Male Microanatomy
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Where are leydig cells located?
Interstitial tissue between seminiferous tubules
What do leydig cells secrete?
Testosterone
What are the red dots in Leydig cell cytoplasm?
Lipid droplets that store cholesterol for testosterone synthesis
Functions of sertoli cells
1. Maintain developing germ cells
2. Secrete inhibin (decreases FSH via neg feedback loop)
3. Synthesize androgen binding protein (maintains testosterone levels)
What are the stages of germ cells in order?
1. Spermatogonia
2. Spermatocytes
3. Round spermatids
4. Elongated spermatids
Germ cell diagram
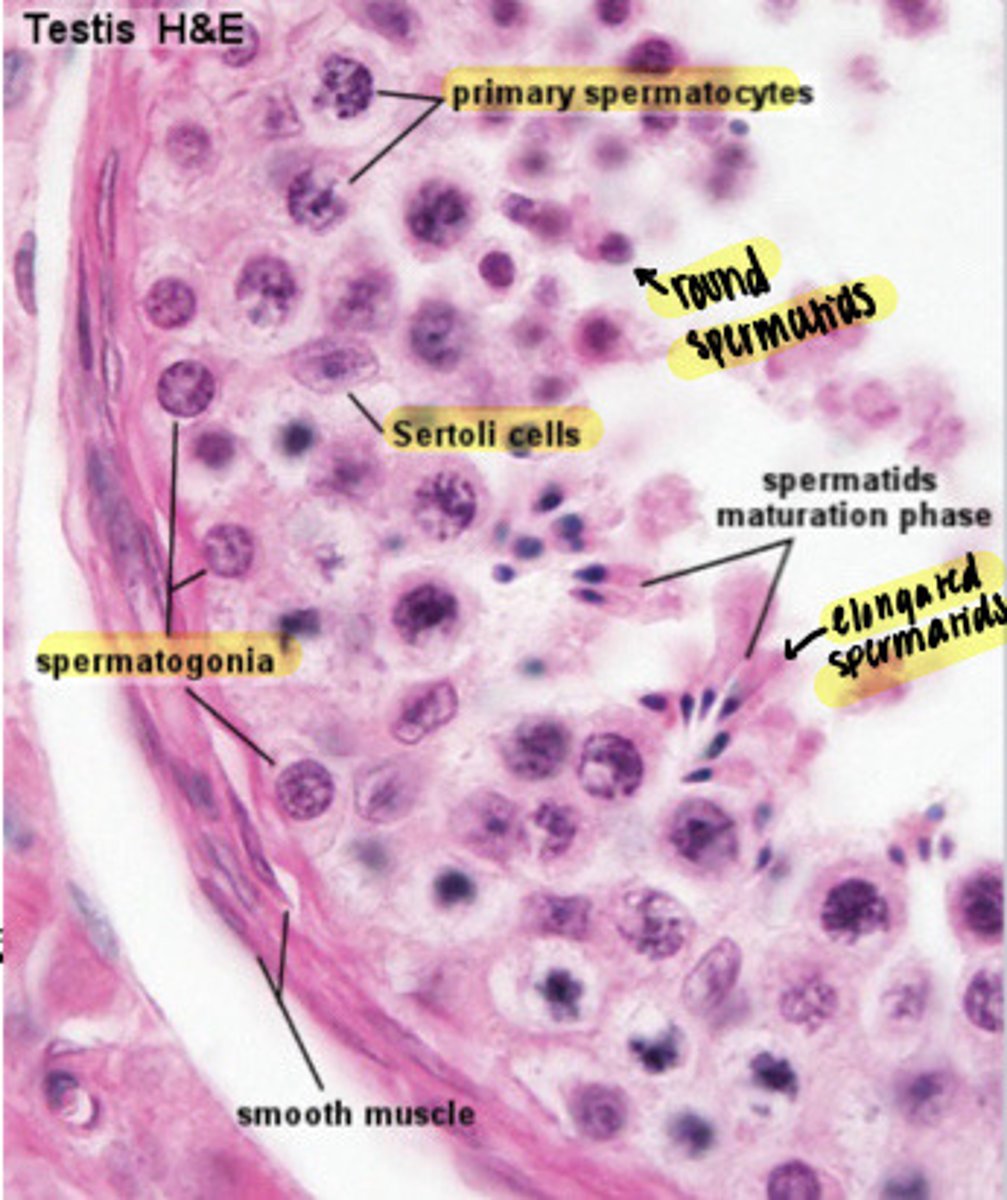
What cell type proliferates in a seminoma?
Germ cells (note all the purple dots)
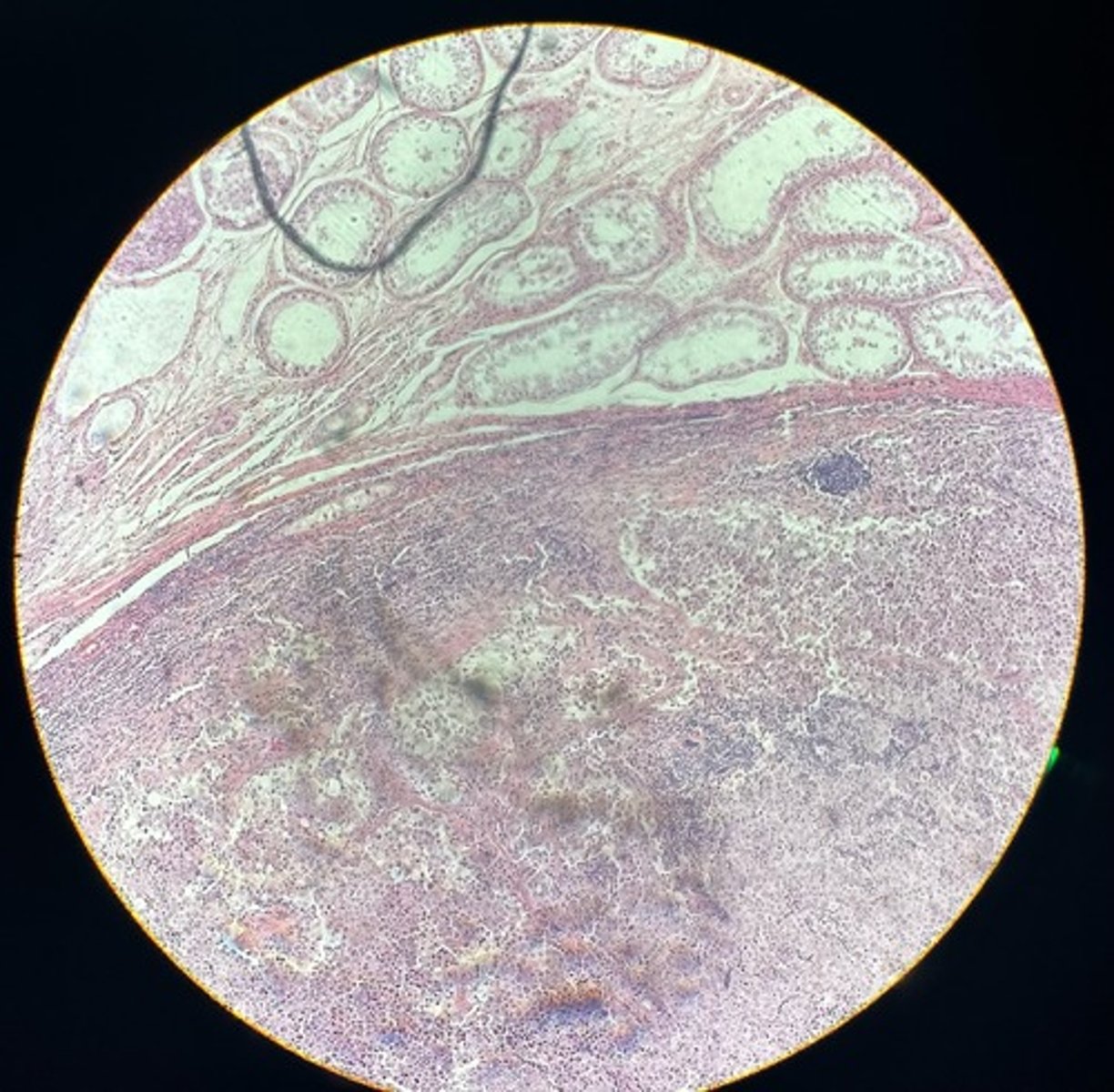
What cell type proliferates in interstitial adenoma?
Leydig cells
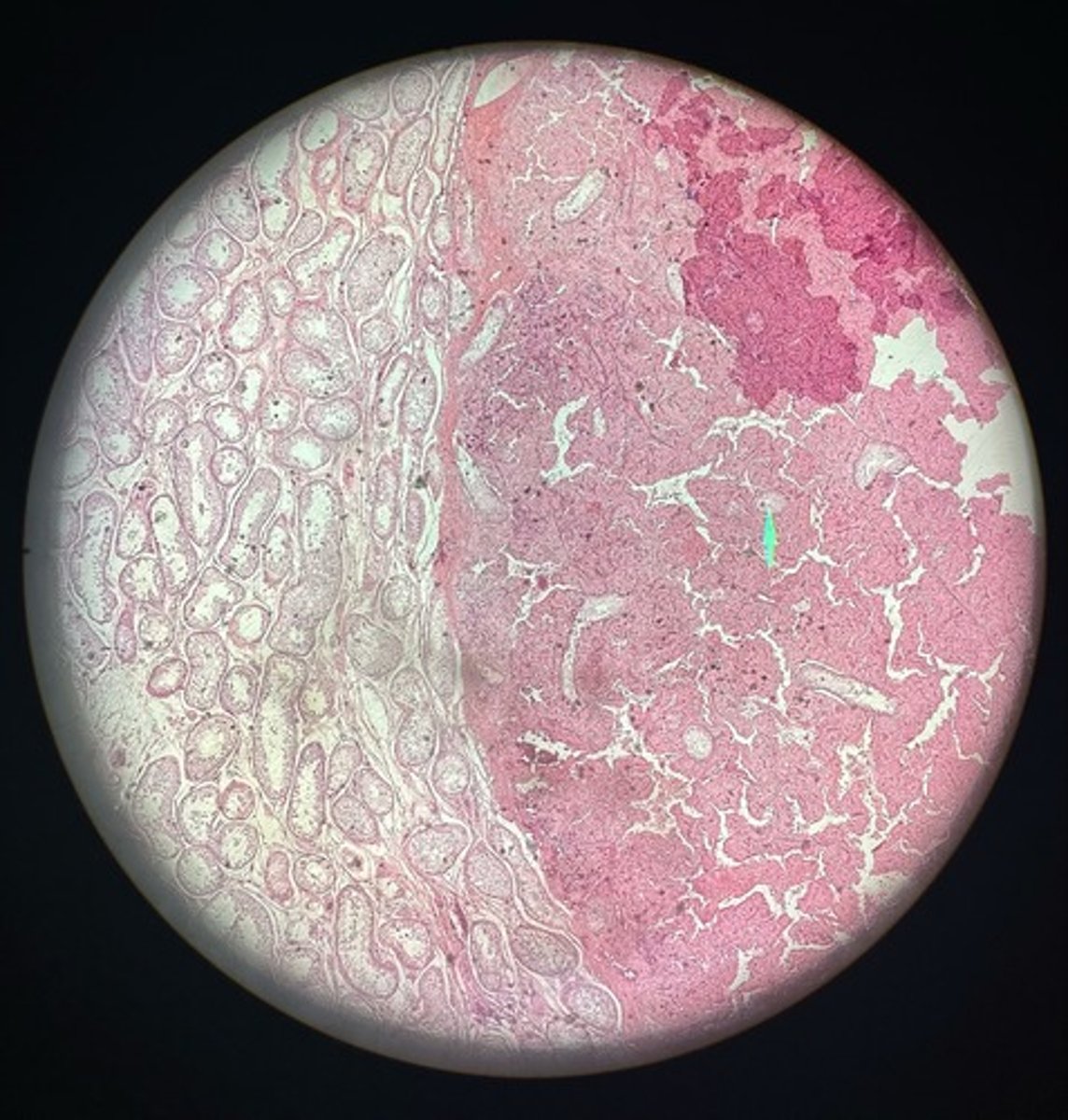
How would you recognize a sertoli cell tumor?
Proliferation of sertoli cells that ruptures the seminiforous tubules
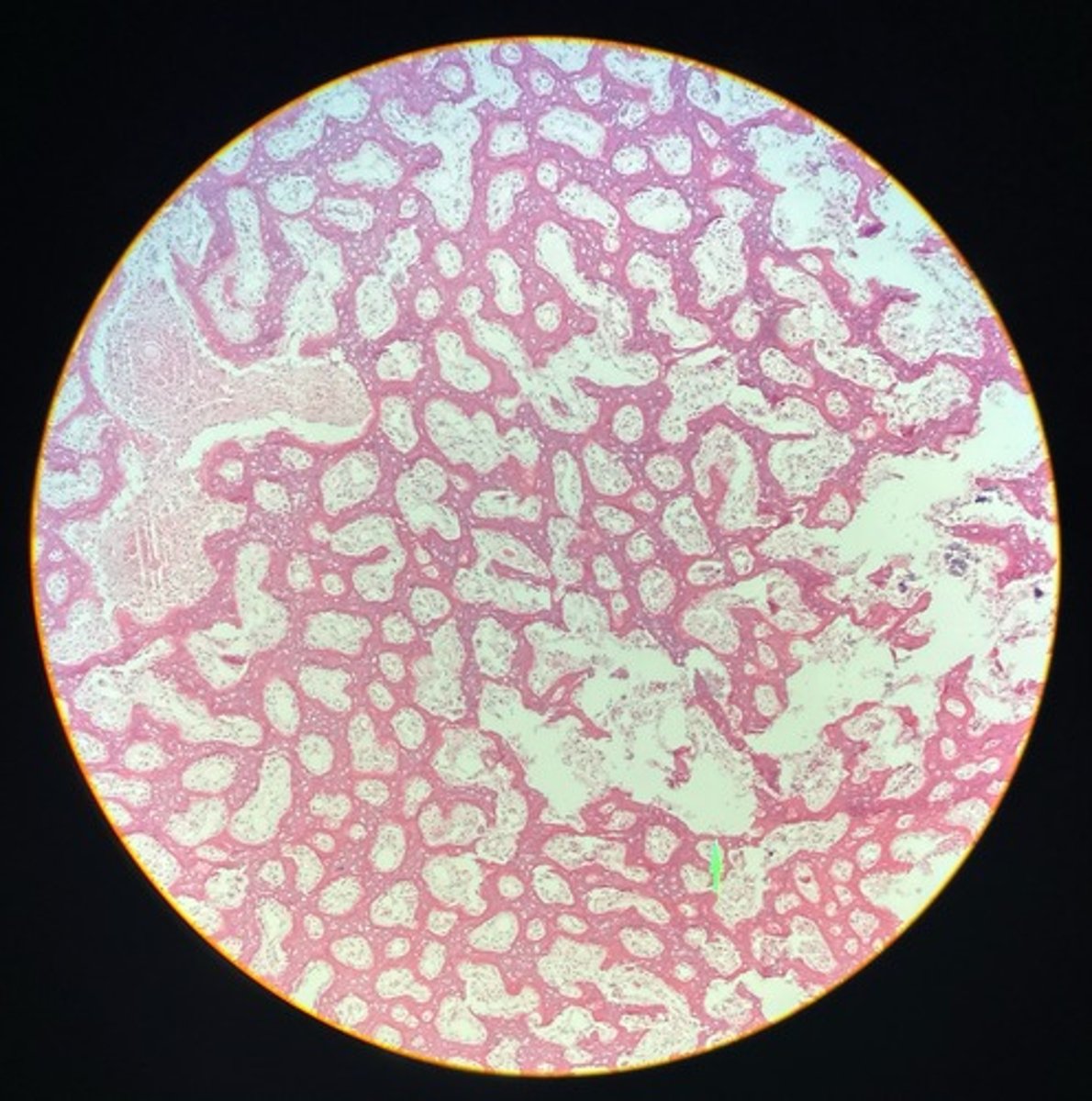
What would a cryptorchid testes look like?
Only single layer of germ cells on the surface of seminifourous tubules
What an infant testes look like?
No lumen (collapsed) because not producing any sperm!
What is the role of efferent ducts?
Takes sperm from rete testis to the epididymis!
Does epithelium look similar in all regions of the epididymis?
Cells are larger in caput vs cauda, microvilli longer in caput vs cauda. Caput cells need to absorb large quantities of testicular fluid and synthesize proteins involved in sperm maturation.
What is the role of the smooth mm in the epidiymis? Is it thicker in head or tail?
Moves the sperm. Tail cause needs to go to ductus deferens for ejaculation
What does epididymis look like in a cryptorchid patient?
Little to no microvilli cause the sertoli cells are not functioning = do not need the microvilli to absorb the incoming fluid OR make proteins for the maturating sperm.
Are sperm in the body of the epidiymis capable of fertilization?
No. Tail has fertile sperm
Type and function of ductus deferens epithelium
Pseudostratified columnar that absorbs excess fluid and provides nutritional support for the sperm
Are sperm motile in the ductus deferens?
No, they are transported via muscle contractions
Is ductus deferens palpable?
Should be in a living male!
Prostate epithelium
Pseudostratified columnar