(Absolutism) Modern - Euro. - Chapter 5 (CP)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is an absolute monarch, and what makes their power “absolute”?
An absolute monarch is someone with unlimited power, and controls all aspects of society.
How did the decline of feudalism and the rise of national kingdoms help monarchs gain power?
Centralize power and govern without opposition.
What does “divine right” mean, and how did it support absolute rule?
The belief that monarchs are gods on earth, and answer only to Him. They thought God sent this monarch and they get absolute rule.
What are the three main tools that absolute monarchs used to keep control?
Standing army, church support, royal bureaucracy.
How did monarchs use the economy to reduce the power of nobles?
Reduced their wealth and independence.
Why was Louis XIV a good example of an absolute monarch?
Excluded the nobles from counsils, controlled religion and the economy, and declared himself “The state”.
How did Louis XIV control religion and limit people’s freedom?
Limited the pope’s authority, revoked Edict of Nantes, ending the Protestant’s freedoms.
What was the purpose of the Palace of Versailles?
To prove that Louis was an absolute ruler. Built to show power. Cultural heart/center. Forced nobles to live there.
What role did the Church play in supporting absolute monarchs?
Supports and legitimizes the monarch’s rule through divine authority. Helps enforce royal power, and also supports divine right.
What were the two negative effects if Louis XIV’s rule on France?
Wars and heavy taxes, lots of debts.
What caused the conflict between Charles I and Parliament?
Clashed with Parliament over taxes + money. Needed parliaments approval.
What was the purpose of the Petition of Right, and how did Charles I respond to it?
This law limited his power, but Charles just ignored this law —> singed document but ignored it.
Who fought in the English Civil War, and what was the outcome?
The Puritans (support Parliament) and the Royalists (support the king), fought against each other. The Puritans won, and Charles I was executed.
How did Oliver Cromwell chnaged England after the war?
He abolished the monarchy, and created a republic where the people have authority as well. —> ruled as military dictator.
What was the Restoration, and whay was it significant?
The Restoration was the restoration of the monarchy after Oliver Cromwell’s death.
What were the causes and results of the the Glorious Revolution?
Parliament didn’t want a catholic dynasty, so they appoint James’ Protestant daughter and husband to rule. Because of this James II was overthrown.
Why was the Glorious Revolution considered ‘glorious’?
iI twas considered glorious because it was a bloddless overtrhow and James just left.
What is a constitutional monarchy, and how is it different from an absolute monarchy?
A constitutional monarchy is where the monarch and the Parliament govern together. An absolute is when the monarch has all the power.
What does the English Bill of Rights guarantee?
A constitutional monarchy is where the monarch and Parliament govern together. An absolute monarchy is whent eh monarch has all the power.
How did the cabinet system help balance power between the monarchy and Parliament?
The cabinet connected the Parliament with he monarchy, and helped them rule together.
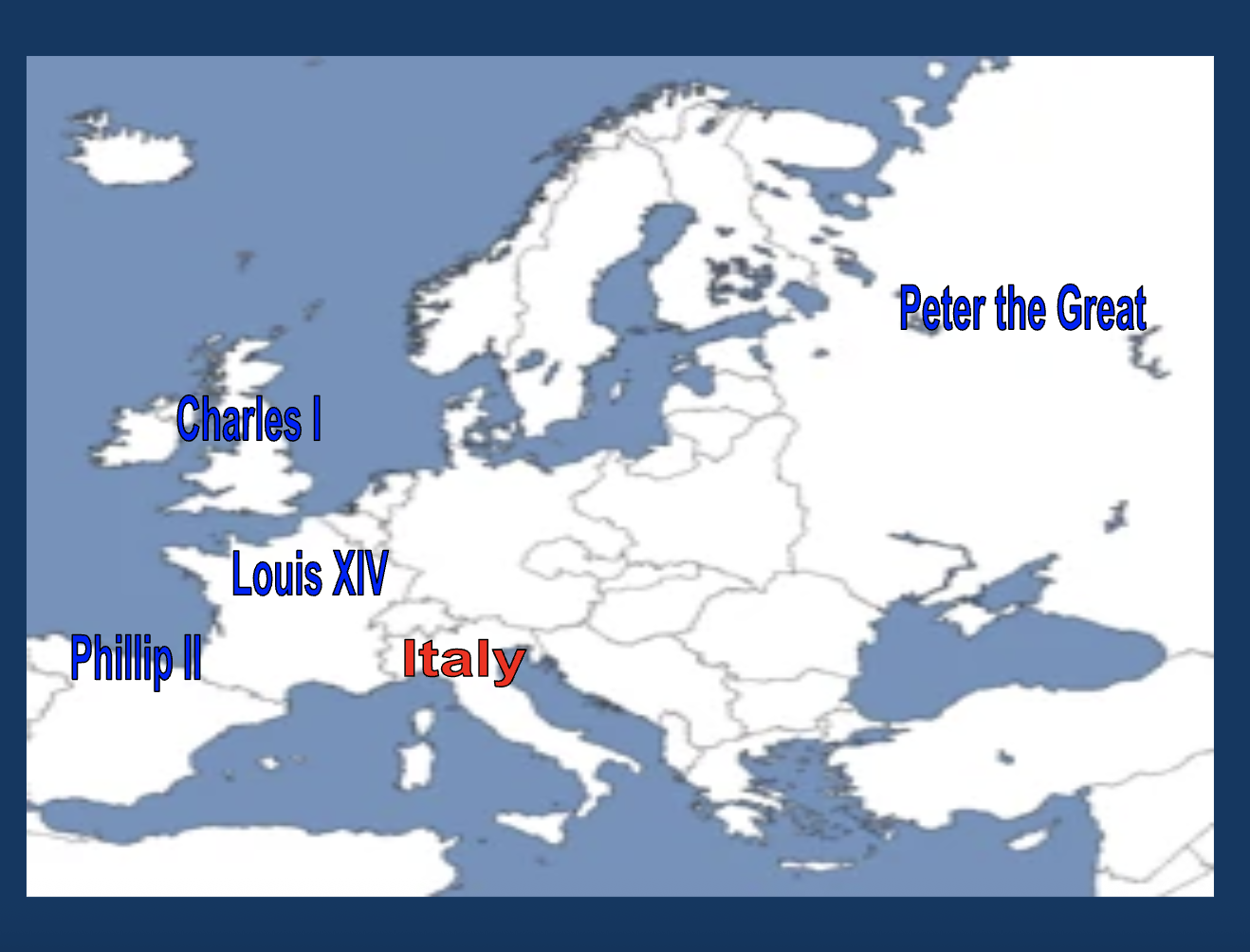
Which country did Philip II rule?
Spain
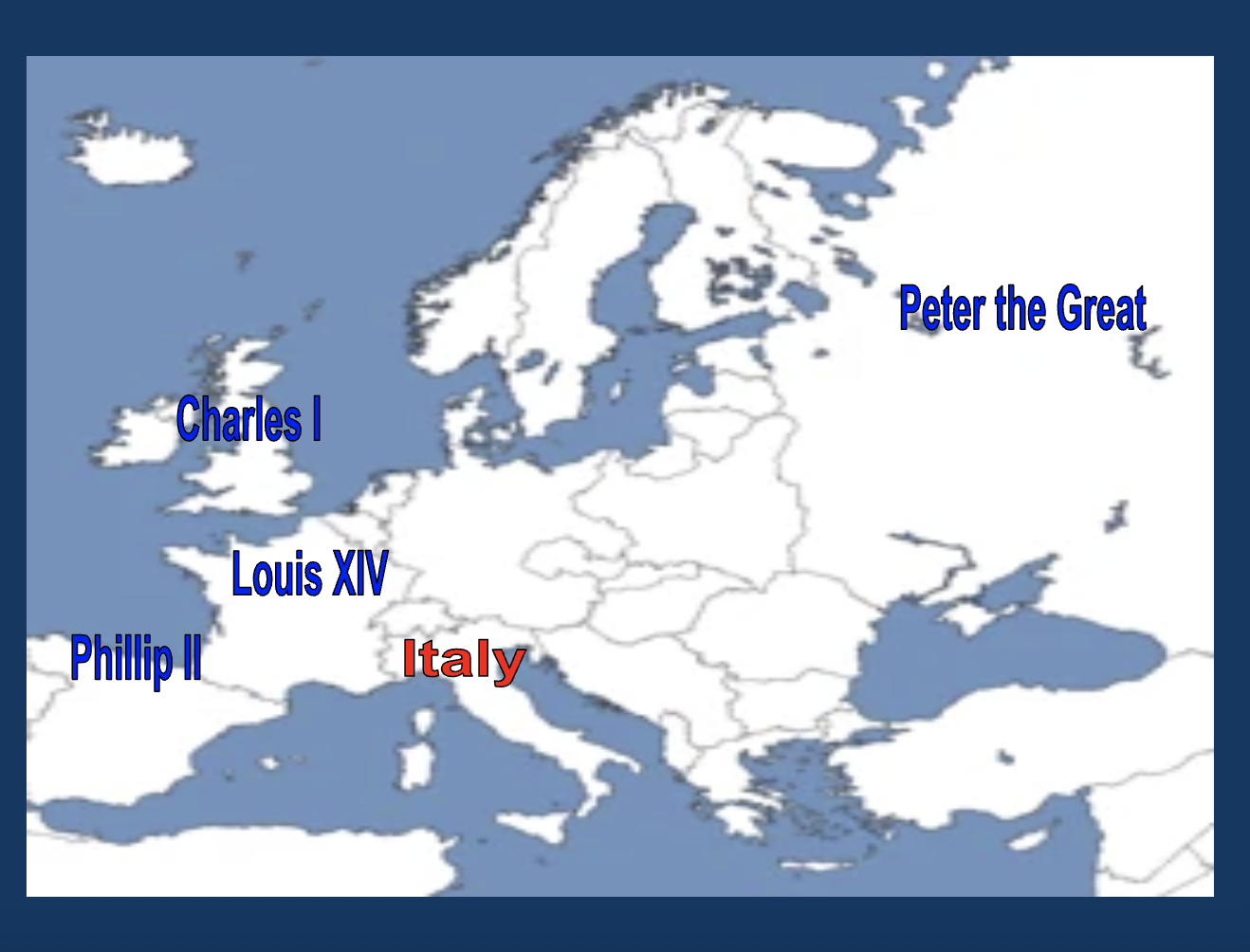
Which country did Peter the Great rule?
Russia
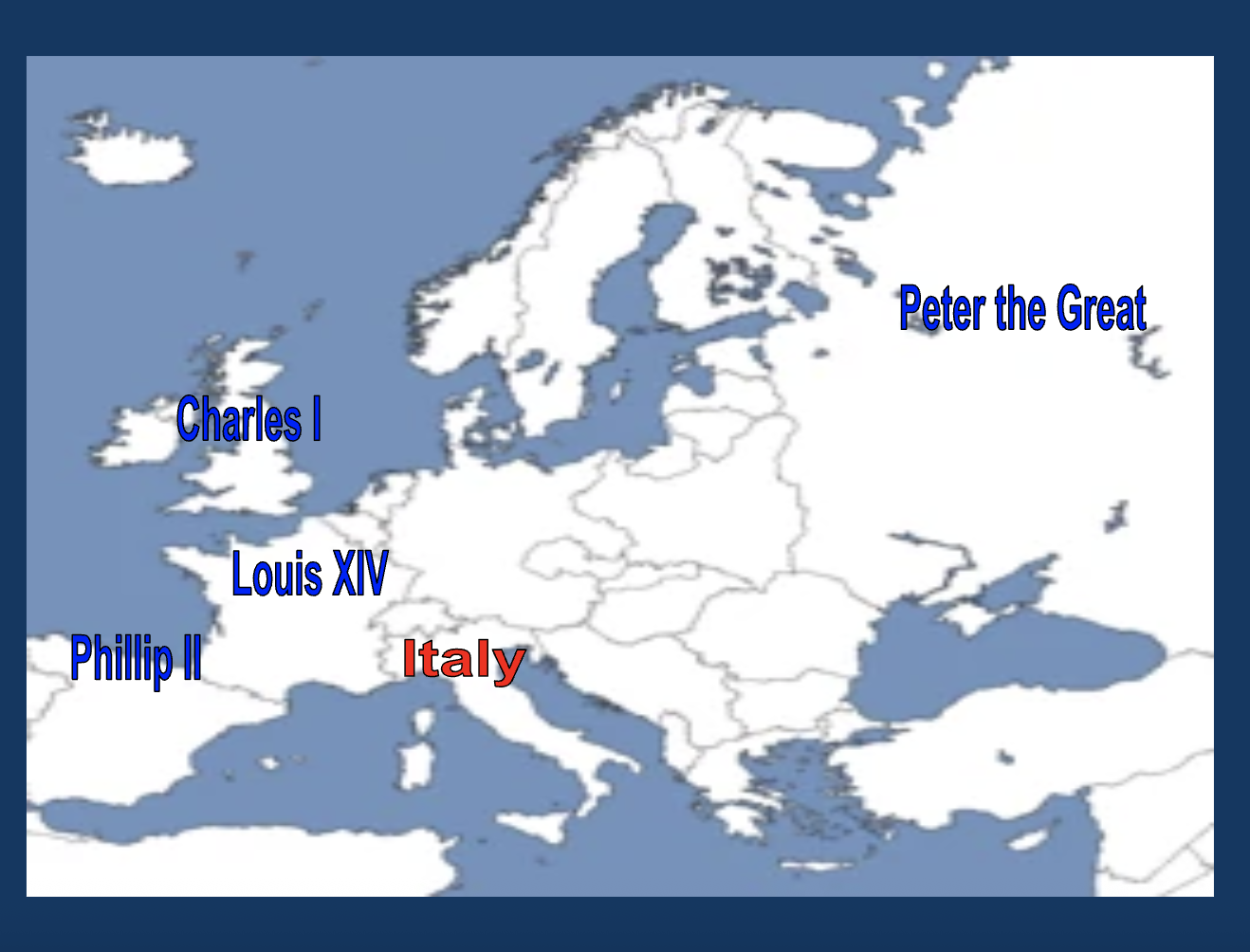
Which country did Louis XIV rule?
France

Which country did Charles I rule?
England

Who ruled Russia?
Peter the Great
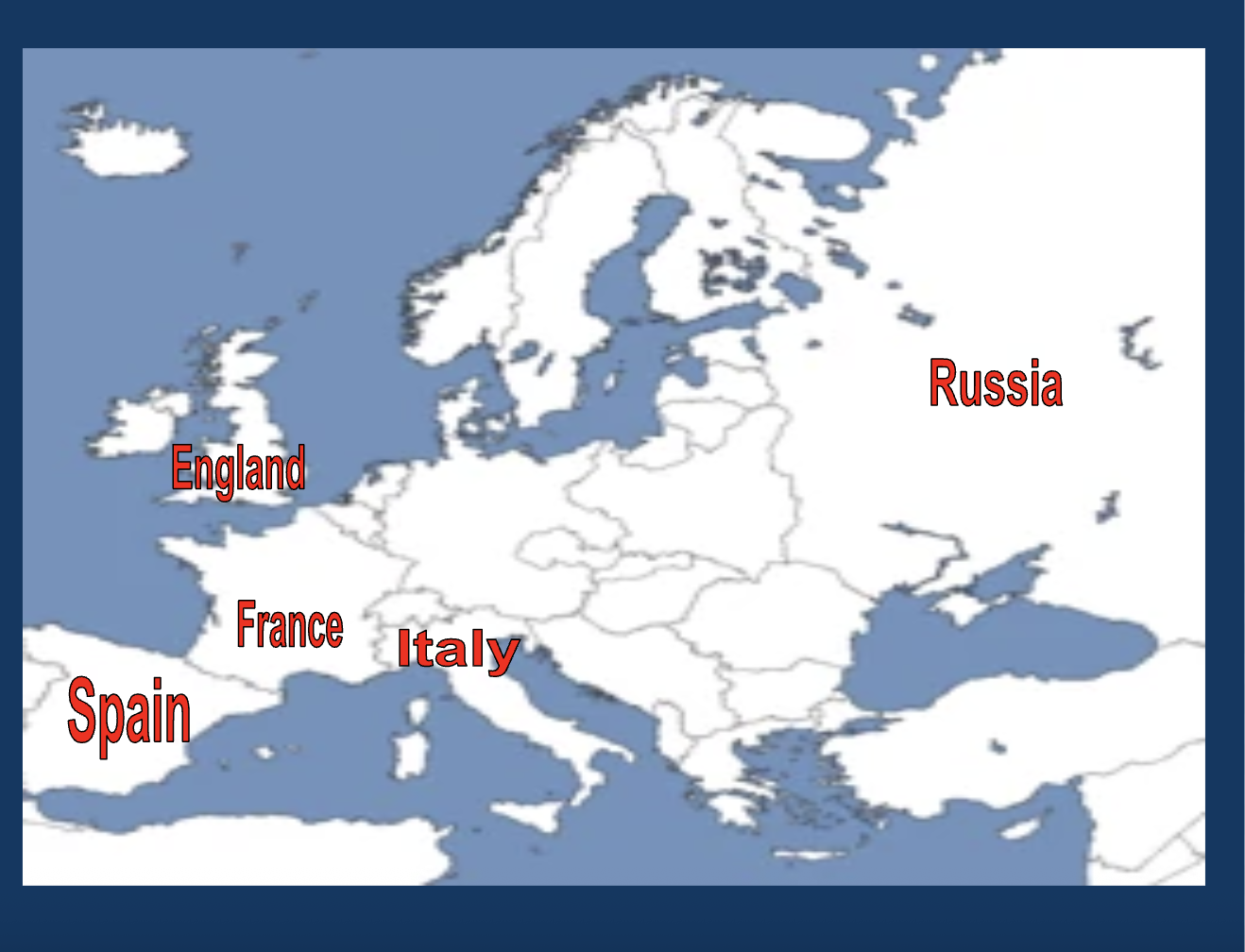
Who ruled France?
Louis XIV
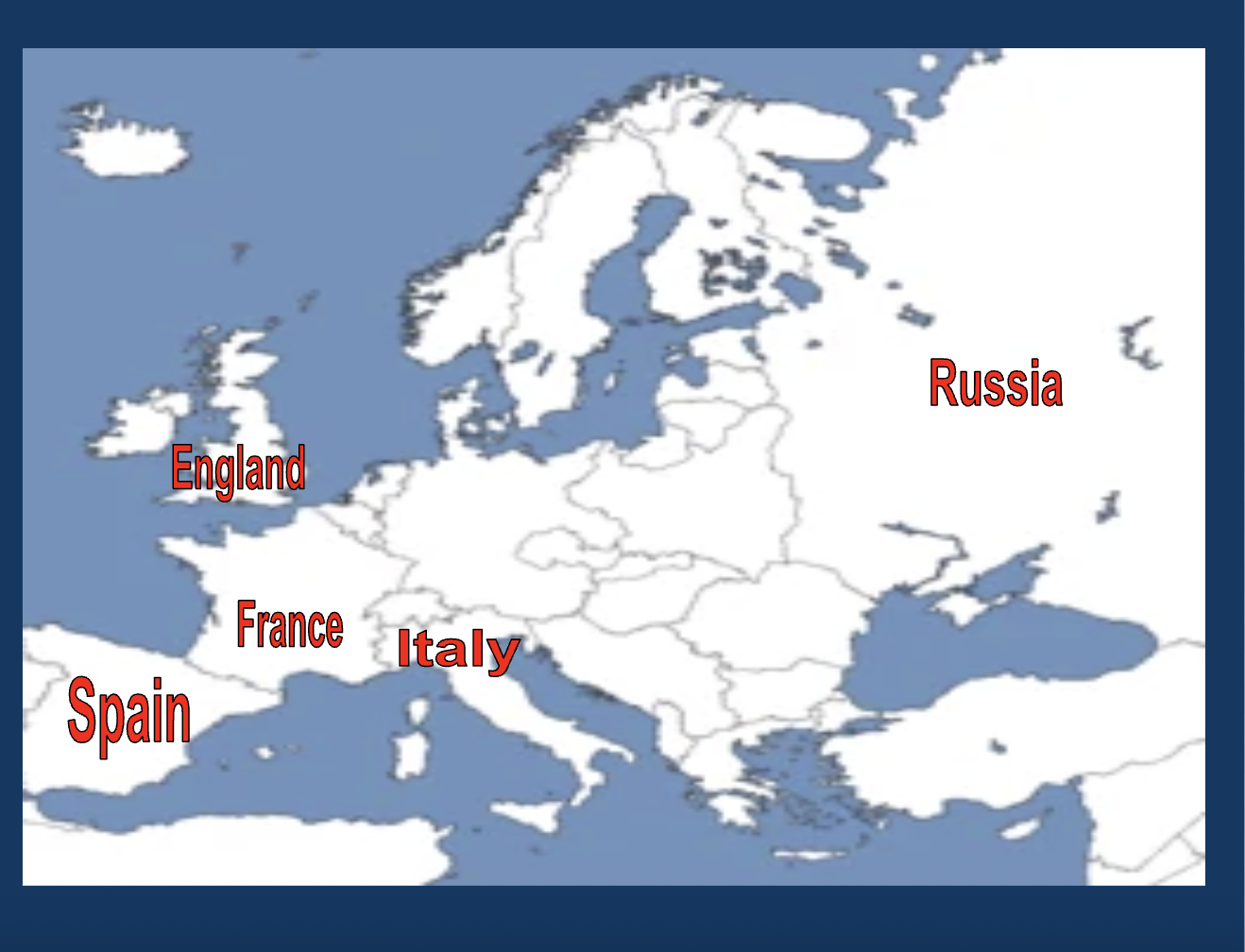
Who ruled England?
Charles I
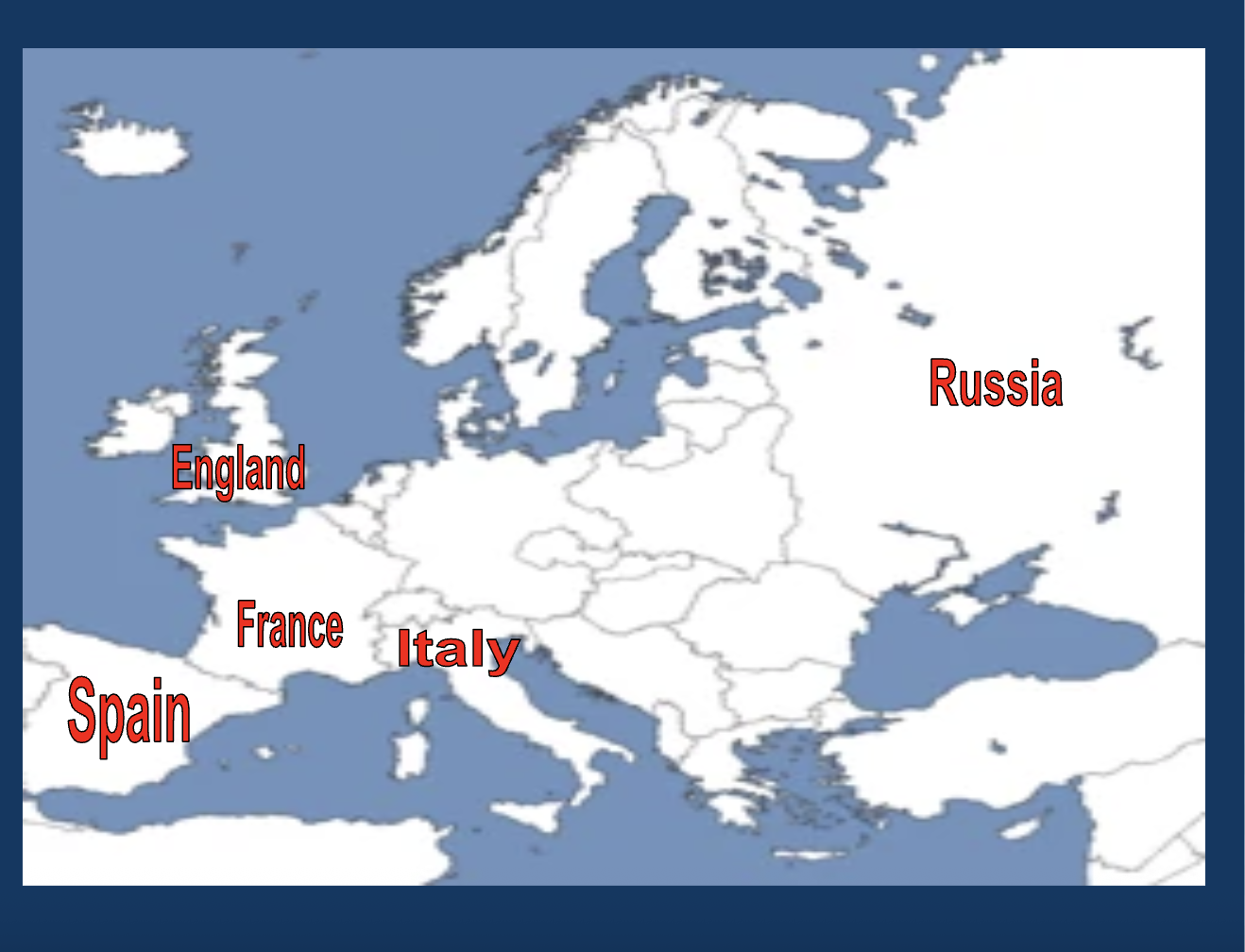
Who ruled Spain?
Phillip II