protein ligand interactions
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
what usually happens when a protein and ligand bind?
conformational change in protein
makes site more complementary for protein (tighter fit)
induced fit
structural adaptation between protein and ligands in response to binding
conformation change in multi subunit proteins cause…
conformation changes in other subunits not just one
conformations of hemoglobin
r state- O2 has higher affinity hem
t state- more stable w/out O2
R state
when hemoglobin has higher affinity for O2
T state
when hemoglobin is more stable with/out O2
deoxyhemoglobin is mostly in this state
How is the T state stablalized?
by a larger number of ion pairs
-many in the \alpha_1\beta_2 and a2b1 interface
when O2 binds to T state…
hemoglobin changes to R state
when T state —> R state
2 ab subunit pairs slide past eighother and rotate
pocket between beta subunit narrows
some stabilization ion pairs break (some new form)
myoglobin
1 O2 binding site
distal His holding oxygen in place
has an equation for binding that is a hyperbola (never fully gets to 1)
hemoglobin and binding
4 subunits
4 heme groups
4 O2 binding events
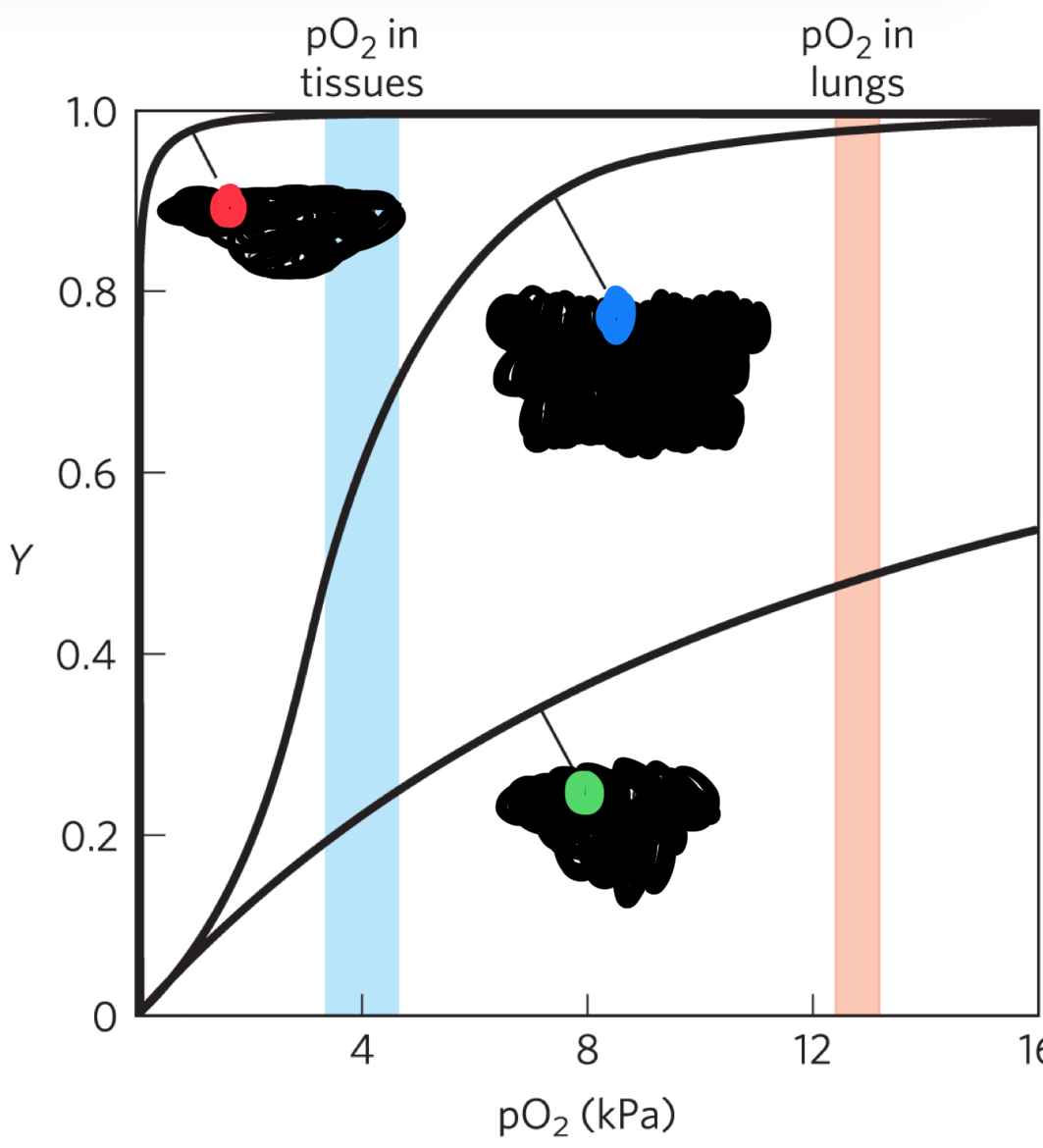
red curve (what state)
R-state (high affinity for O2) also hyperbolic shape
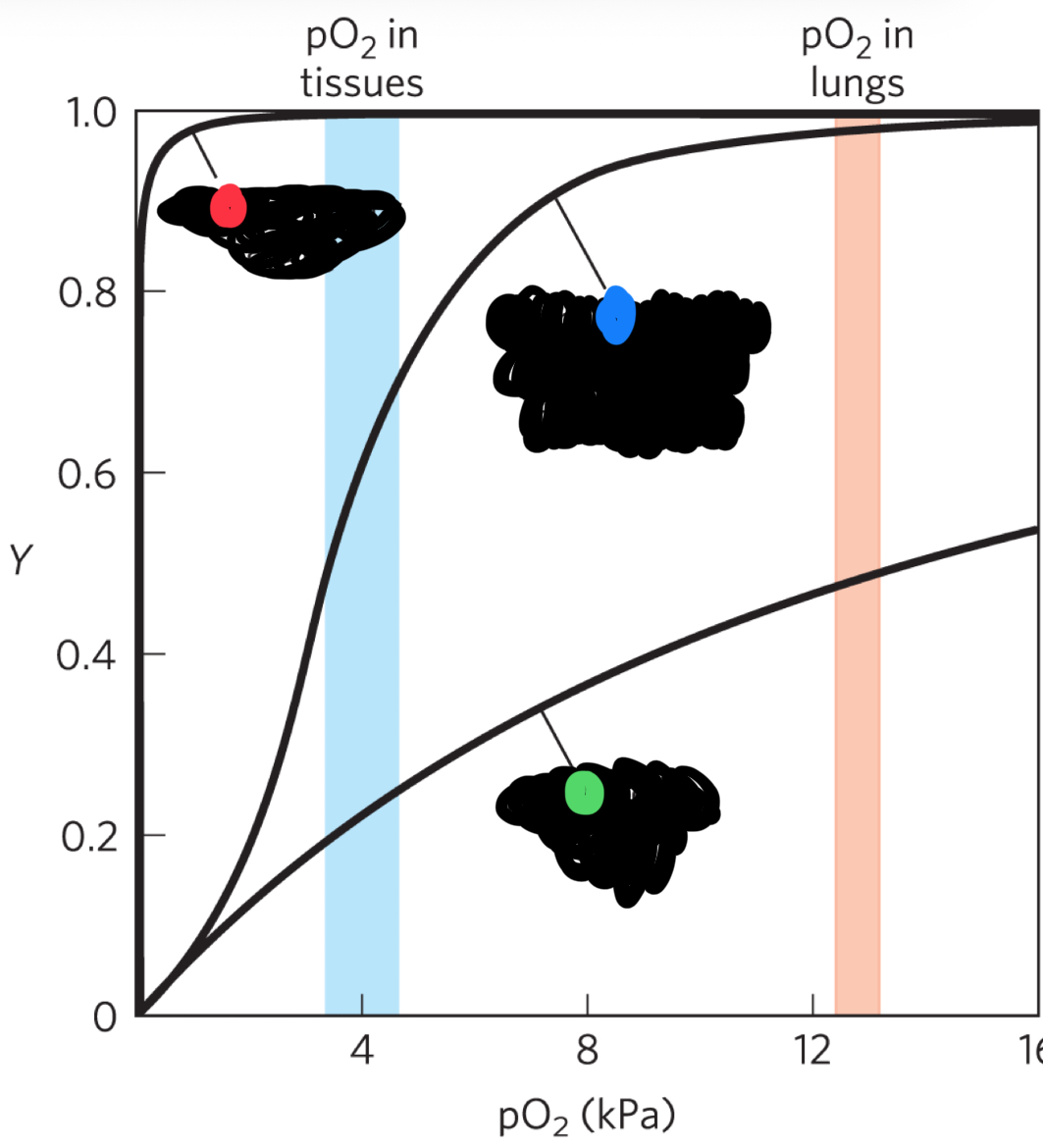
blue curve (state)
intermediate state (sigmoidal curve)
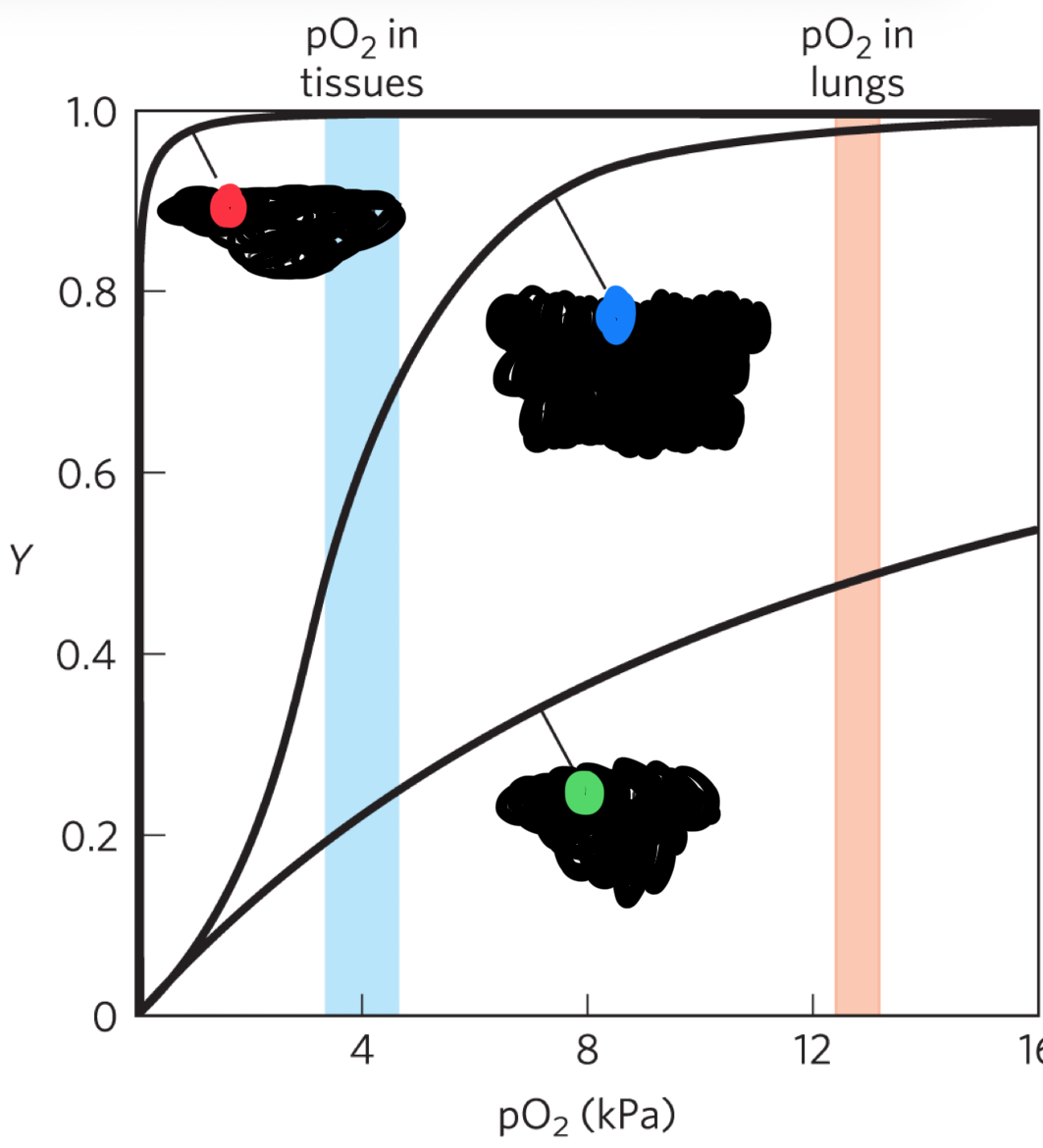
green curve
T-state (low affinity for O2)
why are the is there a shape change in protein-ligand binding?
to regulate the interactions
allosteric proteins
proteins where affinity can change
ex. hemoglobin
modulators
ligands that bind at a separate site to change the binding at another site
2 types- homotropic and heterotropic
homotropic modulators
ligand that is binding affects the another binding site for the same type of ligand
ex. one ligand binds and makes it so no other of the same ligand can bind
heterotropic modulators
molecule other than the normal ligand that affects its binding
what does nL mean in the protein-ligand binding equation
There are more than one binding cite
what type of graph is made from a binding equation with more than one binding site?
sigmoidal graph
the hill equation
equation for cooperative binding (with logs)
hill coefficient
nH
slope of line in hill graph
difference between n and nH
n is the number of binding sites
nH is how the binding at one site affects the binding at another site
nH=1
binding at different sites are independent of each other
affinity state stays the same
nH>1
binding at one site helps binding at other sites
low to high affinity
nH<1
binding at 1 site negatively impacts binding at another
high to low affinity
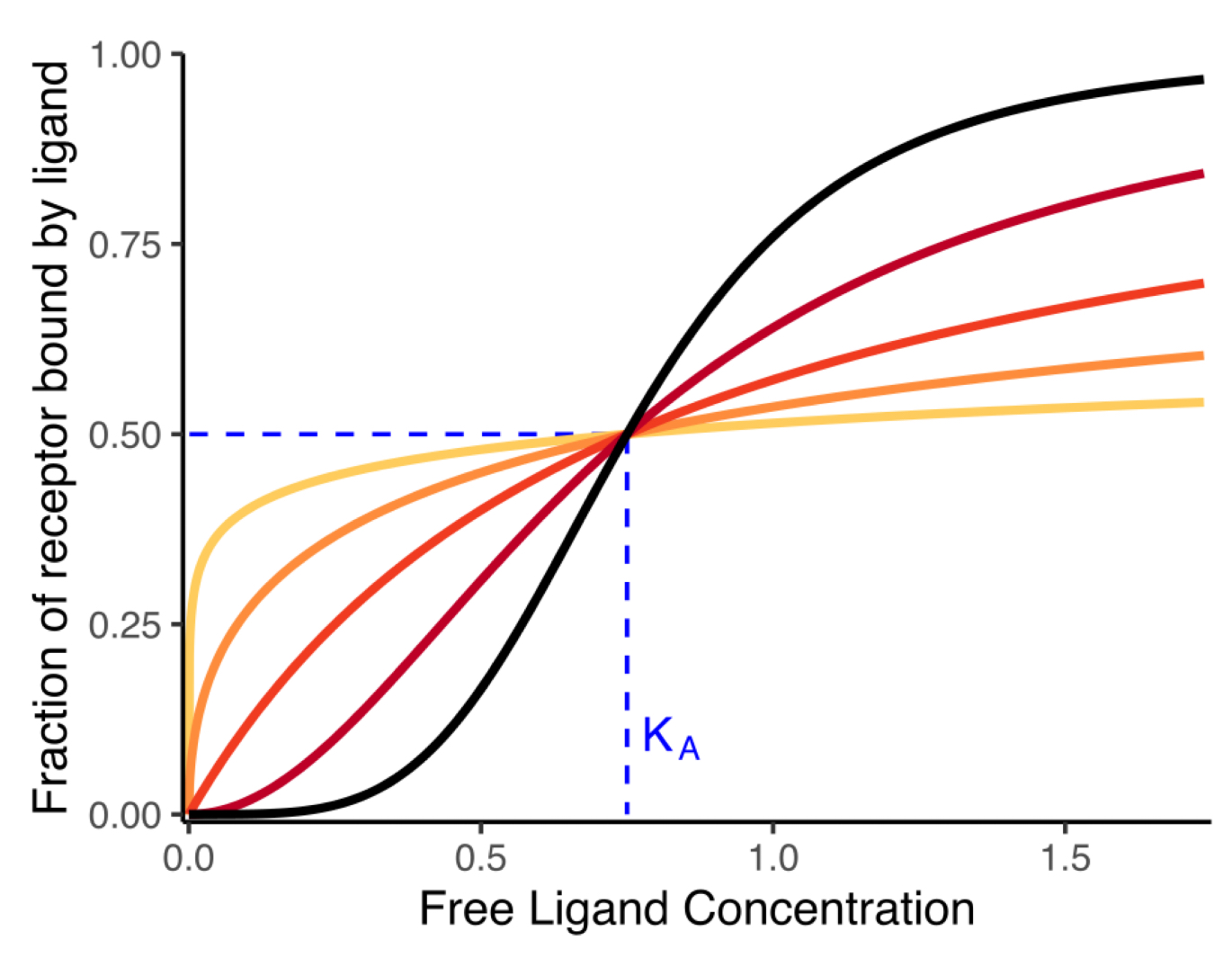
dark orange type of curve
hyperbolic (nH=1)
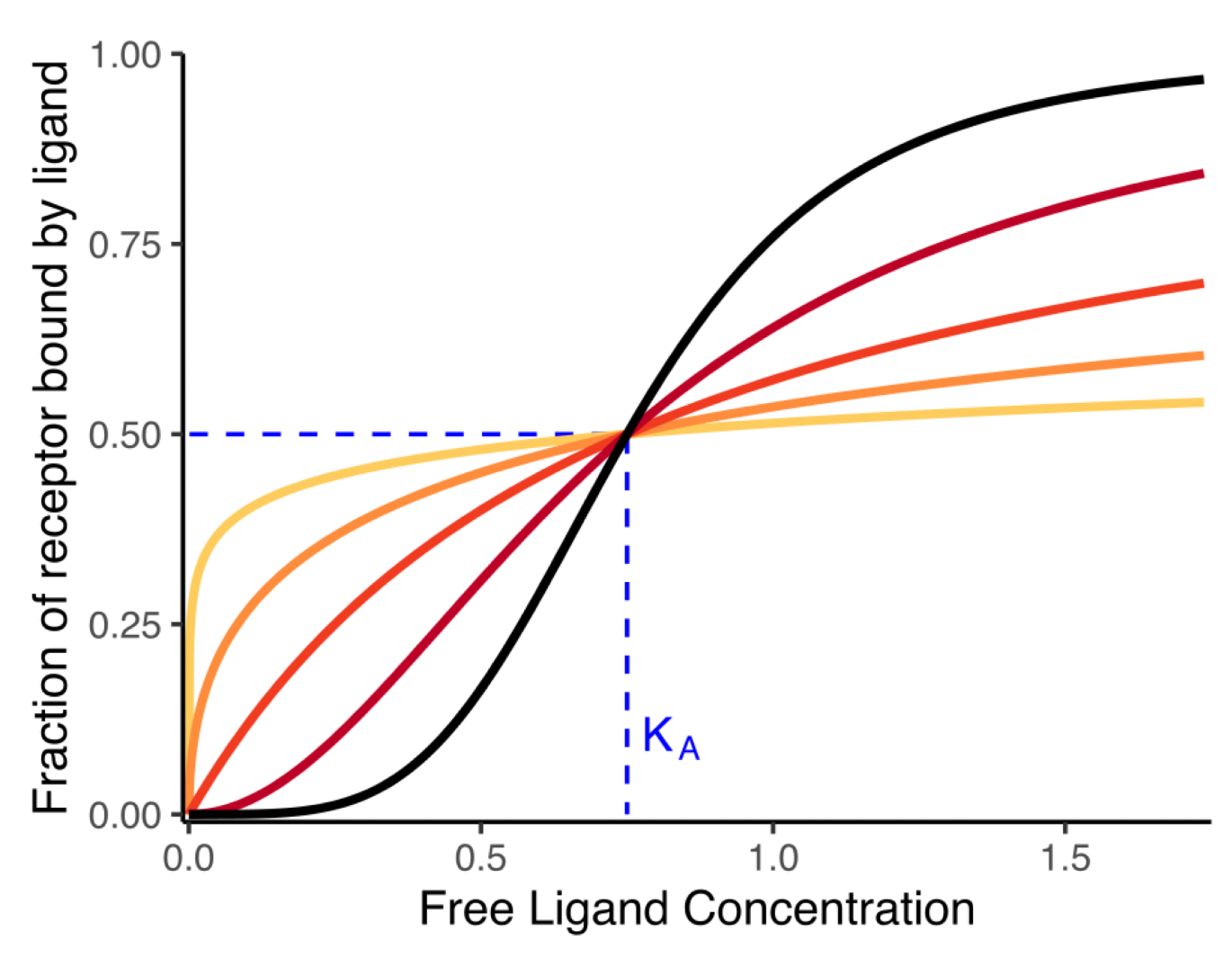
red and black
nH>1
sigmoidal curve
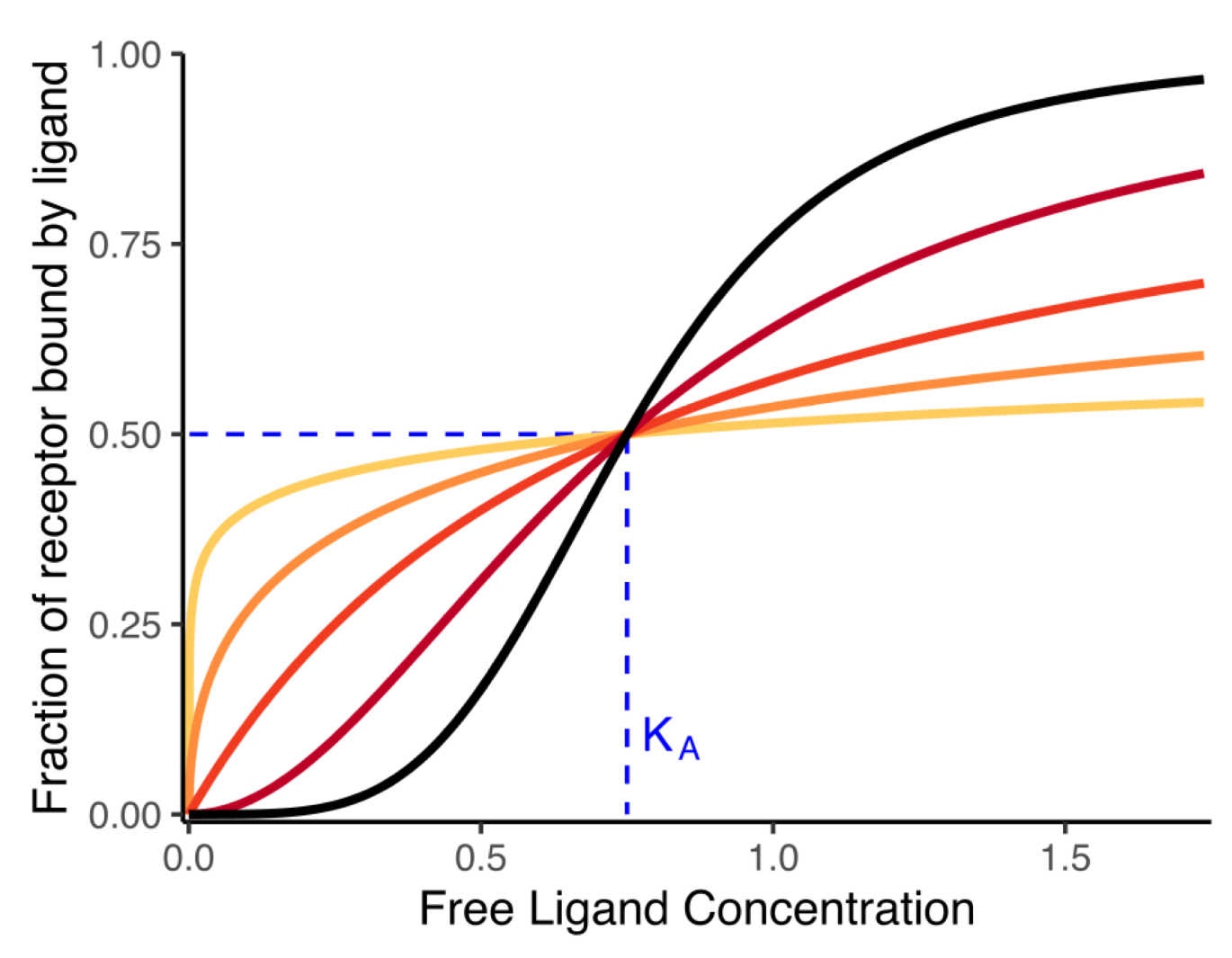
yellow and orange
nH<1
hyperbolic
concerted model
-all subunits in same conformation R or T
-ligands bind more tightly in R state
Sequential model
each subunit can be in either conformation
carbonic anhydrase
takes CO2 released from respiration and turns it into a pronton and bicarbonate
main buffer of blood
farther from the lungs there is ___ CO2 in our blood
more
Bohr effect
amount of CO2 and the pH have an affect on the binding and release of O2 by hemoglobin
when H+ and CO2 is bound to hemoglobin
it makes O2 less likely to bind
when O2 is high…
hemoglobin bind O2 and releases H+
when O2 is low…
hemoglobin releases O2 and bind H+
what does free CO2 do to hemoglobin?
binds to the end terminal and kicks off a proton
this makes it go to the tense state (to push off oxygen)
2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
regulates O2 binding to hemoglobin
heterotropic modulater
reduces affinity for oxygen
at high altitudes BPG…
increases so hemoglobin releases oxygen bc the body needs it
how does BPG work?
it binds hemoglobin between the beta subunits encouraging it to be in the tense state—> kicks off oxygen
fetal hemoglobin
uses gamma instead of beta—> beta has higher affinity for O2
baby needs oxygen more then mom’s blood does
in sickle cell anemia
hemoglobins clump together in a super low affinity tense state -> can’t grab oxygen
Kd
Dissociation constant
low Kd—> higher affinity
High Kd—> low affinity
Analog
Things that look the same and do the same things but have no shared ancestry
Paralogs
Similar because of shared ancestry