pray for me
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
164 Terms
Tissues in Every Plant
Dermal Tissue
Vascular Tissue
Ground Tissue
Dermal Tissue
outer layer of plant
includes epidermis in non-woody plants and periderm of woody plants
Function: prevents water loss, protects against pathogens, facilitates gas exchange
Vascular Tissue
Xylem (water transport) and Phloem (sugar transport)
forms stele in roots and vascular bundles in stems and leaves
Function: long distance transport and structural support
Ground Tissue
tissues that are neither dermal nor vascular
includes pith (internal to vascular tissues) and cortex (external to vascular tissues)
Function: photosynthesis, storage, support
Parenchyma
Ground tissue.
Cells: Thin-walled living cells
Location: leaves, cortex and pith of stems and roots
Function: photosyntheis and other metabolic functions
Collenchyma
Ground Tissue.
Cells: Irregularly thickened living cells
Location: leaves, cortex of stem in young plants
Function: flexible support
Sclerenchyma
Ground tissue.
Cells: Thick, dead-at-maturity cells, secondary cell wall with lignin
Location: around vascular bundles
Function: rigid support
Xylem
Cells: Thick, dead-at-maturity, secondary cell wall with lignin
Location: in vascular bundles
Functions: rigid support
Phloem
Cells: living, interconnected cell walls (no lignin), sieve plates
Location: in vascular bundles
Function sugar transport
Indeterminate Growth
Plants grow indefinitely from meristems.
Apical Meristems
Primary growth (length). Found at root and shoot tips.
Lateral Meristems
Secondary growth (thickness). Found in vascular and cork cambium.
Plant Body: Monocots
Plant Body: Eudicot
Vascular Cambium
Responsible for secondary growth. Adds layers of vascular tissue (secondary xylem) aka wood and secondary phloem.
Most of thickening is due to secondary xylem.
Cork Cambium
Responsible for secondary growth. Replaces epidermis with thicker, tougher periderm.
Secondary Xylem
Wood.
Secondary Phloem
What traits distinguish land plants from algae?
Alternation of Generations
Multicellular, Dependant Embryos
Walled Spores of Sporangia
Apical Merristems
Alternation of Generations
Life cycle of plants alternating between haploid gametophytes (n) and diploid sporophytes (2n)
Multicellular, Dependant Embryos
Zygote develops inside female gametophyte, providing protection and nourishment.
Walled Spores from Sporangia
Spores protected by sporopollenin; prevents dessication (drying out).
Apical Meristems
Regions of active cell division that allow plants to grow from roots and tip.
What helped the transition to land for land plants?
Traits were developed that prevented dessication, promote reproduction, and grow stronger.
Cuticle
Waxy layer covering epidermis. Minimizes water loss and protects against microbial attacks.
Mychorrizae and Land Plants
Fungi and early land plants had associations. Fungi helped with mineral absorbance before true roots were developed.
Groups of Land Plants
Vascular Plants
Non-Vascular Plants (Bryophyta)
Vascular Plants
Have a specilized system (xylem and phloem) which transport water and nutrients. Divided into seed plants and seedless.
Non-Vascular Plants
No vascular tissues or system, no lignin.
Divided into 3 phyla:
Hepatophyta - liverworts
Bryophyta - mosses
Anthocerophyta - hornworts
Dominant gametophyte.
Stomata
Pores in land plants that regulate gas exchane and manages water loss by closing/opening.
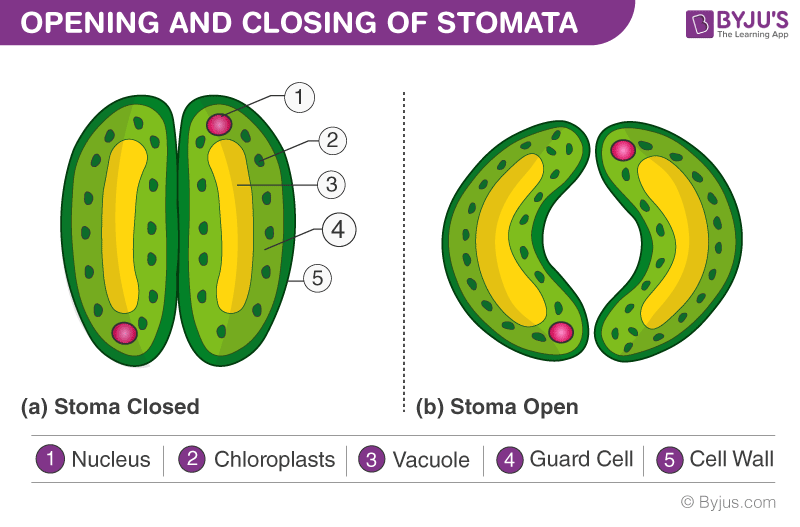
Hepatophyta
A phyla of Non-Vascular Plants (Bryophytes). Does not have a cuticle or stomata.
Bryophyta
A phylum of non-vascular plants (bryophyta). Has a cuticle and stomata.
Lignin
A polymer found in cell walls of plants. Provides structure and support.
Why cannot non-vascular plants grow very tall?
No vascular system to transport water and minerals; they rely on diffusion for water transport.
No vascular tissue for structural support.
Ecological Importance of Mosses
Mosses form peat bogs which store carbon and help regulate climate.
Groups of Vascular Plants
Seed plants
Seedless plants
Traits in Vascular Plants (but not in non-vascular)
Dominant sporophyte generation
Vascular Tissue
Roots and leaves
Basic Structure of a Seed
Embryo
Nutrient Supply
Seed Coat
Function of a Seed
protection and nourishment to embryo
allows for dormancy and delayed germination
allows for dispersal and survival through harsh conditions
Groups of Vascular Seed Plants
Gymnosperms (naked seedplants)
Angiosperms (flowering plants)
Gymnosperms
A group of seeded vascular plants (naked seed plants)
4 phylum:
Ginkgophyta
Cyadophyta
Gnetophyta
Coniferophyta
Ginkgophyta
Only 1 surviving species. Ginkgo biloba.
Coniferophyta
Largest phylum of gymnoperms.
Includes firs, pines, and redwoods.
Needle or scale-like leaves
Cyadophyta
Resembles palm trees.
Gnetophyta.
Diverse group of shrubs.
Gymnosperm’s Adaptation to Land
needle-like leaves for water retention
thick cuticle
pollen eliminates need for water based fertilization
Phyla of Seedless Vascular Plants
Monilophytes
Lycophytes
Reproduces via spores.
Monilophytes
Includes club mosses, spike mosses, and quillworts
Have microphylls
Lycophytes
ferns, horsetails, whiskferns
Have megaphyll
Megaphyll
Complex leaves with branched veins.
Microphyll
Simple leaves with single vein.
Phylum of Angiosperms
Phylum Anthophyta (flowers and fruits)
2 General Categories of Angiosperms
Monocots
Eudicots
Monocots
Parallel leaf venation
1 cotelydon
fibrous root system
Pollen shape
Flower parts in multiples of 3
scattered vascular bundles
Eudicots
netlike leaf venation
2 cotelydon
taproot system
Pollen thing
Flower parts in multiples of 4 or 5
Ring-arranged vascular bundles
Distinguishing Features of Animals
Nutritional mode
Cellular Organization
Development
Nutritional Mode of Animals
Ingestive heterotrophs. Consumes other organisms or organic molecules and digests with enzymes.
carnivores, herbivores, omnivores, detrivores
Cellular Organization of Animals
Multicellular eukaryotes.
No cell walls but have structural proteins (collagen)
unique to animals - muscle and nerve cells
Development of Animals
Embryonic development
clevage - rapid mitotic cell division
blastula formation - hollow ball of cells (blastula) forms
gastrulation - blastula invaginates, forming gastrula with distinct embryonic layers
Common Ancestor of Animals
Choanoflagellates.
similar genes
collar cells only found in animals, not plants or fungi
Bilateral Symmetery
“a line straight down the middle”
leads to cephalization
Cephalization
Concentration of sensory structures in the head; promotes active movement.
Radial Symmetry
“like a pie”
allows immobile or drifting animals to interact with their environment from all directions.
Diploblastic
2 germ layers:
Ectoderm (outer) - gives rise to outer body covering
Endodem (inner) - forms digestive tract lining
Ex. cnidarians
Triploblastic
3 germ layers:
Ectoderm (outer) - outer body covering
Mesoderm (middle) - forms muscle and most internal organs
Endoderm (inner) - forms digestive tract lining
Ex. all bilaterians
Coelomates
have a true coelom (body cavity fully lined with mesoderm)
Ex. annelids, chordates
Pseudocoelomates
body cavity partially lined with mesoderm
Ex. nematodes
Acoelomates
lack a body cavity, restricting organ movement
Ex. platyminthes
Major Clades of Bilaterians
Deuterostomia - echinodermata, chortata
Lophotrochozoa - mollusca, annelida
Ecdysozoa - arthropoda, nematoda
Phylum Porifera
lack tissues, but have some specialized cells
no symmetry
sessile (not moving throughout its life)
filter feeders - filters water through body to capture food particles
Ex. sponges
Phylum Cnidaria
2 tissue layers - contractile and nerve tissues
radial sym.
no organs
diploblastic
has cnidocytes (stinging cells)
gut with one opening (gastrovascular cavity)
2 forms: polyp form and medusa form
Ex. jellyfish, coral, anemone
Cnidaria: Polyp Form
cylinder or tube-like
upward mouth
sessile
Cnidaria: Medusa Form
bell-shaped
downward mouth
freeswimming - pulsing or drifting
Phylum Platyminthes
bilateral sym.
acoelomate
flattened body
gut with one opening (gastrovascular cavity)
organ systems
free-living or parasites (parasites don’t have digestive system)
Ex. flatworms
Phylum Rotifera
bilateral sym.
pseudocoelomate
complete digestive system (gut with 2 openings)
organ systems
Ex. rotifer
Phylum Annelida
bilateral sym.
coelomate
organ systems
segmented body
closed circulatory system
complete digestive system
segmentation differentiates them from nematodes and flatworms
Phylum Mollusca
body (generally shelled) with: foot, visceral mass, and mantle
bilateral sym.
organ systems
complete digestive system
coelomates
classes: gastropods, cephalopods, bivalves
Phylum Nematoda
bilateral sym.
cylindrical body
pseudocoelomate
complete digestive system
free-living or parasites
exoskeleton
Phylum Arthropoda
most species- and lifestyle-diverse animal phylum
flexible chitinous exoskeleton
versatile, jointed appendages
highly developed sensory organs
segmentation
metamorphasis
complete digestive tract
bilateral sym.
open circulatory system
Protostomes
Mouth develops from blastopore.
Ex. mollusks, annelids
Deuterostomes
Anus develops from blastopore.
Ex. echinoderms, chordates
Phylum Echinodermata
bilateral sym in larvae, radial sym. in adults
calcareous exoskeleton
water vascular system
complete digestive system
coelomates
deuterostomes
Ex. starfish. urchins, seacucumbers
Phylum Chordata
notochord, pharyngeal slits, dorsal nerve cord, post anal tail
bilateral sym.
super huge and lots of subphylums
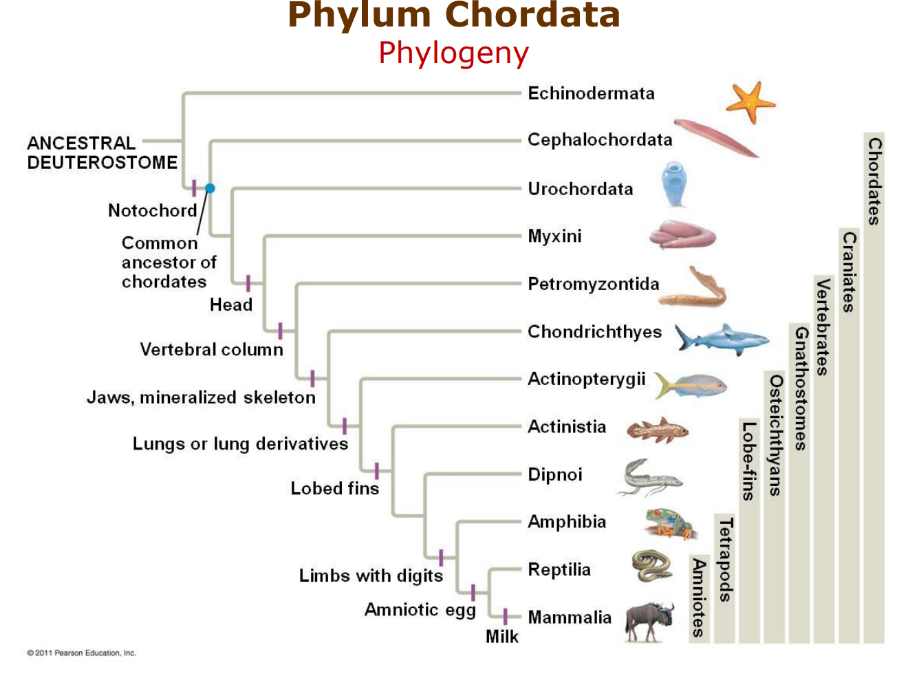
Vertaebrates
muscular post-anal tail
notochord
dorsal, hollow nerve cord
pharyngeal slits or clefts
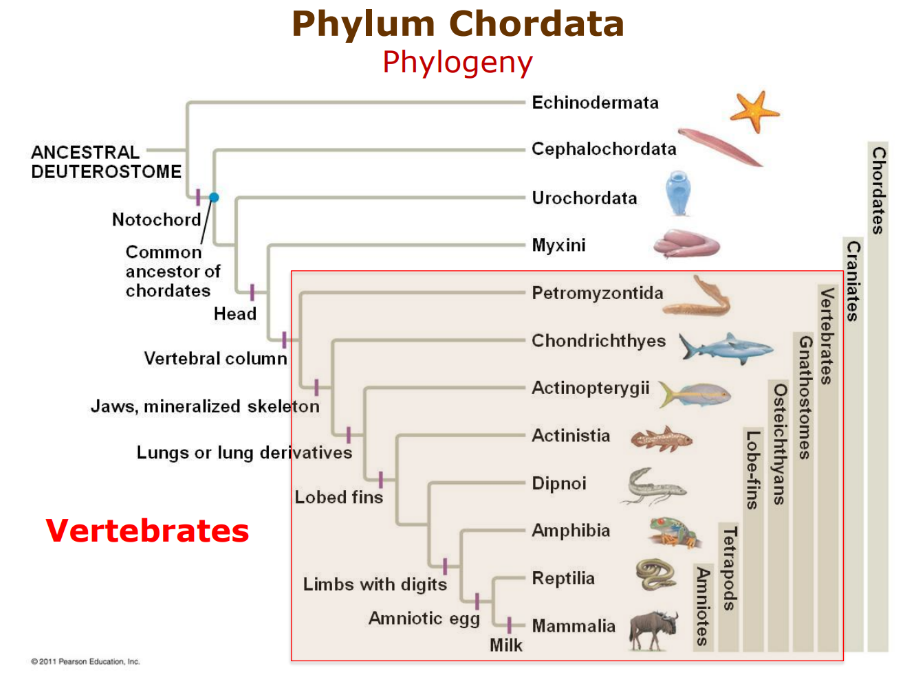
Oldest Lineages of Vertebraes
Hagfish and Lamperys.
lack jaws
no backbone
rudimentary backbone made of cartilage
bottom dwelling scavengers
most are parasitic that latch and pierce with tongue to feed
Osteichthyes
“bony fish”
buoancy control with swim bladder
flat bony scales
Chondrichthyes
“cartilage fish”
skull and jaws
tooth-like scales
predators (sharks) and bottom feeders (rays)
Osteichthyes vs. Chondrichthyes
bony skeleton vs cartilaginous skeleton
Types of Osteichthyes
Ray-finned and Lobed-fin
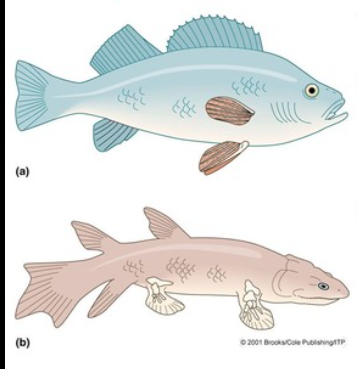
Ray-finned Osteichthyes
bony skeleton
bony rays
Lobed-finned Osteichthyes
lobed fins
rod-shaped bones in pectoral and pelvic fins surrounded by thick layer of muscle
Tetrapods
“4 feet”
in place of pectoral and pelvic fins, limbs with digits
limbs support weight on land
muscles produce force to move
head and neck
lung breathing
Origin of Tetrapods
lobed finned fishes in oxygen poor water could use their lungs to breathe instead
they moved by propping themselves up on their fits and walking in water
wrists, ribs, and necks are ancestral to tetrapods
Amphibians
most basal group of tetrapods; vertebrates
semi-terrestrial
rely on moist skin for gas exchange
Metamorphasis:
aquatic tadpole with gills to semi-teresstrial adult with lungs
Amniotic Egg
pivotal for vertebrae colonization of land
allowed vertebrates to reproduce away from water bodies, reducing reliance on aquatic bodies for reproduction
Structure: protective shell with specialized membranes
Amnion, Chorion, Allantois, Yolk sac
Amnion
Encloses embryo in fluid-filled cavity, cushioning against mechanical shock.
Chorion
Facilitates gas exchange between embryo and external environment.
Allantois
Involved in waste storage and respiration.
Yolk Sac
Provides nutrients.
Classes of Amniotes
Birds (Aves)
Mammals (Mammalia)