Relationships
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
( AO1) what is sexual selection
Characteristics that increase our chance of reproduction are passed on through generations such as male aggression
(AO1) what is anisogamy
difference between male and female sex cells ( sperm and ovum) creates different reproduction strategies and partner preferences
sperm → high quantity and little energy
Ovum → small quantity and produced in limited years
(AO1) types of sexual selection
Intra-selection
Inter-selection
( AO1) what is inter- sexual selection
female strategy → due to greater investment ( more energy into development of ova ) more selective with partner ( longer courtships)
Genetically fit partner who can provide resources ( sexy sons hypothesis)
(AO1) what is intra- sexual selection
Male strategy → quantity over quality
men are competing for females in order to pass on genes
What is the evolutionary theory of relationships
Sexual selection
(AO1) sexual selection what are differences in partner preference
Males → youth and fertility, 7: 10 Hip to waist ratio
Females → Genetically fit with resources
(AO3) what studies support sexual selection theory
Clark → 75% of men agreed to have sex with stranger while no females agreed
Buss → self-report survey over 33 countries found out
female → financial stability and ambition
male → younger / fertile attractive women
(AO3) limitations sexual selection
L: Low temporal validity as women are becoming more financially stable and independent → smaller emphasise on male resources
What factor affects attraction
Self-disclosure
filter theory
( AO1) what is self- disclosure
Gradually revealing personal information to increase trust and intimacy between partners
( AO1) What is social penetration theory
Gradually revealing experiences and emotions increases trust
more reciprocal sharing = more trust
Positive correlation between the depth and breadth of sharing and increasing quality and trust
( AO1) Negatives of self-disclosure
Too much self-disclosure too early into a relationship can be detrimental
(AO3) study supporting self-disclosure theory
Hass → Relationships with high levels of commitment and intimacy use self-disclosure to maintain it ( practical application)
( AO3) advantages and disadvantages of Self-disclosure theory
A: real life application → used in couples therapies increase trust → increases validity of self disclosure / Social penetration
L: all correlational data no cause and effect reduces internal validity
L: Culture bias → based on western and individualist cultures.
Tang et al → China and USA have equal relationship satisfactory even though USA disclose more suggests other factors such as physical attractiveness have greater or equal value
what are the theories of romantic relationships
SET
Equity theory
investment model
Ducks phase model
(AO1) what is the basis principle of SET
its a economic theory, people in relationships seek exchange they based on our CBA
SET (AO1) what is the minmax principle
we try to minimise our costs and maximise profits in relationships
SET ( AO1) how is satisfaction in a relationship created
when Profits are greater then costs = satisfaction
(AO1) Examples of profits and costs in SET
Profit → companionship , sex
Costs → stress, time
(AO1) SET how are profits measured
Comparison levels → based on previous relationships / movies
alternatives → stay in relationship because more profitable then alt
( AO1) what are the stages of relationships
Sampling stage
Bargaining stage
Commitment stage
institutionalisation stage
rewards increase through the stages every relationship must go through to develop
( AO1) SET what happens in the Sampling stage ?
Explore costs and profit through experimenting or observing
( AO1) SET what happens in the Bargaining stage ?
Beginning of the relationship → Social exchange starts
( AO1) SET what happens in the Commitment stage ?
Cost and profits are predictable → rewards increase , costs decrease
( AO1) SET what happens in the Institutionalisation stage ?
Costs and profit is now established
partners are settled
(AO3) what are the studies in SET
Sprecher → best predictor for satisfaction is when profits exceed costs.
101 relationships → satisfaction is low one partner believed losses exceeded profit
(AO3) Limitations and advantages of SET
A: greatest strength explanation why people stay in abusive relationships → Practical applications used to develop help programmes
L: Cause and effect issues → data relies on self-report techniques as SET is abstract
L: Reductionist → simplifies complex romantic relationships to profit and reward ignores with cognitive issues such as equity and sense of fairness
( AO1) basic principles of equity theory
Perceived Economic fairness → Costs and profits should be equal in a relationships → satisfaction
(AO1) Equity theory what does a lack of equity cause
Over benefitting or under benefitting in relationship
Over → cause guilt in relationship
Under → resentment
(AO3) what studies support equity theory
Utne → Satisfied marriages valued equity as relationship success ( ecological validity real life) self report in 118 marriages
(AO3) Limitations and Advantages for Equity theory
L: idiographic approach rather than monoethnic → Equity in loving relationships is emotional and unquantifiable
L: Cultural relativity as evidence from YARVIS populations cant be extrapolated to everyone
(AO1) Ducks phase model what are the stages of a relationship break down ( Dissolution)
Intrapsychic stage → contemplate dissatisfaction in relationship ( internally)
Dyadic stage → confront partner and voice dissatisfaction
Social stage → Make concerns / break up public
Grave-dressing → constructing own version of events → make yourself look better
(AO3) limitations and advantages of Ducks phase model ( Dissolution)
A: Practical application → utilised by relationship counsellors to reverse stages and repair relationships
L: methodological issues → all retrospective , self-report evidence → social desirability bias → less reliable
L: Psychologists suggest may be a resurrection phase due to model oversimplifying
learn from experience in new relationship
L: culture bias → arranged marriages don`t folllow
(AO1) Invest model (Image)
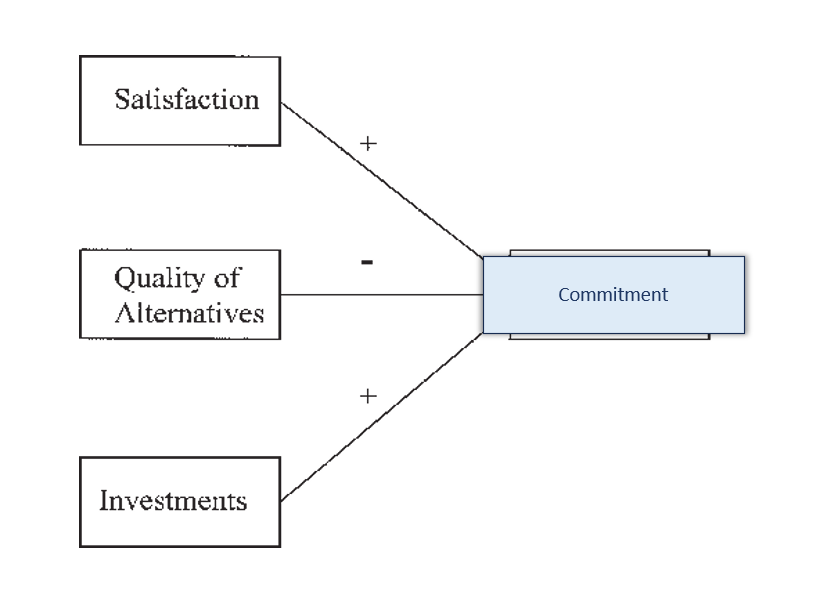
(AO1) Investment model what are the factors that effect commitment
Investment
Satisfaction
Alternatives
( AO1) Investment model how does satisfaction influence commitment
Based on comparison level → profit exceeds costs
getting more from previous relationship
( AO1) Investment model how does Alternatives influence commitment
Alternative options ( new partner or single) Costs exceed Profits then stay in relationship
( AO1) Investment model what are the two types of Investments and example
Intrinsic → put directly into relationship ( money, energy, time)
Extrinsic → Created from relationship ( Children, mutually owned house)
(AO3) studies supporting Investment model
Agnew → meta analysis 52 studies over 5 countries discovered Commitment was best predictor for stable, long lasting relationships → high validity.
(AO3) Limitations and Advantages of Investment model
L: lack of cause and effect → all strong correlational research → states what is associated with commitment not creates it.
A: Practical applications for police / social workers understand why people stay in abusive relationships and offer support
L: Long term relationships may be based on equity
Cultural relativity → population bias YARVIS
Why do humans match ( attractive - attractive / ugly - ugly) when looking for partners ( AO1)
Rejection is traumatic so we try to avoid it by settling for someone at our level
attractive-attractive → balanced relationship easier to maintain.
what is meant by matching (AO1)
We seek partners who are similar to our own perceived attractiveness
( Filter theory) what are the main filters ( AO1)
Social demography
Similarity in attitudes
Complementarity → need to complement each other, adds depth to relationship
( Filter theory) what is social demography and why is it important
location / religion → relationships need accessibility and understanding each others experiences
( Filter theory) what is similar attitudes and why is it important
same values and beliefs
( Filter theory) what is Complementarity and why is it important
need to complement each other, adds depth to relationship
limitations of ALL evolutionary explanations
ALL lack falsifiability required to be seen as scientific. A large body of evidence cant demonstrate a cause and effect relationship.
what are virtual relationships ?
Relationships that begin and function online
what type of people are more likely to be virtual relationships ( AO1)
Introverts
Insecure- resistant attachment type
social awkwardness
How are virtual relationships different to physical relationships? ( AO1)
Textual intonations are important
emoji substitute facial expressions
Greater emphasise on response timing
engage in selective self-presentation
(Virtual relationships) what is disinhibition and what does it lead to? (AO1)
disinhibition can occur due to anonymity and deindividuation
lead to increase in aggressive / not kind comments ( trolling)
(Virtual relationships) what is the reduced cues theory ( AO1)
due to disinhibition → people say and do things they wouldn’t normally?
( Virtual relationships) self- disclosure ( AO1)
more intense and happens quicker lead to better, deeper VR
( Virtual relationships) Gating ( AO1)
Gates are barriers that normally restrict formation of relationships speech - > defect introverts social awkwardness
In VR there’s a absence of Gates
Research evidence for VR ( AO3)
Mckenna → Relationships that originate online are most durable
Bargh → VR develop faster due to increased intimacy then IRL
What are Para-social relationships ( AO1)
Object of a PSR is largely unaware of the existence of person
factors that increase likelihood of forming a PSR increased ( AO1)
object of affection is attractive / high status
perceived similarity
lonely / shy man forming PSR with women
what are the 3 stages of a PSR (AO1)
Entertainment social
intense-personal
borderline- pathological
what is the entertainment - social ( PSR) ( AO1)
Keep up with celebrity for entertainment and gossip
what is the intense-personal ( PSR) ( AO1)
intensive and compulsive feelings towards celebrity
what is the borderline-pathological ( PSR) ( AO1)
Empathise with failures and successes
over- identification and uncontrollable behaviour
fantasies about celebrities life.
What is the explanations for PSR ( AO1)
Adsorption- addiction model
what is the adsorption- addiction model ( AO1)
Adsorption → following celebrity hides them from their own unfulfilled life → find this rewarding so become more, more consumed
Addiction → Gain a dependency on celebrity life as they need to sustain commitment to relationship as primary source of reward
(PSR) how can Bowlby theory be linked to PSR
insecure- resistant → Greater need for fulfilment in PSR without being rejected
attachment issues → poor IWM
Research for PSR ( AO3)
Meloy → strong evidence links stalking to social incompetence
Greenwood → PSR is a mechanism for dealing with recent loneliness / loss
Limitations and advantages of VR ( AO3)
A: Social benefits → help reduce loneliness and easier then IRL relationships
L: Low temporal validity as VR is changing so video calling invalidates a lot of the absence of gating
L: Low Populational validity → due to more young people engaging in social media
groups are over-represented in research ( introverts)
Limitations and Advantages of PSR ( AO3)
A: celebrity attitude scale very useful → contains distractors to remove response bias
makes distinctions between pathological relationships and none
L: EV such as impulsive personalities aren’t controlled → leads to high intense-personal score on CAS even without PSR
L: Adsorption- addiction model is a description doesn’t provide explanation. No practical application or solutions
L: adsorption- addiction model views PSR as pathological / could be argued that PSR are safe exploration of emotion and are positive / no longer lonely.
why are VR relationships different from IRL
state of disinhibition so we are either hyper - honest/ dis-honest
more self-disclosure
absence of gates
selective- self presentation
filter theory ( AO3)
Taylor → people tend to marry own ethnic groups
Temporal validity → society is more diverse / technology taking away physical constraints