Exam 2 - ECON production
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Economic Cost
1. The cost associated with the use of resources
2. The sum of explicit and implicit cost
Long Run total Cost curve GRAPH
see graph
Graphically, firms real LRATCC
See graph
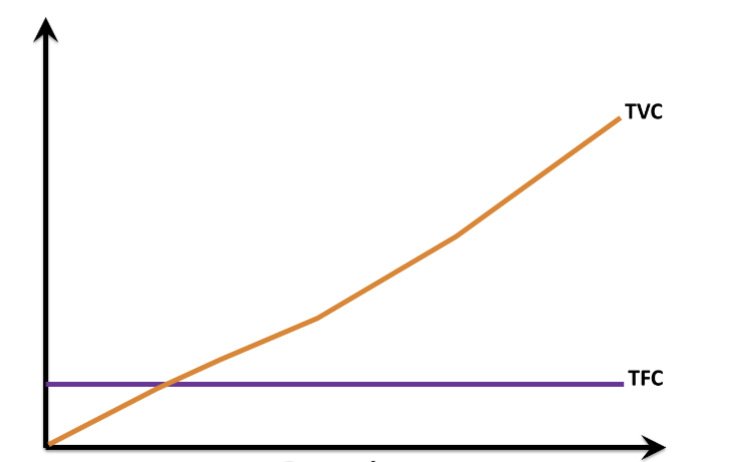
Total Variable Cost Graph
see graph (orange line)
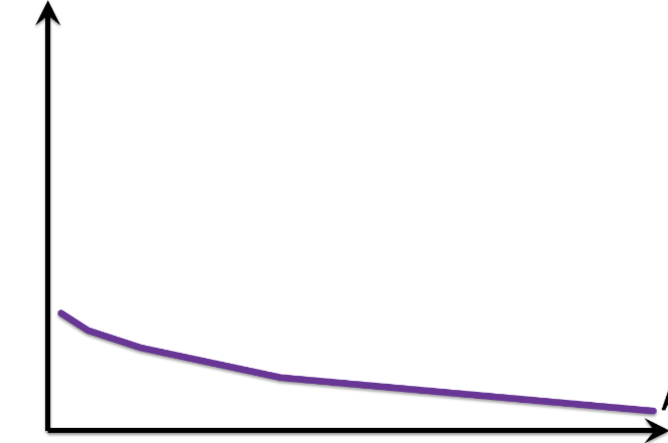
average fixed cost graph
see graph
Explicit Cost
The monetary payments made by individuals, firms, and governments for the use of land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial ability owned by others
Another name for explicit cost
accounting cost
implicit cost
1. the opportunity cost of using owned resources
2. Costs for which no monetary payment is explicitly made
Accounting Profit
Total revenue minus the explicit costs of production
Economic Profit
Total revenue minus economic costs, which include both explicit and implicit costs of production
Accounting profit equation
total revenue - explicit costs
economic profit equation
Total revenue - economic costs
short run
the time period in which at least one input of production is fixed but other inputs can change
Total Product
1. the total amount of output with a given of resources
2. Equal to total output
Marginal Product
The additional output produced as a result of utilizing one more unit of a variable resource
MP Equation
Change in Total product / Change in variable resource
Average Product
1. The average amount of output produced per unit of a resource employed
2. Total product divided by the number of units of a resource employed
AP equation
total product / unit of resource
Increasing Marginal Returns
A characteristic of production whereby the marginal product of the next unit of a variable resource utilized is greater than that of the next previous variable resource
Diminishing Marginal Returns
A characteristic of production whereby the marginal product of the next unit of a variable resource utilized is less than that of the previous variable resource
Fixed Cost
Cost that do not change with the amount of output produced
Variable Cost
Cost that change with the amount of output produced, increasing as production increases and decreasing as production decreases
Total Cost
The sum of fixed and variable cost of production
TC Equation
Total Fixed Cost + Total variable Cost
Average Fixed Cost
total fixed cost divided by the amount of output produced; fixed per unit
Average Variable Cost
total variable cost divided by the amount of output produced; variable cost per unit
Average Total Cost
Total Cost divided by the amount of output produced; total cost per unit
Marginal Cost
1. the additional cost associated with one more unit of an activity
2. For production, it is the change in total cost due to the production of one more unit of output
Average Cost Graph
see Graph:
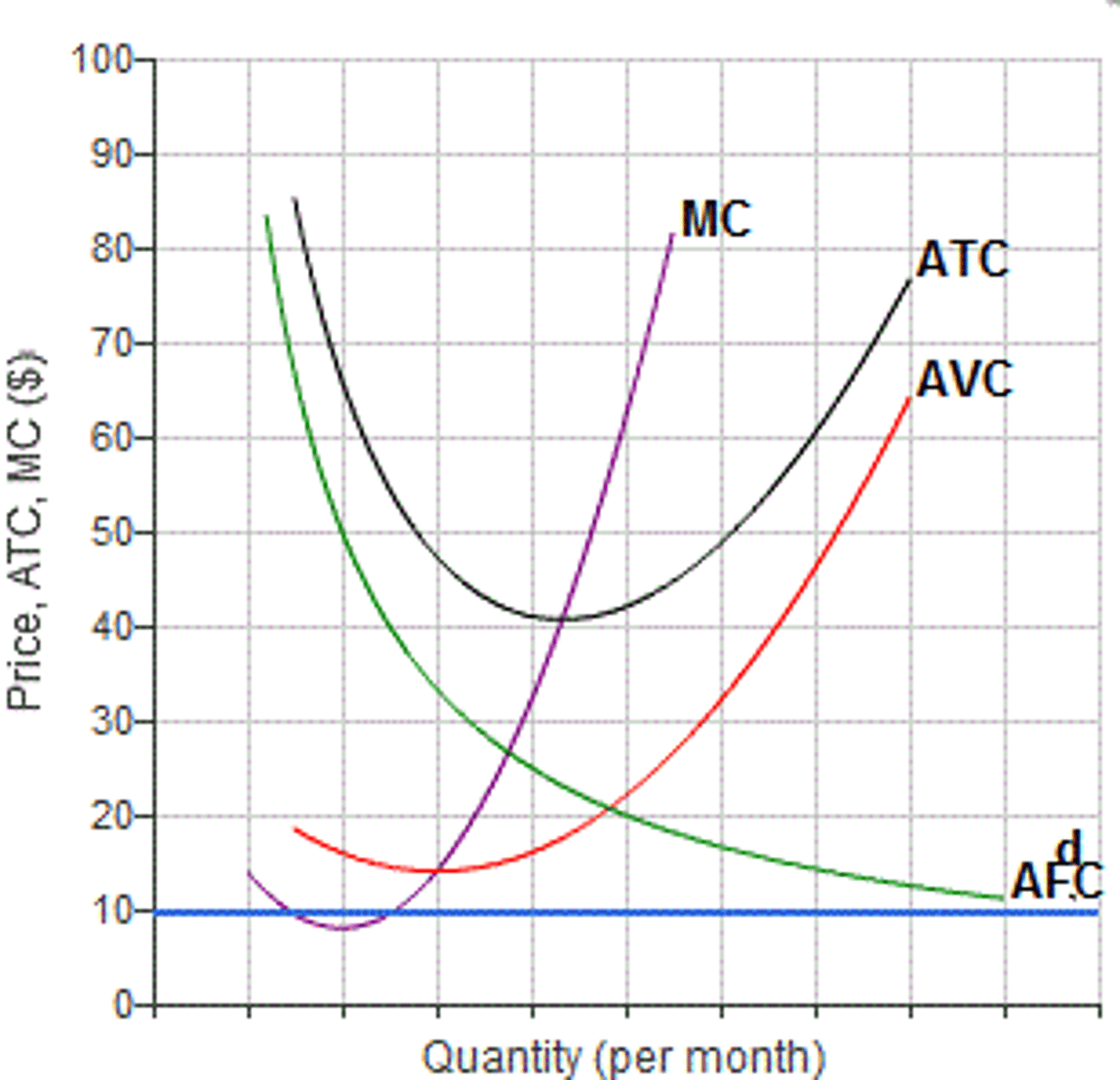
Short-run Average Total Curve
a curve showing the average run for different level output when at least one input of production is fixed, typically plant capacity
Long Run
The time period in which all inputs of production can be changed
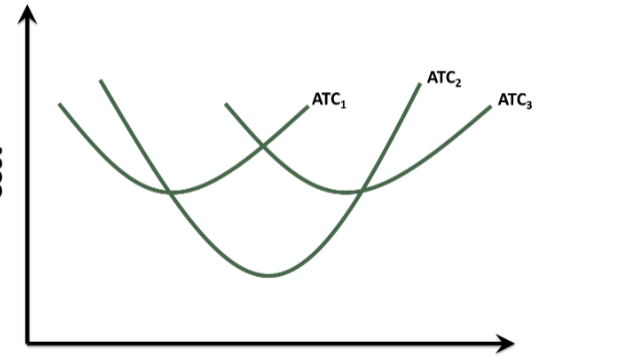
Long-Run Average Total Cost Curve (LRATC)
A curve showing the lowest average total cost possible for any given level of output when all inputs of production are variable
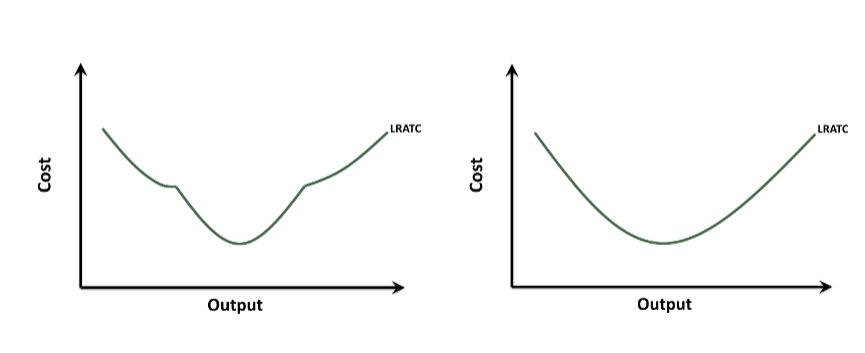
Economies of Scale
a condition on which the long-run average total cost of production decreases as production increases
Diseconomies of Scale
A condition in which the long-run average total cost of production increases as production increases
Constant Returns of Scale
A condition in which the long-run average total cost of production remains constant as production increases
Minimum Efficiency Scale
The lowest level output at which the long-run average total cost is minimized
What is an important in determining the true cost of an economic activity such as the production of goods and services
The factor of Implicit Cost
Total Revenue= ?
price of a good times the quantity sold
What business operating decisions should be based on?
the factor of economic profit
What does positive economic profit encourage?
More firms to enter the market to produce goods and services
When can a company can break even and meet operating cost without loss when it earn?
At ZERO economic profit
When is the value of economic profit negative?
When accounting profit is 0
If a business owner can produce more as a whole with an additional worker even if the marginal product associated with that worker is lower than the marginal product associated with the previous worker, then there are....
The factor of diminishing marginal
Graphically, the average product curve
Is increasing before reaching its peak, then decreasing
Why is it important to be able to calculate total product, average product, and marginal product?
To operate efficiently and maximize profit
If a company decided to produce zero units of output...
then it still has to pay fixed cost of production
Graphically, the fixed curve
perfectly horizontal
Graphically, the total variable curve
1. Is upward sloping
2. at each output level falls below the total cost curve by the amount of the fixed cost curve
The average total cost curve is...
greater than the average variable cost curve for all levels of output
what is important to calculate because it can be compared directly to the price?
Total cost and average cost
The vertical distance between the average variable cost and average total cost curves gets smaller as more output is produced because this distance is equal to the....
average fixed cost which declines as output increases
Patterns of the average fixed cost
always declined with additional output
pattens of average variable and total cost
always decline and then increase
What happens when marginal product increases?
marginal cost declines
How will a firm decide whether to keep production at the current level of output or produce more
compare the marginal cost and marginal benefit
What does the marginal cost curve show?
the relationship between: total cost and output
A profit-maximizing firm should produce a level of output where....
marginal revenue equals marginal cost
How is the long-run average total cost curve of a firm plotted?
by using the minimum short-run average cost for each level of output.
Diseconomies of scale example
A firm is reducing their output from 2,000 units to 1,000 units. This decision results in a reduction in the long run average cost from $300 to $200. What can be said about this firm?
Which of the following is a source of economies of scale for a firm?
An increase in the specialization of labor
What is a reason for diseconomies of scale exist for firms?
firms cannot perfectly replicate its production when it expands.