Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction quiz
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
what is sexual reproduction?
Reproduction involving 2 parents combining genetic material to create diverse offspring (zygote).
male gamete
sperm
female gamete
egg
where is the sperm produced?
testes
where is the egg produced?
ovaries
what are the three stages of sexual reproduction?
1. Mating
2. Fertilization
3. Embryonic development
what is a gamete or sex cell?
male or female reproductive cell
2 stage of sexual reproduction
Fertilization, union of sperm cell and egg cell
what are the two types of fertilization?
internal and external
External fertilization
sperm and egg of the same species unite outside the bodies of the parents
what species use external fertilization?
aquatic animals some plants fern and mosses
how does water help with external fertilization?
water transports gametes so that sperm and egg cells can meet
what are the advantages of external fertilization?
Large amount of offspring are produced. Little energy to find a mate.
what are the disadvantages of external fertilization?
zygotes are unprotected parents don't care for offspring few survive to adulthood.
Many gametes may not be fertilized.
internal fertilization
sperm cells are deposited inside the female and meet a egg cell
What animals use internal fertilization?
most land animals and some aquatic animals (sharsk orcas)
Fertilization steps
1. sperm penetrates the egg forming a zygote
2. zygote undergoes mitosis and cell divison to become a embryo
3. embryo develops and nourished inside the mother
4. offspring are born and protected by the parents
advantages of internal fertilization
offspring are cared for by parents
embryo is protected
disadvantages of internal fertilization
more energy to find a mate
fewer zygote produced
Fertilization
the process in which male and female gametes combine
True or False
only one sperm enters the egg cell
True
What is needed for fertilization to occur?
a egg cell and the head of one sperm
is pollination external or internal fertilization?
internal
what species use pollination?
most plants
Pollination
pollen (male gamete) is transferred from male reproductive part to female reproductive part of the plant
Steps of Pollination
1. pollen grains carry sperm in a protective case to ovules which have the egg cell
2. pollen lands on the female part of the plant a pollen tube forms and delivers the sperm cells to the egg cells
3 . fertilized eggs become a zygote and form into an embryo
4. embryo is protected by a seed coat
3rd stage of sexual reproduction
development
Human prental development
early development of an organism (before birth)
Development of a human zygote stages
1. embryonic stage (0-8 weeks)
2. fetal stage (8-38 weeks)
zygotes (fertilized egg) undergoes _________ and_________________
mitosis and rapid cell division
mass of dividing cells travels and impants to the lining of the __________
uterus
Advantages of sexual reproduction
more care and protection given to embryo
higher chance of survival
offspring are diverse
Disadvatages of sexual reproduction
takes time, energy, and risks
fewer offspring are produced
takes longer to produce and raise offspring
Gametes
specialized cells necessary for reproduction
Are gametes haploid or diploid?
haploid
Fertilization
fusion of male and female gametes results in a diploid cell (zygote)
mathematical equation for fertilization
sperm (n) + egg (n) = zygote (2n)
Embryo
multi-cellular diploid
how does a embryo form
zygote undergoes mitosis and cell division many times resulting in a multi-celled diploid
Do all cells undergo meisosis?
No, only special cells that produce gametes undergo meiosis.
why are offspring genetically different from parents and one another?
because you get random combinations of chromosomes
gametes that a parent produces are not all genetically the same
Meiosis
produces four haploid cells from one diploid cell. These haploid cells are the gametes that take part in sexual reproduction.
True or false
Meiosis is required for sexual reproduction and results in genetic diversity
True
how are diploid and haploid cells different
Diploid a cell with a complete set of chromosomes
Diploid= two sets of chromosomes
A haploid a cell with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell
Haploid=one set of chromosmes
Meiosis 1
chromosomes duplicated during interphase are now sister chromatids joined by centromere
Prophase 1
DNA condenses into duplicated chromosomes
homologous chromosomes are paired
homologous chromosomes
a pair of matching chromosomes in a diploid cell
Metaphase 1
pairs of homologous chromosomes (one from each parent line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase 1
Homologous pairs separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
Telophase 1
results in 2 haploid cells
prophase 1

metaphase 1
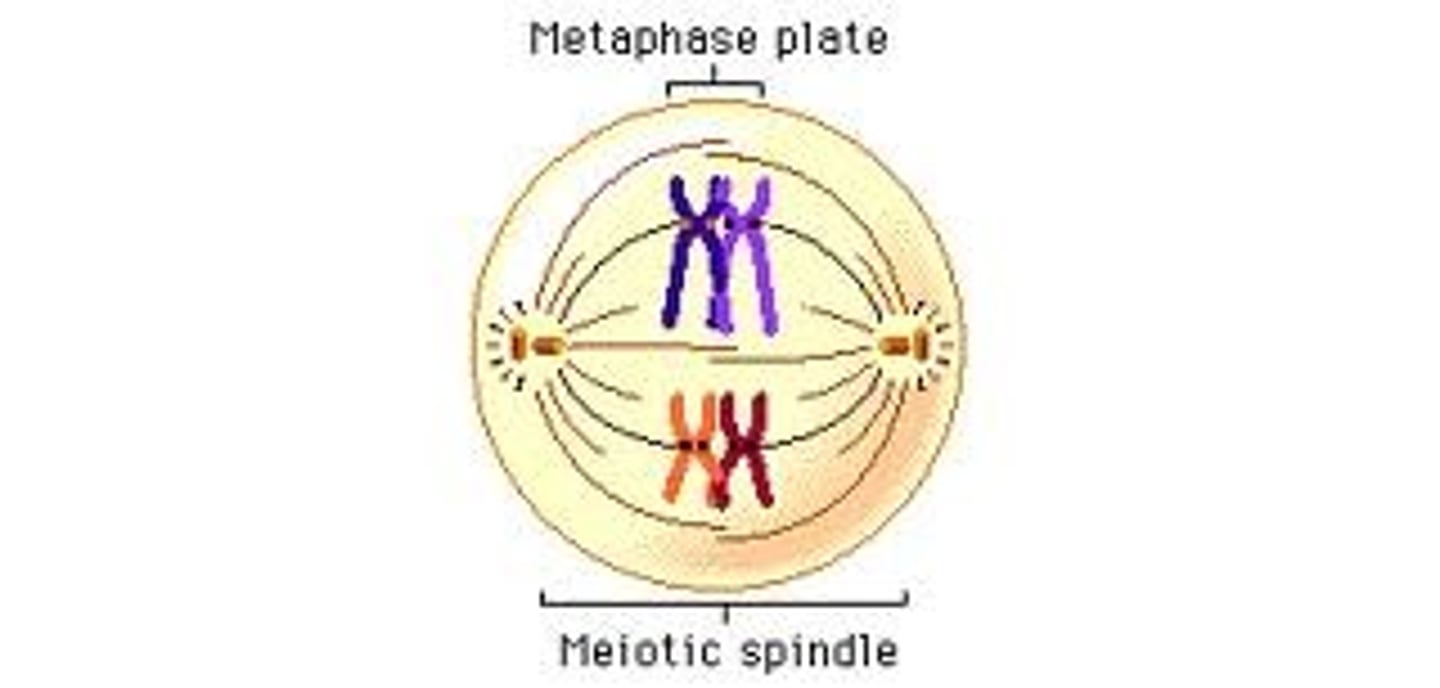
anaphase 1
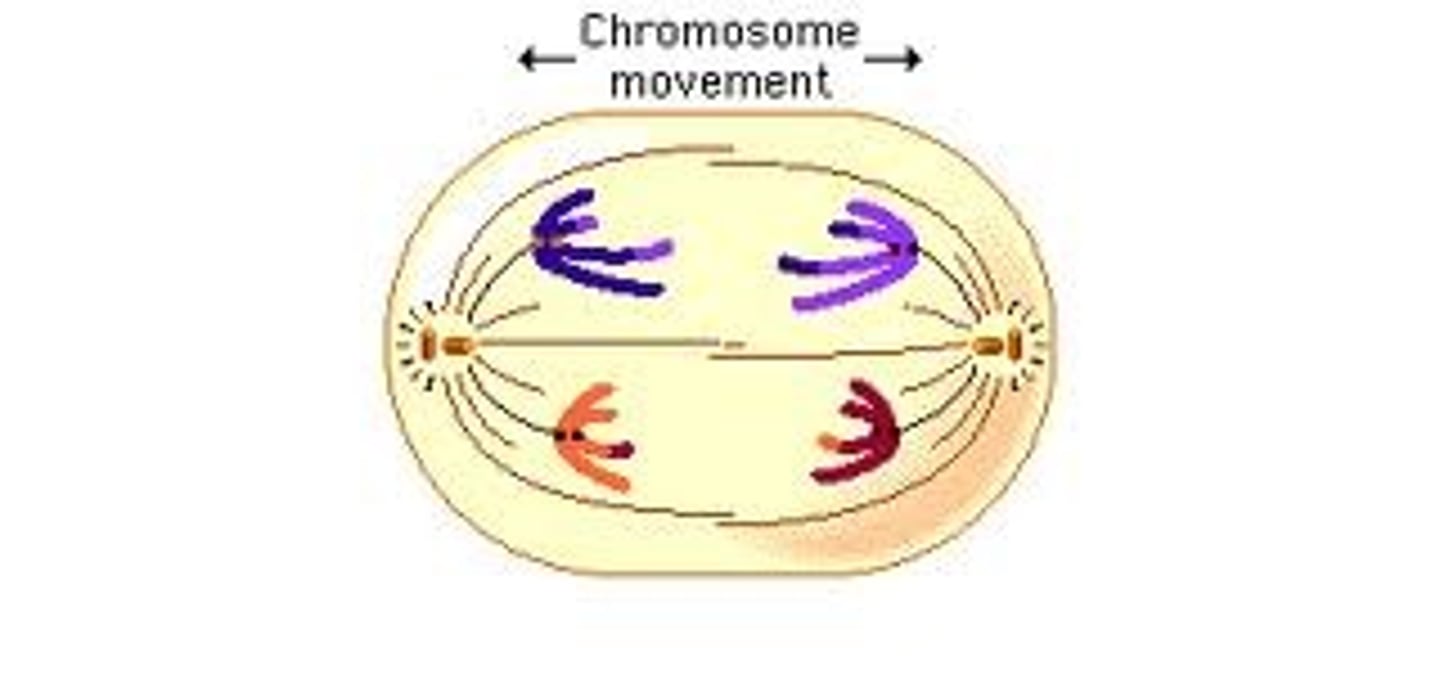
telophse 1
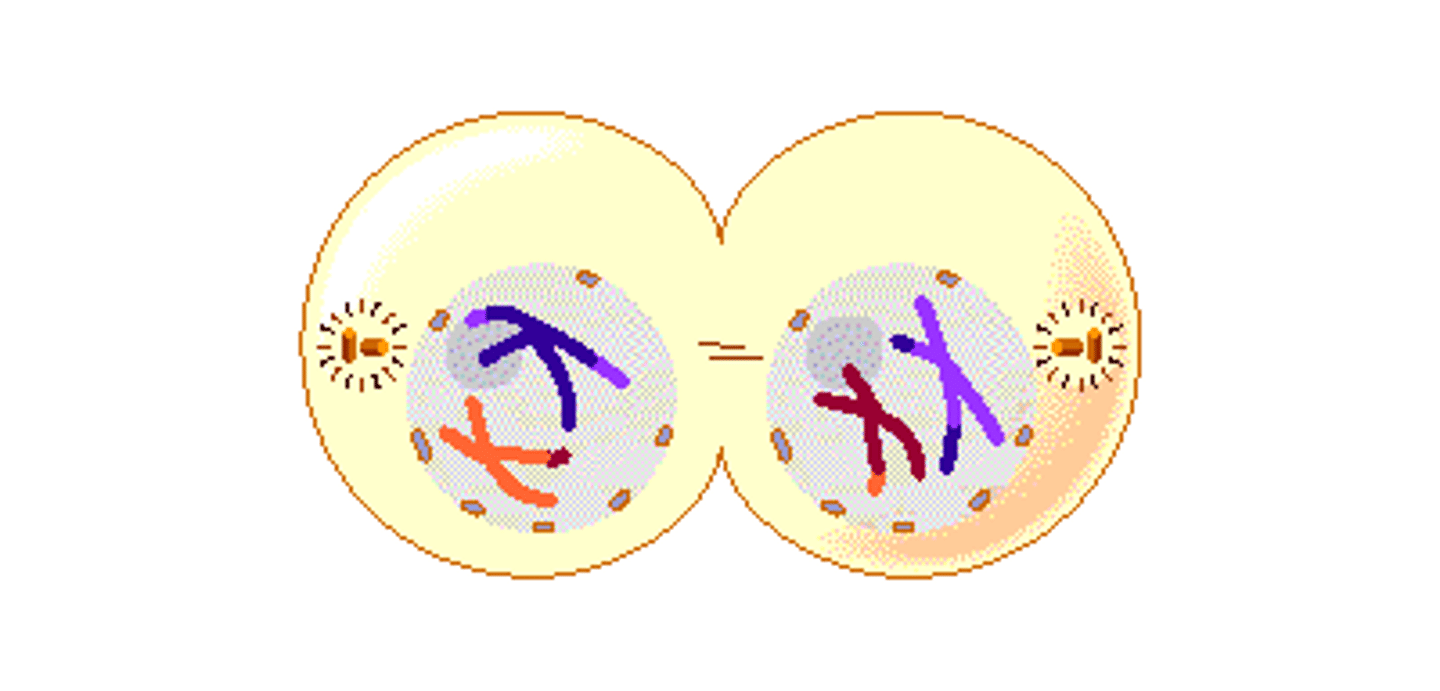
Meiosis II
Sister chromatids separate
Results in 4 haploid daughter cells (gametes)
Is DNA replicated before meiosis 11
No DNA is replicated once before meiosis
Meoisis diagram
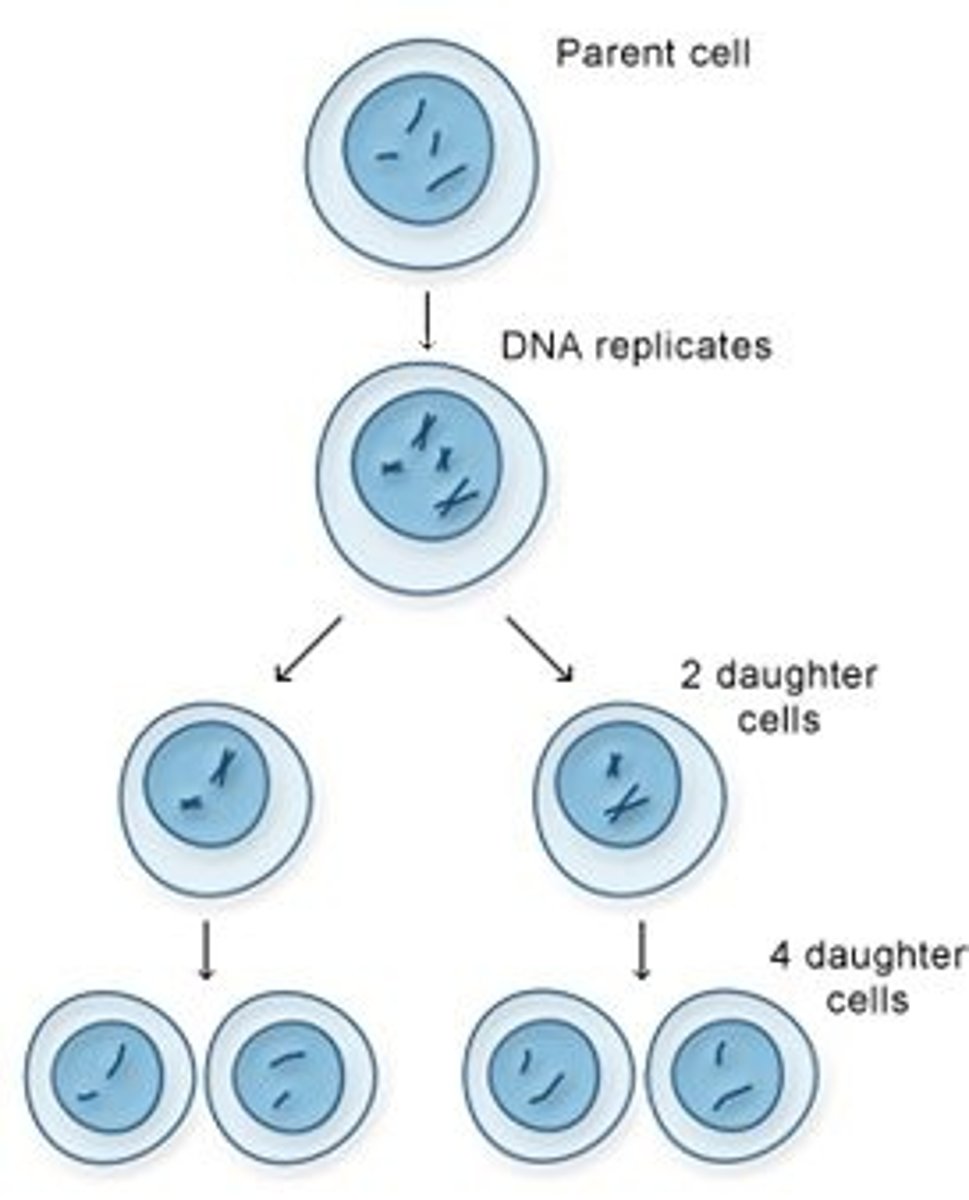
What is the difference between meiosis 1 and meiosis 11?
Meiosis 1 (Homologous pairs separate)
Meiosis 11 (Sister chromatids separate)
How many cell divisions occur during meiosis?
Two complete cell divisions occur one after meiosis 1 and after meiosis 11
What events in meiosis create genetic diversity?
Crossing over
Independent assortment
Crossing over
in meiosis 1 chromatids of homologous chromosome pairs cross-over and exchange segments of DNA (happens in prophase 1)
what does crossing over result in?
chromosomes have new genetic info
Can multiple cross-overs occur?
Yes
Independent assortment
in meiosis 1 homologous pairs line up randomly and move to opposite ends of the cell. There are 2 possibilities for how they will line up and separate for each pair. (happens in metaphase 1)
What are the differences between meiosis and mitosis?
Meiosis is to make sex cells
Mitosis is to make any body cells.
Meiosis makes 4 daughter nuclei that are not genetically identical
Mitosis makes 2 genetically identical daughter nuclei
Meiosis has 2 complete cell divisions
Mitosis has 1
Gamete Formation (female)
Unequal division of cytoplasm and organelles results in one egg cell and three other cells that disintegrate
Gamete formation (male)
four haploid cells with a equal amount of cytoplasm and organelles that all develop into mature sperm
How do mutations occur?
Mutations occur when part of a chromosome is
1. inverted
2. duplicated
3. lost or deleted
4. moved to a different location
how do mutagens cause mutations?
mutations occur when cells are exposed to mutagens ex. radiation or chemicals
What do whole chromosome mutations result in?
offspring that don't survive or cannot reproduce
Karyotype
image showing all of someone's chromosomes arranged in a particular order
chromosomes are arranged in homologous pairs
shows what chromosomes look like during mitosis
How do geneticists use karyotypes to identify genetic disorders?
Certain problems can be identified through the number or arrangement of the chromosomes.
zygote
single celled diploid
How can two chromosomes be identified as a pair of homologous chromosomes?
by size or shape. They will have genes in the same location.
what does a sperm cell look like?
has a flagellum (tail) - 4 sperm cells are the same size and available for fertilization,
what does a egg cell look like?
one egg will be larger than the other eggs, and only the large egg is available for fertilization
How does a gene mutation differ from a chromosome mutation?
Gene mutation is a change in the base sequence of a single gene (substitution, deletion, addition). Chromosome mutation occurs when large pieces of chromosomes are moved, deleted, or added to other chromosomes. Entire chromosomes can be duplicated.
Explain how animals aid plant reproduction through: Pollen transport
animals carry the pollen to another plant of the same species so that the egg and sperm can unite for fertilization
Explain how animals aid plant reproduction through: seed transport
carrying seeds on their fur or by eating fruit and depositing undigested seeds to a new location
How can you tell that a human cell is from a male and not a female when examining chromosomes under the microscope?
men have a x chromosome and a small piece of a y females have two x's