Block 8.3
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is a mutation?
A source of new variation
What is crossing over?
sections of DNA are exchanged between homologous chromosomes
What does crossing over allow?
New combinations of alleles- recombination
What is independent assortment?
The different possible combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes
What does random fertilisation do?
Introduces variation because the combination of gametes that fuse to form a zygote is random
What is a genotype?
The alleles present in a cell
What is a phenotype?
The observable characteristics of an organism
What is a homozygote?
An individual with two identical alleles for a characteristic
What is a heterozygote?
The two alleles in an individual are different for a characteristic
What is a dominant characteristic?
A characteristic that always shows an effect in the phenotype
What is a recessive characteristic?
A characteristic that is only expressed if the gene is homozygous
What is codominance?
The alleles are equally dominant
What are multiple alleles?
When there are more than two possible alleles for a gene
What is a point mutation?
Only one or a small number of nucleotides are inserted, substituted or deleted.
What is a chromosomal mutation?
A change in position of genes on a chromosome
What is a whole chromosome mutation?
An entire chromosome is lost or duplicated during meiosis
What does polygenic mean?
Phenotype is determined by several genes
What is a genetic cross?
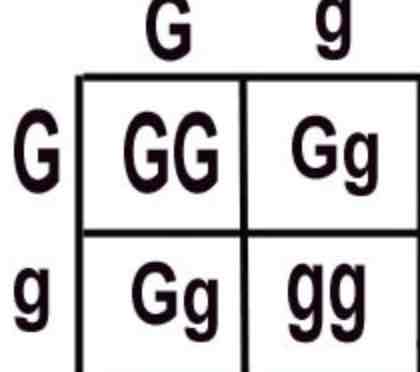
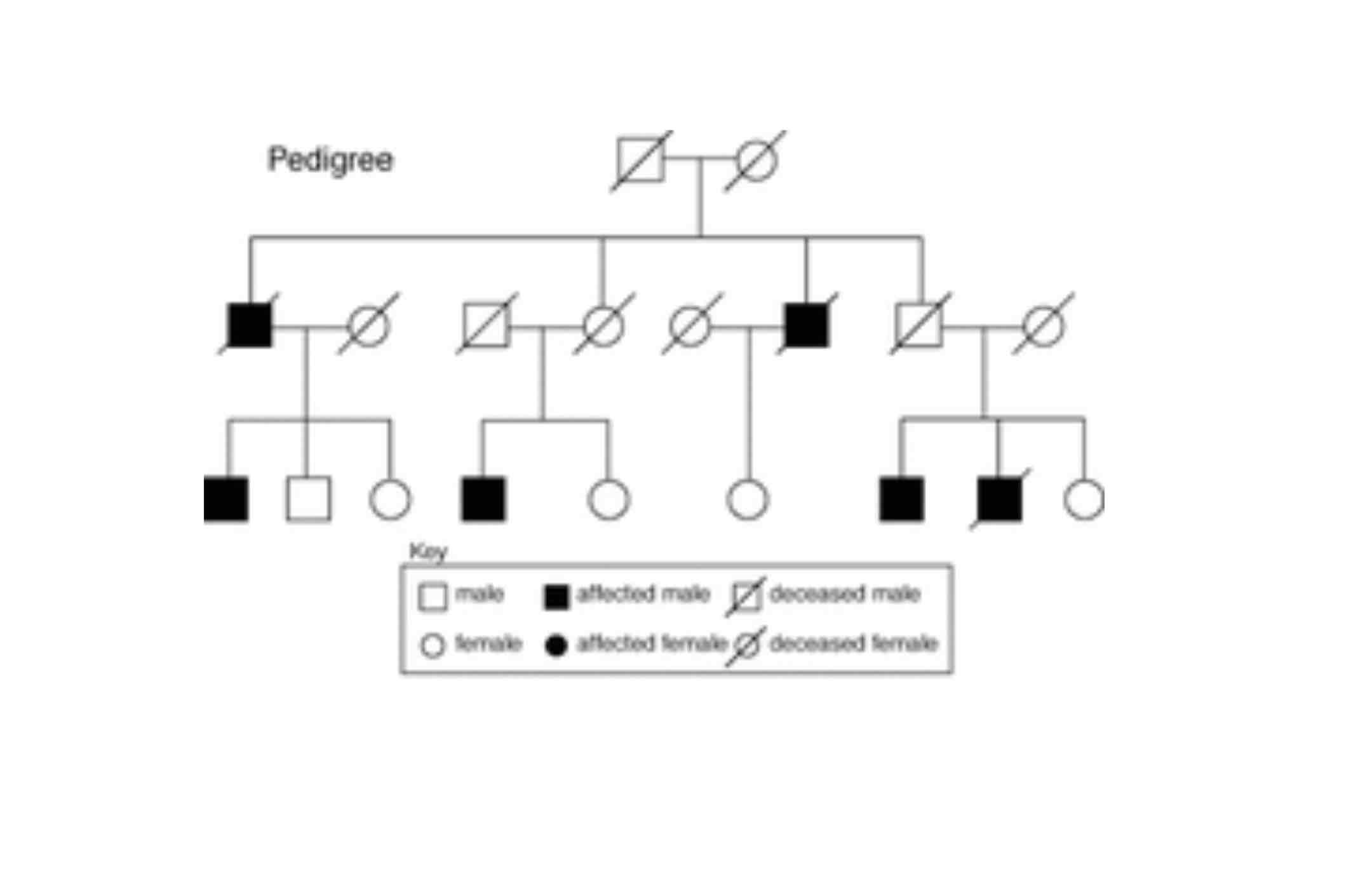
What is a pedigree diagram?
What are some sampling errors of a genetic cross?
-Chance plays a big role in reproduction -Some offspring die before they are sampled -Some offspring may escape before they are sampled
How are the different parts in a pedigree diagram represented?
-A female is represented by a circle and a male by a square -A horizontal line between a male and female links two parents -A vertical line leads down to offspring -A code can be used to show phenotype
What is autosomal linkage?
Two genes are located on the same autosome
How are Drosophila flies' characteristics linked?
Four pairs of chromosomes: one pair of sex chromosomes, three pairs of autosomes.
They can have: dominant grey body (G) or recessive black body (g) and dominant long wings (L) or recessive short wings (l)
Crossing over occurs to link the genes for colour and length
What is the expected ratio from a dihybrid cross?
9:3:3:1
If parental genotypes are LlGg x LlGg, what are the expected gametes?
LG Lg lG lg x LG Lg lG lg
What is sex linkage?
When a gene is carried on the X chromosome
What is an example of an illness caused by a sex linked characteristic?
Haemophilia- a protein needed to clot blood is missing; a recessive allele
What is chromosome mapping?
In genes that are close together (closely linked), the chance of recombination is low
If genes are further apart on a chromosome, recombination is more likely to occur
crossover value= number of recombinant offspring/total offspring X100
What is recombination?
A process by which pieces of DNA are broken off a chromosome and joined elsewhere to produce new combinations of alleles. This creates genetic diversity
What is the Chi-squared equation?
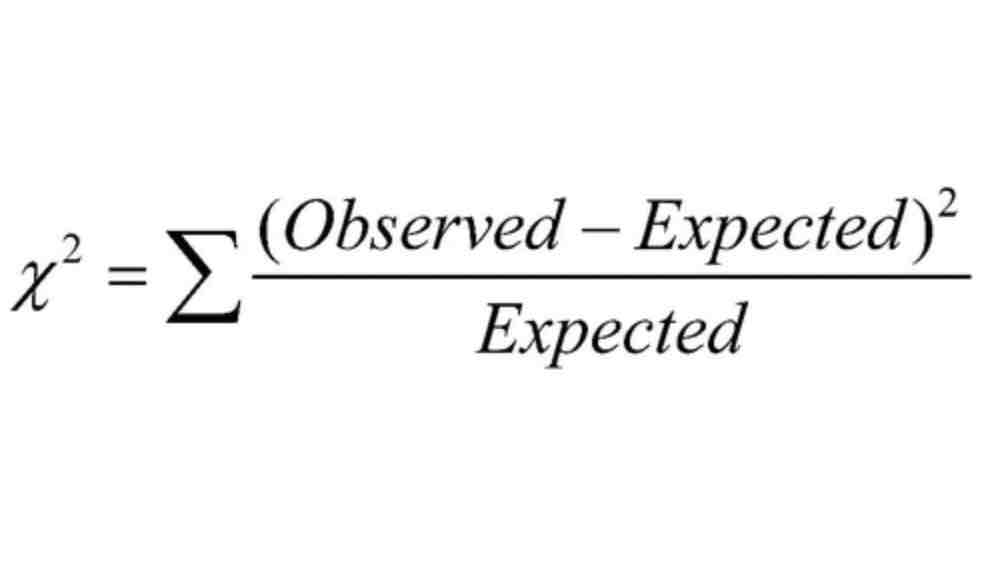
What is a Chi-squared test used for?
To establish whether the difference between observed and expected results is significant
What are the rules of a Chi-squared test?
-Sample size must be large (>20) -Data must be discontinuous -Null hypothesis must be that there is no difference between the observed and expected -Degrees of freedom=(x-1) where x is the number of expected values -If the value is greater than the critical value the null hypothesis is rejected
What is a gene pool?
All alleles of all the genes present in a population
Why does allele frequency change?
Due to natural selection leading to evolution via selection pressures
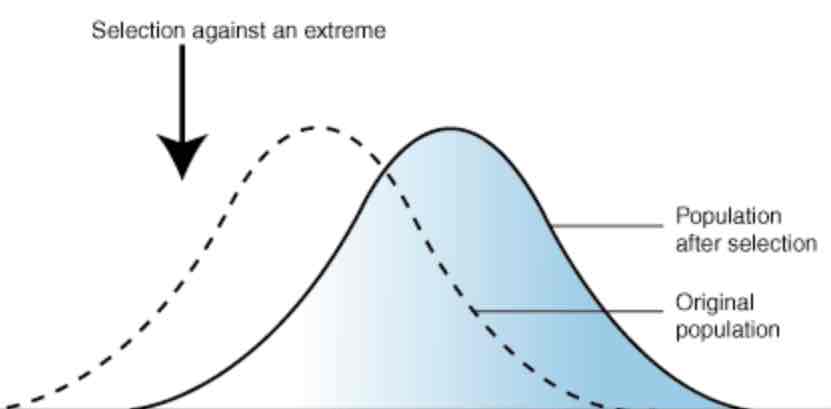
What is stabilising selection?
When the environment favours those with the most common characteristic - those on the extreme dies out and the common characteristic increases and variation decreases. Often used to conserve phenotypes present and maintain continuity
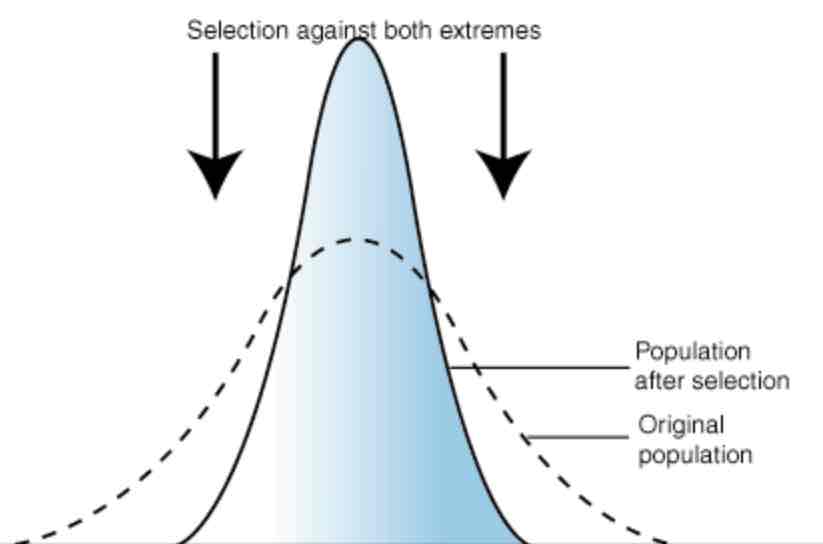
What is directional selection?
When the environment favours those individuals with characteristics on one of the extremes over the other, over time this will become the most common characteristic
What is disruptive selection?
Diversity increases as the conditions are more diverse and subpopulations form. Often leads to speciation
What is genetic drift?
Changes in allele frequency that occur by chance in small populations
What is a population bottleneck?
The severe loss in gene diversity from a catastrophic event that dramatically reduces the population and decreases the gene pool. This causes a change in allele frequencies.
What is the Founder Effect?
Loss of genetic variation that occurs when a small number of a population becomes isolated, forming a new population with allele frequencies not representative of the original population. Known as a voluntary bottleneck
What does the Hardy-Weinberg Equation allow you to do?
Use observations of phenotype frequencies to calculate associated allele frequencies in a population
What is the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
p=frequency of dominant allele q=frequency of recessive allele p^2= frequency of homozygous dominant q^2=frequency of homozygous recessive 2pq= frequency of heterozygous
What are the conditions of the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
No mutations
Random mating
Large population
Isolated population
No selection pressure