14 Genomes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
genome
DNA in haploid set of chromosomes
genomics
study of genomes
cytogenetic map
highlights largest cities like map of Cali in US
Linkage map
depicts smaller cities and large towns
physical map
similar to geographical map indicating towns in area
sequence map
google map showing all buildings in specific town
human genome project
idea to sequence human genome in 1980s under DOE and NIH; draft in 2001; finished sequence in 2003
sequencing genome
clone-by-clone approach (align pieces one chromosome at a time); Celera Genomics uses whole genome shotgun approach (shatter genome and rebuild)
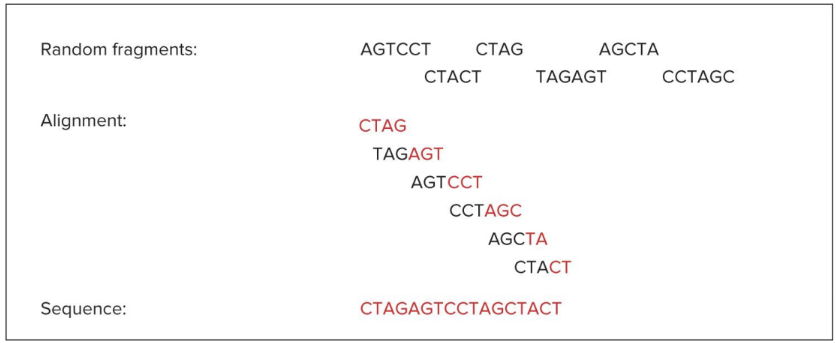
Sequencing: DNA shot gunned into small fragments using restriction enzymes; sequencer devices sequence the fragments
Assembly: Software aligns ends of DNA pieces by recognizing overlaps
deriving DNA sequence
Gene Annotation
description of gene function and significance of likely gene variant; mode of inheritance; genotype; frequency of variance; classification (benign/pathogenic)
human genome content
1.5% of DNA encodes proteins; at end of genome project (2003) 95% protein encoding genes IDd; Viral DNA, noncoding RNA, introns, promoters, control and repeated sequences do not encode protein
exome
sequenced telomere-to-telomere in chromosomes; repeats and reveals structural variants
transcriptome
set of RNA transcripts (coding/noncoding)
Which sequencing technology would be most appropriate for identifying
mutations in protein-coding regions of the genome?
A. RNA sequencing
B. Whole genome sequencing
C. Exome sequencing
D. Single cell sequencing
C. Exome sequencing
A researcher wants to study the differences in gene expression between
cancerous and normal cells. Which NGS method would be most suitable?
A. Whole genome sequencing
B. Exome sequencing
C. Single-cell sequencing
D. RNA sequencing
D. RNA sequencing
If you want to specifically study alternative splicing events in a transcriptome,
which NGS technology would you prefer?
A. Whole genome sequencing
B. Exome sequencing
C. Single-cell sequencing
D. RNA sequencing
D. RNA sequencing
viral DNA
8% of genome from RNA viruses [RETROVIRUSES]; evidence of past infection; sequences increase over time; genetic material in chromosomes is '“human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs)”
HERV sequences have recombines/exchanged parts and mutated to not make us sick; AML, MS, and melanoma are overexpressed HERVs
noncoding RNA
genome transcribed in form of ncRNAs (all RNA except mRNA); transcribed from pseudogenes
tRNAs: connect mRNA codons to amino acids; ~500 tRNA genes are 0.1% of genome
rRNAs: ribosome parts; 243 types grouped on 6 chromosomes
12000 long noncoding RNAs: >200 nucleotides, transcribed from exons introns and between gene regions (chromatin and gene expression control), 1/3 in primates only, most in brain
repeats
highly repetitive sequences holding diff type of information than protein’s amino acid sequence; transposons are most abundant type of repeat; rare classes include telomeres, centromeres, and pseudogenes
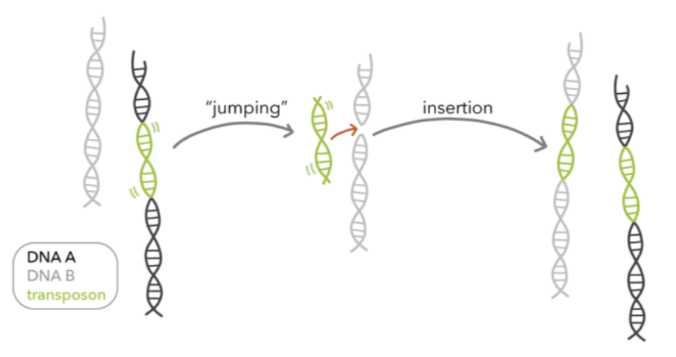
transposons
jumping sequences; Alu repeats can copy themselves and comprise of 2-3% of genome
Large intergenic noncoding RNAs
Between genes
Small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs)
Process rRNAs in nucleolus
Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs)
Parts of spliceosomes
Telomerase RNA
Adds bases to chromosome tips
Xist RNA
Inactivates one X chromosome in cells of
females
introns
genes cut out of mRNA
Promoters and other control
sequences
Guide enzymes that carry out DNA replication,
transcription, or translation
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
MicroRNAs (miRNAs)
control translation
circular RNA
degrades microRNA, mostly in synapses
centromeres
Largest constrictions in chromosomes, providing
attachment points for spindle fibers
genomic medicine
breast cancer - tests for 3 mutations in BRCA1/BRCA2
breast cancer gene test panel - tests for variants/complete sequences of >100 genes
genome editing
restriction endonucleases to cut and paste DNA molecules in patterns; used on somatic/germline cells; techniques include ZFNs (zinc finger nuclease), TALENs (Transcription-activator-like effector nucleases), and CRISPR-Cas9 (Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats-CRISPR associated protein 9)