OChem Exam 3-Ashton Sanchez 11/24/25 (copy)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
In a ring flip for a chair conformation
axial and equatorial are switched, keeping specific bonds
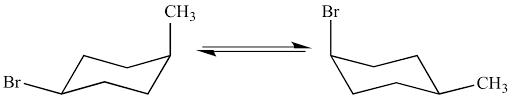
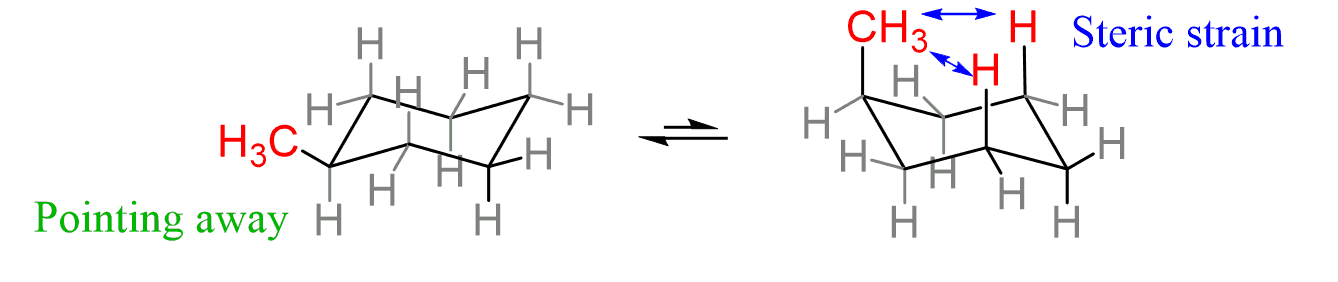
1-3 Diaxial strain
Occurs on axial carbons, when bulky groups have interfering interactions with each other (bulky groups will have less strain when equatorial)
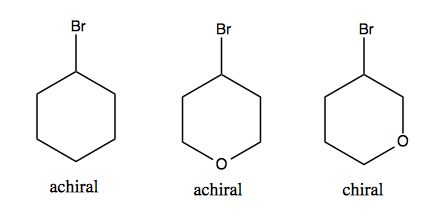
achiral
achiral is one that is superimposable on its mirror image
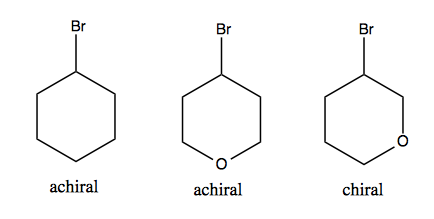
chiral
chiral is one that is NOT superimposable on its mirror image
optically active
pure chemical either S or R conformation
optically inactive
achiral compound or a racemic mixture
Anti addition to a E alkene
substituents will add with opposite bond types (one dashed, one wedged)
Anti addition to a Z alkene
substituents will add to the same bond type e.g. both dashed/wedged
Syn addition to a E alkene
substituents will add to the same bond type e.g. both dashed/wedged
Syn addition to a Z alkene
substituents will add with opposite bond types (one dashed, one wedged)
Strong bases are good nucleophiles
true
SN2 Reaction
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution (always a backside attack of NU compared to LG)
SN1 Reaction
unimolecular nucleophilic substitution
SN2 rxns reverse stereochemistry
true
E2 Reaction
Bimolecular elimination
E1 Reaction
unimolecular elimination
Nucleophiles
Cl-, Br-, I-, OH-, OR-, N3-,CN-, RS-
As you go down a period halogen nucleophiles become
less effective in an aprotic solvent (reversed in a protic solvent)
The more stable a nucleophile is as a base
the less effective it is
protic solvents
methanol. ethanol
1°
Sn2 only
2°
Sn2 & E2
Sn2 rxns are faster in what kind of solvent
polar aprotic
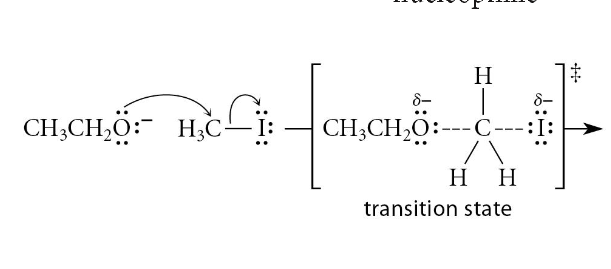
inversion of stereochemistry only at the stereocenter where rxn occurs
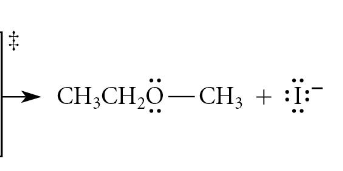
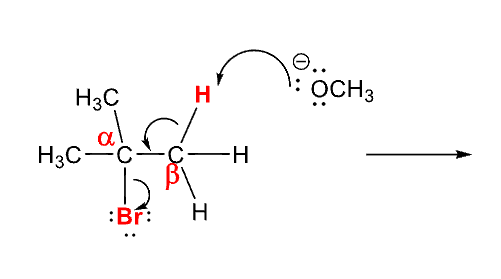
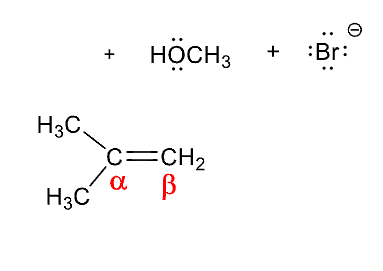
In E2 reactions if there is more than onee B Hydrogen to eliminate
the more substited alkene is formed, unless a bulky group is involved
Enantiomers are generated in a reaction if…
A new stereocenter is formed or an existing one is altered
protic solvent
can act as a H bond donor
aprotic
CANNOT act as a H bond donor
ethanol
protic solvent
methanol
protic solvent
formic acid
protic solvent
H2O
protic solvent
hexane
nonpolar solvent
benzene
nonpolar solvent
diethyl ether Et2O
nonpolar solvent
chloroform
nonpolar solvent
tetrahydrofuran THF
nonpolar solvent
methylene chloride
nonpolar solvent
RO-
Strong Nucleophile and Base
OH-
Strong Nucleophile and Base
RNH2
Strong nucleophile and weak base
RS-
Strong nucleophile and weak base
N3-
Strong nucleophile and weak base
CN-
Strong nucleophile and weak base
X-
Strong nucleophile and weak base
RCO2
Strong nucleophile and weak base
CH3OH
Weak nucleophile and weak base
CH3SH
Weak nucleophile and weak base
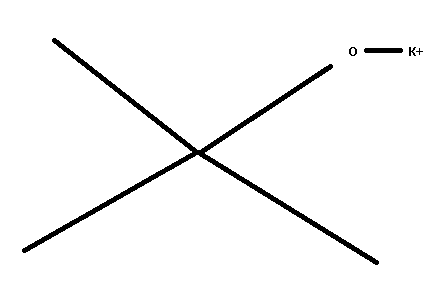
non-nucleophilic base
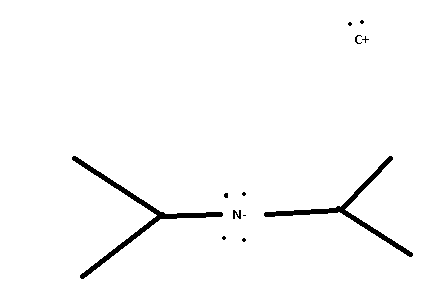
non-nucleophilic base
Na+OET-
Strong base