Exam 1: Ch. 1, 2, 3
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
How are the names of microorganisms written?
Genus is capitalized and species is lowercase
What do variety stains have?
A third name
What are the O and H antigens used in names?
O is the antigen on the cell wall and H is the antigen on the flagellum
Methanogens
Archaea that live in high methane concentrations
Halophiles
Bacteria that survive very high salt concentrations
Thermophiles
Mainly bacteria that like high heat environments
Unicellular / Multicellular / Both (Bacteria, Archaea, Fungi, Algae, Protozoans, Helminths)
Bacteria: Unicellular
Archaea: Unicellular
Fungi: Both
Algae: Both
Protozoans: Unicellular
Helminths: Multicellular
Prokaryote or Eukaryote (Bacteria, Archaea, Fungi, Algae, Protozoans, Helminths)
Bacteria: Prokaryote
Archaea: Prokaryote
Fungi: Eukaryote
Algae: Eukaryote
Protozoans: Eukaryote
Helminths: Eukaryote
Photosynthesize (Yes or No) (Bacteria, Fungi, Algae, Protozoans, Helminths)
Bacteria: Yes (some)
Fungi: No
Algae: Yes
Protozoans: Yes (some)
Helminths: No
Cell Wall Made Of (Bacteria, Archaea, Fungi, Algae, Protozoans, Helminths)
Bacteria: Peptidoglycan
Archaea: Pseudopeptidoglycan
Fungi: Chitin
Algae: Cellulose
Protozoans: No cell wall (cell membrane only)
Helminths: No cell wall
Reproduction (Bacteria, Fungi, Algae, Protozoans, Helminths)
Bacteria: Binary fission (or budding)
Fungi: Sexual or asexual
Algae: Sexual and asexual
Protozoans: Sexual and asexual
Helminths: Sexual or asexual
Nutrition (Bacteria, Fungi, Algae, Protozoans, Helminths)
Bacteria: All nutrients (enzymes break down food)
Fungi: Absorb nutrients using enzymes (decomposers)
Algae: Photosynthesis
Protozoans: Other protozoa; organic or inorganic materials
Helminths: Nutrients from host
Movement (Bacteria, Fungi, Algae, Protozoans, Helminths)
Bacteria: Flagella
Fungi: No movement
Algae: No movement
Protozoans: Flagella, cilia, or pseudopods
Helminths: Muscles
DNA (Yes or No) (Bacteria, Archaea, Fungi, Algae, Protozoans, Helminths)
Bacteria: Yes
Archaea: Yes
Fungi: Yes
Algae: Yes
Protozoans: Yes
Helminths: Yes
Habitat (Bacteria, Archaea, Fungi, Algae, Protozoans, Helminths)
Bacteria: Anywhere
Archaea: Extreme environments
Fungi: Everywhere
Algae: Water and moist soil
Protozoans: Water and soil
Helminths: Inside an organism
Uses UV light to Florence antibodies
Fluorescence
Perfect to use for viewing viruses and their internal structure in thin slices
Transmission Electron
Define a Simple stain and give an example of a stain
Simple stains are one color like methylene blue or crystal violet.
Define Differential stain and give an example.
Differential stains are two colors like the gram stain or acid-fast stain.
Explain why differential stains are preferred over simple stains
Differential stains are preferred because they can show gram-negative bacteria (pink) and gram-positive bacteria (purple). Simple stains only show the shape of the bacteria.
What are special stains used for, to stain what parts of a microorganism?
Special stains are used to stain capsules, endospores, and flagellum.
Define negative staining and give an example of a stain
Negative staining stains the background and creates a halo around the specimen like india ink.
Identify the color of a gram-positive bacterium and a gram-negative bacterium
Gram-positive bacterium appear purple and Gram-negative bacterium appear pink.
Define Acid Fast staining and give two bacteria that stain with this stain
Acid fast staining is a differential stain that binds to bacteria with a waxy material in their cell walls that are not decolorized by acid-alcohol. Mycobacterium and Nocardia stain with this.
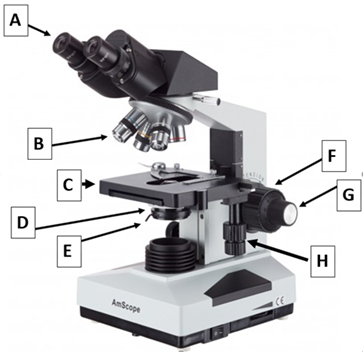
Indicate the parts of the microscope below.
Arrow A Ocular Lens
Arrow B Objective Lenses
Arrow C Stage
Arrow D Diaphragm
Arrow E Condenser
Arrow F Coarse Knob
Arrow G Fine Knob
Arrow H Stage Controls
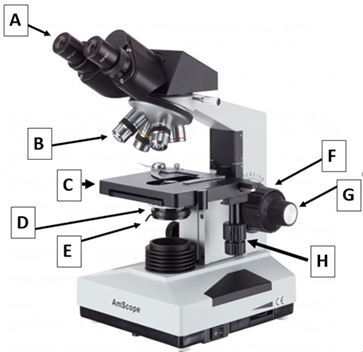
List the function of all microscope parts
Ocular lens is the eyepiece to view specimen. Objective lenses magnify the specimen. Stage holds up the specimen. Diaphragm adjusts light coming through. Condenser captures and focuses light. Coarse knob moves the stage up and focuses. Fine knob refines details and focuses things. Stage controls move the slide.
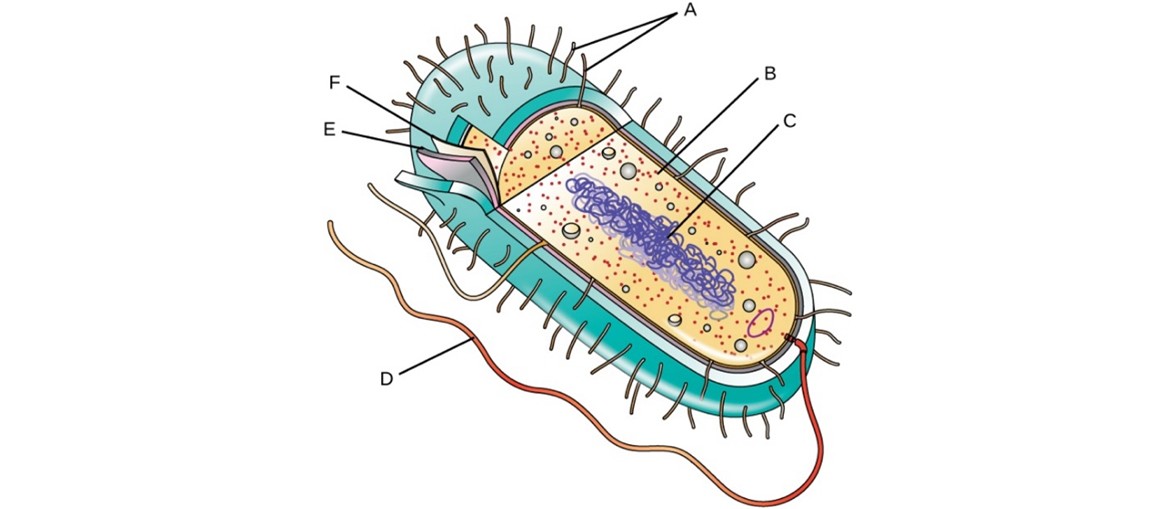
Label the structure of a bacterium
A. Fimbriae
B. Ribosome
C. Nucleoid
D. Flagellum
E. Cell Wall
F. Plasma Membrane
List the functions of Capsule, cell wall and cell membrane
Protects the bacterium
List the functions of DNA chromosome, DNA plasmid
Contains genetic information, Gives bacteria antibiotic resistance
List the functions of Nucleoid
Space that contains the DNA
List the functions of Fimbriae
Helps with attachment to tissues and cells
List the functions of Ribosomes
Makes proteins
List the functions of Flagellum
Helps move bacterium
Bacterial cell membrane consists of phospholipids and proteins. T or F
True
What happens to a bacterial cell when placed in a hypertonic solution?
It shrinks
What happens when the bacterial cell is placed in hypotonic solution?
It expands
How large are the bacterial ribosomes? How many units are they made of?
Bacterial ribosomes are 70S. They are made of two units, as small subunit that is 30S and a large subunit that is 50S.
Define a vegetative bacterial cell.
A vegetative bacterial cell is a normal cell without an endospore
Define an endospore
An endospore is a dormant spore that is formed by bacteria to survive harsh conditions (survival spores, not reproductive).
metachromatic
phosphate
volutin
phosphate.
lipid
lipid
sulfur
sulfur
carboxysomes
enzymes that fix CO2
magnetosommes
magnetic iron oxide
PHB
involved in bioplastics
the structure of gram-negative, gram-positive cell walls
G+ cell wall is ticker; G- cell wall is thinner.
Peptidoglycan wall is found in which microorganisms
bacteria
Identify if both G+ and G- can produce toxins
G+ and G- can produce toxins, but only G- has a toxin built into their cell wall.
List the bacterial group that carries endotoxin LIPID A
G-
Define acid fast cell walls
Acid fast cell walls have peptidoglycan, mycolic acids, and sugars, which make the cell wall waxy and repel stains.
Name a bacterium that is acid-fast.
Mycobacterium
Define Glycocalyx
The cover outside of the cell wall
Glycocalyx attached to cell wall is called
Capsule
Glycocalyx loosely associated with cell wall is called
Slime Layer
Are capsules are linked to pathogenicity. Do all bacteria have capsules?
Yes, capsules cause pathogenicity. No, not all bacteria have capsules.
Identify the importance of capsules during extreme drought and nutrient deficiencies, in water conservation and ability to avoid the immune system
Capsules help bacteria survive extreme drought and lack of nutrients by conserving water. They also protect bacteria by helping them avoid the immune system by preventing phagocytosis.
Define biofilm
Communities of bacteria that are very hard to kill.
List the function of flagella -Identify types of flagella
Flagella helps with movement of bacteria. Types of flagella include monotrichous (one), amphitrichous (both sides), lophotrichous (many on both sides), and peritrichous (all around).
List the function for axial filaments
Axial filaments are used for movement.
Which bacteria have axial filaments?
spirochetes
Identify the function of pili
Pili are used for communication and transfer of DNA.
List the function of Fimbriae
Fimbriae are used for attachment
Name a bacterium that has fimbriae.
Neisseria
Identify the cell wall type of Mycoplasmas
Mycoplasmas do not have a cell wall
Identify the cell wall type of Archaea
Archaea are wall-less, or if they do have cell walls they are made of pseudopeptidoglycan.
Define protoplast
a gram positive bacterium that has lost the cell wall
Define spheroplast
a gram negative bacterium that has lost the cells wall
Define L form
a bacterium that has lost the cells wall and can return to the walled state
Eukaryotic cell membrane consists of phospholipids and proteins, T or F?
True
What happens to an animal cell when placed in a hypertonic solution?
It shrinks
What happens when the animal cell is placed in hypotonic solution?
It swells
What are pseudopods
Pseudopods are extensions of the cytoplasm that can extend and feed on organisms.
What is binary fission
Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction where cells are divided into two identical cells and is how bacteria reproduce.
Color of Gram stain (G+ & G-)
G+: purple
G-: pink or red
Thickness of cell wall (G+ & G-)
G+: Thick
G-: Thin
Types of toxins (G+ & G-)
G+: Exotoxins
G-: Exotoxins and LIPID A Endotoxin
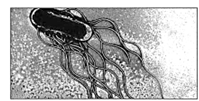
Flagella of the type seen above are called?
peritrichous
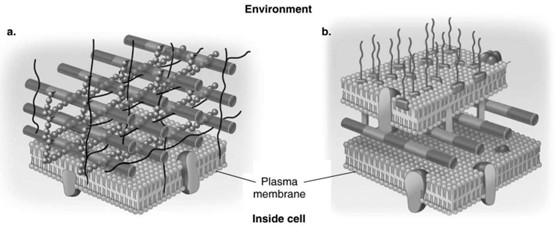
In Figure 4.3, which diagram of a cell wall is a gram-negative cell wall?
b
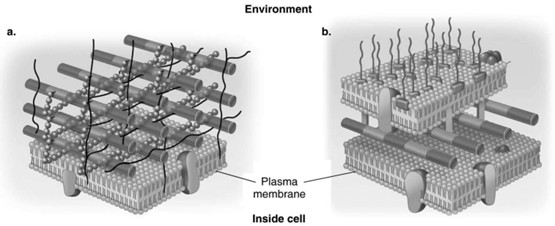
In Figure 4.3, which diagram of a cell wall possesses molecules responsible for symptoms associated with Lipid A intoxication?
b