NUR 314 Exam 1 - SIRS (Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome) and MODS (Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Relationship of shock, SIRS, and MODS
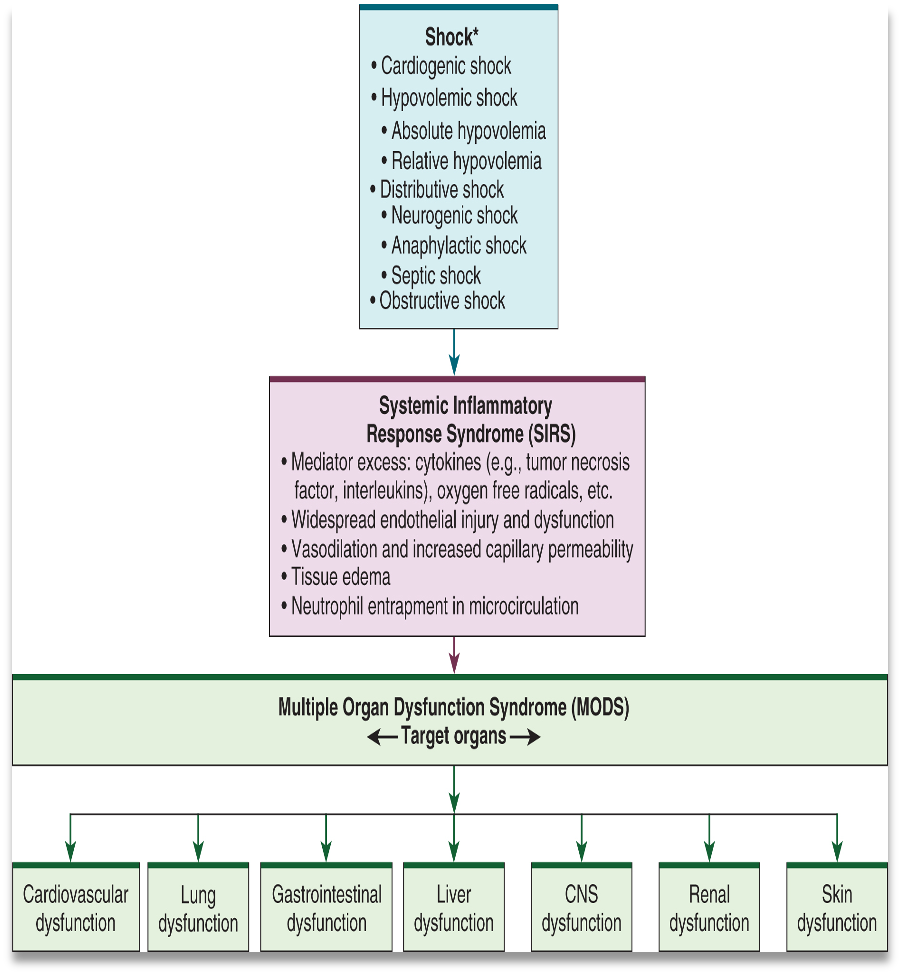
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
A systemic inflammatory response to a variety of insults
Generalized inflammation in organs remote from the initial insult
SIRS triggers
Mechanical tissue trauma: burns, crush injuries, surgery
Abscess formation: intraabdominal, extremities
Ischemic or necrotic tissue: pancreatitis, vascular disease, MI
Microbial invasion: bacteria, viruses, fungi
Endotoxin release: gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria
Global perfusion deficits: postcardiac resuscitation, shock states
Regional perfusion deficits: distal perfusion deficits
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS)
A failure of 2 or more organ systems
Homeostasis cannot be maintained without intervention
Results from SIRS
SIRS and MODS - consequences of inflammatory response
Release of mediators
Direct damage to endothelium
Hypermetabolism
Extreme weight loss/wasting away
Increase in vascular permeability
Activation of coagulation cascade
SIRS and MODS - organ and metabolic dysfunction
Hypotension
Decreased perfusion
Know S and S of decreased perfusion
Cold/pale/blue skin, numbness/tingling, cramping/pain in limbs during activity, slow-healing sores, swelling, weak nails/hair, and sometimes chest pain or erectile dysfunction
Formation of micro-emboli
Redistribution or shunting of blood
SIRS and MODS - respiratory system
Alveolar edema
Decrease in surfactant
Increase in shunt
V/Q mismatch
End result: ARDS
SIRS and MODS - cardiovascular system
Myocardial depression and massive vasodilation
Results in decreased SVR and BP
Baroreceptors respond to enhance CO
Albumin and fluid move out of blood vessels
Increased CVP and PAWP
SIRS and MODS - neurologic system
Mental status changes due to hypoxemia, inflammatory mediators, or impaired perfusion
Often early sign of MODS
Confusion, agitation, combative, lethargy
SIRS and MODS - renal system
Acute kidney injury (AKI)
Hypoperfusion
Release of mediators
Activation of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
Nephrotoxic drugs, especially antibiotics
SIRS and MODS - GI system
Motility decreased: abdominal distention and paralytic ileus
Decreased perfusion: increased risk for ulceration and GI bleeding
Potential for bacterial translocation
SIRS and MODS - hypermetabolic state
Hyperglycemia-hypoglycemia
Insulin resistance
Catabolic state
Liver dysfunction
Lactic acidosis
SIRS and MODS manifestations
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) from dysfunction of coagulation system
Electrolyte imbalances
Metabolic acidosis
SIRS and MODS goal
Prognosis for MODS is poor
Goal: prevent the progression of SIRS to MODS
Vigilant assessment and ongoing monitoring to detect early signs of deterioration or organ dysfunction are critical
Care for patients with MODS focuses on
Preventing and treating infection
Maintaining tissue oxygenation
Nutrition and metabolic support
Appropriate support of individual failing organs
SIRS and MODS infection prevention and treatment
Aggressive infection control strategies to decrease risk for hospital acquired infection
Strict asepsis
Assess need for invasive lines
Aggressive surgery to remove necrotic tissue
Aggressive pulmonary management
Early mobilization
SIRS and MODS oxygenation
Decrease O2 demand and increased O2 delivery
Sedation
Mechanical ventilation
Analgesia
Rest
Treat fever, chills, and pain
SIRS and MODS nutrition and metabolic needs
Goal of nutrition support: preserve organ function
Total energy expenditure is often increased 1.5 to 2.0 times
Use of EN is preferred to parenteral nutrition
Monitor plasma transferrin and prealbumin levels to assess hepatic protein synthesis
Provide glycemic control
SIRS and MODS interprofessional care
Support of failing organs
ARDS: aggressive O2 therapy and mechanical ventilation
DIC: appropriate blood products
Renal failure: continuous renal replacement therapy or dialysis
Consider that further interventions may be futile
Communicate with caregiver about realistic goals and outcomes