Exam 3: Cooking, emulsions, foams, crystallization, health, and poultry slaughter processing
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Denaturation
The breakdown of protein coils when heat and protein are combined ; induces coagulation/gelation
Coagulation
begins at 140 F, egg proteins begin to form web and begin to scramble or cook
Binding agent
when something acts as an agent to bind several ingredients that are not able to bind
Emulsion
when two liquids that do not normally mix together are combined
Lecithin
a phospholipid; one of the most hydrophilic emulsifiers in the food industry and most prevalent dough strengthener
Foaming
when eggs are beaten, air is incorporated creating a lighter more air-filled product ; has a airy texture and smooth mouthfeel
Biosecurity
isolation, traffic control, and sanitation which are all used to practice biosecurity to decrease the likelihood of diseases
Isolation
isolating birds when they are carriers ; A group of poultry goes in at the same time and leaves at the same time
Immobilization
Renders bird unconscious through stunning ; animal welfare and better bleedout ; 2 methods which are electrical and gas and there are types - reversible and irreversible
CAS
Controlled atomsphere stunning which is gas stunning ; birds are immersed in an approved gas or mixture of gases in order to displace oxygen and render the bird unconscious
WOG
without giblets ; processed bird without the heart, liver, and gizzard
Dressing percent
dressing % for poultry is 72% ; the hot carcass weight expressed as a proportion of the live weight
Egg proteins begin to form web and begin to scramble or cook at __ F. Good for when you want scrambled eggs, but bad when you are using eggs to thicken a sauce or custard
140
when using eggs as a thickening agent, eggs are heated gently in __ because coagulation of eggs cause the mixture to thicken or set
liquid
In baking, eggs function as a __ agent ; where high protein traps steam and creates rise, and egg whites can be whipped up to 8 times their original volume
leavening
when food is dipped in egg mixture and other coatings stick to it, eggs act as a __ agent
coating
When eggs are used as an emulsifier, the egg increases the emulsion __ so it does not break
stability
there are no essential differences found in emulsifying properties of __ whole eggs and yolk compared to __ liquid/shell eggs
dried ; fresh
yolk solids content affects emulsifying properties, where __ solids = increases emulsification
increasing
__ is an amphiphilic, phospholipid molecule that is one of the most hydrophilic emulsifiers in the food industry; it is the most common dough strengthener
lecithin
__ eggs causes gradual denaturization of yolk proteins , it increase liquid viscosity, and the irreversible gelation of yolk reduces emulsifying capacity and stability
freezing
The most common emulsified, spoonable egg product is __
mayonnaise
__ is the process when eggs are beaten, air is incorporated creating a lighter, more air-filled product, and it provides an airy texture, smooth mouthfeel and more spongelike texture
foaming
Foam __ is due to ovalbumin, and foam __ is due to ovomucin
volume ; stability
_____ contamination or “fat bullets” destroy them.
Yolk
Old eggs with watery, thin albumen and older hens eggs will produce _____ solids _____ foam stability
lower; less
_____ helps to unwind proteins during initial egg foaming, and _____ delays initial foam formation but stabilizes forms during heating
salt; sugar
_____ Acid improves egg white protein functionality by reducing pH and stabilizes product color
citric
Angel food cakes must be cooled _____ to prevent volume decrease due to moisture accumulation on top
upside down
eggs are used in confectionery products and ice creams to control _____ of water/sugar molecules and create smooth texture and mouthfeel
crystalization
fat and protein reduce size and number of sugar _____ that interfere with orientation of sucrose and molecules
crystals
egg yolk is the predominant egg product found in the most common frozen dessert _____.
ice cream
the standard of identity states that ice cream contains _____ 1.4% yolk
less than
the poultry flock should be checked _____ for any signs of disease
daily
to avoid bringing in contamination _____ should be kept at a minimum inside production facilities
traffic
Microorganisms that need to live in a host to duplicate themselves can cause _____ diseases.
viral
Single-celled microscopic organisms that require certain temperatures and moisture to survive can cause a _____ disease
bacterial
Preslaughter management requires feed withdrawal for animals for _____ hours
12-14
Going into processing, birds are transferred from transport cages to a dark room where they are hung upside down from _____ atttached to an automated line
shackies
During CAS stunning, birds are immersed in a n approved _____ gas in order to displace oxygen and render the bird unconscious
CO2
Carcasses are submerged in the _____ that contains water heated to 125 to 150 F, to loosen the feathers to facilitate removal
scalder
A _____ is automated machine that contains rubber finger-like projections that rotate in a circular motion to remove feathers without damaging the carcass
picker

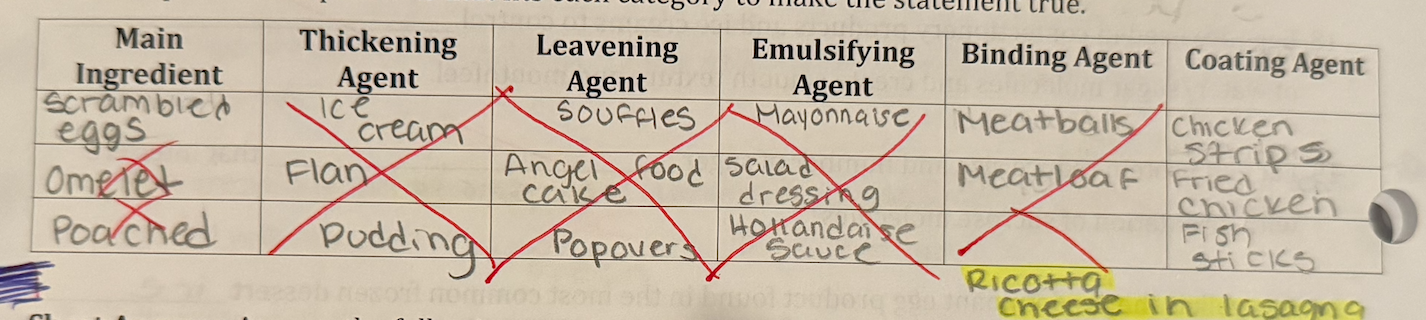
Eggs have many functions during cooking. Give examples of food products that fits each category to make the statement true
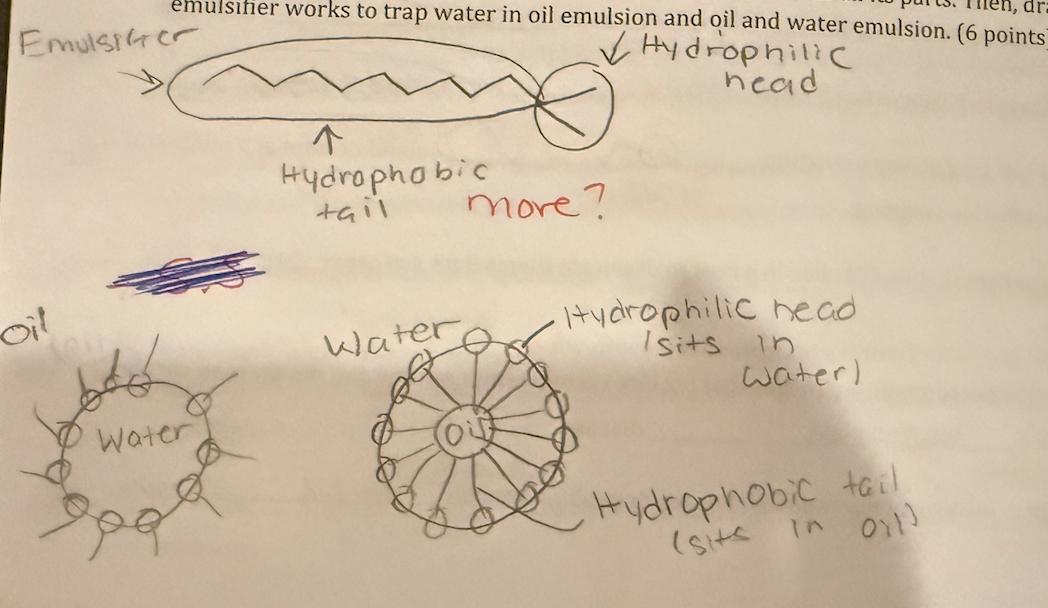
Draw a picture of the molecular structure of an emulsifier with all its part. Then draw how the emulsifier works to trap water in oil emulsion and oil and water emulsion.
What are three functions of eggs in frozen desserts?
import flavor (especially custards), improves whipping ability and fat formation in mixes and increases viscosity of mix.
What are the two types of stunning methods approved for poultry in the U.S.? What types of stunning do they use in europe? describe each in detail
The two types are electrical stunning and controlled atmosphere stunning (CAS)
CAS - birds are immersed in an approved gas or mixture of gases in order to displace oxygen and render the bird unconscious
electrical stunning - delivers a current through a water bath to immediately create a state of unconsciousness
They use irreversible electrical stunning in Europe which can be CO2 and/or Argon and nitrogen. It takes 2-3 minutes and poultry are unable to regain consciousness and birds are hung on shackles after stun can also cause quality issues
The US use reversible electrical stunning which is CO2 and it takes 35-50 seconds and poultry are able to regain consciousness if neck is not cut
What is exsanguination? Why is it so important? If not done within seconds of stunning, what defect condition occurs and how?
It is the removal blood by cutting jugular vein and carotid artery which leads to death to bird. If not done within seconds of stunning, capillaries will burst and bloodsplash will occur
What are the differences between “soft” scalding and “hard” scalding? describe each
Soft
No effect on cuticle (yellow/white pigment)
the temp is low 128 F
takes a long time 120 sec
more difficult to pick
better yield
Hard
loosens cuticle and epidermis
cuticle must be removed for batter breading, waxy substance won’t let batter stick
the temp is high 140-145 F
the time is short 45 seconds
loses yellow pigment from feed
better coating adhesion
What is this?
primarily affects birds raised on the range. lives in the intestines and linings of poultry. causes slow growth and lower meat and egg production. specific treatments for each type. check flock periodically for presence. rotate flocks on the range and maintain a strict sanitary environment
internal parasites
What is this?
can cause internal tumors that may lead to paralysis, weight loss and eventually death. there is no treatment or vaccine. hens can pass the disease into their eggs. the only option for elimination is to eradicate the entire flock, clean, and sanitize to start flock over again. can only be diagnosed through histopathological testing
avian leukosis virus
what is this?
highly contagious, highly virulent, and very high mortality rate. causes respiratory: coughing, nasal discharge, and nervous disorders: paralysis, wryneck, tremors, and convulsions. bright green diarrhea. there is a vaccine available
newcastle disease
what is this?
spread through infected chicken dander. it causes internal lesions and tumors that cause paralysis, weight loss and eventually death. there is no treatment, and disease can live in the soil for 5+ years. there is a vaccine available. can only be diagnosed through histopathological testing
marek’s disease
what is this?
hen passes salmonella subspecies to chicks via the egg. spread by contaminated chicks from one to another. outbreaks occur in chicks less than 3 weeks old. chicks have ruffled feathers, labored breathing, they huddle together for warmth and have white diarrhea
Pullorum disease