Lecture 30 - Urine formation pt 2
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
two types of transepithelial transport
tubular reabsorption — movement of substance from the lumen into the peritubular capillary
tubular secretion — movement of substances from the peritubular capillary into the lumen
PCT made of
simple cuboidal and microvilli
LOH (thin limbs) made of
simple squamous
thick ascending limb and DCT made of
simple cuboidal + reduced microvilli
collecting duct made of
simple cuboidal
what do the renal epithelial cells consist of?
a luminal membrane — faces filtrate
a basolateral membrane — base and sides - facing interstitium
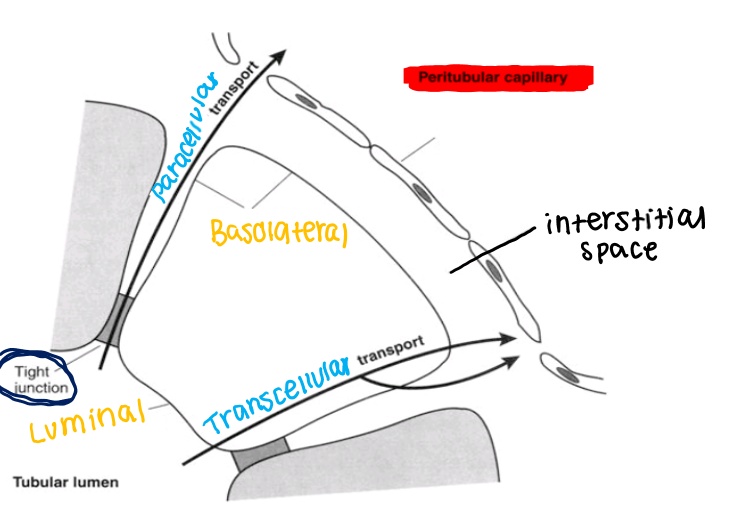
how can transport occur across the epithelial cells?
through: transcellular transport
primary route
typically requires proteins on both side
between: paracellular transport
diffusion
peritubular capillary
paracellular - between
transcellular — through the cell
luminal side to the interstitial space
what are the transport mechanisms?
active transport - requires ATP
osmosis - movement of water through aquaporins (H2O channels)
some are constitutively (permanently) expressed, others are not
passive transport - requires favorable electrochemical gradient
simple diffusion = slow/non-selective
ion channels = highly selective; open or gated
facilitated diffusion = transport proteins
uniporters - move 1 solute across mem
symporters - move 2 solutes in same direction
antiporters - move 2 solutes in opposite direction
transport mechanisms in secretion and reabsorption in proximal tubule
transport proteins function passively, but they can be maintained thru active transport
secondary active transport
so why does each part of nephron have different job?
because they vary in:
types of channels/transporters present
hormone receptor presence/absence
type of epithelial cells
interstitial fluid tonicity
describe reabsorption and secretion in the PCT
1st point of filtrate modification
more substances move across mems of PCT than any other part of nephron
2/3 of glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in PCT
what are the reabsorption rates in the PCT
glucose = 100% filtered load
Na = 65%
K+ = 65%
water = 67%
reabsorption in LOH
thin asc. and thick asc. have different jobs
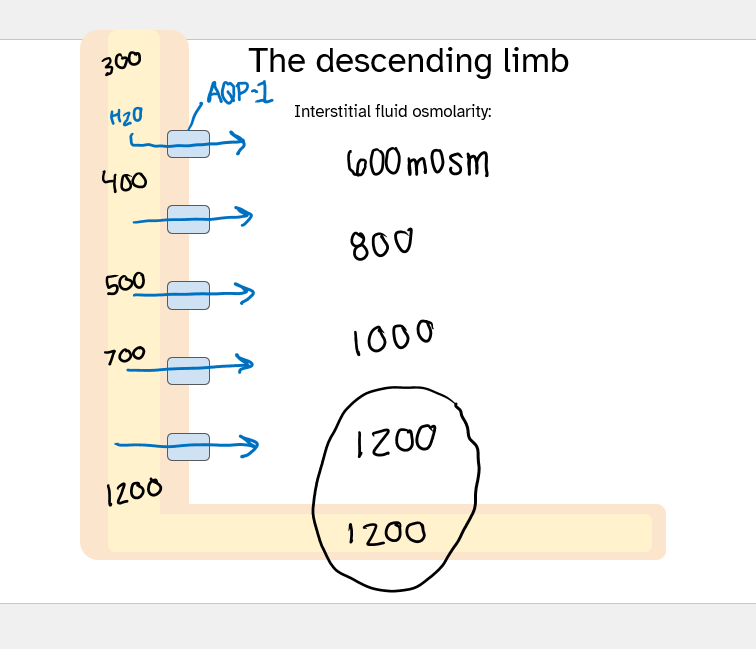
descending limb = permeable to water ONLY
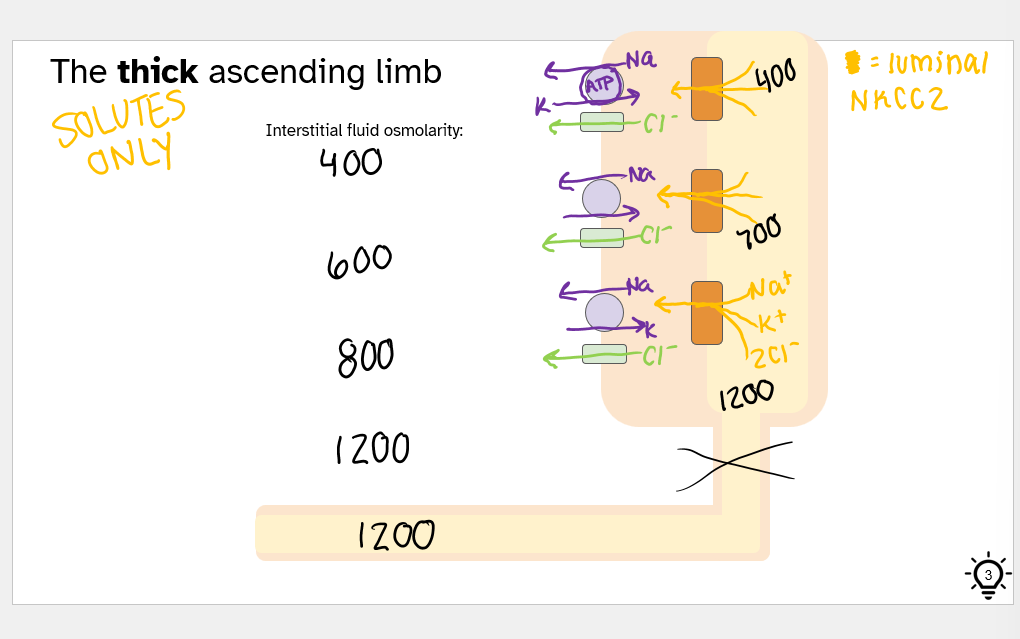
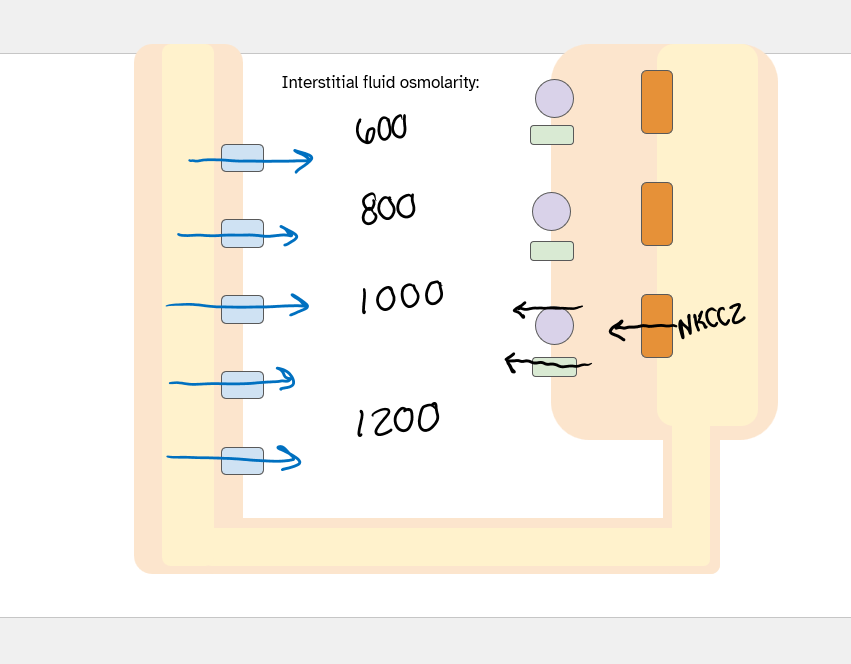
ascending limb = permeable to solutes ONLY
interstitial osmolarity progressively INC from cortex → inner medulla
interstitial fluid osmolarity
thick ascending limb - interstitial fluid osmolarity. what channel involved?
NKCC2
solutes only
descending
water only
aquaporin-1
the descending limb fxn and how
function: reabsorb H2O
15% filtered load of h2o
how: aquaporin-1
the concentrating segment
the ascending limb function and how
function: reabsorb NaCl
25% filtered load of Na+
20% filtered load of K+
how: Na-K-2Cl cotransporter
the diluting segment

aquaporin-1 — NKCC2 — Na/K-atpase
NKCC2 → Bartter syndrome