xray interactions with matter
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
attenuation
the reduction in the number of xray photons, resulting in the loss of energy.
gradual decrease in exposure
attenuation includes both _______ and ________
absorption and scatter
attenuation is influenced by
tissue type/atomic number
subject thickness
kv/photon quality
greater atomic number
greater attenuation
greater volume
greater attenuation
higher kv
less attenuation
x ray photons can either
change direction and scatter (compton), or be absorbed (photoelectric)
when kv increases…
greater chance of compton scatter, less photoelectric
LOW energies/kv
most interactions with tissue are photoelectric
compton interactions
not dependent on atomic number
happen when high energy photon rejects a loosely bound outer shell electron
ionization occurs
Ei = Es + Eb + Eke
incident photon is Deflected
PARTIAL energy trasnfer
most common interaction in the human body!
compton scatter
impacts image quality by decreasing contrast
k shell
highest binding energy
farther from nucleus
greater total energy
scatter radiation is the primary source of __________ exposure
occupational
Photoelectric effect

more likely to occur in bone than soft tissue
contributes mostly to pt dose
electron vacancy/hole causes a characteristic cascade
responsible for subject contrast and contributes mostly to PATIENT dose
occurs with absorbers with a HIGH atomic number (ex contrast media)
coherent scattering
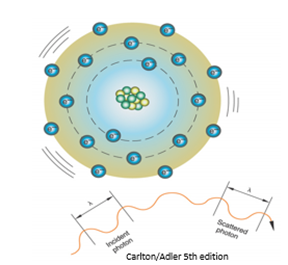
insignificant in diagnostic radiology
below 10kev, very low energy photons
Pair production

occurs between high energy, 1.02 mev and higher
comes close to strong nuclear field and loses nearly all its energy
energy creates a pair of electrons (megatron and positron)
after, each photon posesses .51 mev
not for diagnostic xray. maybe nuc med.
subject density
how tightly packed at the atomic level
__ times more likely photoelectric interaction will happen in bone v tissue
7