Session 1c: Nodes, Linear, Superposition
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What do we understand by a Node ?
A node is a point in an electrical circuit where two or more circuit elements (resistors, batteries, capacitors, or wires) are connected
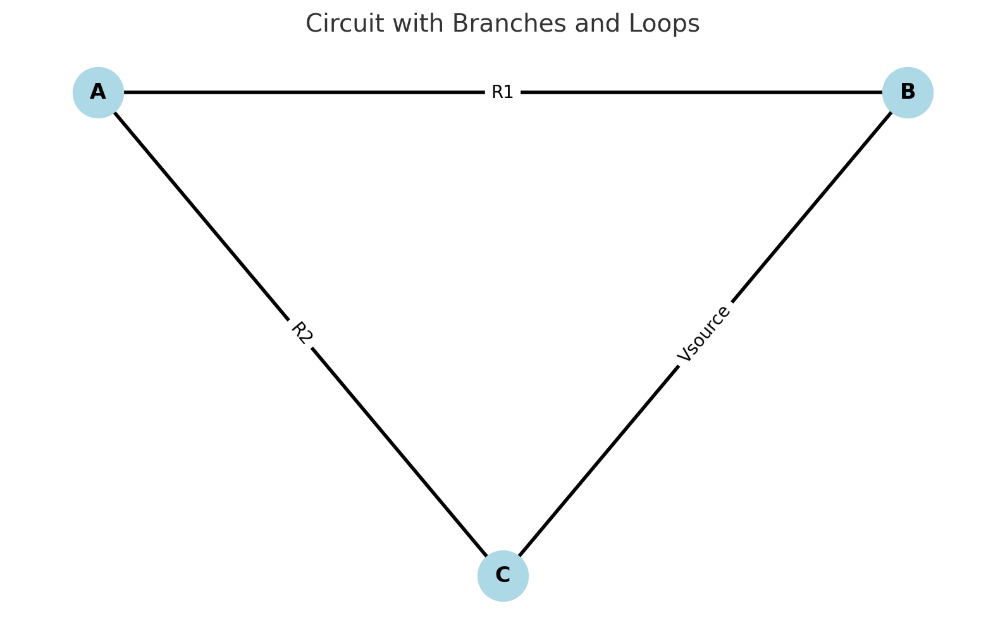
What are Branches?
A branch is a portion of a circuit between two nodes
what are Loops?
oA loop is any closed conducting path within a circuit.
oExample – Loop is formed with A R1 B Vsource
o
R2 C
R2
what is the Importance of Nodes in Circuit Analysis?
Nodes are essential for nodal analysis which is a technique that is used to find voltages at different points in a circuit.
Instead of tracking current through each wire, voltages can be analysed at each nodes. Node voltage method is among the most efficient techniques in circuit analysis.
What does a Linear Circuit mean?
A linear circuit is one where the relationship between voltage and current follows the principle of linearity.
Proportionality
Doubling the input (voltage or current) doubles the output (voltage or current)
Superposition
The response to multiple inputs is just the sum of the responses to each input individually.
Few Linear Elements
a)Resistors
b)Inductors
c)Capacitors
All give straight-line relationships between voltage and current (when graphed).
Few Non-Linear Elements
a)Diodes
b)Transistors
Their voltage-current curve is not a straight line but is curved
Linear Property
Of an Element describing a Linear relationship between Cause and effect. Although the Property applies to Many circuit elements.
V=iR
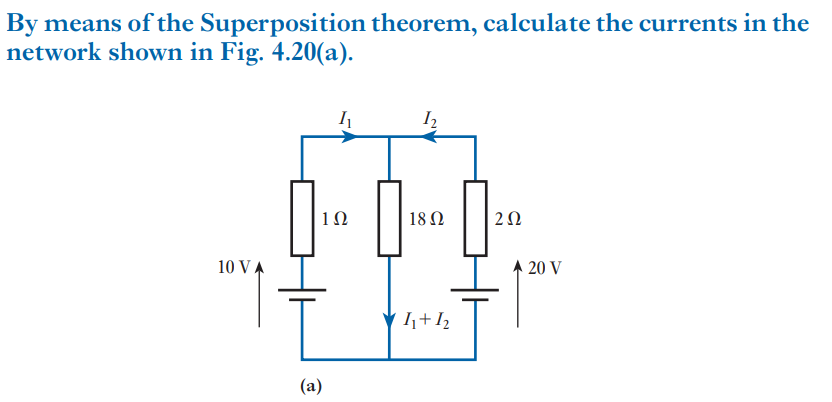
what is Superposition Theorem?
States that in any network containing more than one source, the current in, or the potential difference across, any branch can be found by considering each source separately and adding their effects: omitted sources if e.m.f are replaced by resistances equal to their internal resistances.