6.5 ECOSYSTEMS
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
6.5.4
RECYCLING WITHIN ECOSYSTEMS
What are saprotrophs?
Organisms that live on, or in, dead organic matter
Examples of saprotrophs
bacteria and fungi
The steps in saprotrophic decomposition are:
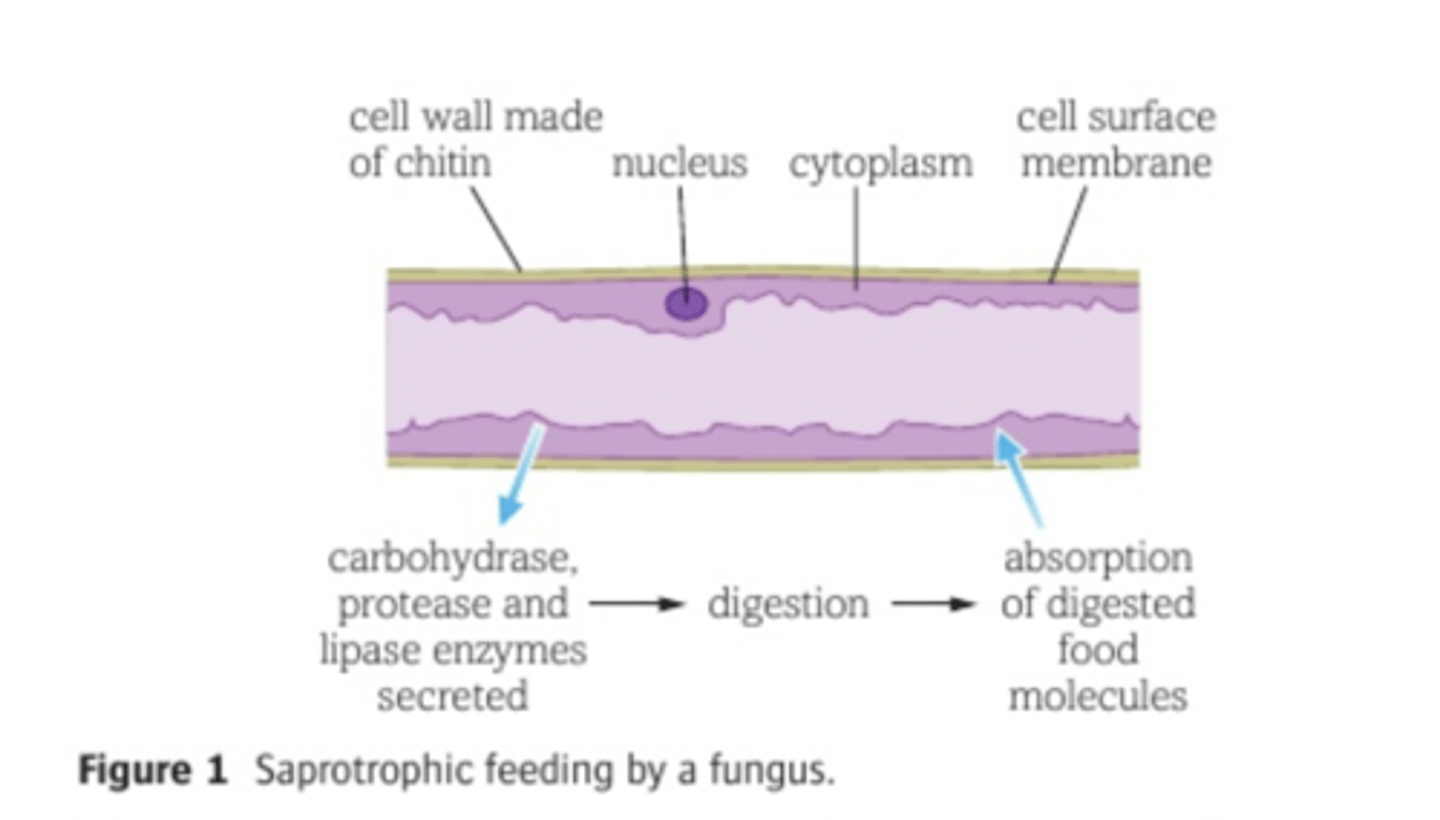
1) Saprotrophs secrete enzymes onto dead and waste material.
2) Enzymes digest the material into smaller molecules, which are then absorbed into the saprotroph's body.
3) Having been absorbed, the molecules are stored or respired to release energy.
What would happen is saprotrophs did not break down dead organisms?
Energy and valuable nutrients would remain trapped within the dead organisms.
By saprotrophs digesting dead organisms:
Microorganisms obtain a supply of energy to stay alive, and trapped nutrients are recycled.
Diagram of saprotrophic feeding by fungus
What is ammonification?
the process in which microorganisms such as bacteria break down organic matter and animal waste into ammonia, which can be used by plants as a natural fertilizer.
What is nitrogen fixation?
Process of converting nitrogen gas into ammonia
What is nitrification?
a process that breaks down ammonia into nitrites or nitrates
What is denitrification?
Conversion of nitrates into nitrogen gas
The nitrogen cycle
The transfer of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere
Diagram of the nitrogen cycle
LOOK AT PHOTO IN TEXTBOOK
Why does nitrogen-fixation by bacteria occur?
Proteins such as leghaemoglobin in the root nodules of plants absorb oxygen and keep the conditions anaerobic. Under these conditions, the bacteria use an enzyme, nitrogen reductase, to reduce nitrogen gas to ammonium ions that can be used by the host plant.
Why does nitrogen need to be fixed?
Because most organisms can't use nitrogen gas since it is very unreactive, so nitrogen needs to be fixed.
What does nitrogen-fixing by free-living bacteria in the soil (e.g. azotobacter) do?
Azotobacter are bacteria that live freely in the soil and fix nitrogen gas.
Where is the nitrogen fixing bacteria, Rhizobium found?
In root nodules of plants such as peas, beans and clover which are all members of the bean family.
What does the nitrogen-fixing bacteria, Rhizobium do?
These nitrogen-fixing bacteria have a mutualistic relationship with the plant: the bacteria provide the plant with fixed nitrogen and recieve carbon compounds such as glucose in return.
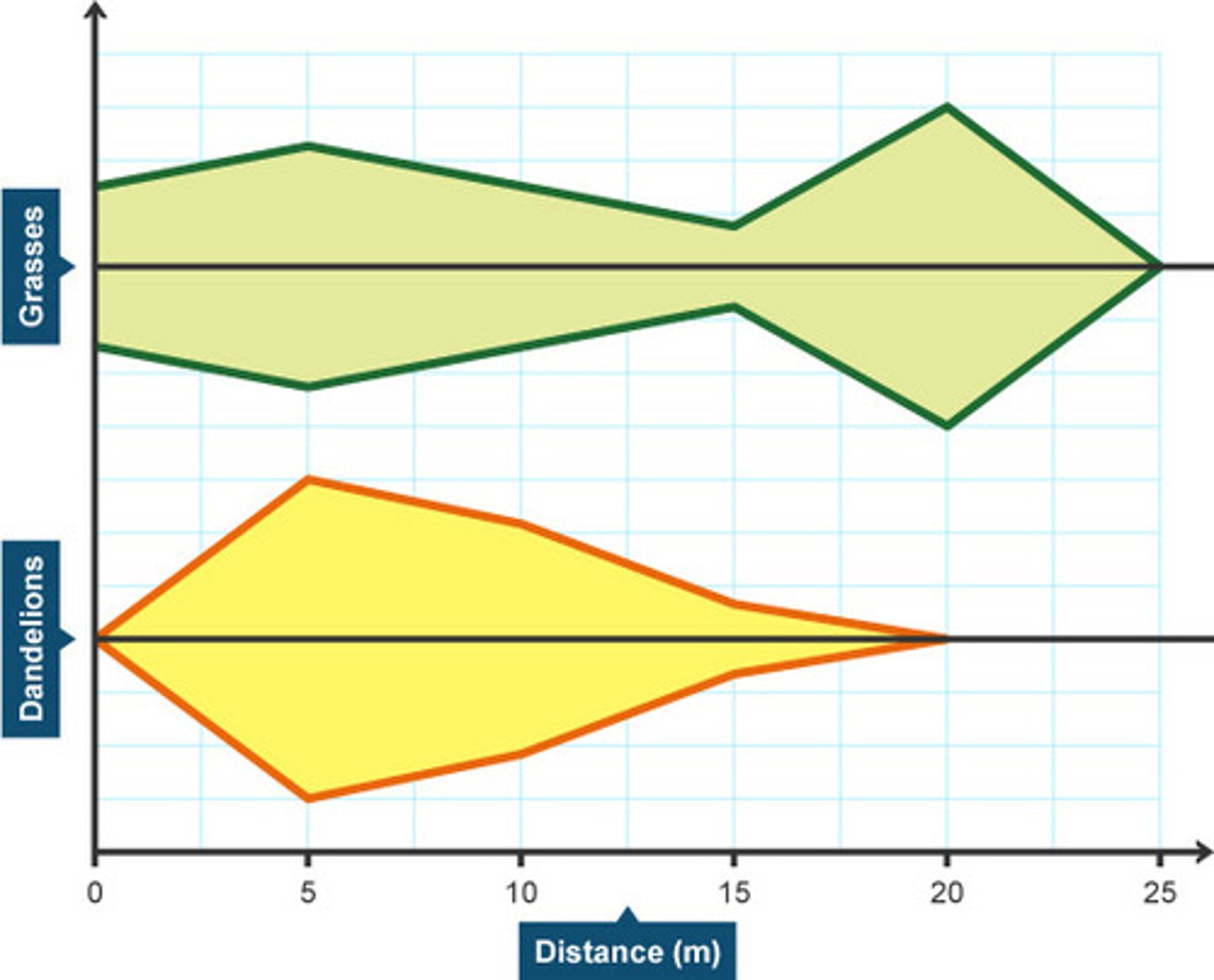
Kite diagram