accounting final exam lets fucking go
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
136 Terms
what is the purpose of budgeting
should be possible for management to maintain enough cash to pay creditors as well as have sufficient raw materials to meet production requirements
planning
setting company-wide objectives
budgeting
formal written statement of management plans for a specified time period, expressed in financial terms
what is budgeting good for
it deters waste and inefficiency and is a good basis for evaluating performance
primary benefits of budgeting
defines objectives
early warning system
coordination of activities
greater management awareness
motivates personnel
what are the essentials of budgeting
approval from all management personnels
research and analysis
sound organization structure
factors in choosing length of budget
type of budger
nature of organization
need for periodic approval
prevailing business conditions
budget commitee
consists of president, treasurer, chief accountant, and management personnel
budgeting characteristics
short term, annual profit objectives, very detailed
long-range planning characteristics
long term, long term goals and how to execute, less detailed
the master budget
set of interrelated budgets that constitues a plan of action for speciified time period
what are the two components of the master budget
operating budgets and financial budgets
operating budgets
individual budgets that result in budgeted income statementf
financial budget
cash resources needed to fund expected operations and planned capital expenditures
sales budget
derived from sales forecast—gives best estimate of sales reveneue by management totals
sales budget setup
quarter
expected sales
unit sell price
total sales
production budget setup
quarter
expected sales
add:desired end finished goods
total required units
less:beginning finished goods
required production units/units to be produced
how is desired end finished goods calculated
its a percentage of next quarters expected sales
how is beginning finished goods calculated
its a percentage of current periods expected sales
required production units=
expected sales+ desired end FG - beginning FG
direct materials budget setup
units to be produced
direct materials per unit produced
direct material units required for production
add: desired end direct materials
total materials required
less: beginning direct materials
direct materials units to be purchased
cost per pound ($)
cost of direct materials purchases
how is desired end direct materials calculated
percentage of next quarters units required for production
how is beginning direct materials calculated
percentage of current periods direct materials required
direct labor budget setup
units to be produced
Direct labor hours per unit (hours)
total required direct labor hours
direct labor cost per hour (wages)
total direct labor cost
manufacturing overhead budget setup
direct labor hours
variable costs
fixed costs
total manufacturing overhead
manufacturing overhead rate per direct labor hour
selling and administrative costs budget setup
budgeted sales in units (from sales budget)
variable expenses
x
y
z
fixed expenses
a
b
c
total s&a expenses
budgeted income statement
sales
COGS
gross profit
s&a expenses
income from operations
(less) interest expense
income before taxes
income tax expense
net income
cash budget
shows anticipated cash flows—most important budget
cash budget setup
beginning cash balance
add: cash receipts
total available cash
less: cash dispersments
excess/deficiency of available cash
financing
end cash balance
what is financing/borrowing in the cash budget
borrowing money to get back to desired/minimum cash balance
total unit cost
direct materials + direct labor + manufacturing overhead
cost of goods sold using unit cost
unit cost * units sold
schedule of expected earnings
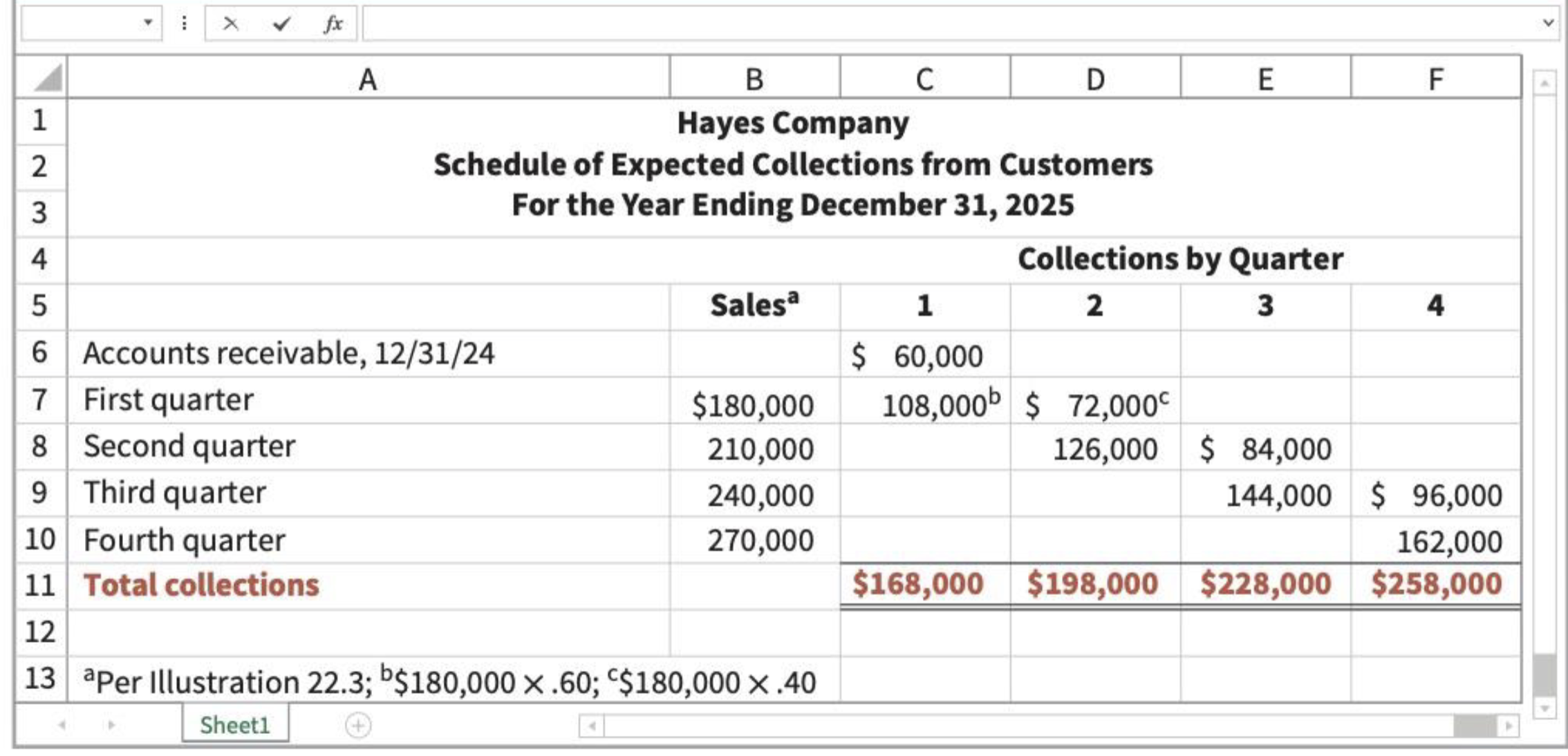
required merchandise purchases=
budgeted cogs (cogs*%) + desired end inventory - beginning merchandise inventory
service companies budget set up
___to be serviced
DL time per ___
total required DL hours
DL cost per hour
total DL cost
service problems if overstaffed:
Disproportionately high labor costs
Lower profits due to additional salaries
Staff turnover due to lack of challenging work
service problems if understaffed:
Lost revenues because existing and future client needs for services cannot be met
Loss of professional staff due to excessive work loads 41
what establishes goals for the companies sales and production personnel
operating budgets
what does participative budgeting do
doesnt allow unrealistic budgets to happen
budgets are created with the framework of a
sales forecast
budgetary control
use of budgets in controlling operations
what do budget reports do
compare actual results with planned objectives—without monitoring, planning objectives will lose value
what does a formalized reporting system do
identifies name of budget report, states frequency of report, specified purpose of report, and identifies recipients
static budget report
projection of budget data at a single level of activity before actual activity occurs
flexible budget report
series of static budgets at various levels of activity
steps to developing a flexible budget
indentify activity index
indetify varible costs, determine budgeted variable cost per unit
identify the fixed costs, determine budget for each
prepare budget for selected increments of activity when in relevant range
total budgeted costs=
fixed costs + variable costs(total var cost per unit * activity level)
responsibility accounting
identifying and reporting costs and relevant revenues on the basis of manager
as you move up in management,
there are more controllable costs
responsibility reporting system
preparation of report at every level of responsibility
order of rankings for responsibility reporting
cost center, profit center, investment center,
cost center
production/service departments—incurs costs and expenses but does not directly generate revenue
profit center
costs, expenses, and generate reveneue
investment center
costs, expenses, generate revenue—decisions over assets available for use
direct fixed costs
relate specifically to one center, controllable by profit center manager
indirect fixed costs
overall operating activity, benefit multiple centers—uncontrollable by profit manager
controllable margin
CM - controllable fixed costs
responsibility report setup
-—-————budget——-actual——U or F?
sales
var costs
-COGS
-sell&admin
CM
controllable fixed costs
-COGS
-sell&admin
controllable margin
what is the best basis to measure performance
ROI
ROI equation
controllable margin/average operating assets
how can you increase controllable margin
increase sales or decrease expenses
how can you improve ROI
decreasing average operating assets
what are standard costs
predetermined unit costs, used as a measure of performance
Materiality
Without
quantitative guidelines,
management would have to
investigate every budget
difference regardless of the
amount
Controllability of the Item -
Exception guidelines are
more restrictive for
controllable items than for
items the manager cannot
control
report D
department manager
report C
factory manager
report B
vice president looks at costs in his area
report A
president looks at production of VP
advantages of standard costs
facilitate management planning, promote greater economy by mamking employees “cost-conscious”, useful in setting prices, provides basis of evaluation for cost control, highlights variends in management by exception, simplifies cost of inventory
standard cost
unit amount
budget cost
total amount
manufacturing overhead in standard costing
budgeted OH cost / (activity index/normal capacity)
overhead varience
actual overhead - applied overhead
applied overhead
OH rate * std DL hours
variance report income statement
sales rev
cogs (at standard)
gross profit (at standard)
variances
gross profit (actual)
s&a expenses
net income
balanced scorecard
financial and non financial measures linked to measuring performance with strategic goals
4 perspectives of a balanced scorecard
financial, customer, internal, and learning & growth
if cash flow information isnt available, what do you do
adjust accrual numbers—add back depreciation expense
budgeting decision factors
availability of funds, relationship among proposed projects, company’s basic decision-making approach, risk associate with particular project
cash payback period
cost of capital investment / net annual cash flow
net annual cash flow is the same as
net cash from operating activities
when do you not accept a payback period
when period is over 60% of investments useful life
in uneven cash payment scenarios,
find cash flow needed for the fraction of the year, and divide by entire cash flow from year
what does cash payback ignore
time value of money and expected profitability
what are the two disscounted cash flow techniques
NPV and IRR
net present value method
disouncing net cash flows to present values and then comparing PV with capital outlay required
discount rate/required rate of return
minimum acceptable rate of return on investments—decided by management
when is the NPV method accepted
when NPV is 0 or positive
if cash flow is even over life time, use what table
PV of annuity (its a lump sum!!!)
if cash flow is uneven, use what table
PV of 1, multiply cash flow by decimal and get PV!
NPV then equals
PV - price of capital investment
cost of capital
rate it must pay to obtain funds from creditors and stockholders
choosing a discount rate/required rate of return/hurdle rate/cutoff rate
entails cost of capital and risk component
net annual cash flows
inflows - outflows - maintenence - other direct operating costs
profitability index
present value of net cash flows / initial investment
internal rate of return finds what
interest yield of a potential investment
how do you find IRR
financial calculator or trial and error
internal rate of return factor
captial investment / net annual cash flows
finding IRR with even cash flows