OPT 114: Blood Vessels - Overview
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
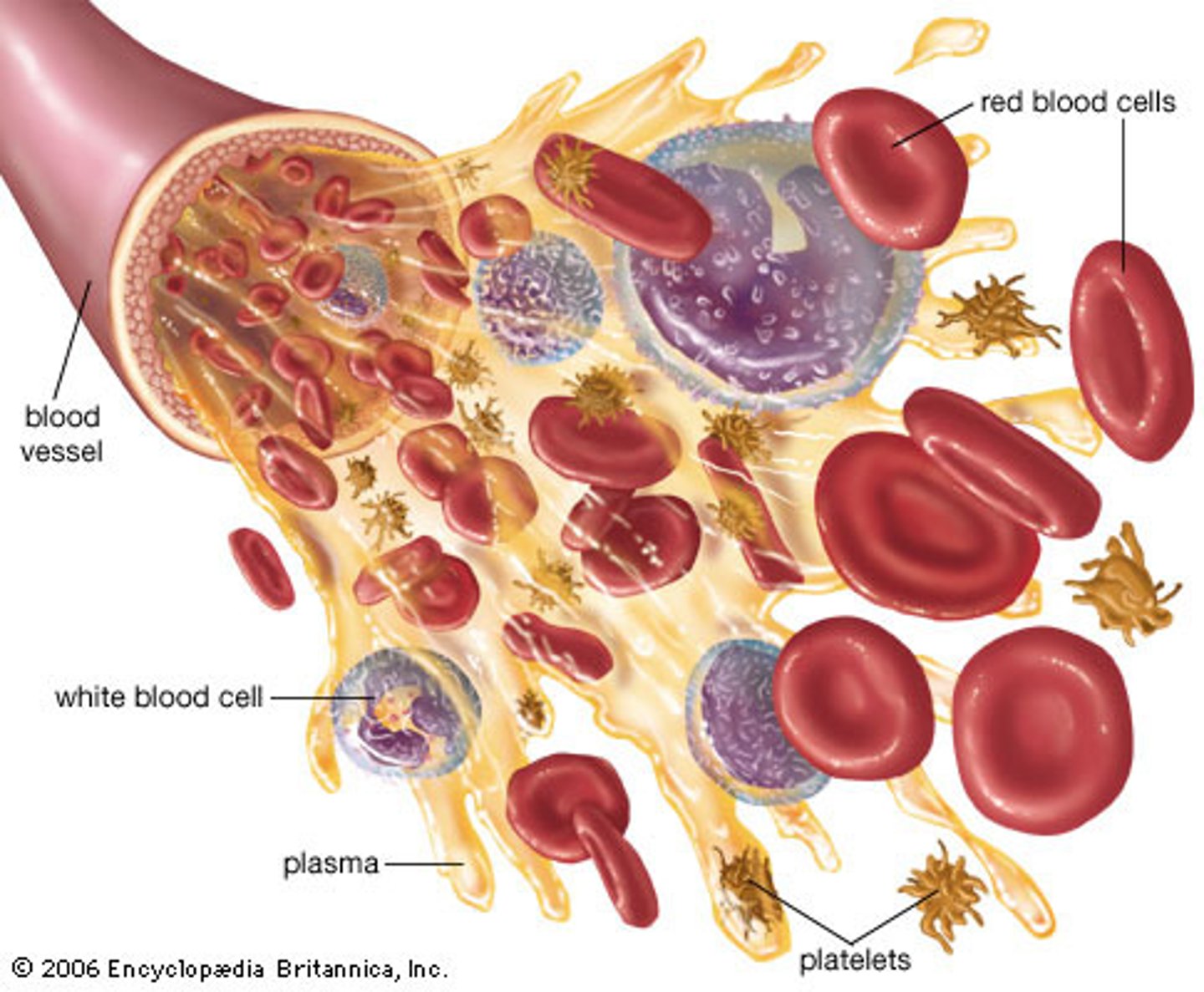
plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
4 main components of blood
plasma
liquid component of blood, 91% water, 7% protein, 2% other
red blood cells
most abundant cell in the blood; shape is diconcave disk with a flattened center; does not have a nucleus; contain special protein called hemoglobin
hematocrit
percentage of blood volume that is made up of RBCs (measure of RBC levels)
Why do red blood cells not have a nucleus?
allows them to change shape easily, which helps them fit through blood vessels and limits the life of the cell
Average life span of a cell
120 days
hemoglobin
carries oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body; returns carbon dioxide from the body to the lungs so it can be exhaled; gives RBCs its' red color
white blood cells
protect the body from infection
platelets
small fragments of cells; helps the blood clotting process (coagulation)
the way platelets help in the blood clotting process
gather at the site of an injury; stick to the lining of the injured blood vessel; cover the wound and prevent blood from leaking out; form the scaffolding upon which new tissue forms
function of blood
transport nutrients and oxygen to cells; remove waste products from cells and deliver it to the kidneys and liver, which filter and clean the blood; transport hormones (messages) from one part of the body to another; protect the body from infection and foreign bodies; form blood clots to prevent excess blood loss and initiate wound healing; regulate body temperature and pH levels
arteries, capillaries, veins
blood travels through...
components of blood
arteries
transport oxygenated blood away from the heart and deliver it to tissues in the body
large vessels
arteries are...
small vessels
arterioles are...
capillaries
arterioles become...
capillaries
location for exchange of gases, fluids, and nutrients between blood and tissues; where cells can deposit waste and carbon dioxide to the blood
venules
capillaries become...
veins
drain the capillary beds (venules); return deoxygenated blood to the heart
veins
venules become larger vessels called....
arteries -> arterioles (smaller) -> capillaries -> venules -> veins
progression of blood movement structures