Honors Chemistry Intermolecular Forces
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
bond moment (dipole)
a vector that indicates the size of the polarity of a particular covalent bond (within a molecule)- points in the direction of the more electronegative atom
(in the eg- The C−H and C=C bonds are non-polar bonds, so have no bond moments associated with them)
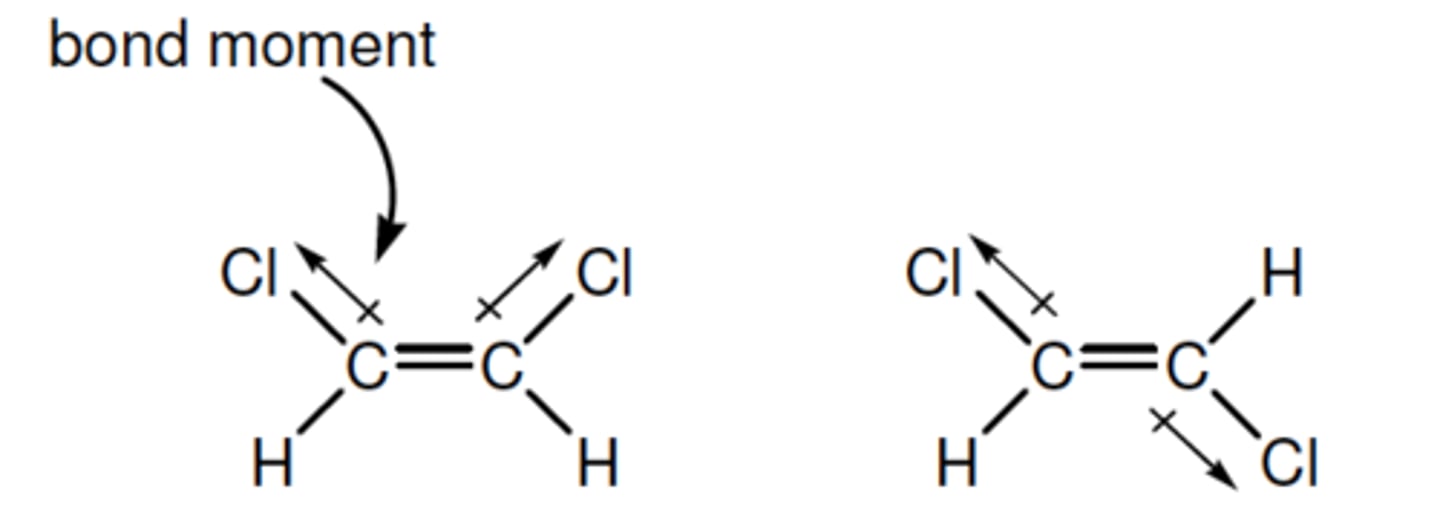
dipole moment
sum of individual bond moments. If the molecule has an overall dipole moment it is polar- the moment will indicate its direction
EG- The molecule on the left had two bond moments
which, by vector addition, give the overall dipole
moment shown.
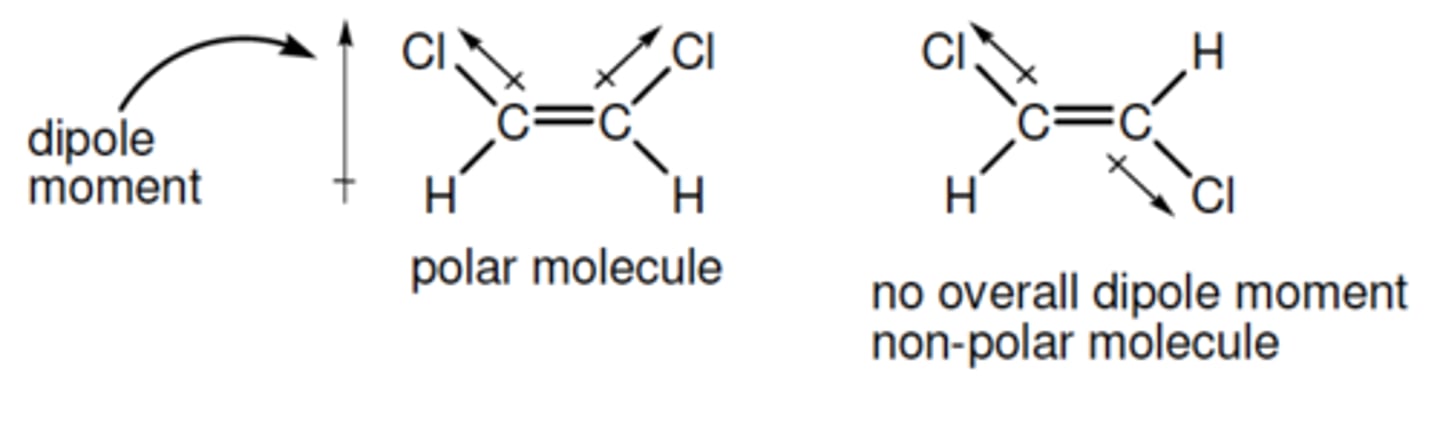
polar molecule
molecule that has an overall dipole moment
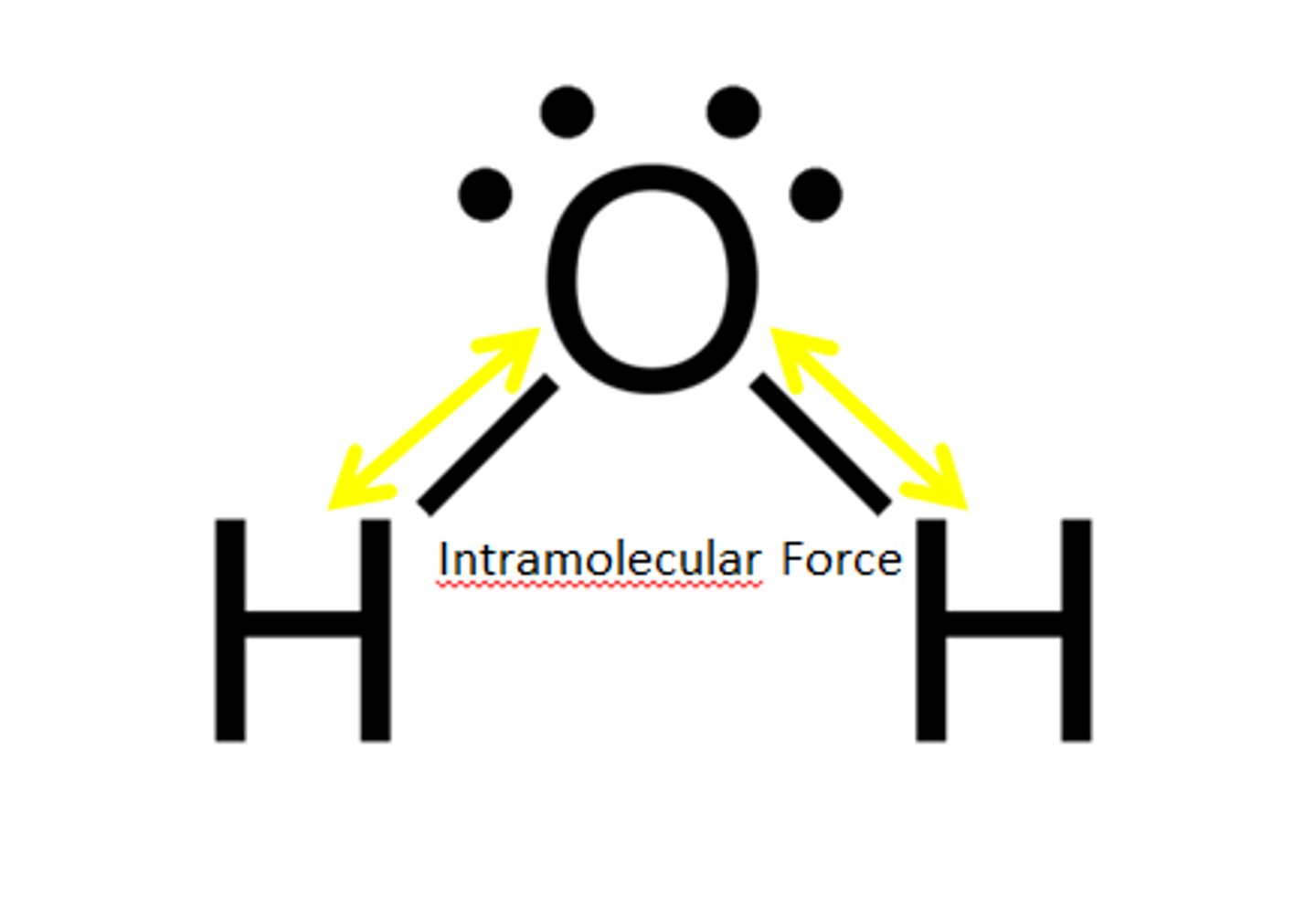
Intramolecular forces
forces that hold the atoms together in a molecule
Intermolecular forces
interactions between molecules (much weaker)
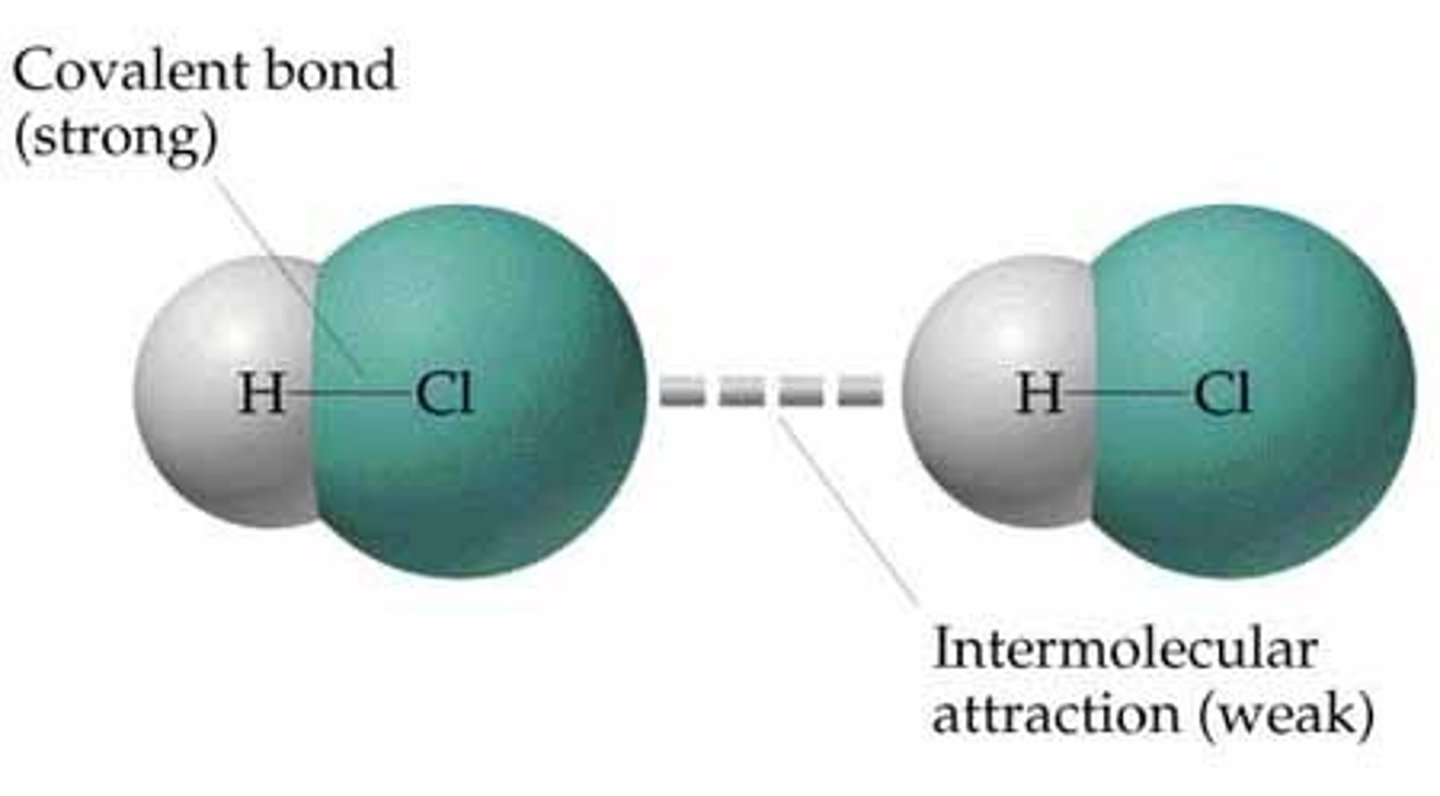
intermolecular force strength
measures by: boiling and melting point- the higher, the stronger the forces
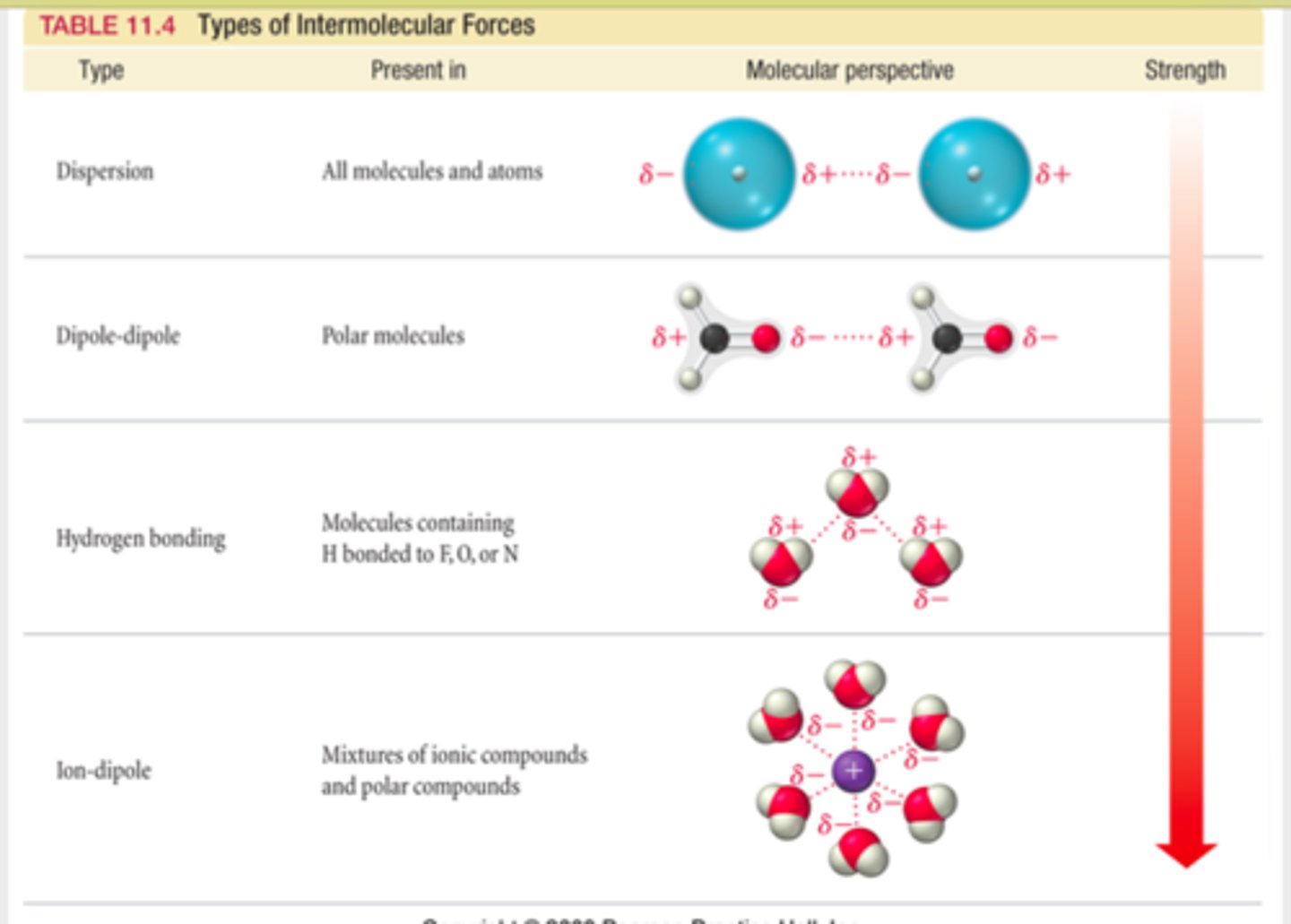
Types of intermolecular forces:
Dipole-dipole
Ion-dipole
Dipole-induced Dipole

Dipole-dipole forces
forces between polar molecules (partially charged)- opposite poles match up by electrostatic attraction
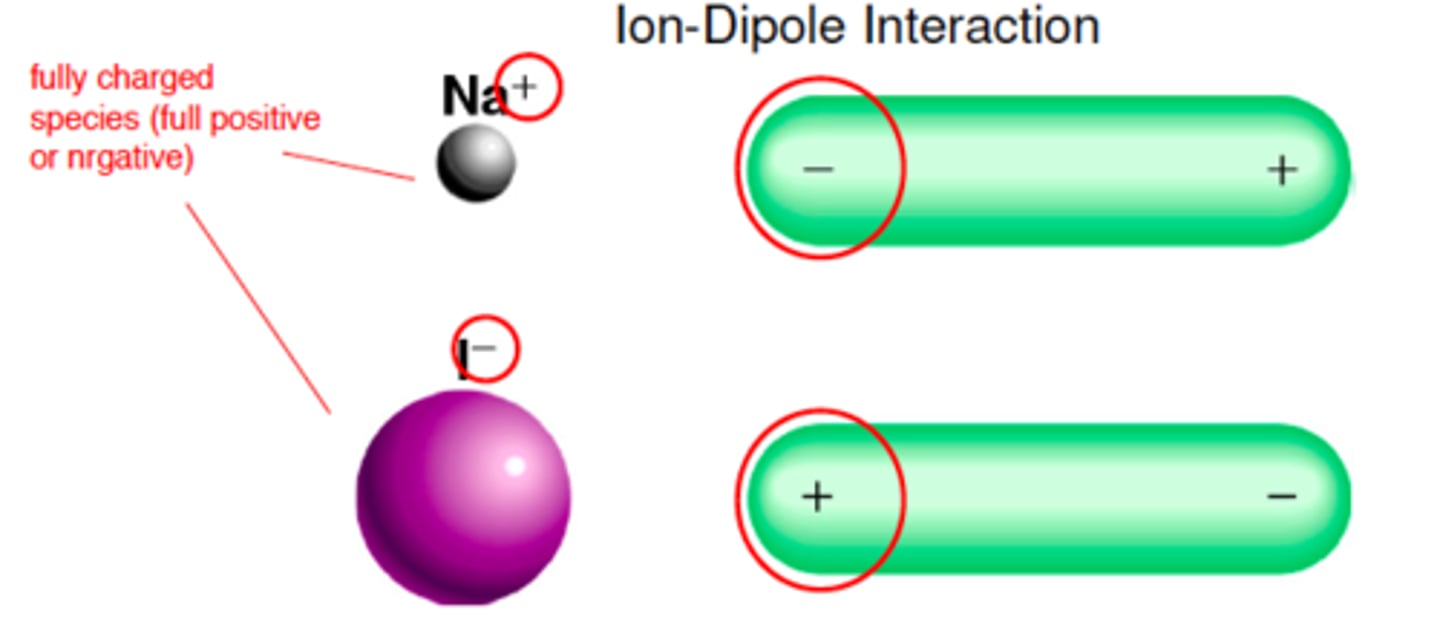
Ion-dipole forces
forces between a fully charged species (ion) and a dipole by electrostatic attraction.
Increase in strength with increase in charge or decrease in size of ion
(how ions are dissolved in water- attract to the H2O and pulled away by electrostatic charge)
Dipole-induced-dipole forces
forces arising from temporary dipoles induced in atoms by ions with a permanent dipole (either ion or dipole).
Temporary dipoles created when non-polar molecule interacts with polar- temporarily shifts the electrostatic charge to attract the polar molecule, then returns when removed

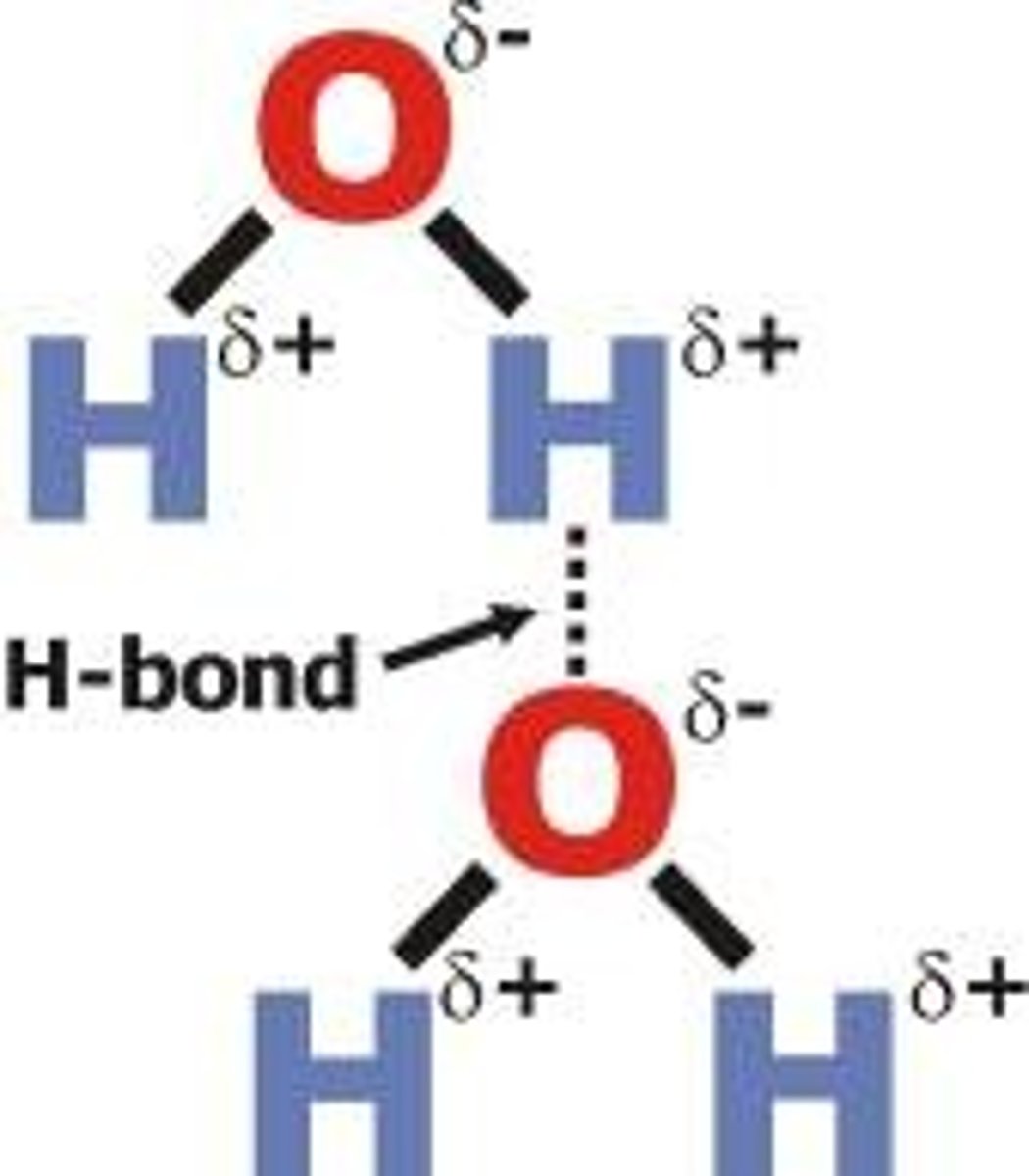
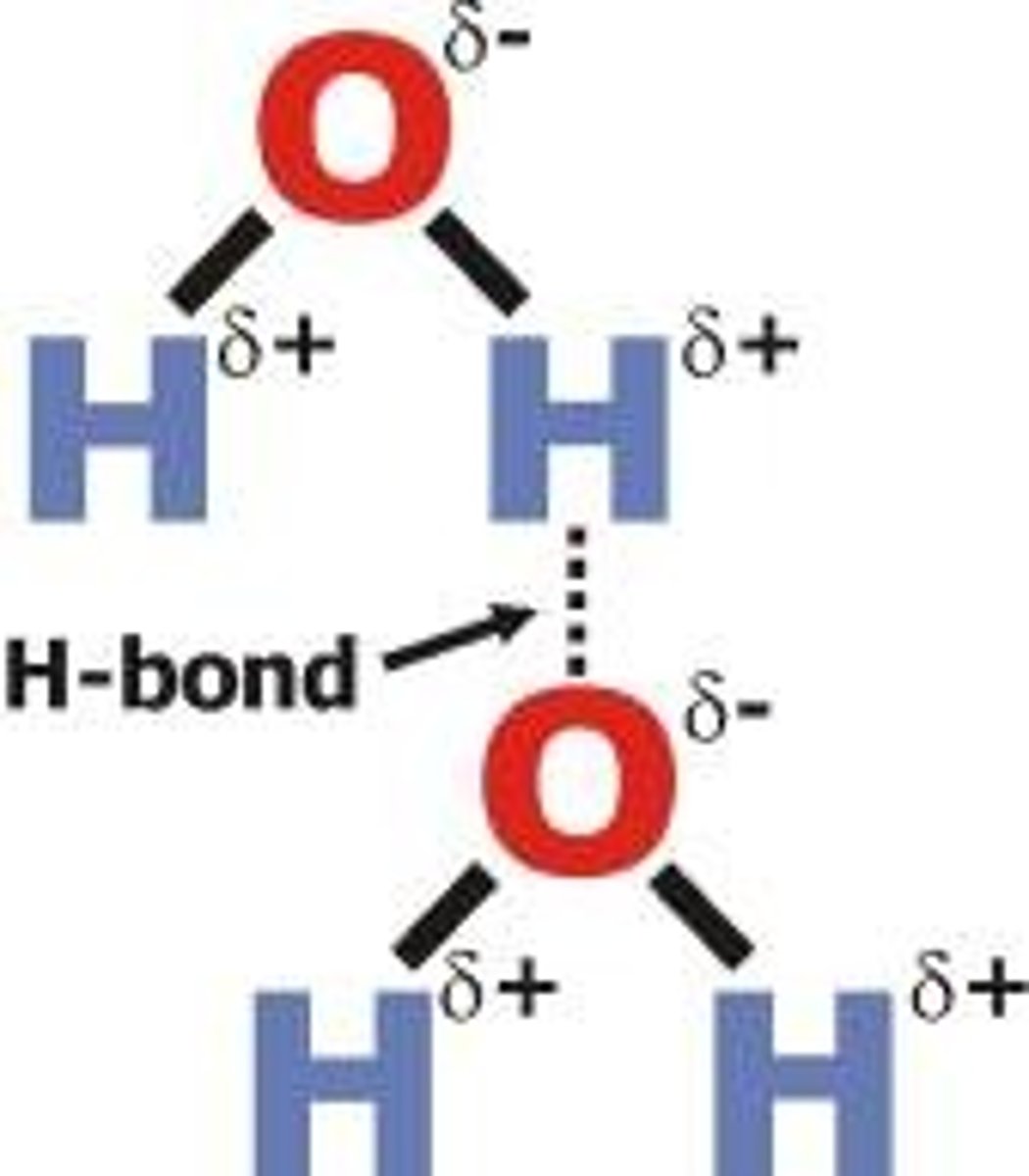
Hydrogen bonds
A special dipole-dipole interaction between a Hydrogen atom and either N, O, or F atom (smallest and most electronegative on PT)
- the lone pair on either N, O, F (in a molecule) is what causes the bond- strongest interaction with H
- reason why solid form of water floats on liquid form- H bonds- once frozen becomes less dense than liquid
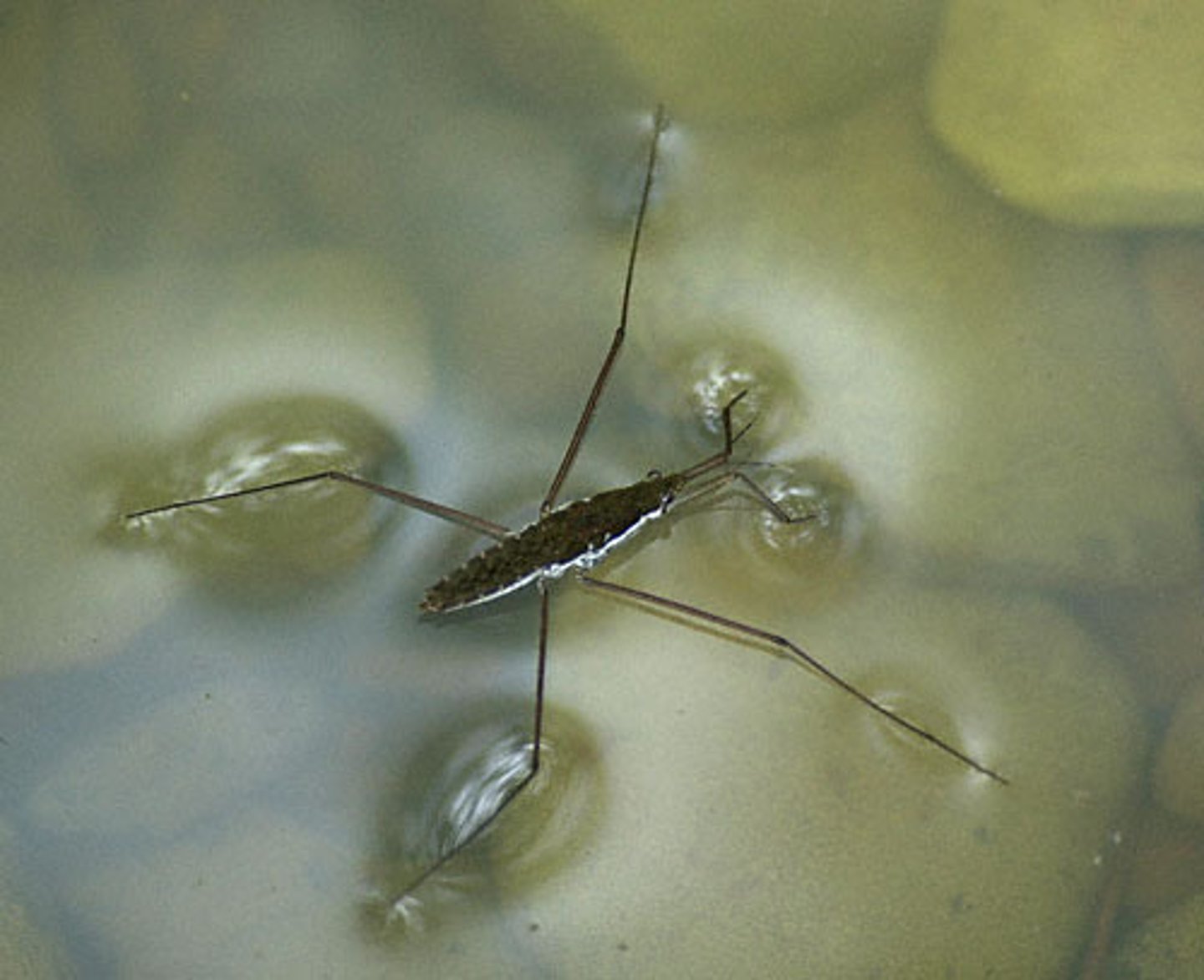
surface tension
Surface tension is the amount of energy required to stretch the surface area of a liquid by unit area
- strong intermolecular force = strong surface tension

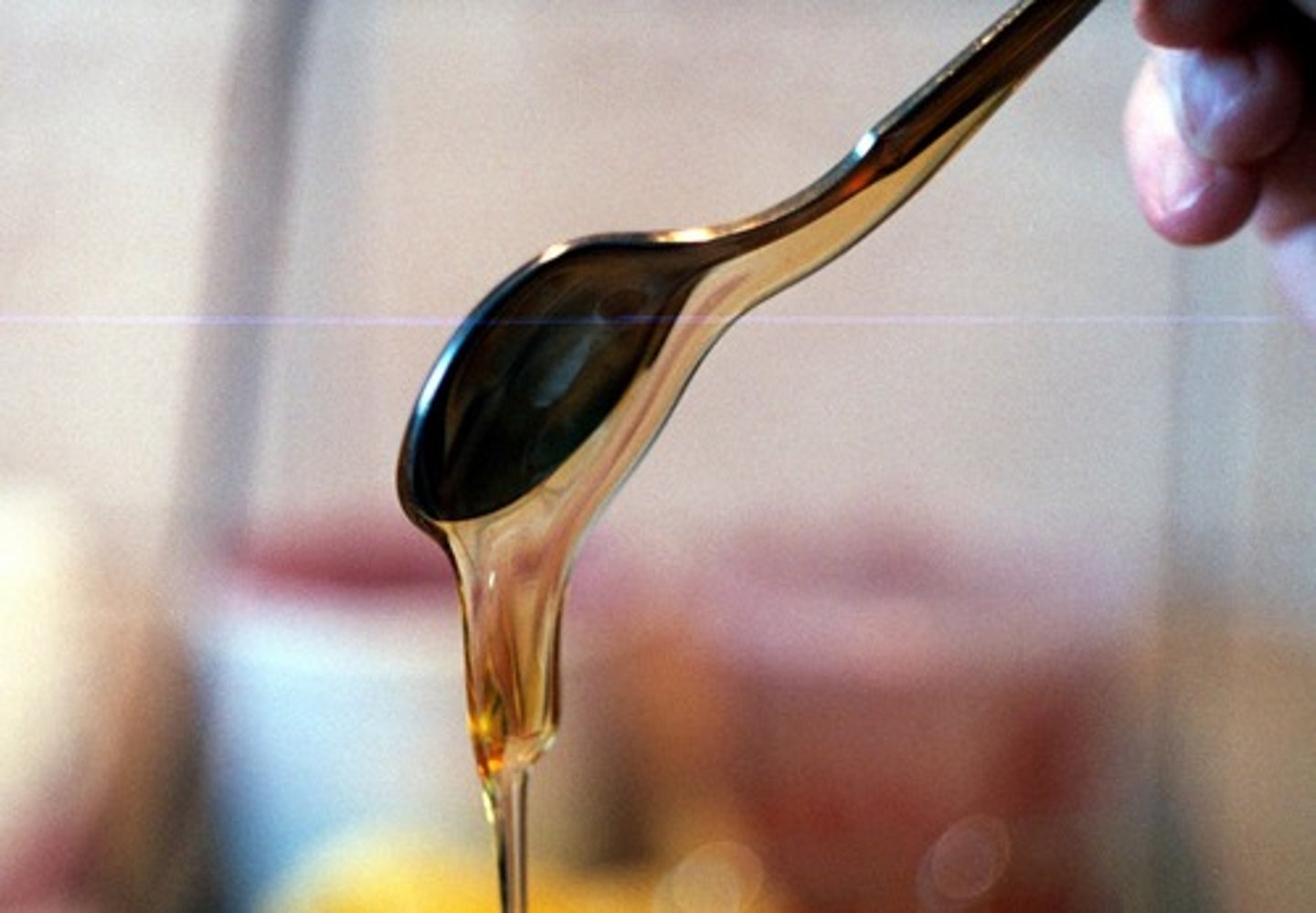
viscosity
Measure of fluids resistance to flow
- strong intermolecular force = high viscosity

solubility
- Polar compounds dissolve other polar compounds
- Non-polar compounds dissolve non-polar
- Polar compounds insoluble in non-polar

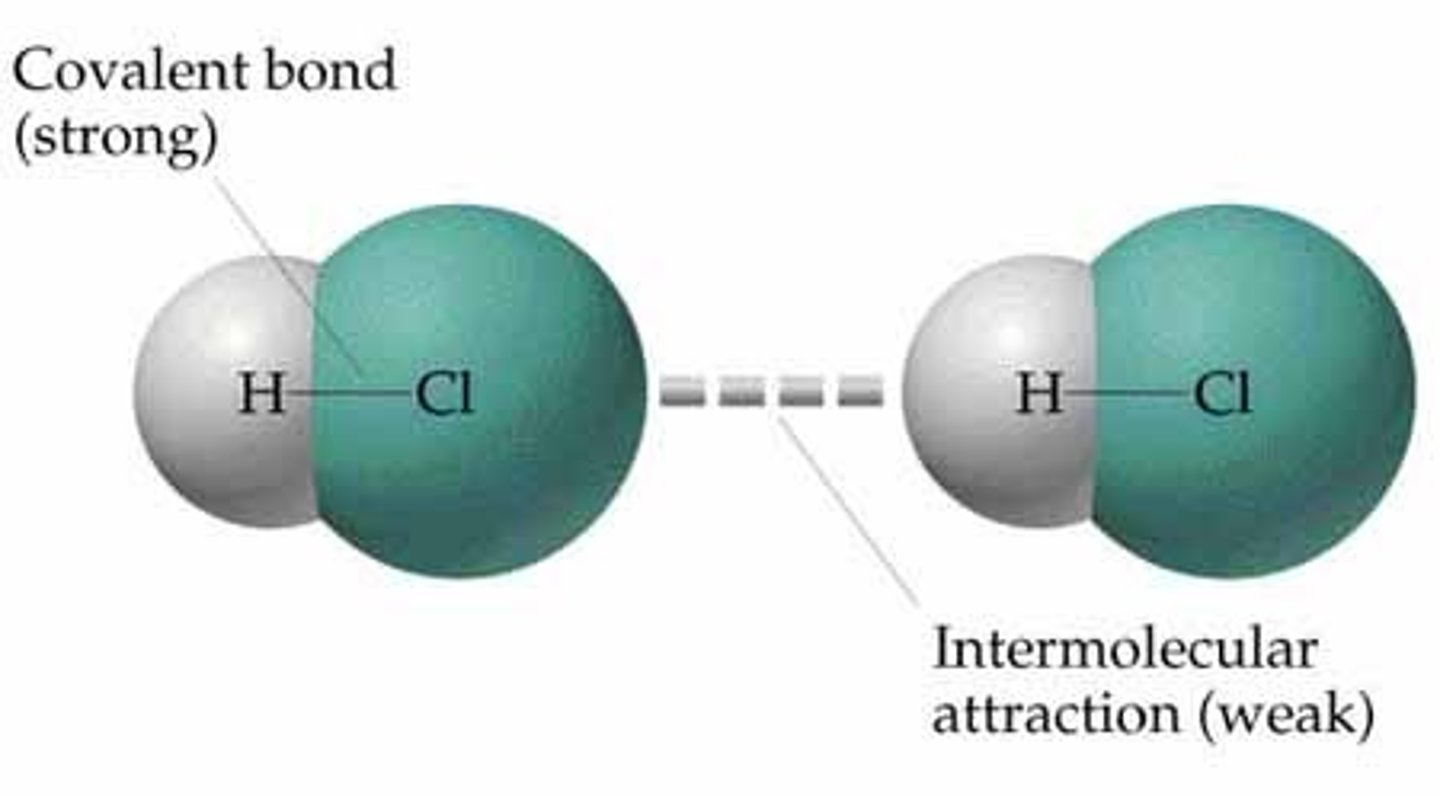
Intermolecular Force
Force between molecules
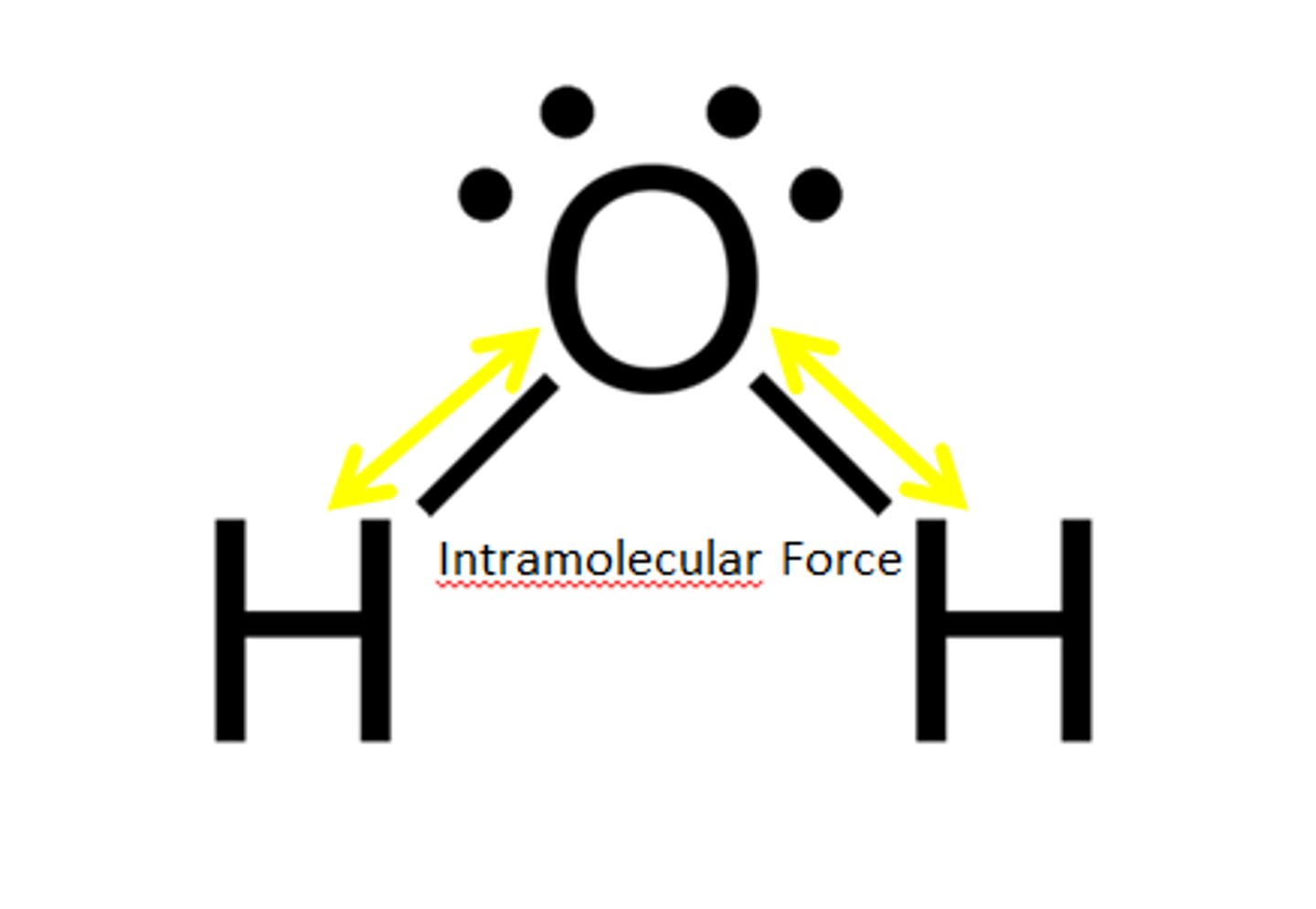
Intramolecular Force
Force within a molecule
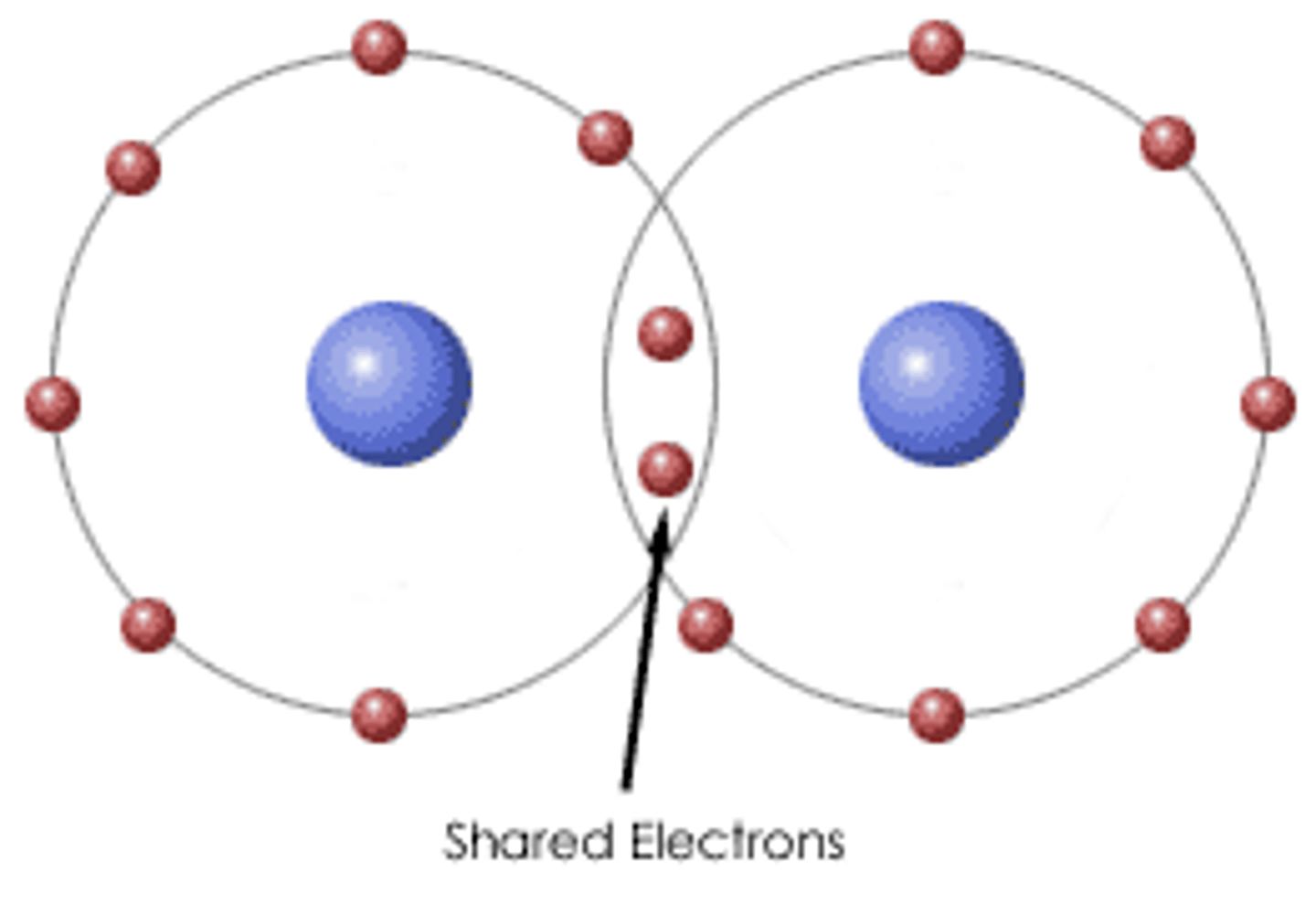
Covalent Bond
Force of attraction within a molecule created by the sharing of electrons
Ionic Bond
Force of attraction created by the transfer of electrons between atoms
Polar Molecule
A molecule in which the covalent bonds are asymmetrically arranged
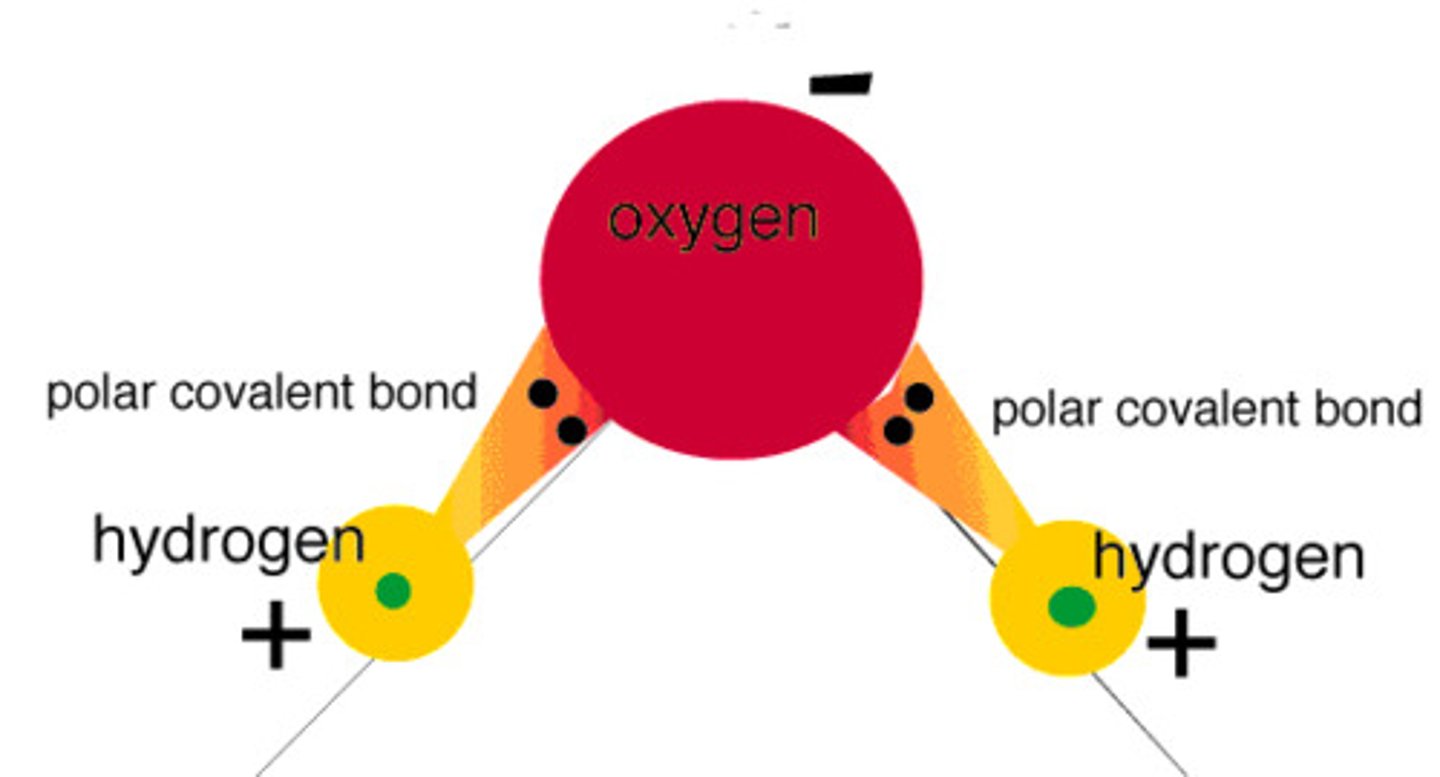
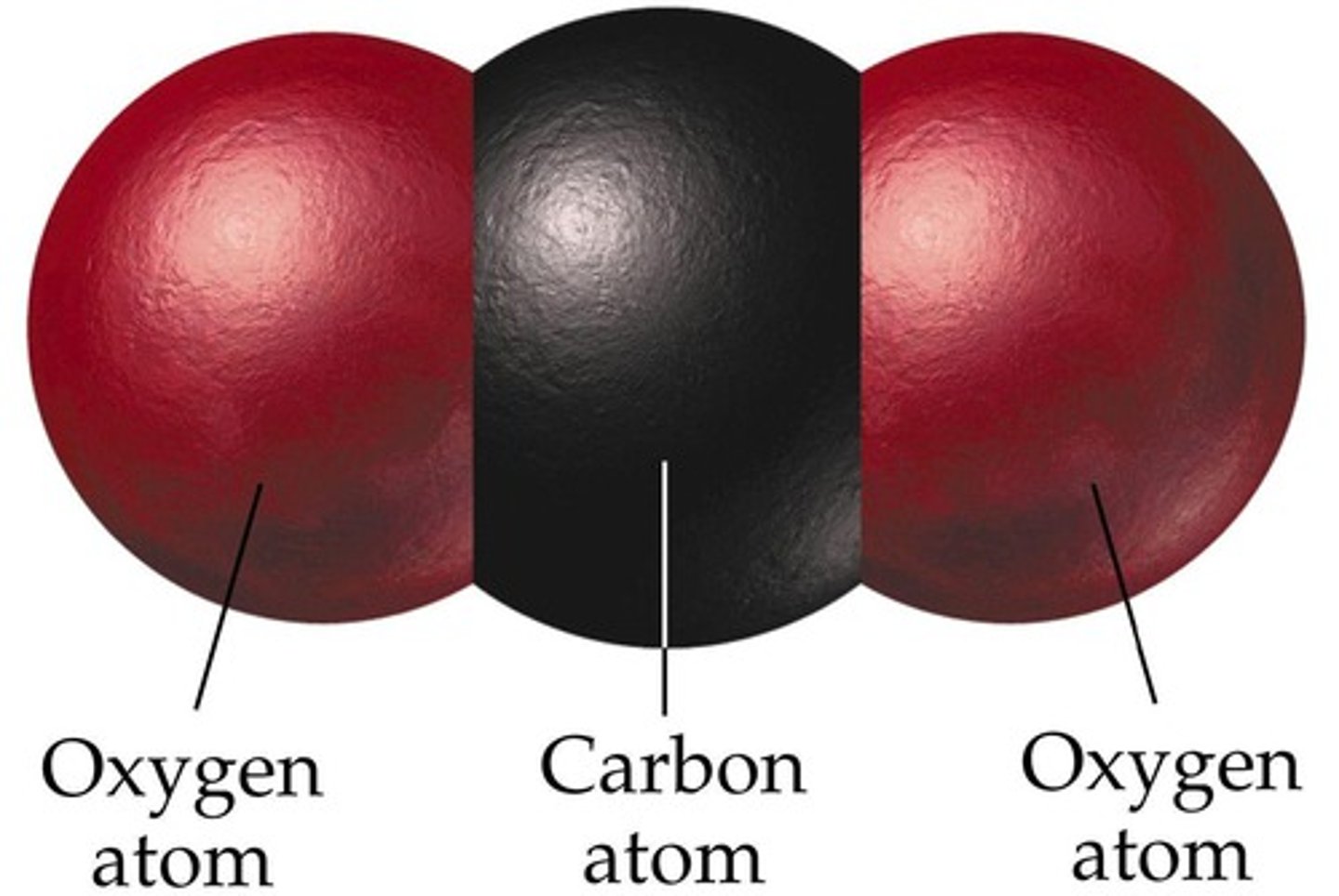
Nonpolar Molecule
A molecule in which the covalent bonds are symmetrically arranged
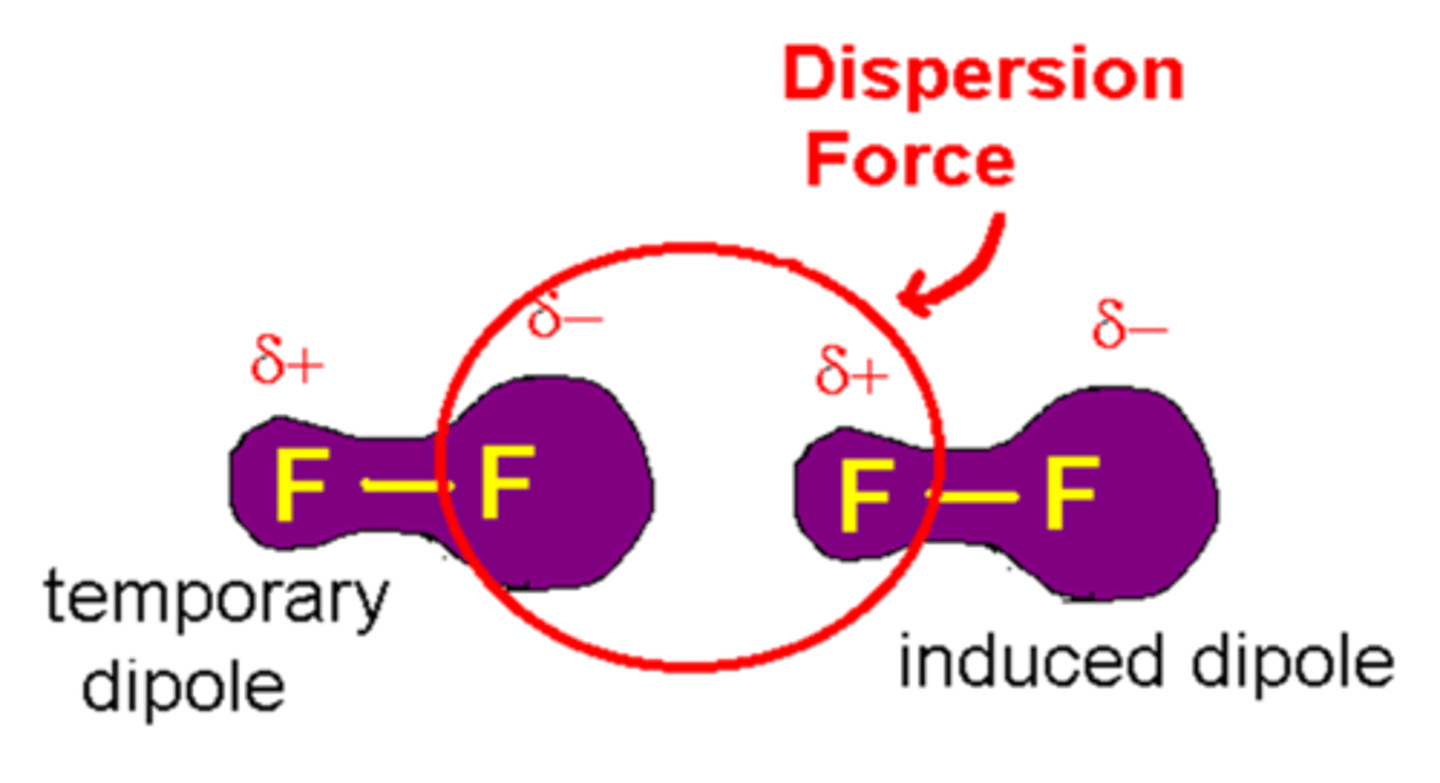
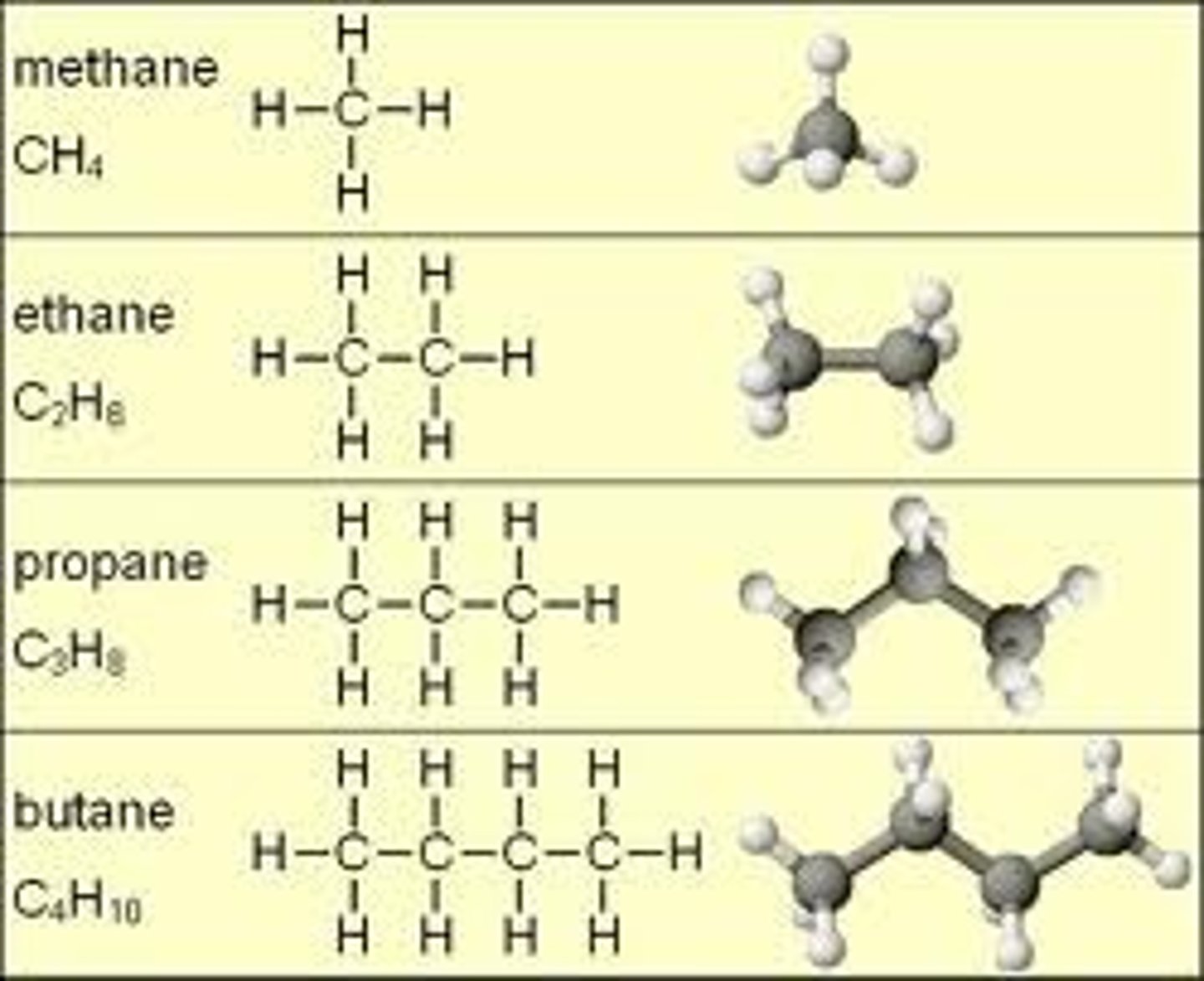
London Dispersion Force
Intermolecular force between nonpolar molecules
Heavier molecule = stronger force
Longer Chain molecule = more polarizable
Dipole-Dipole Force
Intermolecular force between polar molecules
Heavier Molecules = More Polarizable=Stronger Forces
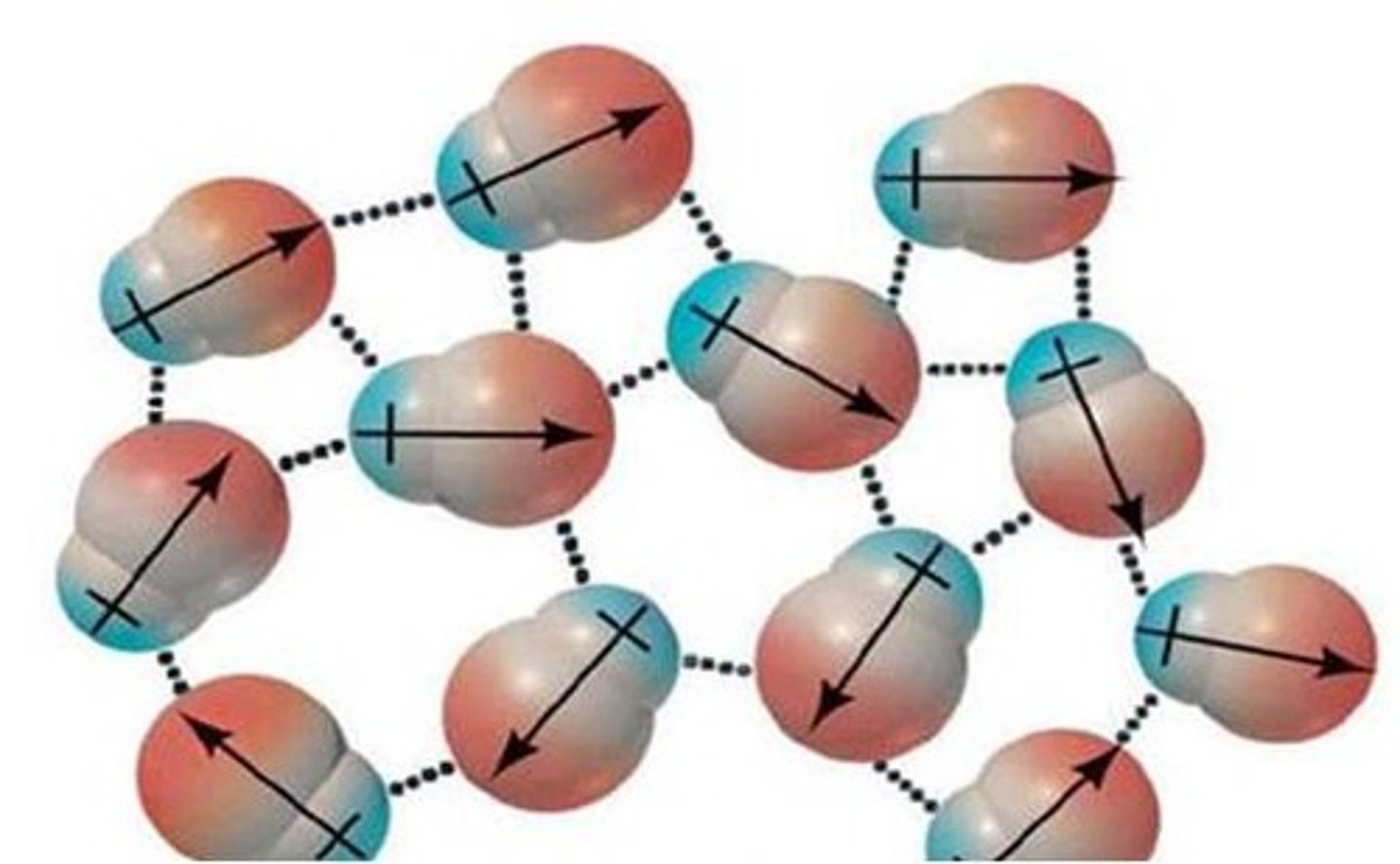
Hydrogen Bond
Intermolecular force between molecules containing hydrogen bonded to N, O, or F
More H-O, H-N, H-F connections= Stronger Force
Surface Tension
The force exerted along the surface of a fluid that causes it to "bead up" and form into drops

Vapor Pressure
Pressure exerted on the surface of a liquid by the vapor
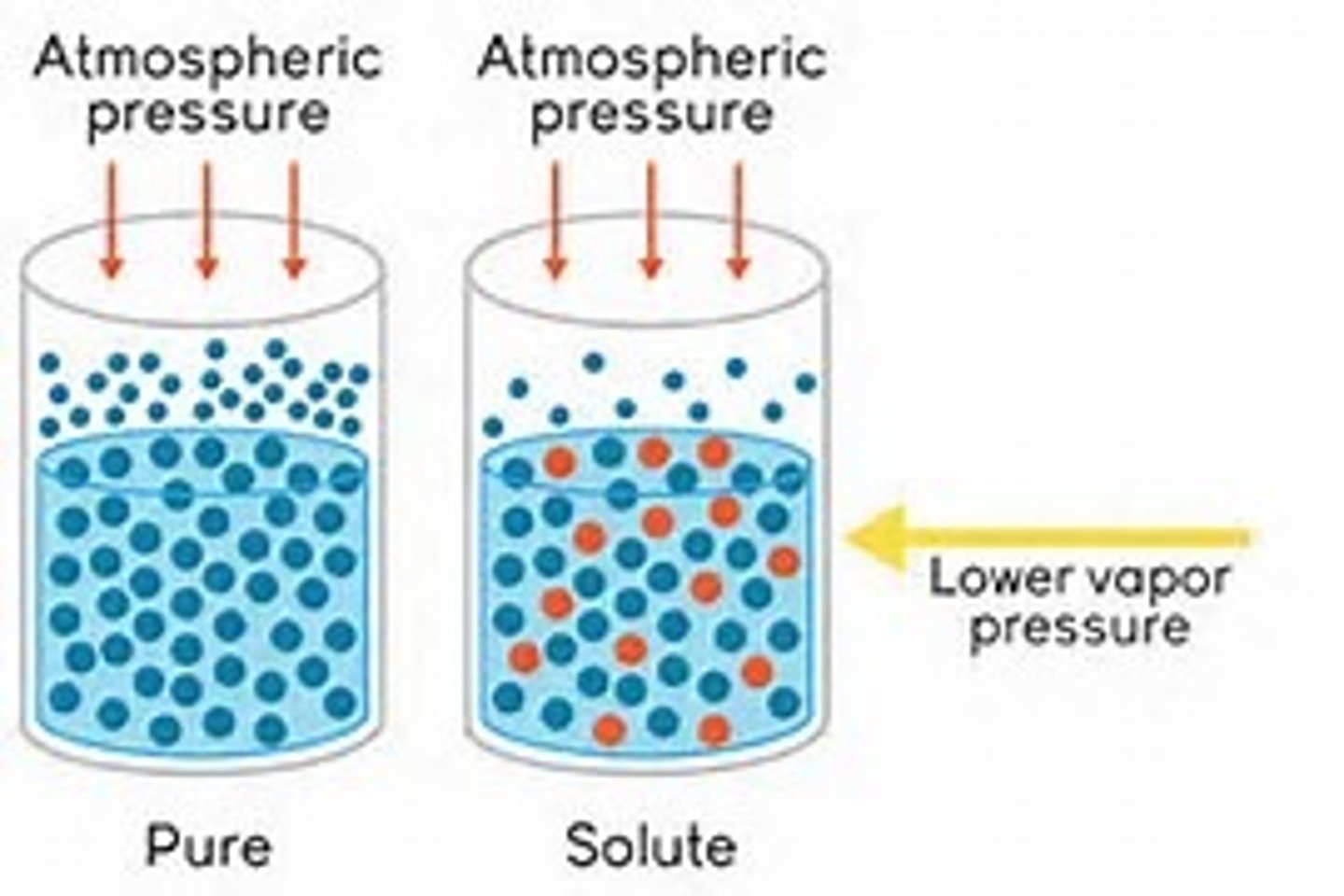
Boiling point
Temperature at which the vapor pressure is equal to the atmospheric pressure

Water
Substance exhibiting hydrogen bonding

hydrocarbons
Substance exhibiting London dispersion forces
sp hybridization
a type of bonding where the 2s orbital mixes with only one of the three p-orbitals resulting in two sp orbitals and two remaining unchanged p orbitals

sp2 hybridization
1. Trigonal planar structure
2. sp2 hybridization creates 3 identical orbitals of intermediate energy and length and leaves one unhybridized p orbital
3. 3 effective pairs of electrons surround the carbon (double bond treated
as one effective pair)

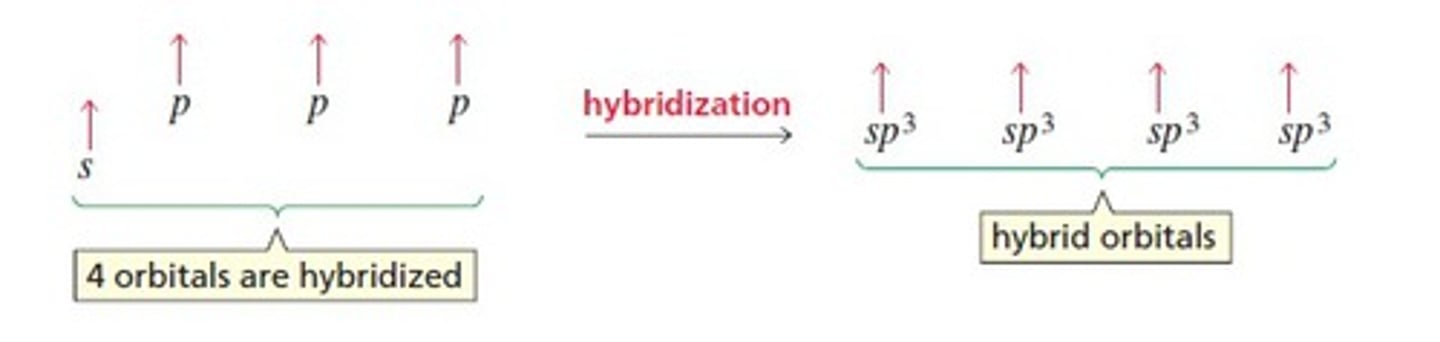
sp3 hybridization
the formation of a hybrid orbital from one 2s and three 2p orbitals
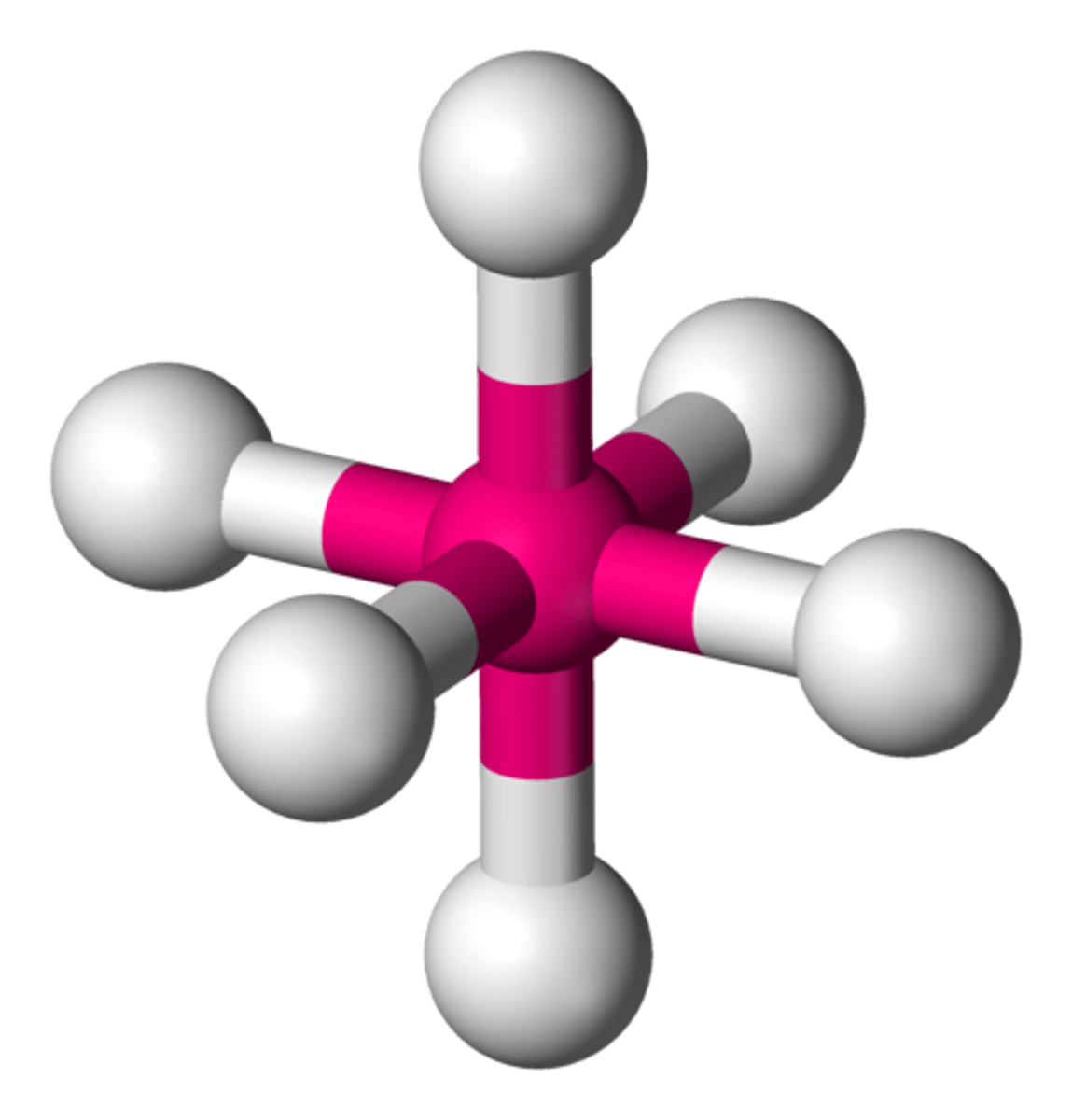
sp3d hybrid orbitals
five equivalent hybrid orbitals with lobes pointing toward the vertices of a trigonal bipyramid that form by mixing one s orbital, three p orbitals, and one d orbital from the same shell
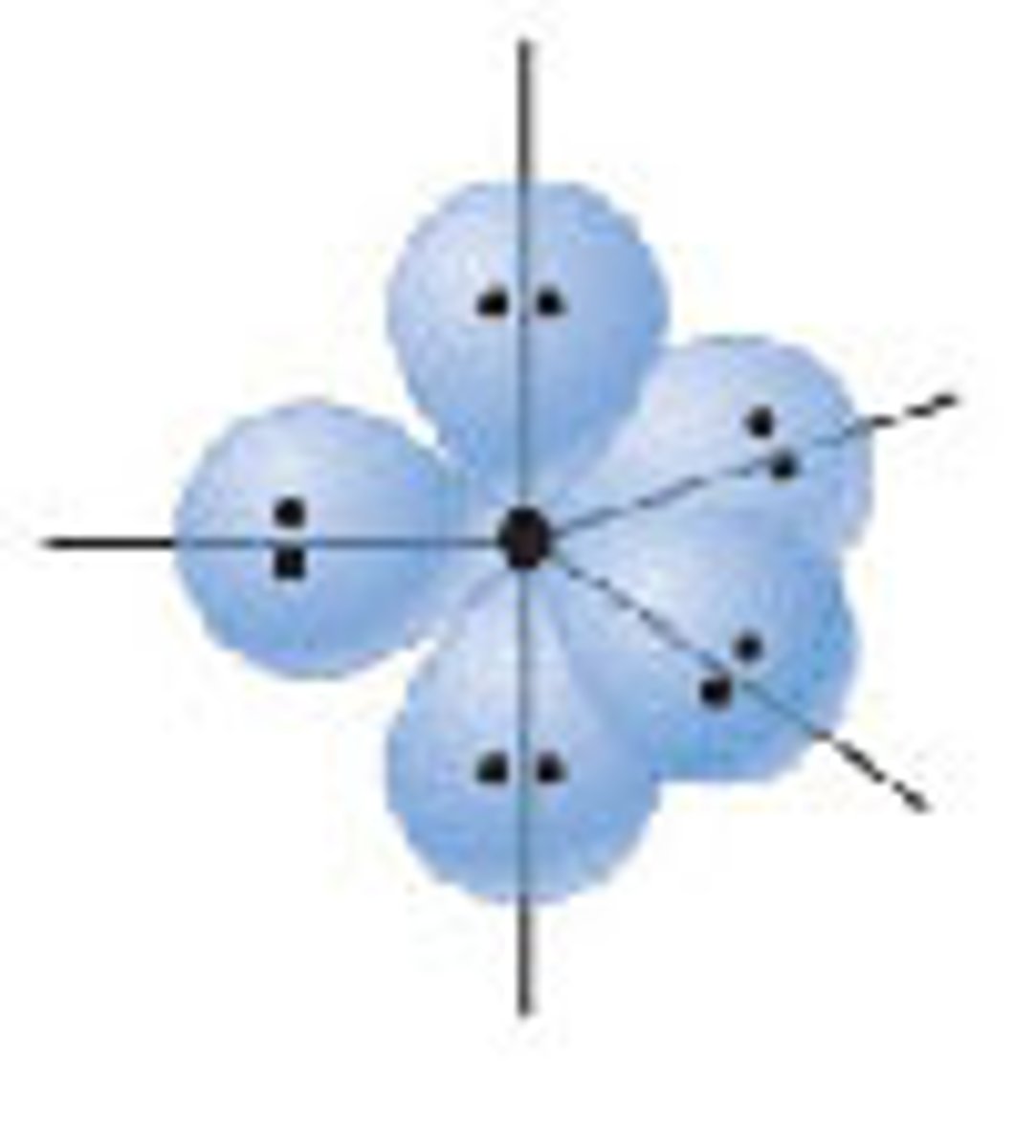
d2sp3 hybridization
six hybrid orbitals arranged in a octahedral shape around the central atom involving one 2, three p and two d orbital
Valence Bond Theory
a model of chemical bonding in which an electron-pair bond is formed between two atoms by the overlap of orbitals on the two atoms
molecular orbital theory
a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule.
sigma bond
a single covalent bond that is formed when an electron pair is shared by the direct overlap of bonding orbitals
pi bond
a bond that is formed when parallel orbitals overlap to share electrons
found in double and triple bonds only
delocalized electrons
electrons that are free to move
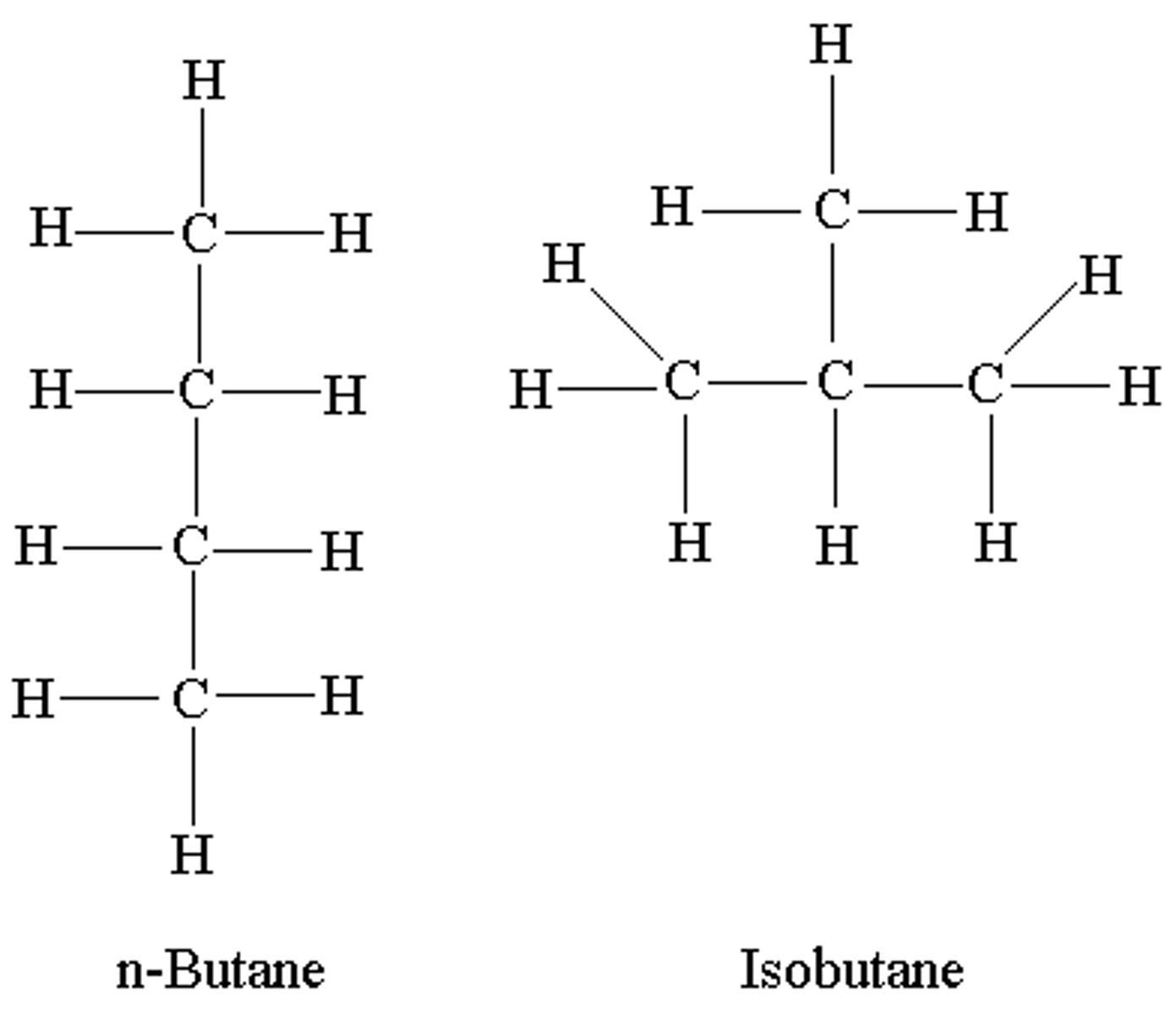
Isomers
Compounds with the same formula (mass)but different structures.
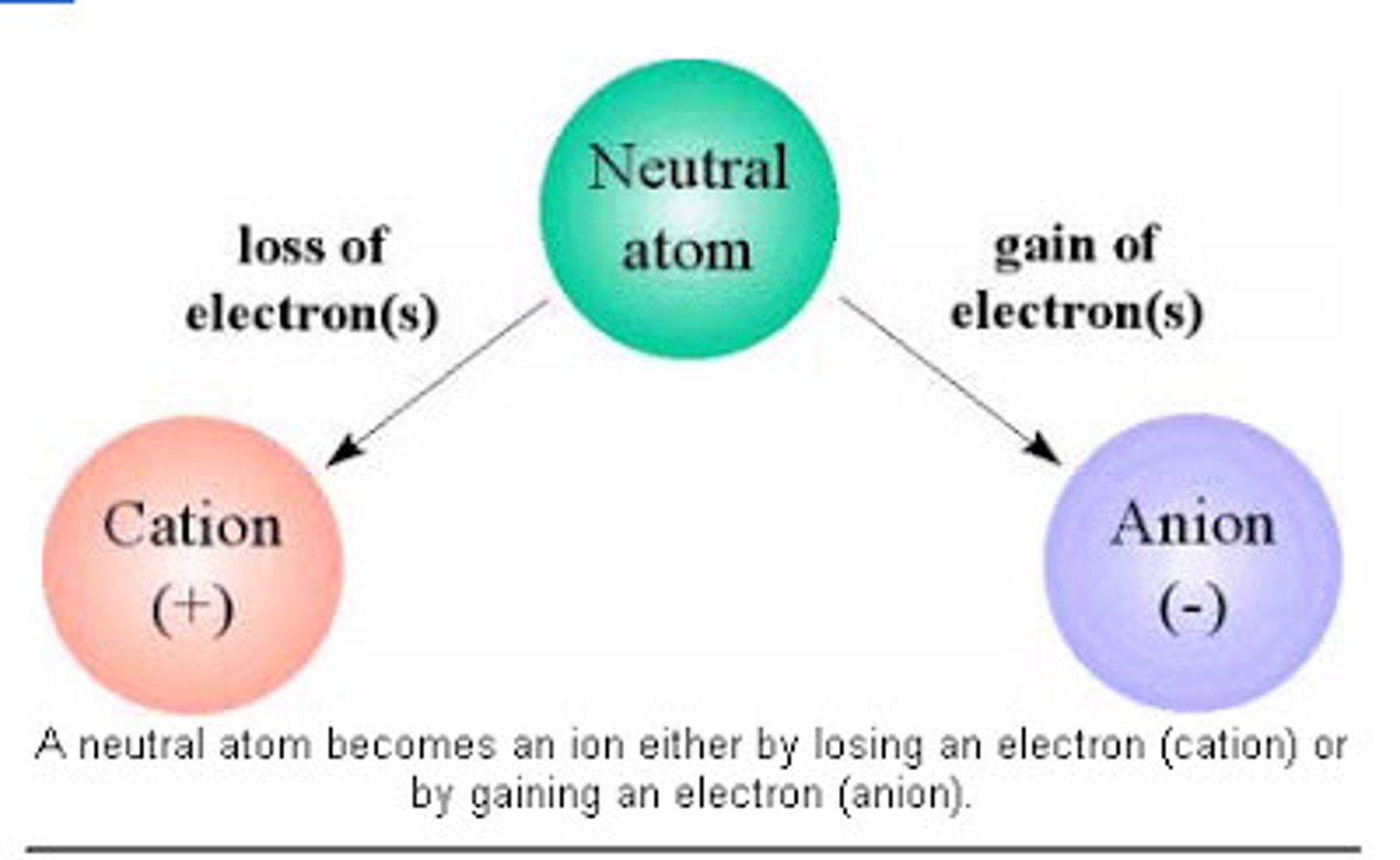
Cation
A positively charged ion
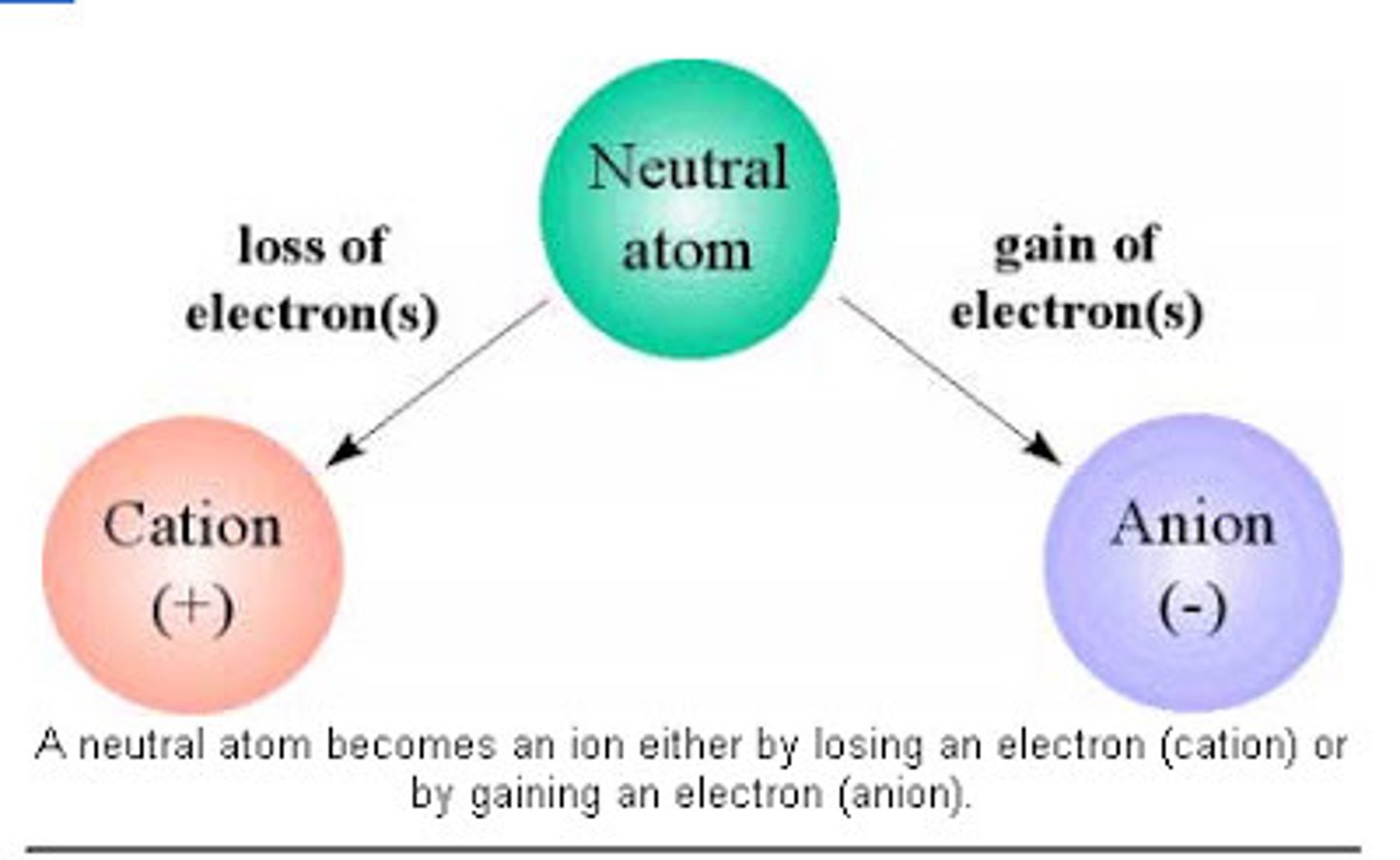
Anion
A negatively charged ion
Coulomb's Law
electric force between charged objects depends on the distance between the objects and the magnitude of the charges.
ion-dipole interactions
occurs between ion (from an ionic compound) and a molecule from a polar covalent substance.
Can a London Force form between HI and HBr?
No, because they form dipole-dipole forces.