Systems Path Section 6 - Restrictive Lung diseases (pg 54-79)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
disease of the lung that causes a decrease in lung expansion and vital capacity
restrictive lung disease
group of fibrotic disorders that are diffuse, bilateral, and patchy, MC idiopathic, result in hypoxia/dyspnea, and progressively lead to respiratory failure and/or pulmonary HTN
chronic interstitial lung diseases
widespread interstitial fibrosis of lungs leading to dyspnea and cyanosis, non-productive cough, and have a poor prognosis
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
how does idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis develop?
repeated alveolar damage causing faulty repair leading to fibrosis
who is most likely to get idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
males 55+
traditional pneumoconioses
coal, silica, asbestos
what type of pneumoconiosis is the accumulation of coal/carbon in lungs leading to minimal symptoms (dyspnea) which may progress in certain individuals
coal dust (worker's) pneumoconiosis
who is most likely to get coal worker's pneumoconiosis?
coal workers
Coal Worker's Pneumoconiosis MC affects....
upper lobes
coal dust accumulates in the lungs, asymptomatic, no inflammation
anthracosis
complicated coal worker's pneumoconiosis
progressive massive fibrosis
MC pneumoconiosis which causes significant inflammatory reaction leading to pulmonary fibrosis, dyspnea, for pulmonale and lung cancer & TB
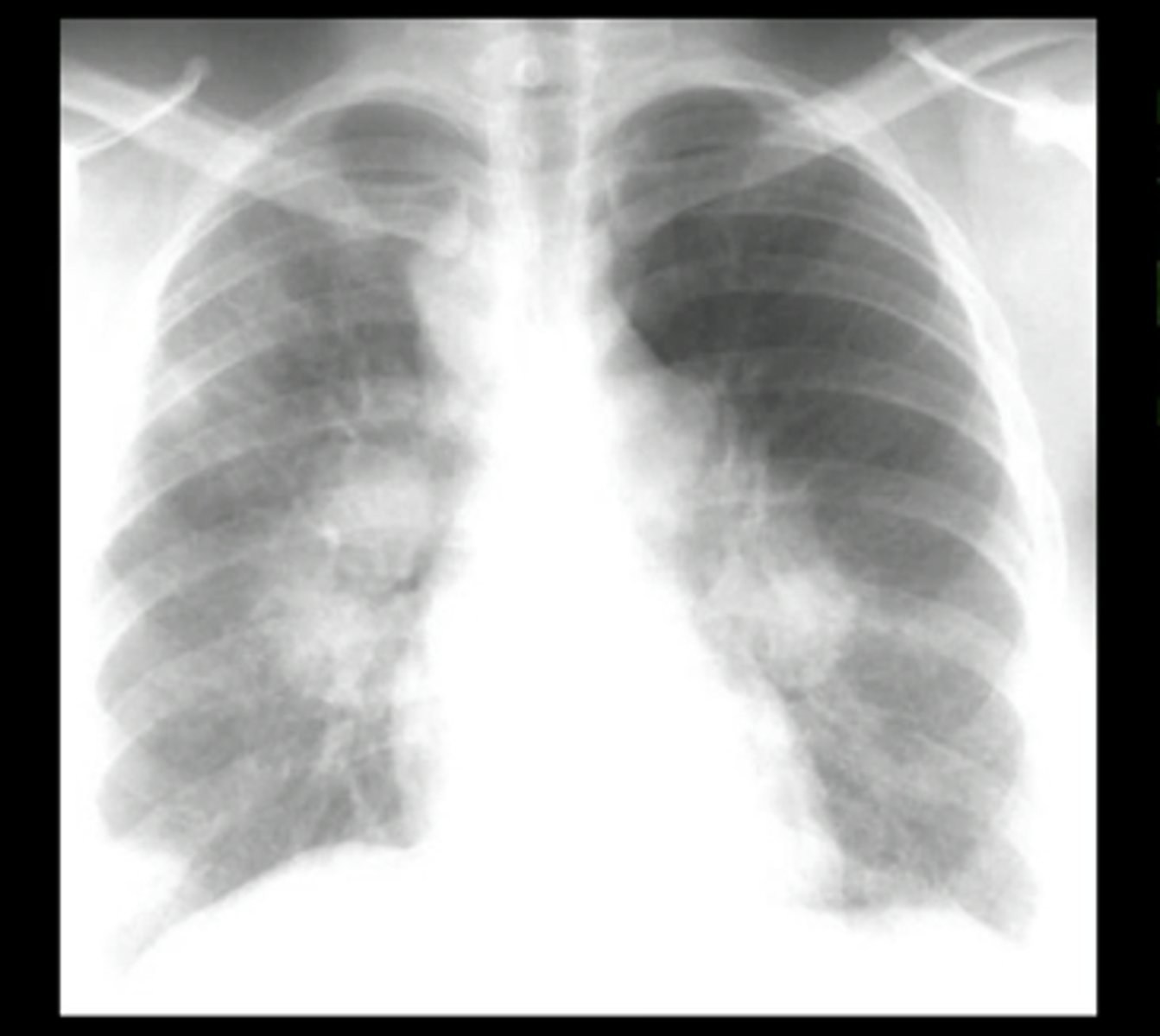
silicosis
characteristics of silicosis
silicotic nodules, egg-shell calcifications
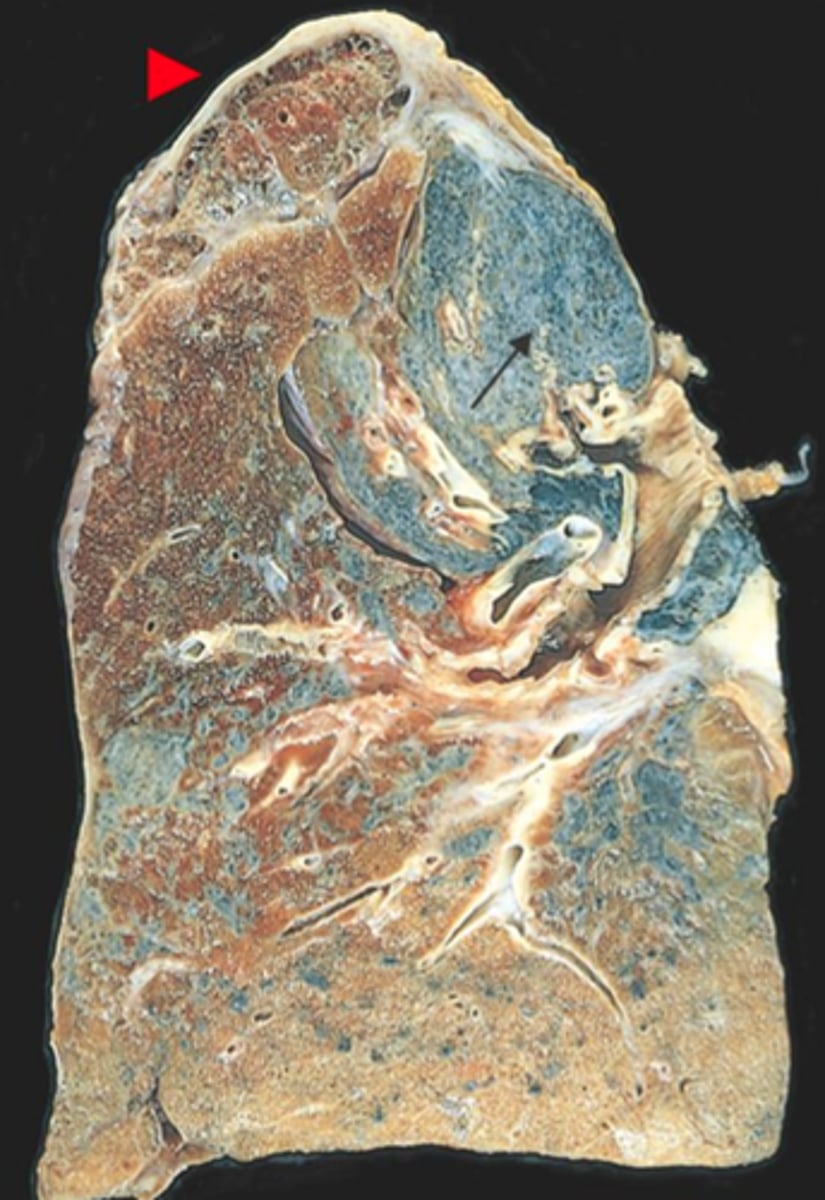
asbestos exposure leading to significant inflammatory response and resulting in fibrosis of lungs, progressive cough, dyspnea, and increased risk for mesothelioma and lung cancer
asbestosis
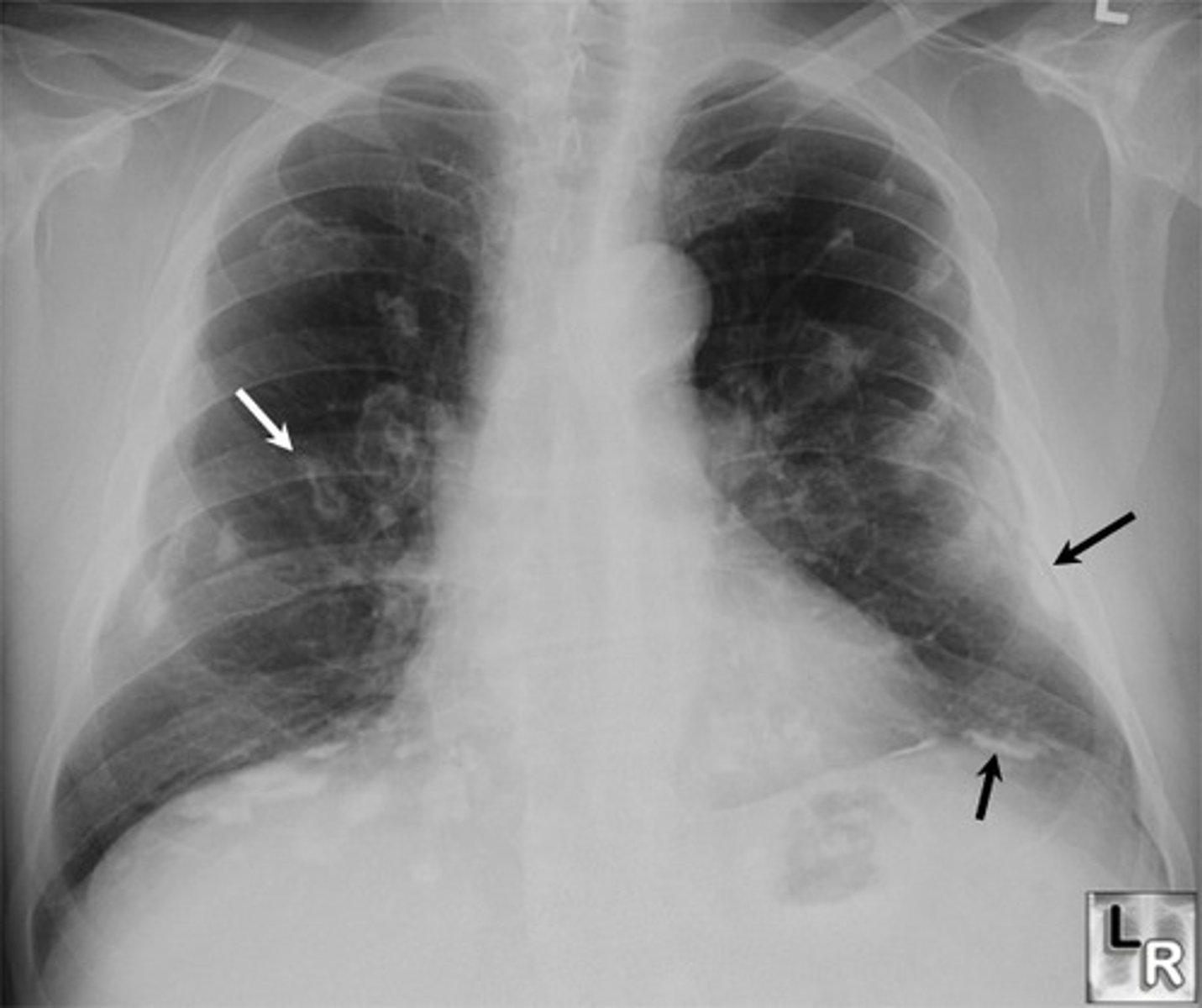
how does asbestosis develop?
asbestos causes significant inflammatory response with fibrosis
asbestos exposure is most likely to cause
fibrotic pleural plaques
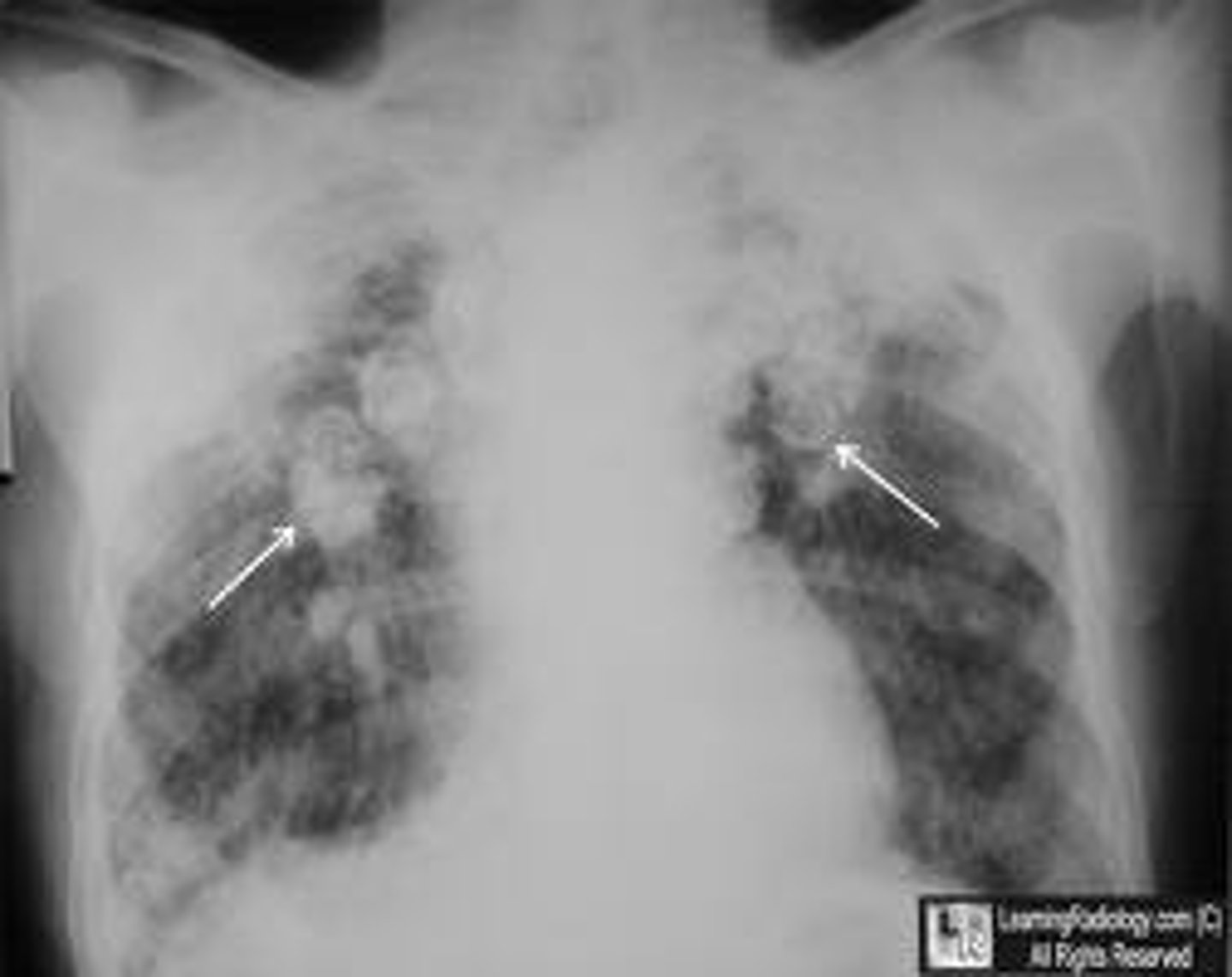
multisystem inflammatory disorder characterized by fibrosis, non-caseating granulomas, substernal chest pain, dry cough and dyspnea
sarcoidosis
how does sarcoidosis develop?
chronic inflammation -> fibrosis, bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
who is most likely to develop sarcoidosis?
young adults, African Americans, Scandinavians, Hx or TB or borrelia bugodorferi exposure
what occurs in 90% of people with sarcoidosis?
hilar lymphadenopathy
what is found in 25% of people with sarcoidosis?
erythema nodosum
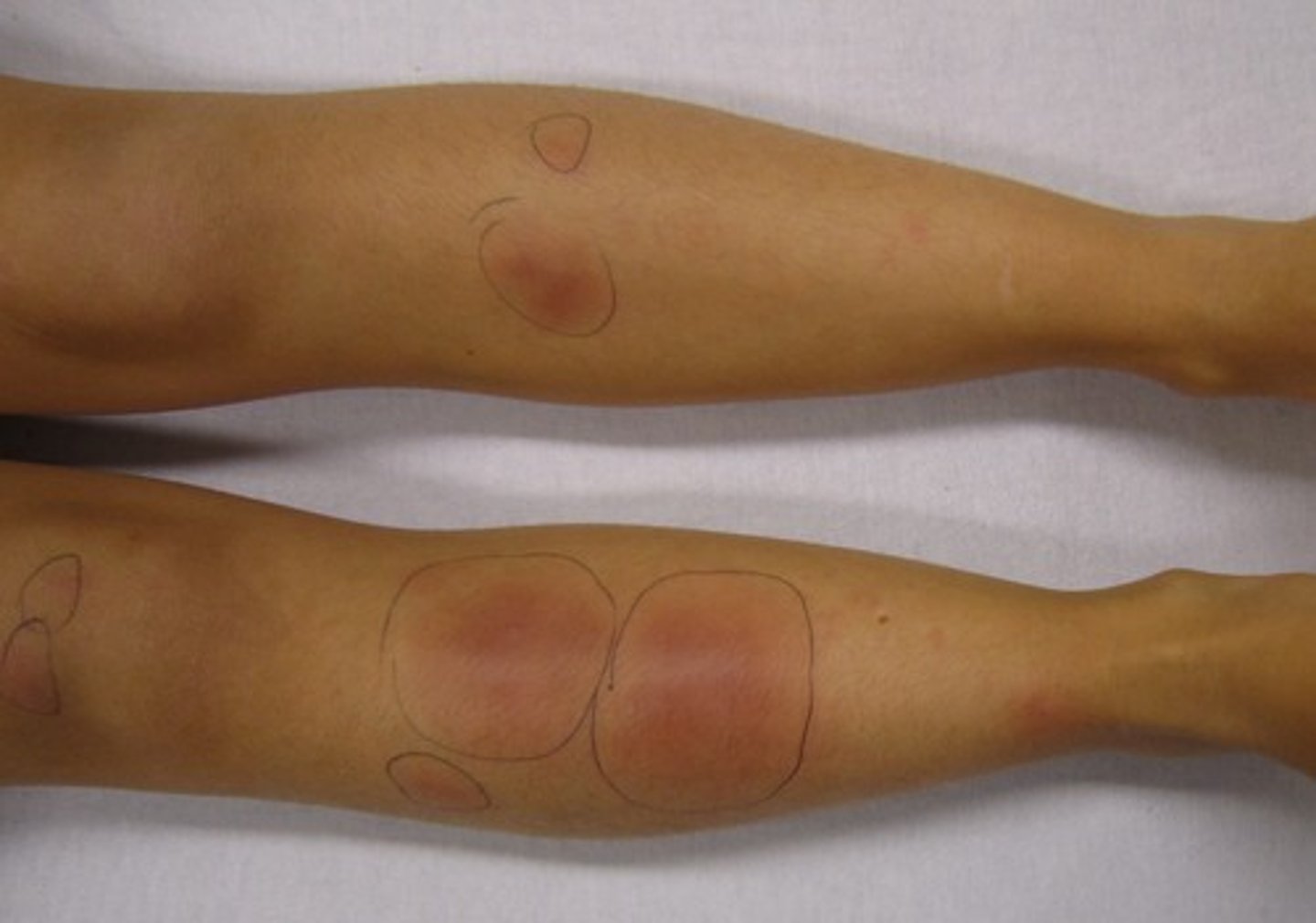
potato nodes is associated with which pathology?
sarcoidosis