pharmacology week 6 -opthalmic dye staining agents
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what are the use of staining agents
examination of anterior eye
evaluation of lacrimal drainage system
contact lenses( fit assessment,aftercare)
tonometry
angiography
what are we examining in anterior eye
cornea
conjuctiva
Tear film
what dyes are relevant to optoms
flourescine sodium
rose bengal
lissamine green
when is floruescine used (lots of examples)
corneal epithelium and conjuctiva integrity (dry eye, suspected trauma, suspected foreign body, CL aftercare)
fit of RGP
contact tonometry- Goldman (to see mires)
examination of lacrimal drainage and TF
floruescin angiography
suspected penetrating injury
how is it administered for angiography
intravenous administration
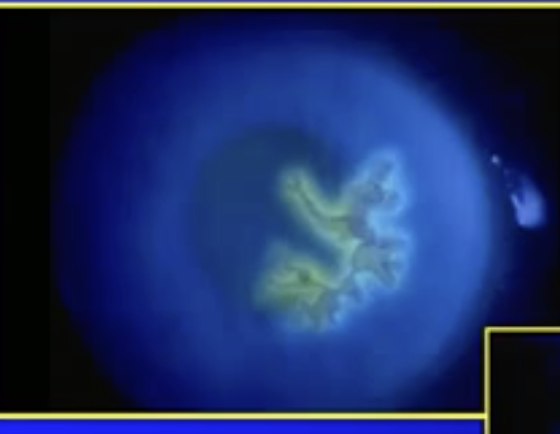
what’s been identified here
dendritic ulcer in Herpes simplex virus

what has been identified
a superiore epithelial arcuate lesion
when does this occur
typically in silicone hygrogel lenses - more rigid
how does floruescine work
mixes with TF( does not stain cells itself) then tear film enters damaged cells or tissues
pH indicator
highly ionised at physiological pH
when does it not penetrate the cornea
because it has low lipid solubility
what factors affect florescence
pH highest at 8
concentration ( only occurs below 1%)
intensity and wavelength of incident light
what incident light is best
475- 535nm
suitable light sources
cobalt blue filter with wratten filter
white light- fluoresces but low contrast
UV tube in Burton lamp
what does the wratten filter do
increases contrast
where is wratten filter placed
placed in front of observation system only not illumination
NaFL availability
Fl impregnated strips-1mg fl
minims of NAFl(1% and 2% single eye drops)
minims of lidocaine (1%)and FL(0.25%)
is Fl a PoM
no
Fl installation
explain procedure to px
4- D test ( drug,dose, date, disposal)
wet with saline
apply to inferior bulbar conductive by lowering eyelid
px blinks to distribute
how does Rose bengal work
stains cells and its nucleus red( dead corneal and conjunctival cell and mucus)
potent stain
what main clinical identification does it cause
identification of keratoconjuctivis- dryness of anterior ocular surface due to TF, blinking, or lid deficiencies
Lissamine green what does it stain
degenerated cells, dead cells and mucus
other features
less irritation that rose bengal
long lasting staining
light absorption for LG
peak at 624-635nm
how is it used
q.5mg impregnated strip
white light
view 1-4 min post installation
what is indocyanaine green used for
used in angiography
reacts to longer wavelength than Fl
detects leakage at deeper levels(retina/choroid)
peak excitation at 805nm