Health Policy 21 | Short History of Health Reform and Values, Legislative Process, Key Federal agencies
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Who helped start the idea of health insurance?
Otto Von Bismarck introduced sickness insurance in Germany in 1883.

Why did Bismarck support health insurance?
To support workers and prevent them from joining socialist movements.

What did Teddy Roosevelt believe about health insurance?
He thought it was important for a strong military, but Congress didn’t support him.

What group tried to bring health insurance to workers?
Economists in the American Association for Labor Legislation; they were supported by national AMA but opposed by unions and private insurers.

Why did health reform ideas stall after WWI?
Anything German, like social insurance, was unpopular.

What did research say about U.S. medical care in the 1930s?
More care was needed, but many opposed mandatory insurance.

What health reform was proposed after WWII?
Wagner-Murray-Dingell Bills
National health insurance funded by payroll taxes. but it never passed.

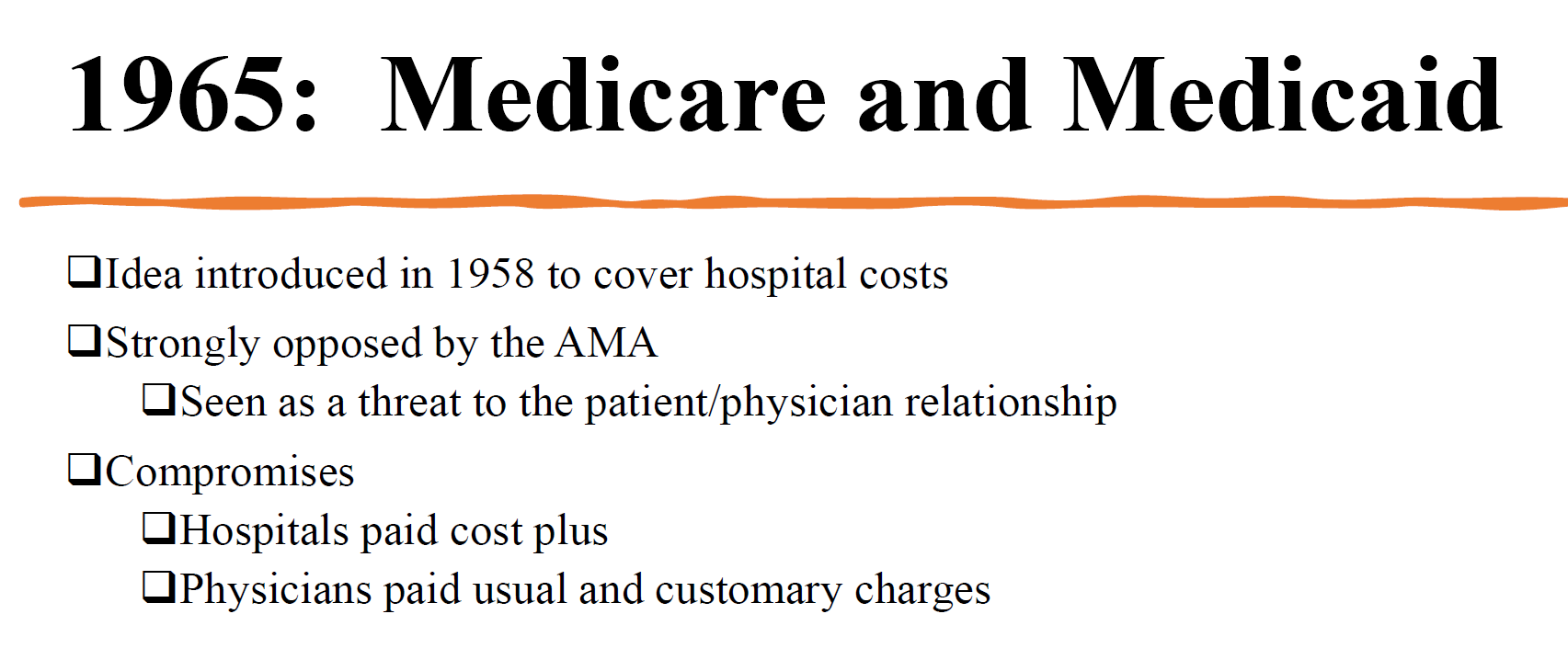
What programs started in 1965?
Medicare and Medicaid; both faced strong opposition from doctors.
Why did Hillary Clinton’s health reform fail?
The plan lacked clarity, had little expert input, and faced public pushback.

What makes health policy successful?
It must reflect what people value like fairness, safety, and compassion.


What healthcare values do Democrats and Republicans support?
Democrats favor care for all through government;
Republicans support care for all with more personal choice and free markets.


Who can introduce a law?
Members of Congress, the Executive Branch, and sometimes individuals or interest groups.

What happens to a bill in committee?
It’s studied, possibly changed, and then voted on to move forward or it can be tabled (set aside).

What happens if the House and Senate pass different versions of a bill?
A Conference Committee resolves the differences, and both must vote again.

What can the President do with a bill?
Sign it into law
Veto it
Let it become law after 10 days without signing.

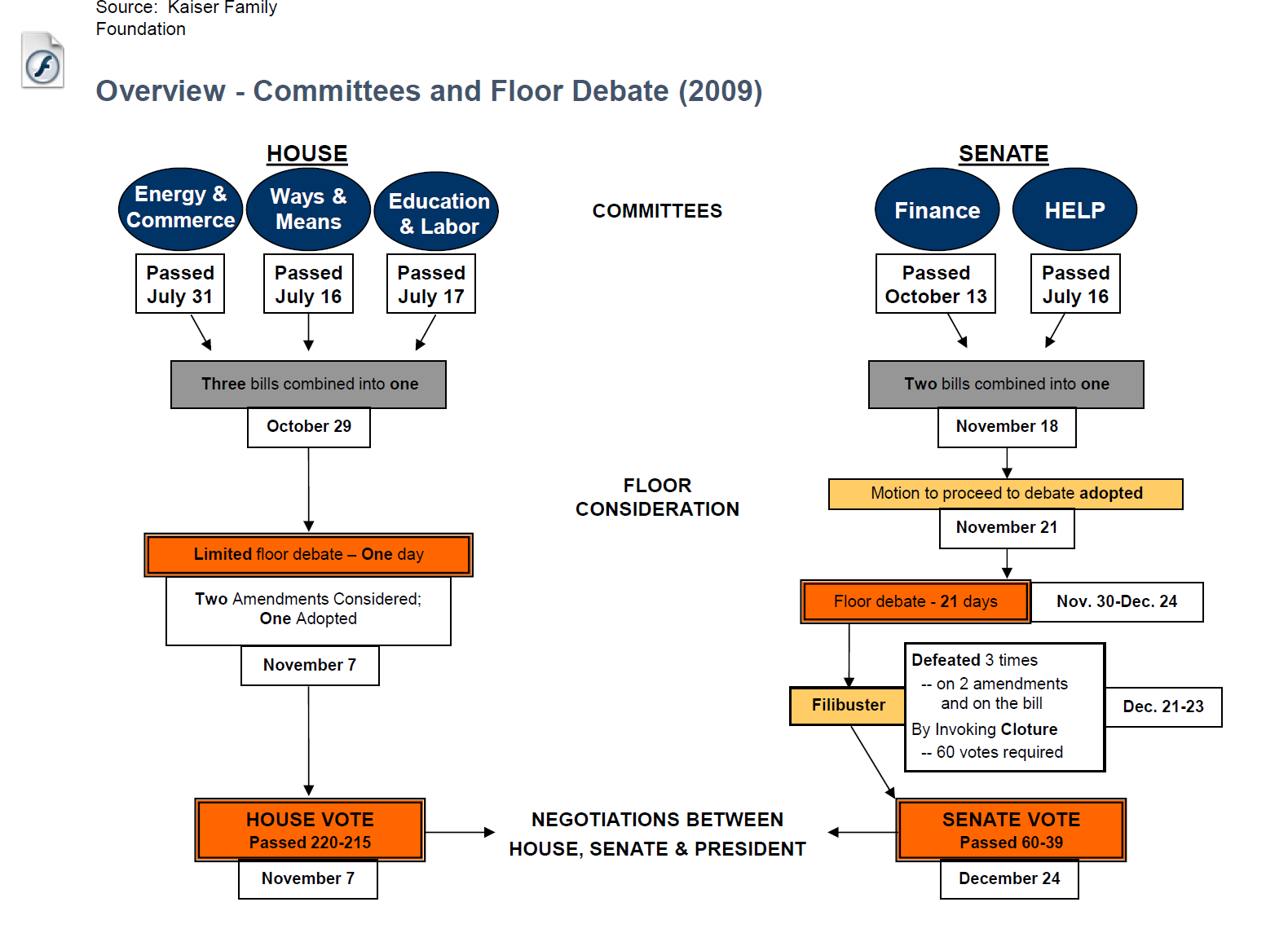
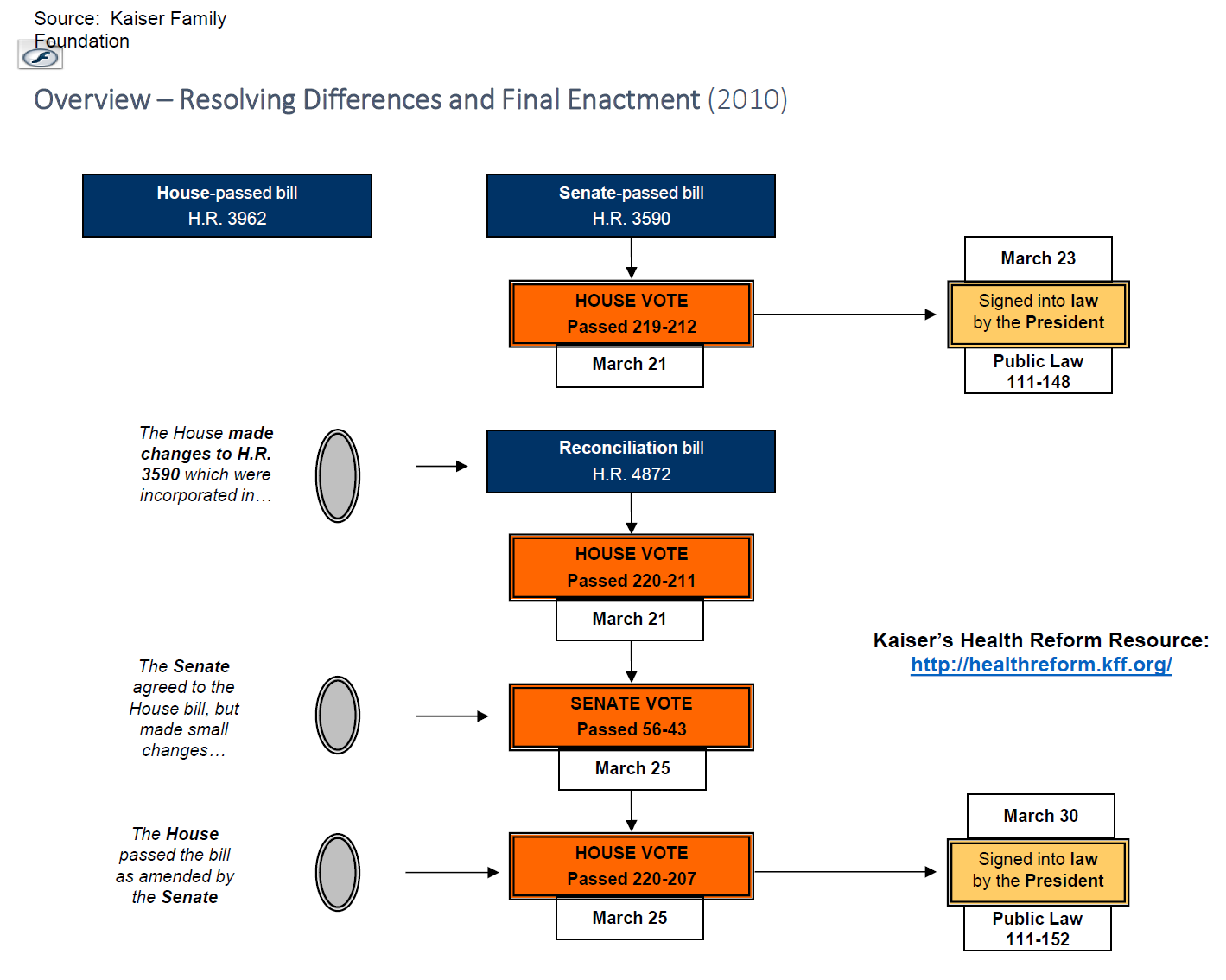
How was the ACA passed?
Through many rounds of debate, votes in both chambers, and negotiations. It was signed into law in March 2010.
Is the process done once the law is signed?
No. Agencies still write rules, hold hearings, and finalize how the law works.

What’s the difference between a department and an agency?
Departments are large and cabinet-level
Agencies are part of departments.
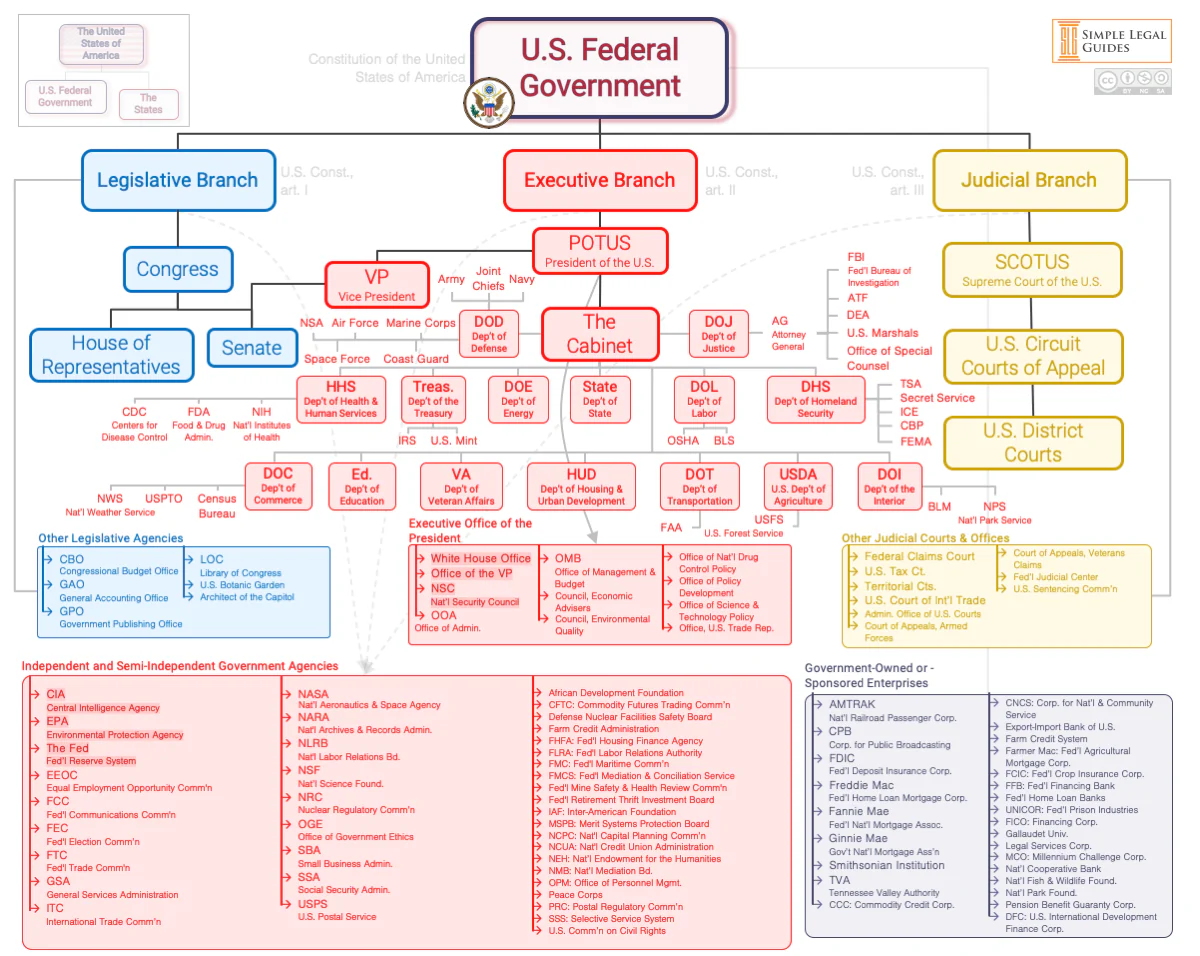
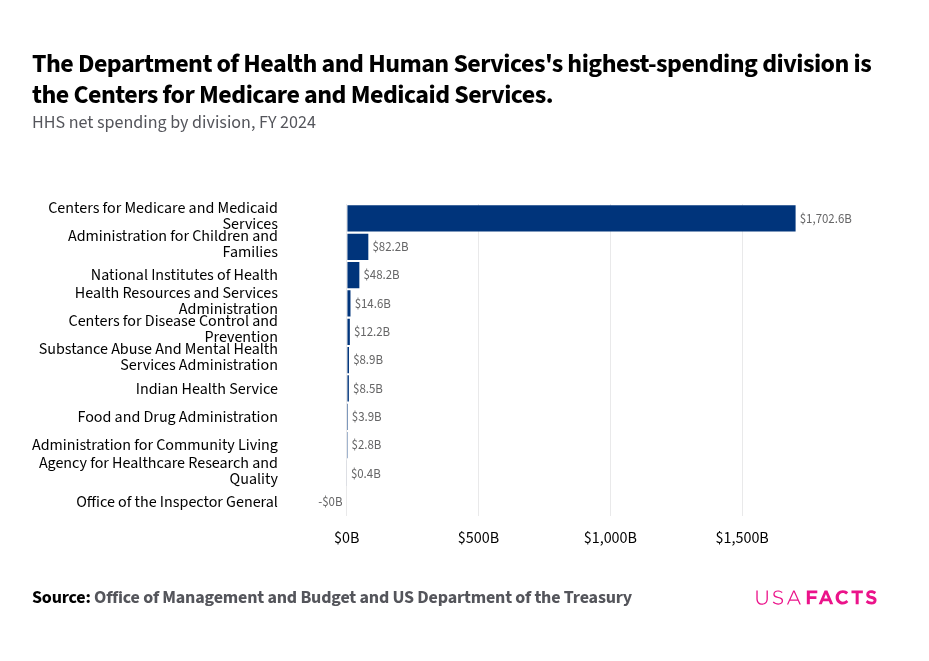
What does the Department of Health and Human Services do?
Oversees programs like Medicare, Medicaid, and CHIP with a $1.7 trillion budget.


What are some major agencies under Department of Health and Human Services?
CMS, HRSA, CDC, FDA, NIH, and more.

What does Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services do?
Runs Medicare, Medicaid, and helps implement the ACA.

What does Health Resources and Services Administration focus on?
Helps underserved populations and funds clinics and training.

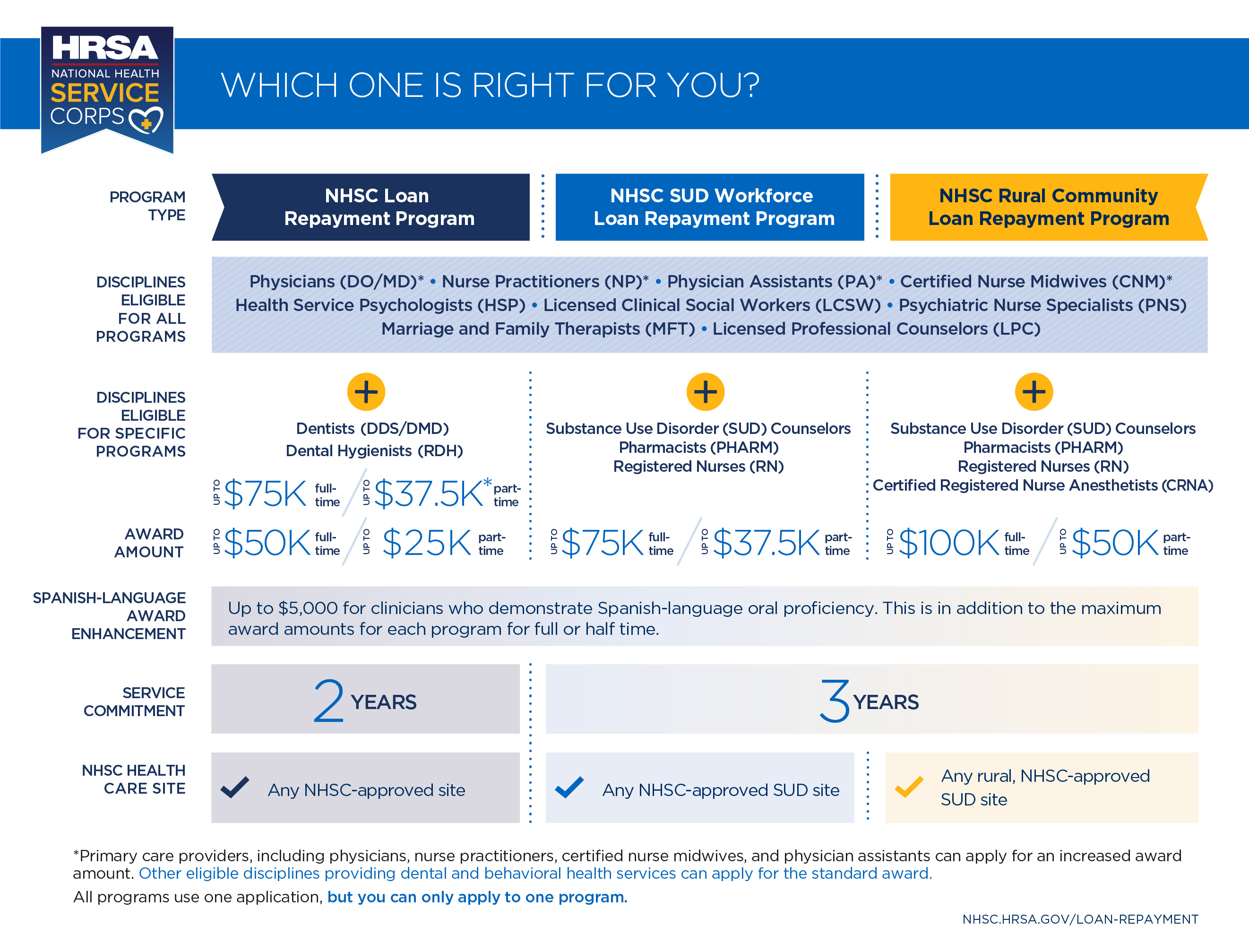
What is the National Health Service Corps?
It offers loan repayment to health providers working in shortage areas.

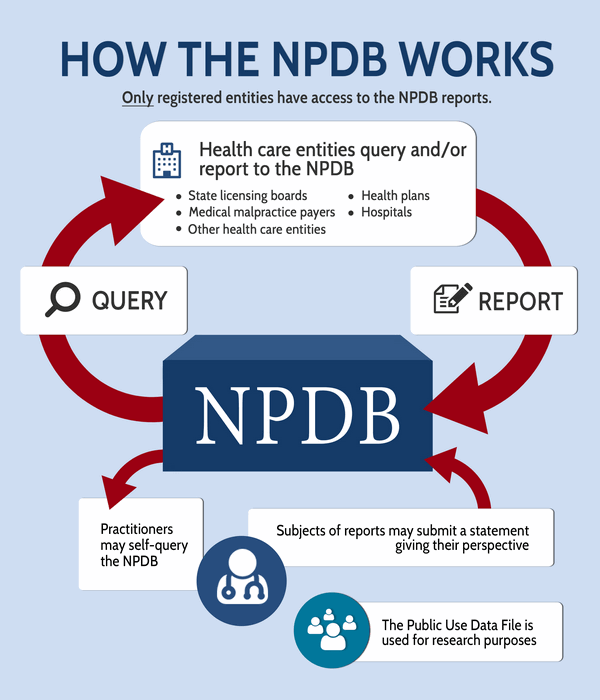
What is the National Practitioner Data Bank for?
Tracks malpractice claims to prevent doctors from avoiding accountability by moving states.


What does the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention do?
It protects public health, especially from disease outbreaks, bioterrorism, and health emergencies.
