L21 Phototransduction (Imported from Quizlet)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
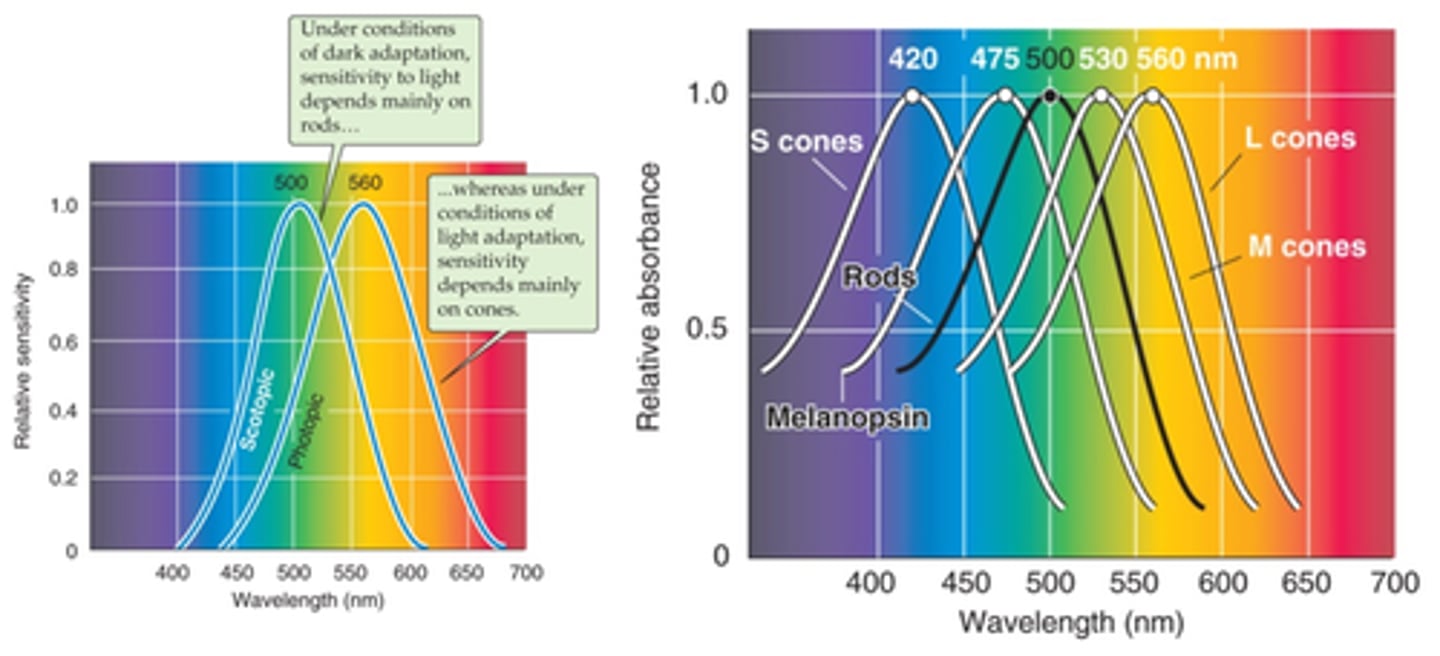
Rhodopsin
What is rod photopigment?
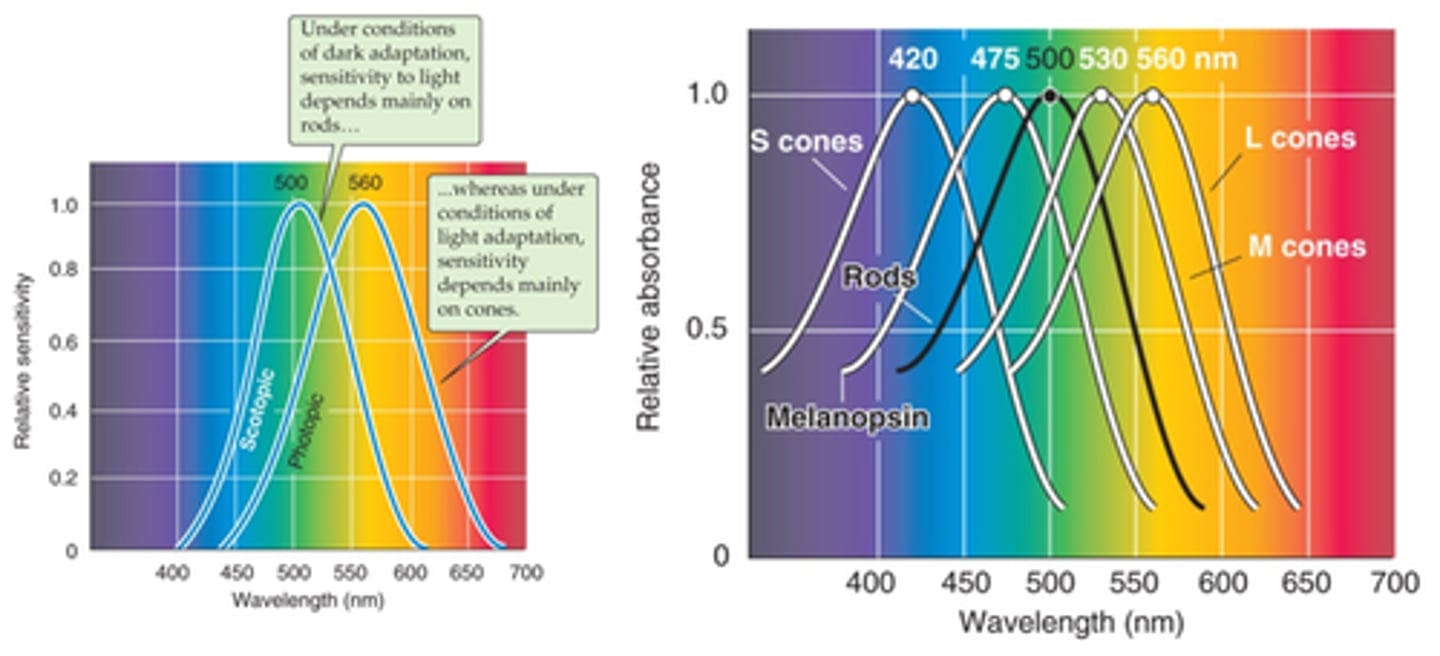
Three varieties of opsins - S, M and L
What are cone photopigments?
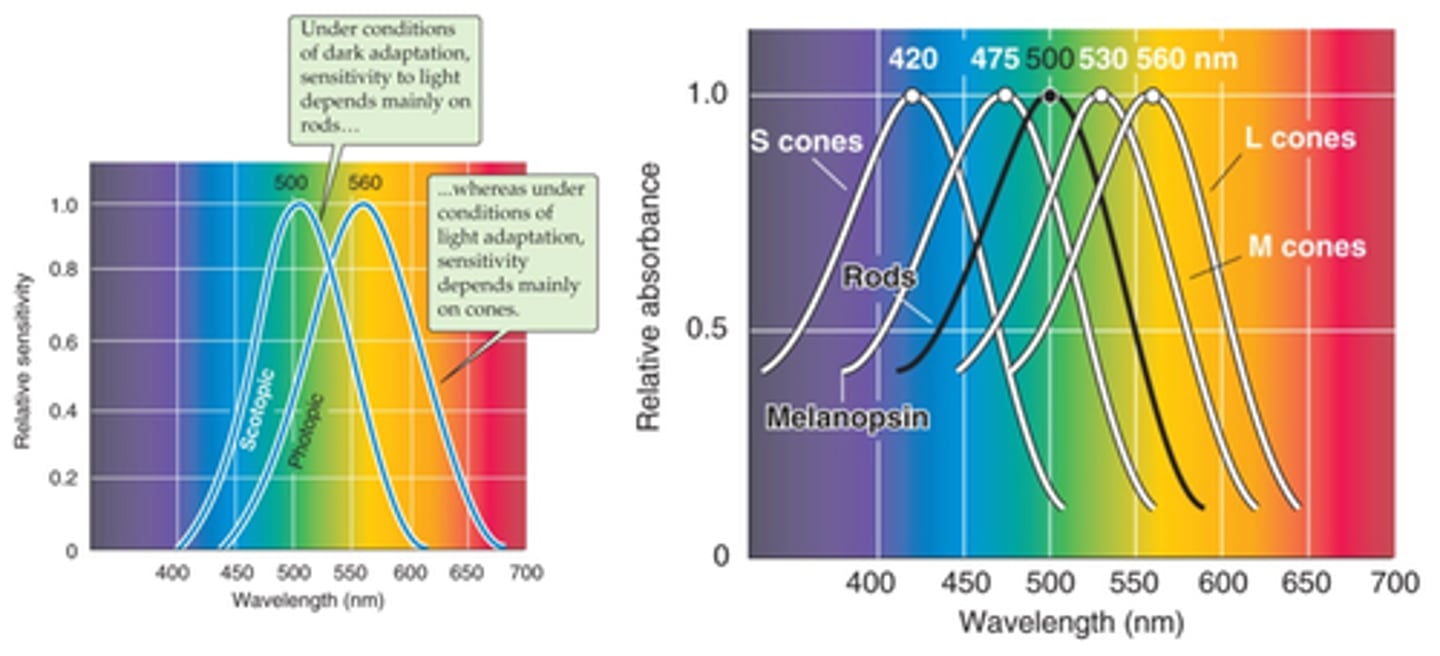
Melanopsin
What is retinal ganglion photopigment?
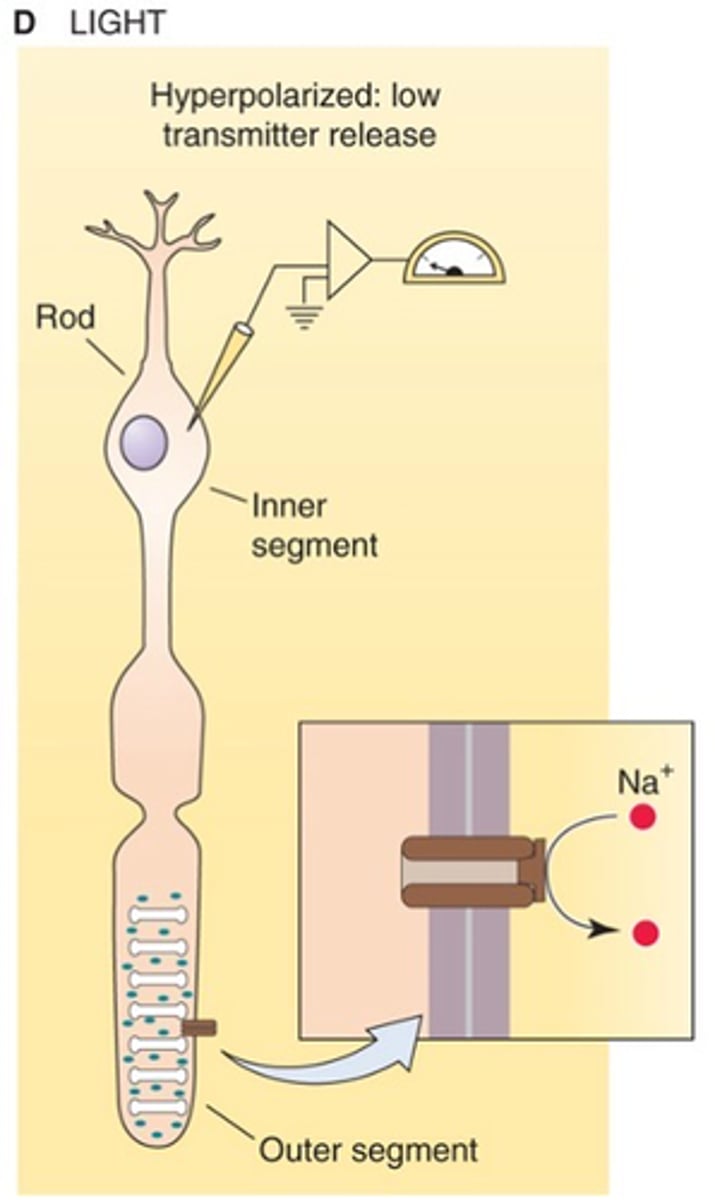
Hyperpolarised
Photoreceptors are ________________ by light
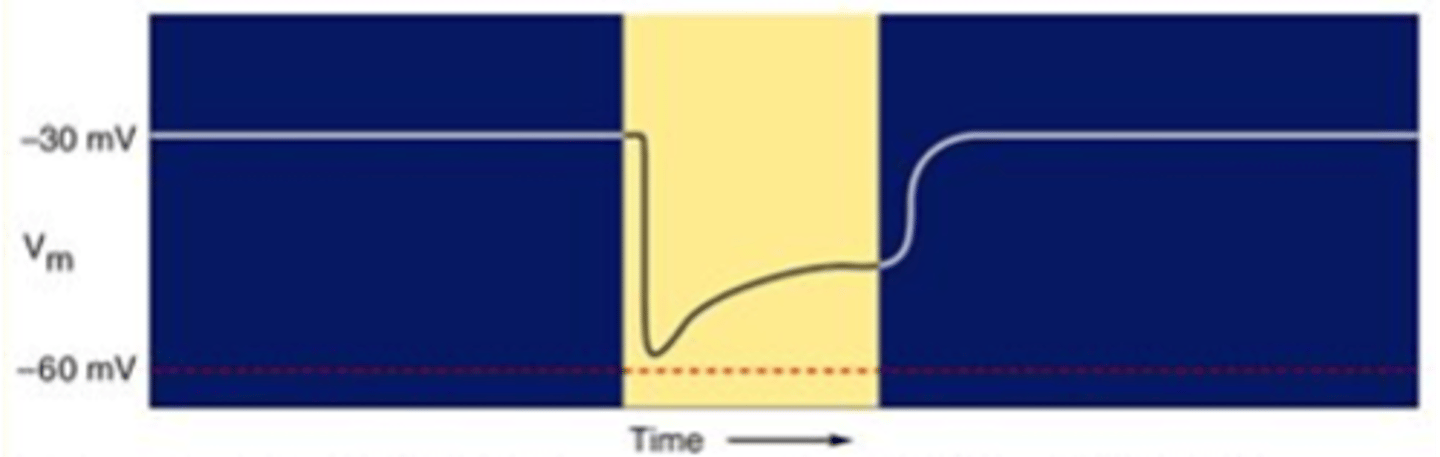
It becomes more negative
When light is switched on, what happens to the membrane potential?
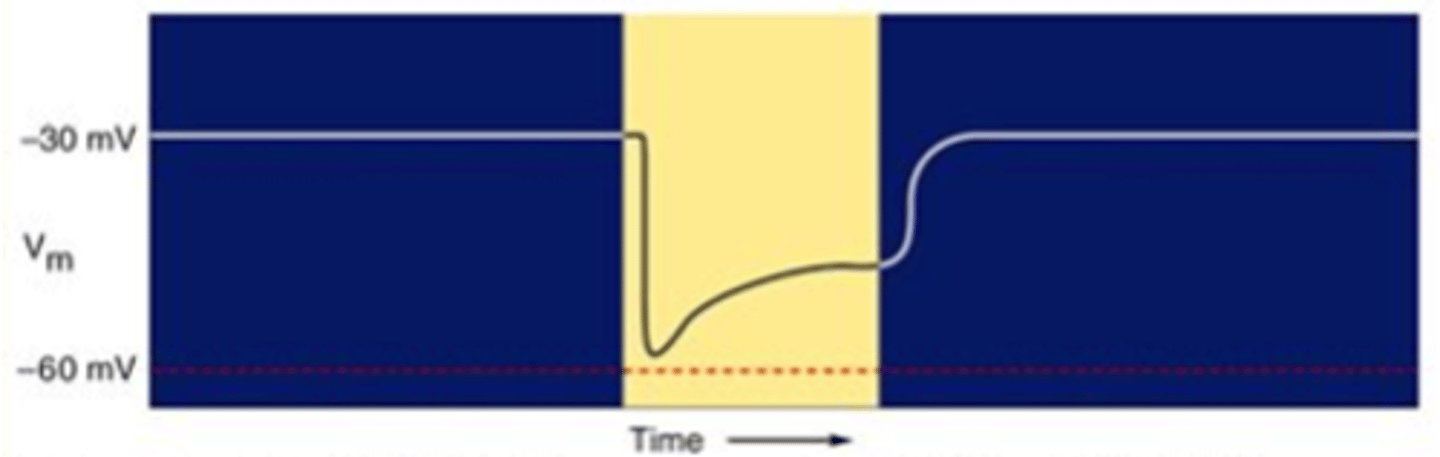
It becomes more positive
When light is switched off, what happens to the membrane potential?
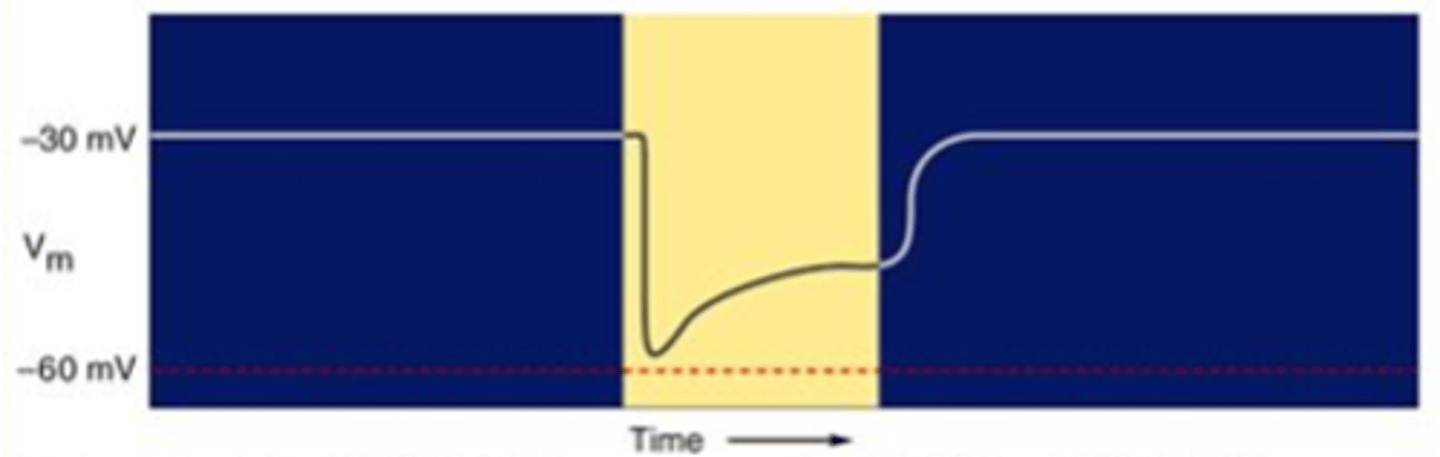
Open, dark current, depolarise
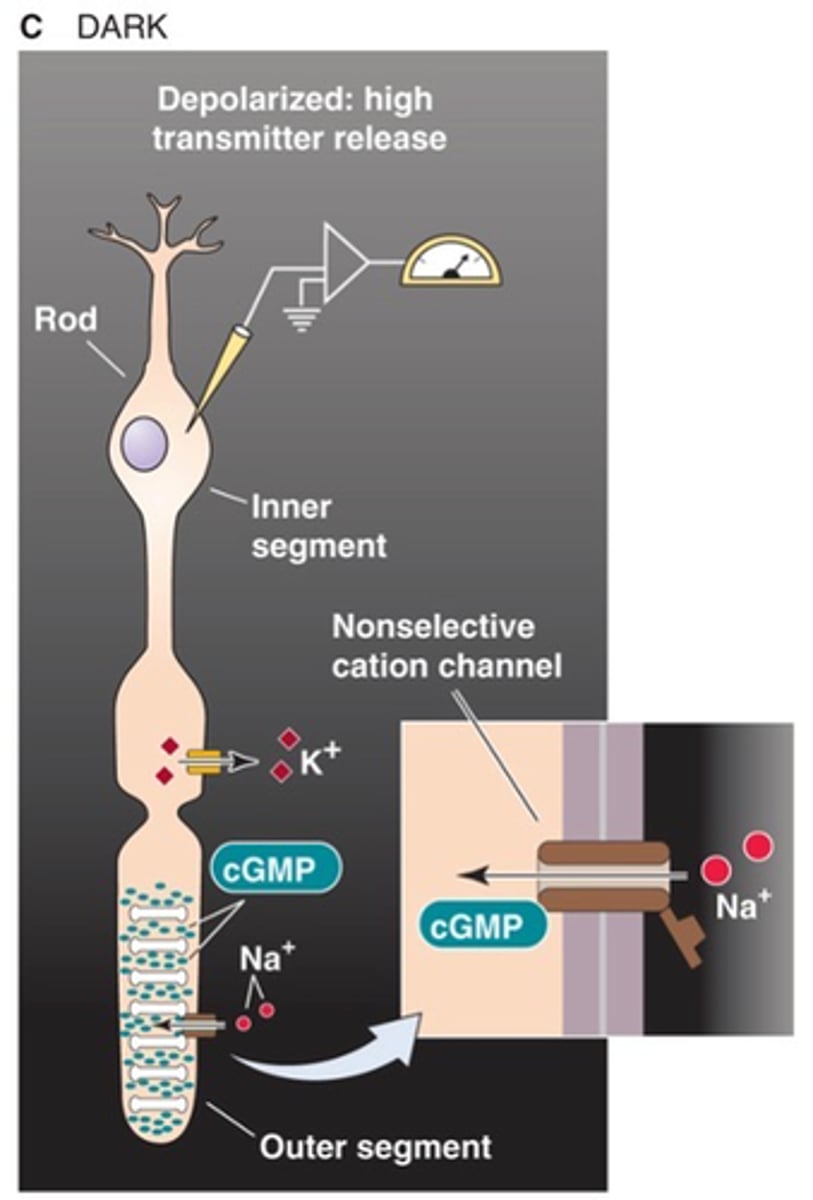
cGMP-gated non-selective cation channels are ______ in the dark allowing a Na+ influx known as the ______ ___________ to _______________ photoreceptors

Potassium channels that are always open, potassium moves out of the photoreceptor which prevents the photoreceptor from become too depolarised
What is present in the inner segment and what does it do?
Decreases, closing, hyperpolarising
Light _____________ cGMP levels, __________ the channels and preventing Na+ influx, _____________ photoreceptors
Cyclic guanosine monophosphate
What does cGMP stand for?
Na/K pump is found in the inner segment that removes Na in exchange for K
To maintain the Na gradient, what is found and what does it do?
5-7
_-_ photons can evoke a sensation of light in humans
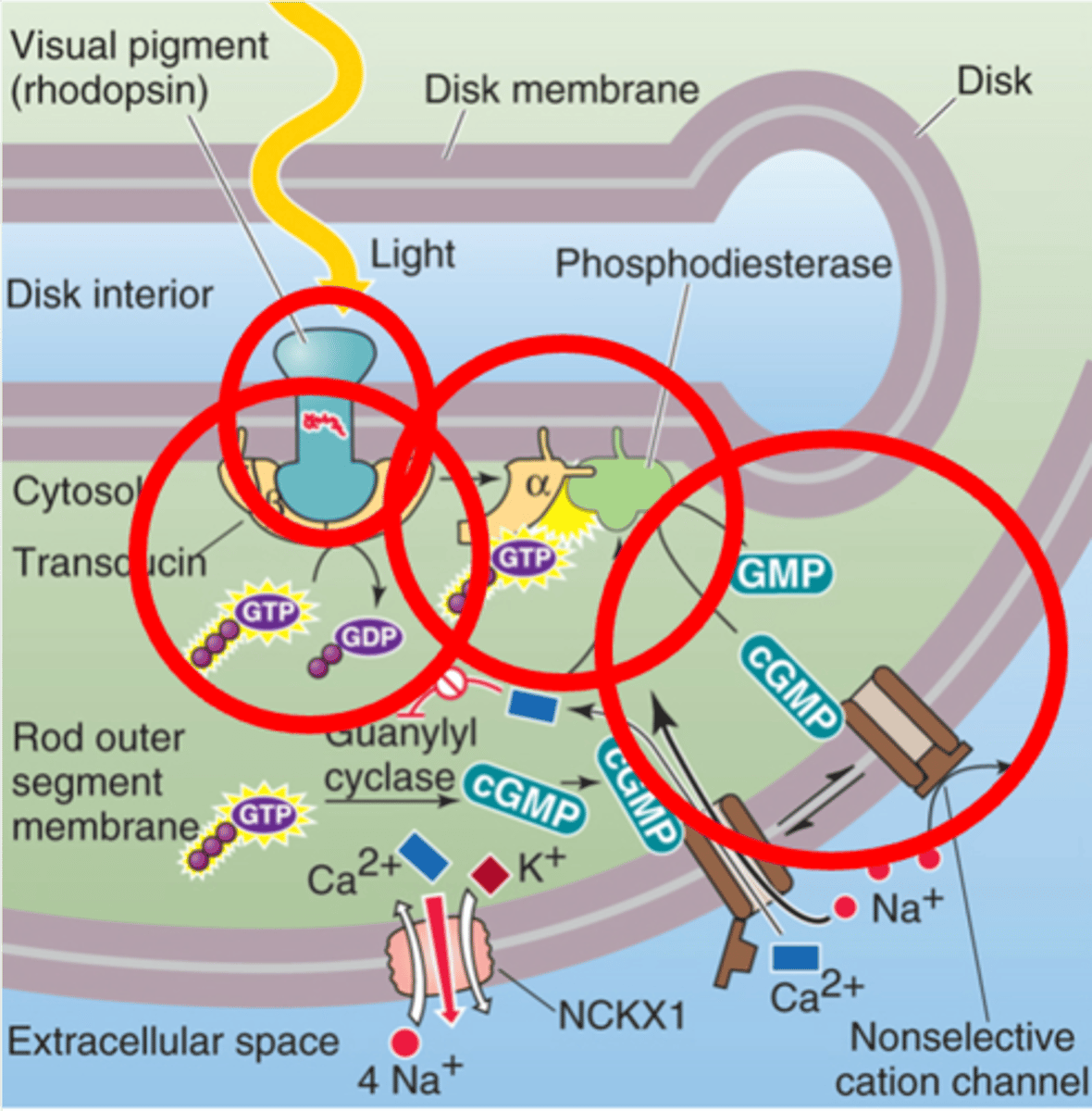
Rhodopsin
______________ is activated by light
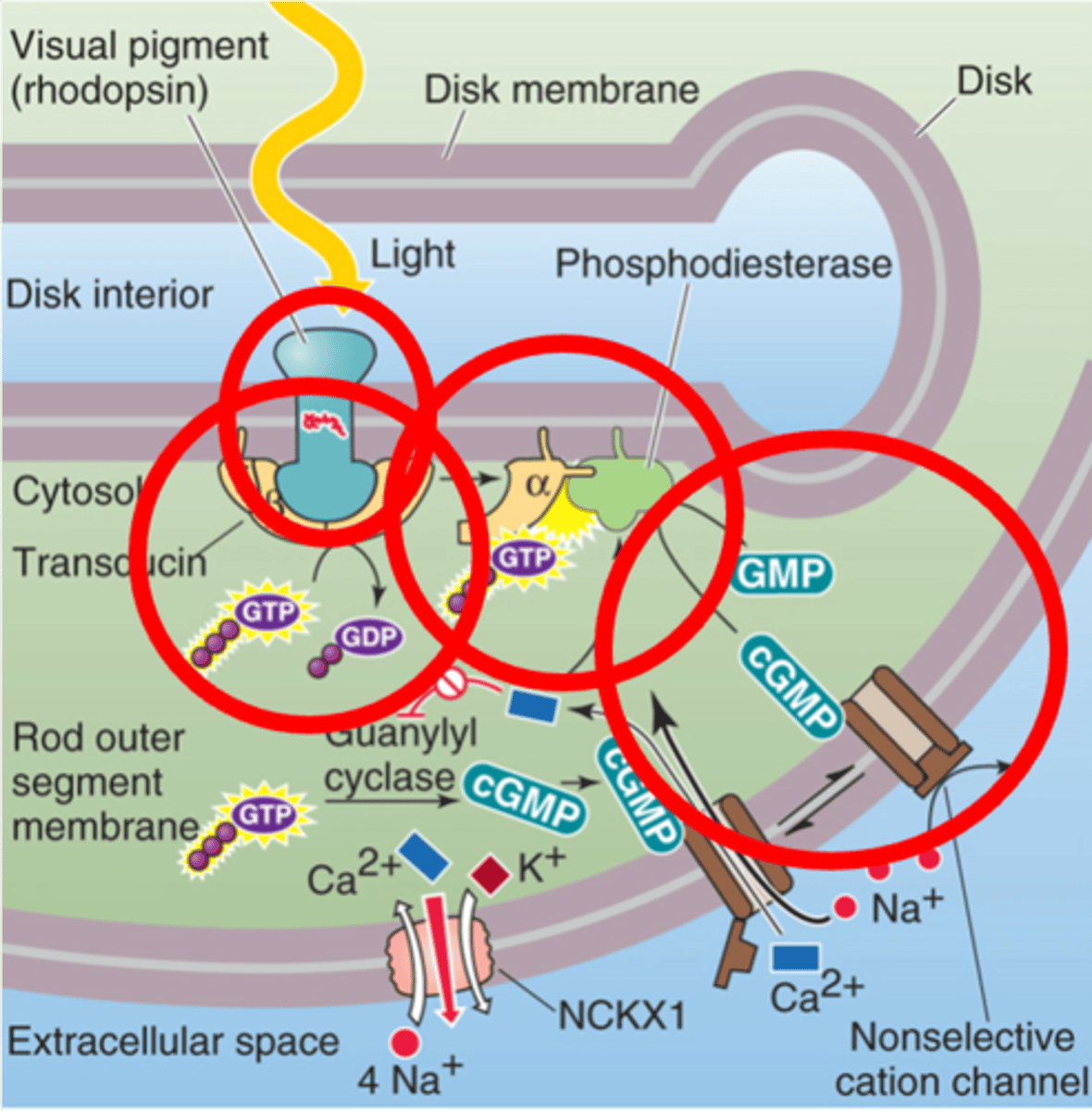
Transducin, transducin GTP
Rhodopsin stimulates the G-protein ____________, to become ____________ _____
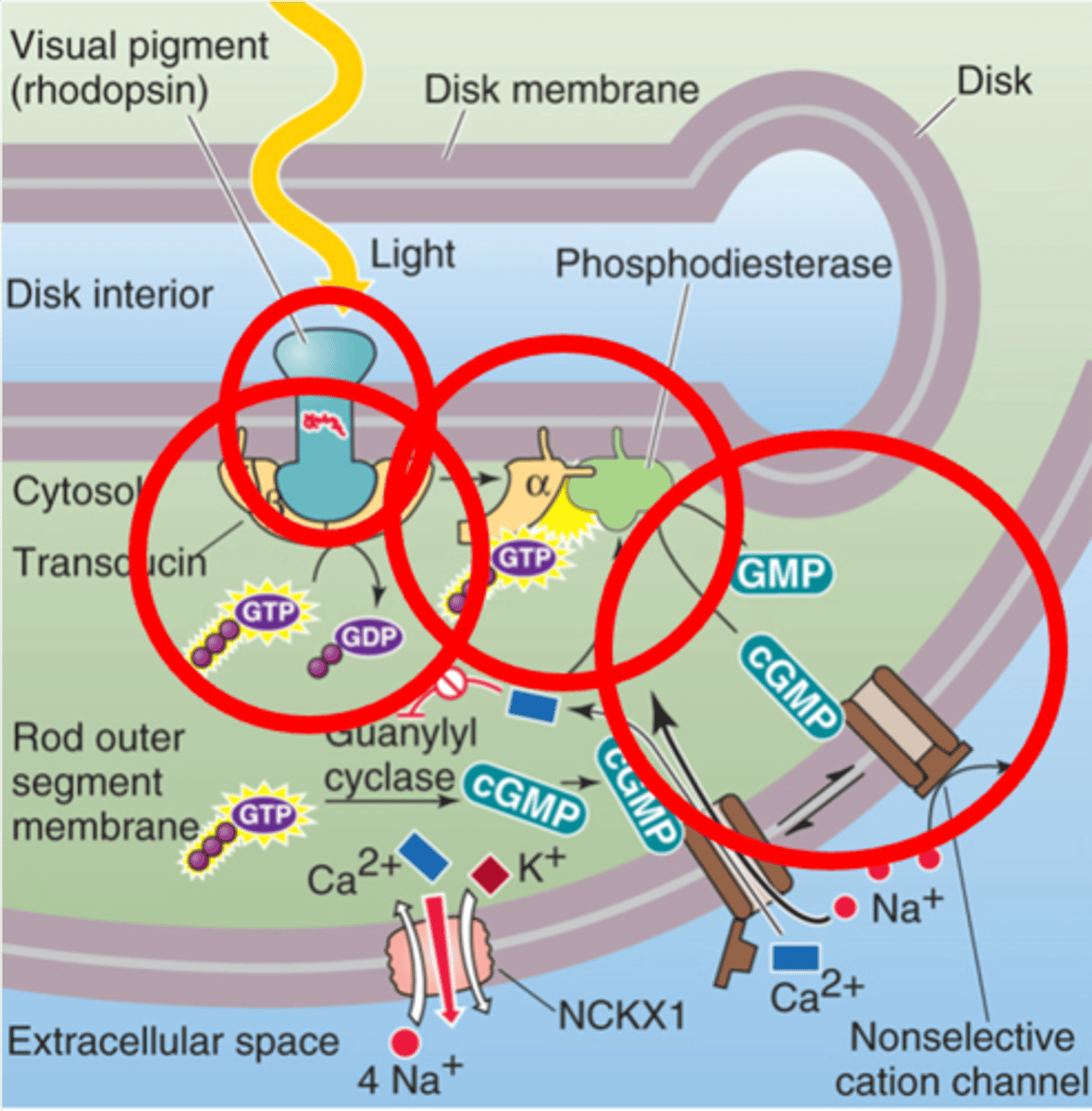
Phosphodiesterase
The α subunit activates the enzyme _______________________ (PDE)
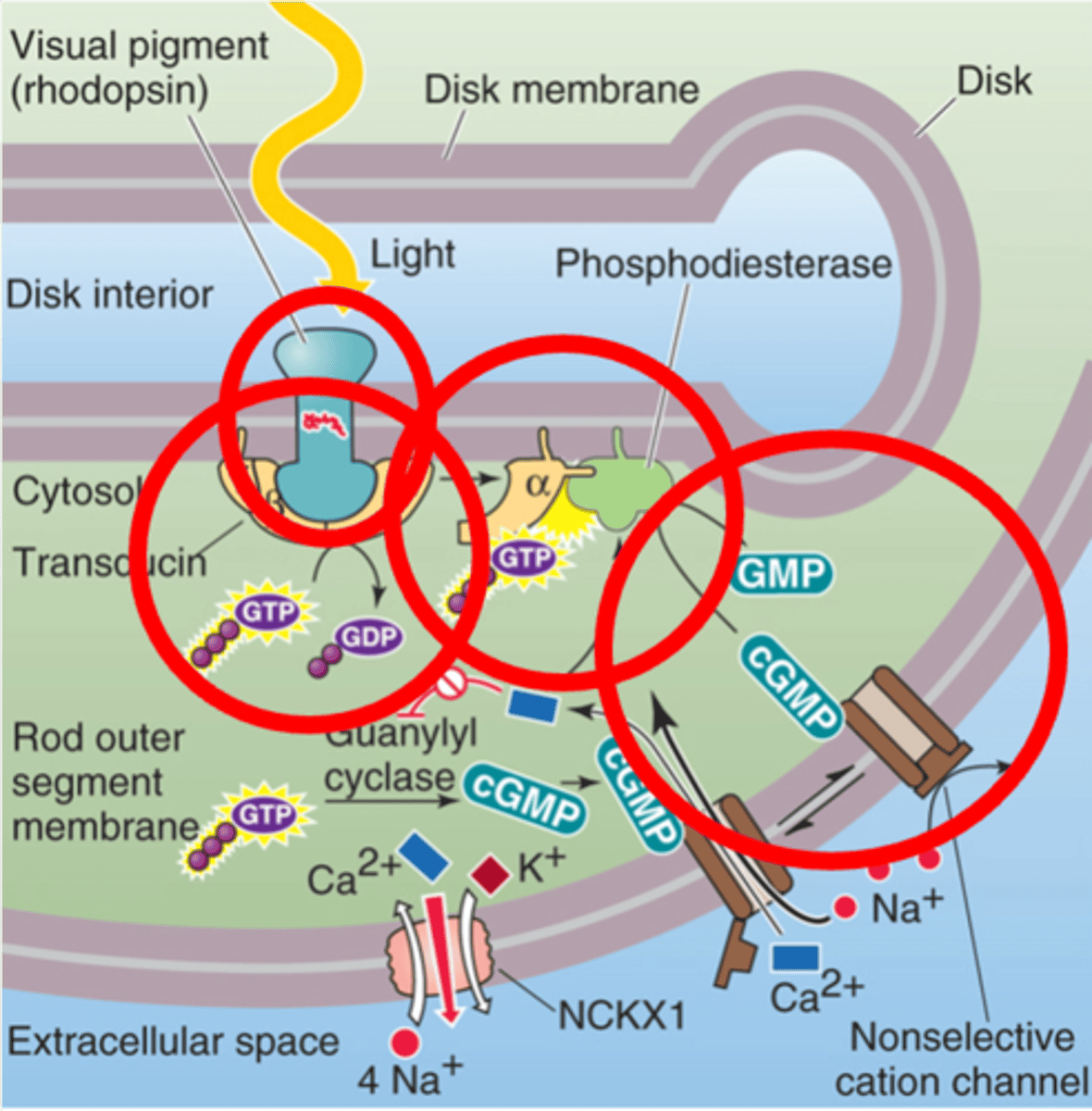
cGMP, Na+ channels
PDE reduces _________ levels, closing ___ _____________
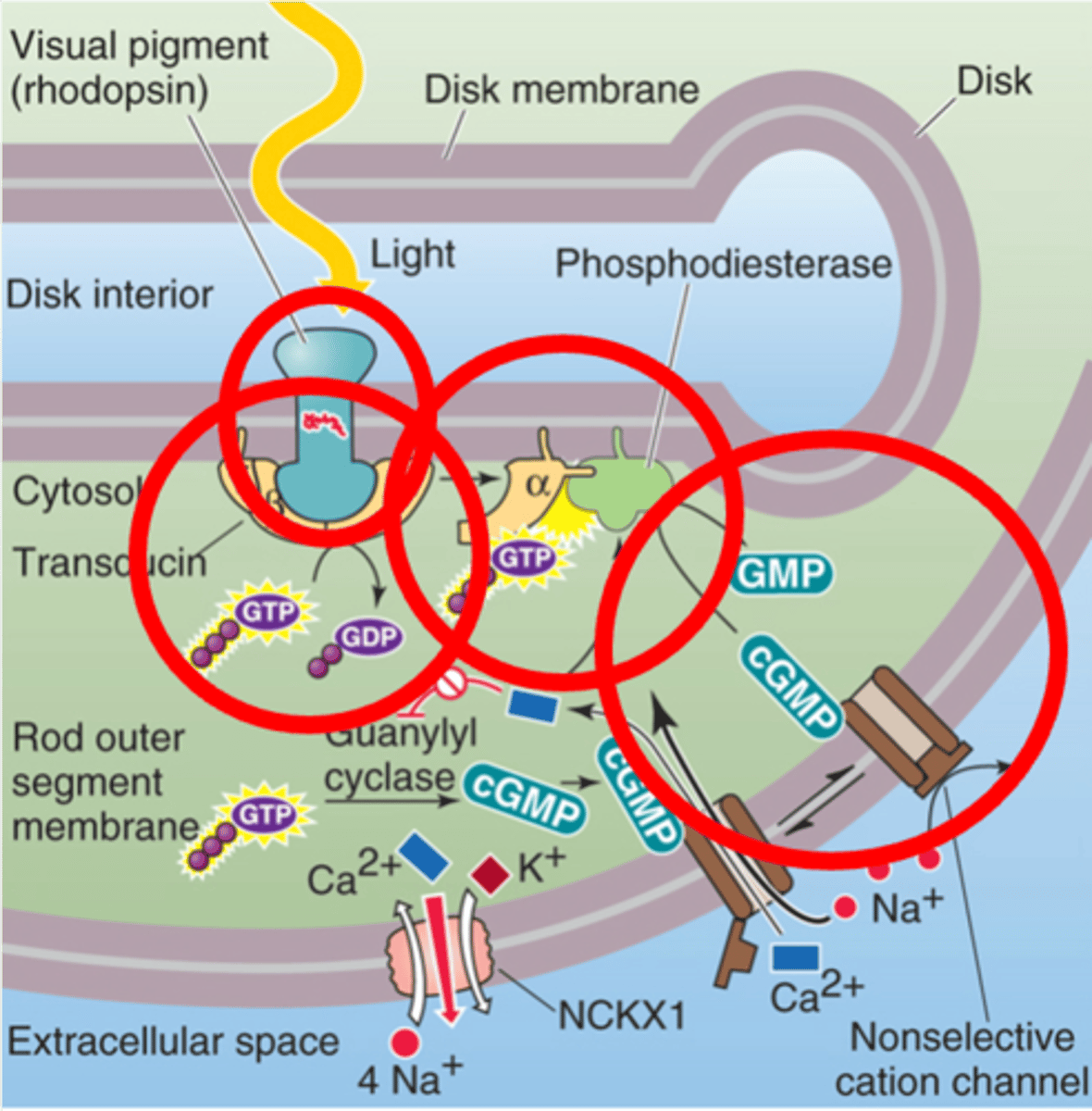
Amplification, enzyme cascade
Signal ______________ occurs as this is an _____________ ____________
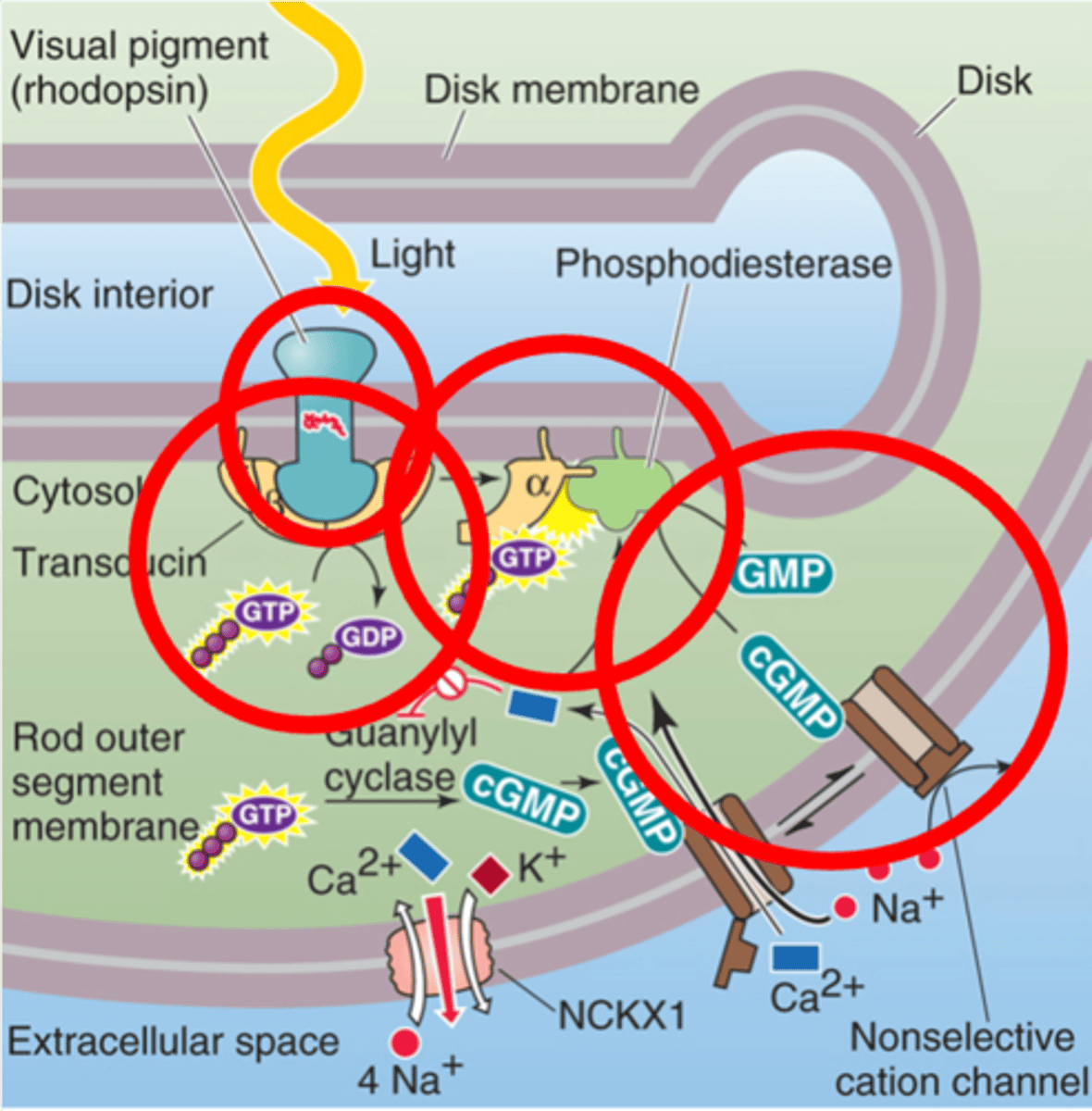
Retinal and opsin
Rhodopsin is made of 2 key components, what are they?
G-protein coupled receptor
Opsin is a member of what family?
Shape, conformational change, transducin
Retinal absorbs the photos and changes its _________, leading to a _______________ ________ in opsin - this allows opsin to activate ______________
A current equivalent to 1 million Na+ ions
Absorption of 1 photon can lead to the hydrolysis of ~1400cGMP molecules and suppresses what?
Guanylyl cyclase
In the dark cGMP is constitutively produced by the enzyme ____________ __________
Cone
This example response is from which: a rod or cone?
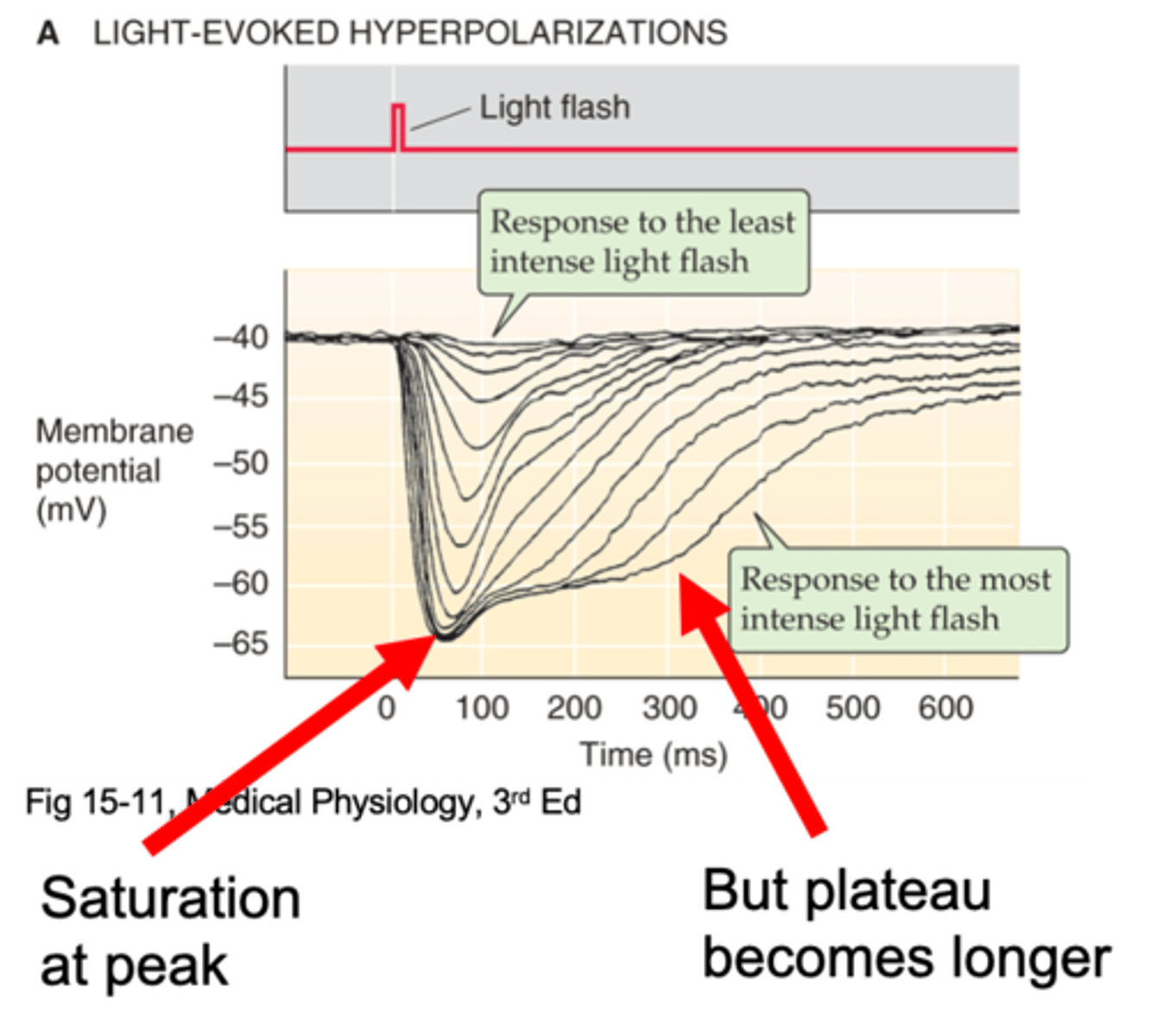
They become easily saturated
Rods cannot process bright light, why?
Bleached, low, hyperpolarisation
Rhodopsin is ___________, cGMP levels are so _______ that no additional _________________ can occur
In bright light
Cones are not saturated as easily, so when are they used?
Hyperpolarise greatly
Photoreceptors initially do what?

Depolarise, bright light
Photoreceptors gradually _______________ with continued ________ ________
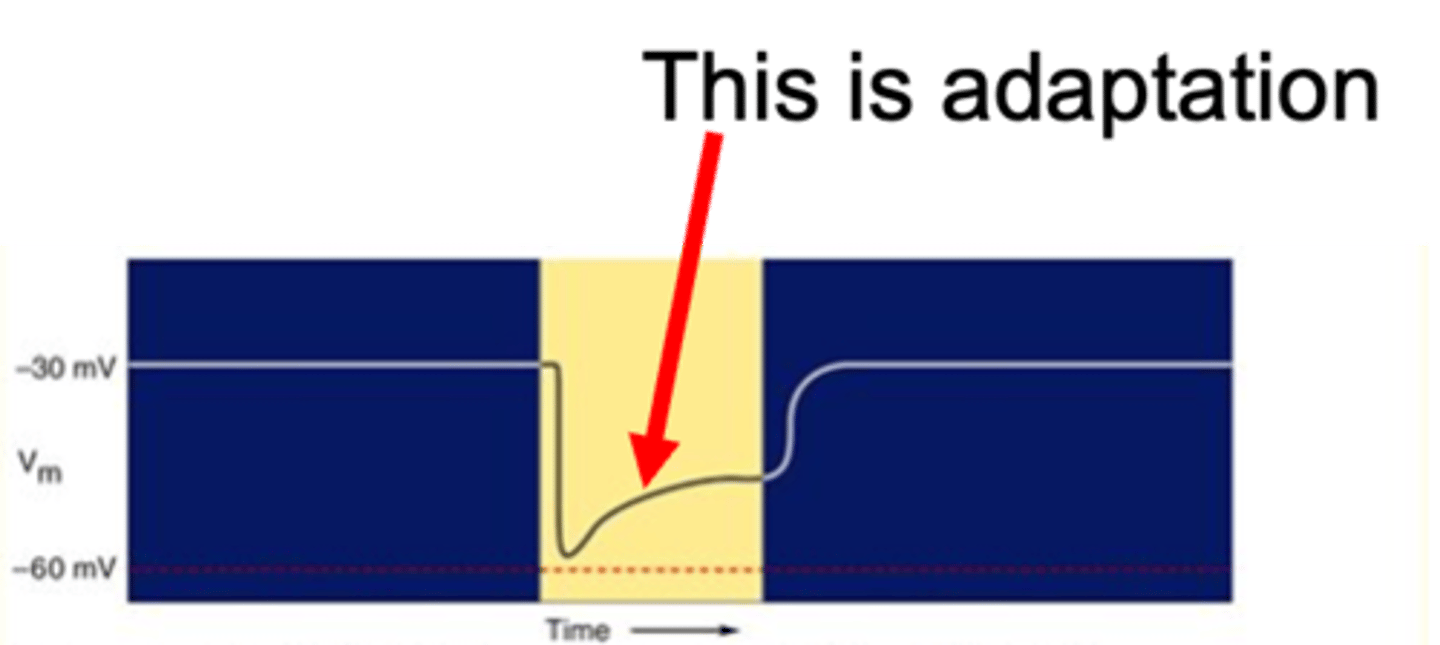
Calcium
What does light adaptation require?
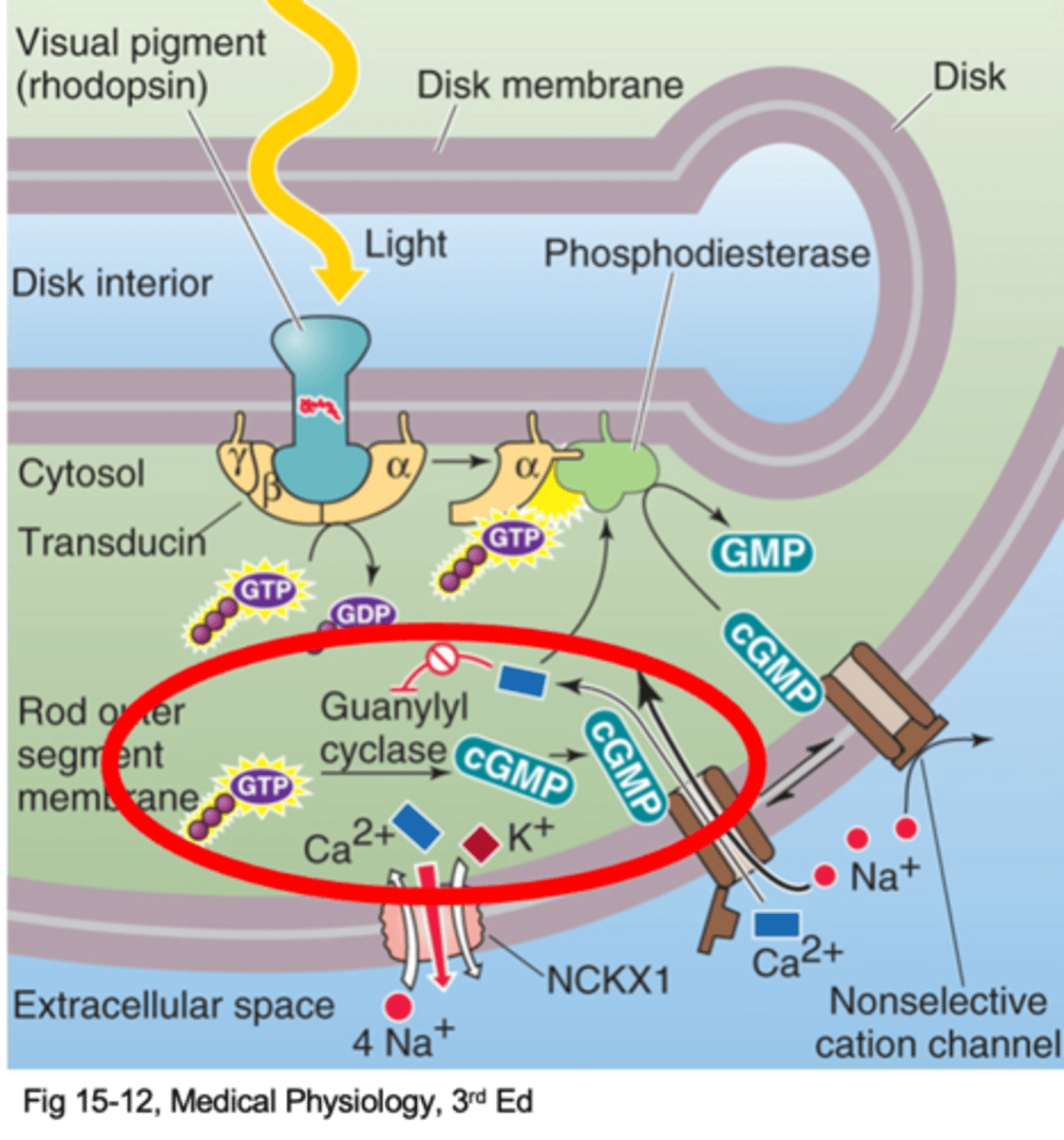
Ca2+ normally enters the cells and blocks guanylyl cyclase
This reduces cGMP production, so closes some ion channels
Describe light adaptation in the dark
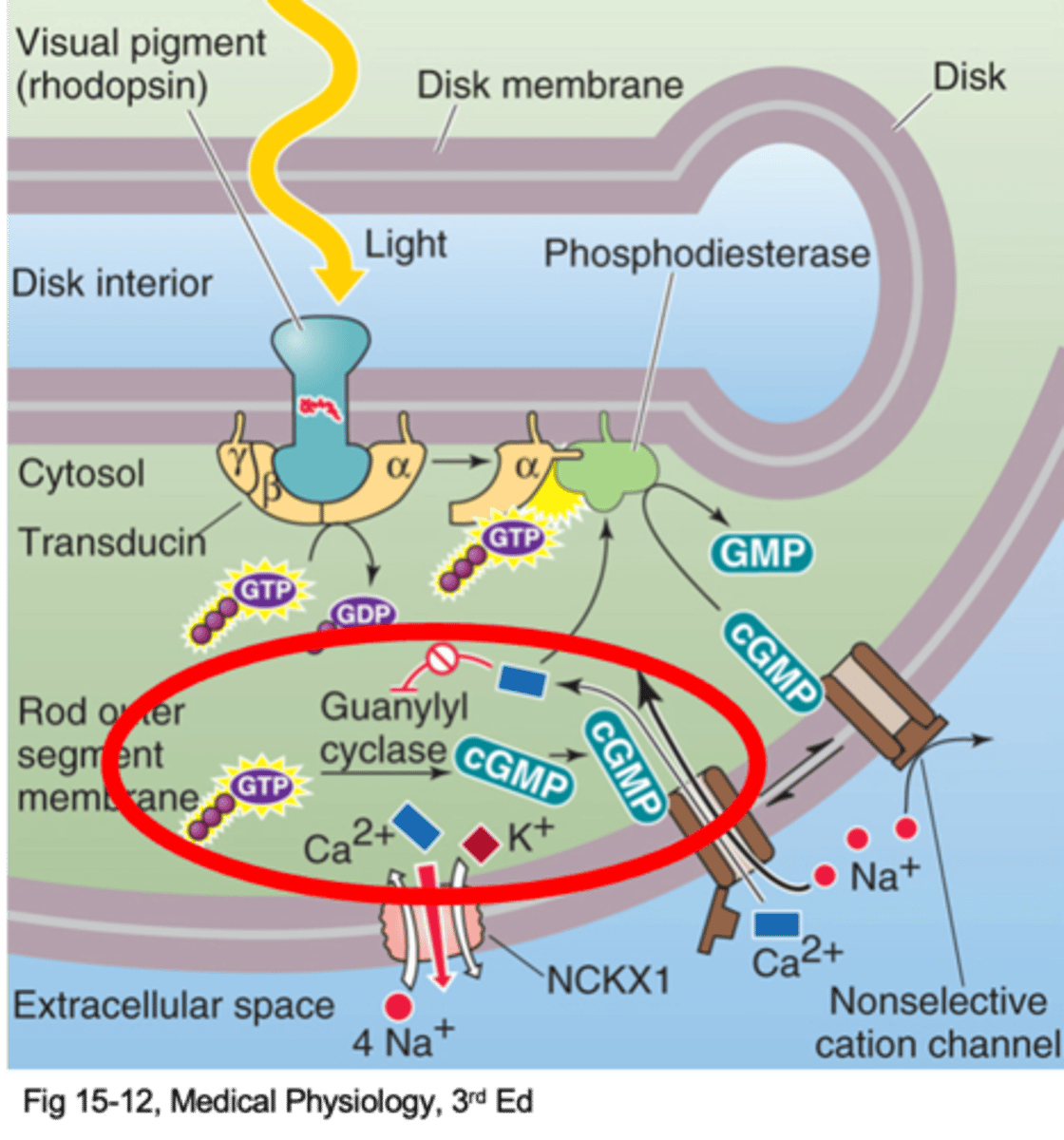
Channels are shut so Ca2+ cannot enter cells
Block on guanylyl cyclase is relased
More cGMP produced = more channels open
Describe light adaptation in the light
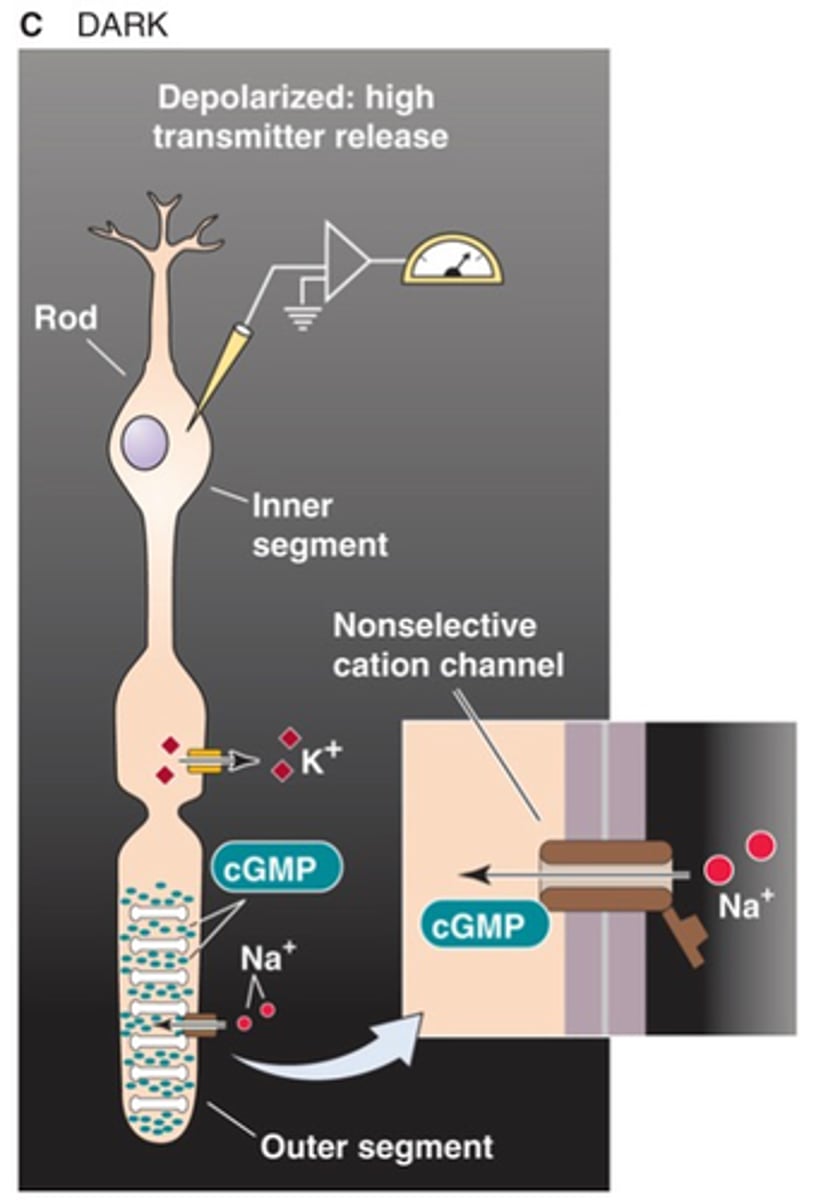
Depolarises photoreceptors
The Na+ entry through cGMP-dependent non-selective cation channels (the dark current) does what in dark conditions?
Photopigments, breakdown
Photons activate ______________ leading to cGMP ______________
Adaptation to continued light stimulation
Calcium mediates what?
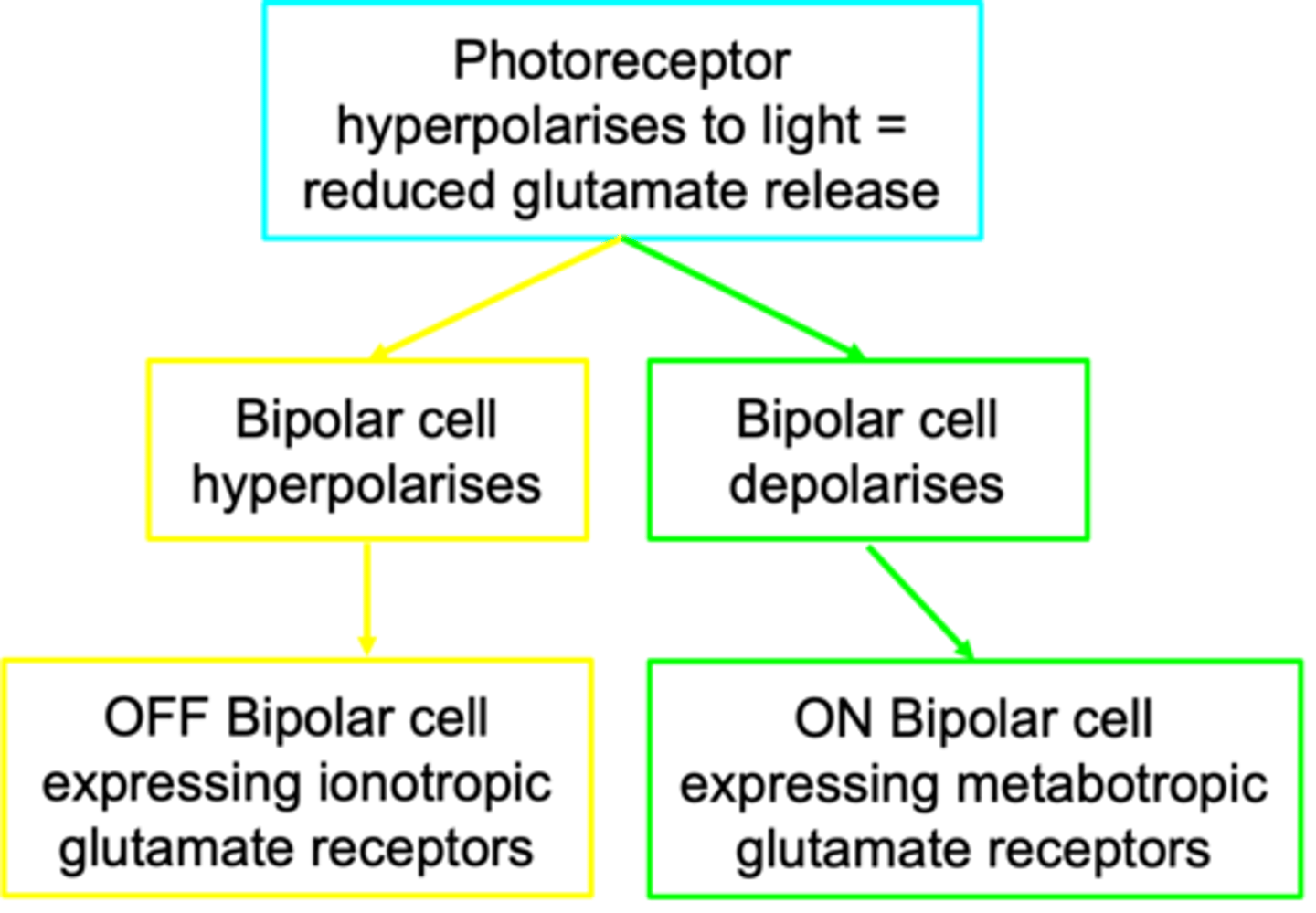
No, there are different types of bipolar cells and bipolar cells have complex receptive fields
Are bipolar cells just relay neurons that pass information straight from photoreceptors to retinal ganglion cells? Explain your reasoning
Glutamate
This is classified based on bipolar response to _____________
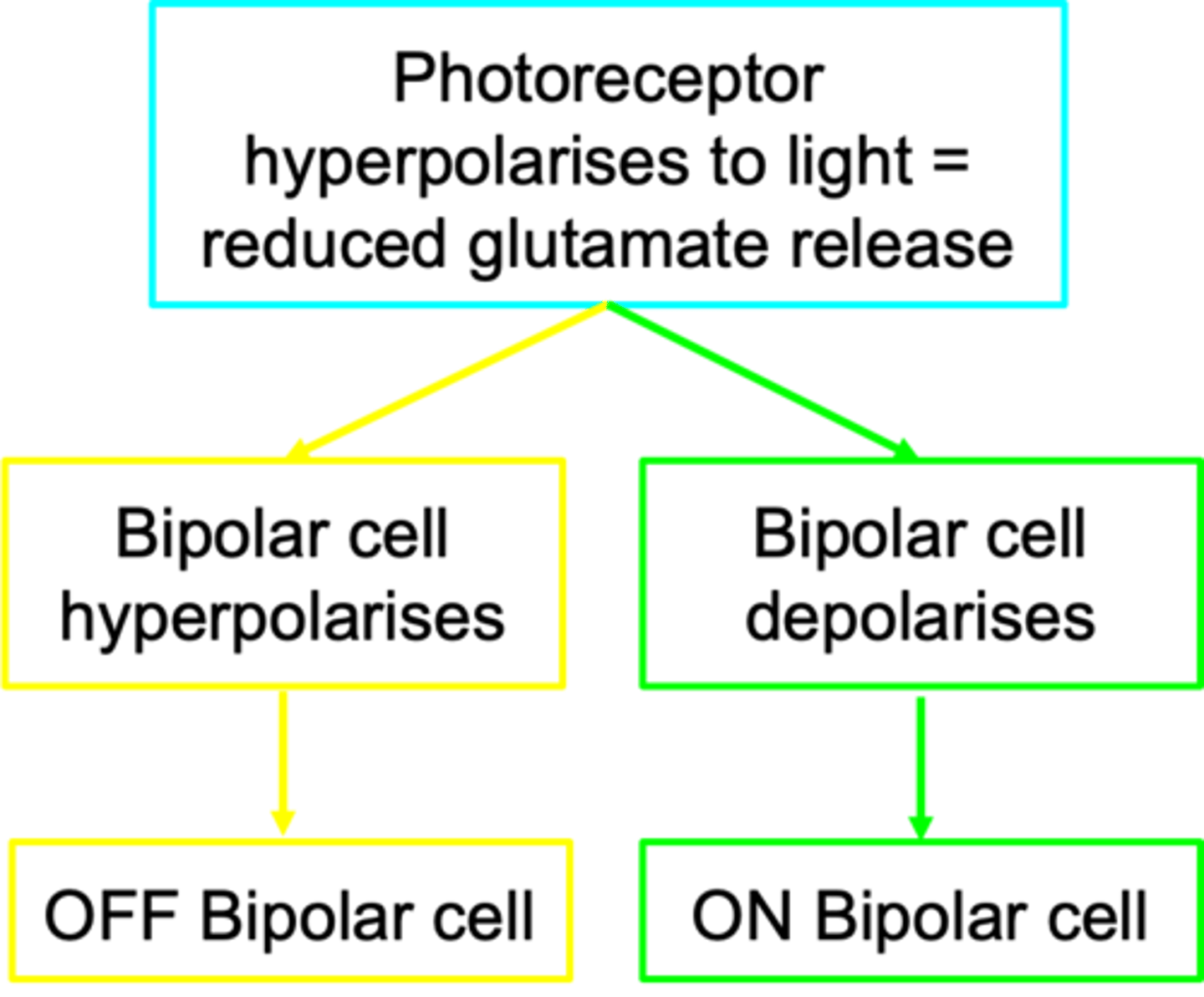
OFF bipolar cells
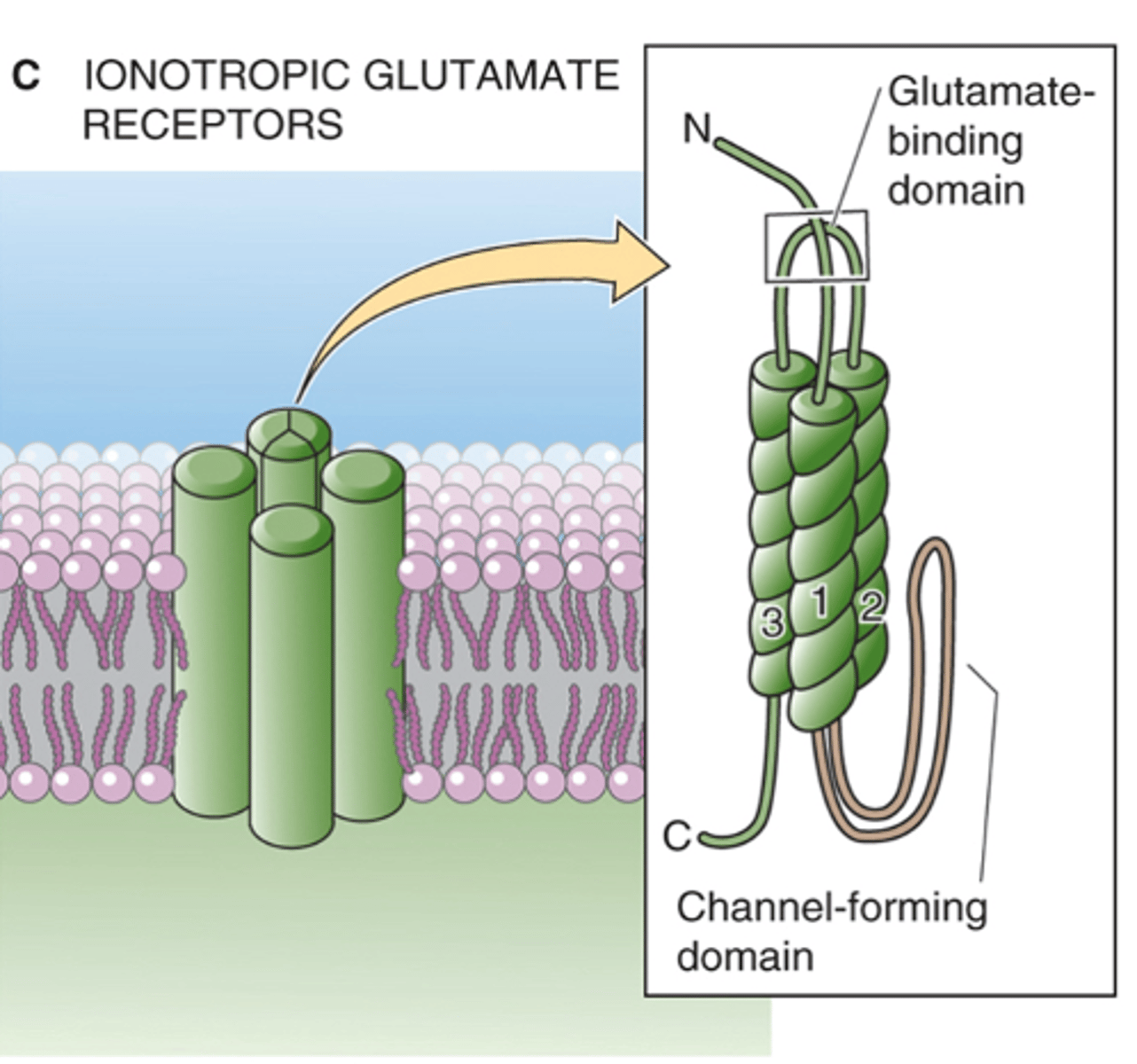
Which bipolar cell uses ionotropic glutamate receptors?
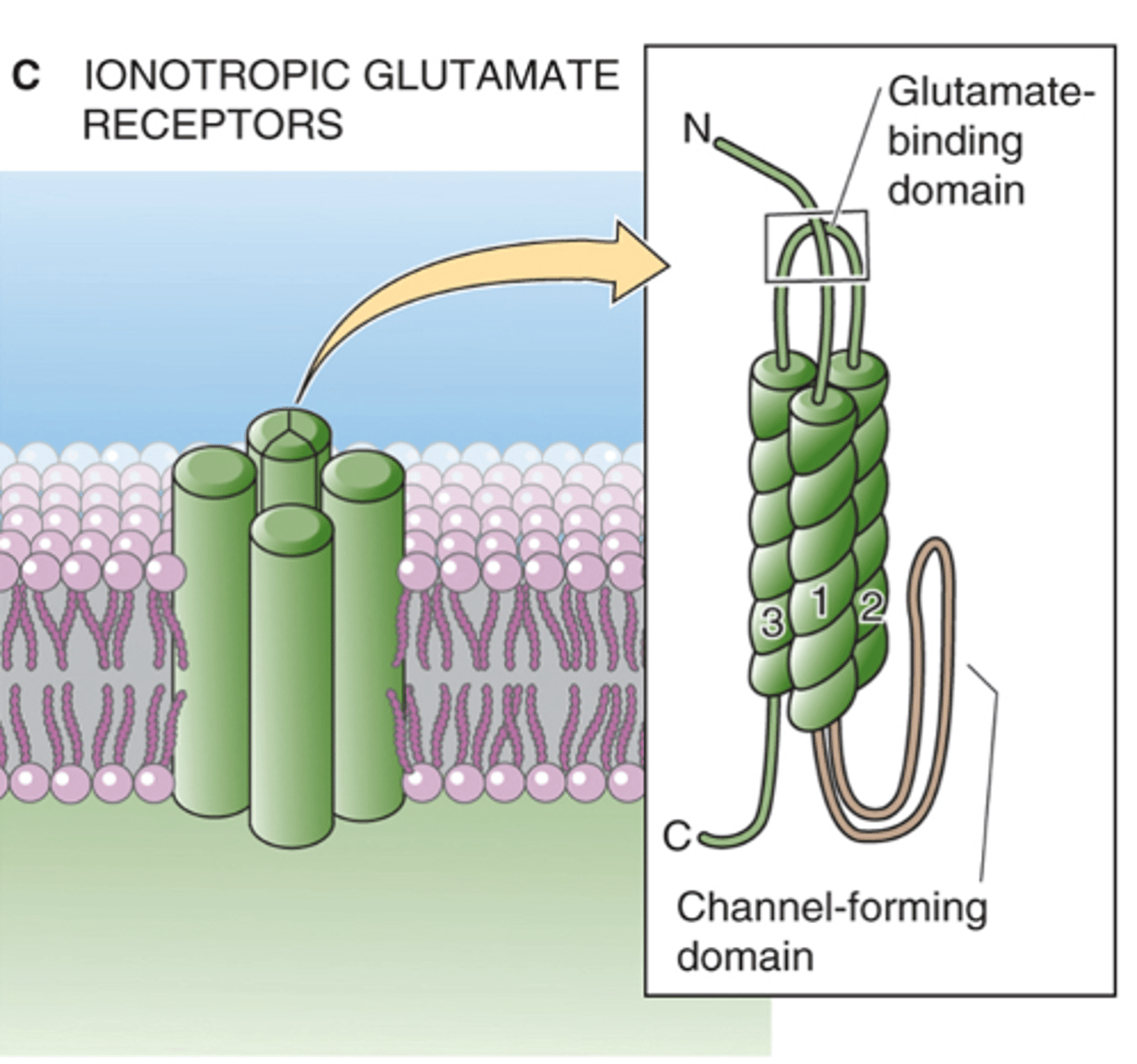
Positive ions come into the cell and depolarisation occurs
In the dark, what happens with OFF bipolar cells?
ON bipolar cells
Which bipolar cell uses metabotropic glutamate receptors (GPCRs)?
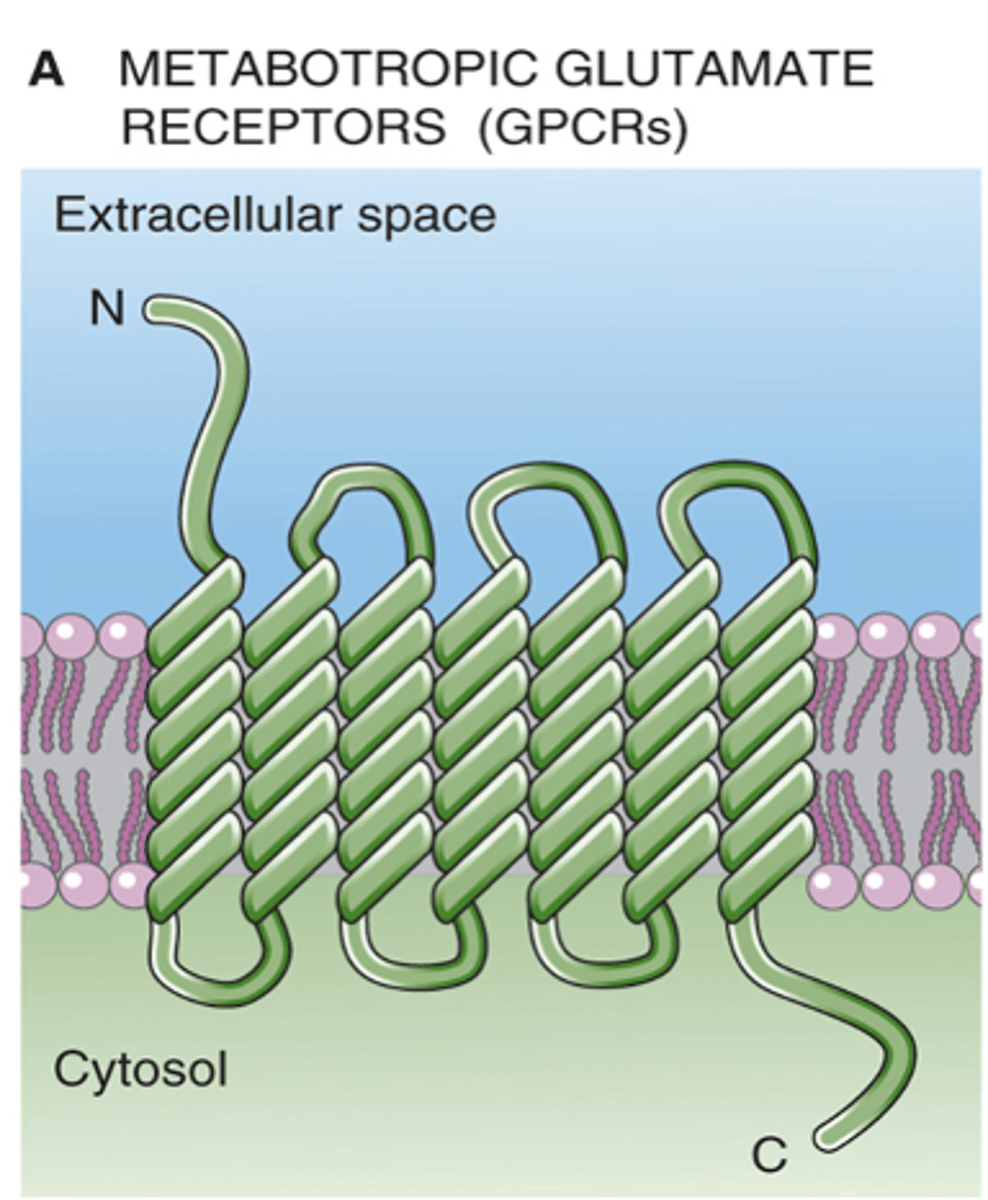
Releasing glutamate and binds to inhibitory metabotropic glutamate receptors, hyperpolarisation occurs
In the dark, what happens with ON bipolar cells?
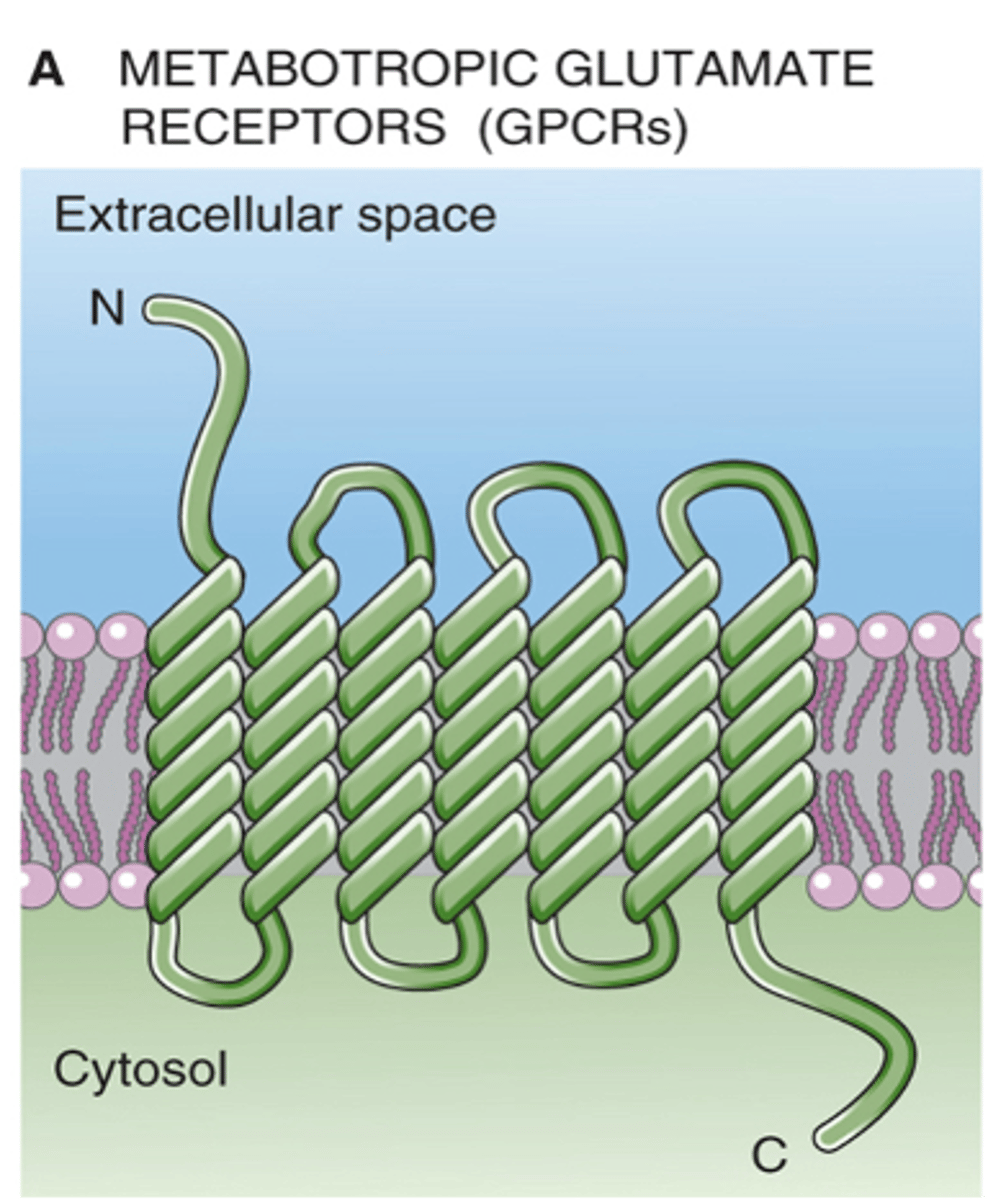
Reduction in glutamate binding to them and more likely to get depolarisation
In the light, what happens with ON bipolar cells?
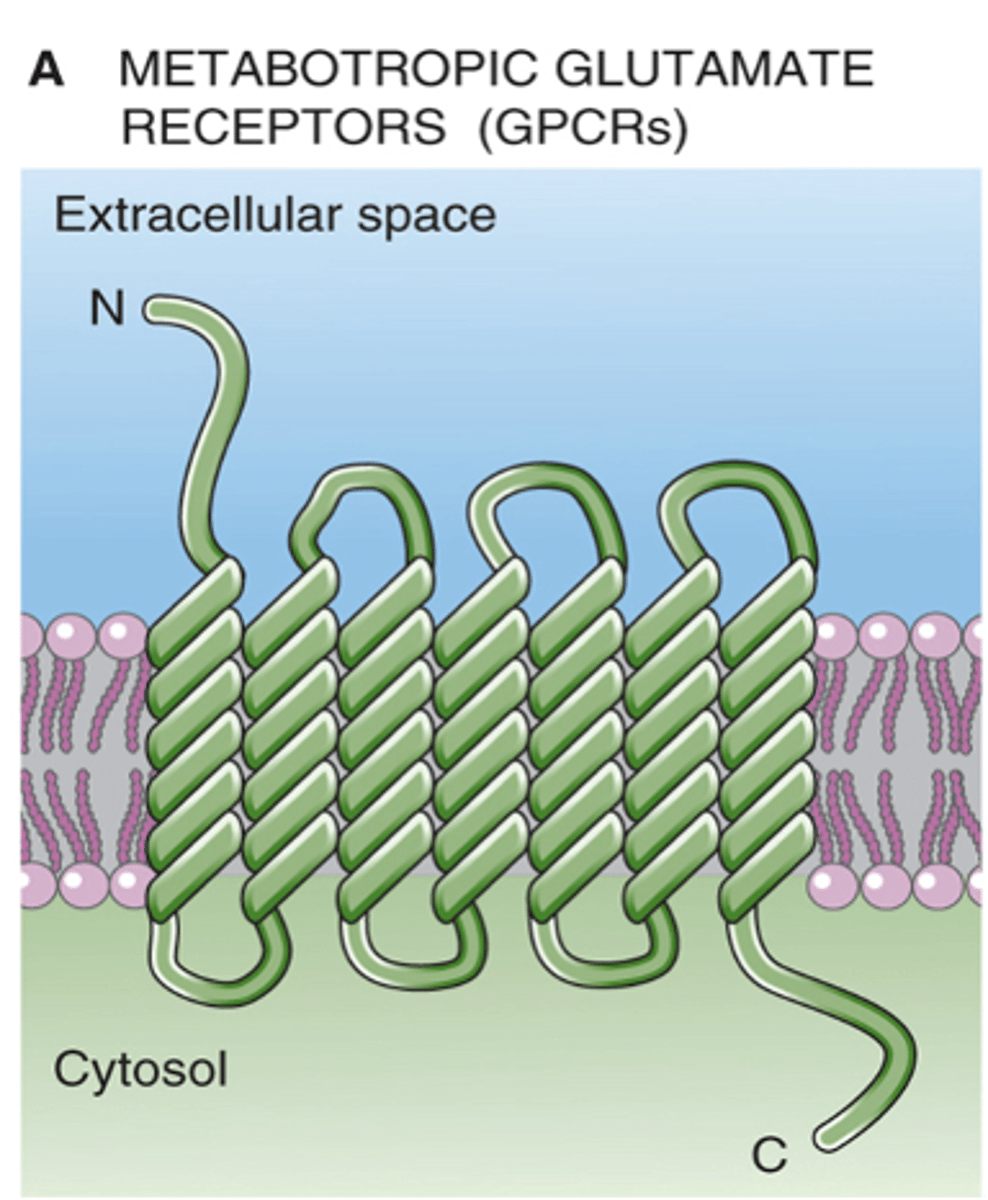
When specific areas of the retina are illuminated
When will retinal ganglion cells fire action potentials?
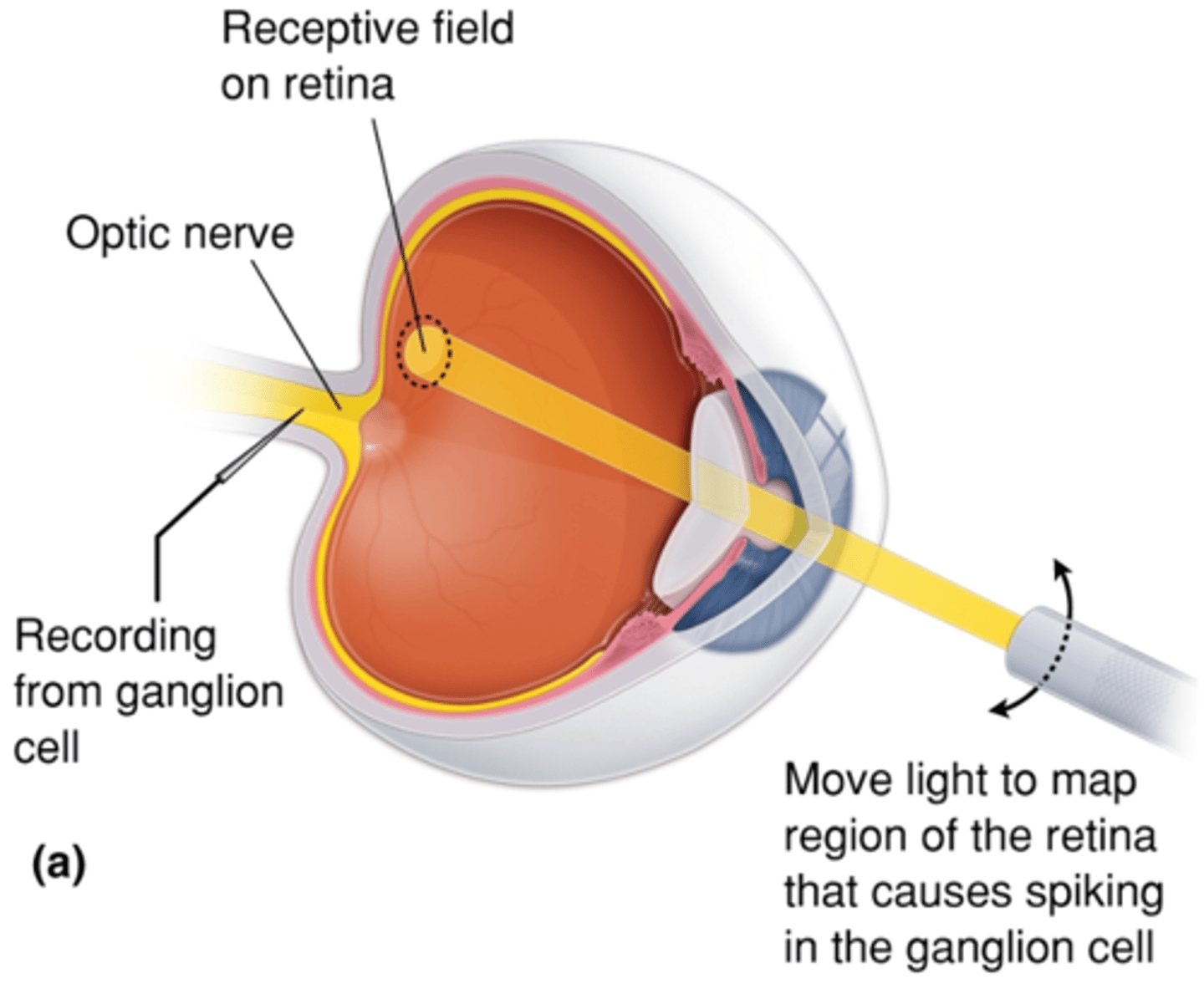
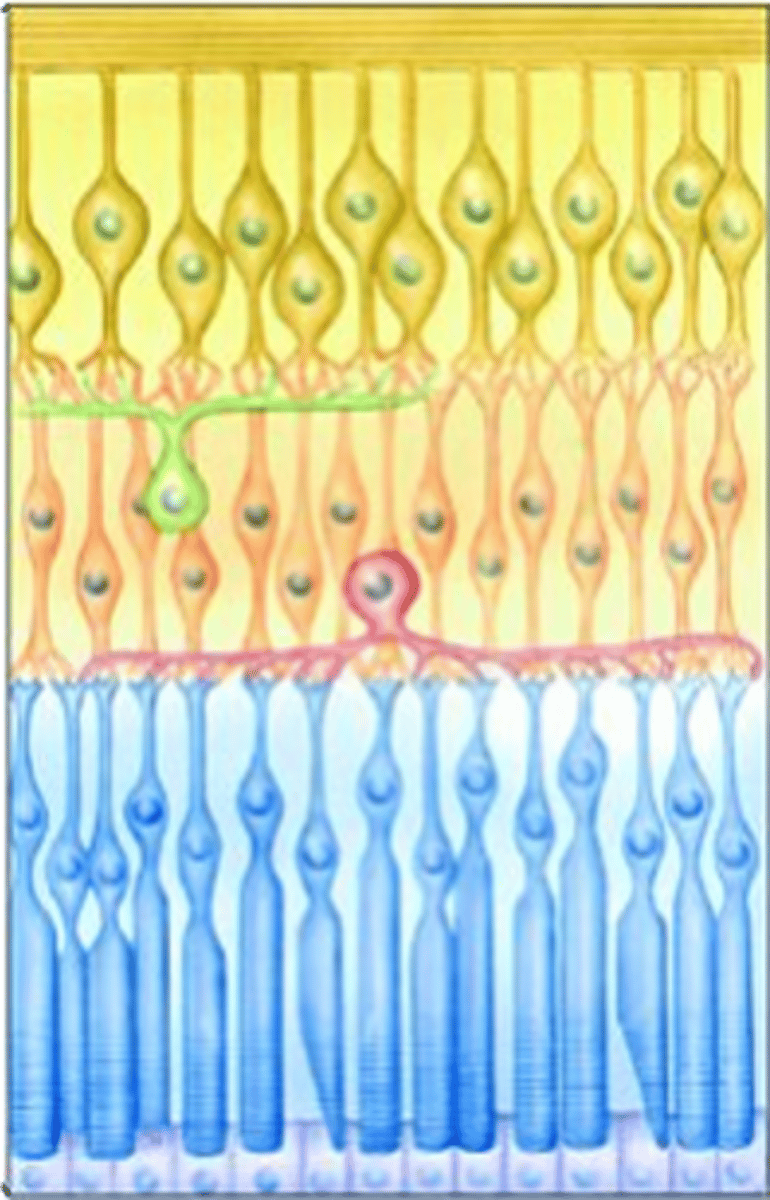
Centre-surround
Bipolar cells have what kind of organisation?
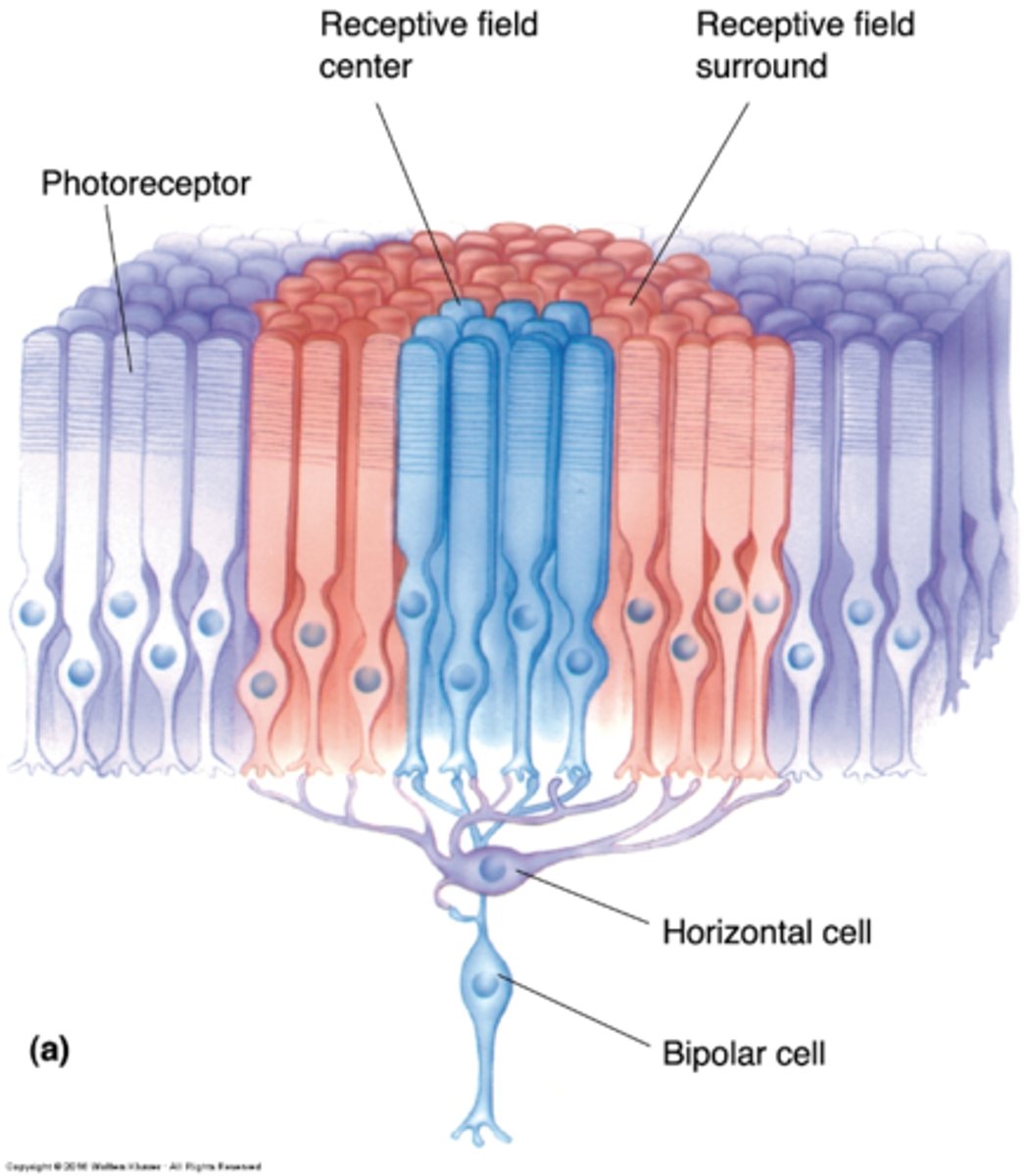
Direct contact with photoreceptors in the centre, indirect contact via horizontal cells to photoreceptors in the field surround
What does centre-surround organisation mean?
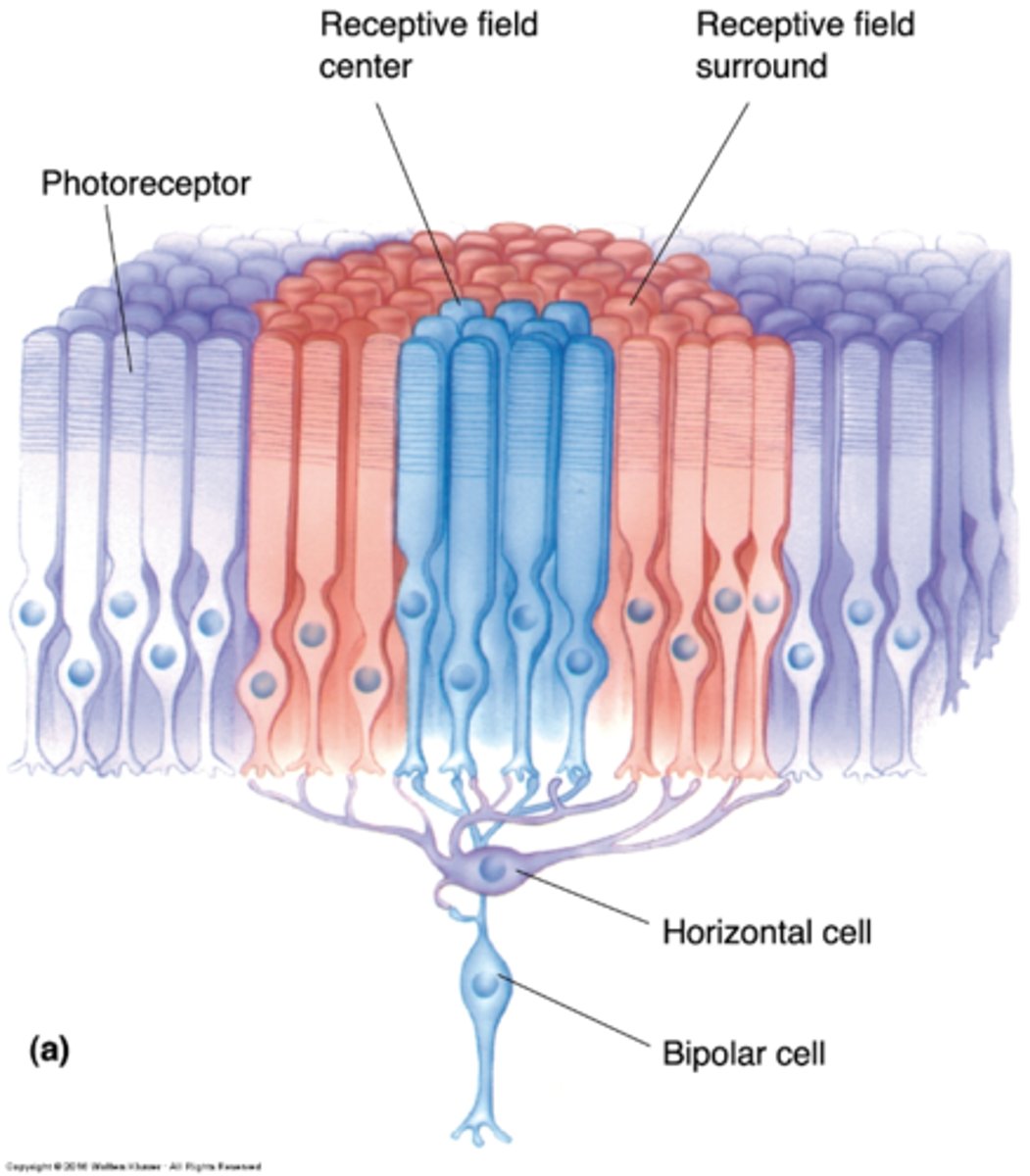
Centre-surround receptive fields
Bipolar cells have _______-_________ ______________ _______