Radiology Lecture 3: Abdominal Radiology, Gastrointestinal Tract
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
variable, storage organ
Normal Roentegen Signs Stomach: Size
"J" or "U" shaped
Normal Roentegen Signs Stomach: Shape
soft tissue and gas
Normal Roentegen Signs Stomach: Opacity
caudal to liver, cranial to spleen
Normal Roentegen Signs Stomach: Location
smooth serosal margins, smooth rugal fold margins
Normal Roentegen Signs Stomach: Margination
cats
Do dogs or cats tend to have fat in the sub-mucosa of the stomach?
cat
Does the dog or cat stomach sit mostly to the right of the midline?
dog
Does the dog or the cat stomach sit more centered on midline?
gas - fundus
fluid - body and pylorus/antrum
Where does the gas and fluid accumulate on a DV?
gas - body and pyloric antrum
fluid - fundus
Where does the gas and fluid accumulate on a VD?
gas - pylorus
fluid - fundus
Where does the gas and fluid accumulate on a left lateral?
gas - body and fundus
fluid - pylorus
Where does the gas and fluid accumulate on a right lateral?
barium, iodinated contrasts
What are some options for positive contrast?
room air, nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide
What are some options for negative contrast?
both barium and air used
mucosa
What does "double contrast" mean? And what are you most likely assessing?
-identify the location of the stomach
-investigation of a cranial abdominal mass of unknown origin
-evaluate mucosal margins
-identify filling defects (intraluminal, mural, extraluminal)
-to assess gastric emptying
What are some indications for positive gastrography?
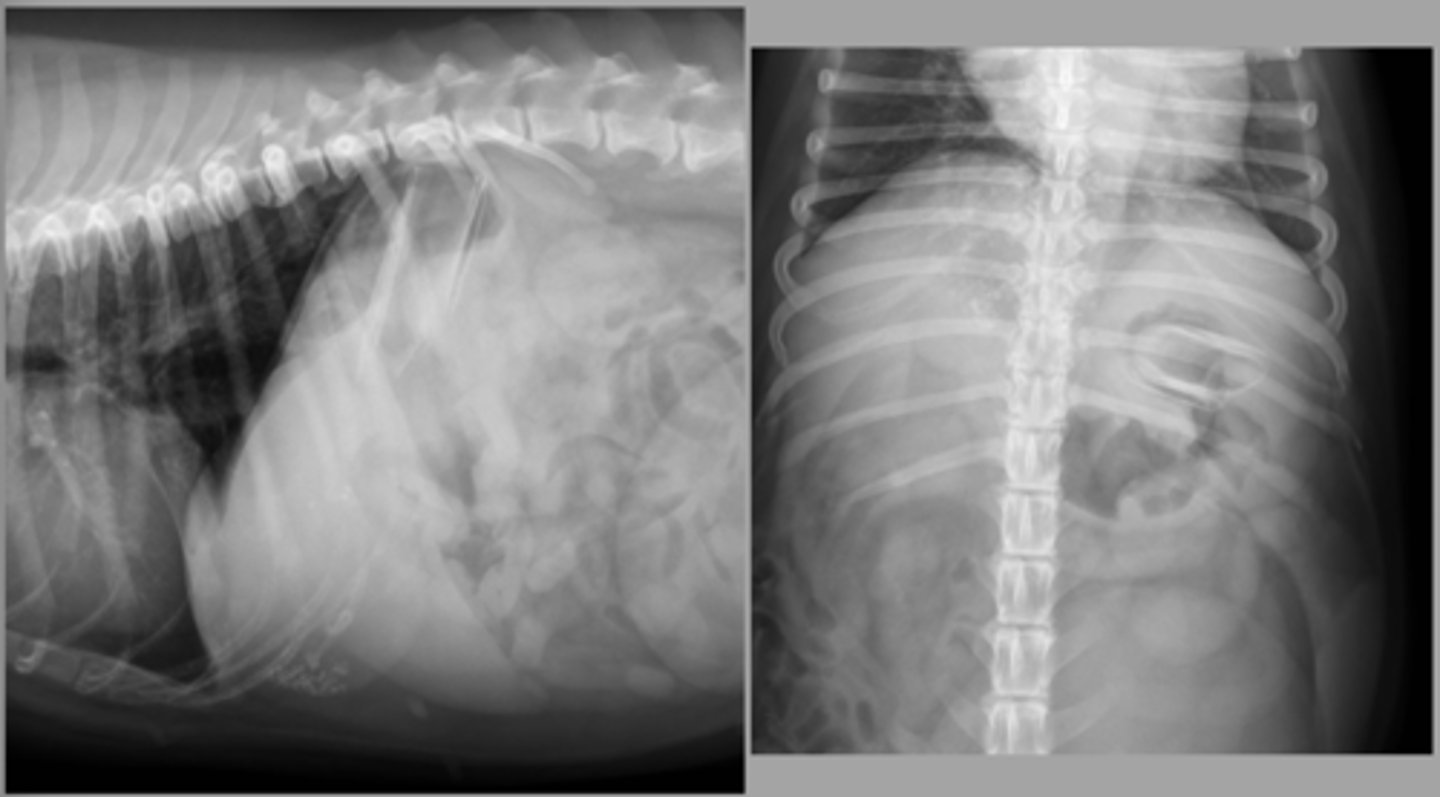
abdominal wall hernia with passage of the stomach
What abnormality is seen here?
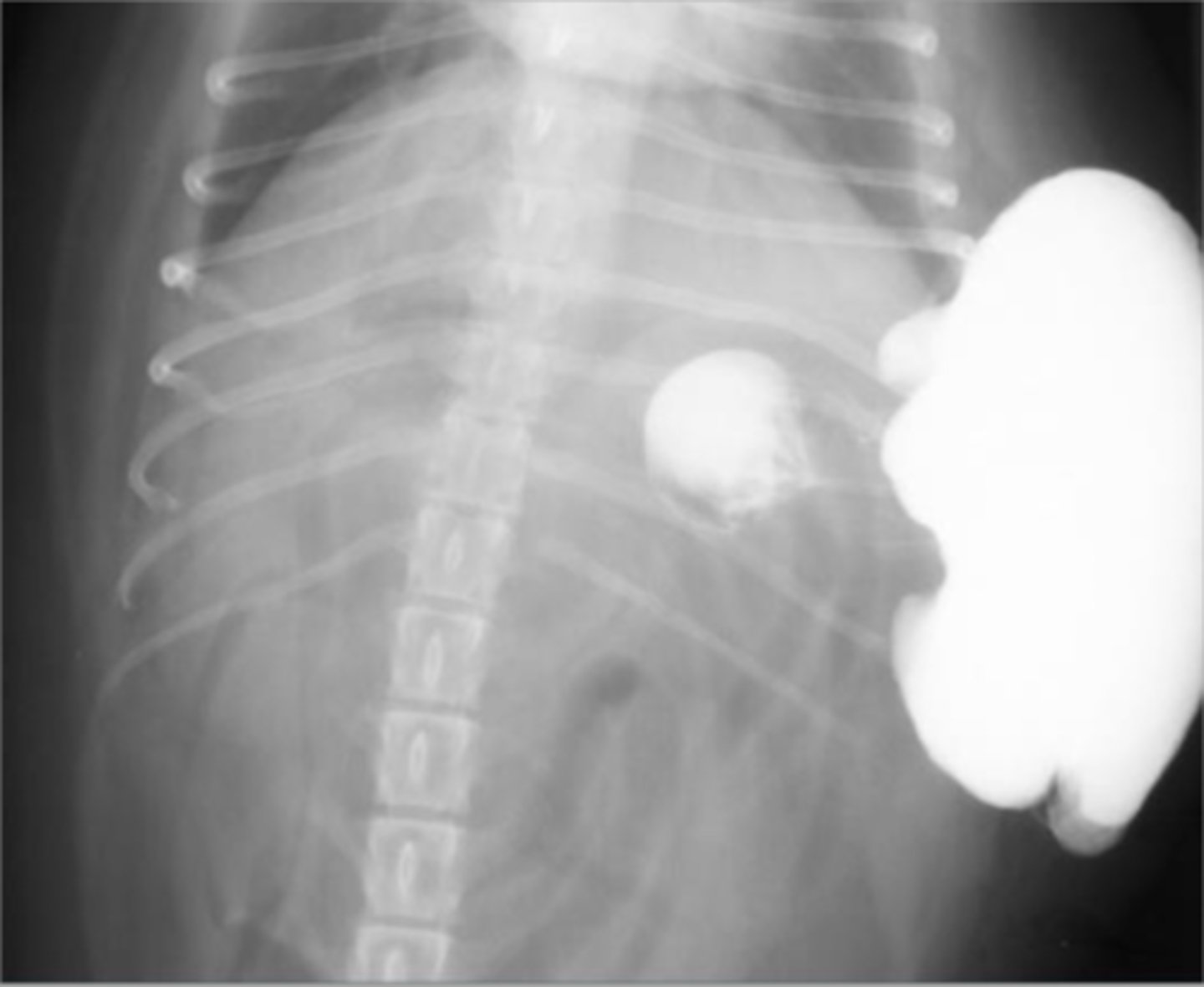
hepatic mass
What abnormality is seen here?
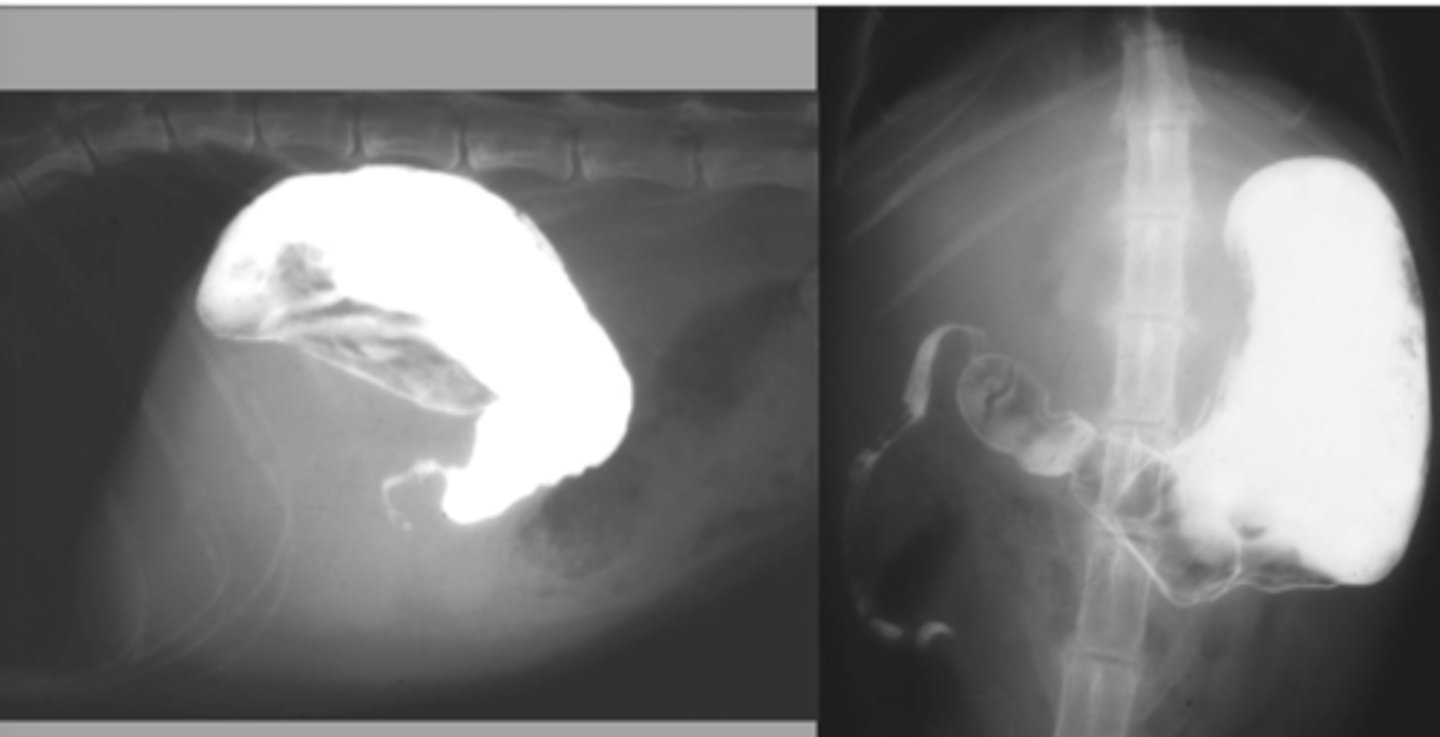
-identify the location of the stomach
-assessment of radiolucent FB and intraluminal masses
-little information about the wall and mucosa
What are some indications for negative gastrography?
-identify the location of the stomach
-assessment of radiolucent FB and intraluminal masses
-assessment of the wall thickness and evaluation of the mucosa
What are some indications for double contrast gastrography?
four
How many views are recommended to assess a GDV?
right lateral
If you can only get one view to assess a GDV what should you get first?
-180 degrees is most common
-gas filled stomach
-abnormal location of stomach: pylorus is dorsal and to the left
-compartmentalization: soft tissue bands cross the stomach
-possibly gas in gastric wall (poor prognosis)
What are some common radiographic findings of GDV?
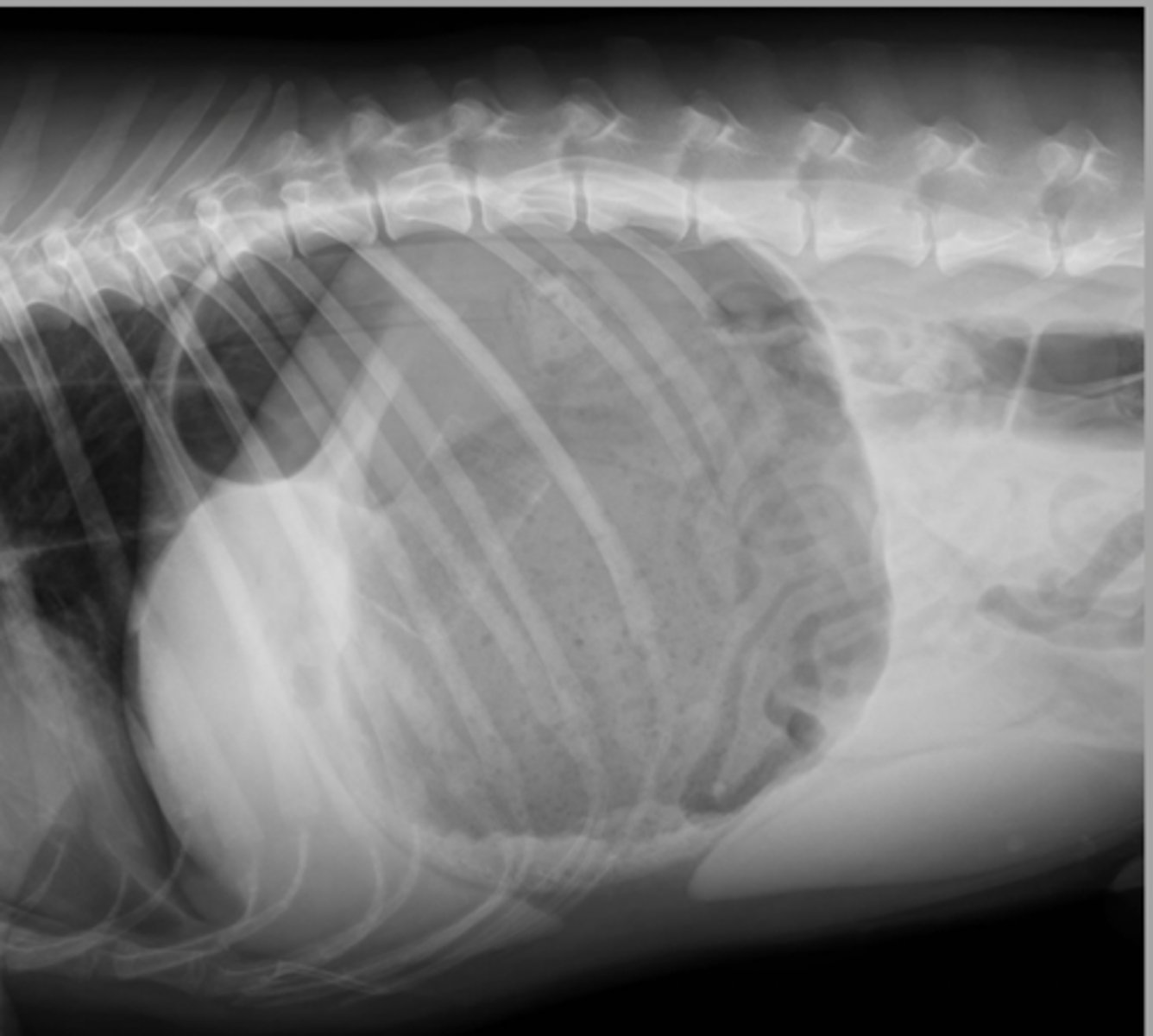
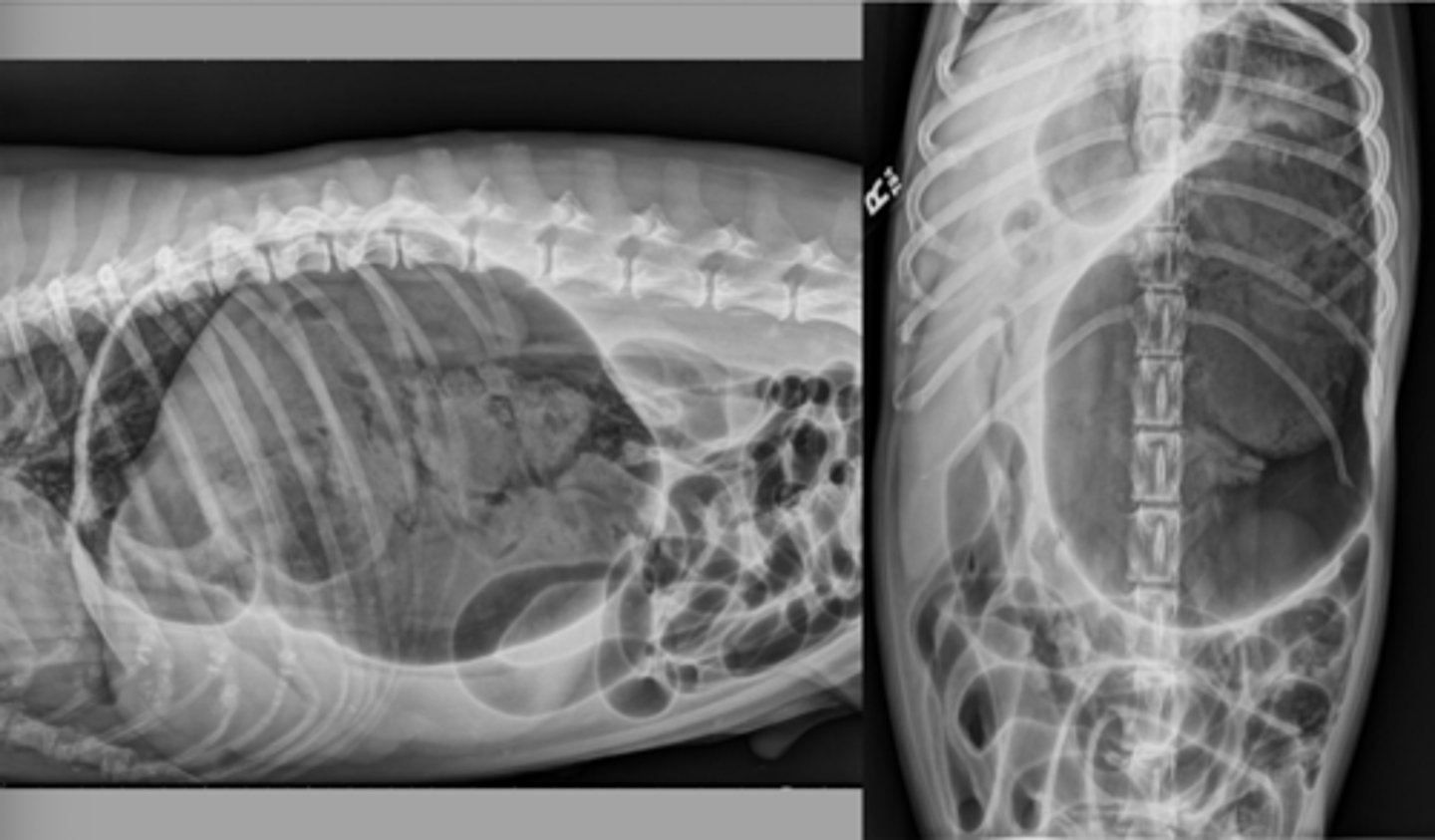
GDV (180 degrees)
What abnormality is shown here?
-splenomegaly
-splenic malposition or torsion
-hypovolemia: small CVC, microcardia, small pulmonary vessels
-esophageal dilation
-aspiration pneumonia
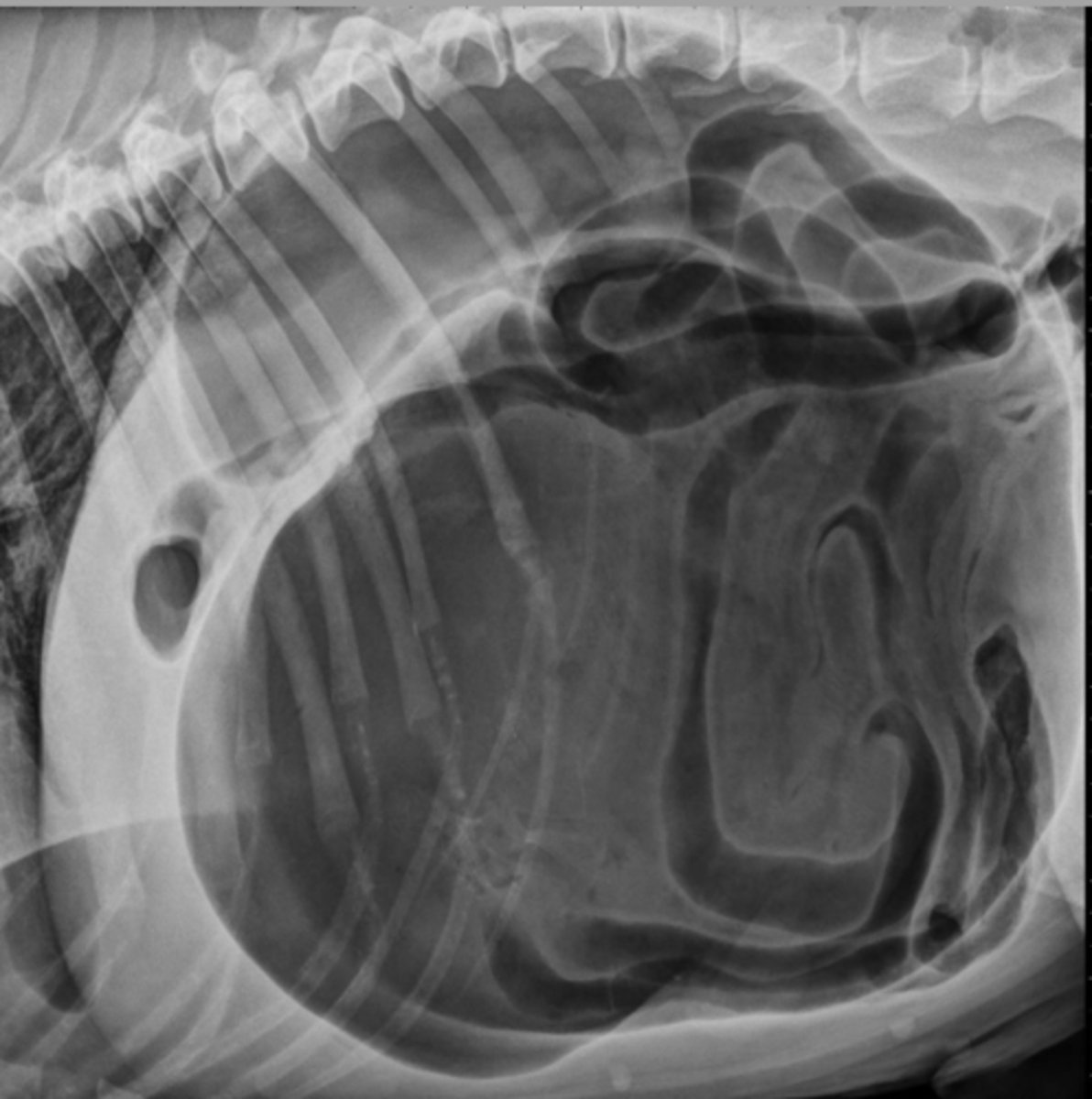
What are some secondary findings with GDV?
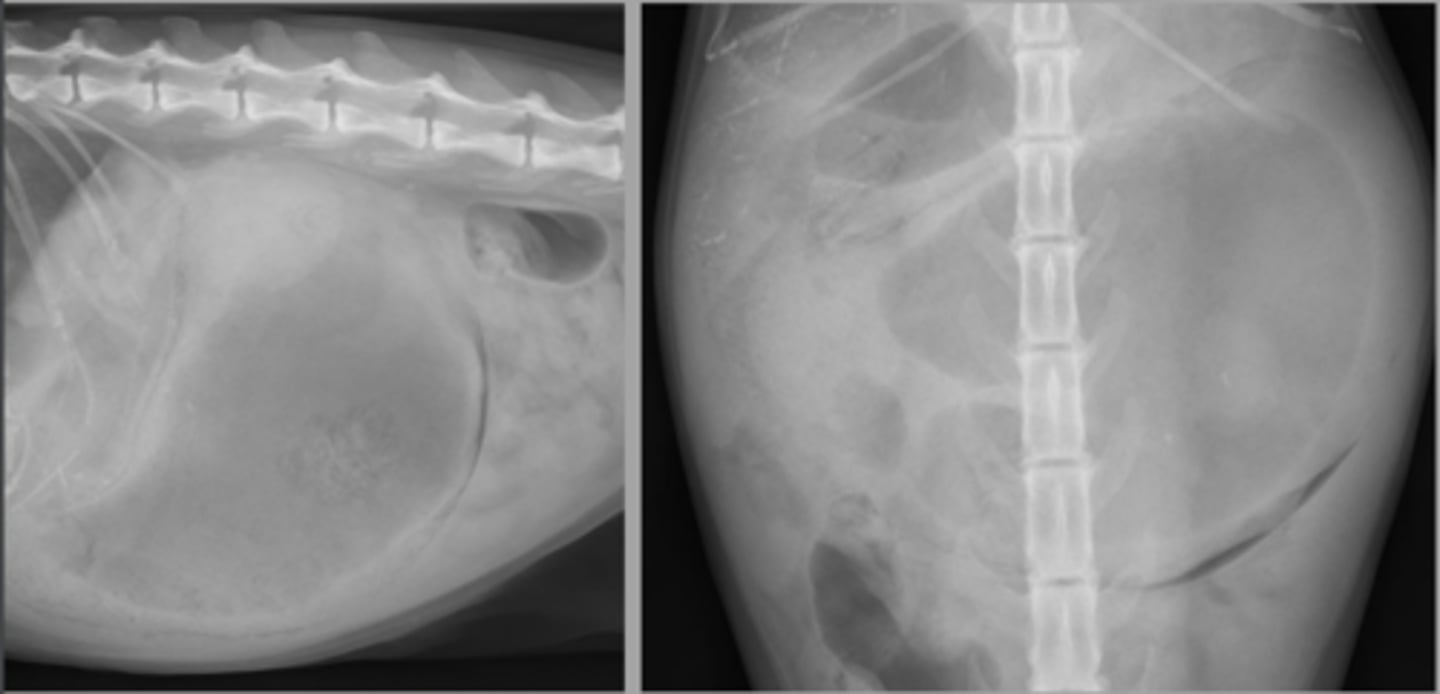
gastric penumatosis
What abnormality is shown here? (secondary to GDV)
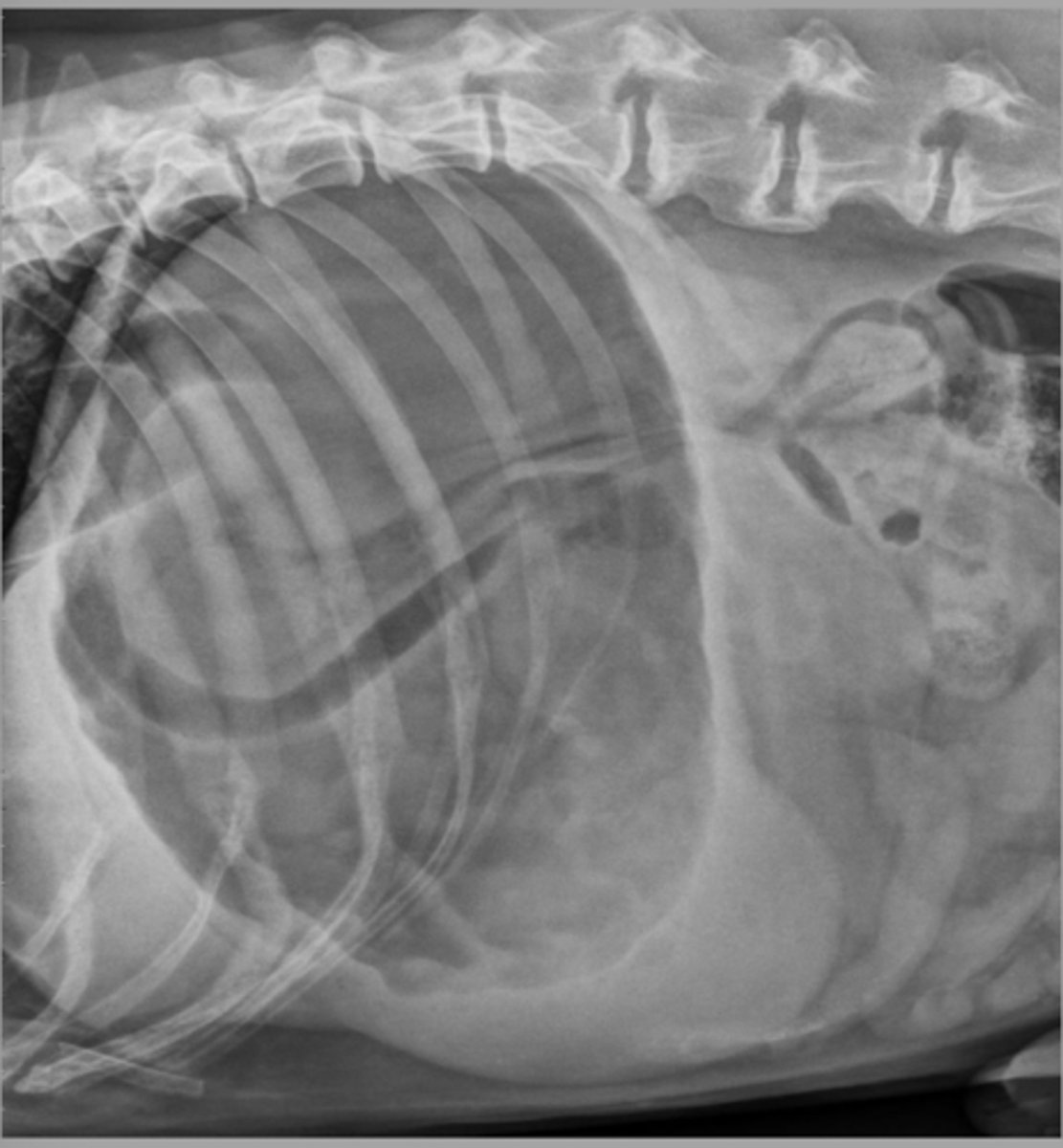
GDV (270 degrees)
What abnormality is shown here?
severe distension
What abnormality is shown here?
severe distension with volvulus
What abnormality is shown here?
gastric dilation without volvulus
What abnormality is shown here?
food bloat
What abnormality is shown here?
12-24 hours
How long should you fast and then wait to retake radiographs for a gastric foreign body?
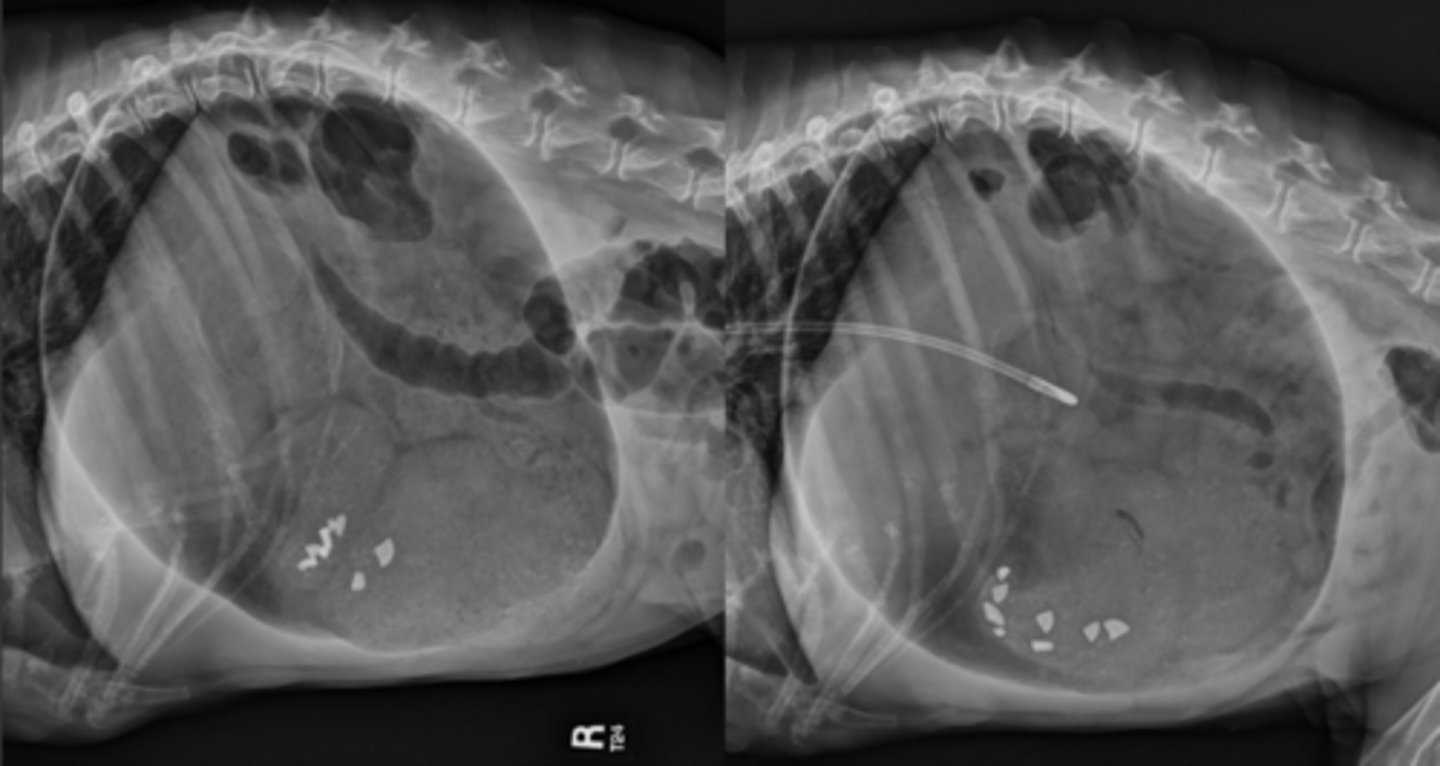
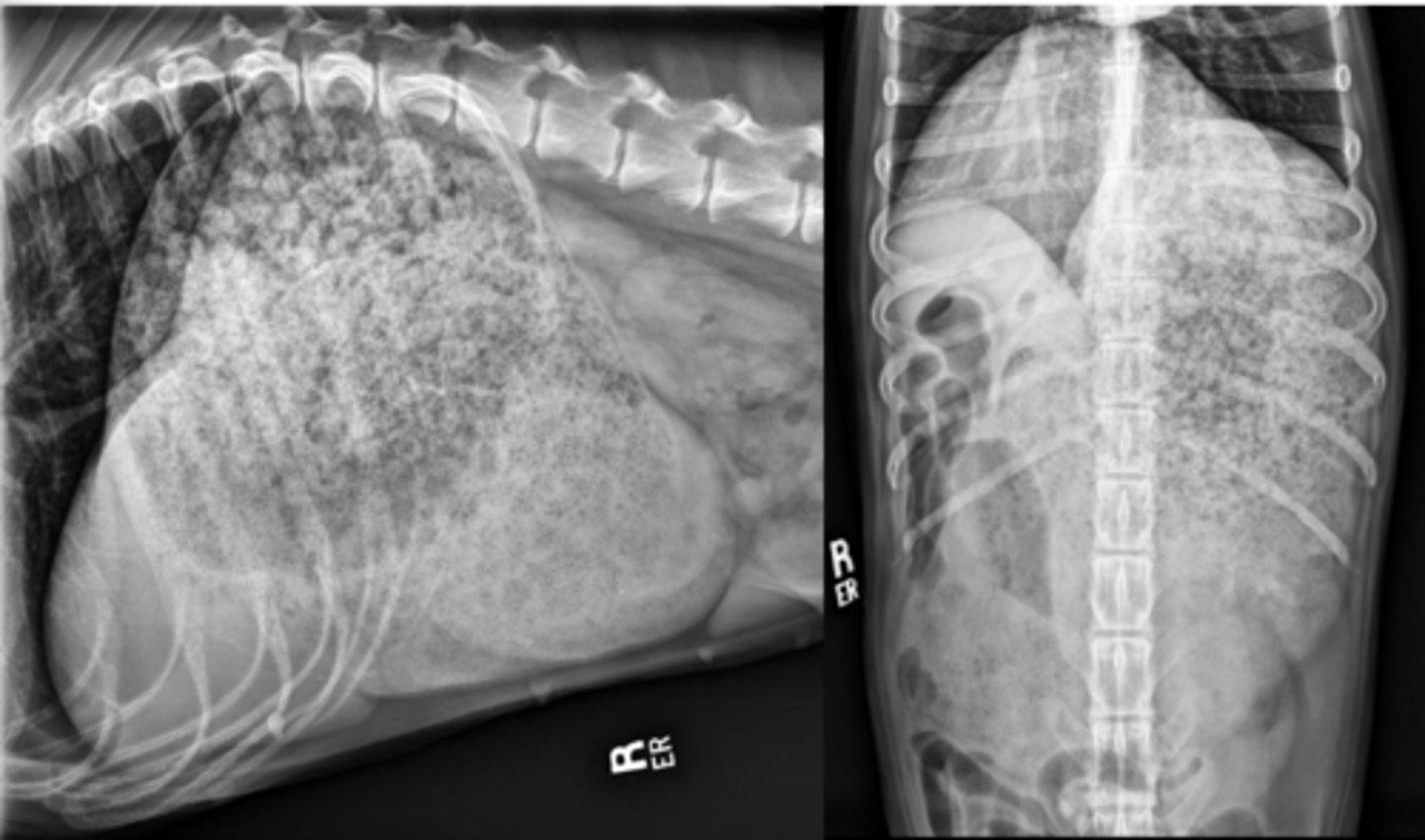
gastric foreign body (hairties)
What abnormality is shown here?
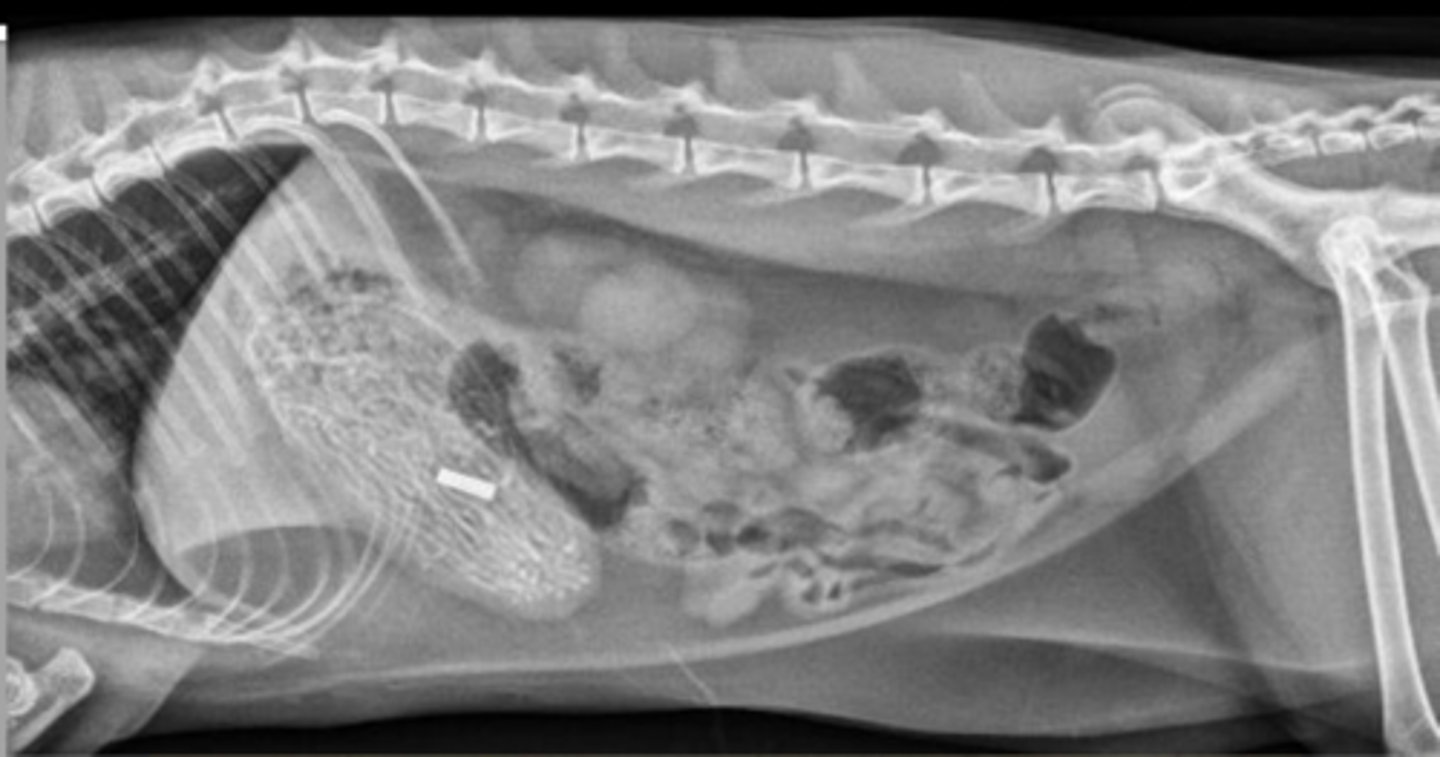
gastric foreign body (bottle cap)
What abnormality is shown here?
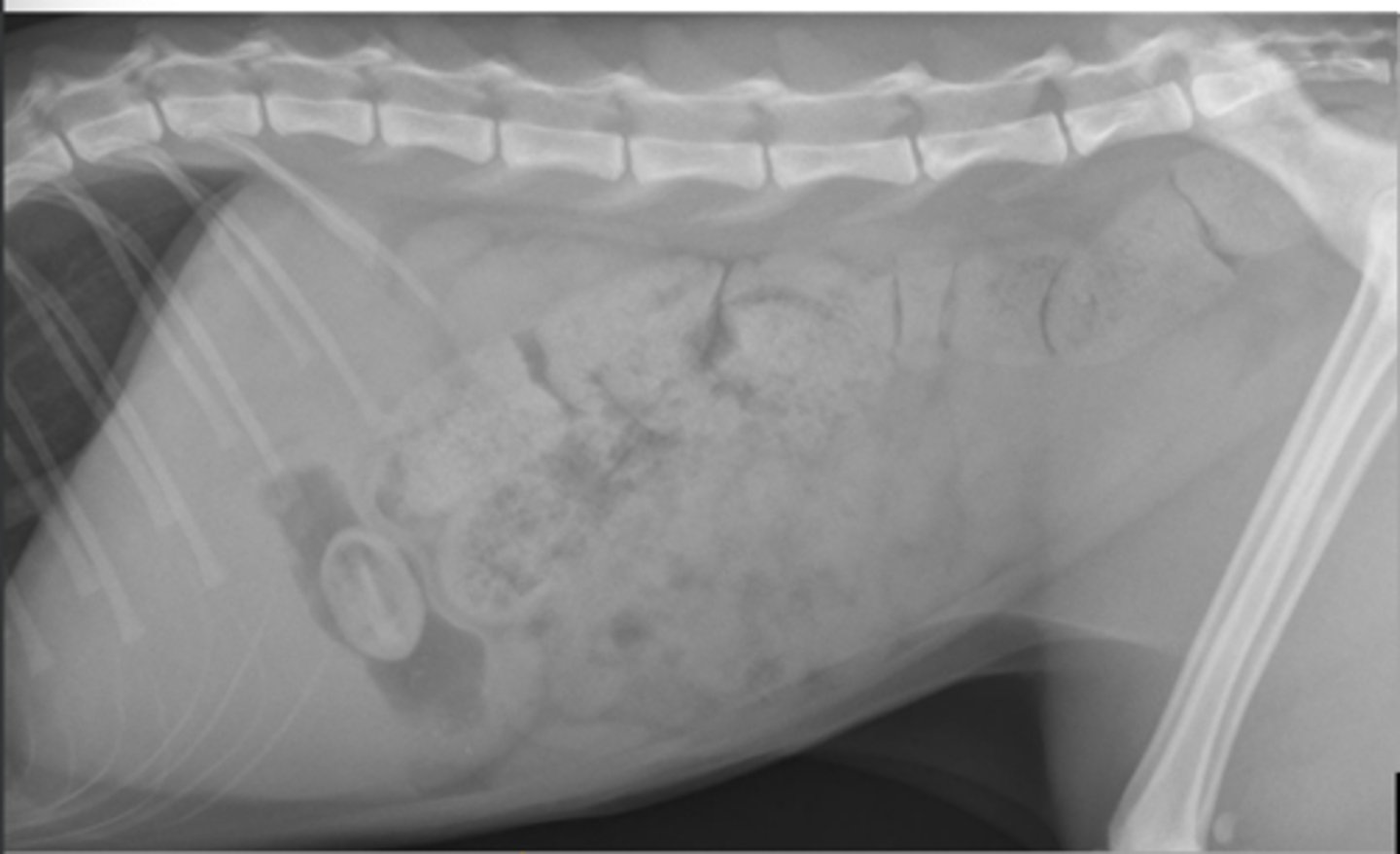
gastric foreign body (hair ball/trichobezoar)
What abnormality is shown here?
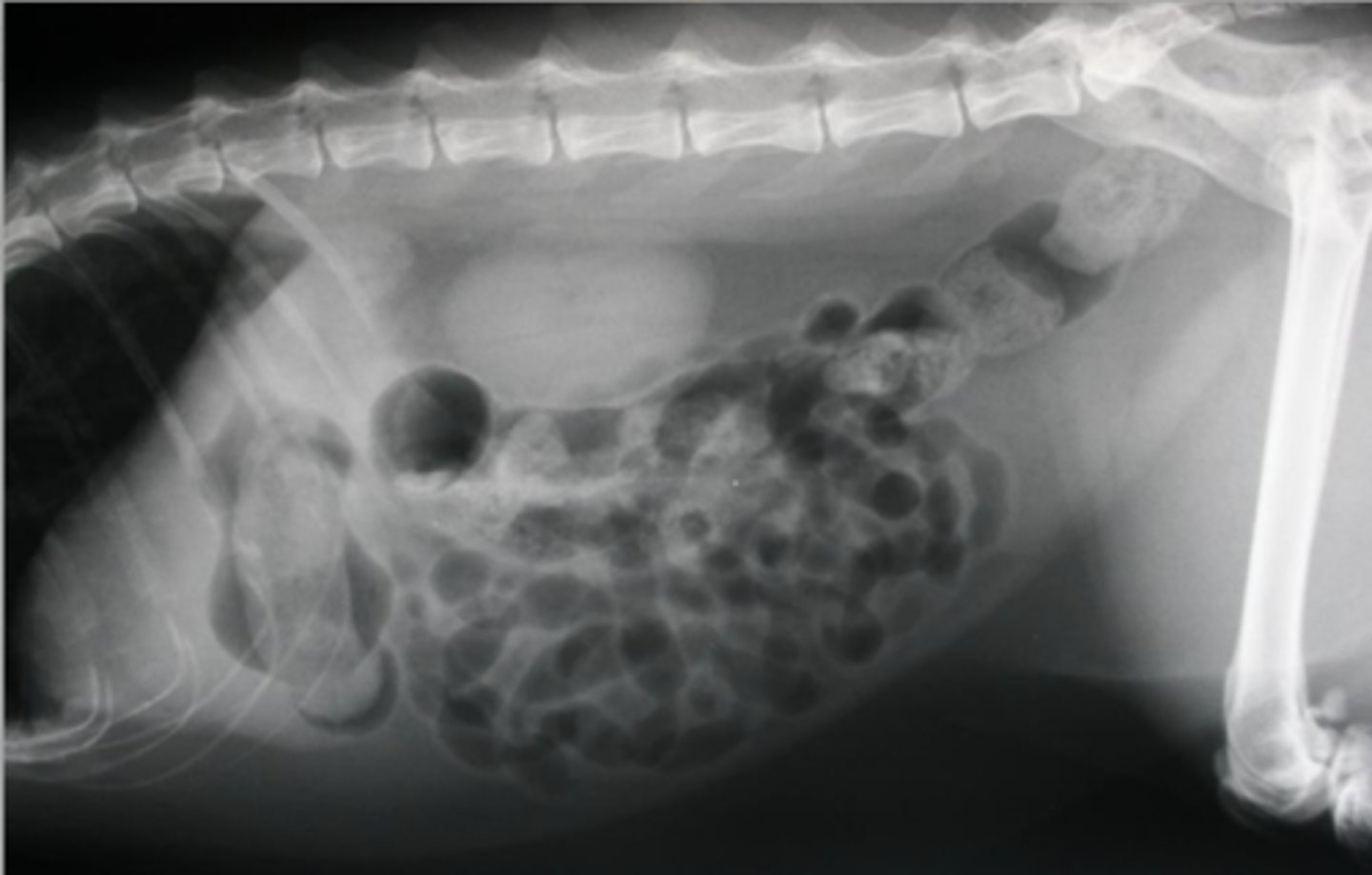
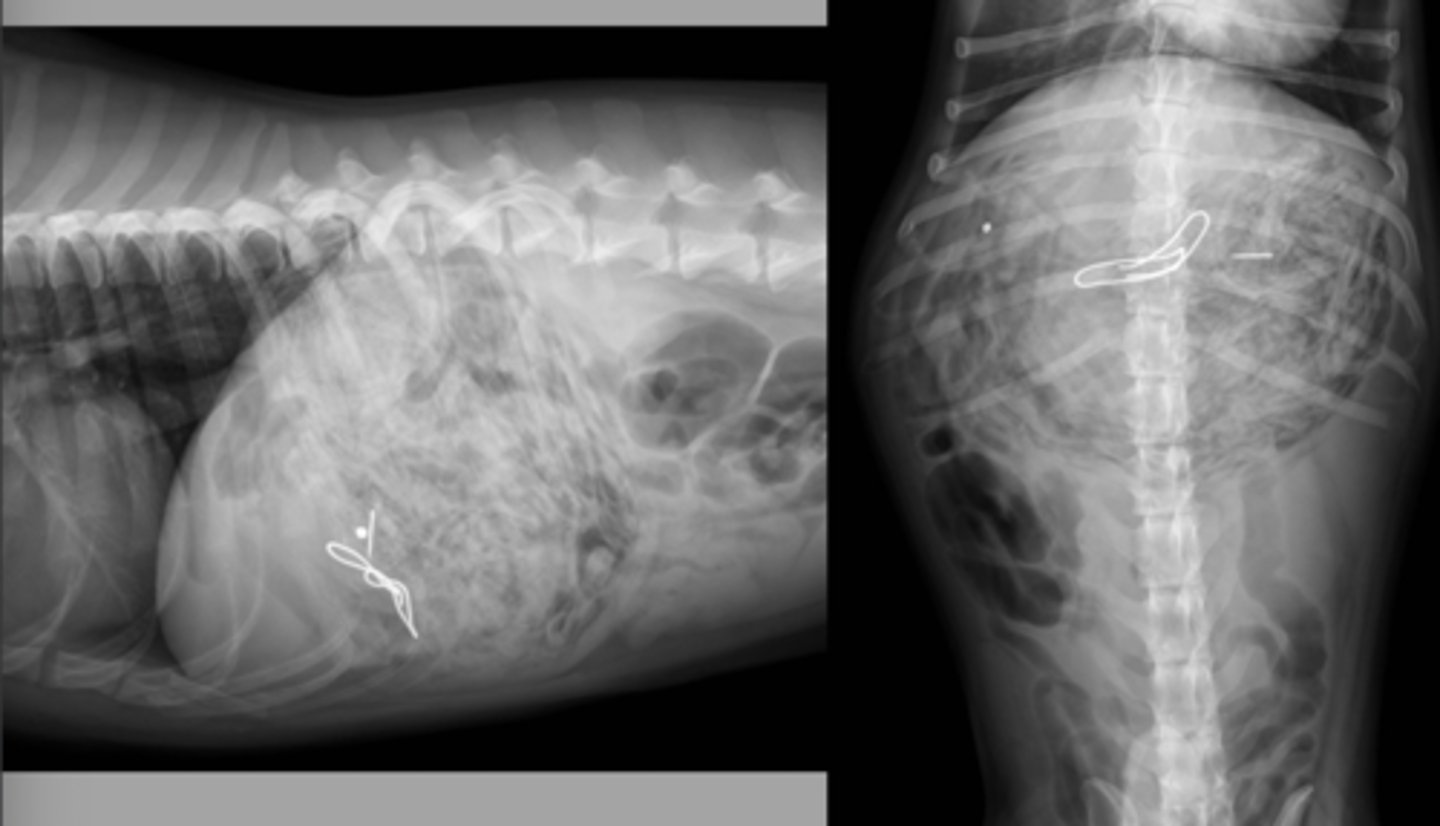
gastric foreign body
What abnormality is shown here?
gastric foreign body
What abnormality is shown here?
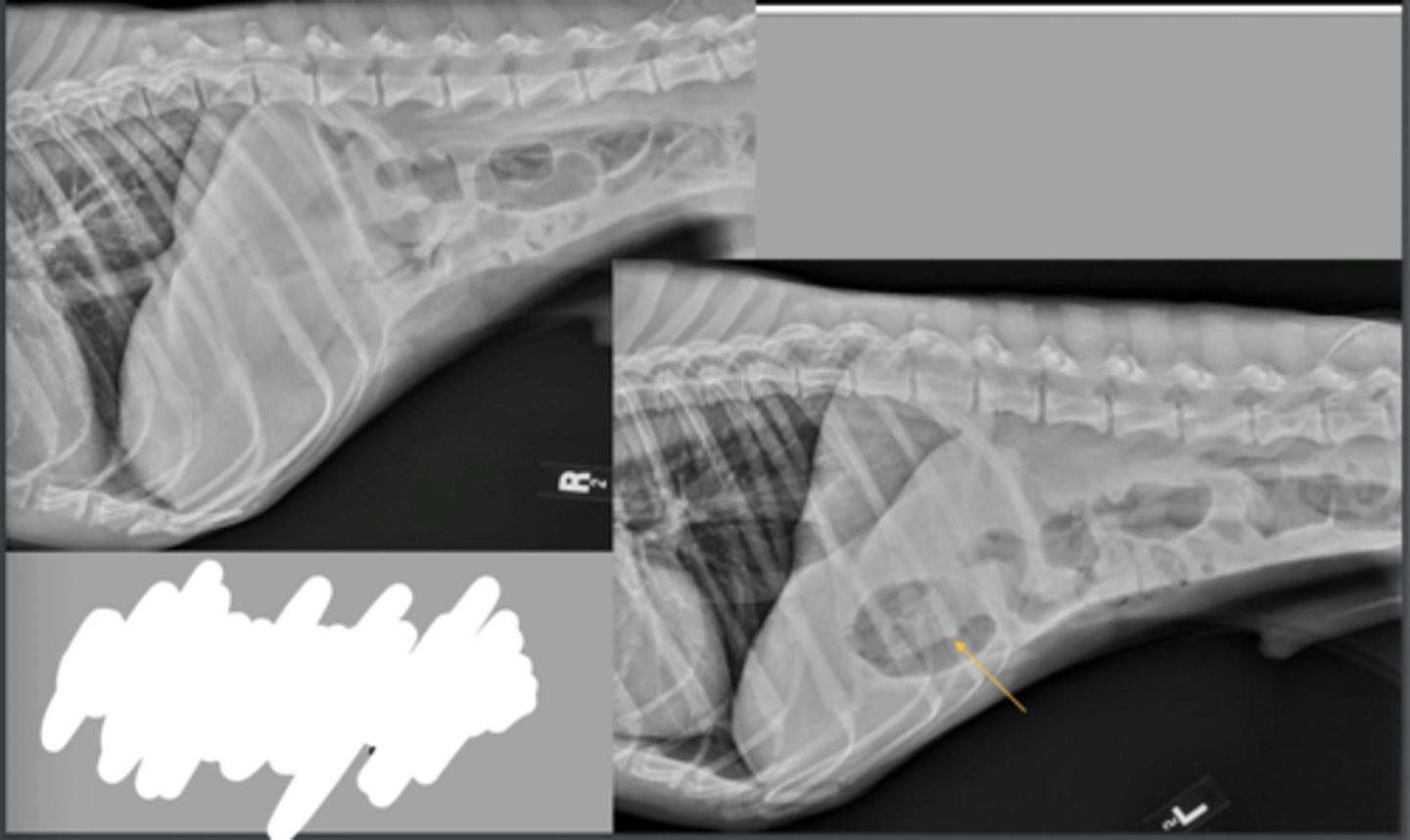
pyloric outflow obstruction - foreign body
What abnormality is shown here?
pyloric outflow obstruction - linear foreign body
What abnormality is shown here?
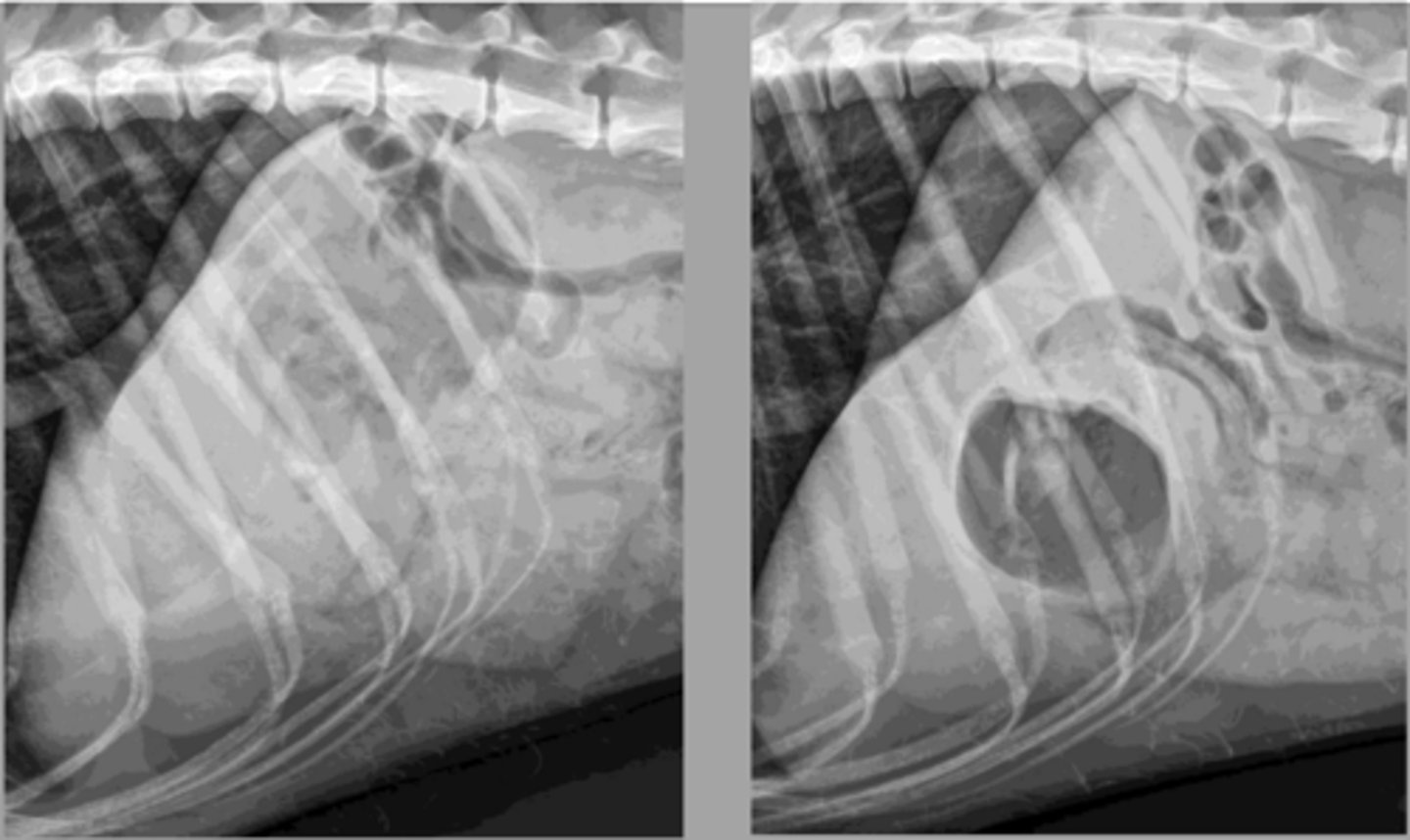
chronic pyloric outflow obstruction
What abnormality is shown here?
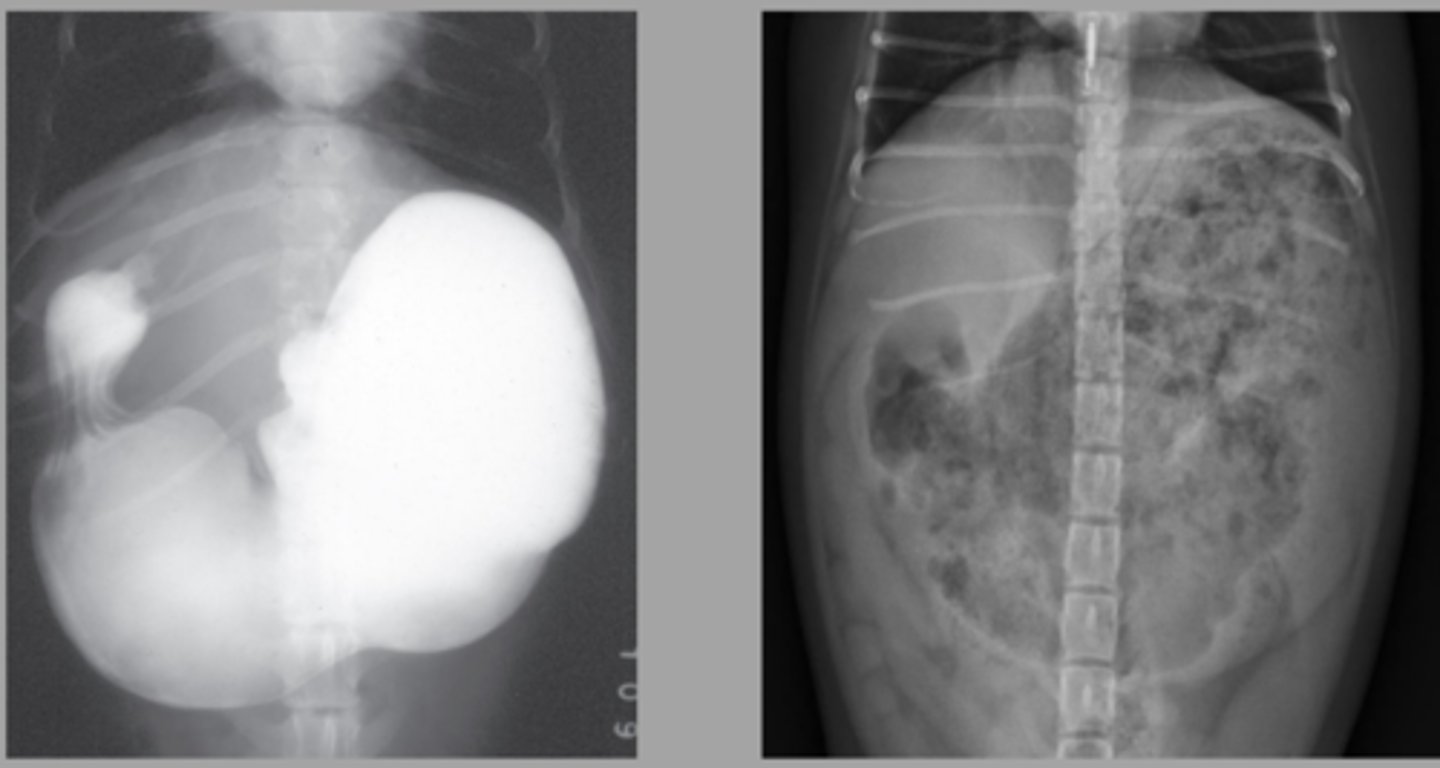
gravel sign
What is this "sign" called that is seen with chronic pyloric outflow obstruction?
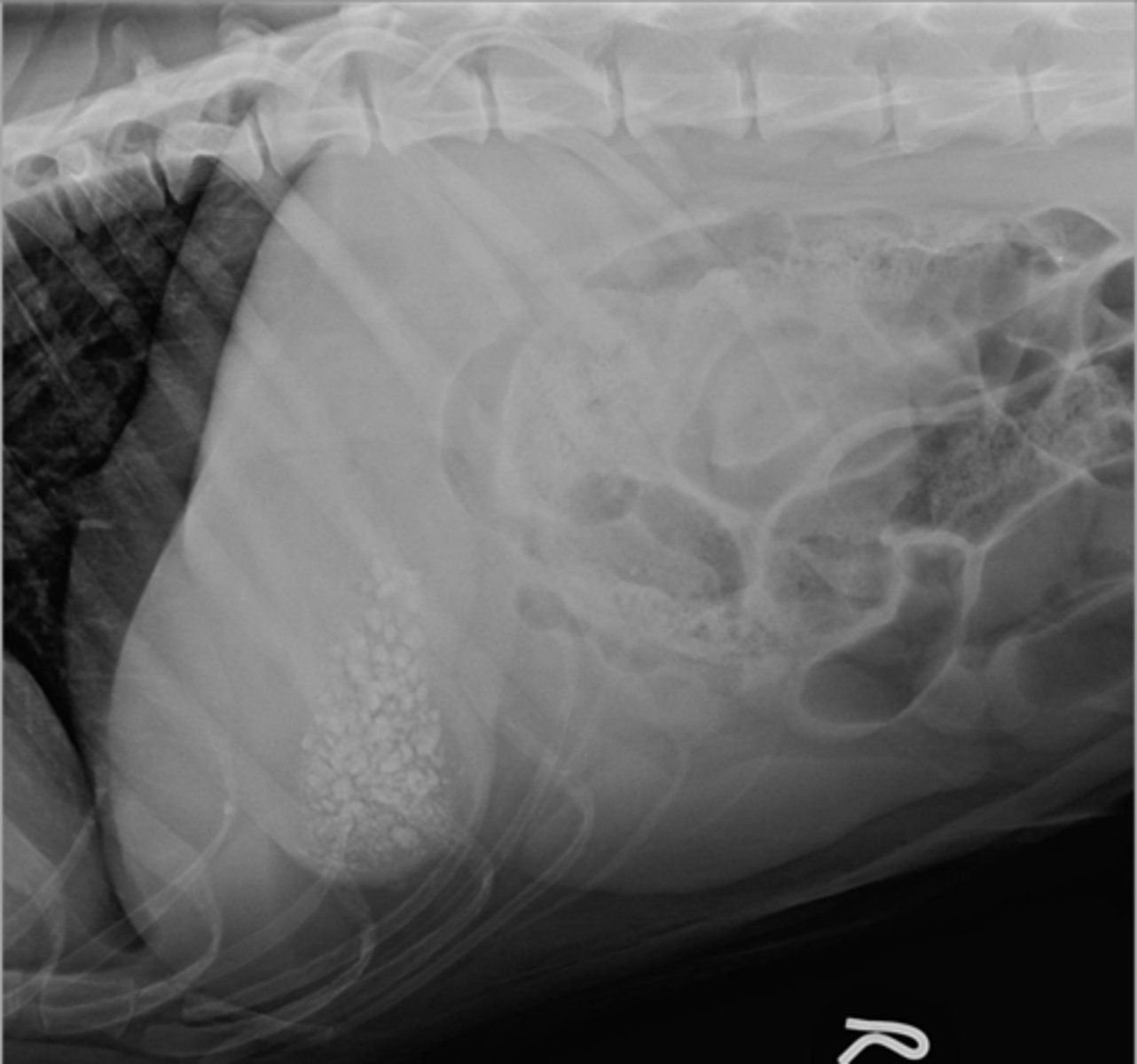
pyloric stenosis
What abnormality is shown here?
no, normally need contrast studies or other imaging modalities such as ultrasound or CT (can see gastric wall tumors if there is enough gas within the stomach)
Can you usually see gastric masses with radiographs?
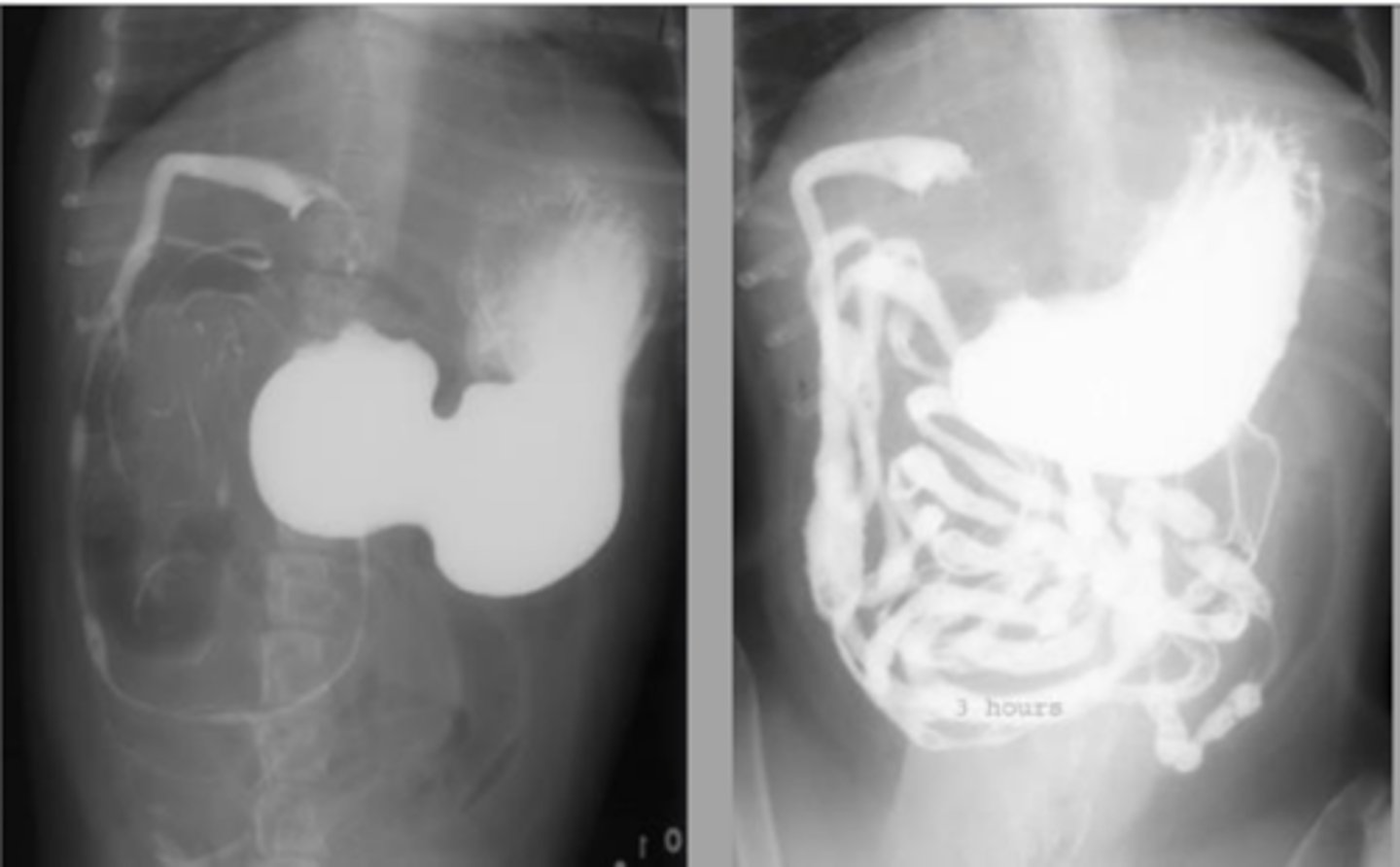
pyloric mass with associated obstruction
What abnormality is shown here?
pyloric mass without associated obstruction
What abnormality is shown here?
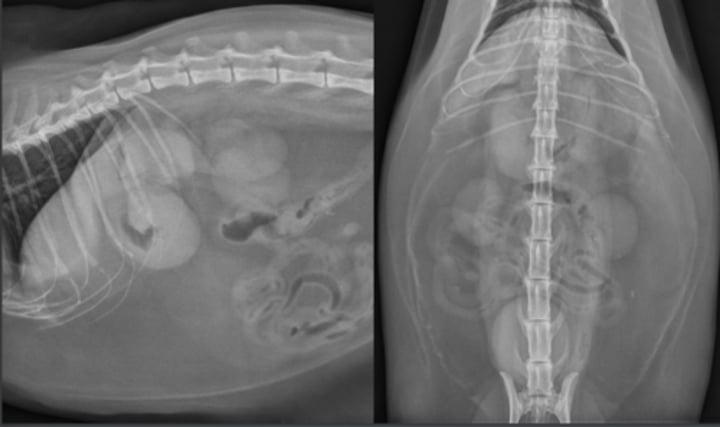
uremic gastropathy (mineralization of mucosa)
What abnormality is shown here?
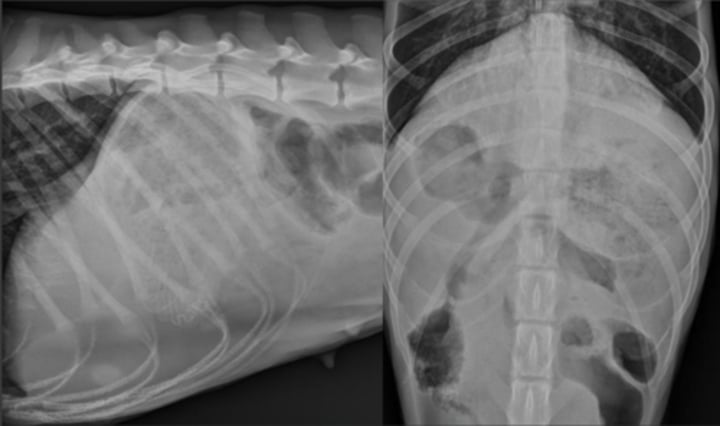
yes, fat cat. Excess fat is causing a mass effect
Is there a mass effect here?
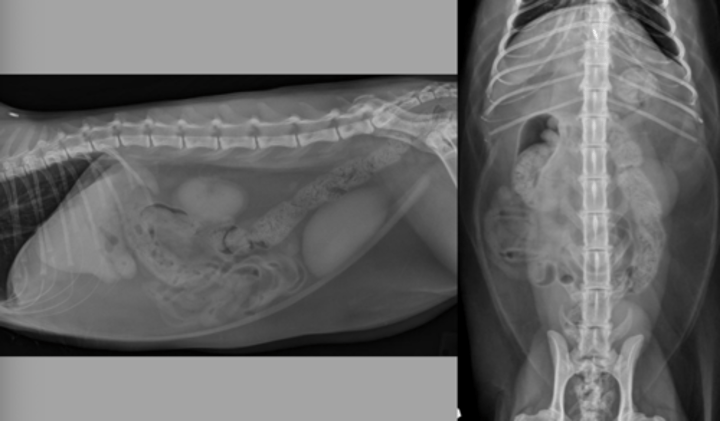
< 1.5x the height of the central body of L5
Normal Roentgen Signs Small Intestine: Size (dogs)
< 1.5x the height of the cranial endplate of L5 or < 12mm
Normal Roentgen Signs Small Intestine: Size (cats)
tubular, circular, curvilinear
Normal Roentgen Signs Small Intestine: Shape
1, divisions of duodenum, jejunum, ileum
Normal Roentgen Signs Small Intestine: Number
soft tissue and gas, small amount of gas in cats
Normal Roentgen Signs Small Intestine: Opacity
central ventral abdomen - even distribution
fat cats: right mid ventral abdomen
Normal Roentgen Signs Small Intestine: Location
smooth serosal and mucosal margins
Normal Roentgen Signs Small Intestine: Margination
-lumen diameter
-mucosal margination +/- bowel wall thickness
-motility/transit time
-location
-obstruction
What does an upper GI contrast study help assess?
Peyer's Patches
normal in dogs
What is this finding? Is is normal? Which animal can it be seen in
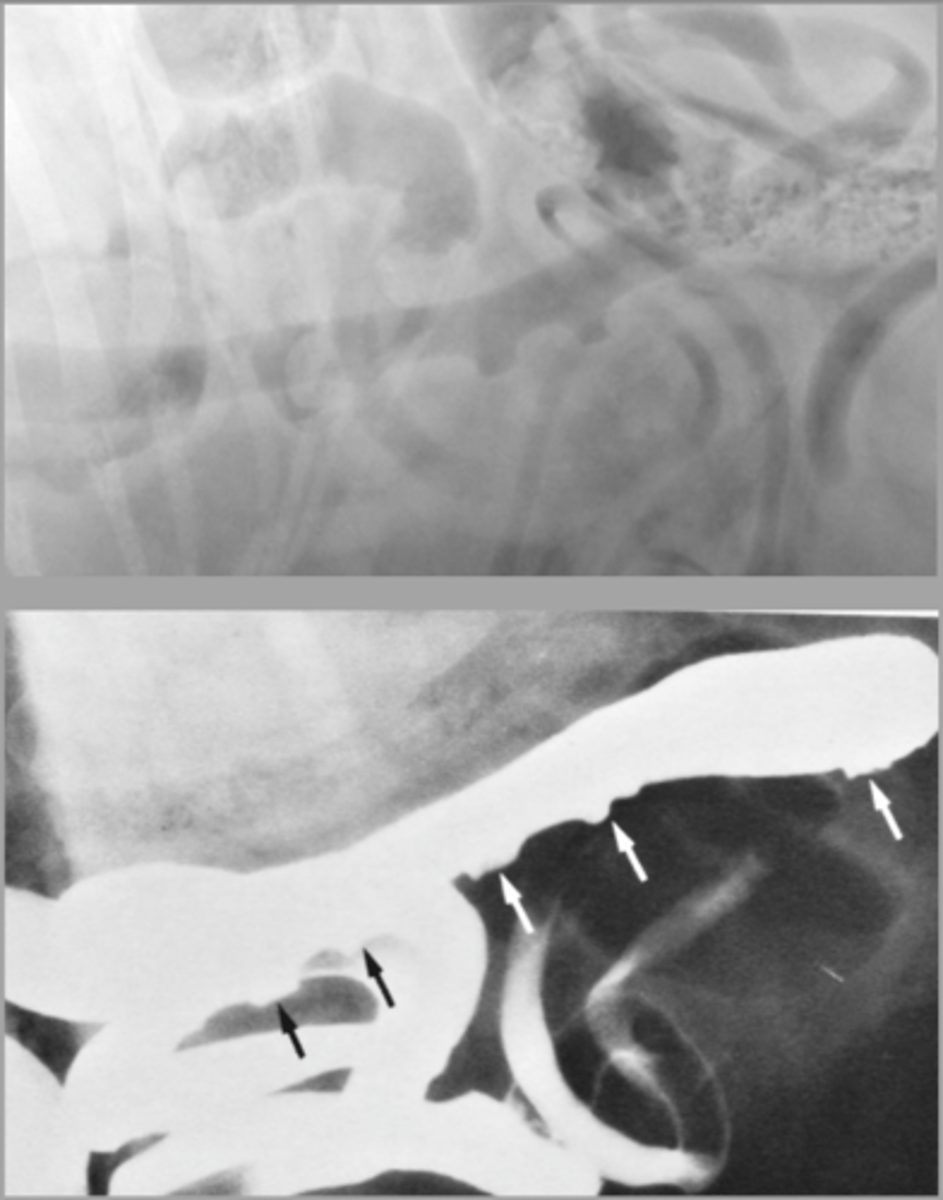
"string of pearls" which indicates motility. Seen more often in cats but can be seen in dogs
What is this finding? Is it normal?
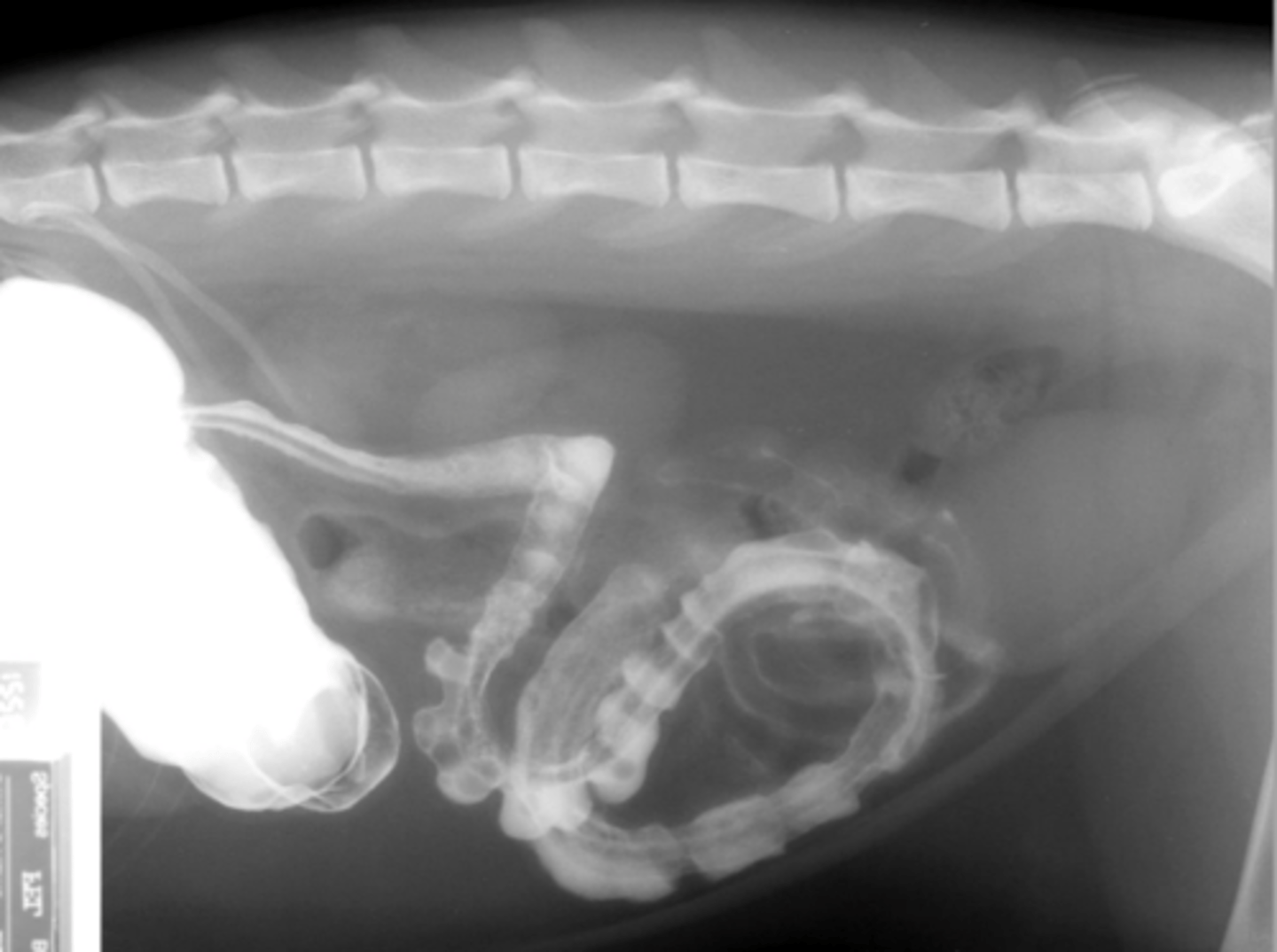
traumatic diaphragmatic rupture
What abnormality is seen here?
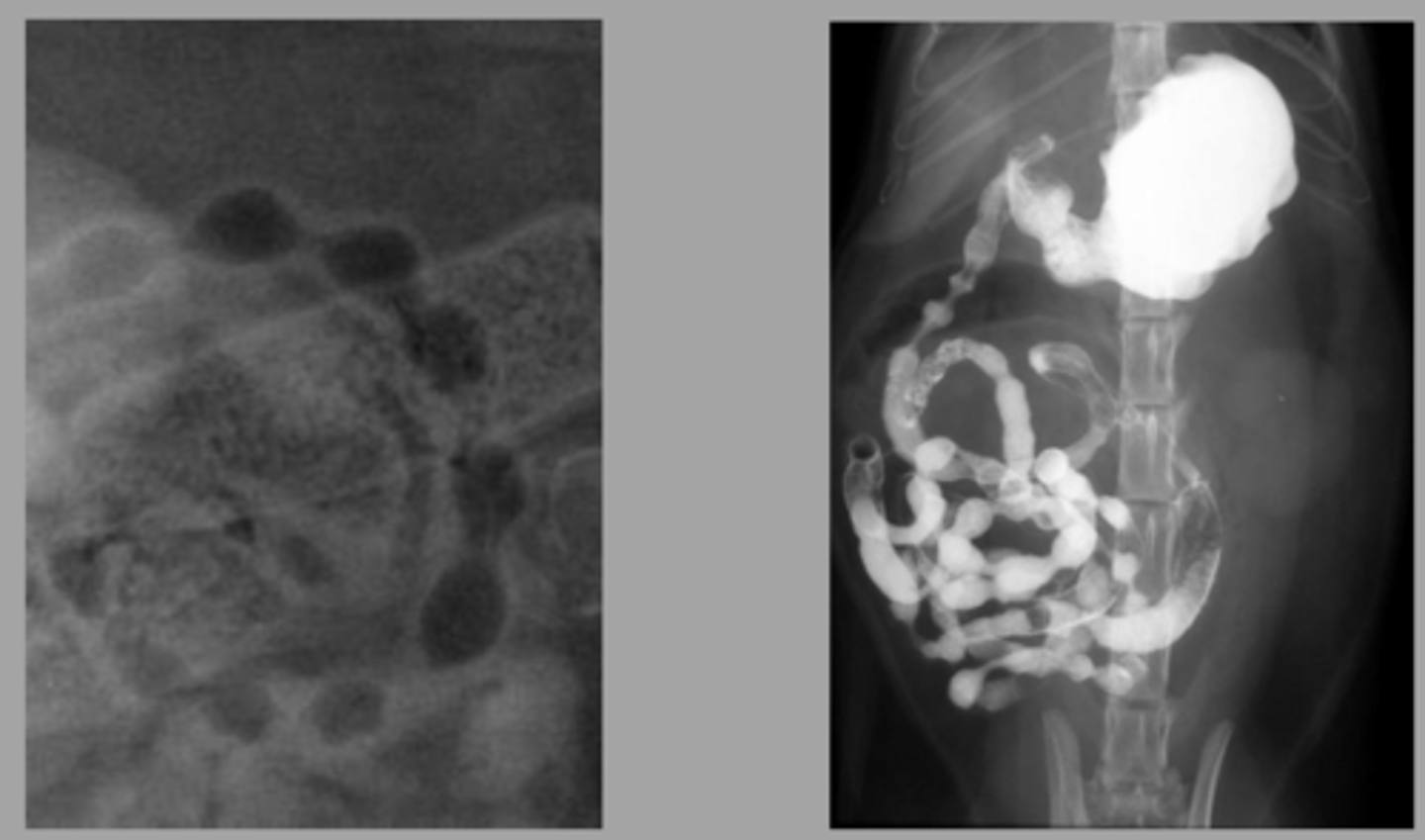
foreign body
What abnormality is seen here?
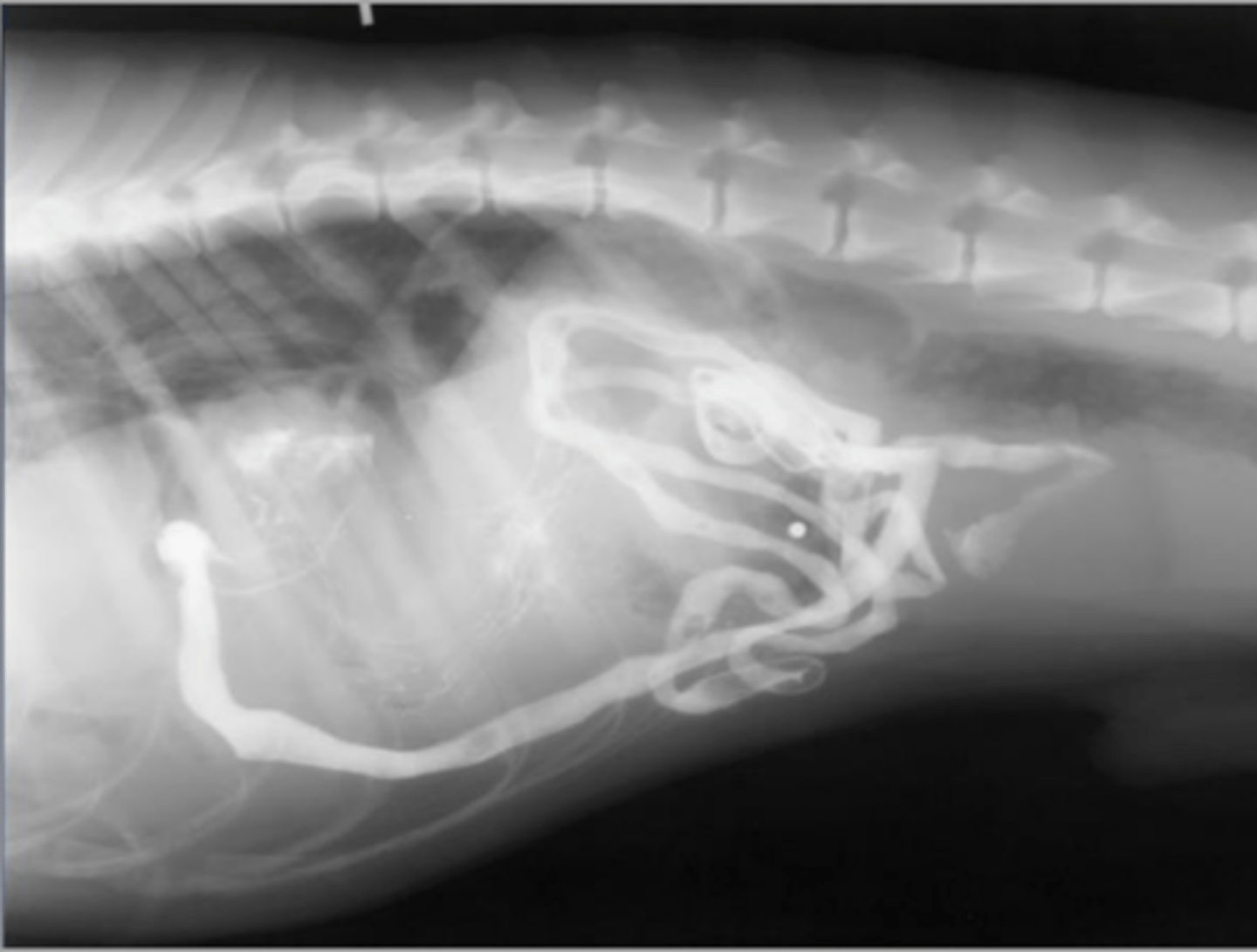
linear foreign body
What abnormality is seen here?
failure of intestinal contents to move through the GI tract
What is ileus?
lumen obstructed, any combination of opacities, segmental dilation (unless distal SI obstruction)
What do you usually see with a mechanical ileus?
decreased motility (vascular or NM abnormalities of the GI wall), usually gas opaque, usually generalized dilation
What do you usually see with functional ileus?
small intestinal functional ileus
What abnormality is seen here?
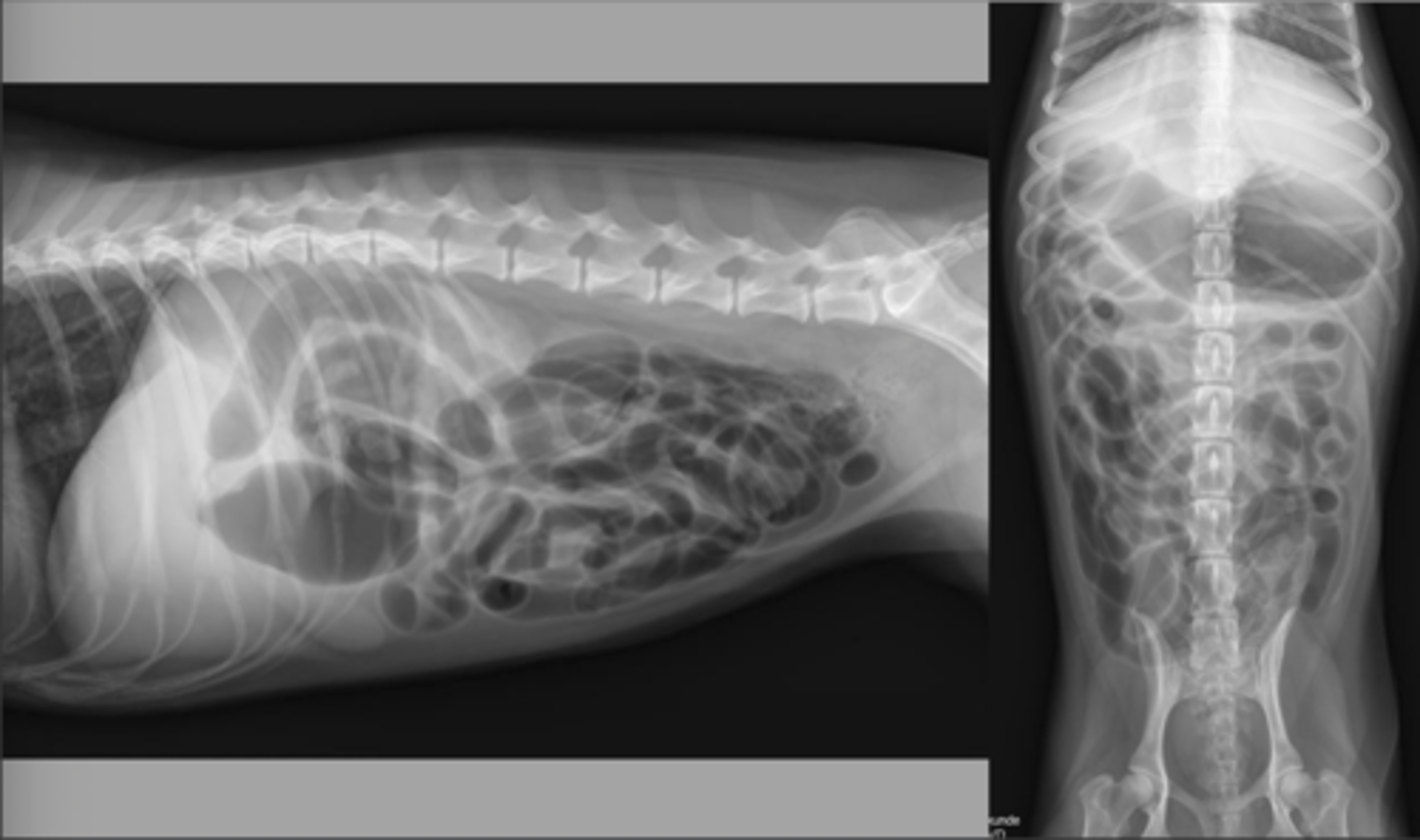
small intestinal mechanical obstruction. Looking for sentinel bowel sign, two different populations of loops
What abnormality is seen here? And what specific signs are you looking for?
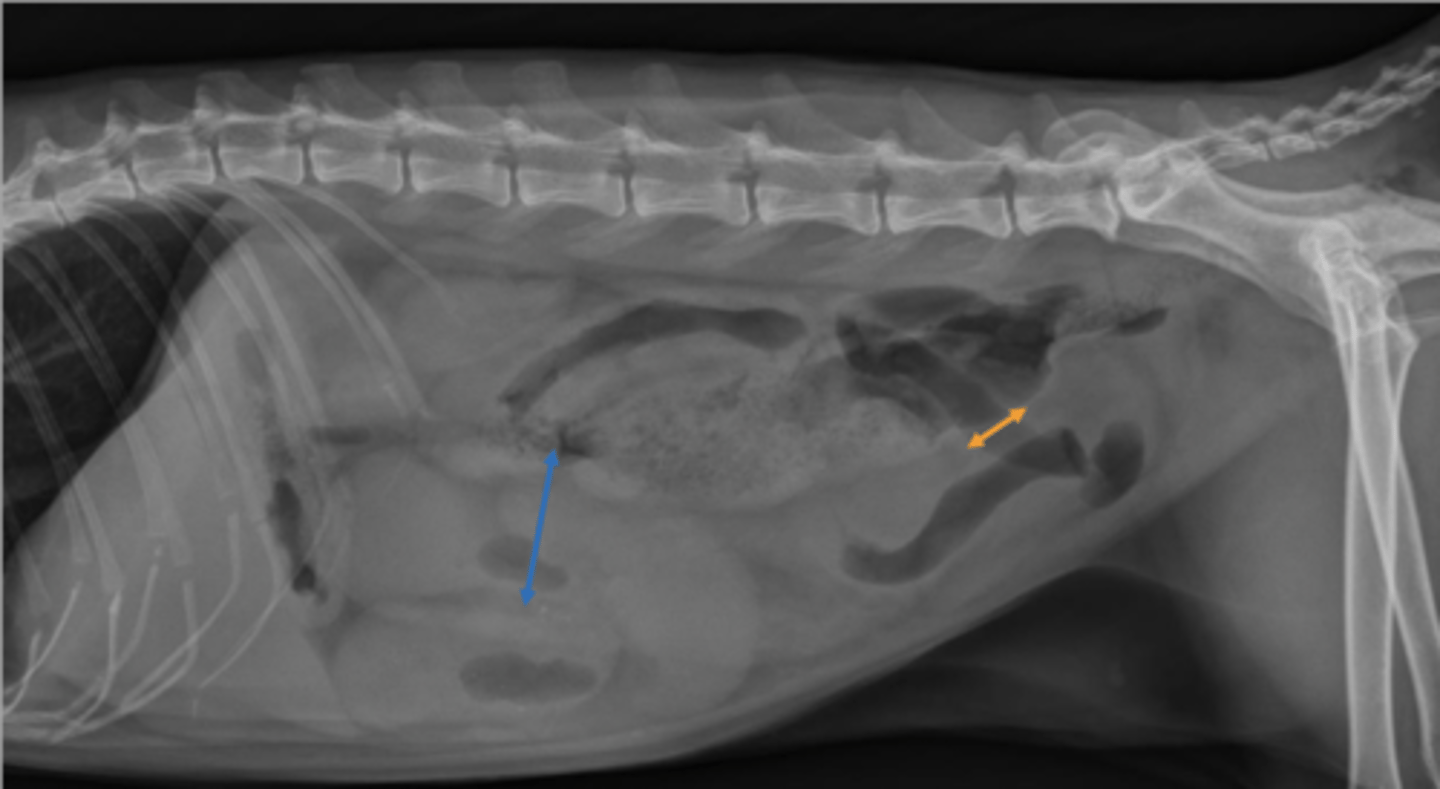
serosa-serosa
When you measure the SI diameter are you measuring the lumen or serosa-serosa?
normal:
For a dog, what are the normal, "may be obstructed," and obstructed widths of the SI?
>1.6x the height of the cranial endplate of L5 or >12mm
What are abnormal SI measurements for cats?
to differentiate SI from colon, assessment of colonic strictures or colonic masses
What would you use a pneumocolonogram for?
pneumocolonogram
What is being done here?
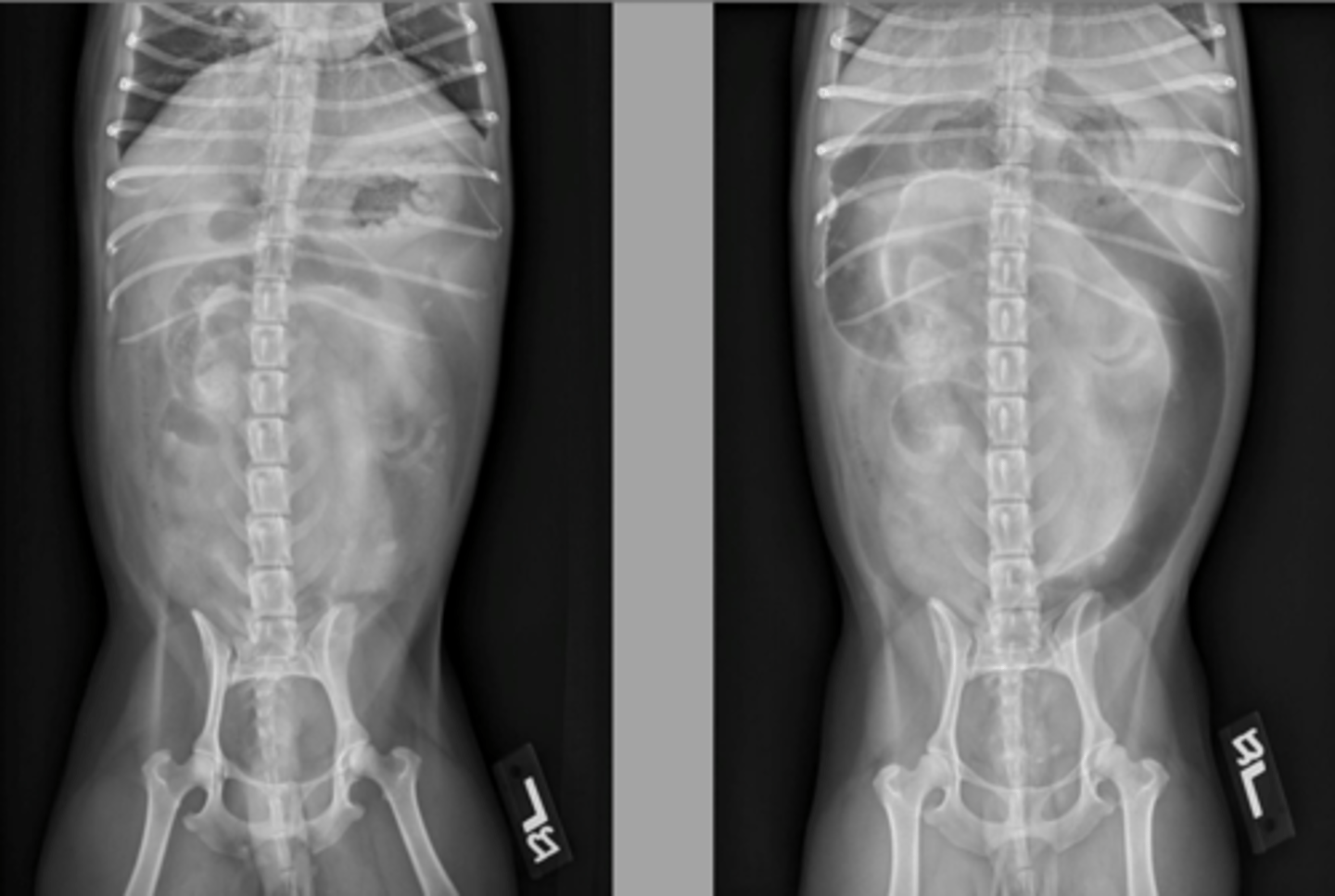
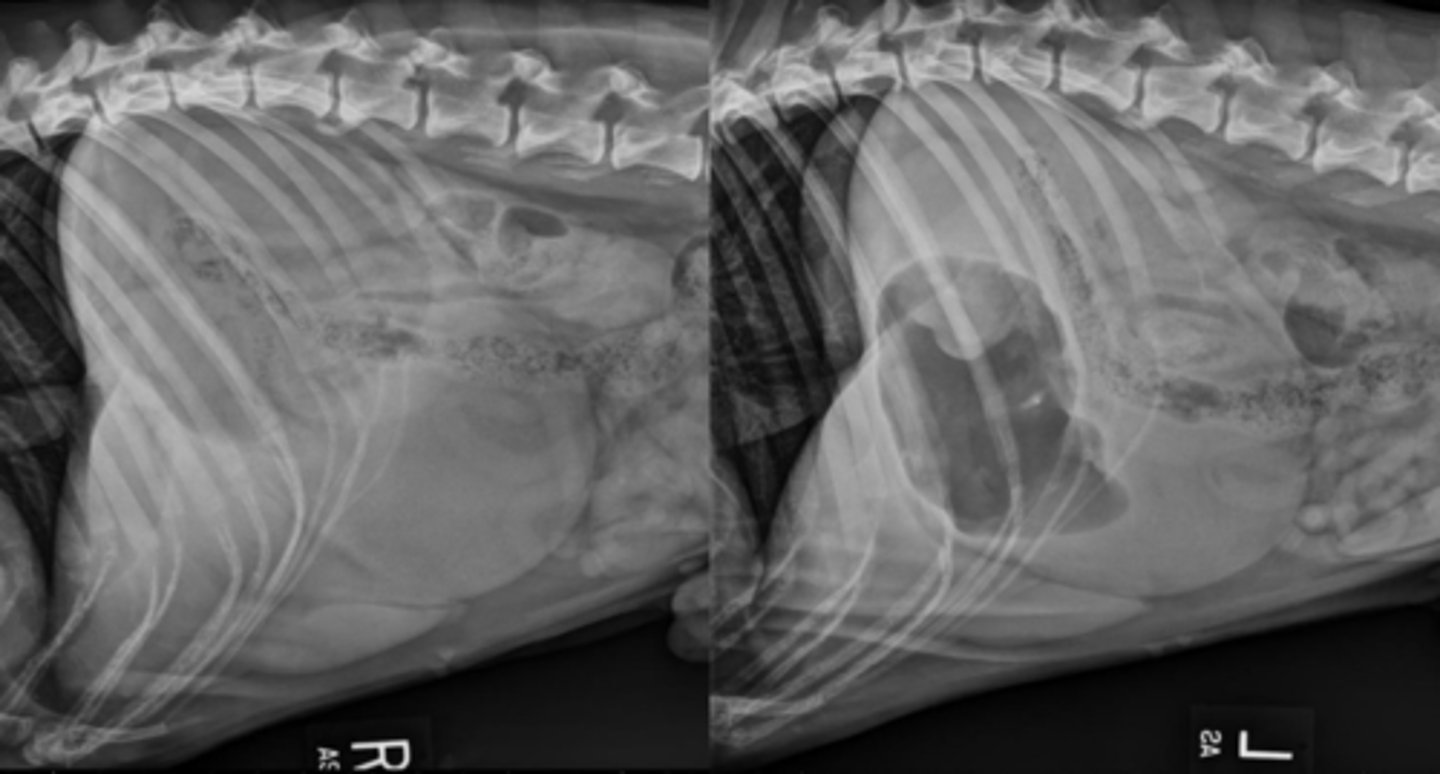
small intestinal obstruction
hair-pin turn and plication
What abnormality is seen here? And what specific signs are you seeing?
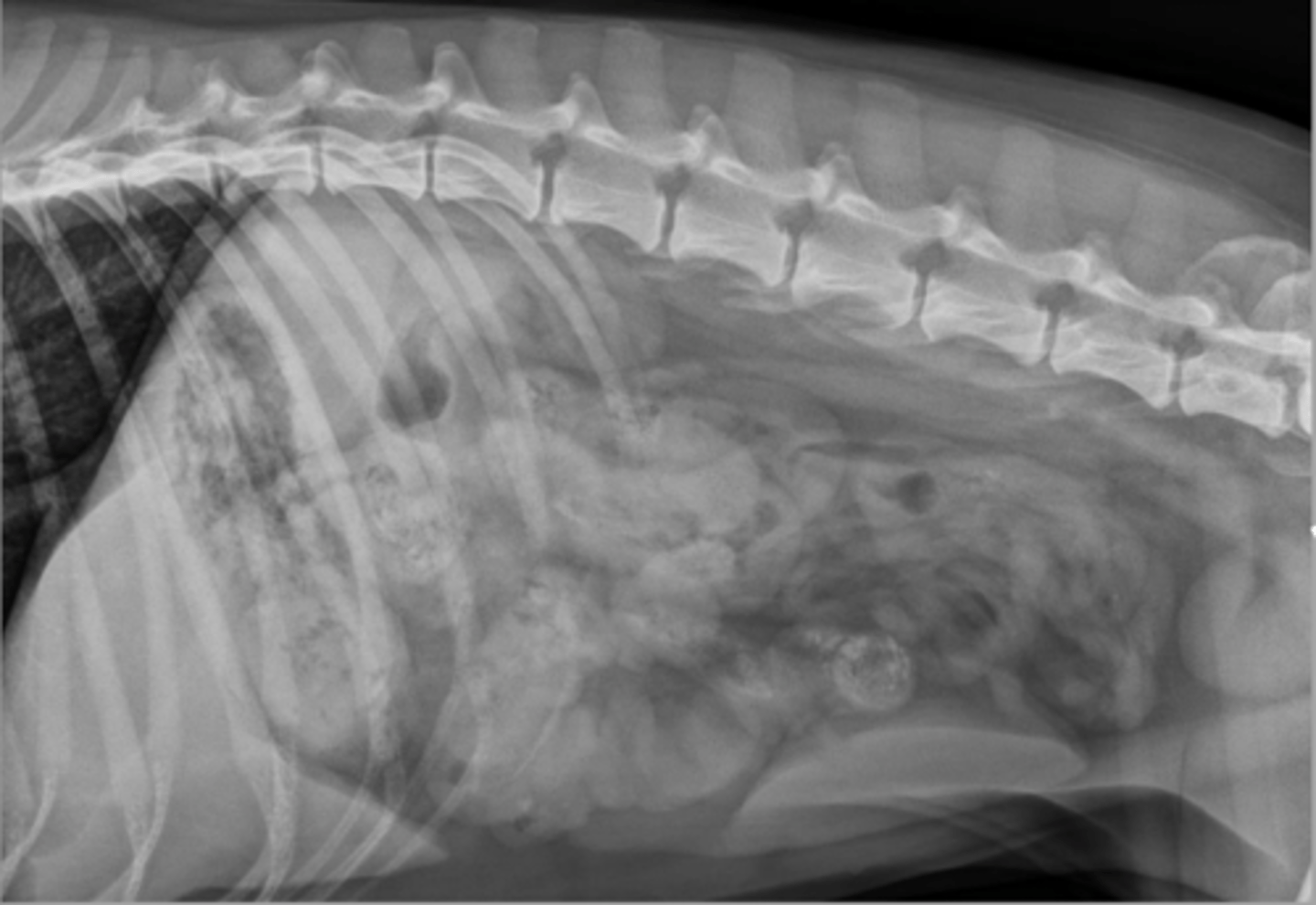
stacking
What SI obstruction sign is seen here?
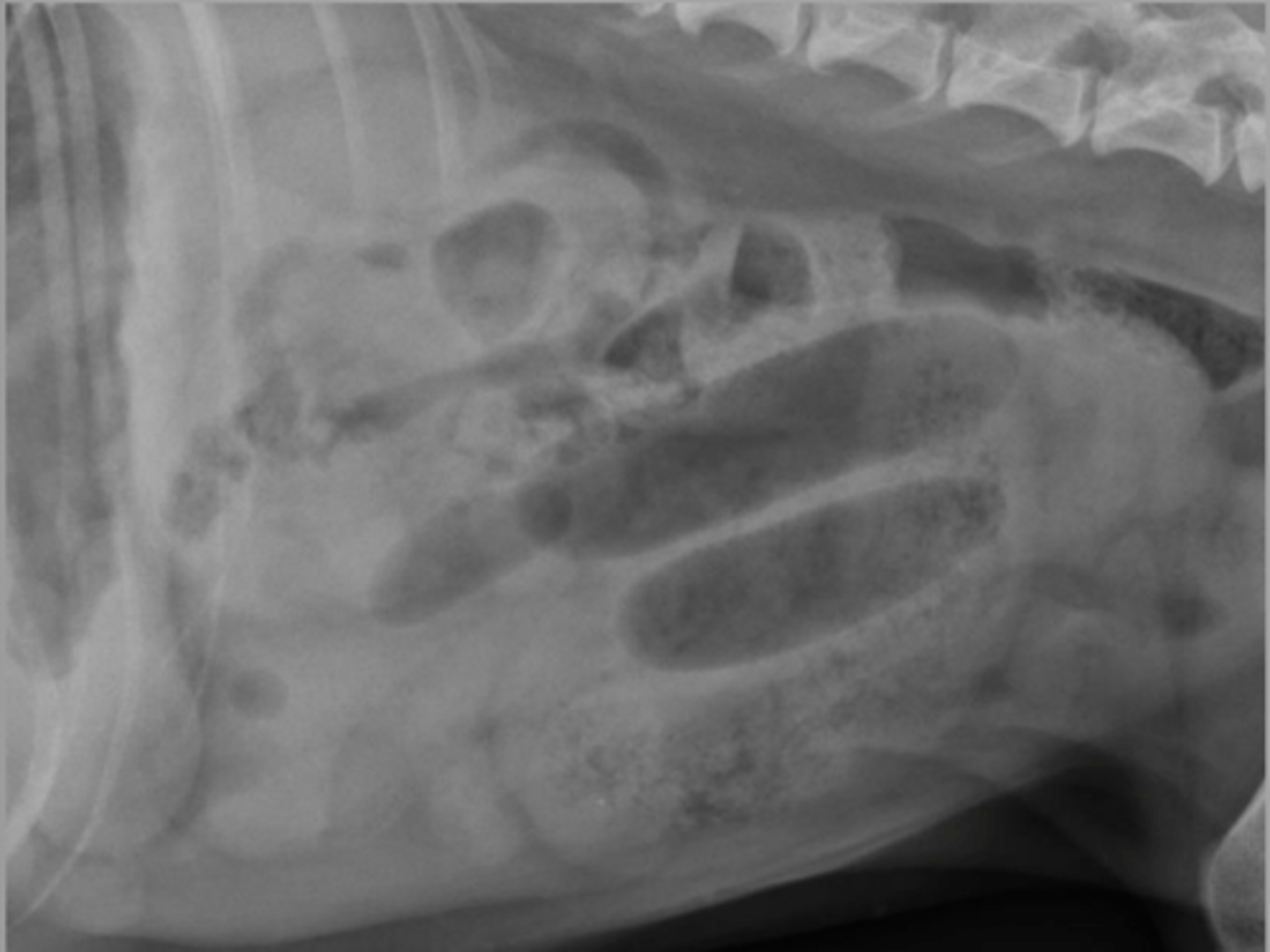
plication, coma shaped gas/geometric shapes
What small intestinal obstruction sign is seen here?
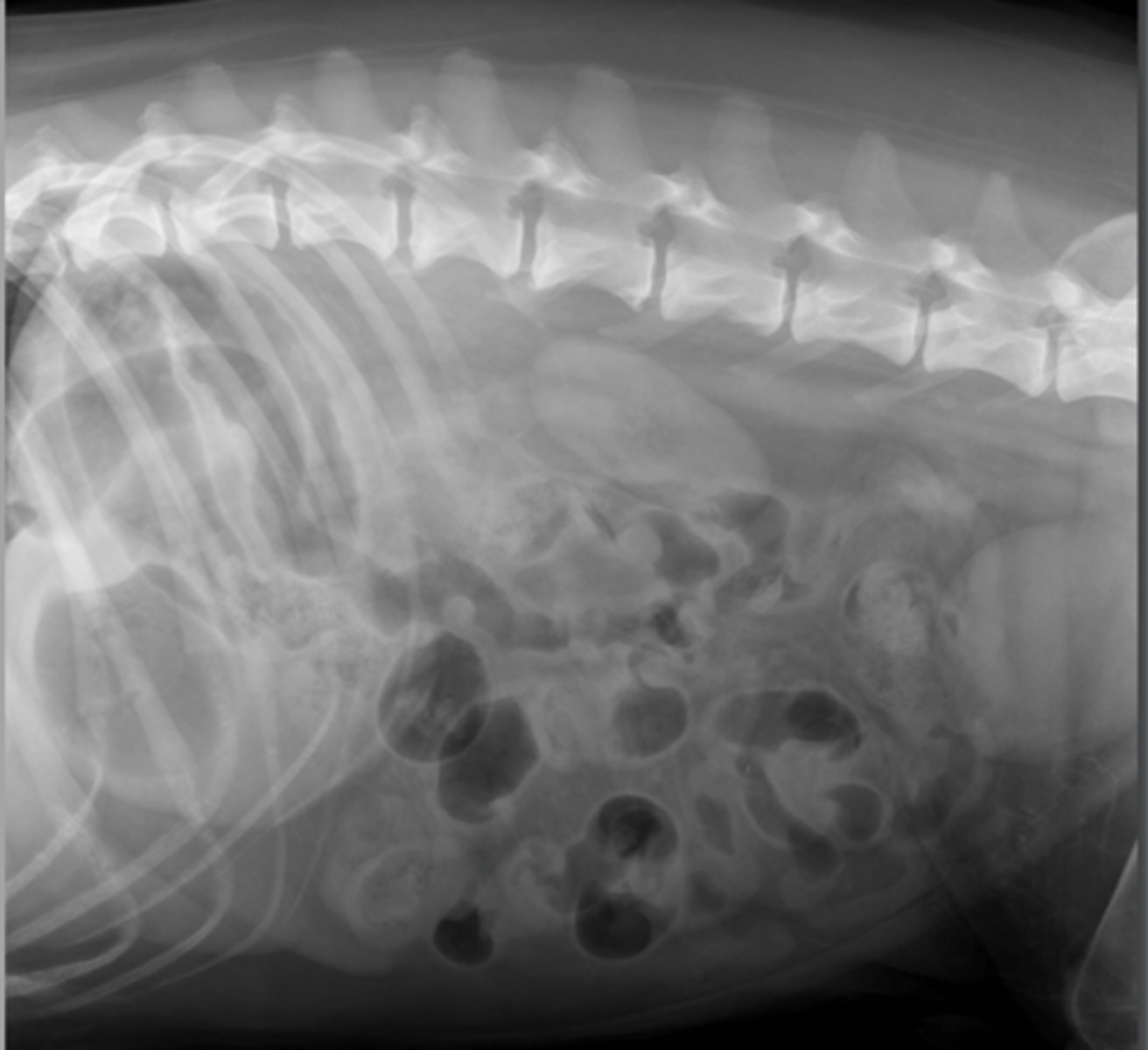
small intestinal obstruction
What abnormality is seen here?
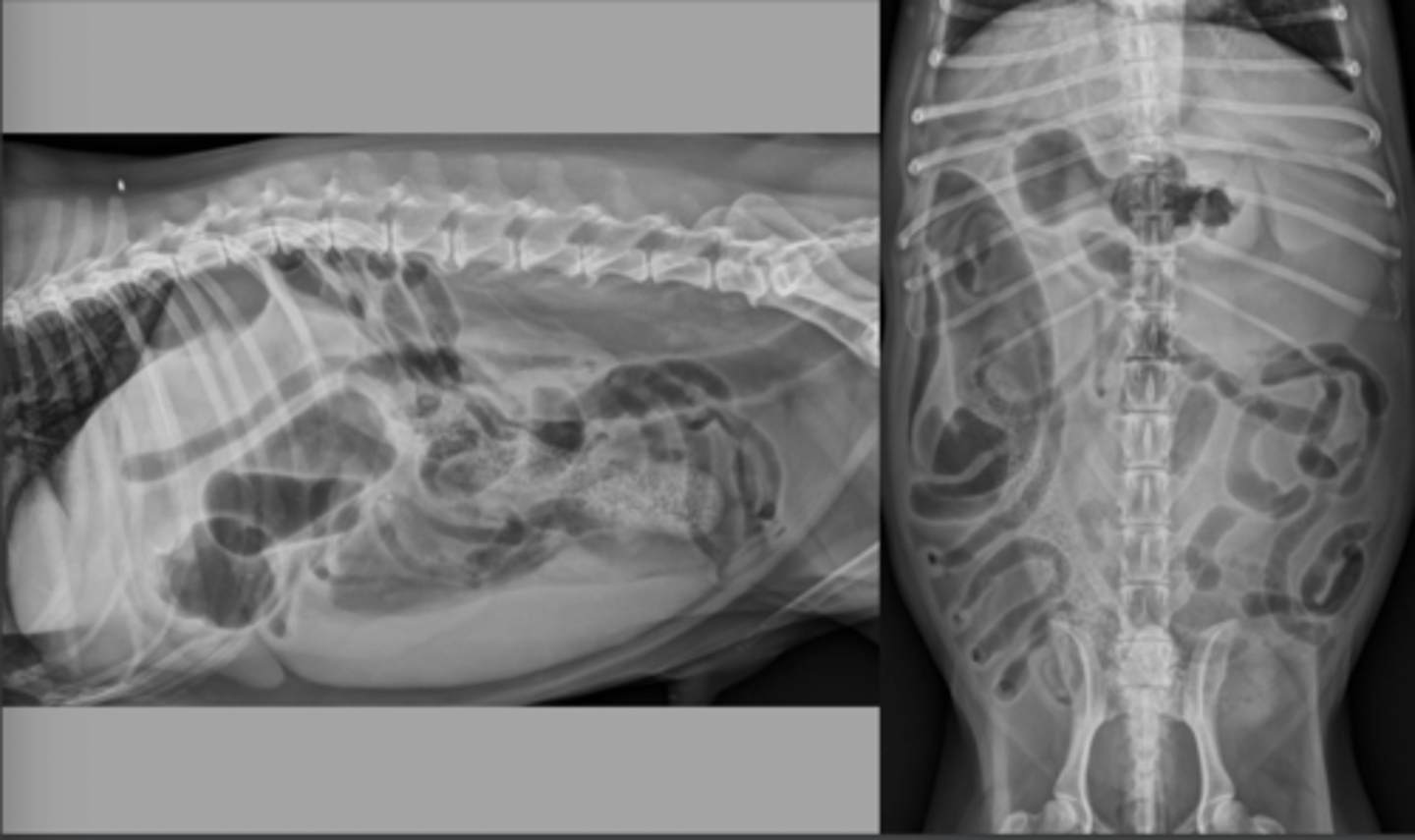
small intestinal foreign body: sock
What abnormality is seen here?
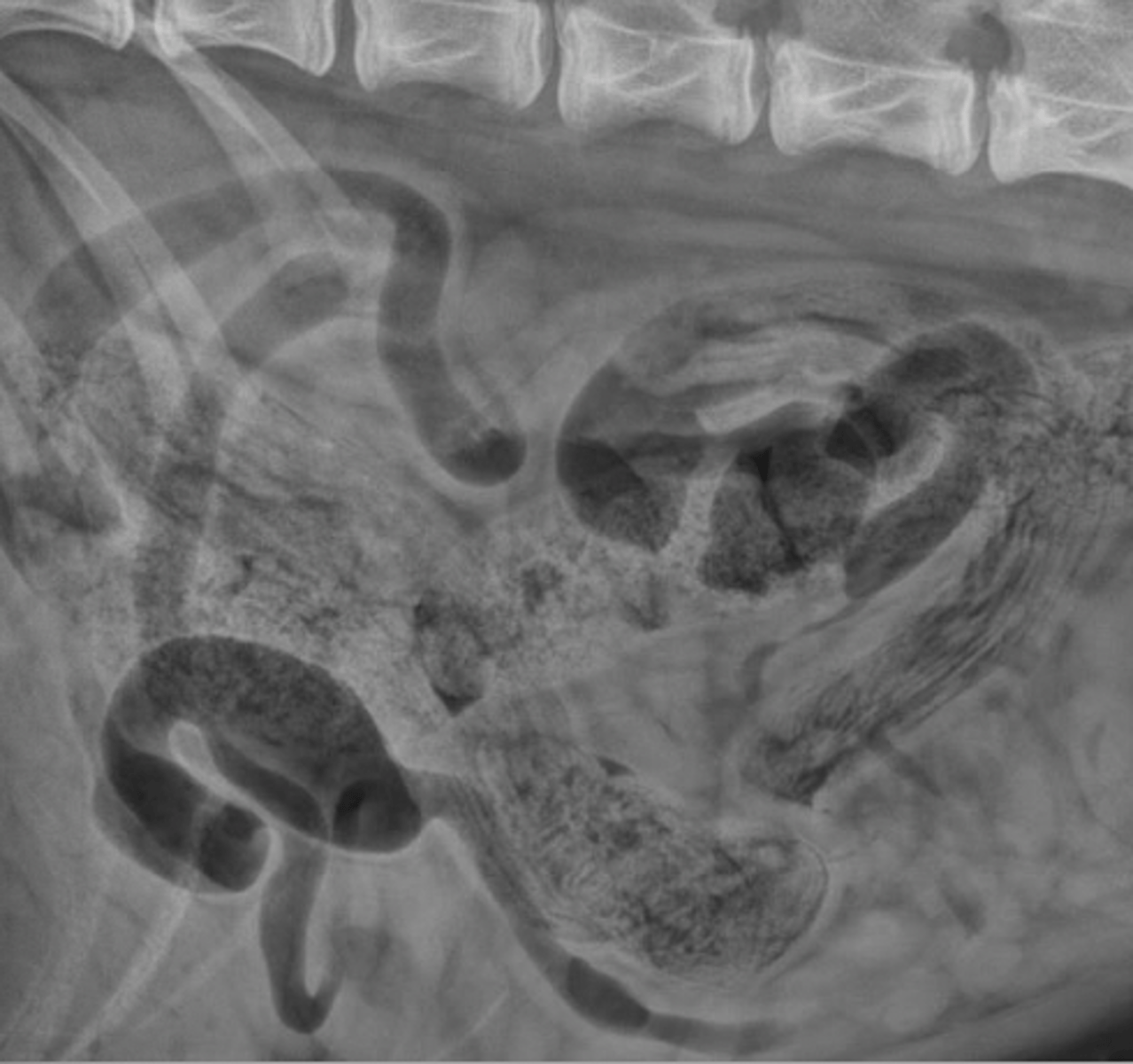
small intestinal foreign body: corn cob
What abnormality is seen here?
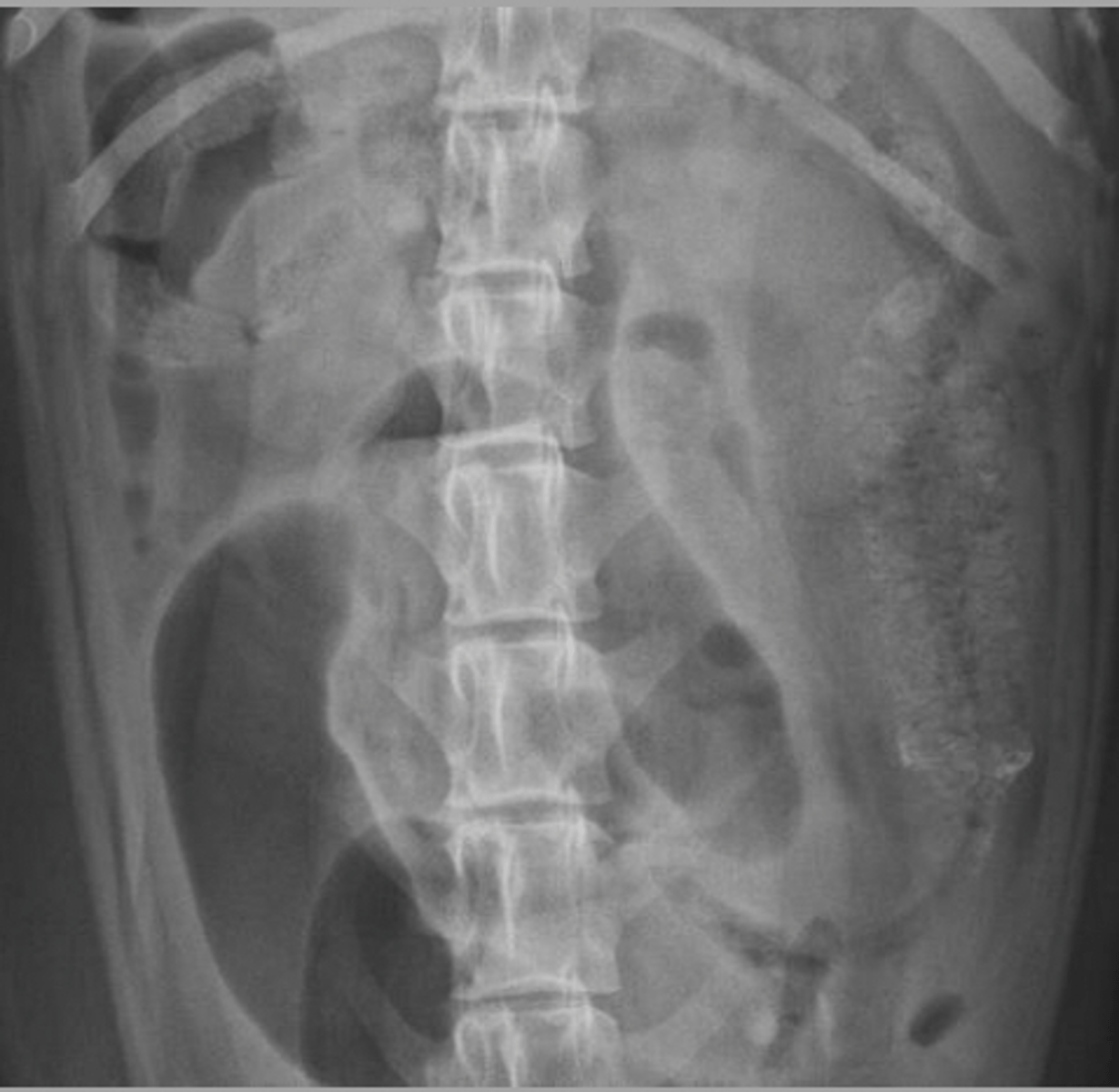
small intestinal foreign body: rock
What abnormality is seen here?
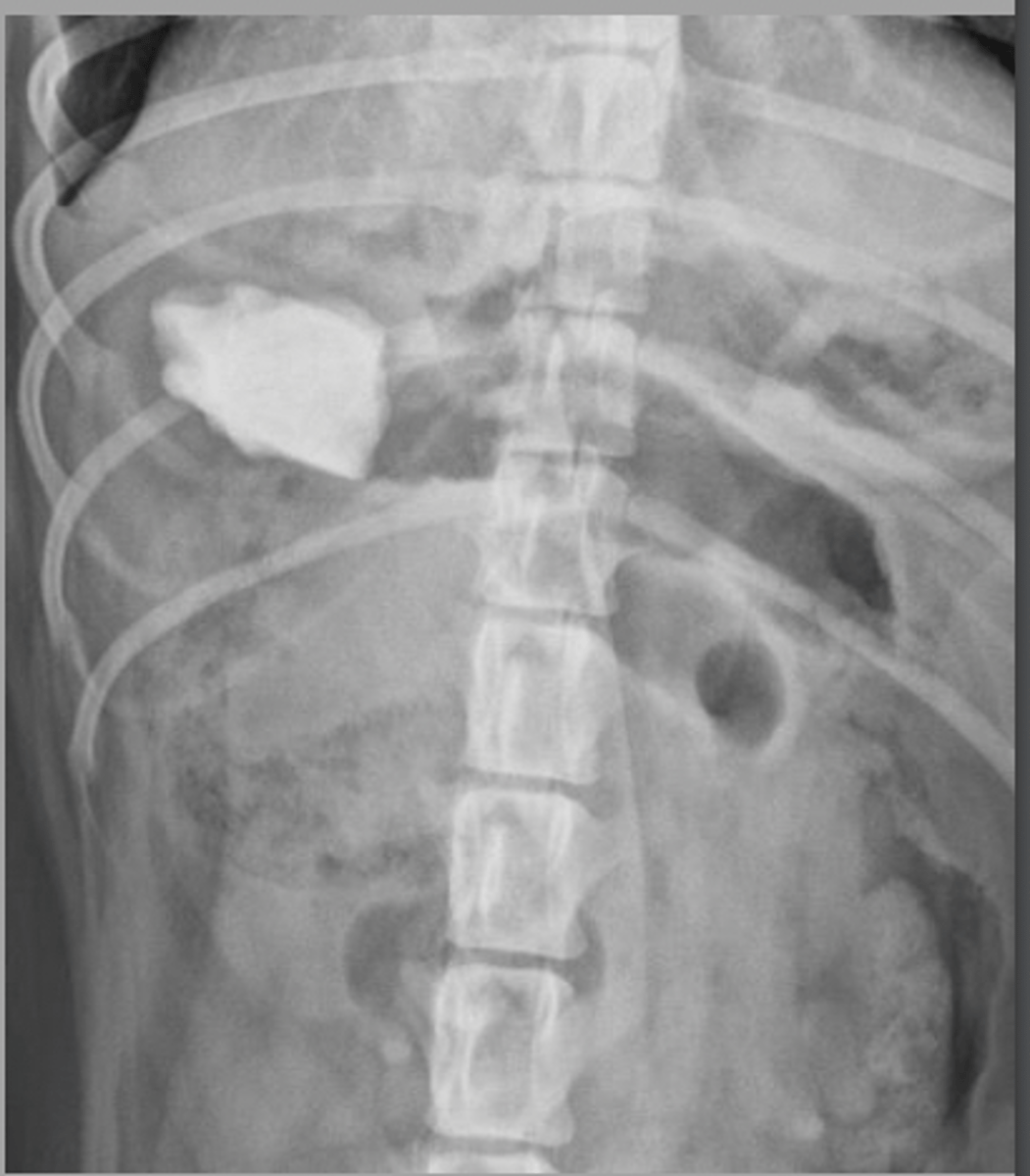
mechanical obstruction - foreign body
What abnormality is seen here?
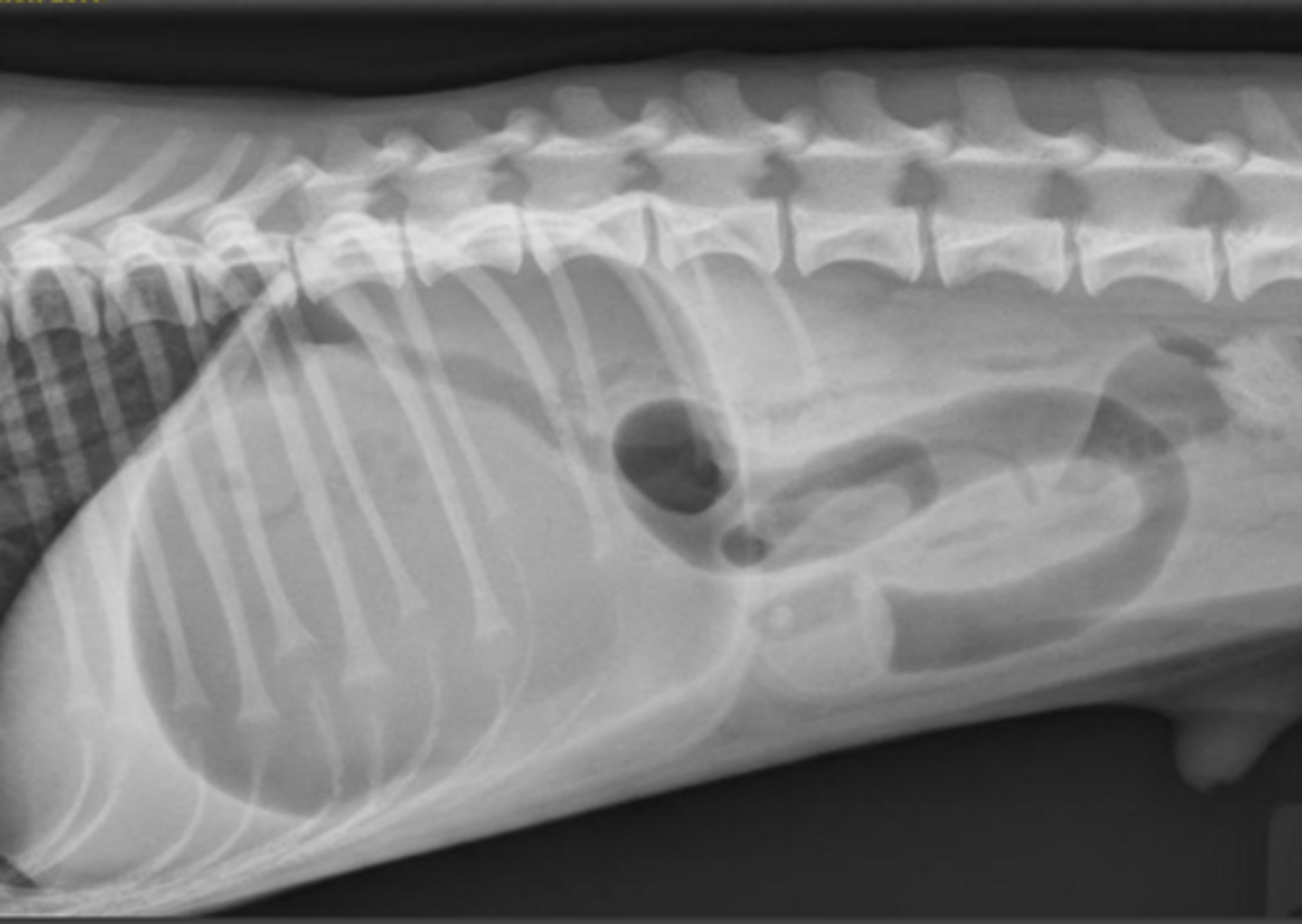
mechanical obstruction - linear foreign body
What abnormality is seen here?
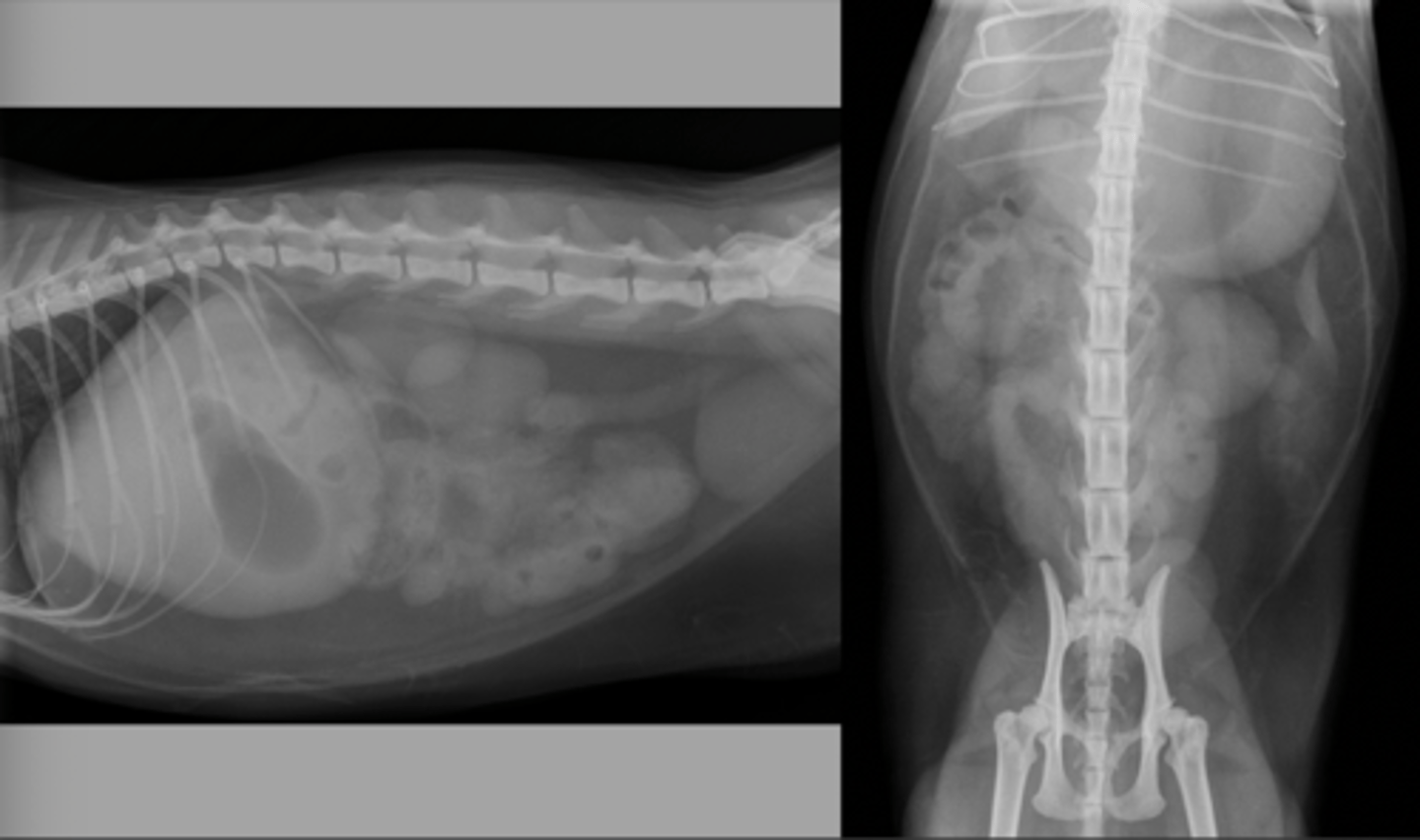
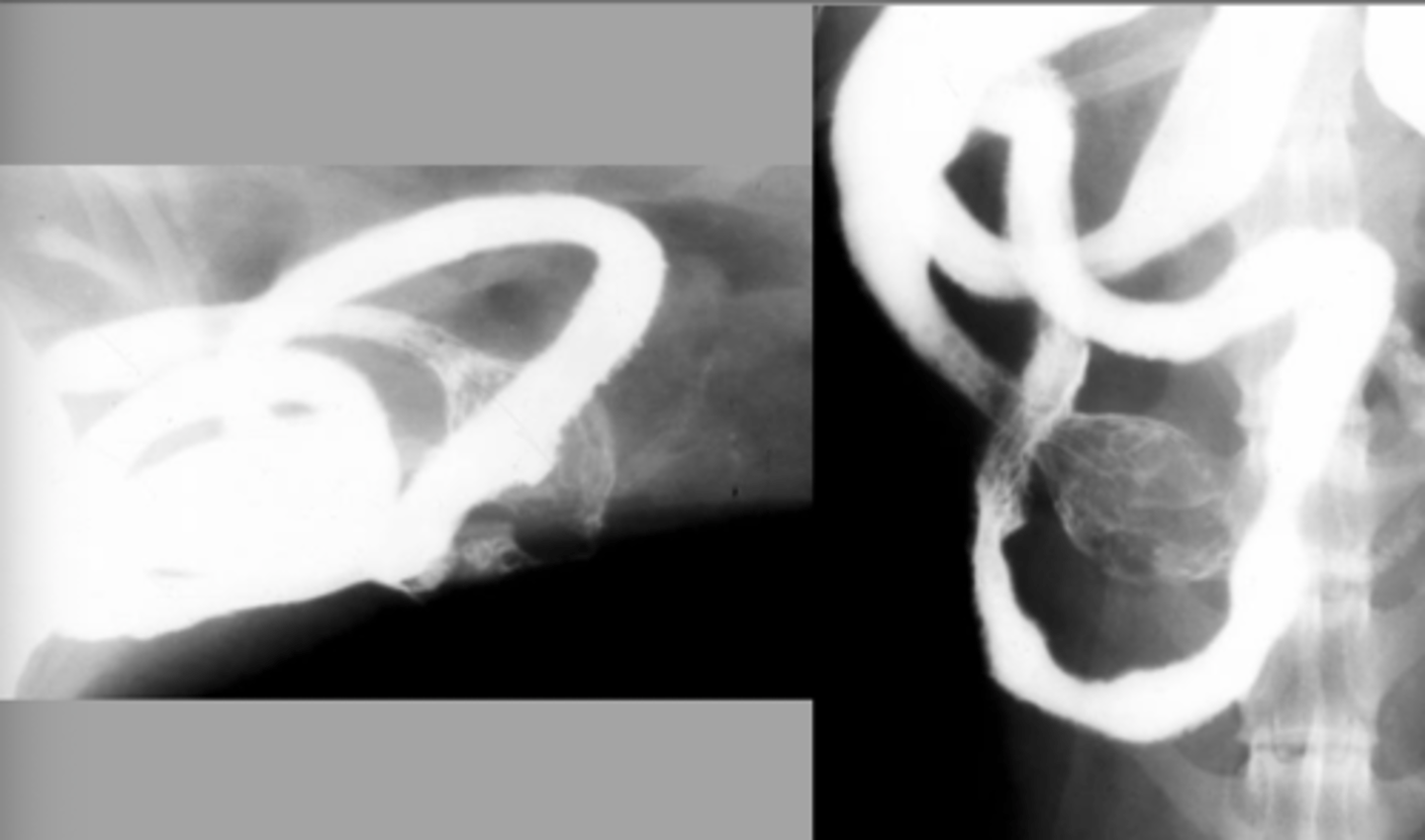
mechanical obstruction - intussusception
What abnormality is seen here?
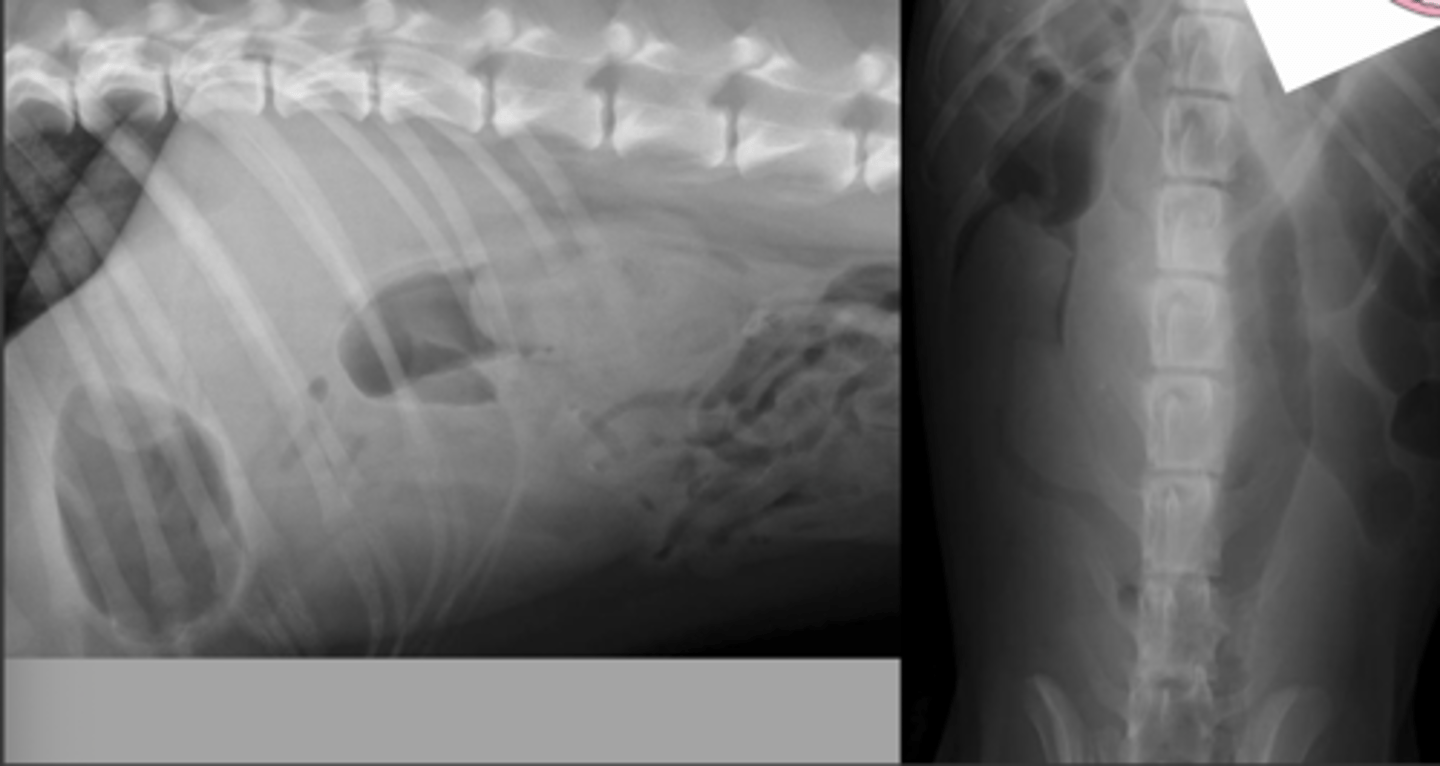
mechanical obstruction - mesenteric volvulus
-see generalized severe small intestinal dilation
What abnormality is seen here?
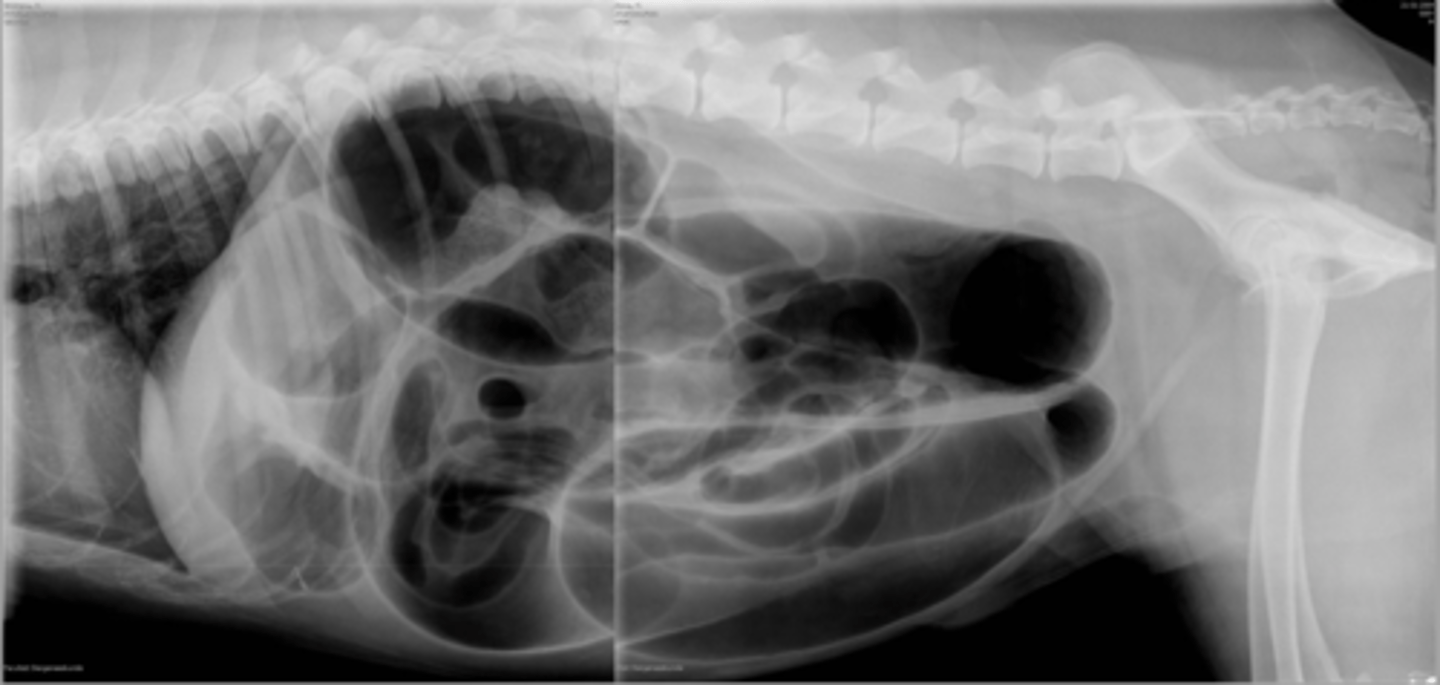
mechanical obstruction - incarceration of loops (herniation of loops through hernia)
What abnormality is seen here?
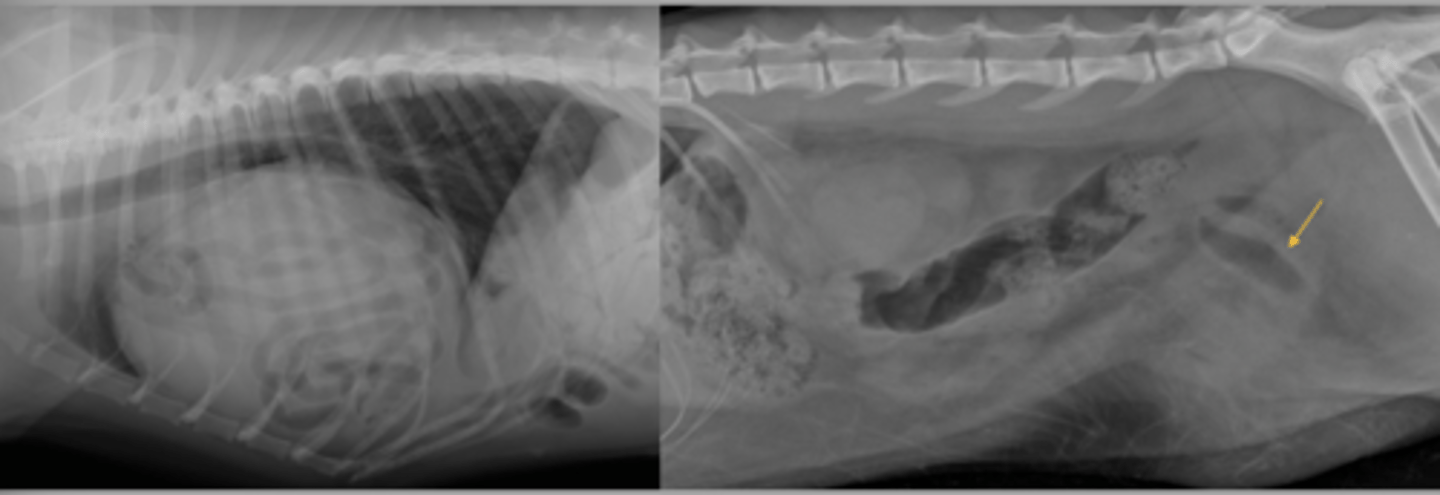
Gravel sign.
-radiopaque material
-proximal to the site of chronic obstruction
-abnormally dilated small intestinal tract
What is a sign associated with chronic small intestinal mechanical obstructions? And what are some of its features?
gravel sign
What sign of an abnormality is seen here?
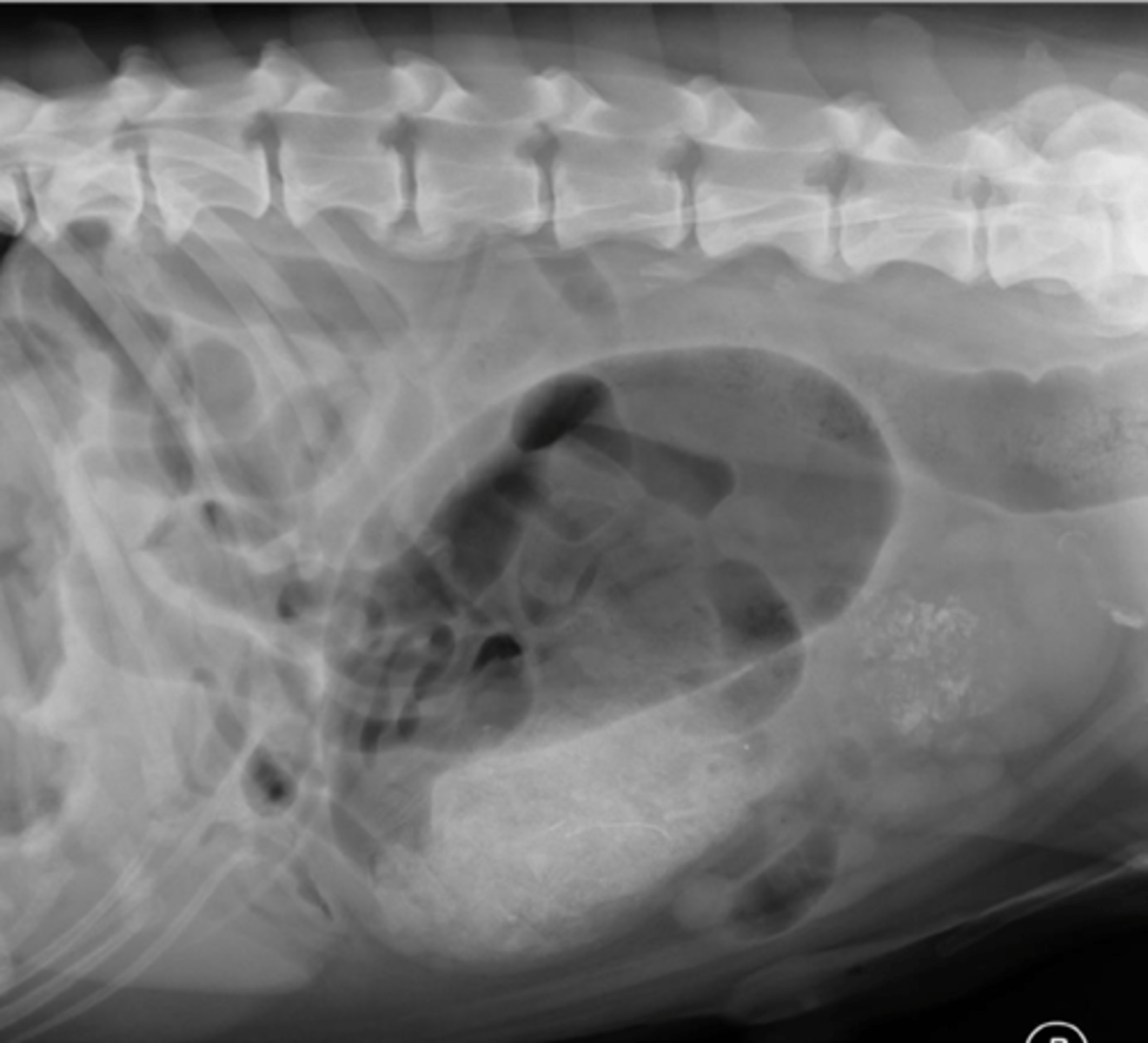
obstructed. segmental dilation (patient was also vomiting)
Obstructed or not?
-foreign material/body
-intussusception
-torsion/volvulus
-incarceration of SI loop (hernias, mesenteric rents, gastropexy site, etc)
-SI masses (neoplasia, granuloma, abscess, etc.)
What are some possible causes of small intestinal obstruction?
mass effect, associated with small intestine on all projections, irregular gas pattern, +/- evidence of obstruction (dilation, gravel sign)
What are some radiographic findings associated with small intestinal masses?
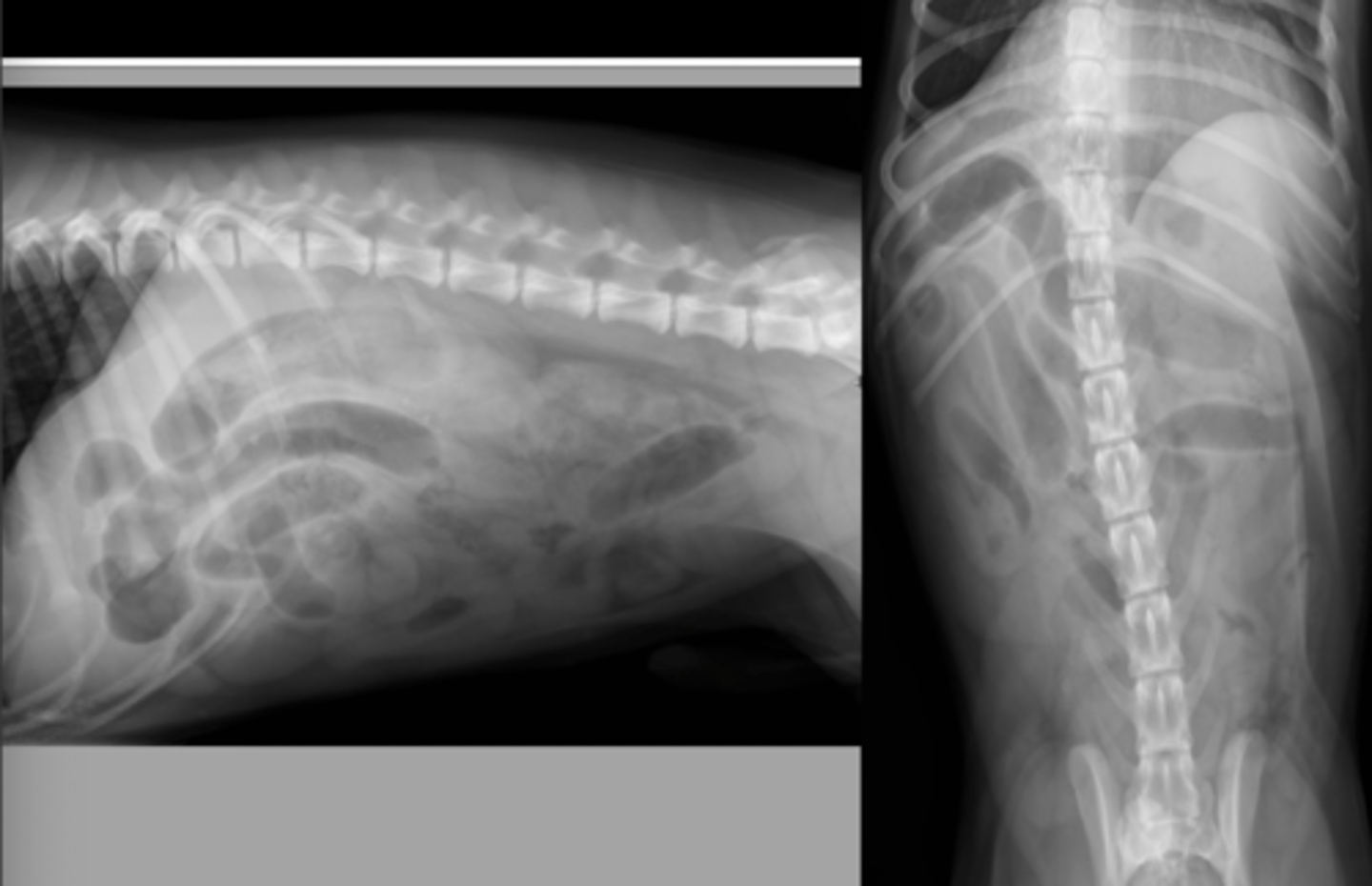
cat small intestinal mass: round cell neoplasia
What abnormality is seen here?
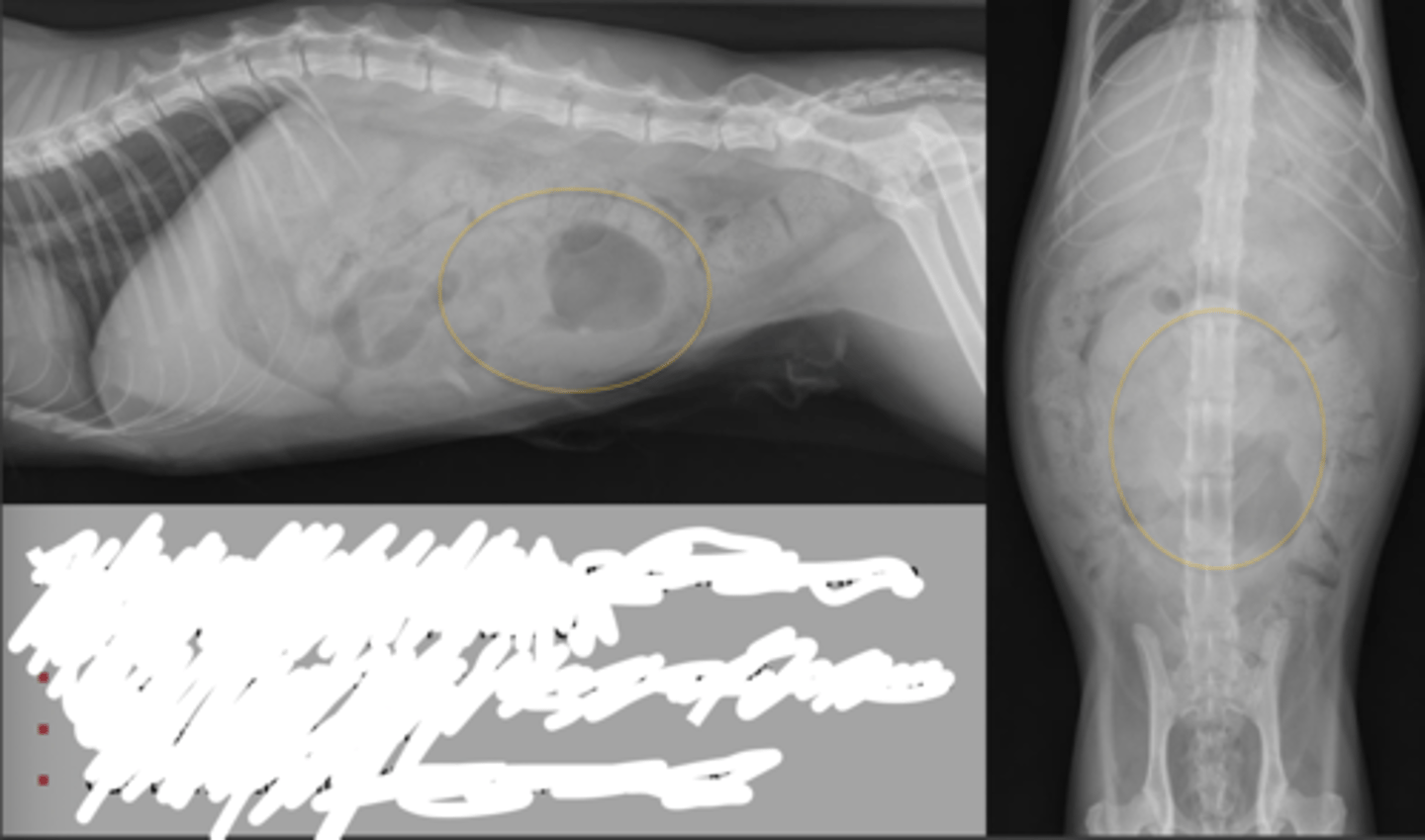
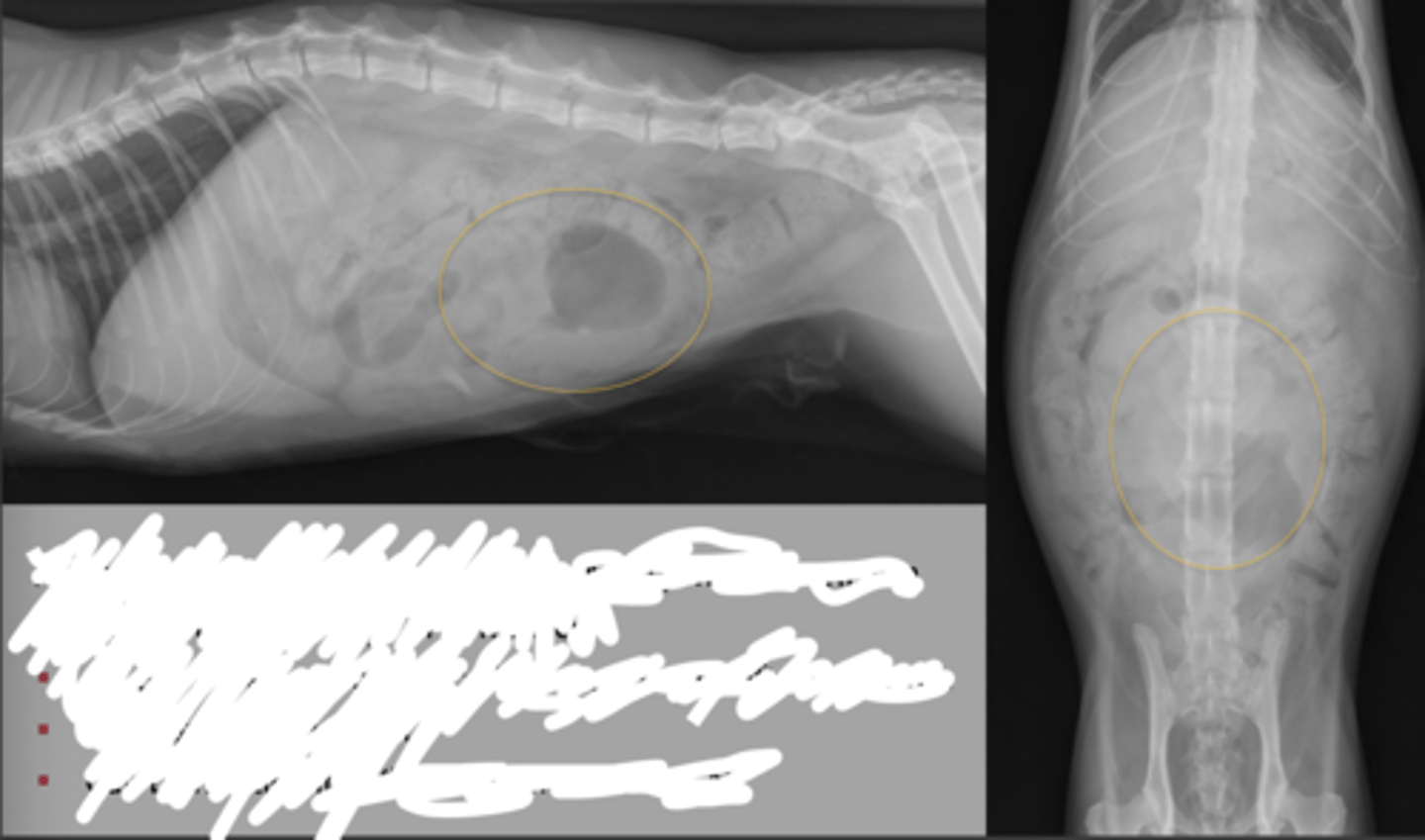
dog small intestinal mass
usually adenocarcinoma, lymphoma, smooth muscle tumors
What abnormality is seen here?
variable, storage organ
Normal Roentgen Signs Large Intestine: Size
tubular, "?" or "shepherds crook" shape
Normal Roentgen Signs Large Intestine: Shape
1: divisions of cecum, ascending/transverse/descending colon and rectum
Normal Roentgen Signs Large Intestine: Number
soft tissue and gas, formed feces: mixed granular soft tissue and gas opacity
Normal Roentgen Signs Large Intestine: Opacity
variable
ascending: short, right of midline
transverse: caudal to stomach
descending: left abdomen
cecum (dogs): often gas filled "C-shaped" in mid right abdomen
Normal Roentgen Signs Large Intestine: Location
smooth serosal and mucosal margins
Normal Roentgen Signs Large Intestine: Margination
assessment of colonic strictures and colonic wall/mucosa
What are some indications for a barium enema?
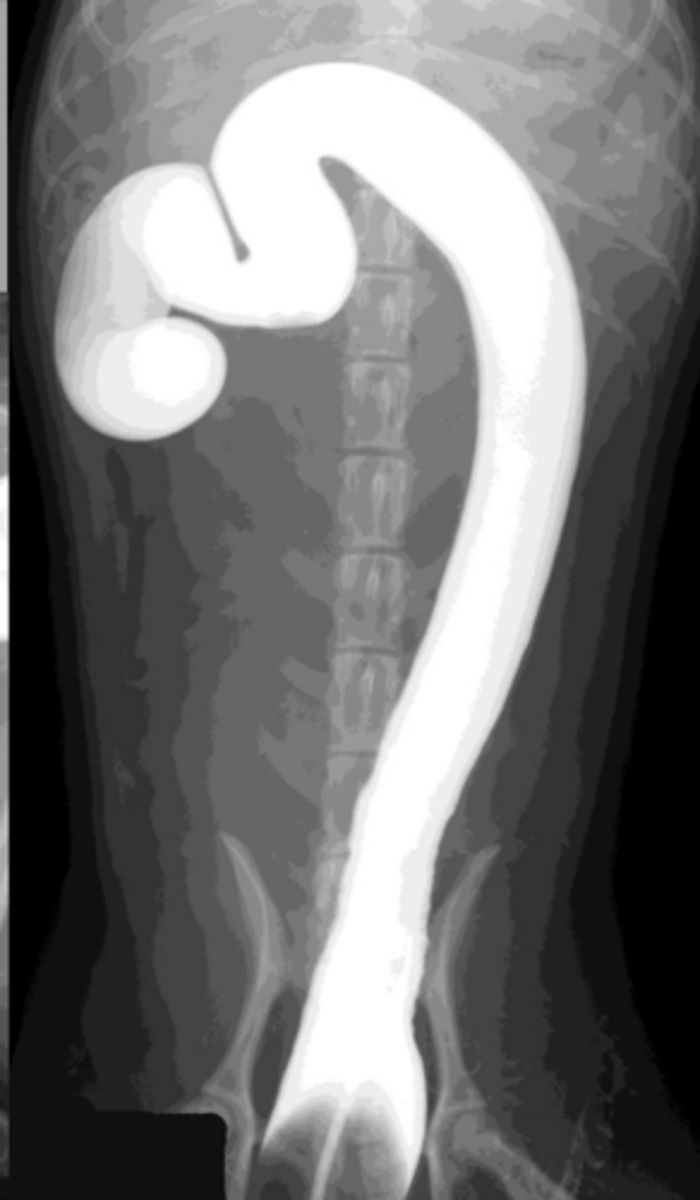
rectal neoplasia
What abnormality is seen here? (with contrast from barium enema)
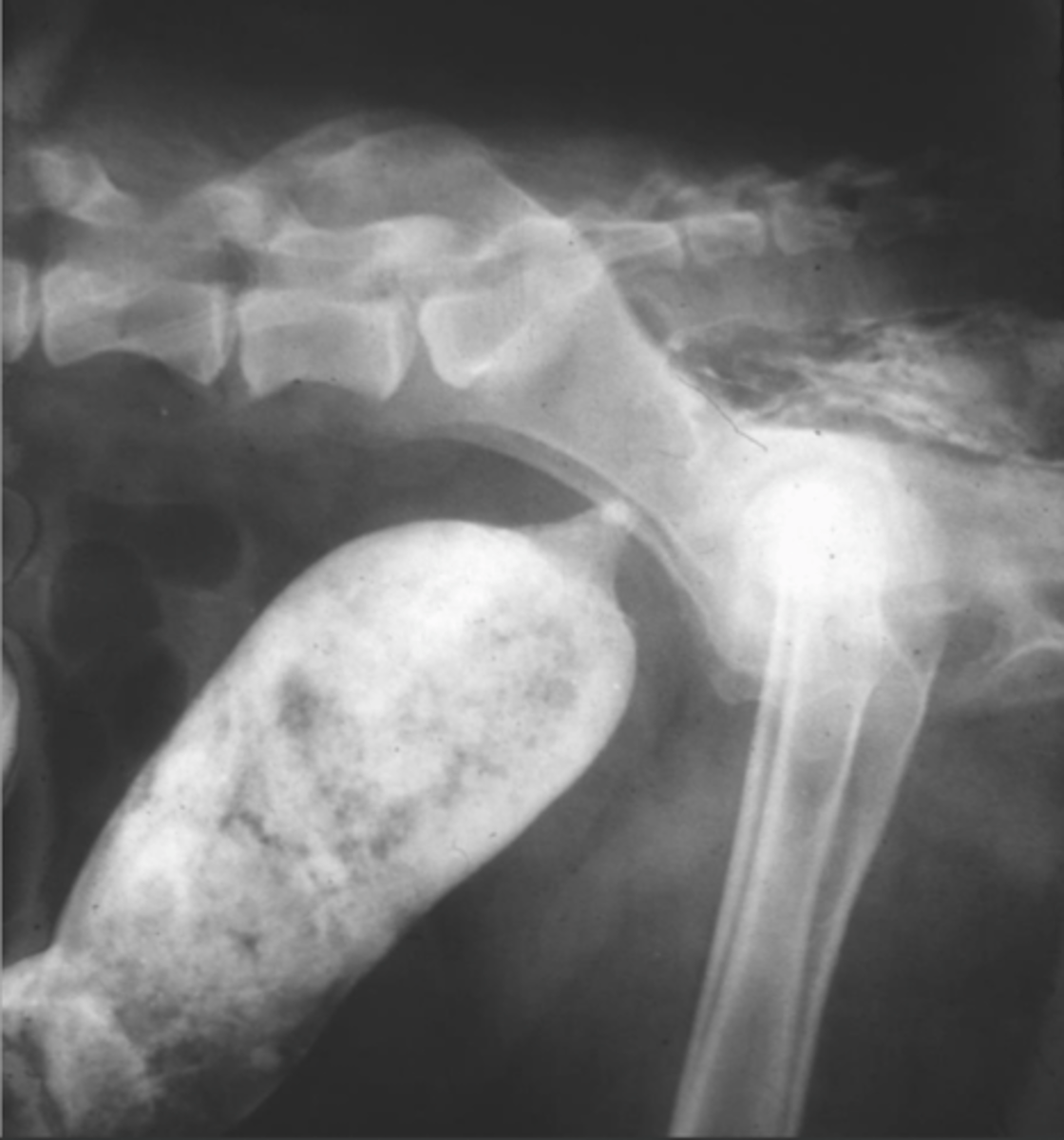
assessment of colonic wall, colonic mucosa
What are indications for a double contrast colonogram?
infrequent or difficult defecation associated with the retention of feces
What is the definition of constipation?
constipation that is refractory to treatment, which occurs where there is a permanent loss of function
What is the definition of obstipation?