Nephrons
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
structure
glomerulus, Bowman’s (renal) capsule, proximal convoluted tubule, distal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, collecting duct
glomerulus
‘knot’ of capillaries
tubules function
allow transportation of filtrate to and from the Loop of Henle
collecting duct function
collects urine and passes to the ureter
nephron structure diagram
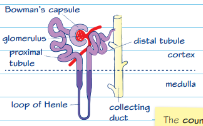
nephron function
site of 3 processes of the kidneys: ultrafiltration - removing substances from the blood
selective reabsorption - reabsorbing the substances the body needs
urine formation - substances which are not reabsorbed travel as urine along the nephron to the collecting ducts where the waste travels to the bladder
counter current multiplier mechanism
allows concentrated urine to be produced e.g. animals with longer loops of Henle - such as desert animals
in loop of Henle
descending limb - permeable to water. Water leaves the nephron by osmosis and is reabsorbed. As much water as the body needs is reabsorbed here
ascending limb - permeable to ions. Because the tissue around the loop has a high concentration of water, Na+ and Cl- ions diffuse out of the nephron. Concentration of salt in the ascending limb decreases further up the limb. Towards the top, some Na+ and Cl- are actively pumped out of the nephron
distal convoluted tubule - where final reabsorption of ions and water occurs to adjust water balance. ADH has an effect on the amount of water reabsorbed here
where does ultrafiltration occur?
in the renal capsule
ultrafiltration process
blood enters via the renal artery and flow through many capillaries under high pressure (renal capsule)
specialised cells called podocytes make up the basement membrane, leaving small gaps. Here, small molecules and ions are squeezed out of the blood by the pressure and into the nephron. Larger molecules e.g. proteins stay in the blood
where does selective reabsorption occur?
mostly in the proximal convoluted tubule
selective reabsorption process
in the proximal convoluted tubule, simple ions, amino acids and glucose diffuse into the blood via channel proteins
some larger molecules are reabsorbed by endocytosis
loop of Henle is important in reabsorption of water and salt
ADH increases the amount of water reabsorbed in the kidneys. Released from the pituitary gland to maintain homeostasis