P6 Space Physics
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
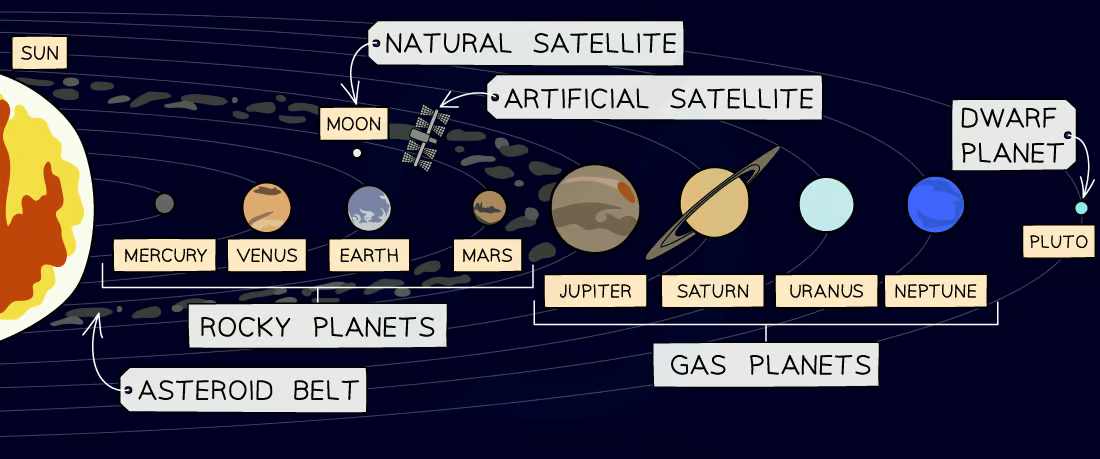
What does the Solar System consist of?
One star, the Sun
Eight planets
Minor planets (dwarf planets & asteroids)
Moons
Name the planets in order from their distance from the Sun
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
What is the closest star to the Earth?
The Sun
How can astronomical distances be measured?
Using light years
What is a light year?
Distance travelled in (the vacuum of) space by light in 1 yr
Equation for the time taken for light to travel a distance
Time = distance/speed of light
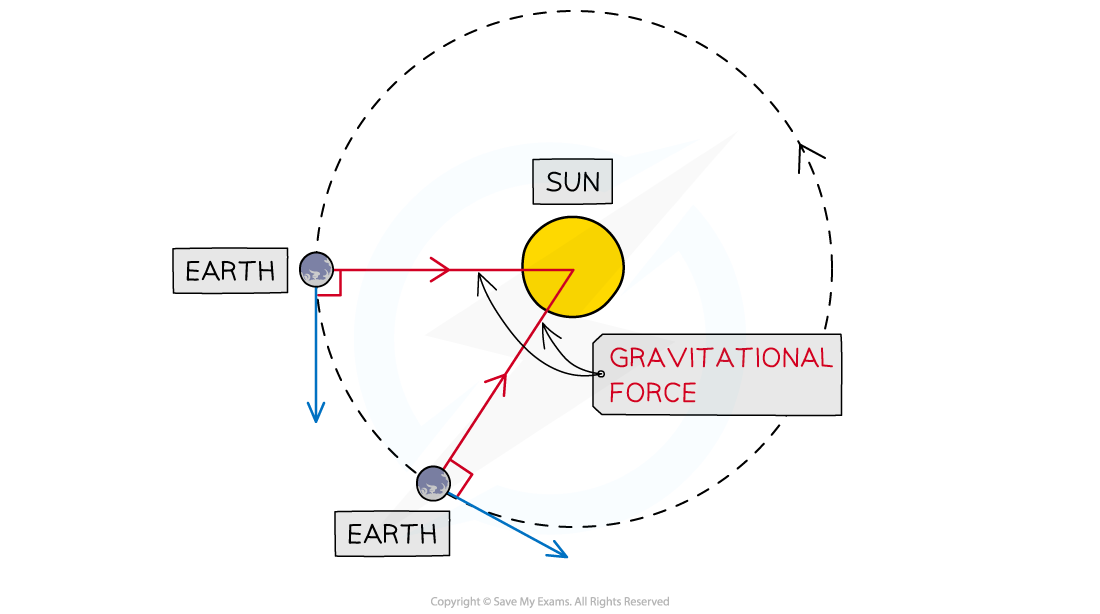
Why do planets orbit the Sun?
The Sun contains most of the Solar System's mass, so its gravitational attraction pulls planets into orbit around it
What is the Sun?
Star of medium size
Consists mostly of hydrogen & helium
Radiates most of its energy in the infrared, visible & ultraviolet regions of the electromagnetic spectrum
Orbital speed equation
v = orbital speed (m/s)
r = average radius of the orbit (m)
T = orbital period (s)
