Small and Large Intestines
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
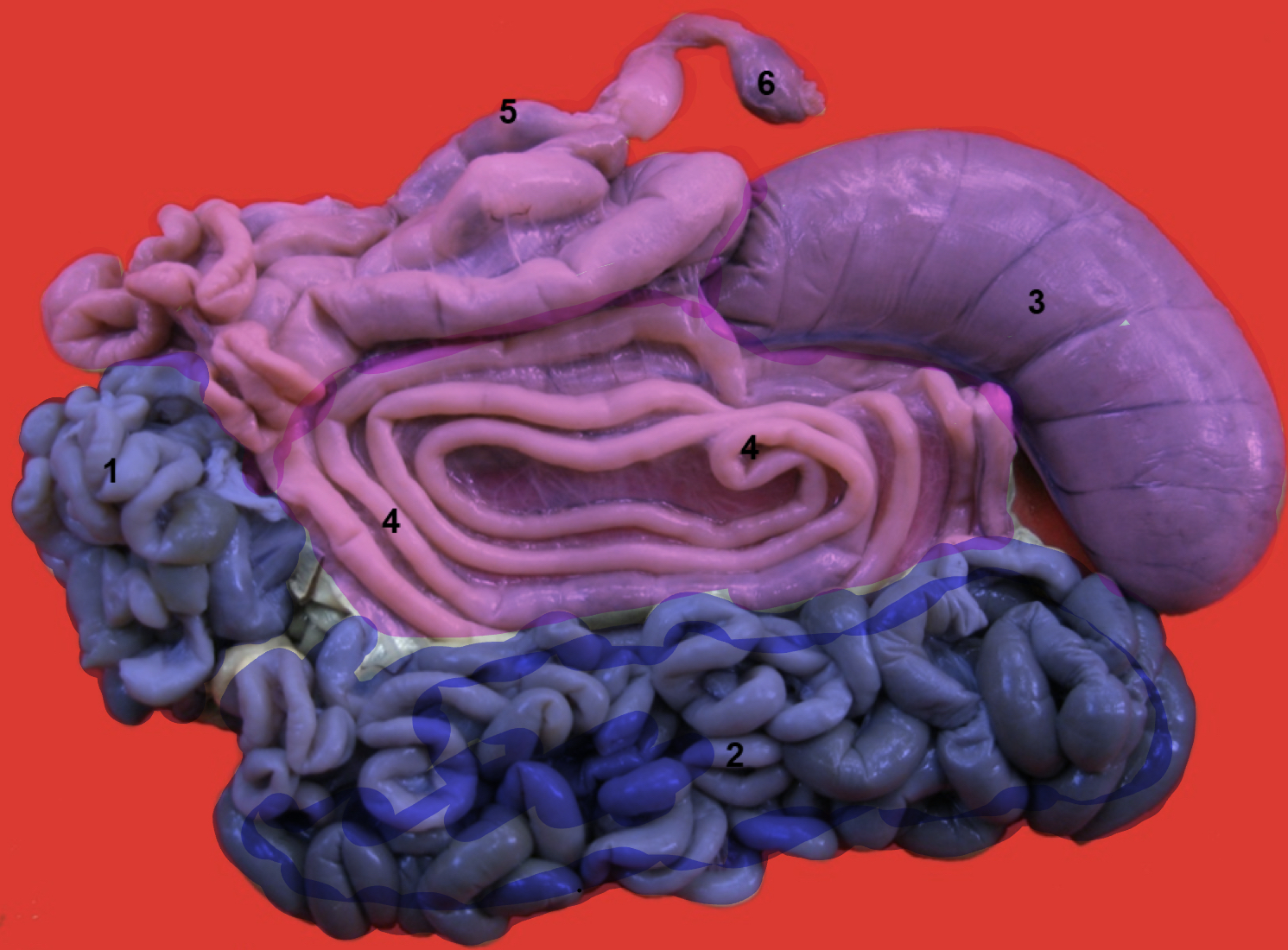
What are the 3 sections of the small intestine
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
What is the general function of small intestine?
For digestion and absorption
Histological Features of Small Intestine
Does it have villi and why
What secretes digestive enzyme
What are enterocytes
What secretes mucus
Does it have villi and why: Yes, to increase surface area for absorption
What secretes digestive enzyme: Crypts of Lieberkun
What are enterocytes: Absorptive cells
What secretes mucus: Goblet cells
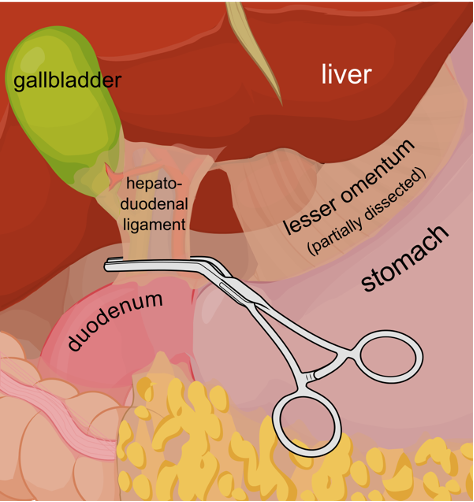
Duodenum
What
Location
Describe its mesentery
Cranial part closely related to
Forming
Attach to, by
Function
What: First part of small intestine
Location: Extend from pylorus to beginning of jejunum
Describe its mesentery: Short except in carnivores
Cranial part closely related to: Liver and pancreas
Forming: Sigmoid loop in horse, ruminants and pigs
Attach to: Liver by hepatoduodenal ligament
Function: Receives bile ducts and pancreatic ducts
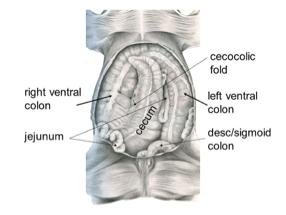
Jejunum
Characteristic
Describe its mesentery
In carnivores
Occupies
Covered by
Lies against
In ruminants
Location
Characteristic: Longest part, usually empty
Describe its mesentery: Long, allowing great range especially in carnivores and horse
In carnivores:
Occupies ventral part of abdominal cavity
Covered by greater omentum
Lies against lateral and ventral abdominal wall
In ruminants:
Intestines entirely to the right
Ileum
What
Suspended by
Attached to
By
Terminates at
What: Short terminal part connecting to large intestine
Suspended by: Caudal part of mesentery (mesoileum)
Attached to: Cecum
By: Ielocecal fold
Terminates at: Ceococolic junction forming ileal orifice
What are the 4 structures of the large intestine?
Cecum
Ascending colon
Descending colon
Rectum
What is the general function of the large intestine?
Absorbing water and electrolytes and forms feces
Histological Features of Large Intestine
Does it have villi
What gives it immune protection
What produces mucus
Why does it have a thicker muscularis externa
Does it have villi: No, flat mucosa
What gives it immune protection: Lymphatic nodules
What produces mucus: Goblet cells
Why does it have a thicker muscularis externa: To move solid waste
What are the 4 layers of the large intestine?
Mucosa
Submucosa
Muscularis
Serosa
Cecum
What
General location
How join to colon
Describe its length in cat, dog, pig and ruminants
In
Horse
Carnivores
Pig
What: Initial blind part of large intestine
General location: Right flank (excluding pig)
Join to: Colon at ileal orifice
Describe its length in cat, dog, pig and ruminants:
Shortest in cats
Longer in dog, pig and ruminants
In
Horse: Large and elongated for fermentation
Carnivores, ruminants and horse: Lies on right side of abdominal cavity
Pig: Lies on left side
Rectum
Continues from
Before ending at short anal canal, it becomes
Forming
Very prominent in
Continues from: Descending colon into pelvic cavity
Before ending at short anal canal, it becomes: Enlarged
Forming: Ampula recti (stores feces)
Very prominent in: Horse
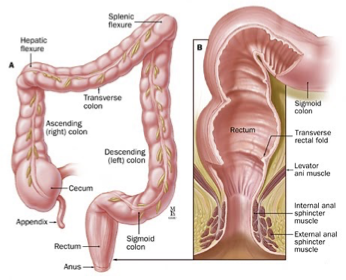
Anal Canal
What
What anal orifice mean
What type of epithelium is the mucous membrane
What surrounds the anus
Describe them (smooth or striated muscles)
What: Short terminal portion
Anal orifice: Opening of anus
Type of epithelium in mucous membrane: Stratified squamous epithelium
What surrounds the anus: External and internal sphincters
Internal sphincter: Continuation of circular smooth muscle of rectum
External sphincter: Striated muscle from the caudal vertebrae, lying superficial to internal sphincter
How does the large intestine differ from the small intestine (3)
Villi are absent in large intestine
Microvilli of large intestine are less abundant
Goblet cells are more prominent
What are these terms:
Cecocolic junction
Mesentry
Heptaoduodenal ligament
Ampula recti
Cecocolic junction: The junction between cecum and ascending colon
Mesentry: Fold of peritoneum (thin layer of tissue) that attaches to intestines to posterior abdominal wall
Heptaoduodenal ligament: Part of less omentum and connects liver to the duodenum
Ampula recti: Expanded part of rectum
What is the location of the intestines?
From pylorus (last part of stomach) to anus
What is the anal canal?
Short passage at the end of rectum (final part of digestion)
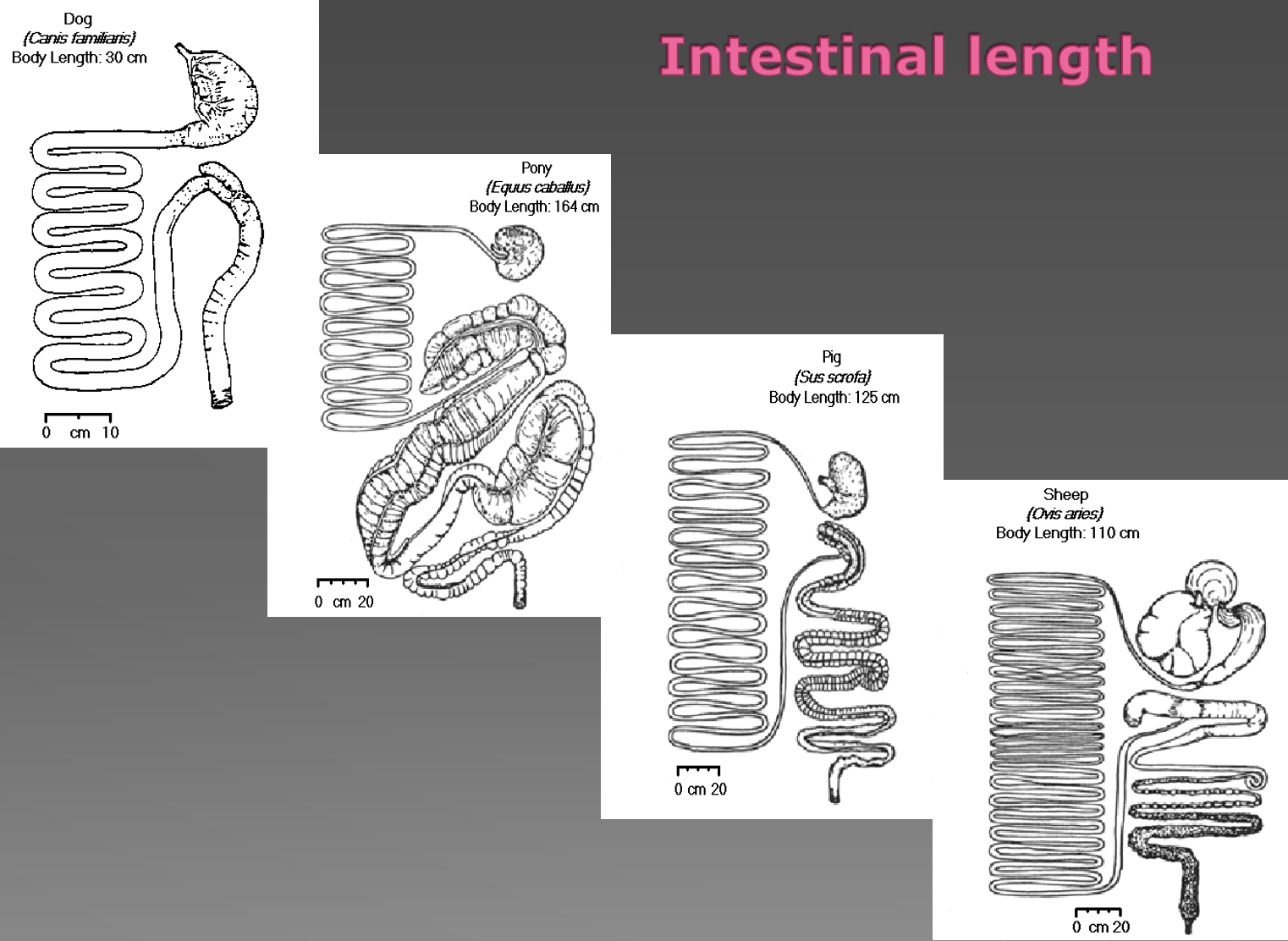
What is the intestinal length for these animals
Dog
Horse
Pig
Ox
Small ruminants
Dog: 5x body length
Horse: 10x body length
Pig: 15x body length
Ox: 20x body length
Small ruminants: 25x body length
What are the 3 types of colon?
Ascending colon
Transverse colon
Descending colon
What is the colon like in these animals
Ruminants, pig and horse
Generally the ascending colon is longer than of carnivores
Ruminants: Flat, disc shaped coil
Pig: Cone shaped coil
Horse: Double on itself twice, forming a large horseshoe-shaped loop
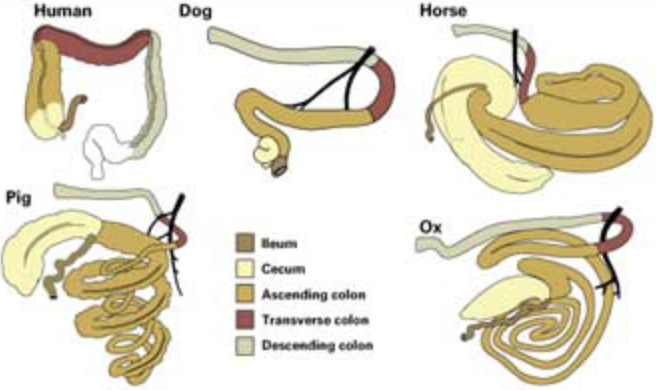
Descending Colon
In pig
In horse
In ruminant
What is rectum
In pig: Straight colon before rectum
In horse: Elongated and suspended from roof of abdominal cavity by mesentery
In ruminant: Sigmoid flexure at pelvic inlet
What is rectum: Straight terminal part in the pelvic cavity (short anal canal)
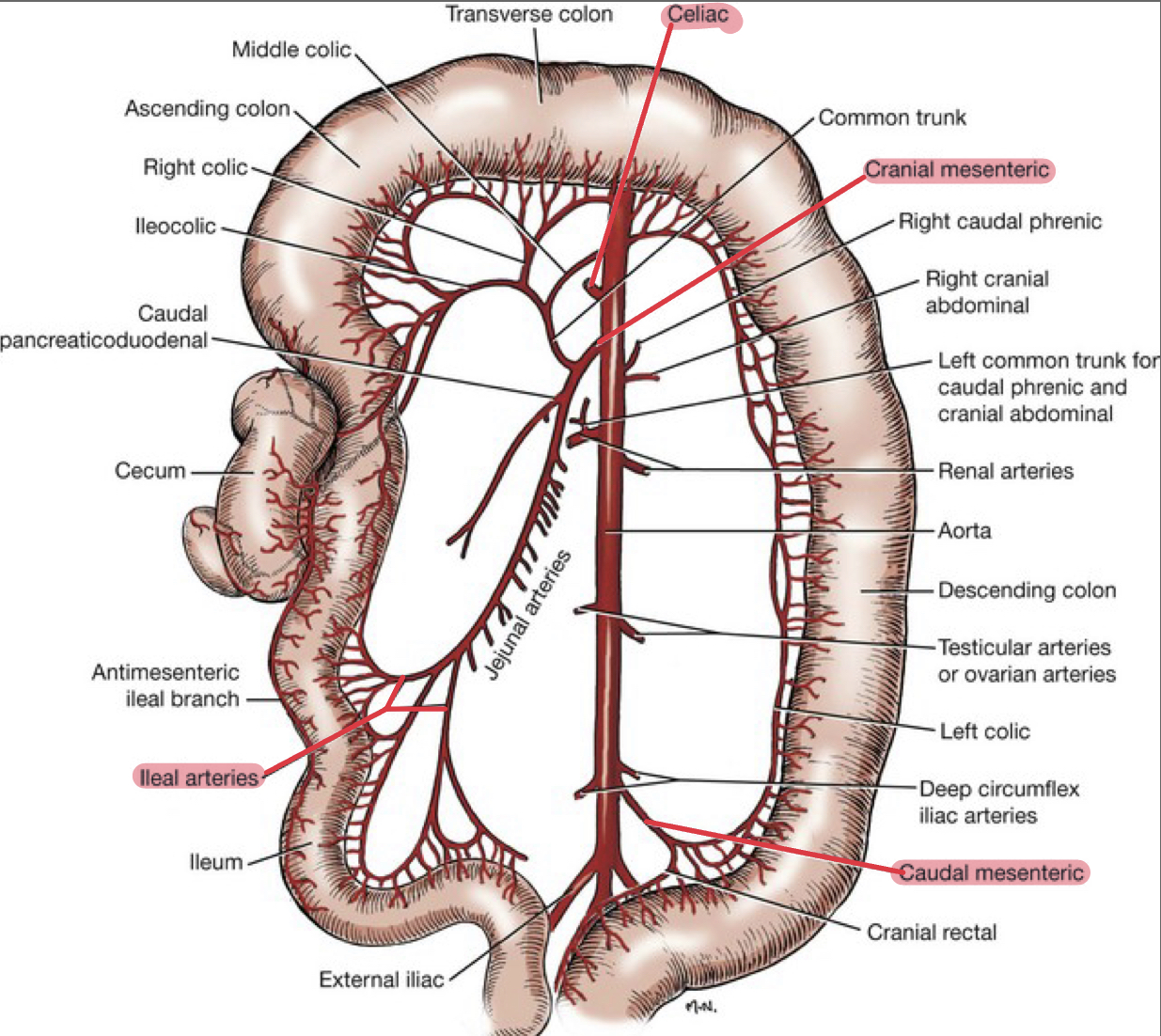
Blood Vessels
Which blood vessels supply:
Small intestine
Proximal duodenum
Large intestine
Rectum
Veins of intestinal tract go to
Blood from rectum return to
Which blood vessels supply:
Small intestine: Cranial mesenteric artery
Proximal duodenum: Celiac artery
Large intestine: Cranial and caudal mesenteric artery
Rectum: Internal iliac artery
Veins of intestinal tract go to: Portal vein
Blood from rectum return to: Caudal vena cava
Innervation
What does sympathetic innervation cause
What does parasympathetic innervation cause
Parasympathetic fibers originates in
What does sympathetic innervation cause: Slowing down activity (retardation)
What does parasympathetic innervation cause: Increases activity
Parasympathetic fibers originates in: Cranial and sacral regions