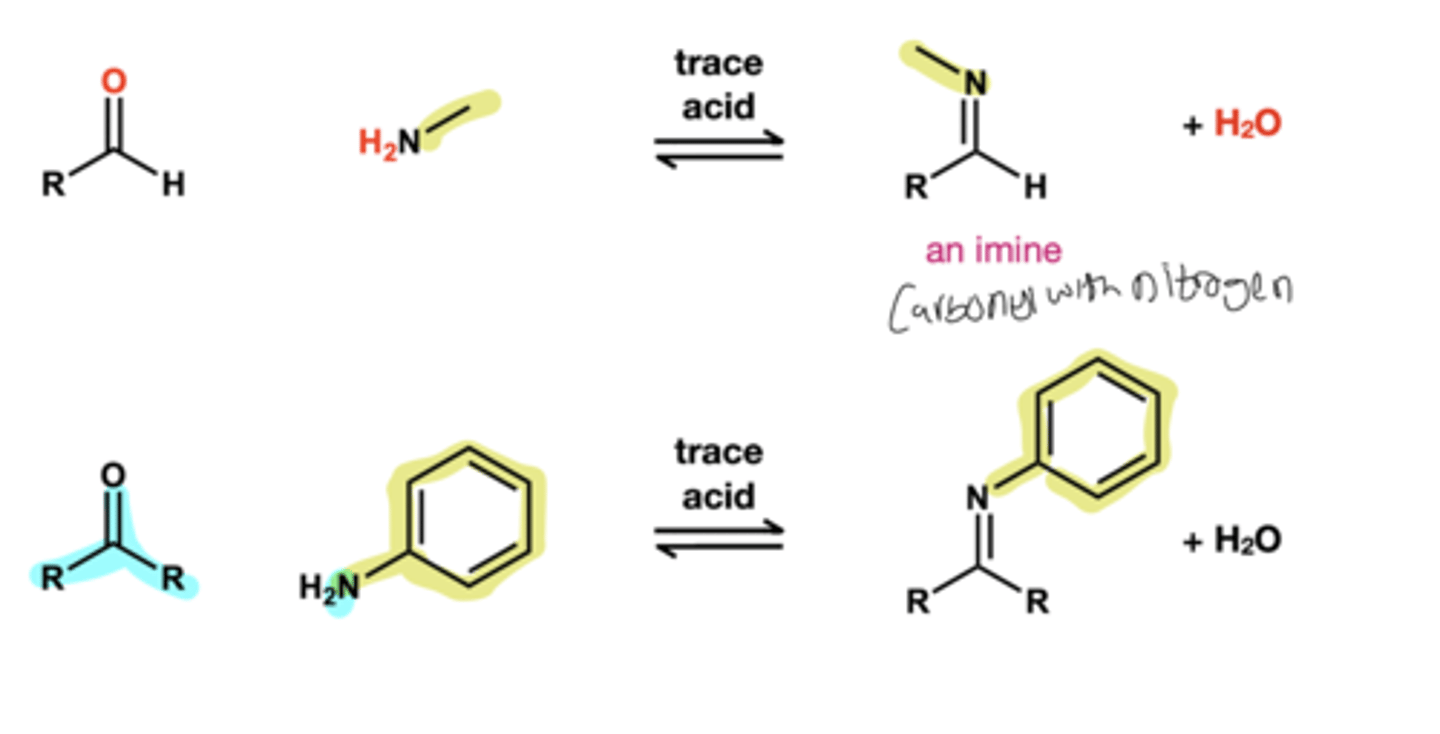
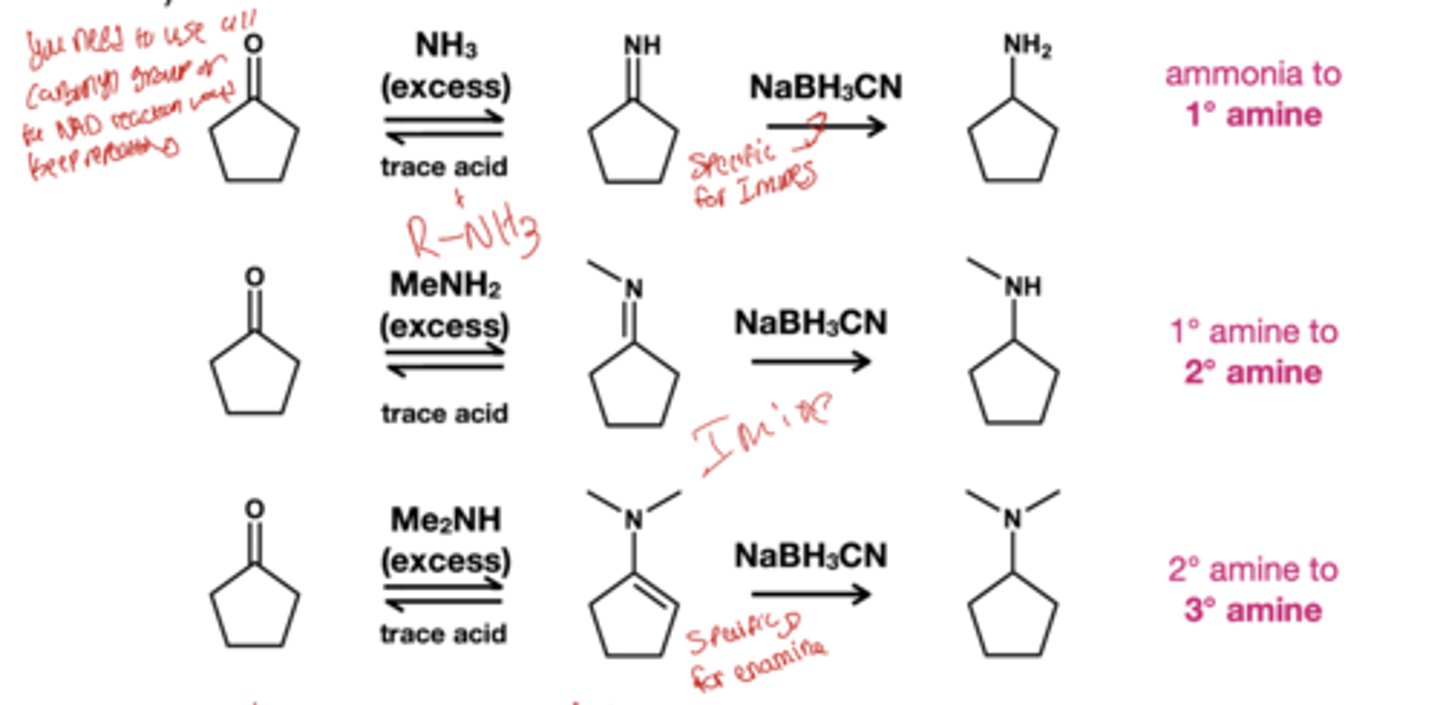
Ketone and alehyde to imine reagent?
primary amine, trace acid
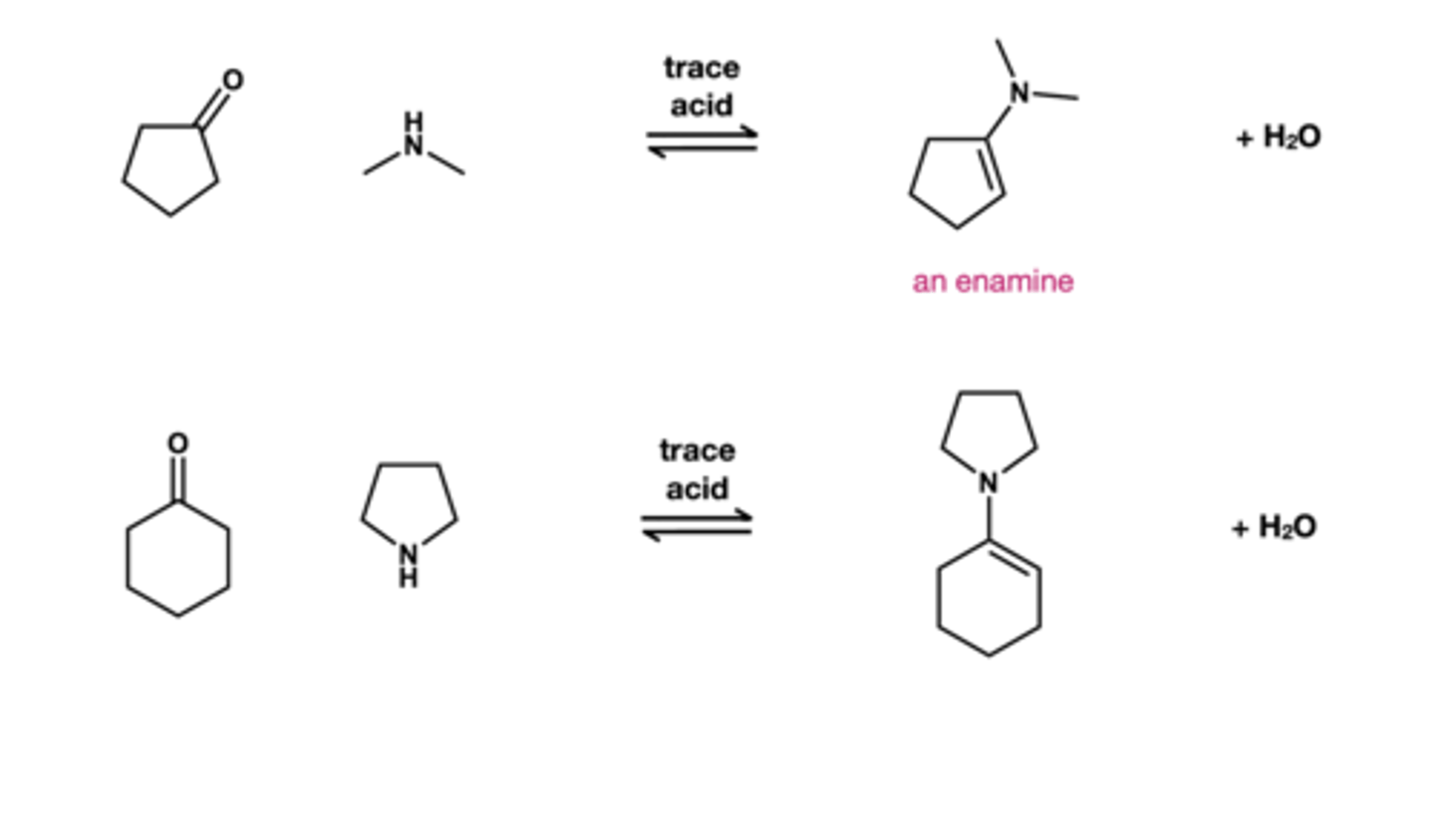
Enamine reagents
secondary amine + trace acid
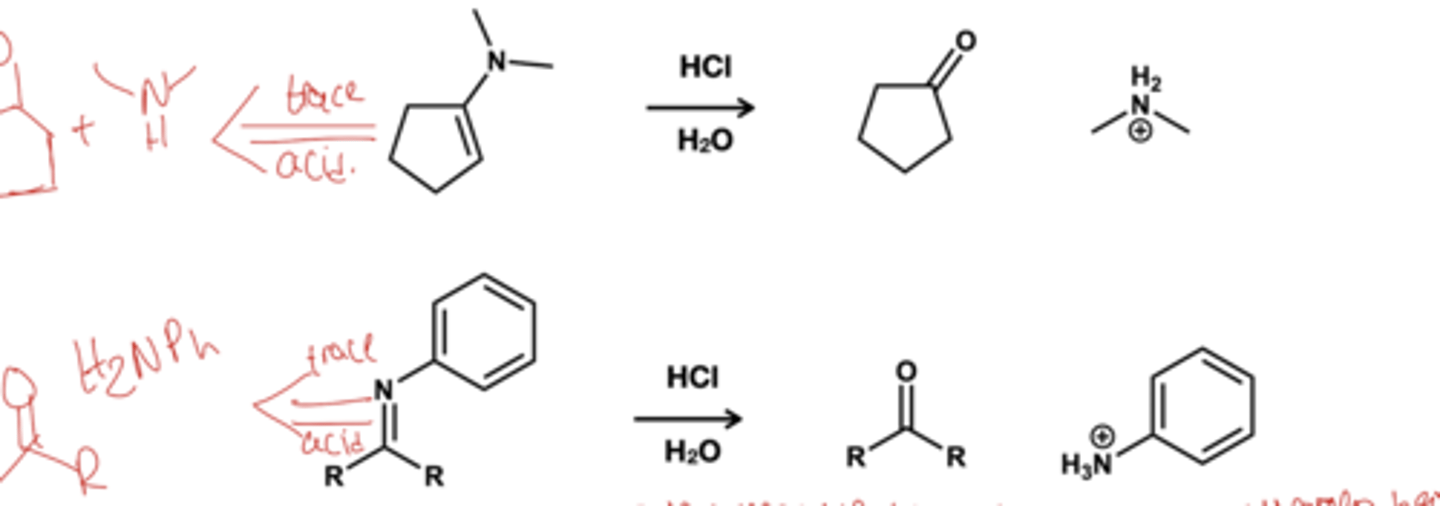
Imine and enamine hydrolysis?
reagent: HCl, H2O this turns the imine and enamines back to the aldehydes or ketone and amines that made them. This time the amine is protonated making the step irreversable
what reagent reduces imines and enamines to amines?
NABH3CN
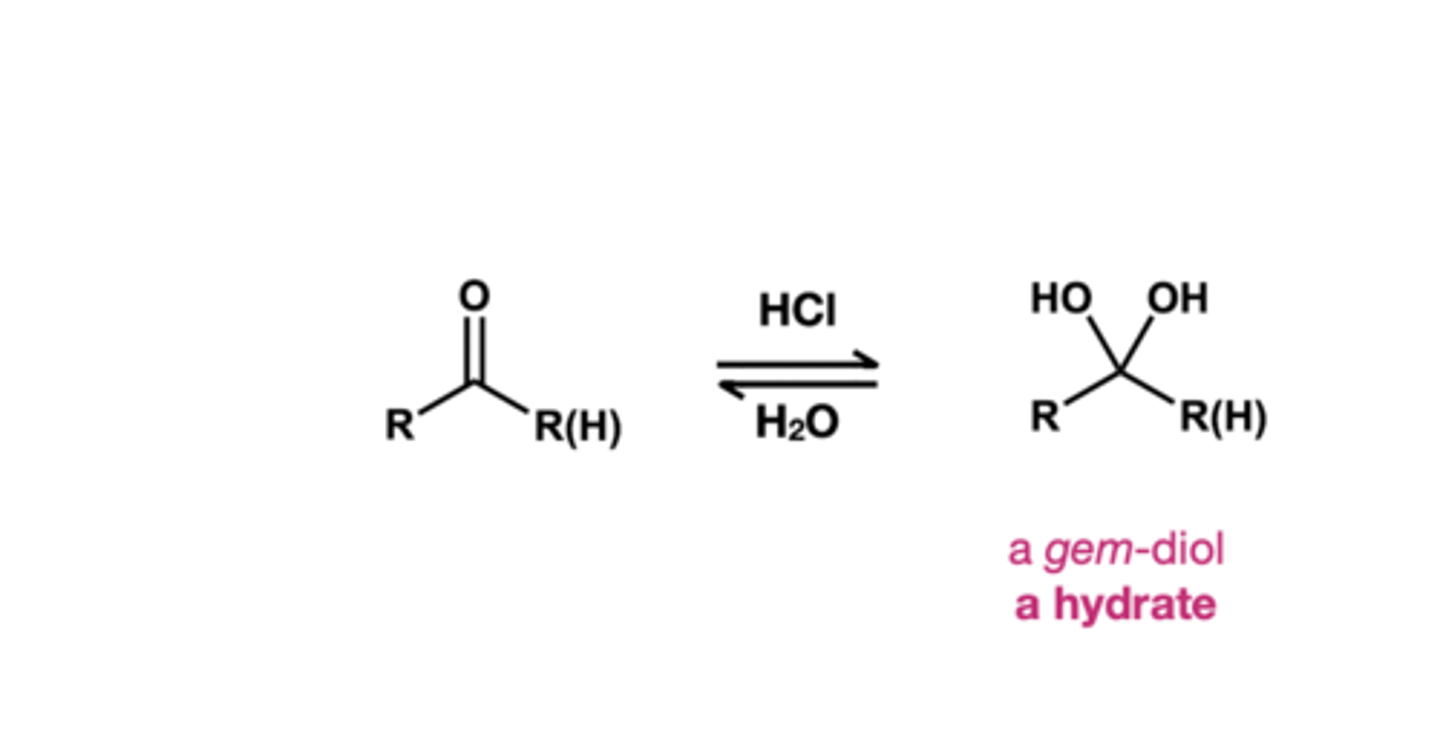
reagent of hydrate and what S.M makes it?
1.) Starting material is ketone or aldehydes
2.) reagent is HCl, H2O
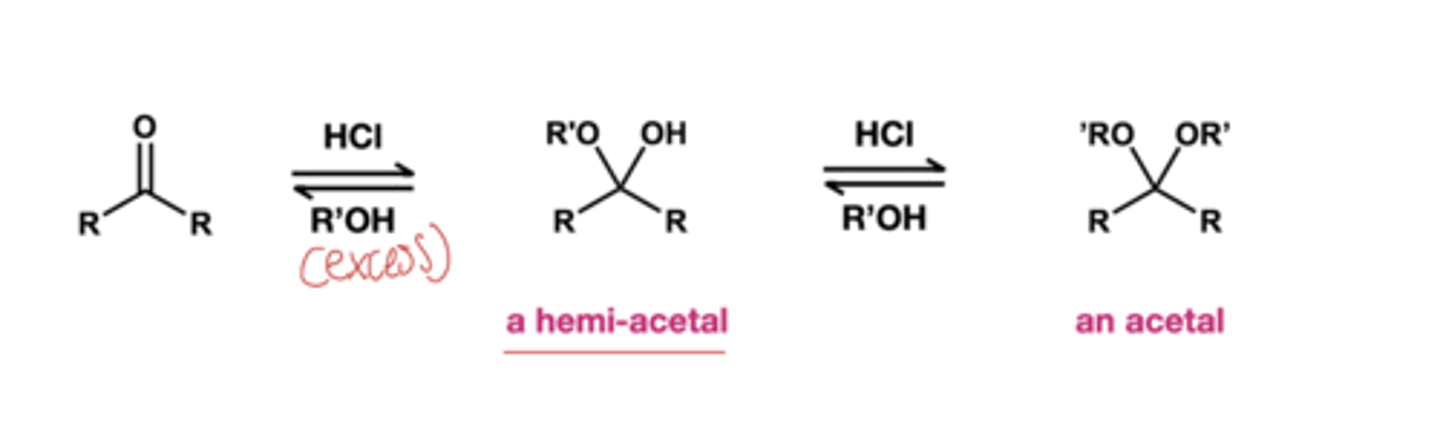
acetal formation S.M and reagent?
S.M: ketones and aldehydes with excess alcohol in acidic conditions
reagent: HCl, R'OH
wha does m-CPBA do to aledhyde and ketone
it turns aldehydes to carboxylic acid and ketones to esters
For aldehydes and ketones woith a,B-unstauration what adds driect and what adds conjuagate?
Weak bases add conjuage and strong bases adds direct

Addition of weak base to a,B- unsaturated carbonyls
direct addition is reversible, while conjugate is irreversible; since thermodynamic is favored conjugate addition is favored.
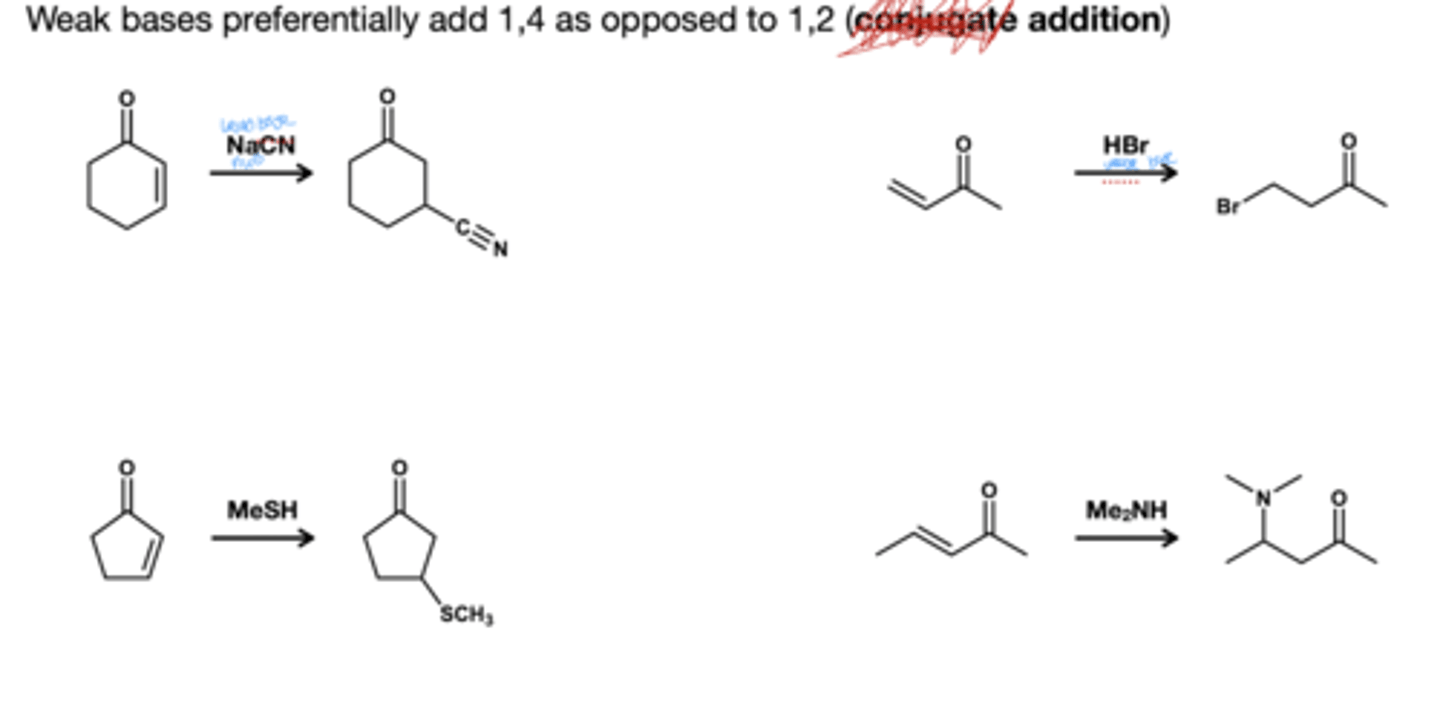
Addition of strong base to a,B- unsaturated carbonyls
both direct and conjugate addition is irreversible; strong bases preferentially add direct
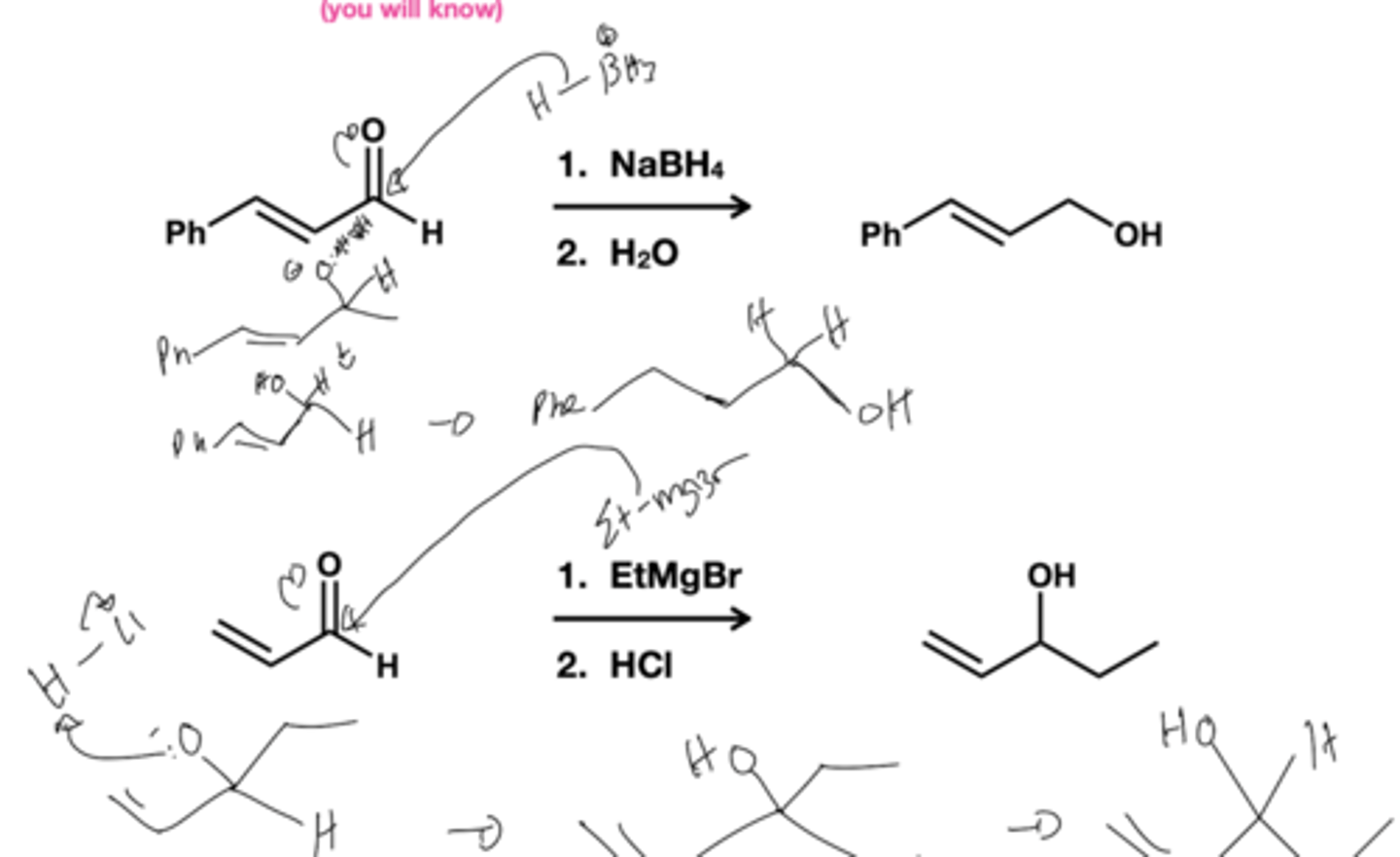
a,B- unsaturated carbonyls is hindered, what product forms?
conjugate addition
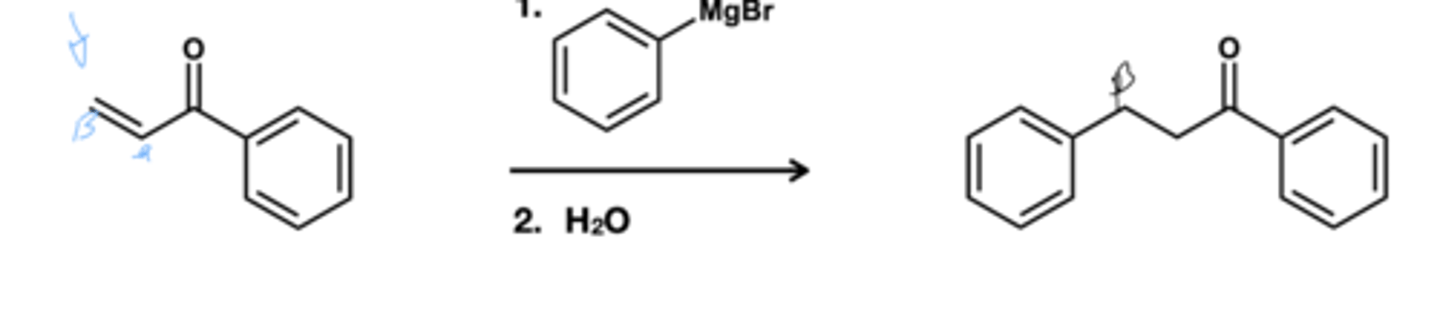
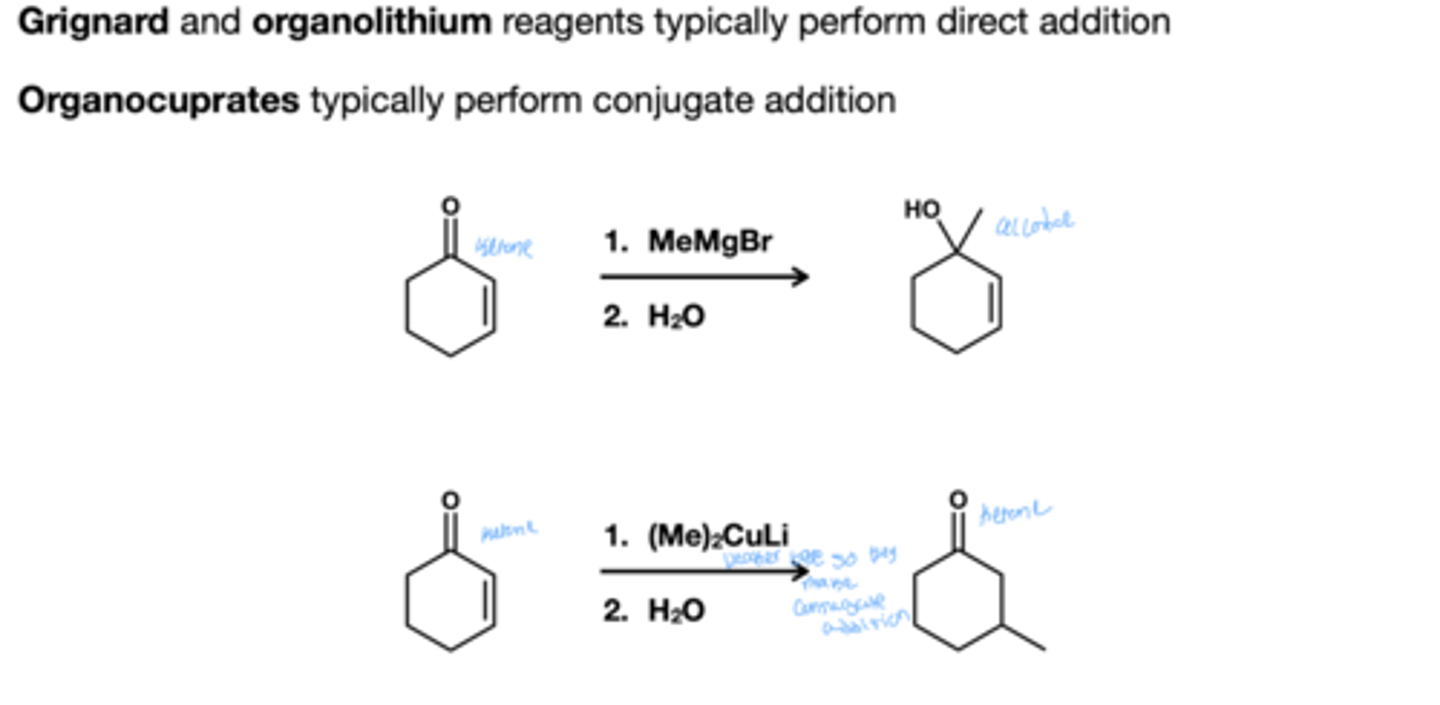
Grignard and organolithium and organocuprate addition to a,B- unsaturated carbonyls?
Grignard and organolithium does direct addition
organocuprate does conjugate addition
Acid-catalyzed halogenation reagent?
Br2/HCl; replaced just one alpha proton
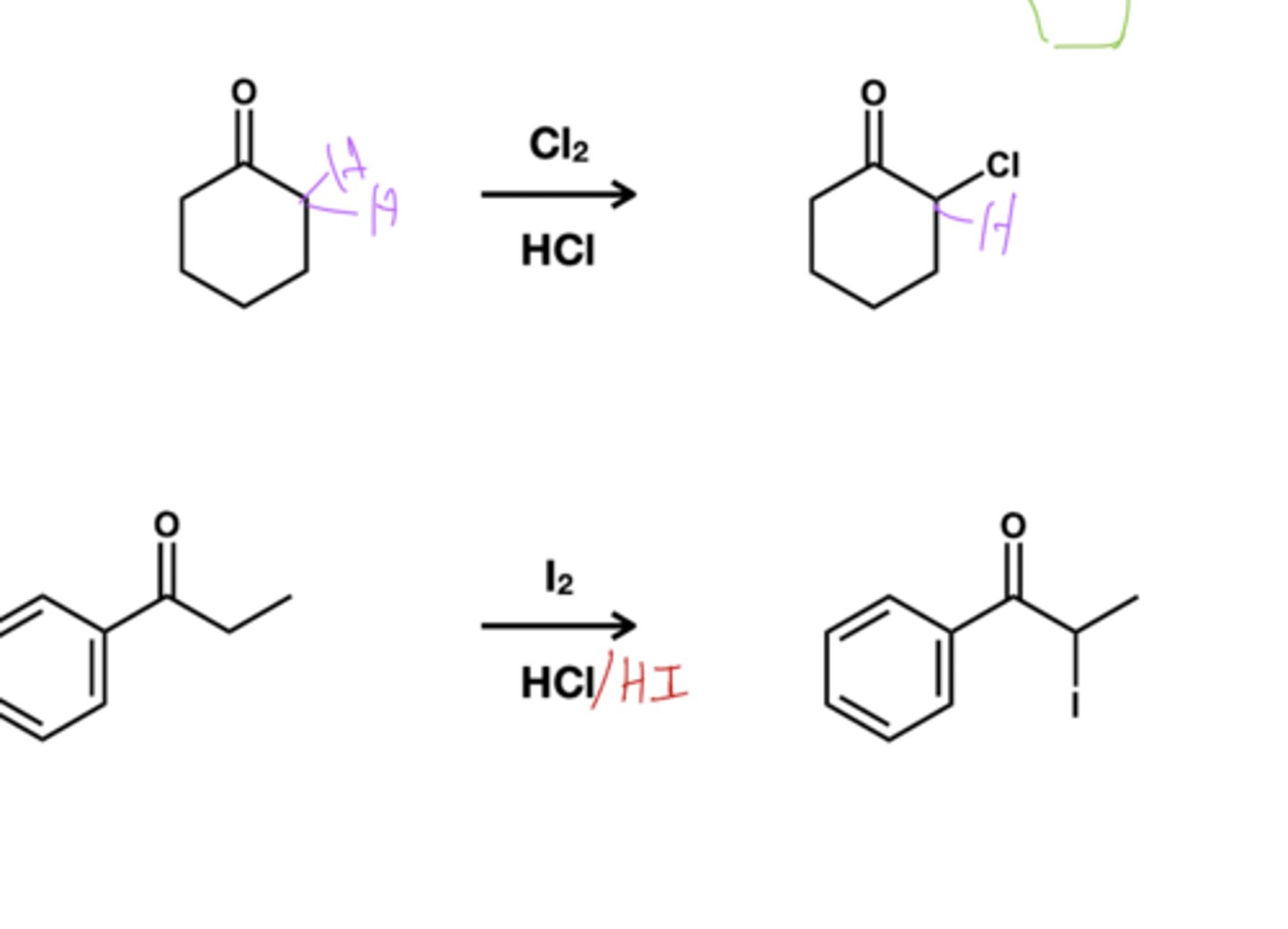
Base-catalyzed halogenation reagent?
Br2/ NaOH; replaces all alpha carbons
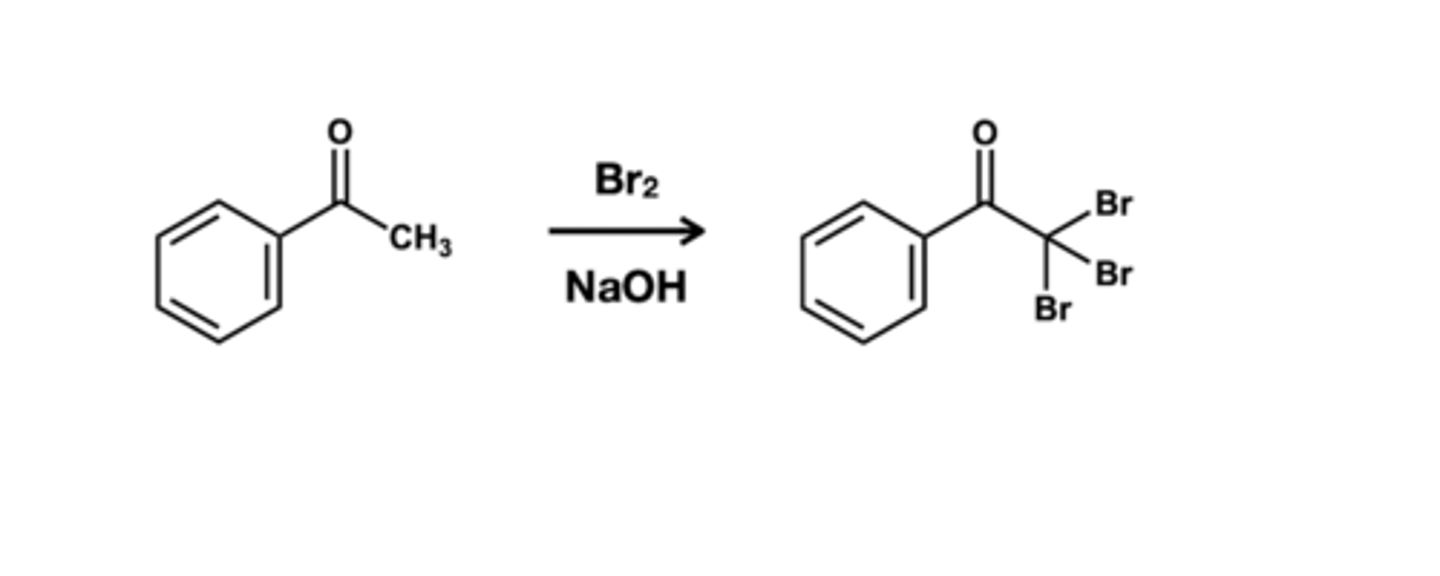
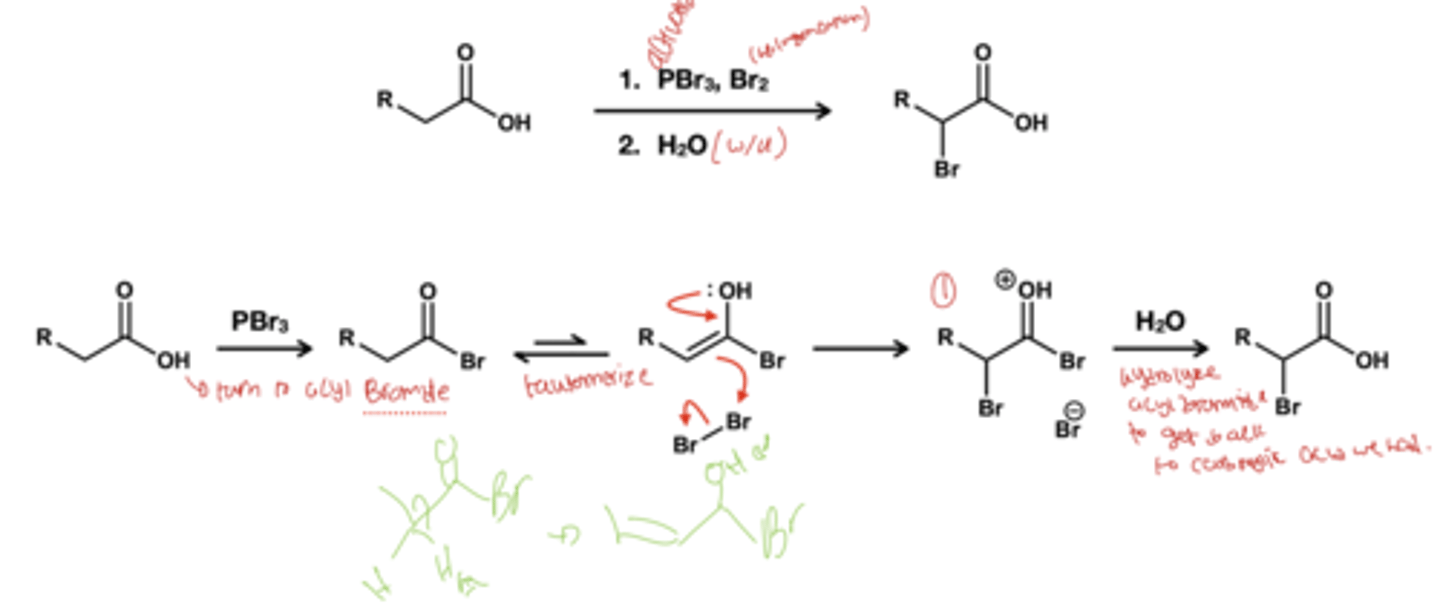
HVZ regents and what does it do?
1. PBr3, Br2
2.) H2O
This reagent replaced alpha proton with bromine as carboxylic acid do not readily undergo halogenation
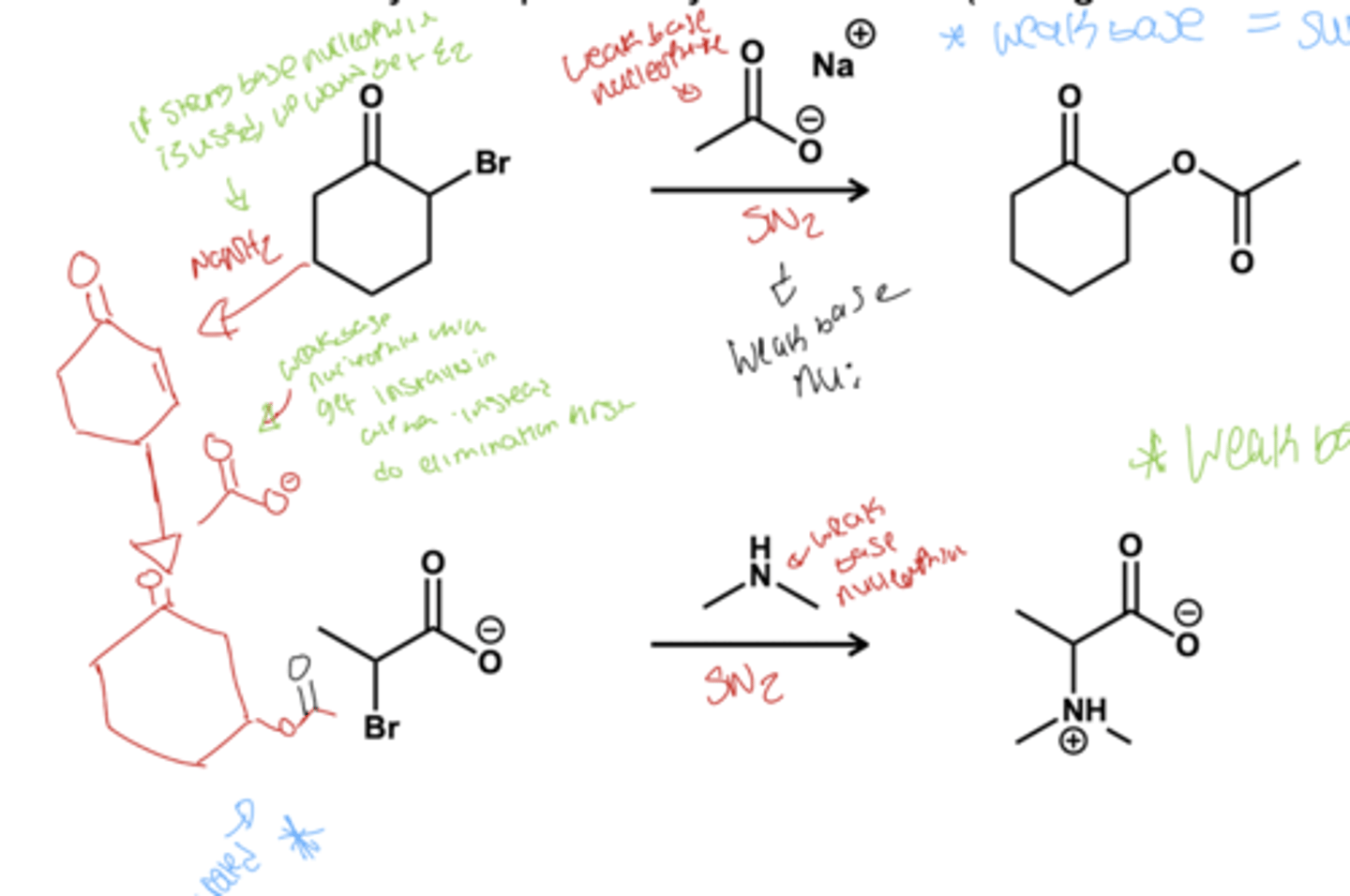
what is the only reagents that replaces alpha bromides?
weak bases
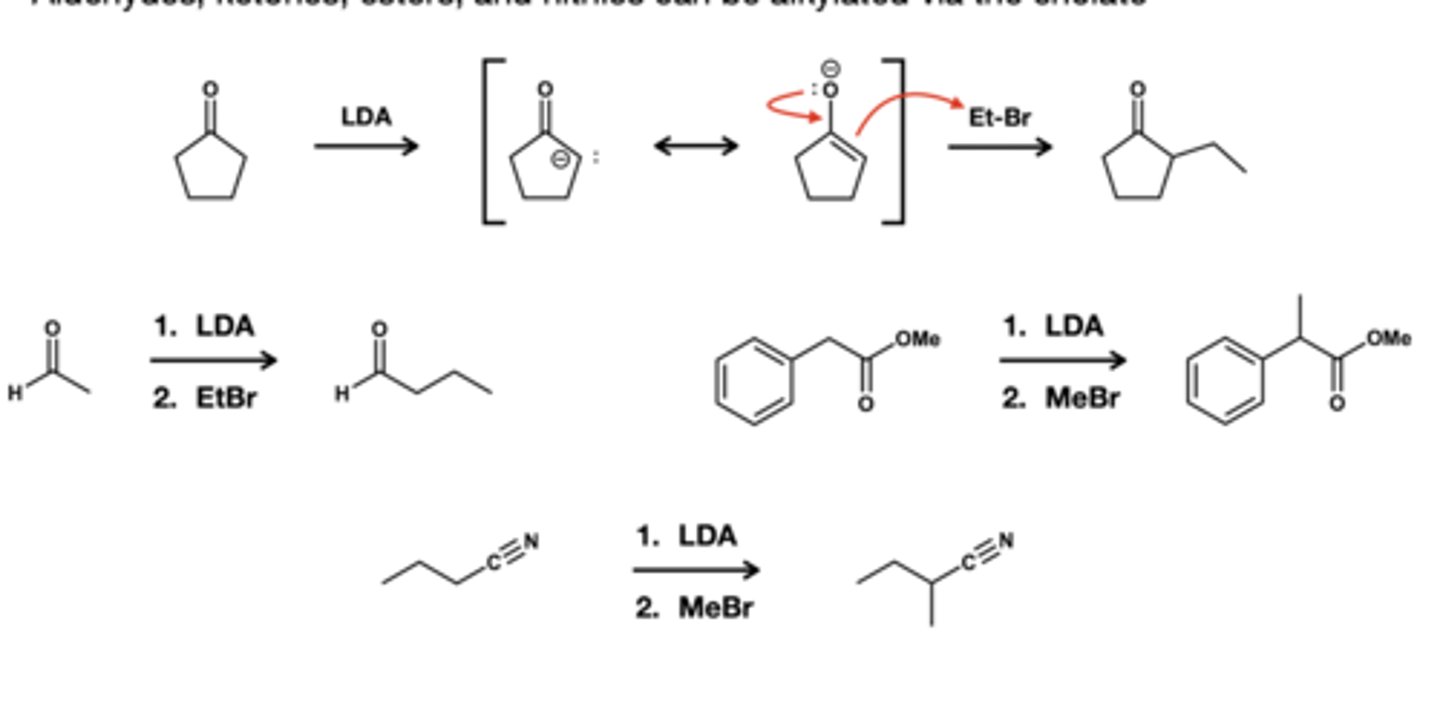
aldehyde ketone, and ester akylation via enolate reagent?
1. LDA
2. MeBR
unsymmetric enolate formation in cold conditions reagent?
LDA
-78 degree celcius
enolate froms ad least substituted carbon
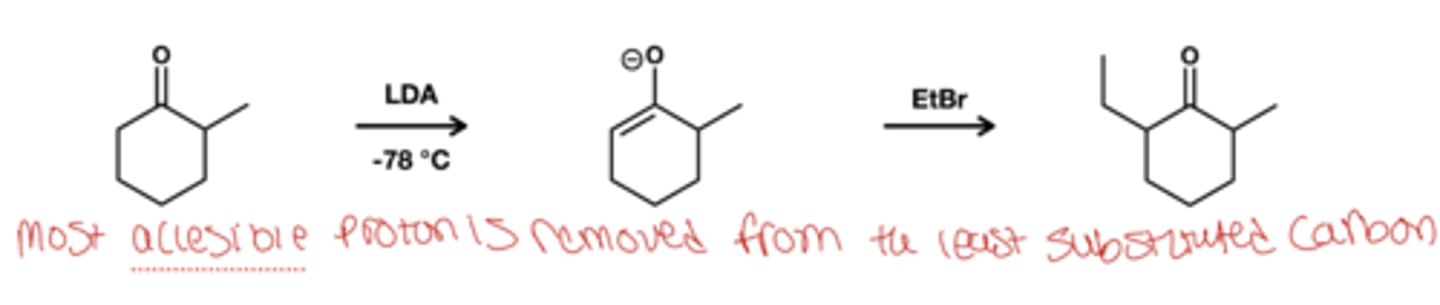
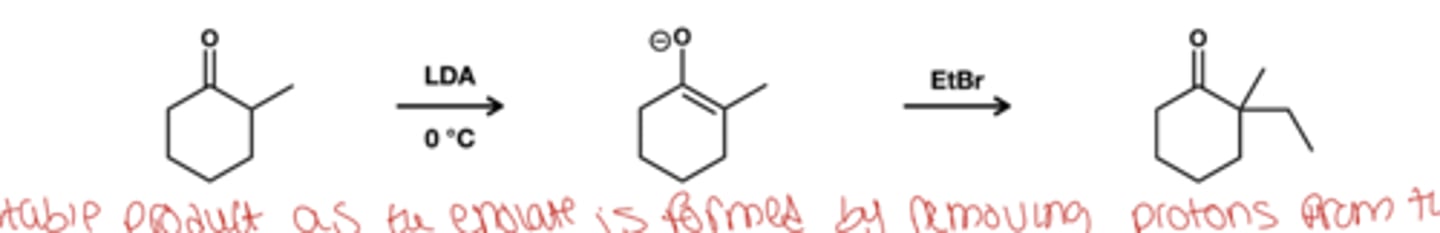
unsymmetric enolate formation in warm conditions reagent?
LDA
0 degree celcius
enolate forms art most substituted carbon
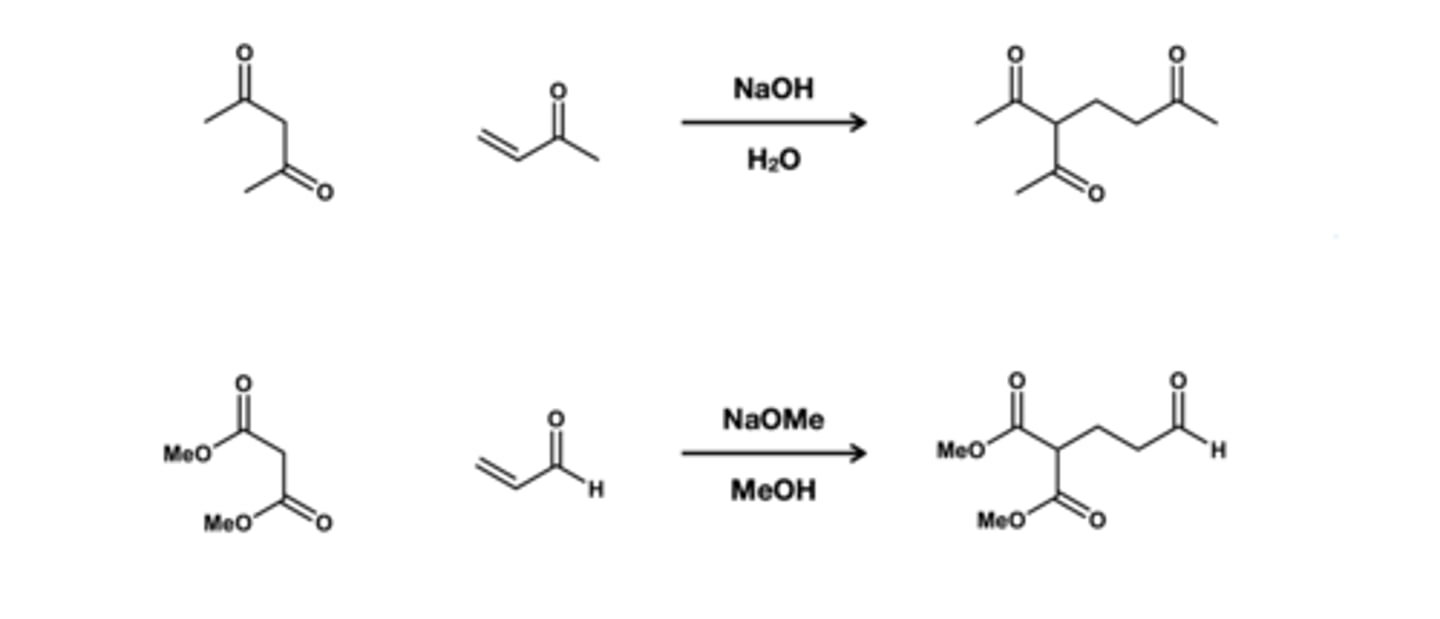
Beta-diketon or betadiester + a,B-unsturated keton/aldehyde reagent?
if diketone: NaOH/H2O
If Diester: NaOMe/MeOH