Medical Imaging
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 6: Describe the main imaging modalities used in MSK imaging and be able to interpret normal and abnormal standard diagnostic images (e.g. X-ray) of the upper and lower limbs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
radiographic appearance description
attenuation
radiographs: radiolucent, semi-radiopaque, radiopaque
MRI: void, intermediate signal intensity, high signal intensitiy
ultrasound: anechoic (black), hypoechoic, hyperechoic (bright)
radiological characteristics (fracture classification)
comminuted
spiral
rotation
linear
transverse
oblique
compression
displaced (and how)
greenstick
stress
pathological
open
location
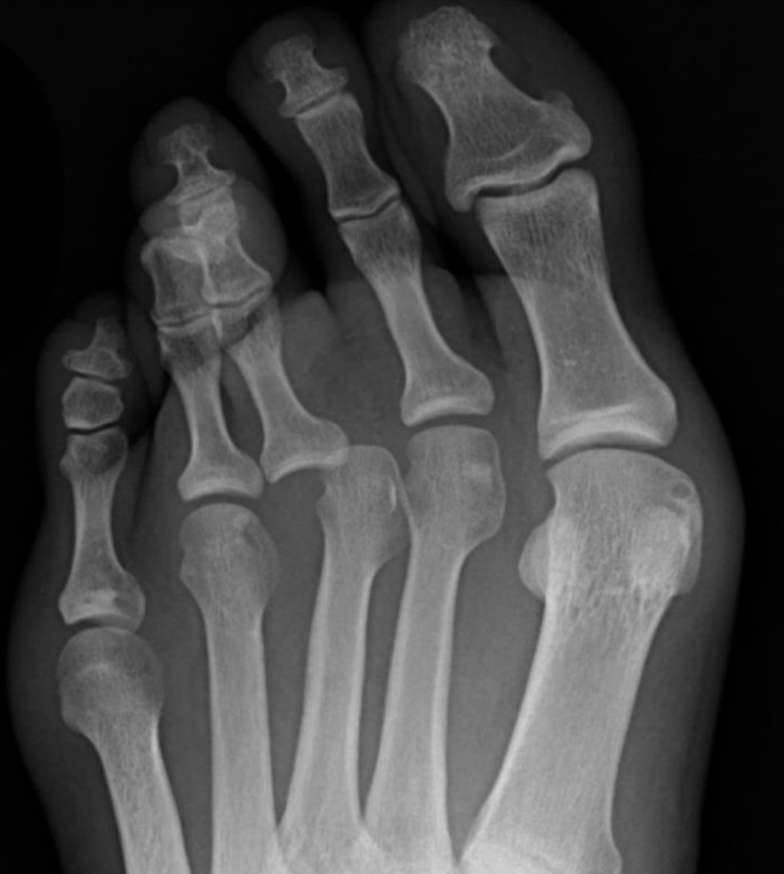
describe the scan + indication
loss of alignment of the 3rd metatarsophalangeal joint
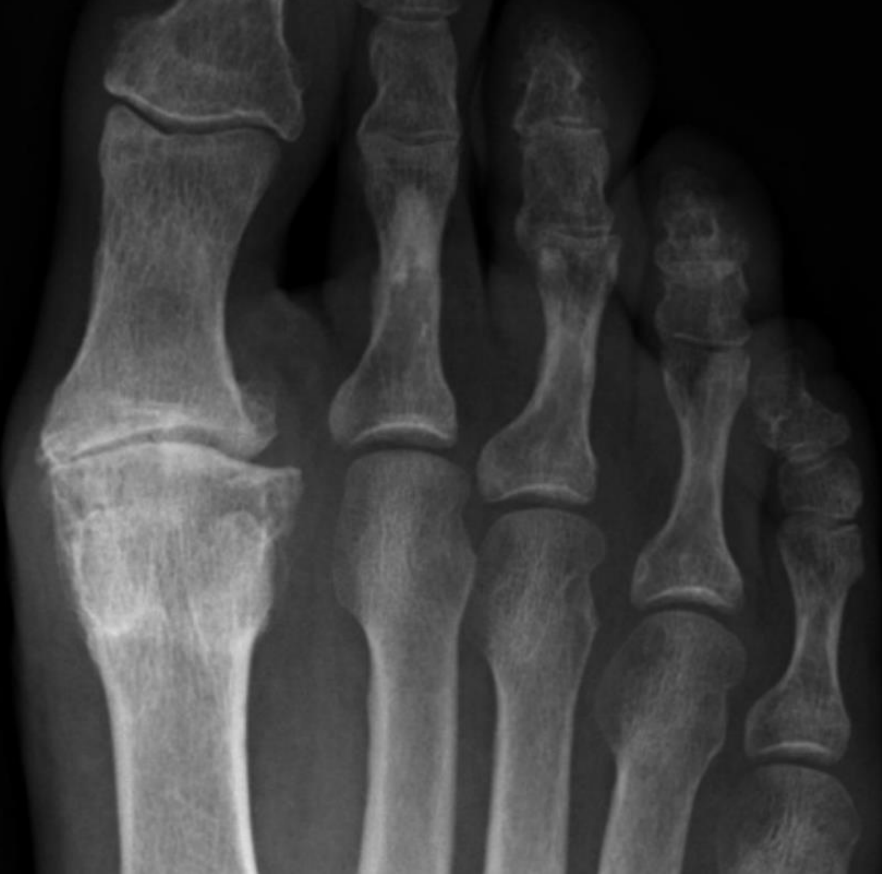
describe the scan + indication
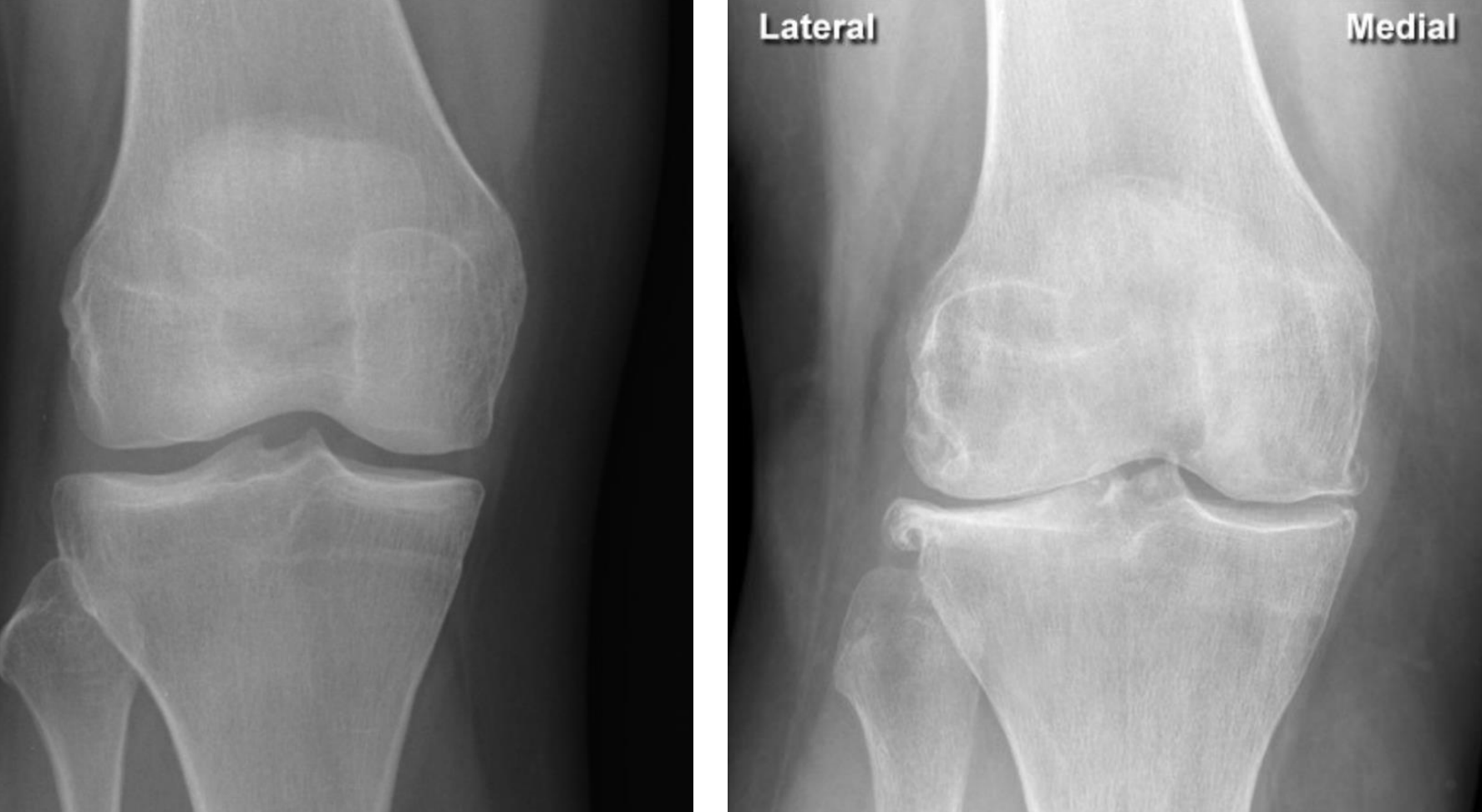
Loss of joint space (fusion of bones) indicating cartilage loss at the 1st metatarsophalangeal joint with osteophytes (sign of OA)
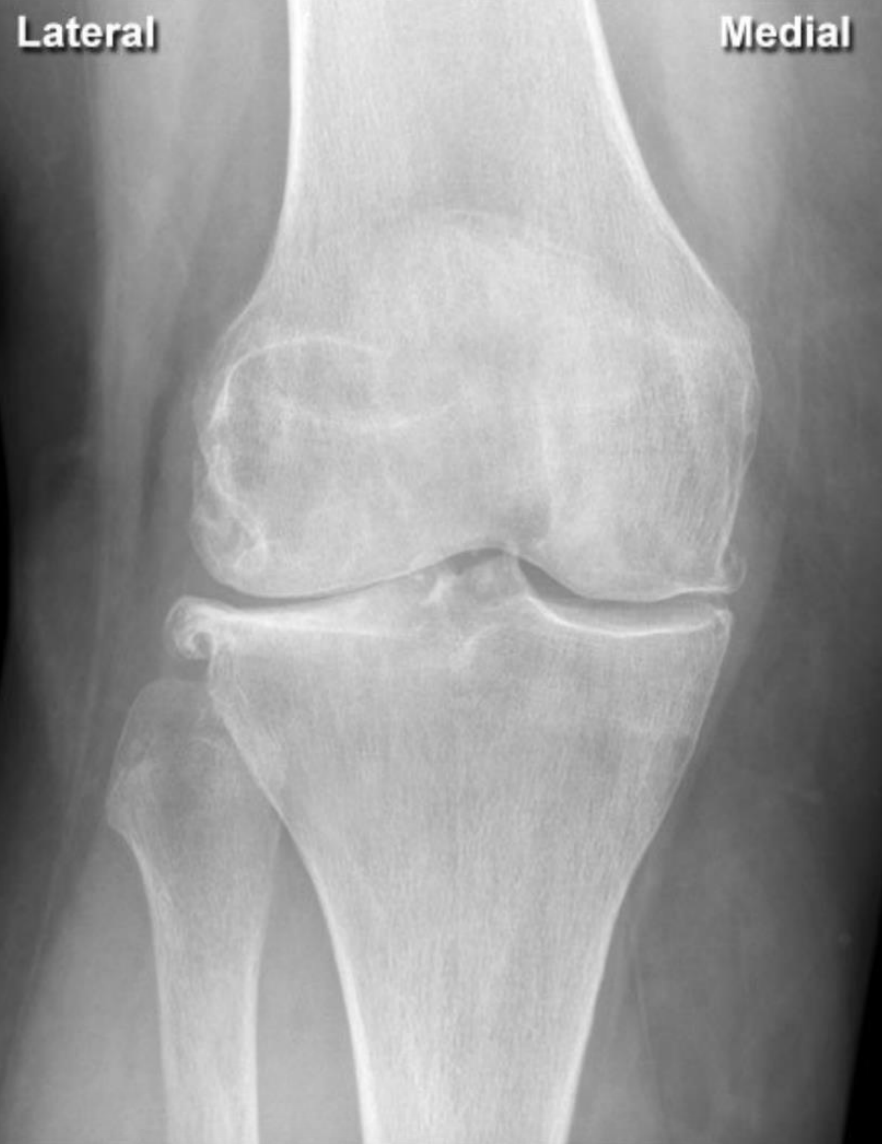
Loss of joint space (fusion of bones) indicating cartilage loss at the lip of the femur with osteophytes
(indicating OA, sometimes also formation of cysts - erosions are not a feature)
normal shenton’s line
lined formed by anatomical landmarks in a normal AP scan of a hip
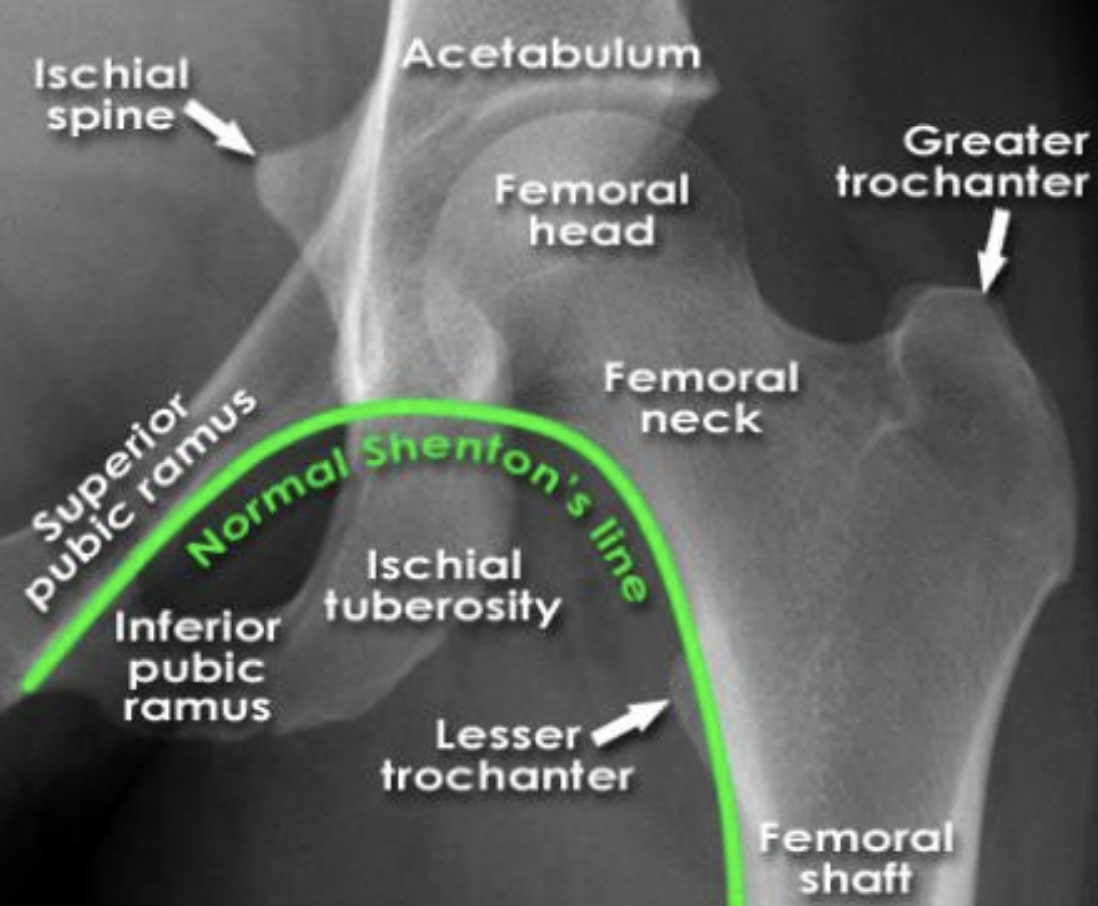
intra-capsular vs extra-capsular classification
intracapsular: involving the head or neck of femur
fracture through neck of femur (most common in younger patients)
mechanism of trauma: axial loading during high force trauma (feet on dashboard)
if hip is abducted position
extracapsular: involving the femur excluding head or neck of femur
fracture through the trochanters
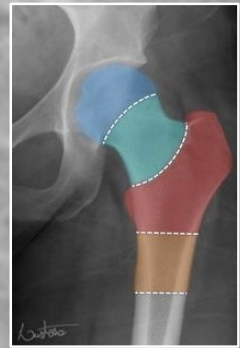
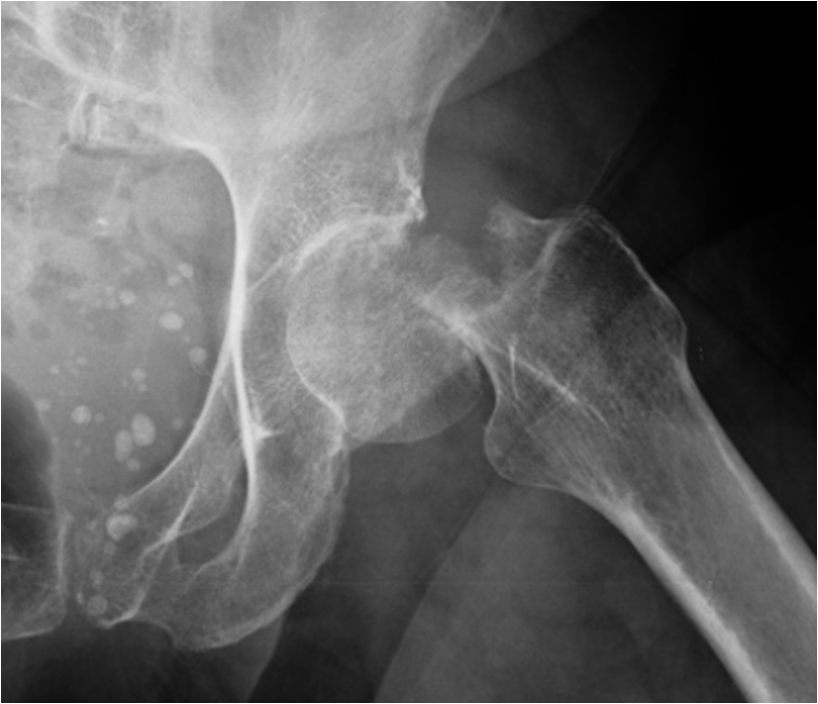
comminuted fracture (radiolucent) of the left proximal femur
intertrochanteric fracture (between the two trochanters)
extra-capsular classification
intracapsular fracture
approach to lumbar xrays
ABCCP
Alignment
follow corners of vertebrae from one level to the next
Bones
Cortical outline, VB height, integrity of pedicles & transverse pro.
Cartilage
IVD grad
Increase in height from sup-inf. L5/S1 narrower
Coverage
ensure entire lumbar spine is visible in each scan
Posterior Elements
check elements (Pedicles, lamina and Pars inter
Articularis)
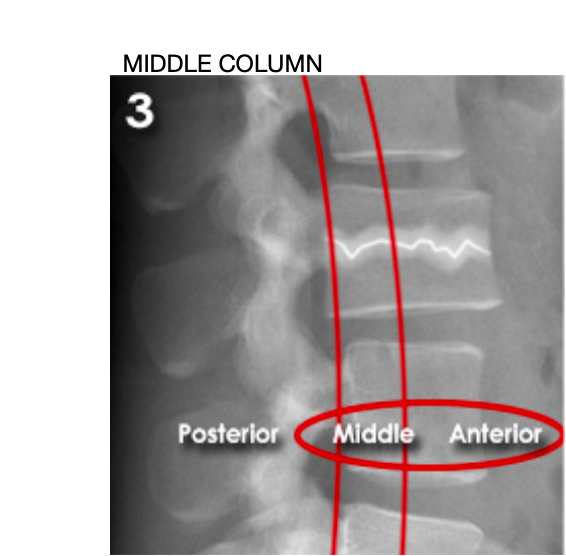
Lumbar three column model
Divides the spine into three columns: anterior, middle, and posterior
Used to determine the stability of thoraco-lumbar spine fractures
severity depends on how many columns are implicated
If spinal instability is suspected further imaging with CT or MRI should be considered
ANTERIOR (Stable):
Anterior compression injury
e.g. compression fractures (most common)
between the anterior longitudinal ligament to the middle of the vertebral body
MIDDLE (unstable):
'Burst' fracture (vertebral body crushed in all directions) due to axial loading
between middle of vertebral body to posterior longitudinal ligament
POSTERIOR (unstable):
Flexion-distraction fracture (caused by severe compression or rotation)
between posterior longitudinal ligament to spinous process
spinal cord implicated
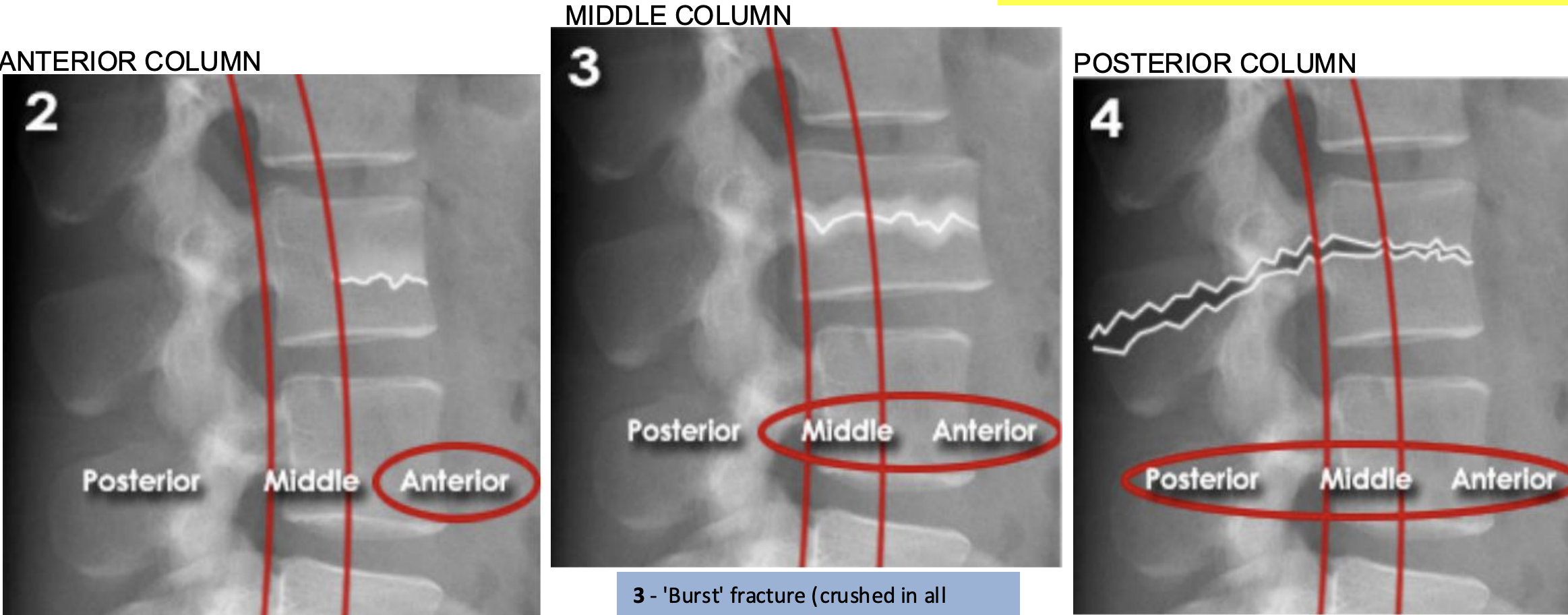
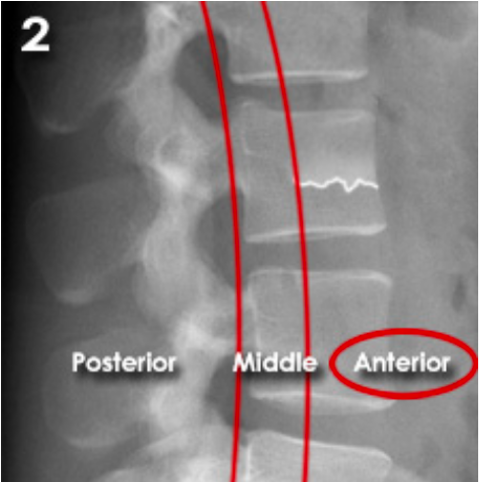
Anterior compression injury
e.g. compression fractures (most common)
displacement
broken bone ends are no longer aligned
with reference to the distal/lower segment of the bone:
medial vs lateral, posterior vs anterior
e.g. medial displacement of femur
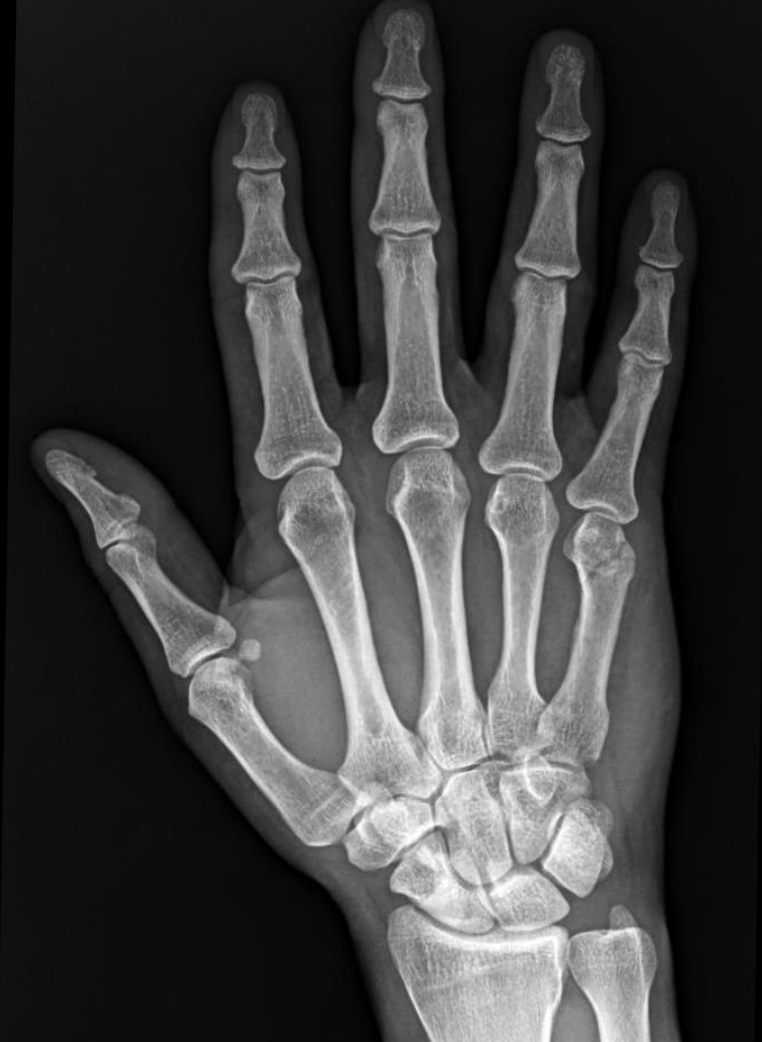
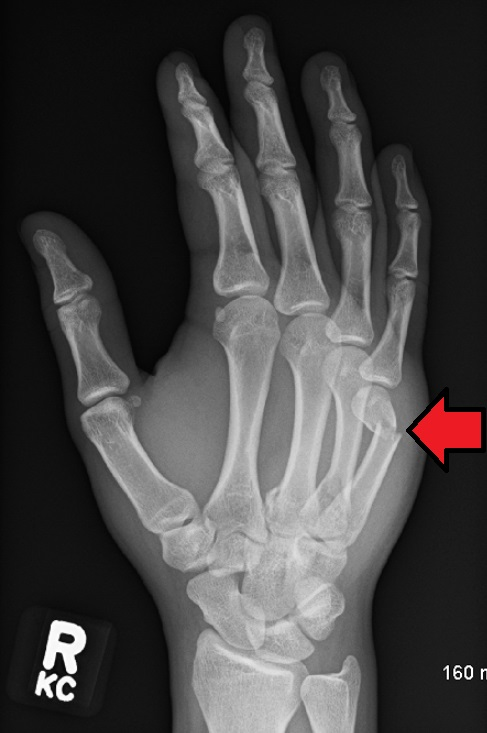
25 y/o male, punched a wall, description?
Radiolucent oblique fracture of the neck of the 5th metacarpal (“boxer fracture”)
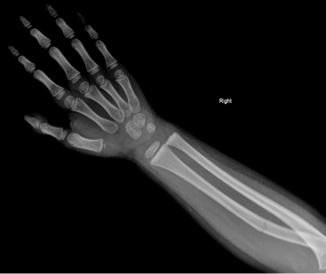
Greenstick Fracture
comprises a bend in the bone on one side and a visible break in the bone cortex on the other side, which is incomplete
due to the pliable nature of bones in children, complete fractures are less common
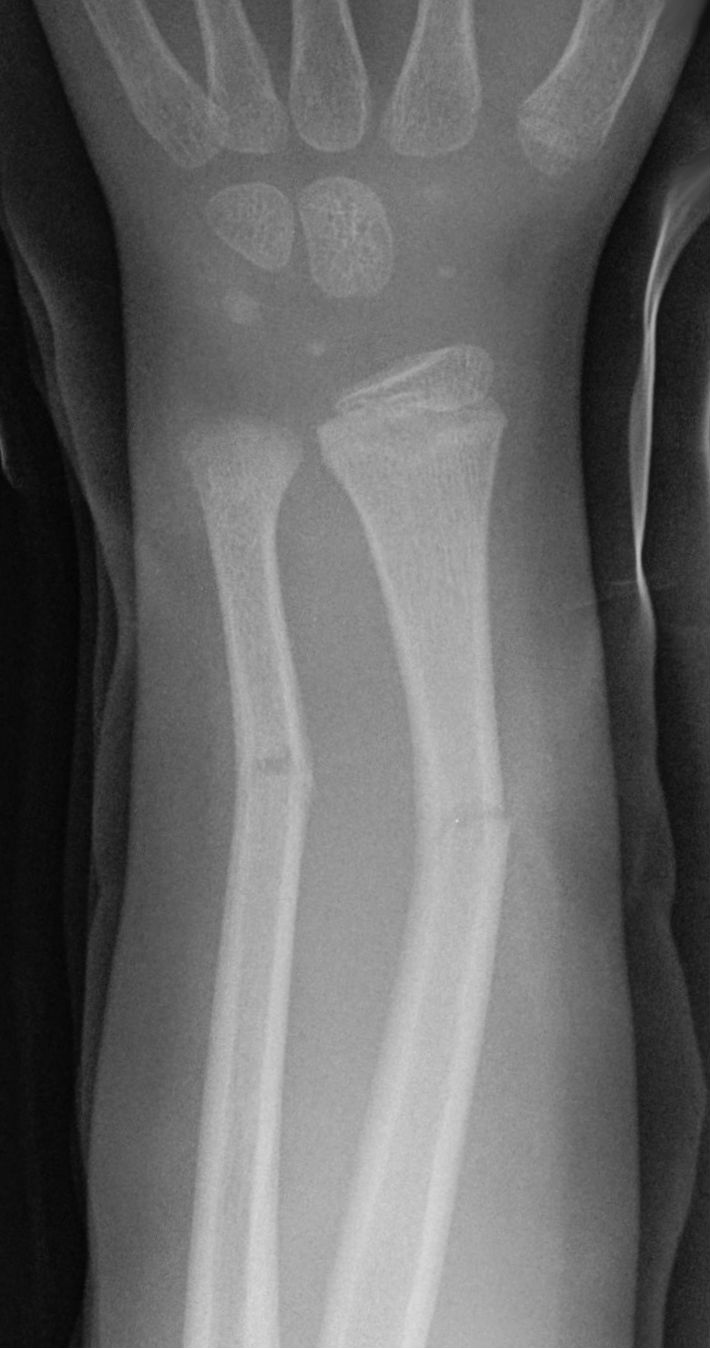
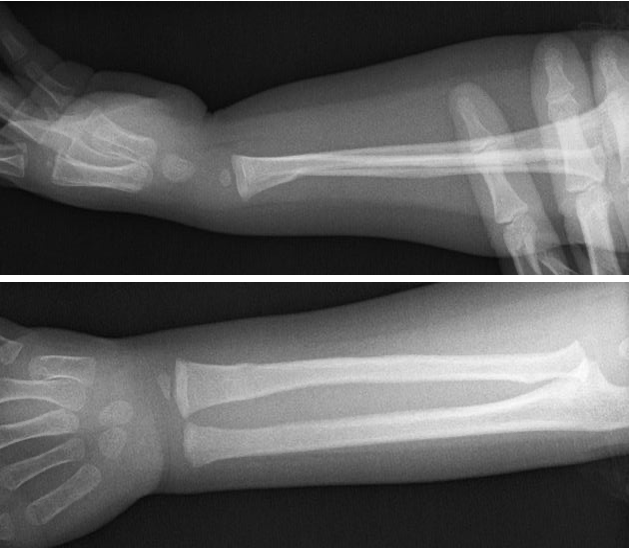
TORUS/BUCKLE FRACTURE
referred to as a circumferential buckle fracture, commonly of the distal radial metaphysis. No distinct fracture line, but subtle deformity of buckle of the cortex may be evident. torus = protuberance in latin
Pathological midshaft medial displaced fracture of the right femur
black spot (lower cortical density): lytic bone region
(therefore important to look at before and after fractures)
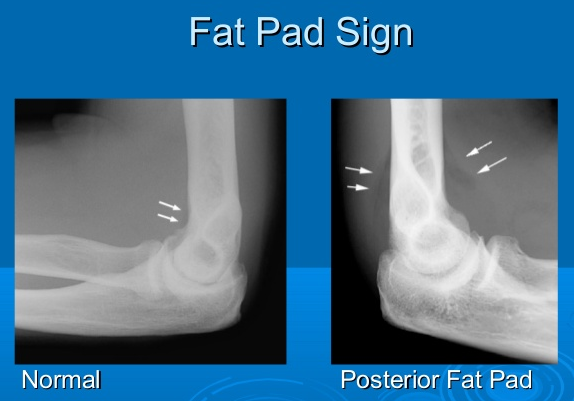
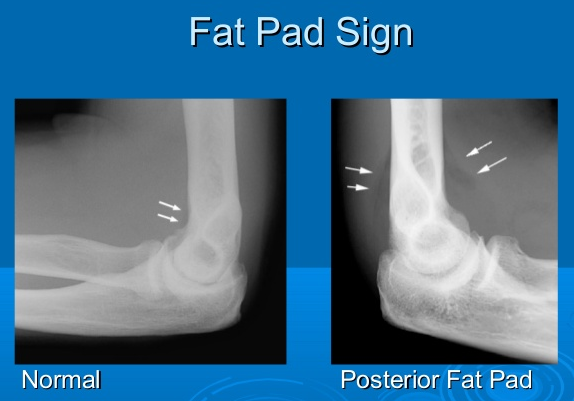
Joint effusion
abnormal fluid acculuation within the synovial compartment due to infection, inflammation or trauma
‘fat pad’ sign due to a joint effusion - observed on many abnormal elbow radiographs
extra fat deposited to help protect the bone
relevant in adults: head of radius fracture
relevant in children: supracondylar fracture
→ fat pads get pushed out, become visible on an X-ray due to swelling and displacement of fat pads → obscure the fracture visibility

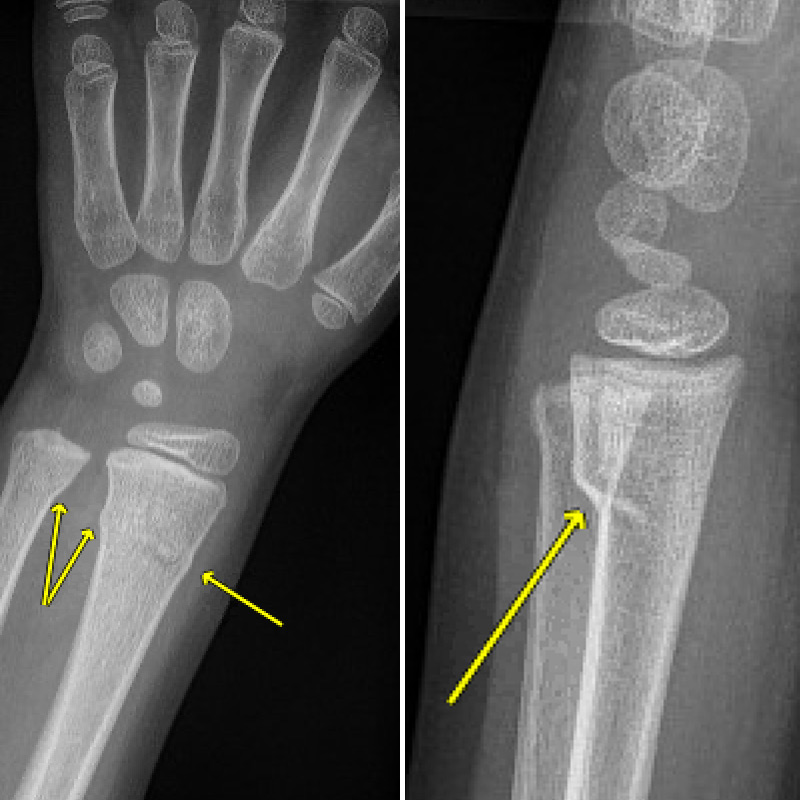
63 year old female:
acute pain and swelling in her distal forearm after falling on her outstretched hand.
History:
postmenopausal
bone mineral density from forearm indicated osteoporosis
Physical Examination:
deformity of distal forearm
posterior displacement of distal radius
Acute tenderness and swelling of distal forearm/wrist
Paraesthesia over lateral palm /digits & weakness in thumb opposition
Radiolucent distal radius fracture with posterior and medial displacement
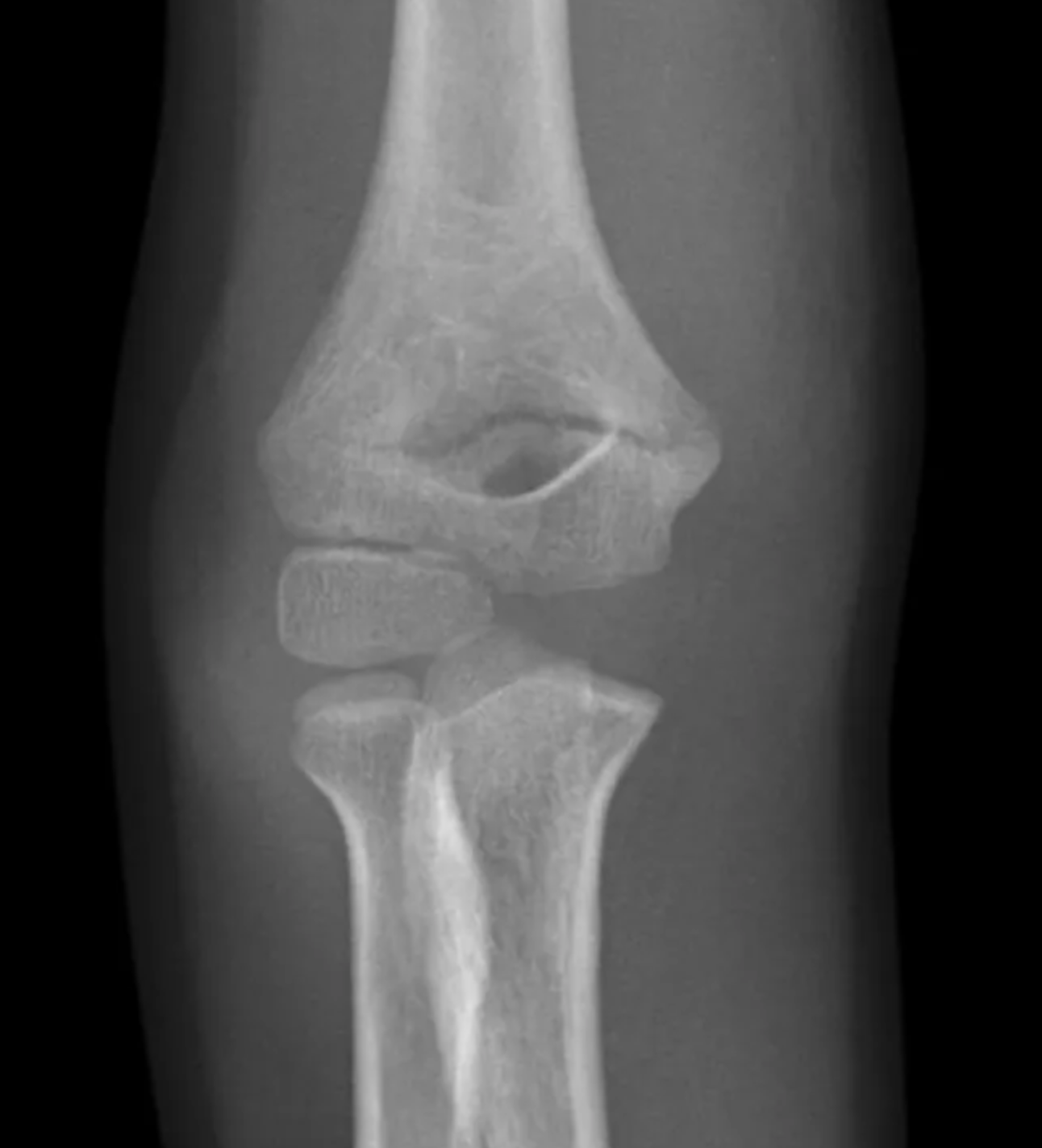
Paediatric patient
fall from the monkey bars, landing on extended hand
very painful elbow
Swelling and bruising is evident in the area
Unable to make an ‘OK’ sign (flexion of thumb IPJ and index finger DIPJ)
Weak radial pulse
radiolucent supracondylar fracture of the medial epicondyle (damage to the median nerve)
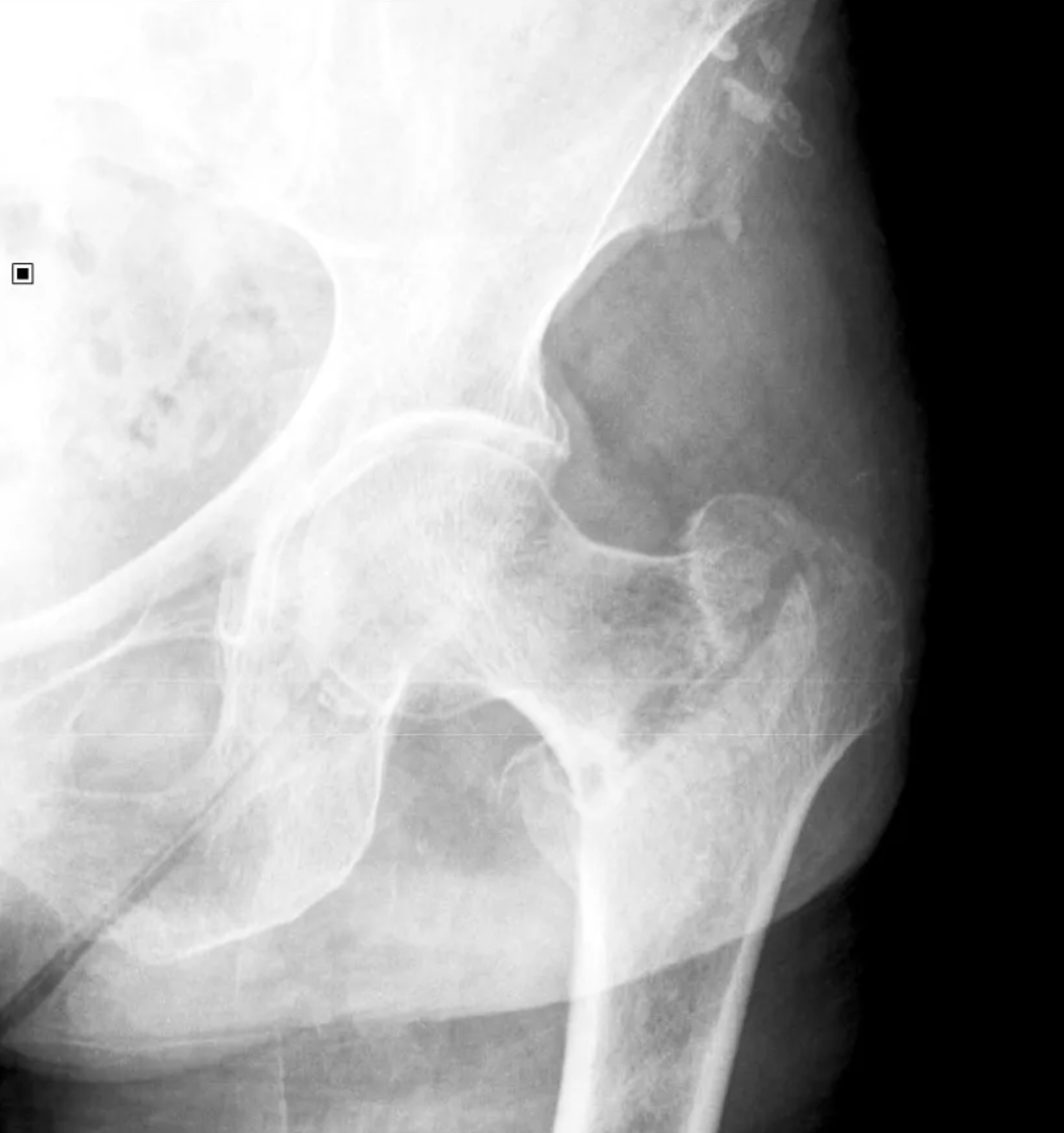
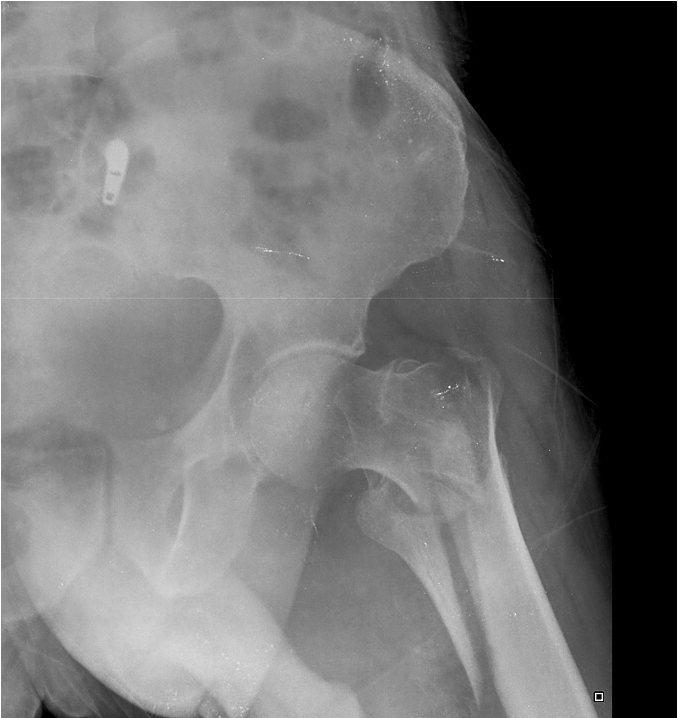
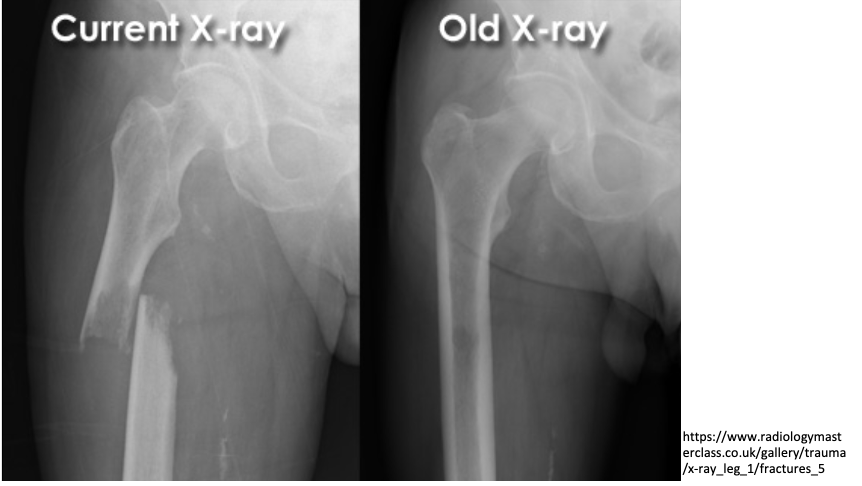
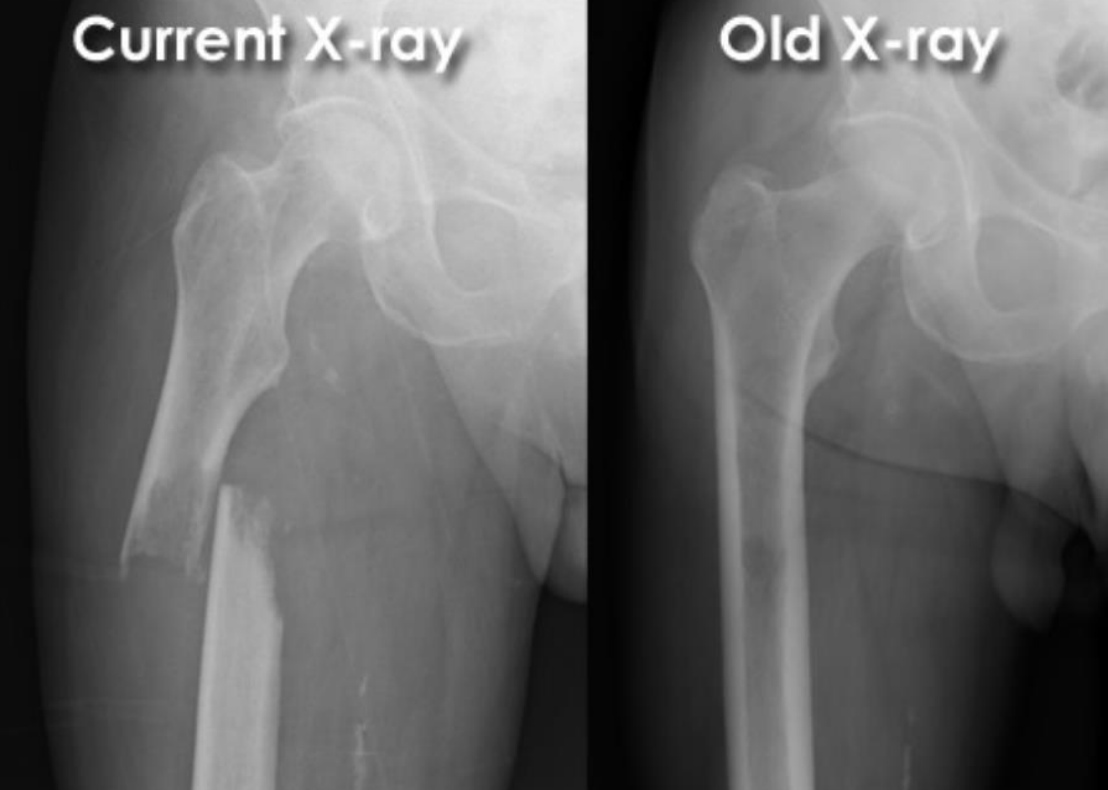
65 year old male:
fall onto left side while getting out of bed
AP radiograph of the hip
Prior DXR (bone density) scan showed marked osteoporosis
(extracapsular classification)
radiolucent intertrochanteric fracture of the left proximal femur
or
radiolucent oblique fracture through the greater trochanter and neck of the femur on the left side
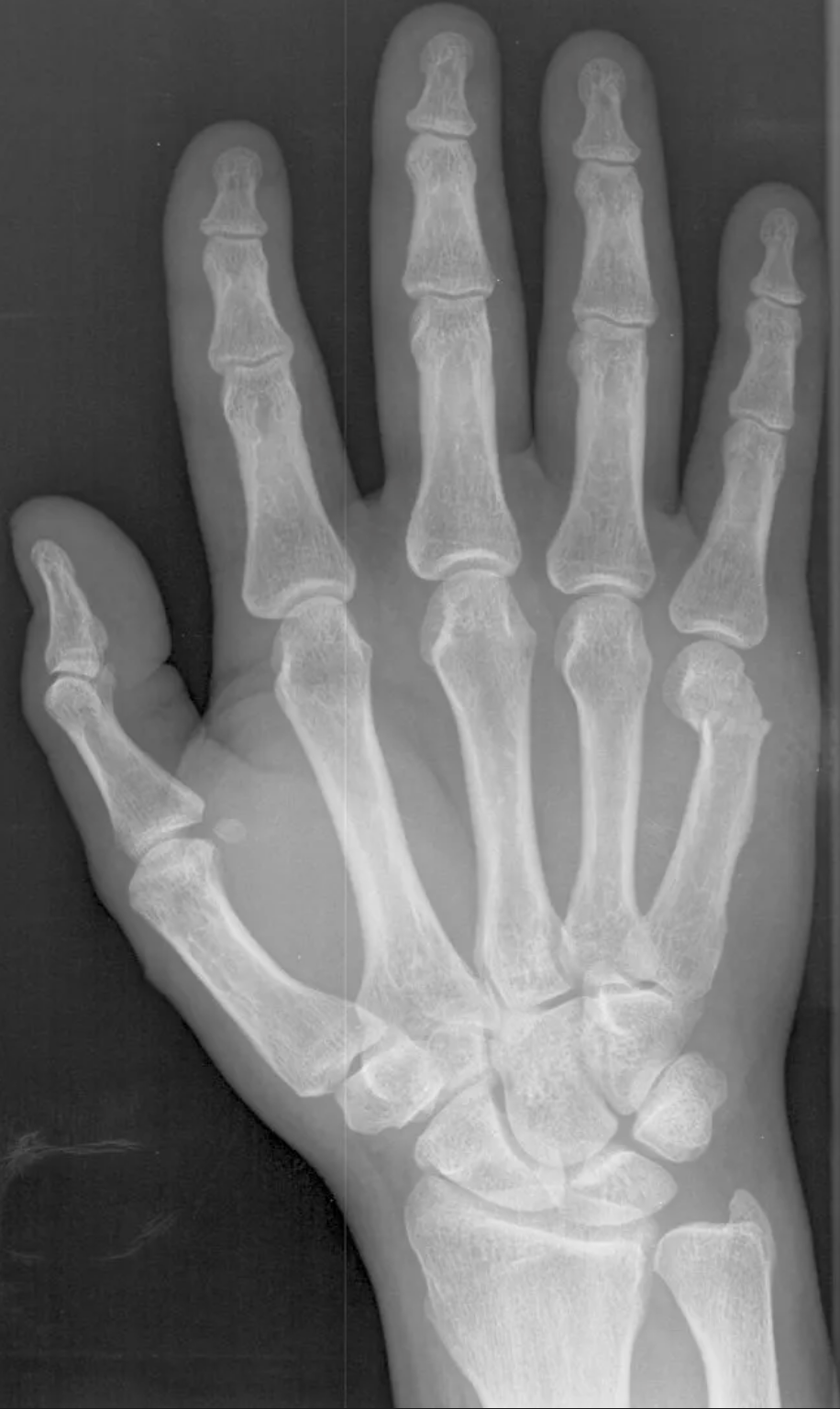
57-year-old man:
found face-down outside a bar
poorly responsive and unable to provide a history
scattered abrasions over the arms and legs
swelling of the right hand
radiolucent ‘boxer’s fracture’/fracture + lateral displacement of the head of the fifth metacarpal
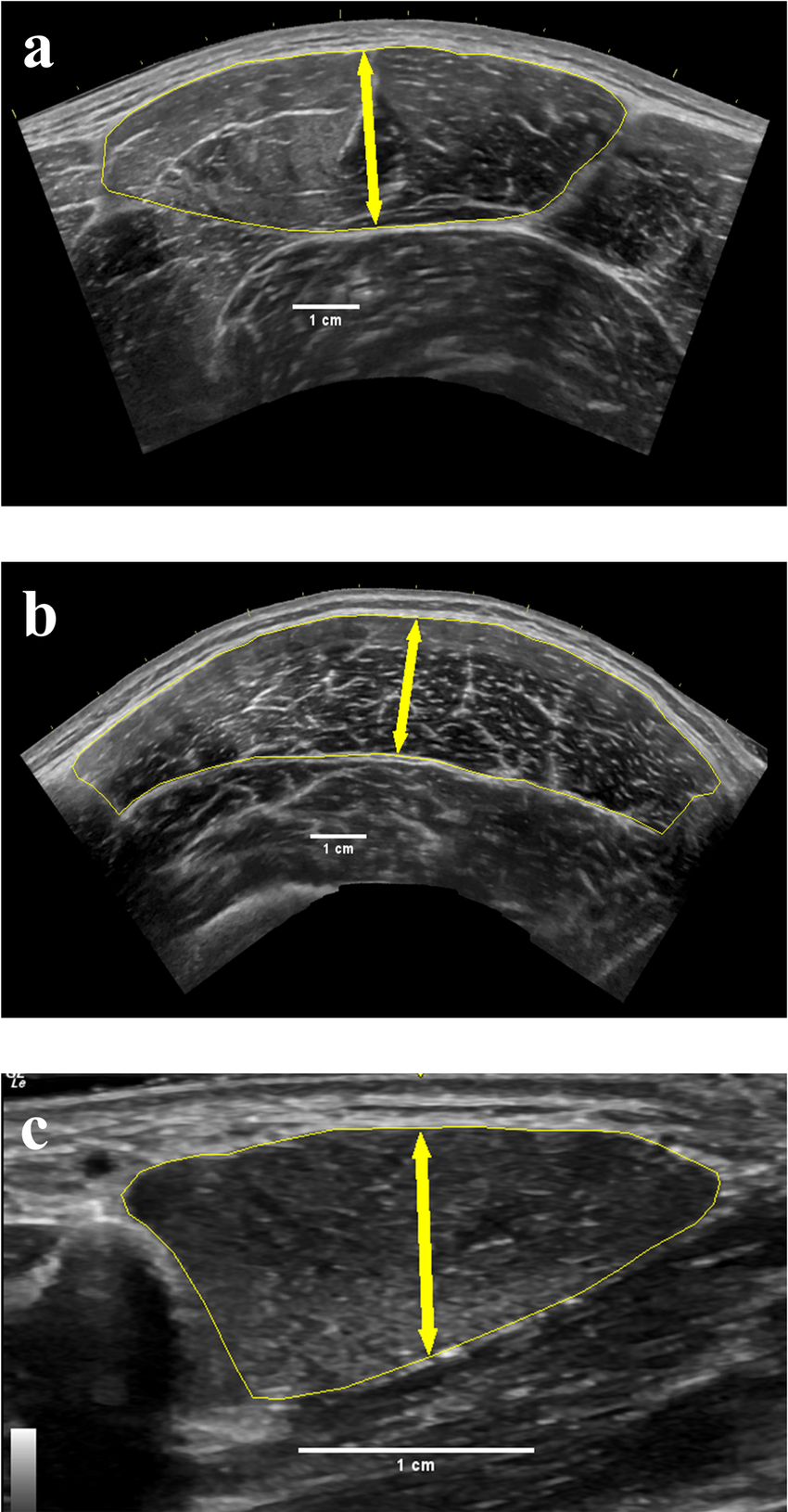
ultrasound: skeletal muscle
Hypoechoic fiber bundles interspersed with hyperechoic stromal connective tissue
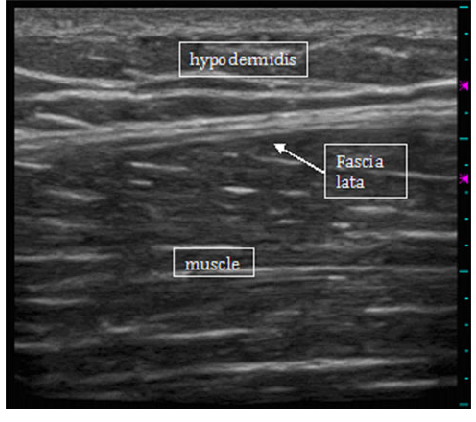
ultrasound: fascia
Thin, hyperechoic (bright) structure
ultrasound: cortical bone
Hyperechoic (bright) linear line with posterior acoustic shadowing due to complete reflect
(high density of molecules, with hard material properties)
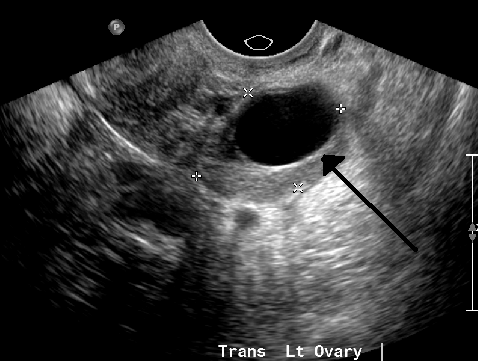
ultrasound: cyst
anechoic
ultrasound: nerve
'Honey-comb' appearance in transverse view; 'train track' in longitudinal view
ultrasound: articular cartilage
Anechoic (black) layer overlying the periosteum
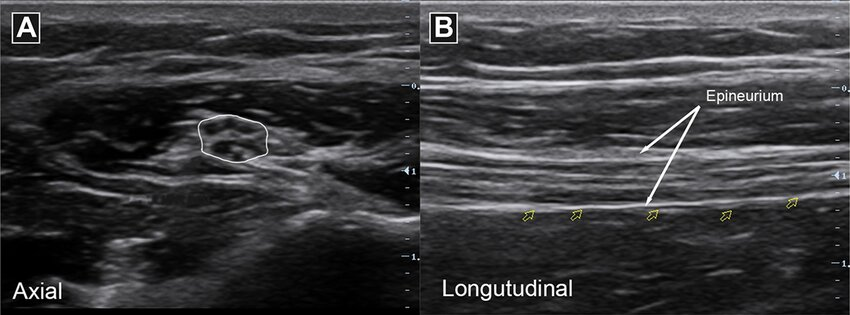
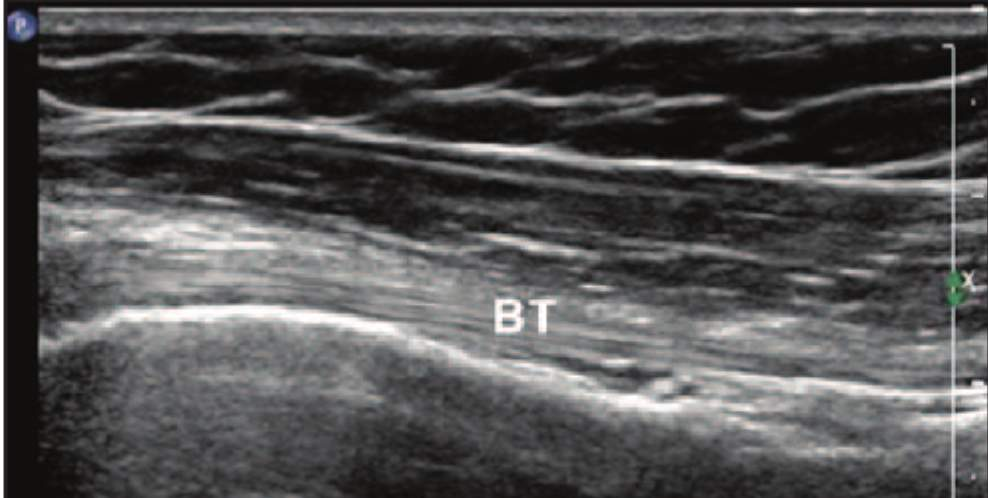
ultrasound: tendon
comprise multiple individual, longitudinally oriented, parallel collagen fibers that are tightly bundled, resulting in a fibrillary pattern on ultrasound
This results in the characteristic hyperechoic appearance of tendons when the US beam is oriented 90 degrees to the tendon
rotation
bone breaks due to a twisting or rotational force
evident by superimposition (overlap) of structures
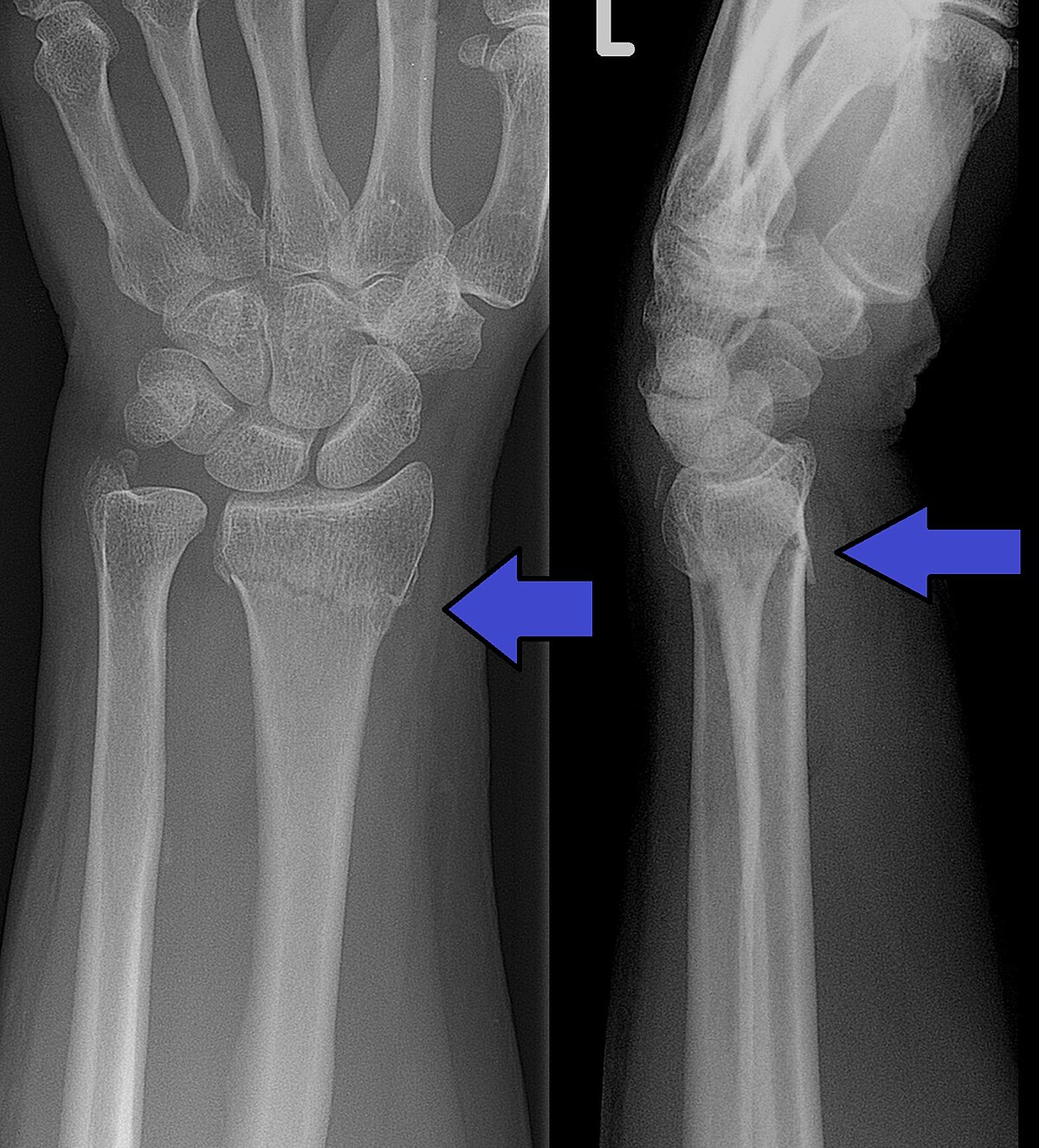
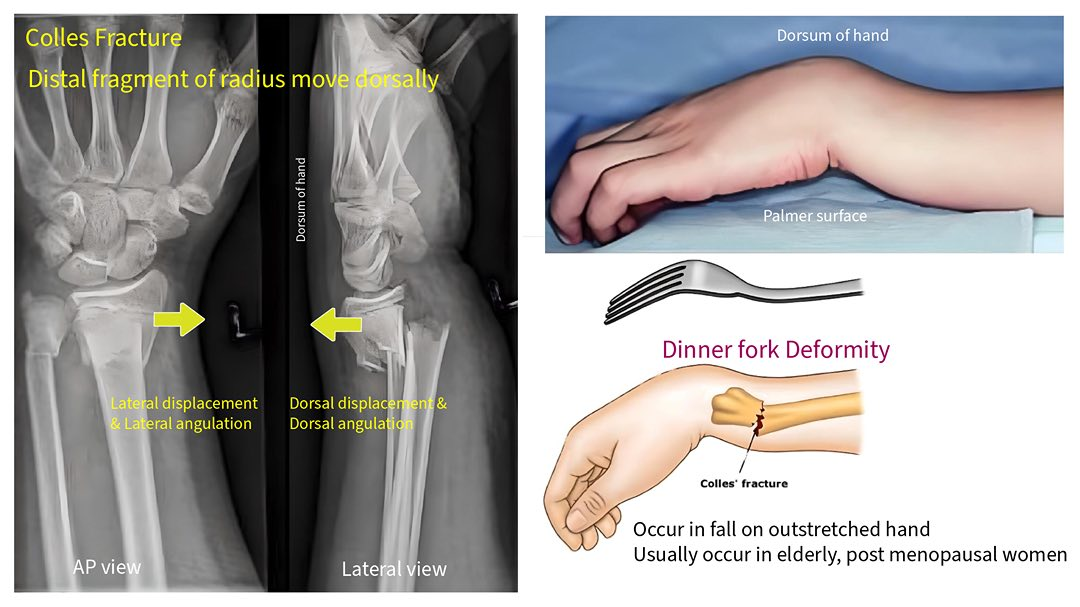
colles fracture
common extra-articular fracture
bone break that does not involve the articular surface (the surface of the bone that forms part of a joint)
occurs as a result of a fall on an outstretched hand
posterior displacement
medial angulation of the distal radius (tilting of the distal fragment of the radius bone toward the ulna)
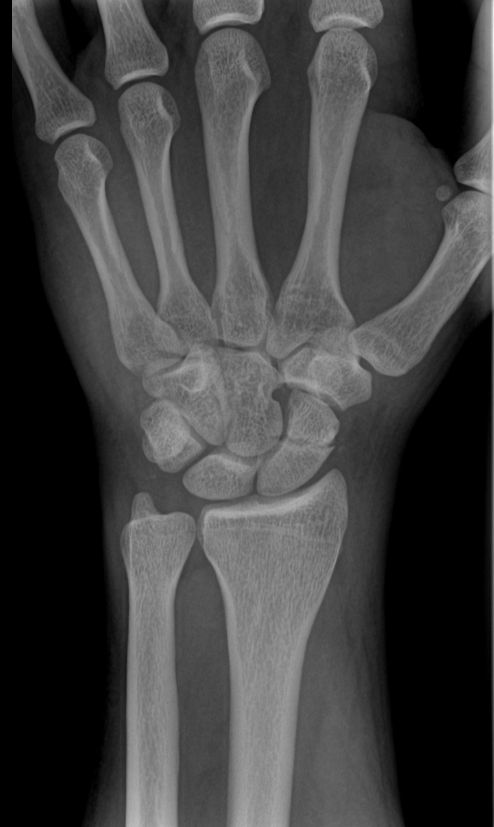
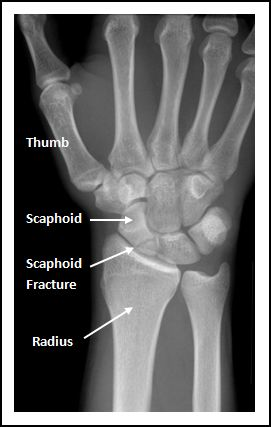
left scaphoid fracture
pain in the anatomical snuffbox → median nerve damage
numbness in the radial three digits of the hand
attenuation of any fracture
radiolucent
occult fracture
not readily visible on standard X-rays, often requiring further imaging like MRI for diagnosis
might see joint effusion
AP image
anteroposterior
xray machine in front of patient, film receptor behind patient’s back
(often used when patient is supine)
e.g. kidney scan
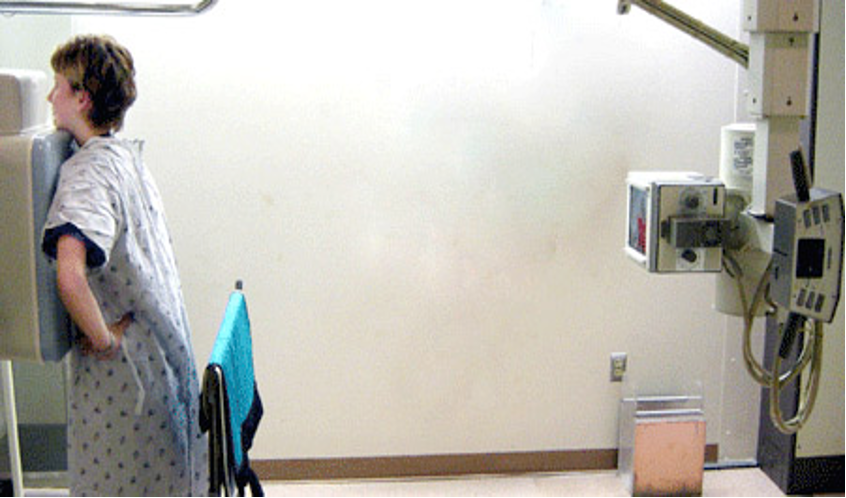
PA scan
posteroanterior
xray machine behind patient’s back, film receptor in front of patient
e.g. heart scan, hand scans

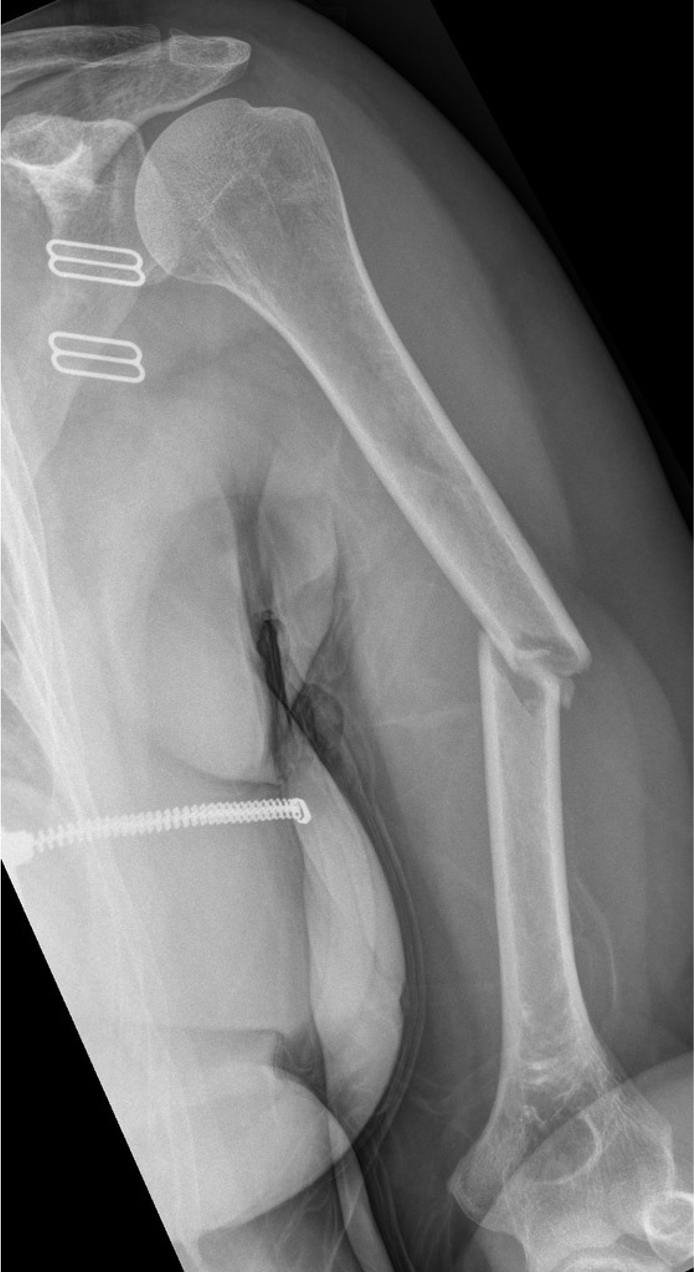
A 22 year old woman presents to her local hospital following an electric scooter accident. She presents with significant pain and weakness, limiting movement at the shoulder and elbow.
radiolucent, oblique fracture of the shaft of the left humerus, with medial displacement
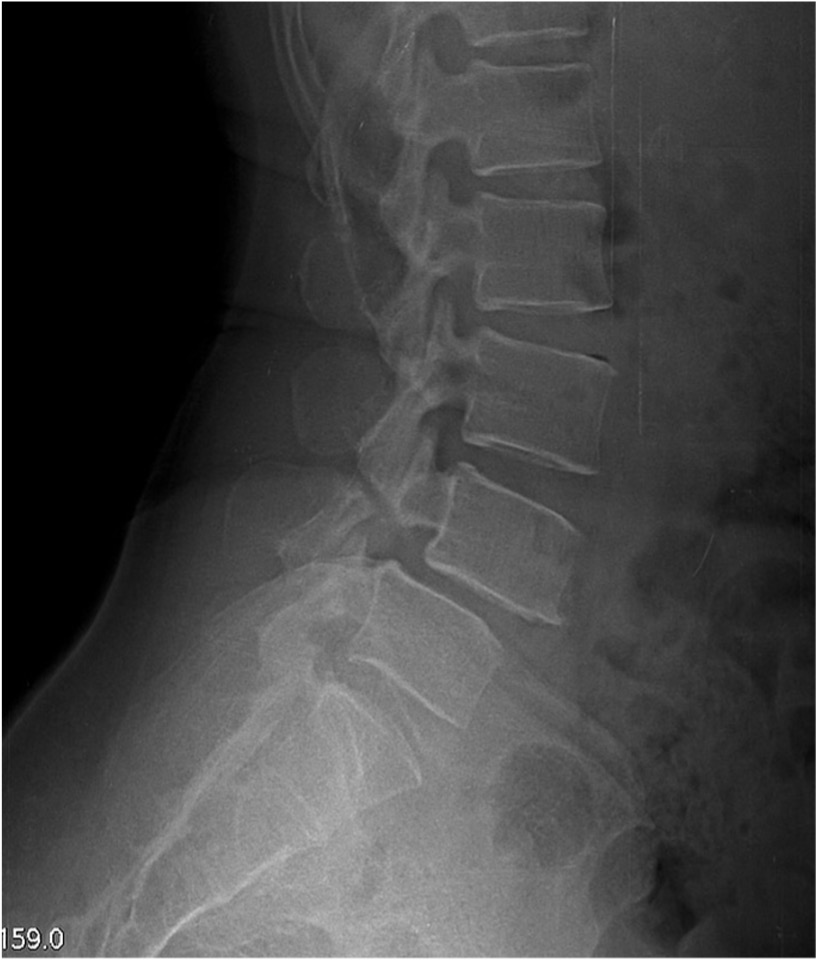
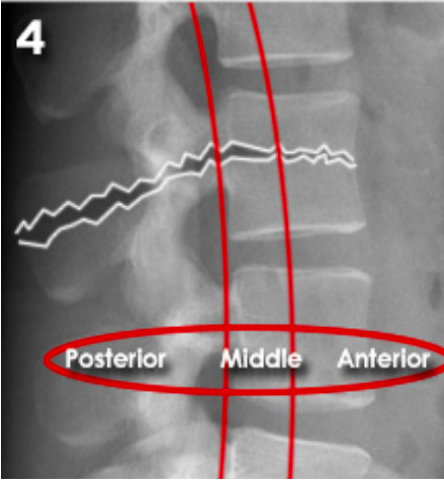
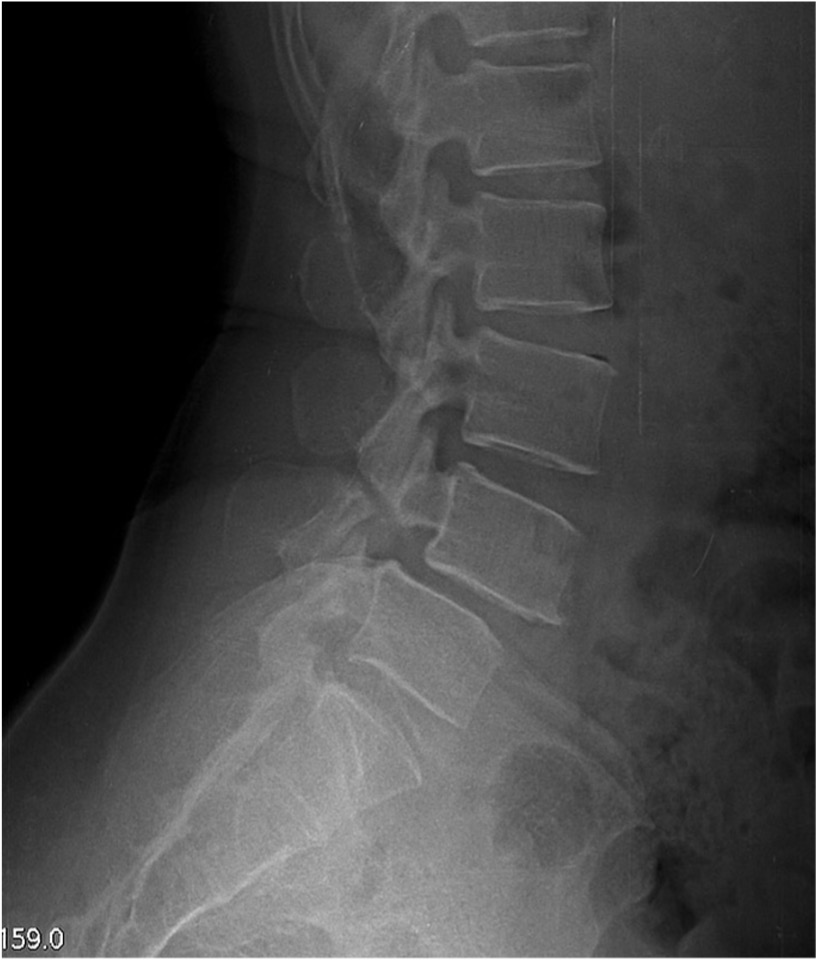
A 17 year old elite gymnast presents to her GP with a 5-month history of lower back pain, which increases in intensity upon hyperextension.
Lateral lumbar-spine x-ray reveals translation of a vertebral body due to a bilateral pars interarticularis fracture.
Which vertebral body and which columns are abnormal?
radiolucent fracture is seen at the pars interarticularis (facet joint) of L4 and L5, causing anterior dislocation (spondylolisthesis) of the vertebral body (L5 in this case)
Middle column: posterior shift at the L5 vertebral level
This would also stretch/displace the anterior longitudinal ligament due to posterior translation in the anterior column
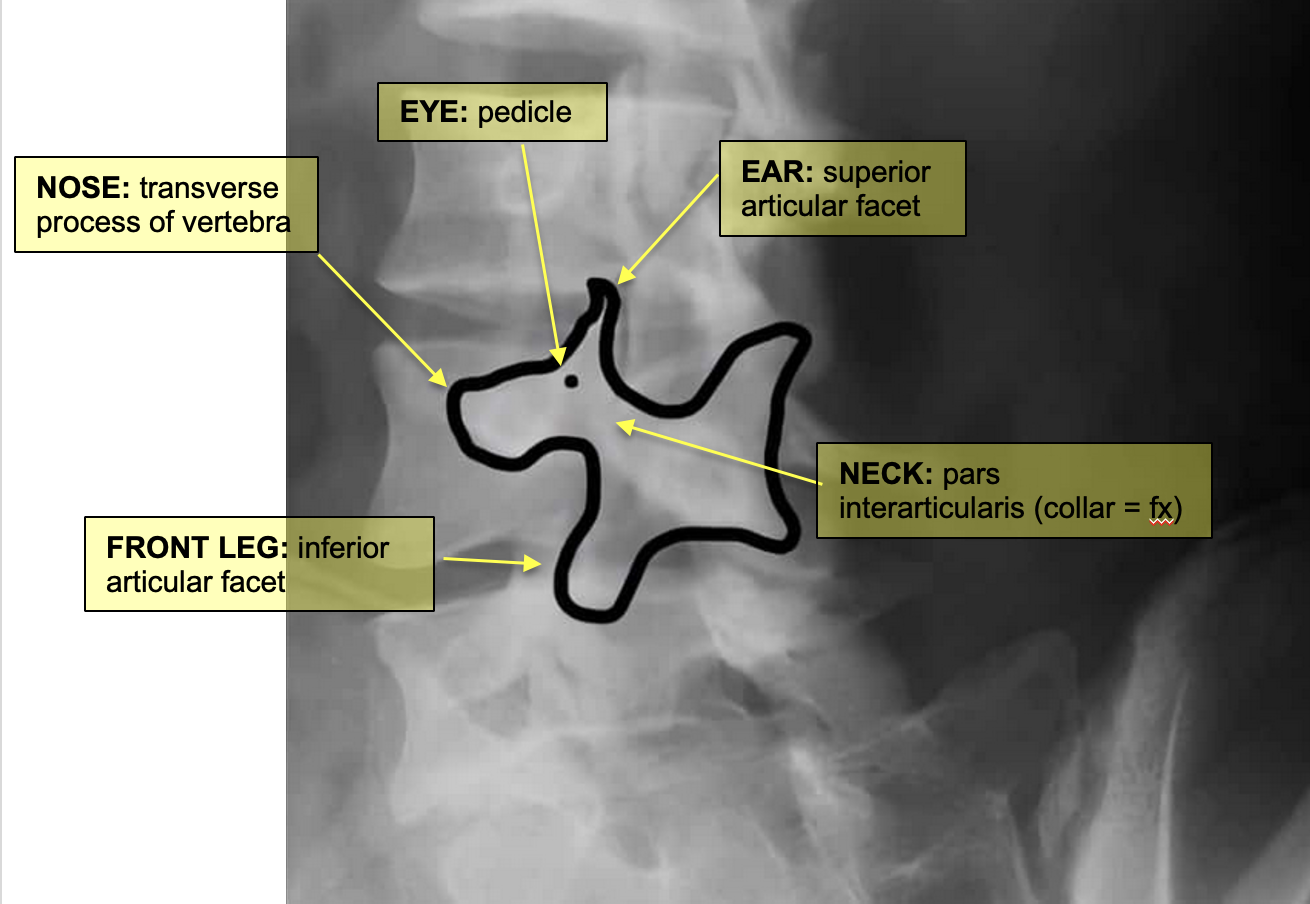
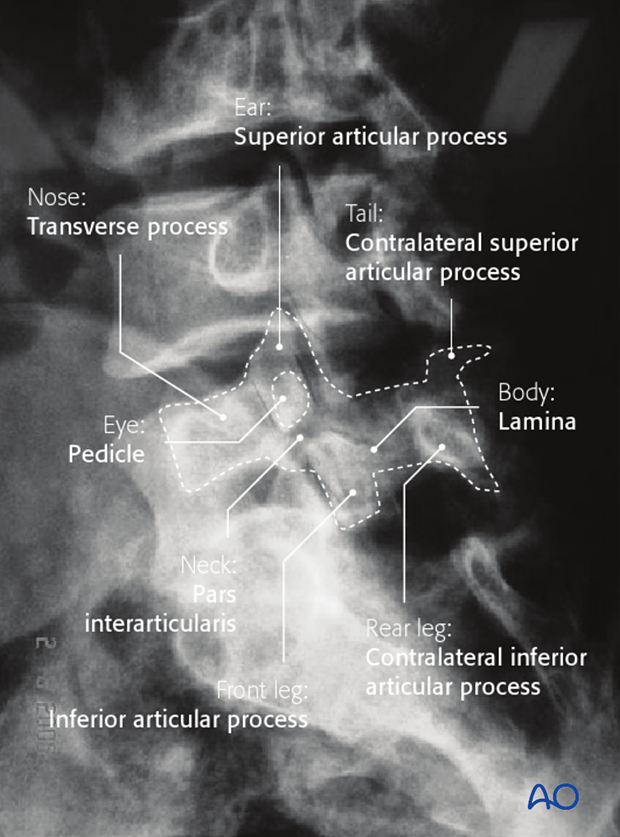
pars interarticularis fracture
pars interarticularis (pars) lies between the superior and inferior articular process at each zygapophyseal/facet joint
usually L5 level
bilateral: spondylolisthesis
unilateral: spondylolysis
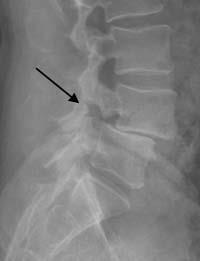
spondylolisthesis
bilateral pars interarticularis fracture at the L4/L5 level
disc has slipped posteriorly
stretches/displaces the anterior longitudinal ligament due to posterior translation in the anterior column
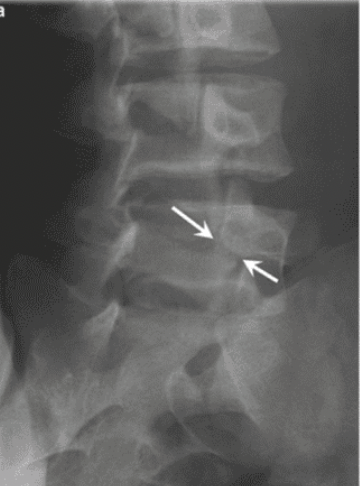
spondylolysis
unilateral pars interarticularis fracture
disc has not moved
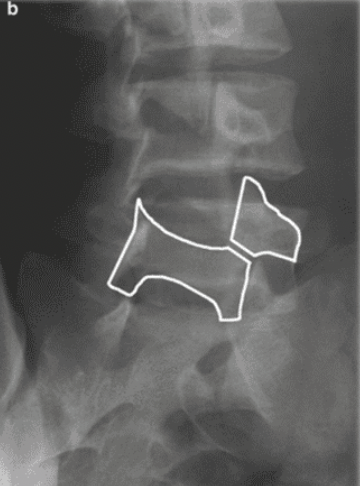
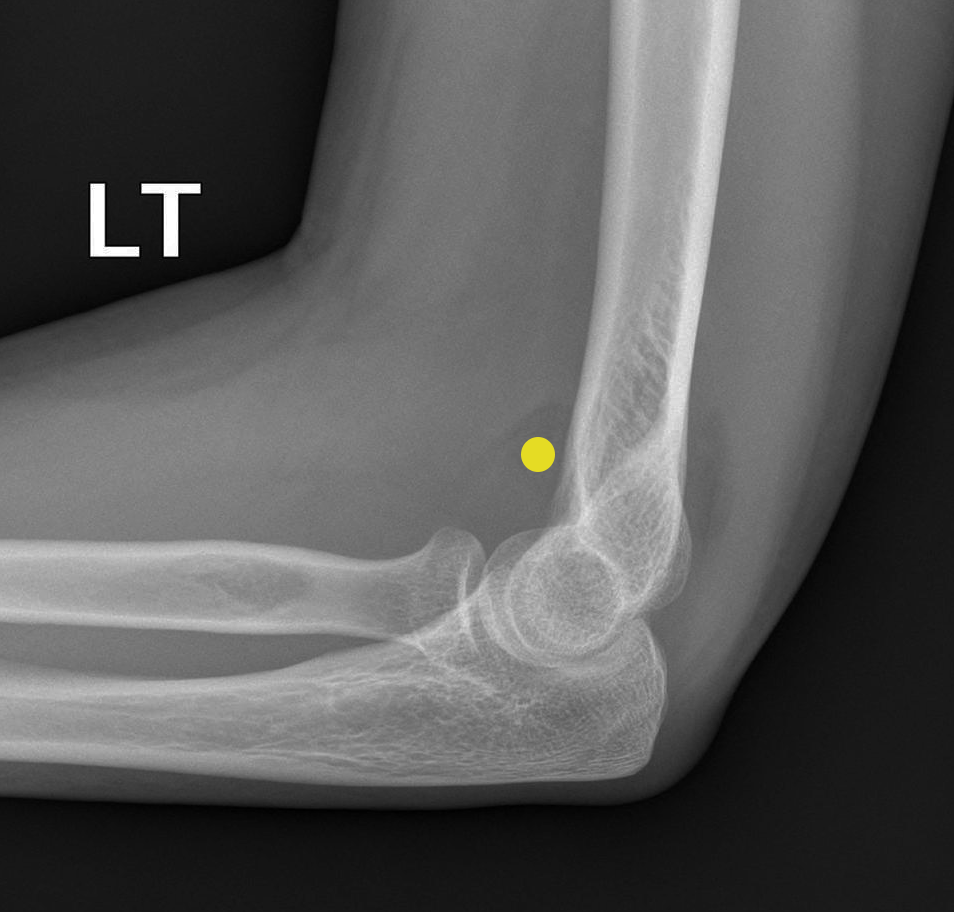
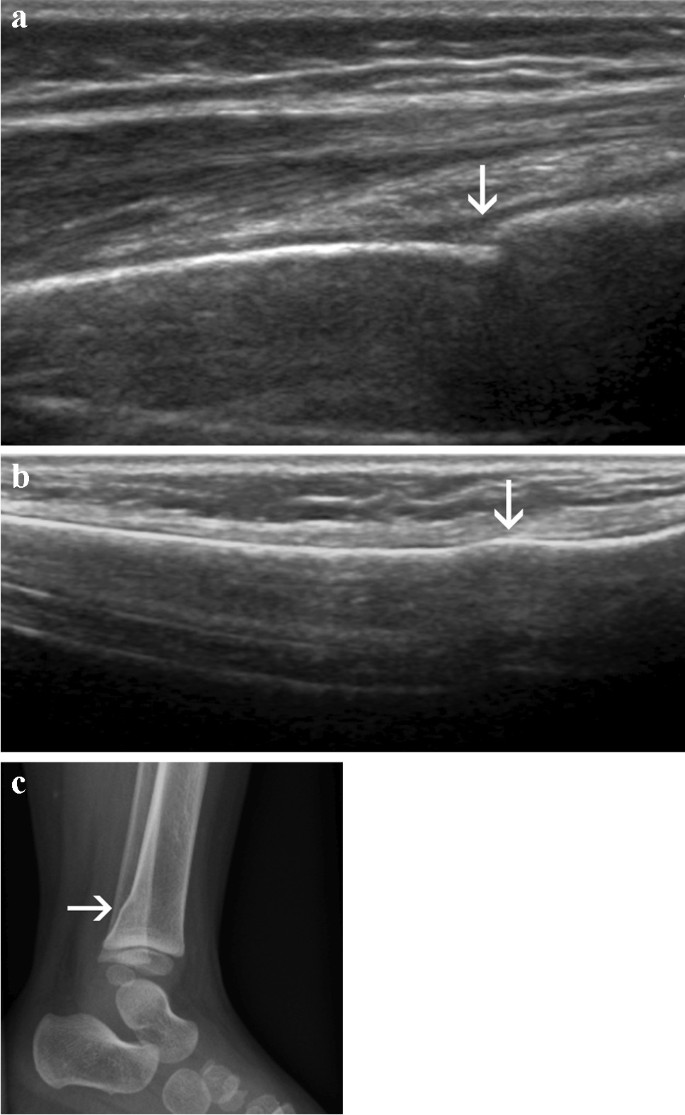
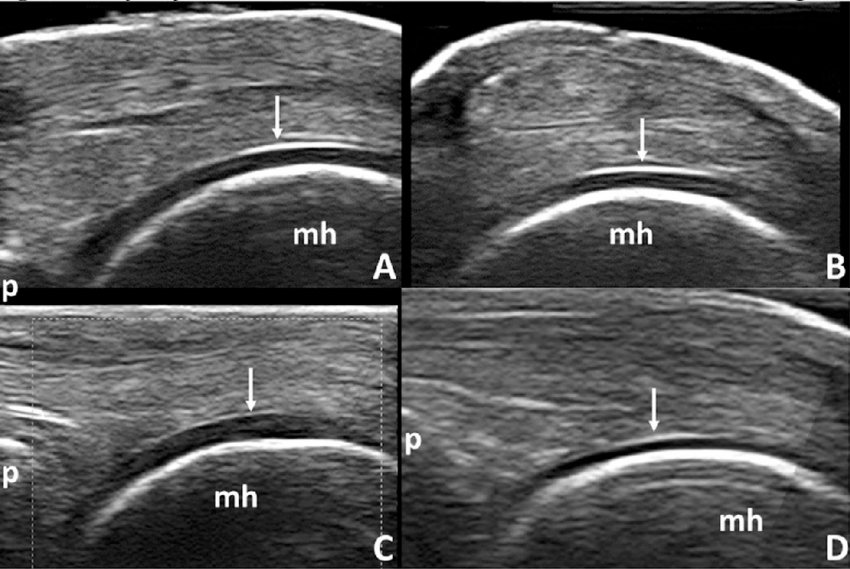
A 30 year old woman fell off a push-bike onto the left arm. A lateral radiograph shows elbow joint effusion, indicated by the 'sail sign' (yellow dot) of the anterior fatpad.
anterior fat pad is visible and raised
posterior fat pad visible
Their visibility is a result of an elbow joint effusion
adult → occult fracture of the radial head
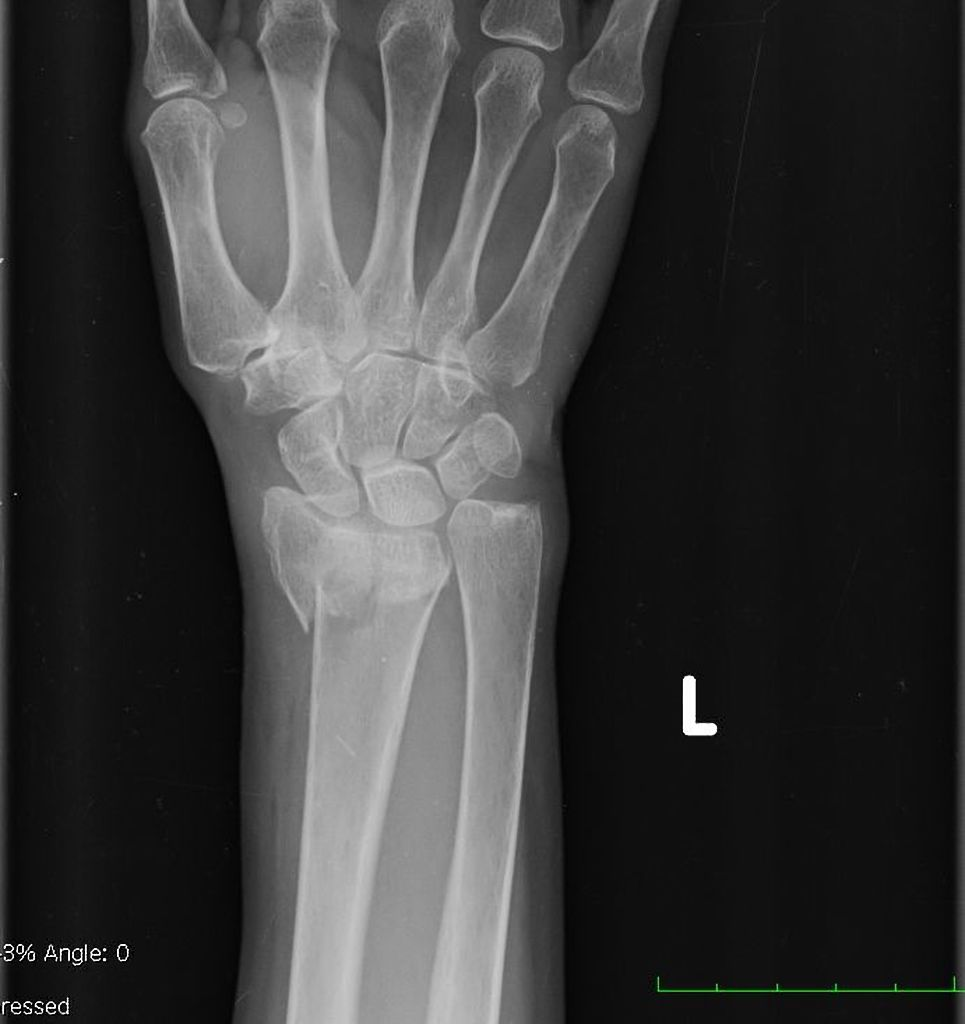
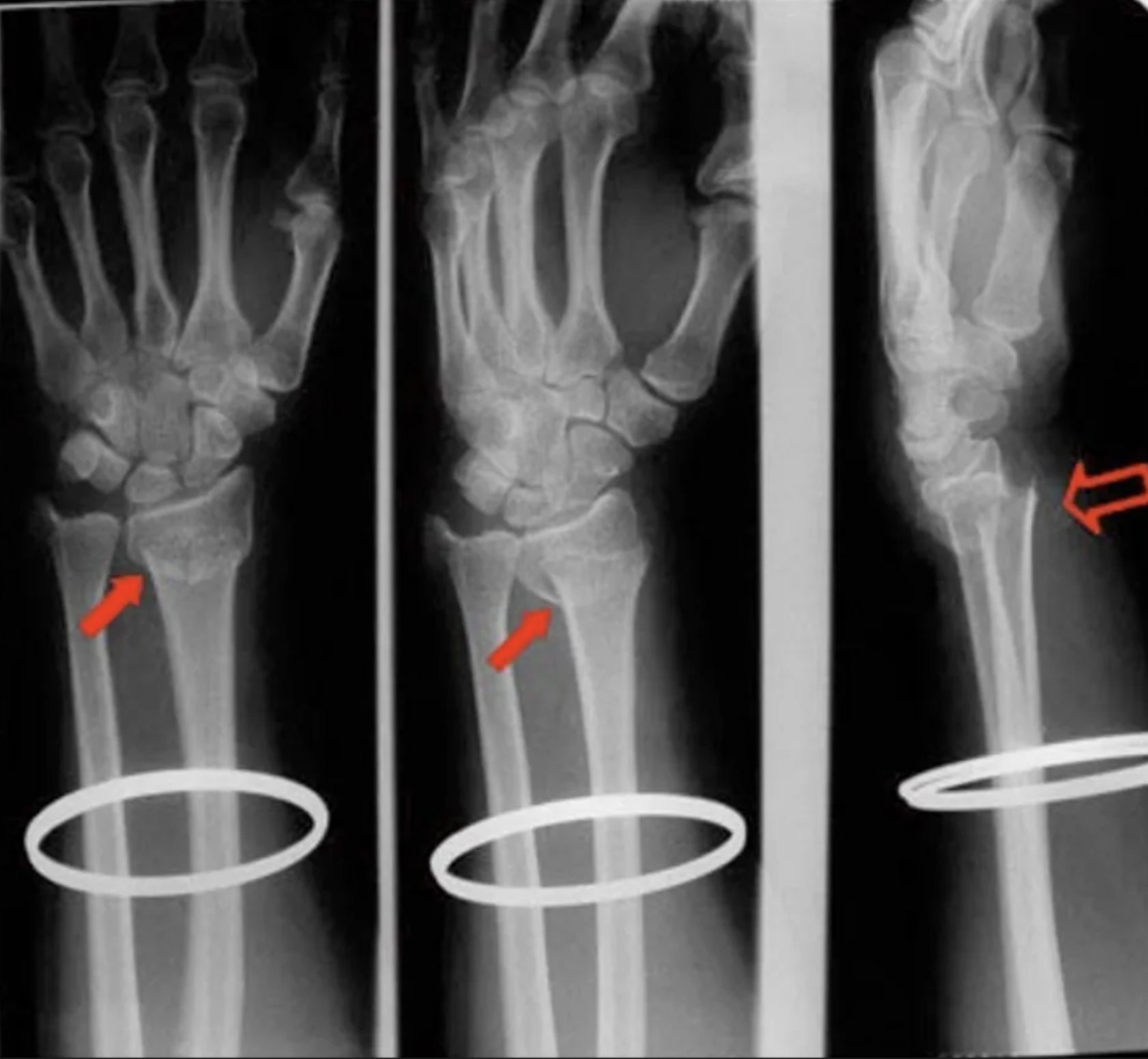
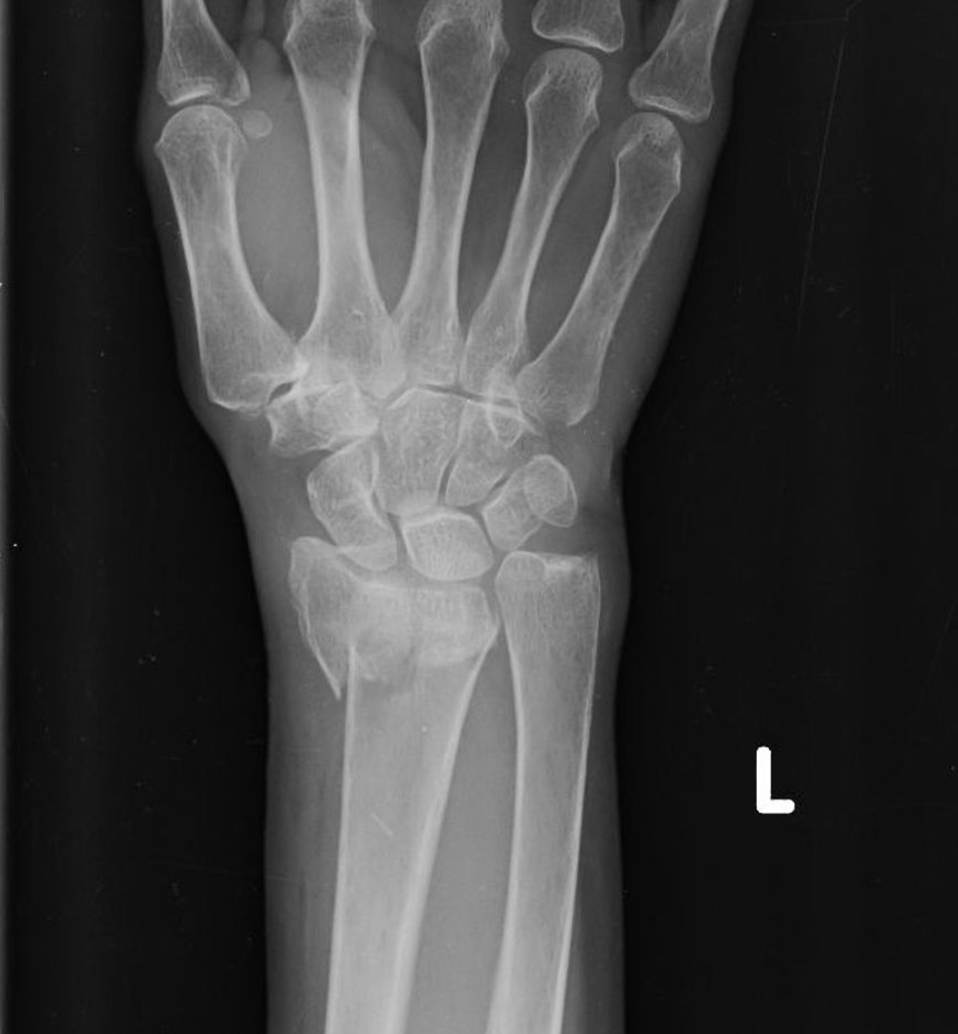
posteroanterior hand radiograph of a 63-year-old female who fell
colles fracture
Radiolucent, linear (?? i think this is meant to be transverse) fracture of the distal radius, with rotation
rotation evident by superimposition (overlap) of structures
Angulation and displacement cannot be commented on without a lateral view
sail sign
anterior fat pad, usually concealed within the coronoid fossa, becomes elevated and takes on a triangular shape
indicates joint effusion
In adults: sign of an occult fracture of the radial head
in children: supracondylar (distal humerus) fracture
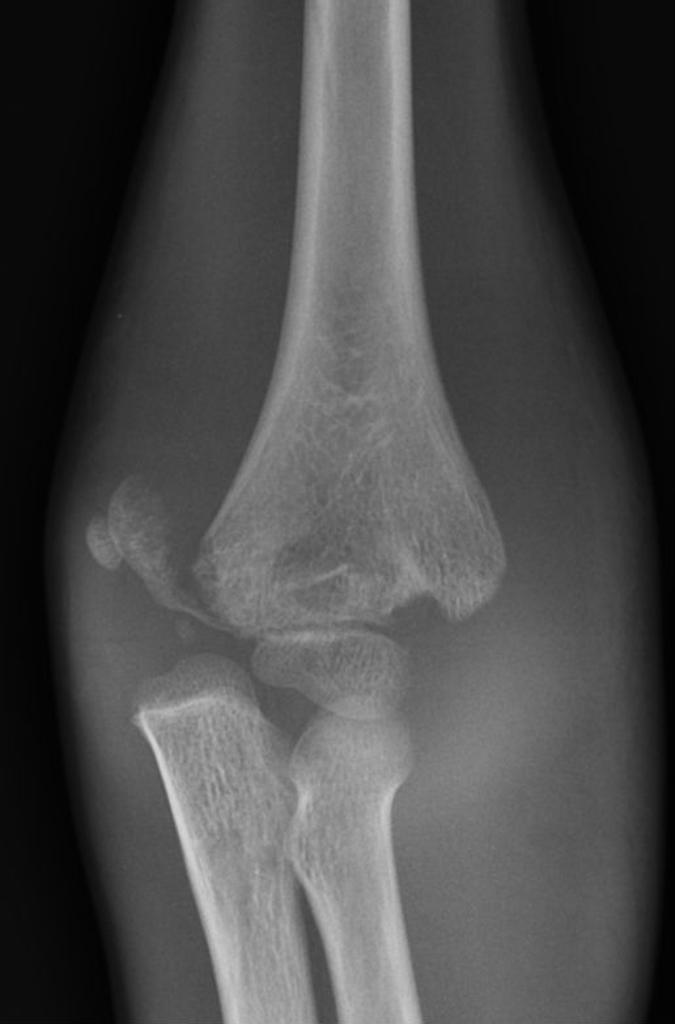
A six year old boy presents to the emergency department following a fall from the monkey bars.
Clinical examination demonstrates tenderness, significant swelling and deformity of the left elbow.
distal humerus fracture (comminuted)
damage to median nerve
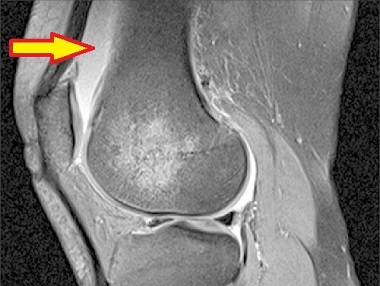
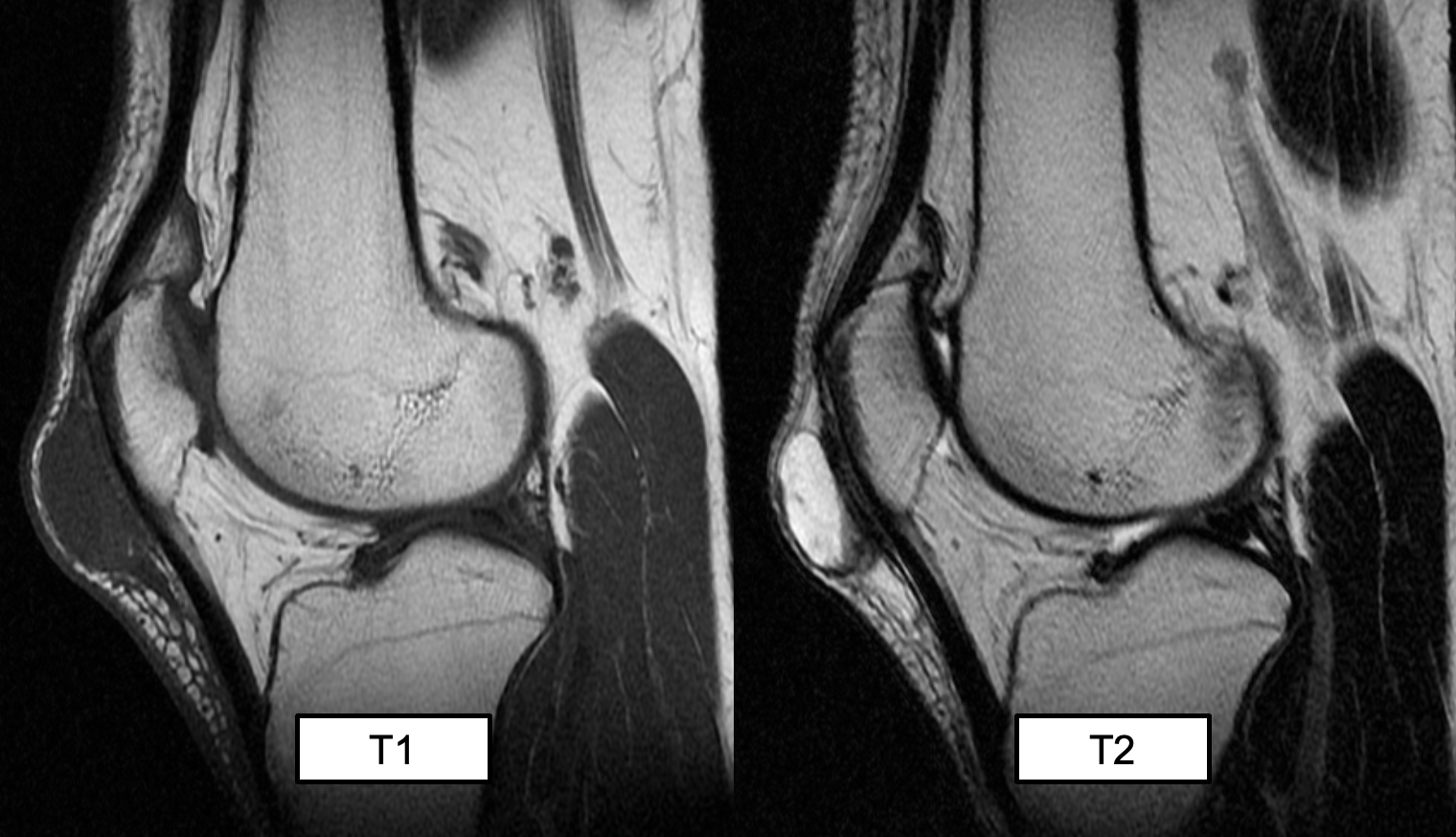
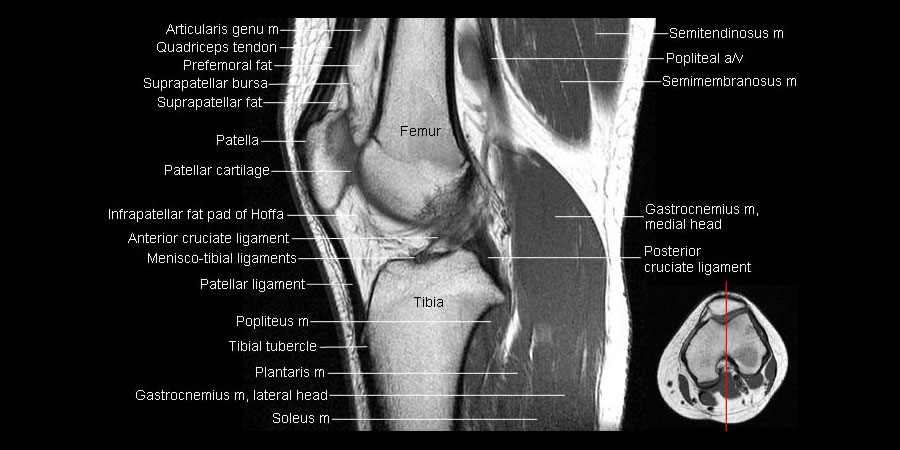
suprapatellar bursitis (likely not examined)
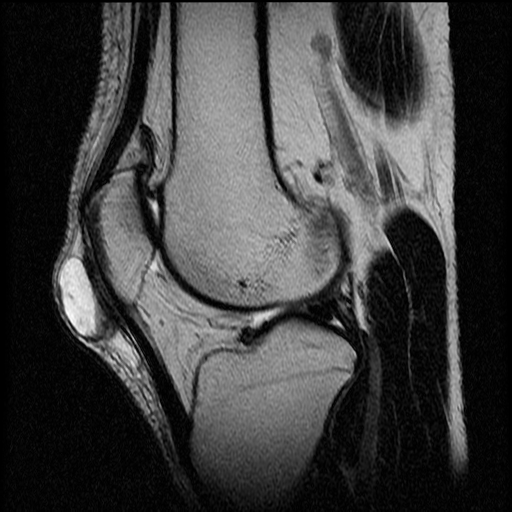
(T2 MRI)
prepatellar bursitis
A round high signal intensity structure, consistent with a fluid given the T2 weighted MRI, is located superficial to the patella ligament
(inflammation within the prepatellar bursa)
(prepattar = most common)