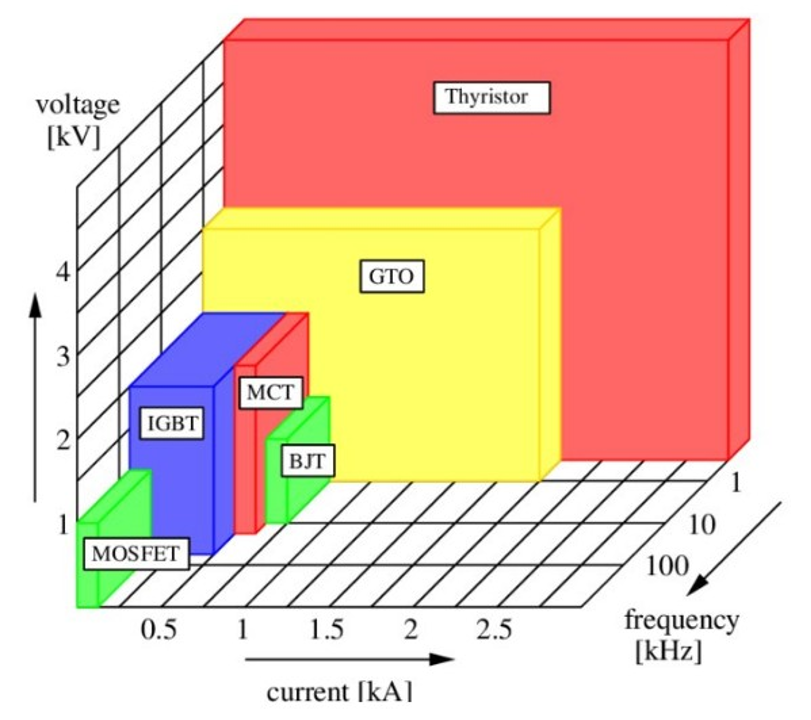
BJTs, IGBTs, MOSFETs
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is a power transistor?
A power transistor is a semiconductor switch used to amplify or switch electrical power, operating in fully on or fully off states for efficiency.
What are the three main types of power transistors?
BJT, MOSFET, and IGBT.
How is a BJT controlled?
It is current-controlled - base current controls collector current.
How is a MOSFET controlled?
It is voltage-controlled - gate voltage controls drain current.
How is an IGBT controlled?
Like a MOSFET, it is voltage-controlled at the gate but behaves electrically like a BJT on the output side. Controlled by Gate but has Collector and Emitter.
Compare input impedance among transistor types.
BJT has low input impedance, MOSFET and IGBT have high input impedance.
Which transistor is best suited for low-frequency, high-current switching?
BJT, due to high current capability but slower switching speed.
Which transistor is best for high-frequency, low-power applications?
MOSFET, because it switches very fast and has low switching losses.
Which transistor combines high input impedance with high current capability?
IGBT, as it merges the MOSFET's gate control with BJT's current handling.
What is the typical control signal polarity for a MOSFET?
A positive gate-to-source voltage (usually +10-15V) turns it on for n-channel, a negative gate-to-source voltage for p-channel MOSFETs
Why do MOSFETs not suffer from second breakdown like BJTs?
MOSFETs avoid second breakdown because their conduction is by majority carriers and their channel resistance increases with temperature, which naturally limits current
Why are IGBTs often used in medium- to high-power converters?
They handle higher voltages than MOSFETs and switch faster and more efficiently than BJTs.
What is the main disadvantage of an IGBT?
It has a slower turn-off time due to stored charge in its bipolar section.
Compare the switching speeds of BJT, MOSFET, and IGBT.
MOSFET is fastest, IGBT moderate, BJT slowest.
List common power transistor applications.
DC-DC converters, motor drives, inverters, and switching power supplies.
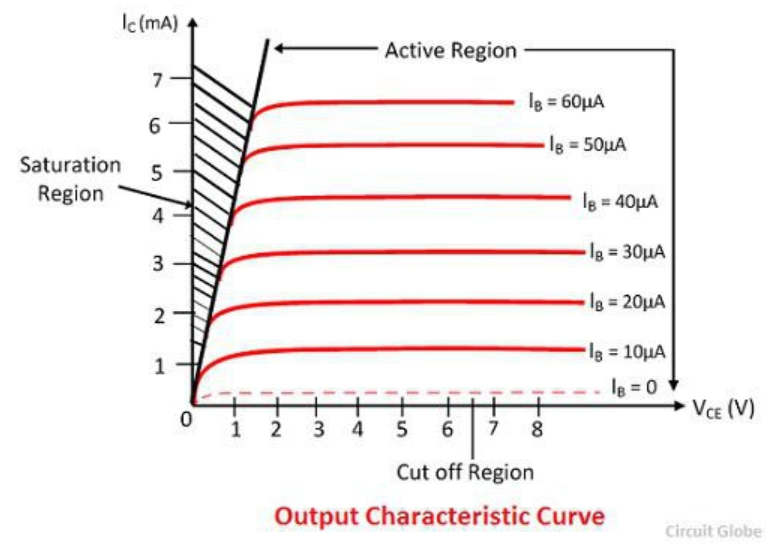
Describe the output characteristics of a BJT.
Collector current (IC) vs. collector-emitter voltage (VCE) shows distinct active, saturation, and cutoff regions; base current controls IC in the active region.
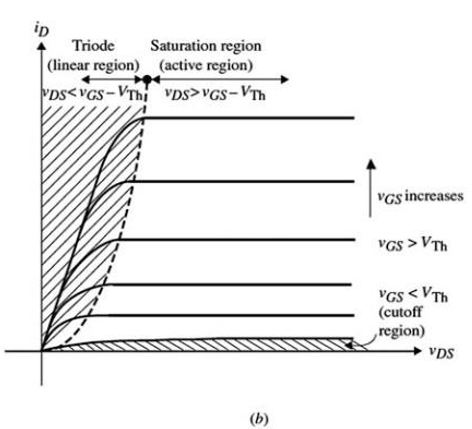
Describe the transfer characteristic of a MOSFET.
Drain current (ID) increases sharply once gate voltage (VGS) exceeds threshold (Vth), showing a steep rise and then saturation.
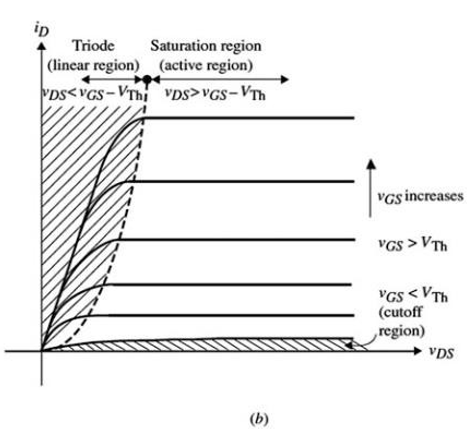
Describe the I-V characteristic of an IGBT.
It has a threshold gate voltage — below this, no collector current flows.
Once the gate voltage exceeds the threshold, the device turns on and the collector current rises sharply with collector–emitter voltage, similar to a BJT in saturation.
In the on-state, it shows a low voltage drop (typically 1.5–3 V).
In the off-state, it blocks high collector–emitter voltage with very small leakage current.
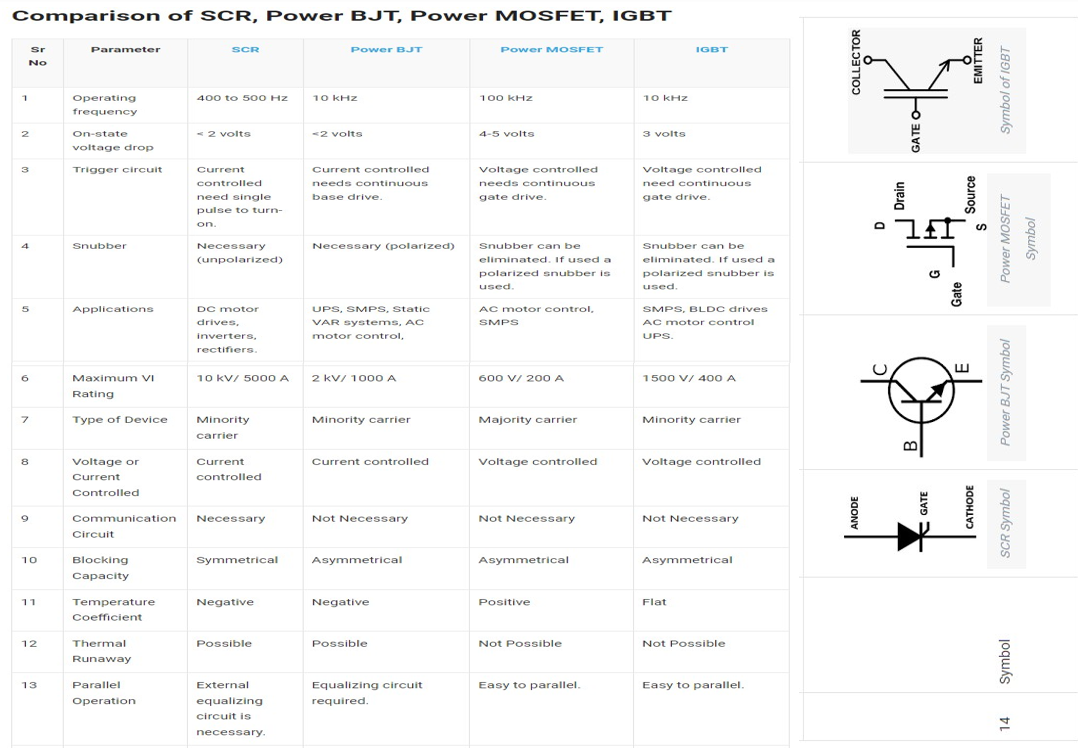
Explain how transistor comparison tables are typically organized.
Columns list BJT, MOSFET, and IGBT with rows for control type, speed, input impedance, power level, and typical use cases.