AQA A Level Biology Lipids
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what type of molecule are lipids?
large molecules, not polymers
what are the two main types of lipid?
triglycerides
phospholipids
(cholesterol)
what are the functions of lipids?
energy storage
insulation
protection of internal organs
what type of molecule do all lipids contain?
hydrocarbons
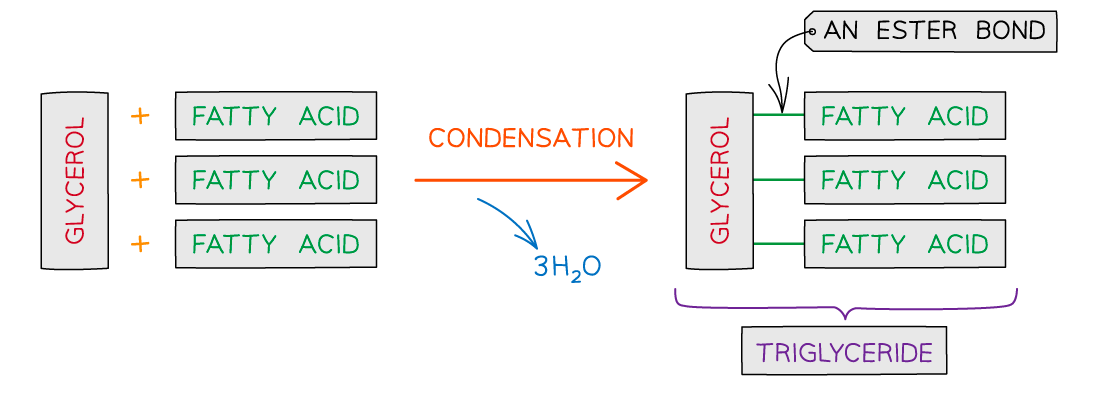
describe the structure of a triglyceride
made up of 1 glycerol molecule
and 3 fatty acid molecules
joined by ester bonds
non polar molecule
describe the structure of a fatty acid
carboxyl group bonded to a hydrocarbon tail
hydrocarbon tail is hydrophobic
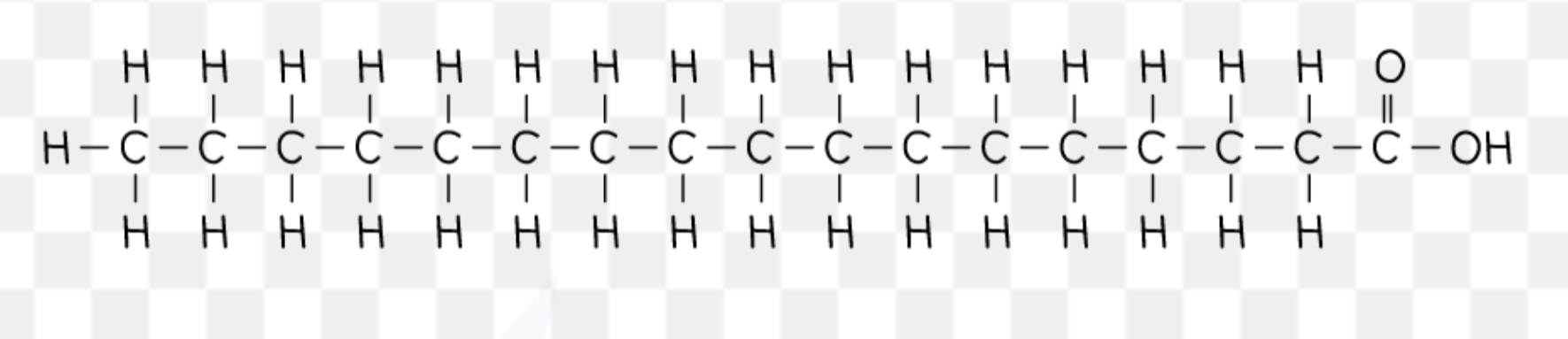
what is the formula of a fatty acid?
RCOOH (C=O)
R is the variable hydrocarbon tail
what are the two types of fatty acid?
saturated
unsaturated
what is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids?
saturated fatty acids contain no double bonds
unsaturated fatty acids contain C=C double bonds, which cause the chain to kink
saturated fatty acids are normally solid at rtp
unsaturated fatty acids are normally oils at rtp
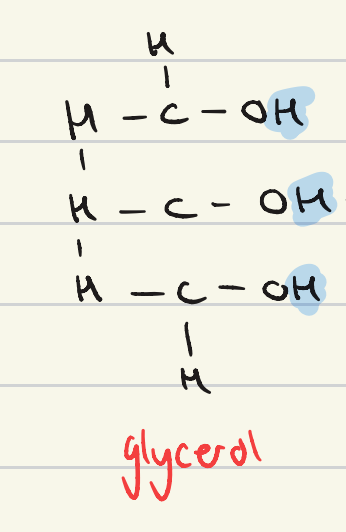
describe the structure of a glycerol molecule
propanol, but with 3 OH groups
CH2OHCHOHCH2OH
what type of reaction forms a triglyceride?
condensation
3 water molecules produced
draw the condensation reaction used to produce glycerol
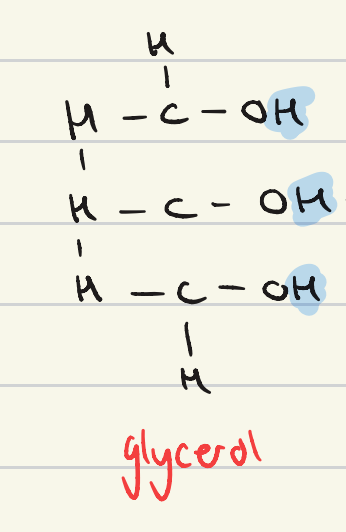
which molecules are removed from glycerol and fatty acids in a condensation reaction?
H from glycerol
OH from fatty acid
describe the structure and function of triglycerides
hydrophobic tails make the molecule insoluble, also non polar - have no osmotic effect on cells so good for storing energy - as tails are hydrophobic, they form droplets in cells (why they emulsify)
large - cannot cross cell membranes so good energy stores
high proportion of carbon and hydrogen atoms - contains lots of energy, more per gram tahn carbohydrates
good heat insulators - stored as blubber in marine animals
low density - buoyancy aid in animals
describe the structure of phospholipids
similar to triglycerides, one fatty acid is replaced by a phosphate group
so glycerol, 2 fatty acids, phosphate group
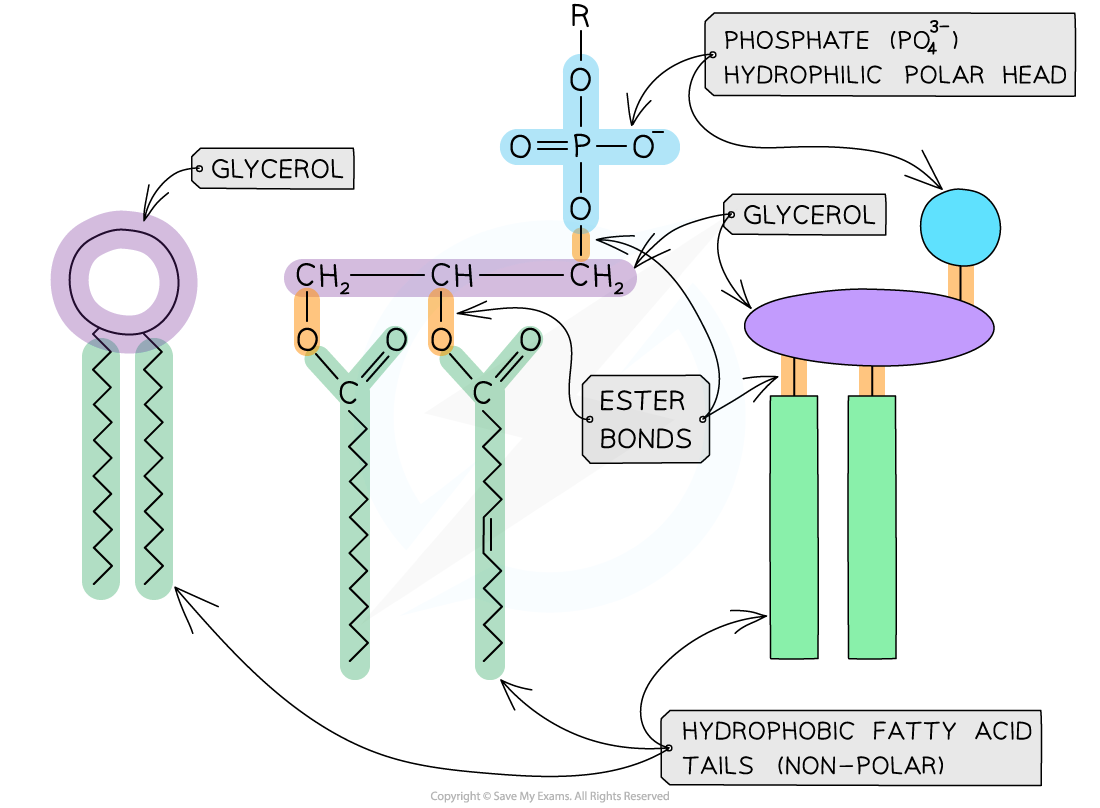
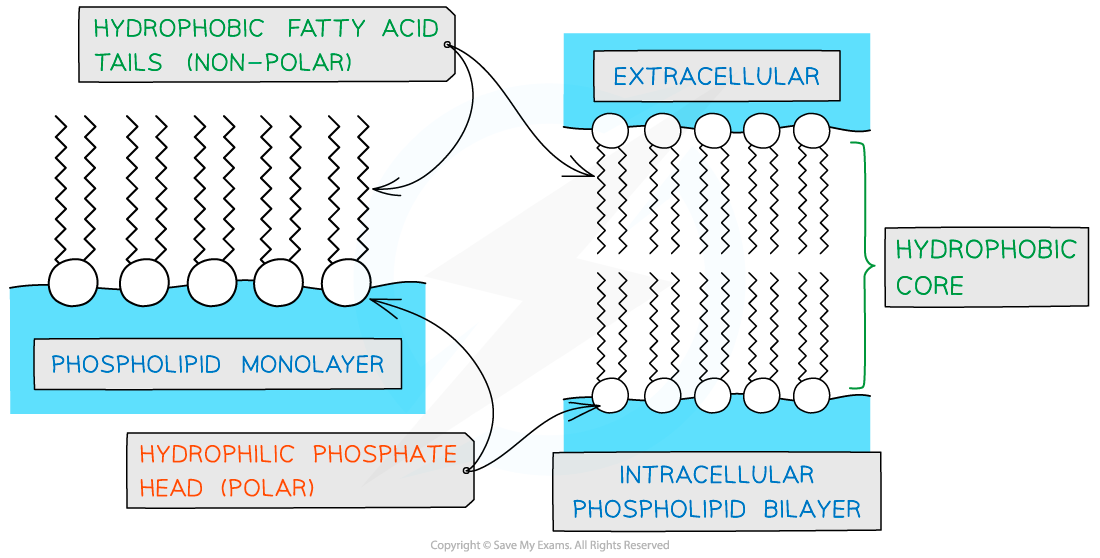
describe the structure and function of phospholipids
heads are hydrophilic and tails hydrophobic, so they form a double layer with heads facing out towards the water on both sides of the cell membrane
water soluble substances can’t easily pass through the membrane - acts as a barrier
in water single or double layered spheres called micelles can form, or monolayers on the surface
what test is carried out to test for the presence of lipids?
emulsion test
describe how the emulsion test would be carried out
2cm³ of sample added to 2cm³ of ethanol in a test tube
shake for 30s
decant into test tube of cold water
if a white emulsion forms, sample contains lipids
how does the emulsion work chemically?
ethanol dissolves lipids,
so if the food sample contains lipids when added to water the insoluble dissolved lipids form droplets
these prevent light passing through