Physics 2 Exam 1 study guide
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms

Three identical conducting spheres on individual insulating stands are initially
electrically neutral. The three spheres are arranged so that they are in a line and
touching as shown. A negatively-charged conducting rod is brought into contact
with sphere A. Subsequently, someone takes sphere C away. Then, someone
takes sphere B away. Finally, the rod is taken away. What is the sign of the final
charge, if any, of the three spheres?
A B C
a) + + −
b) + − +
c) + 0 −
d) − + 0
e) − − −
A = (-) B = (-) C = (-)
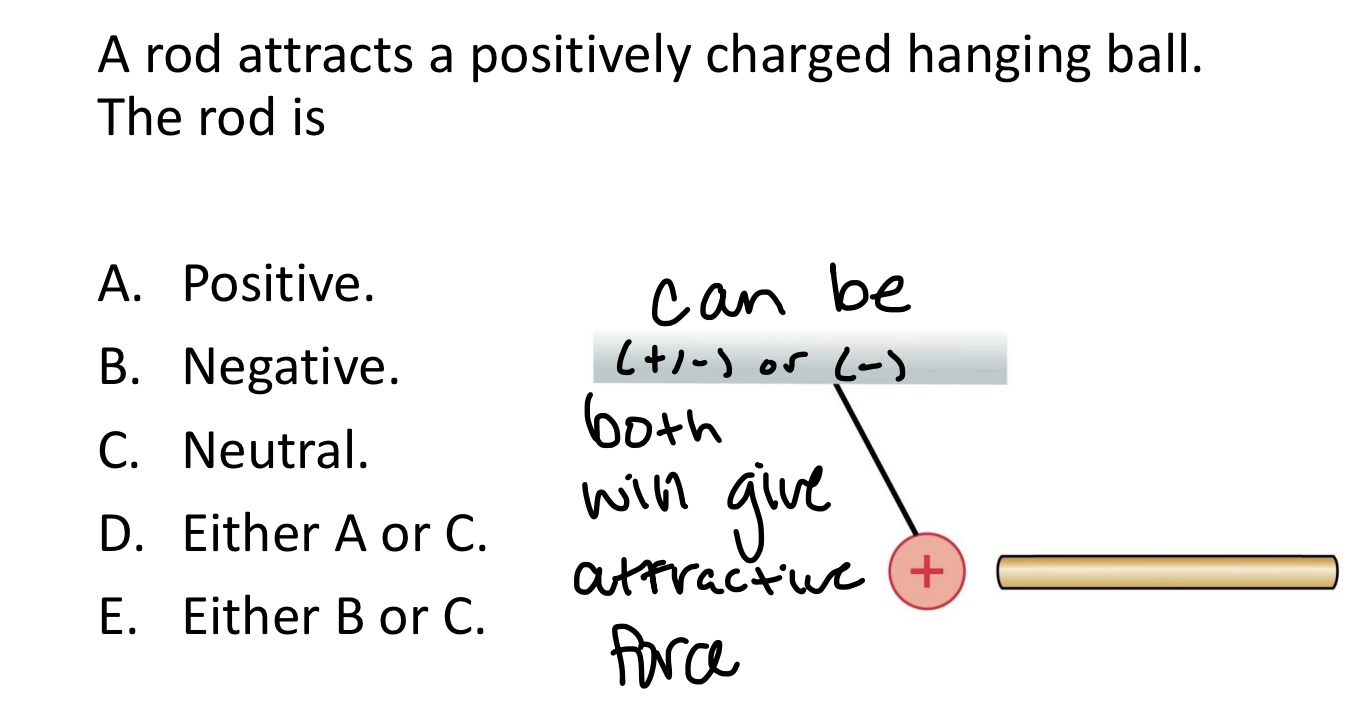
A rod attracts a positively charged hanging ball.
The rod is:
A. Positive.
B. Negative.
C. Neutral.
D. Either A or C.
E. Either B or C.
Either B or C

Consider two objects A and B. Object A has a net
charge while B is uncharged. Based on this
information, it must be true that:
A. A is a conductor, B is an insulator.
B. A is an insulator, B is a conductor.
C. A and B are both insulators.
D. A and B are both conductor.
E. There’s not enough information to tell.
E. There’s not enough information to tell
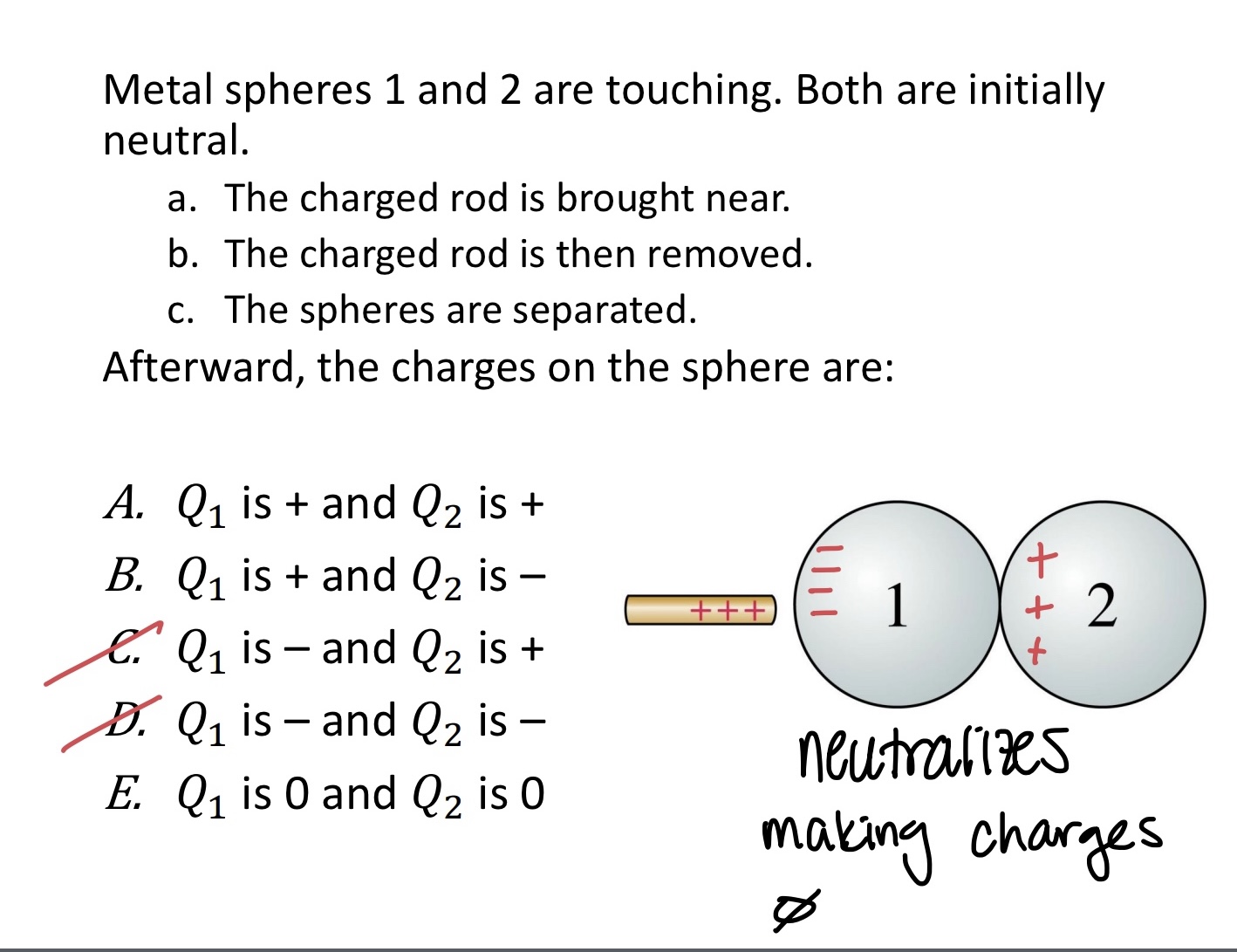
Metal spheres 1 and 2 are touching. Both are initially
neutral.
a. The charged rod is brought near.
b. The charged rod is then removed.
c. The spheres are separated.
Afterward, the charges on the sphere are:
A. 𝑄1 is + and 𝑄2 is +
B. 𝑄1 is + and 𝑄2 is –
C. 𝑄1 is – and 𝑄2 is +
D. 𝑄1 is – and 𝑄2 is –
E. 𝑄1 is 0 and 𝑄2 is 0
E. 𝑄1 is 0 and 𝑄2 is 0
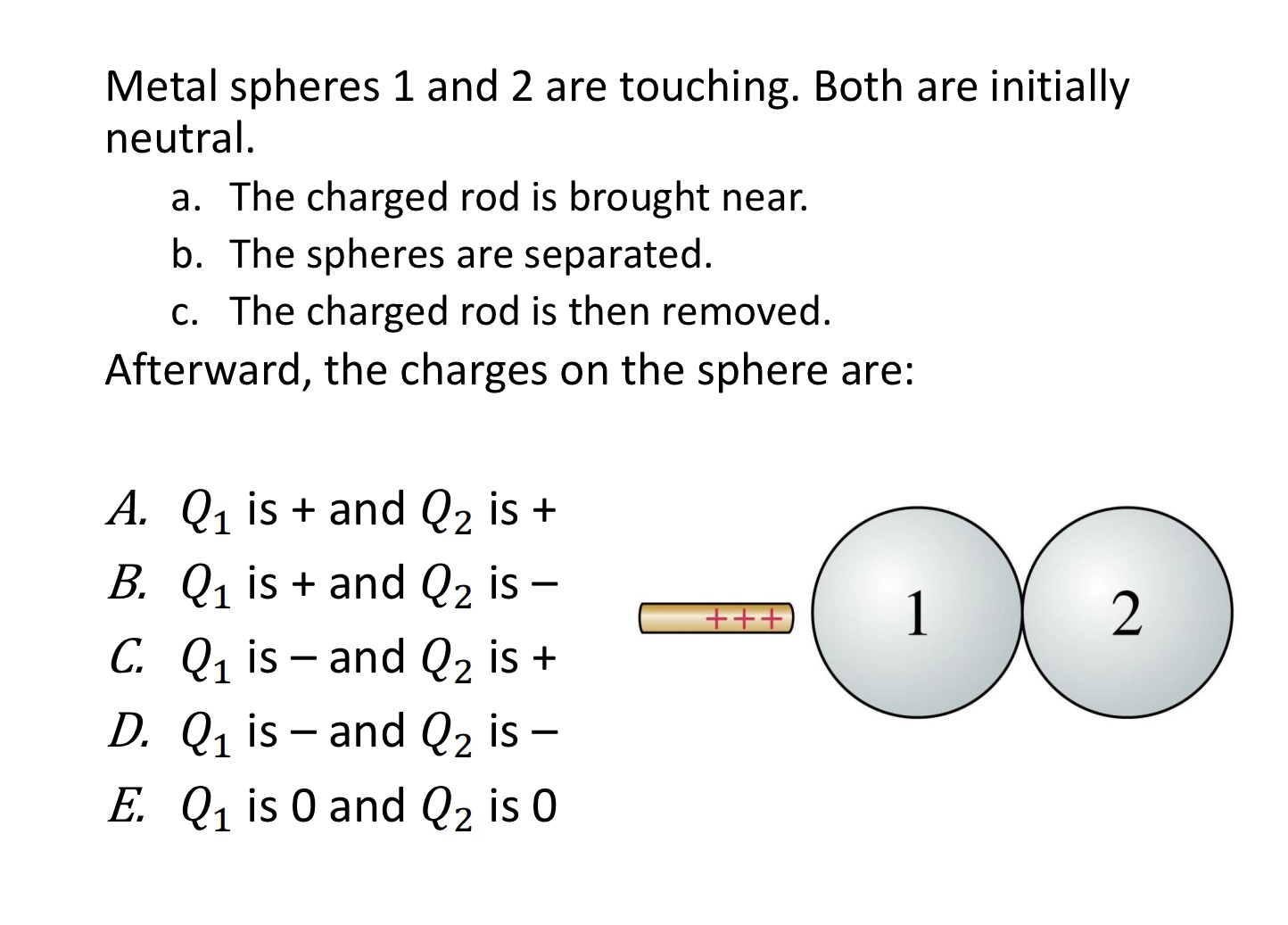
Metal spheres 1 and 2 are touching. Both are initially
neutral.
a. The charged rod is brought near.
b. The spheres are separated.
c. The charged rod is then removed.
Afterward, the charges on the sphere are:
A. 𝑄1 is + and 𝑄2 is +
B. 𝑄1 is + and 𝑄2 is –
C. 𝑄1 is – and 𝑄2 is +
D. 𝑄1 is – and 𝑄2 is –
E. 𝑄1 is 0 and 𝑄2 is 0
C. 𝑄1 is – and 𝑄2 is +
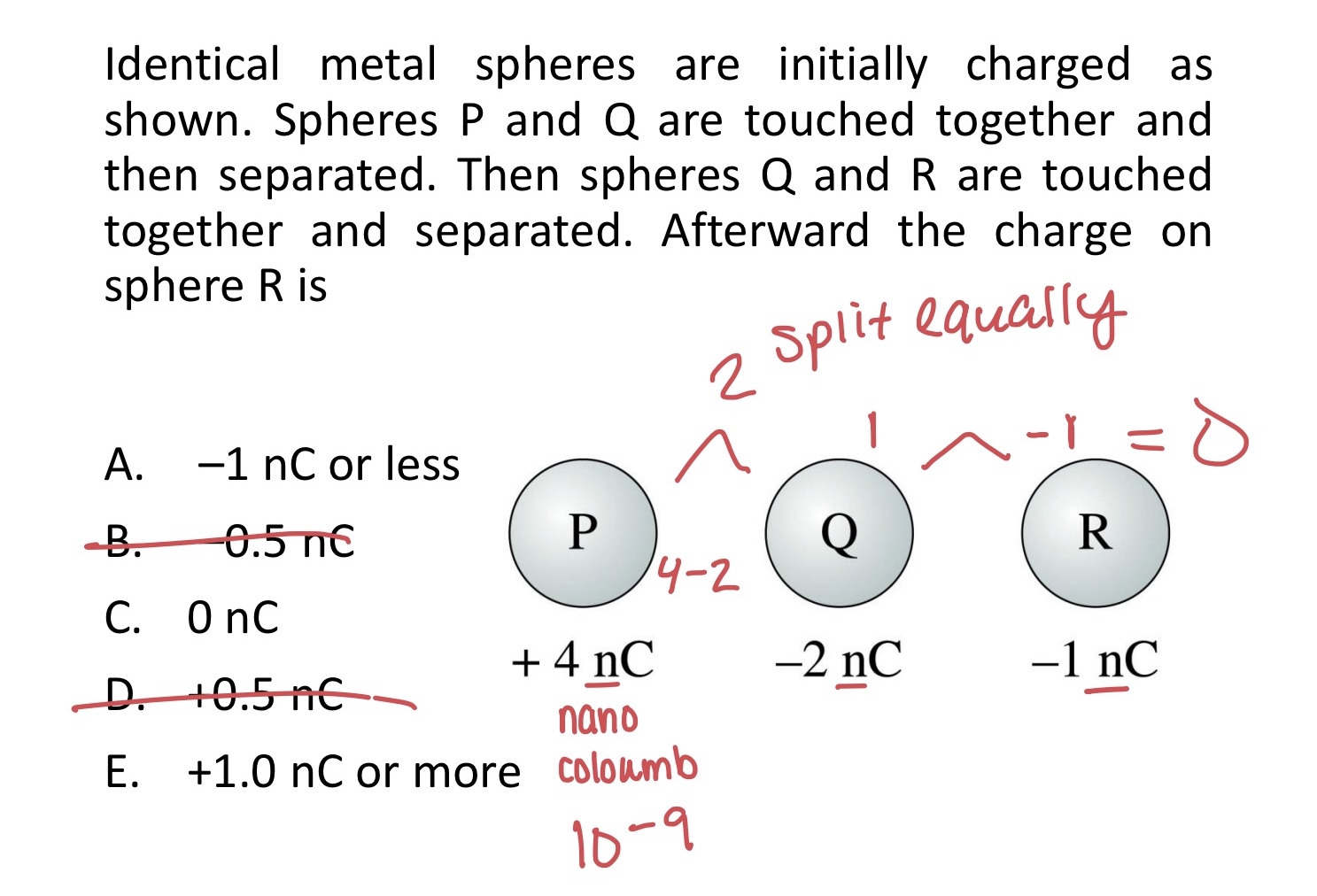
Identical metal spheres are initially charged as shown. Spheres P and Q are touched together and then separated. Then spheres Q and R are touched together and separated. Afterward the charge on sphere R is
A. –1 nC or less
B. –0.5 nC
C. 0 nC
D. +0.5 nC
E. +1.0 nC or more
C. 0 Mac
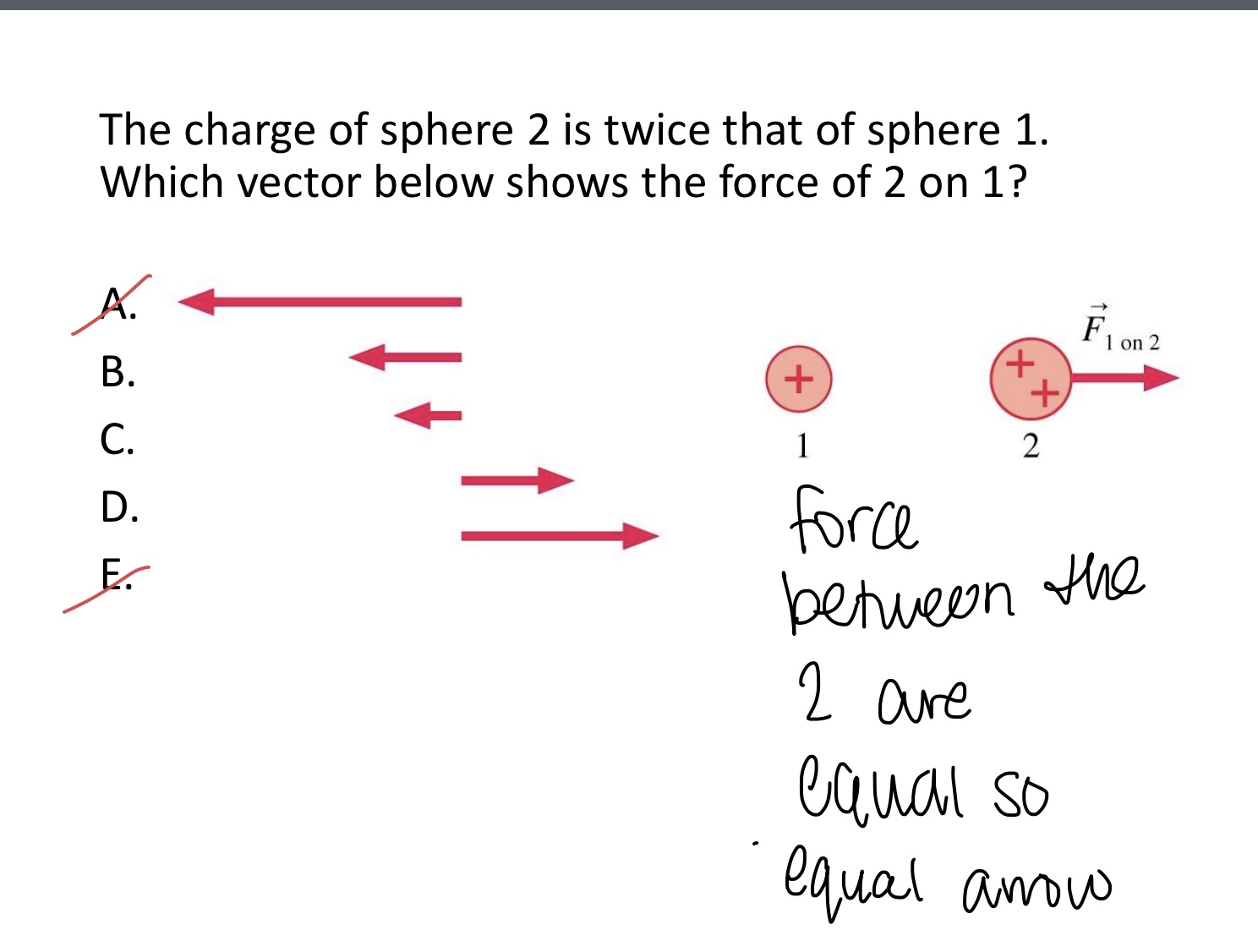
The charge of sphere 2 is twice that of sphere 1.
Which vector below shows the force of 2 on 1?
A,B,C,D, or E
B. Medium arrow to the left
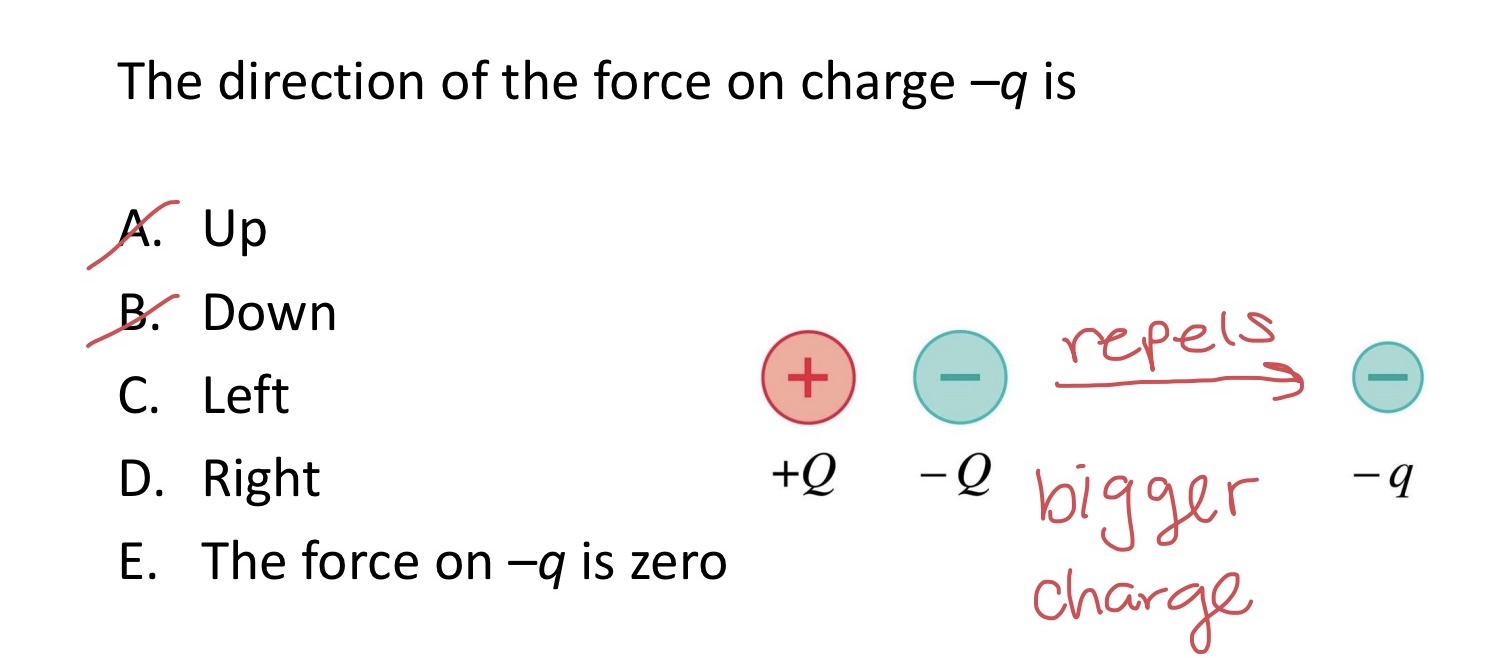
The direction of the force on charge –q is:
A. Up
B. Down
C. Left
D. Right
E. The force on –q is zero
D. Right
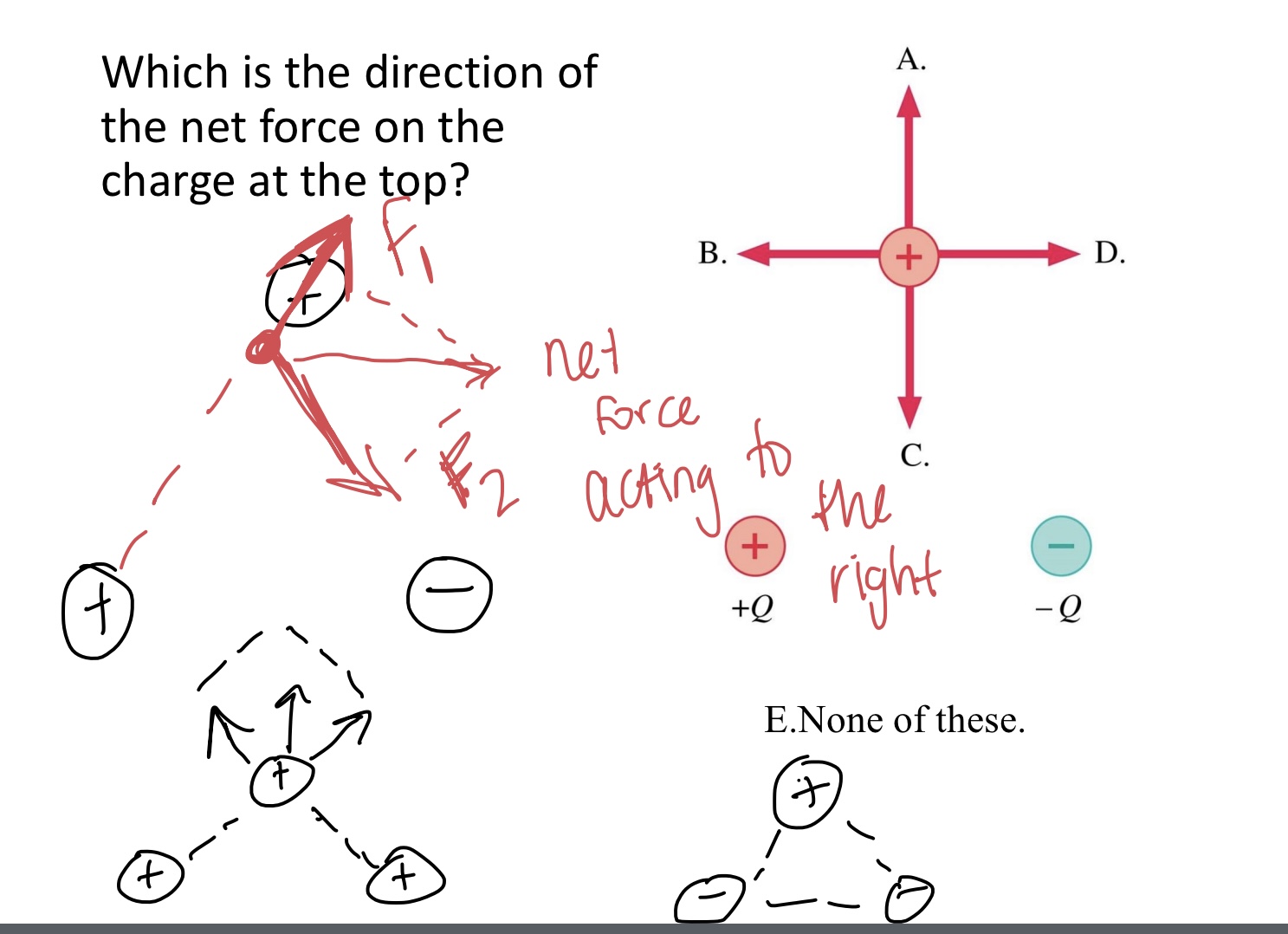
Which is the direction of the net force on the charge at the top?
A,B,C,D, or E. none of these
D
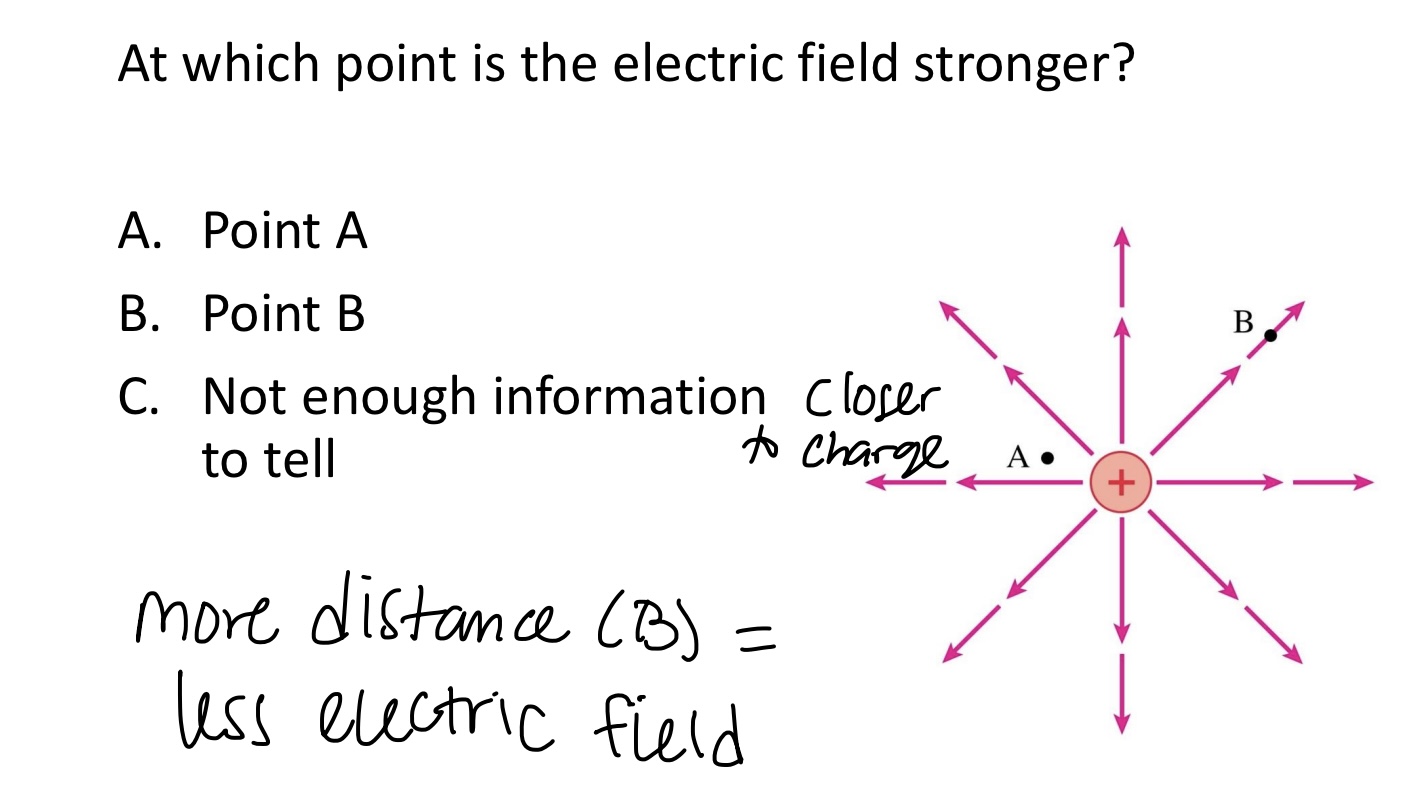
At which point is the electric field stronger?
A. Point A
B. Point B
C. Not enough information
A. Point A
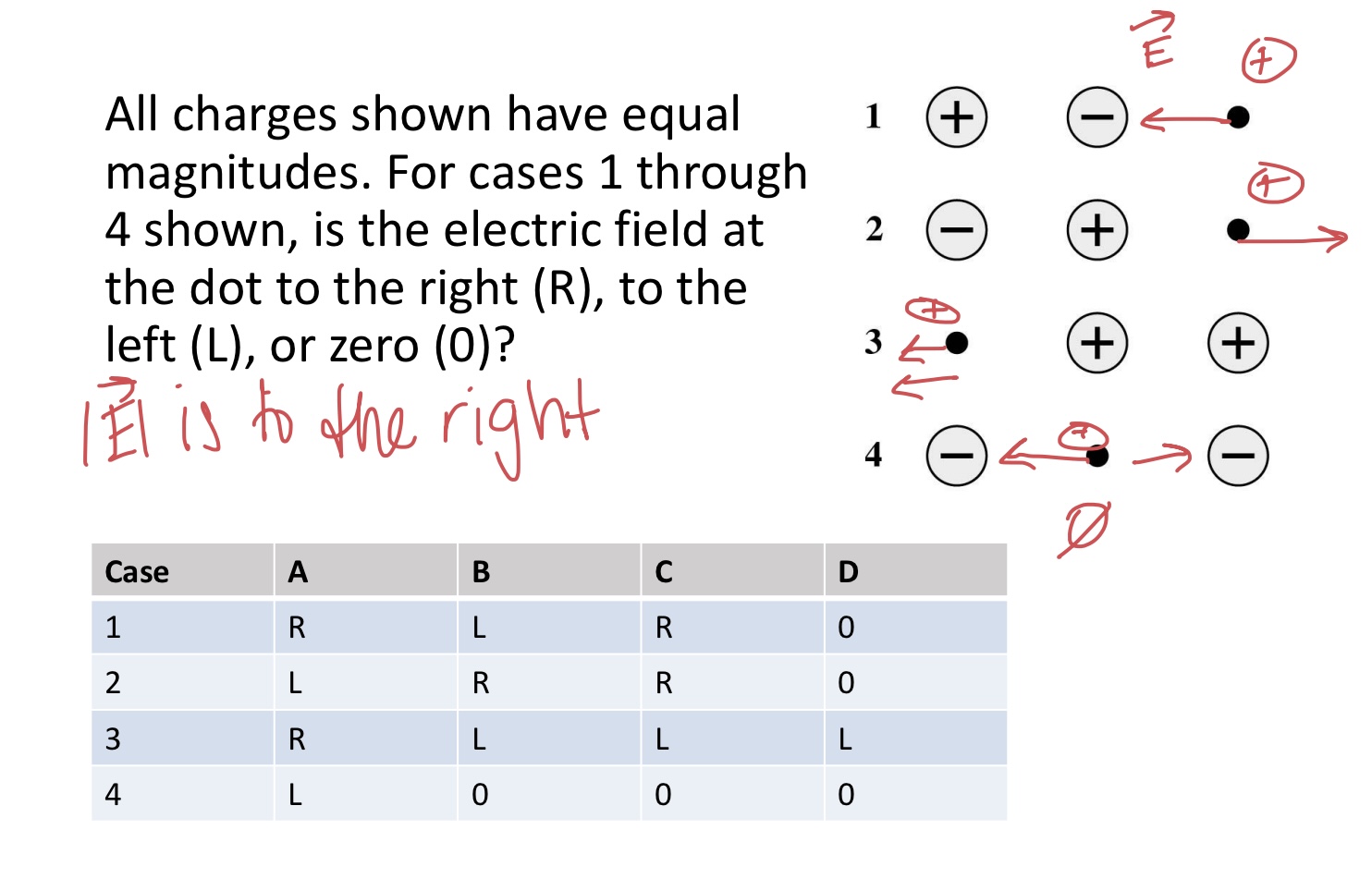
All charges shown have equal magnitudes. For cases 1 through 4 shown, is the electric field at the dot to the right (R), to the left (L), or zero (0)?
Case A B C D
A B C D
1 R L R 0
2 L R R 0
3 R L L L
4 L 0 0 0
Case B: Left, Right, Left, and 0
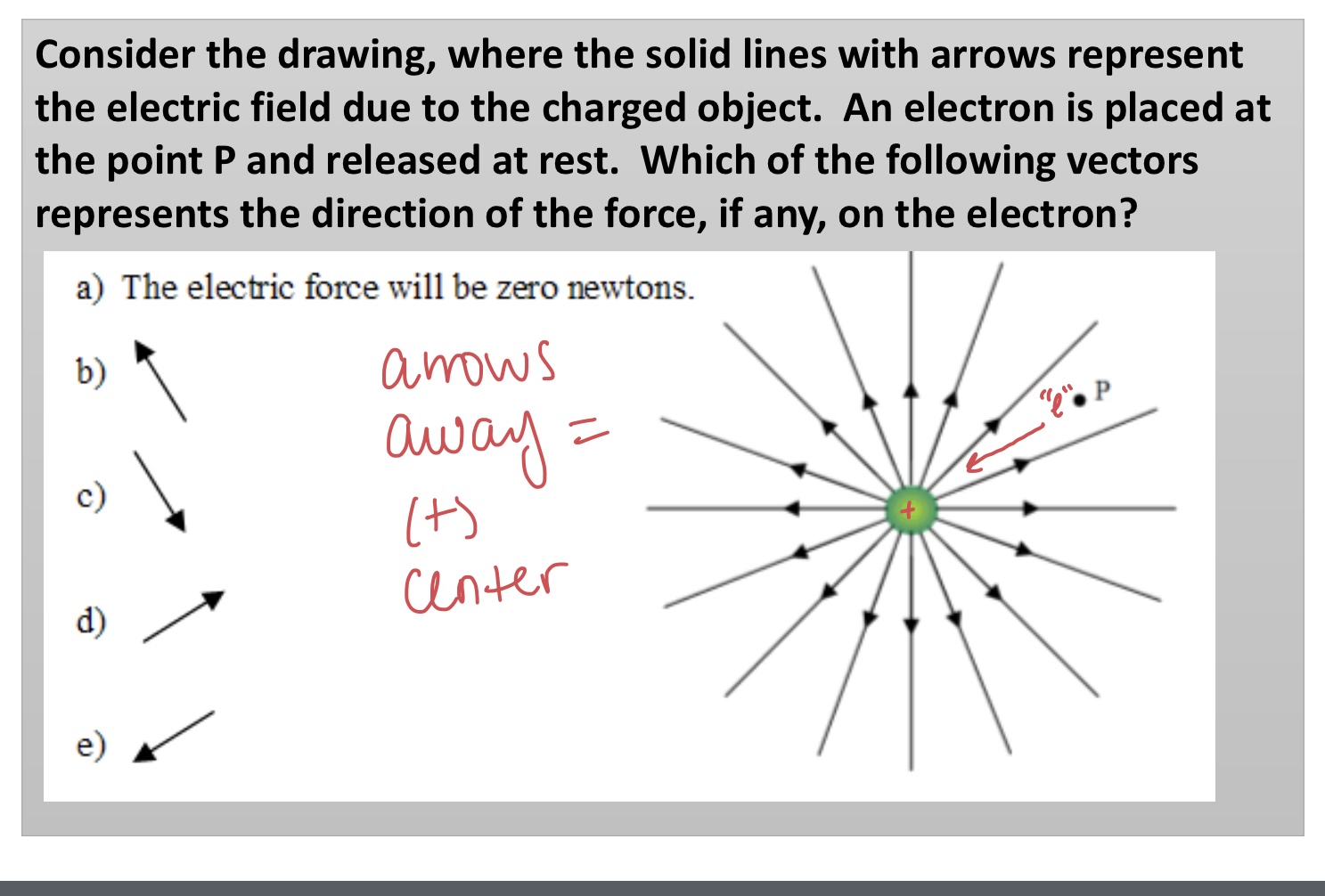
Consider the drawing, where the solid lines with arrows represent the electric field due to the charged object. An electron is placed at the point P and released at rest. Which of the following vectors represents the direction of the force, if any, on the electron?
E because it attracts it towards the charge
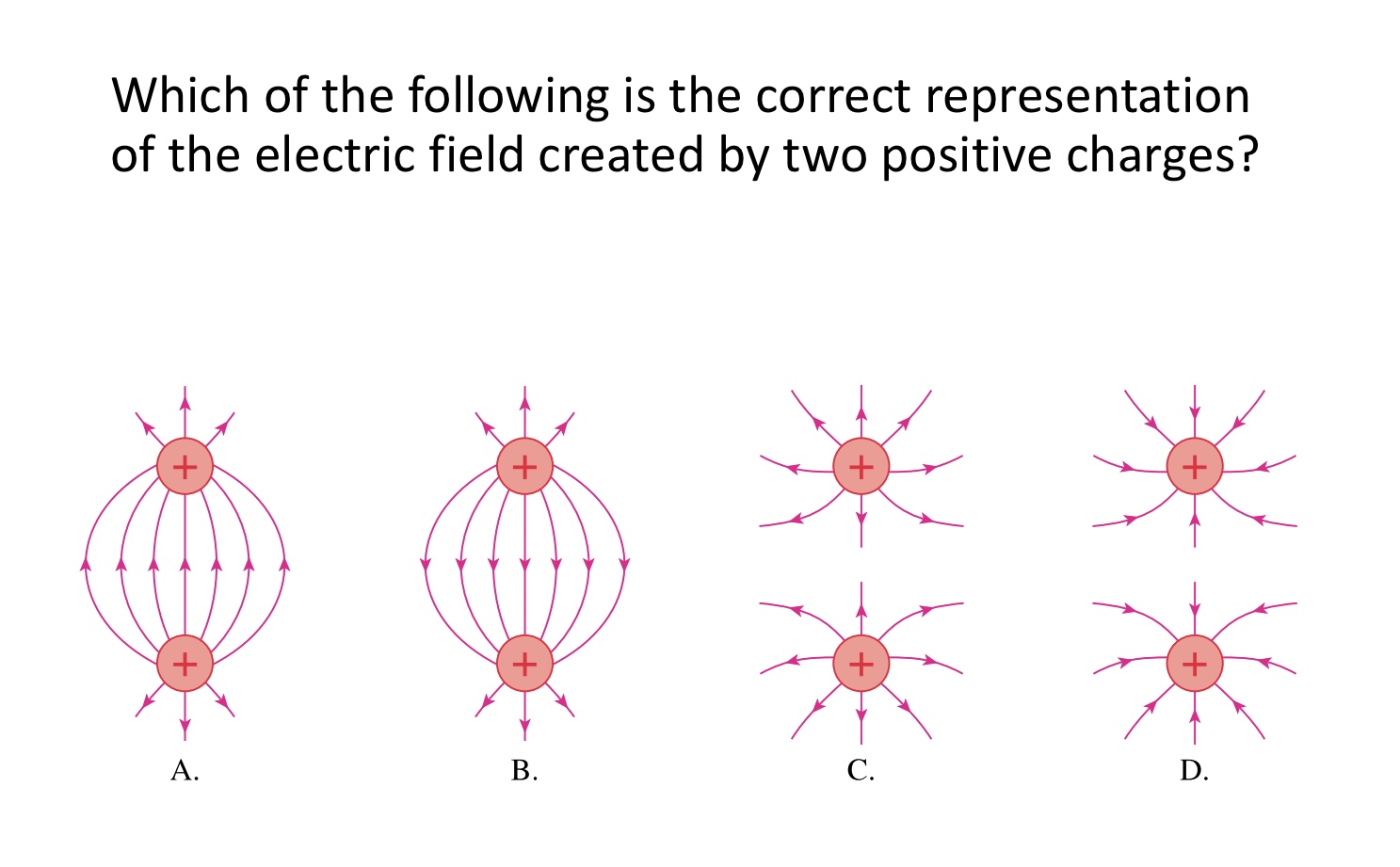
Which of the following is the correct representation of the electric field created by two positive charges?
C
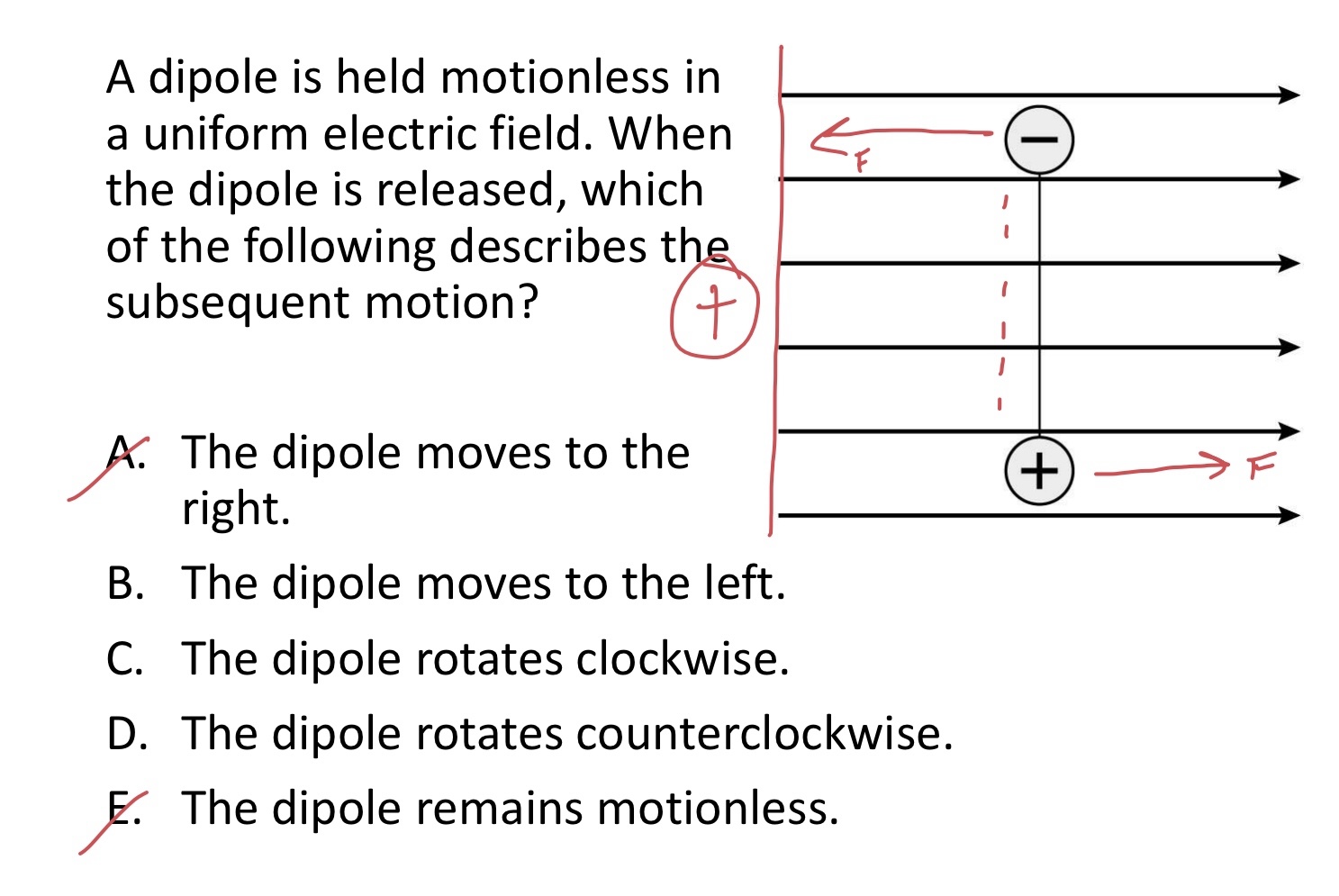
A dipole is held motionless in a uniform electric field. Whenthe dipole is released, which of the following describes the subsequent motion?
A. The dipole moves to the right.
B. The dipole moves to the left.
C. The dipole rotates clockwise.
D. The dipole rotates counterclockwise.
E. The dipole remains motionless.
D. The dipole rotates counterclockwise
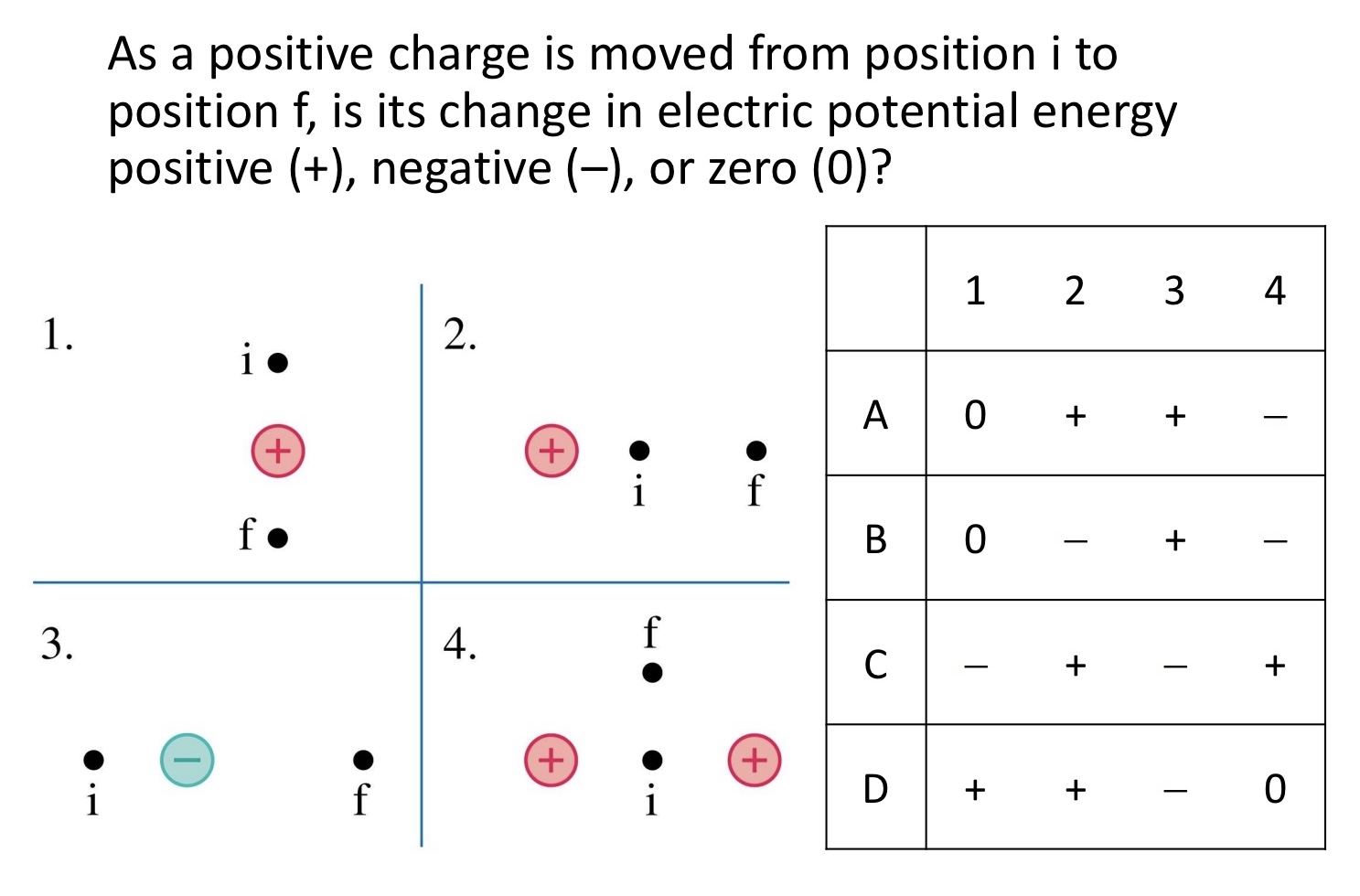
As a positive charge is moved from position i to position f, is its change in electric potential energy positive (+), negative (–), or zero (0)?
1 2 3 4
A 0 + + −
B 0 − + −
C − + − +
D + + − 0
B. 0, (-),(+),(-)
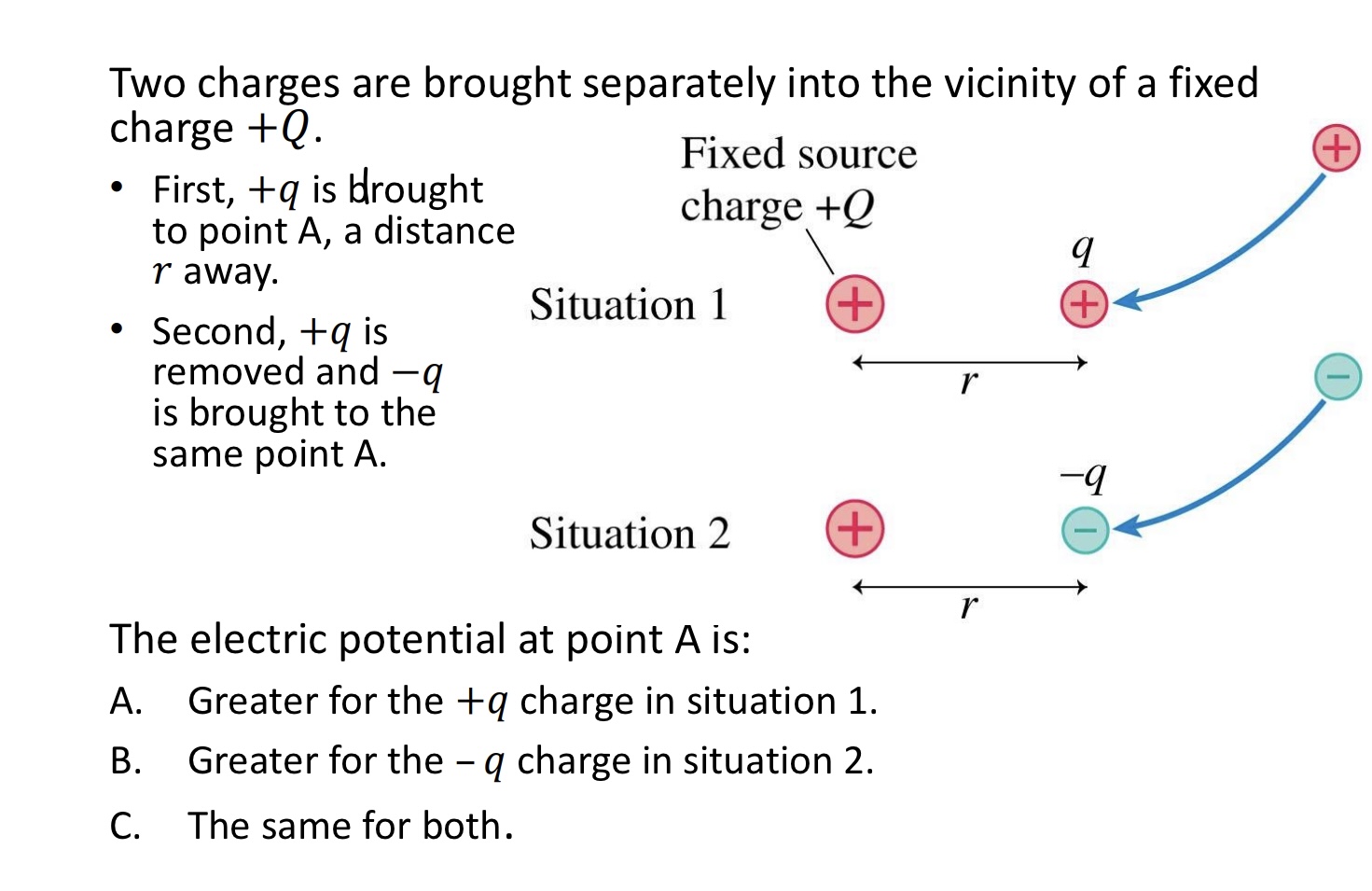
Two charges are brought separately into the vicinity of a fixed charge +𝑄.
• First, +𝑞 is brought to point A, a distance 𝑟 away.
• Second, +𝑞 is removed and −𝑞 is brought to the same point A:
The electric potential at point A is:
A. Greater for the +𝑞 charge in situation 1.
B. Greater for the – 𝑞 charge in situation 2.
C. The same for both.
C. The same for both
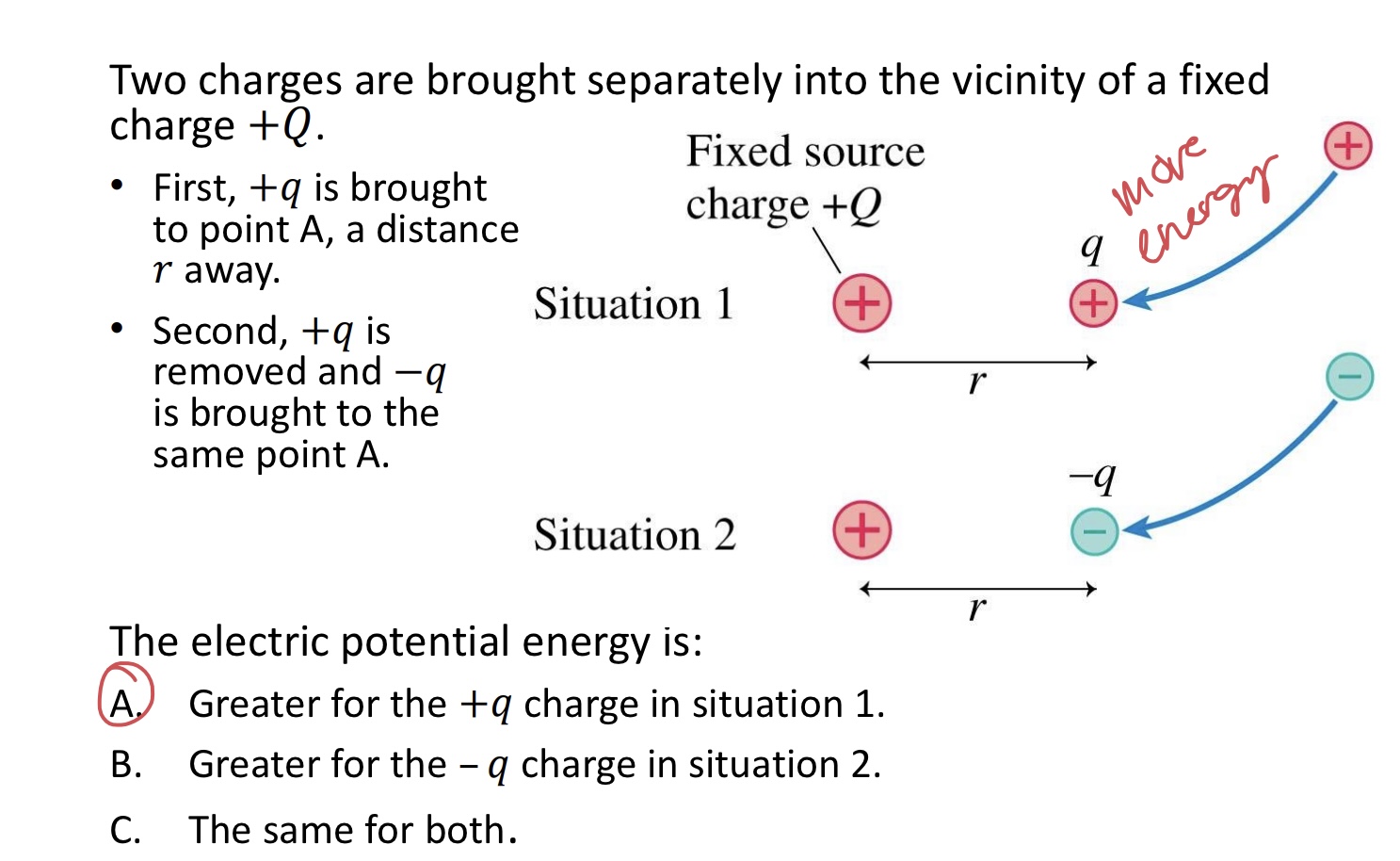
Two charges are brought separately into the vicinity of a fixed charge +𝑄.
• First, +𝑞 is brought to point A, a distance 𝑟 away.
• Second, +𝑞 is removed and −𝑞 is brought to the same point A.
The electric potential energy is:
A. Greater for the +𝑞 charge in situation 1.
B. Greater for the – 𝑞 charge in situation 2.
C. The same for both.
A. Greater for the +𝑞 charge in situation 1
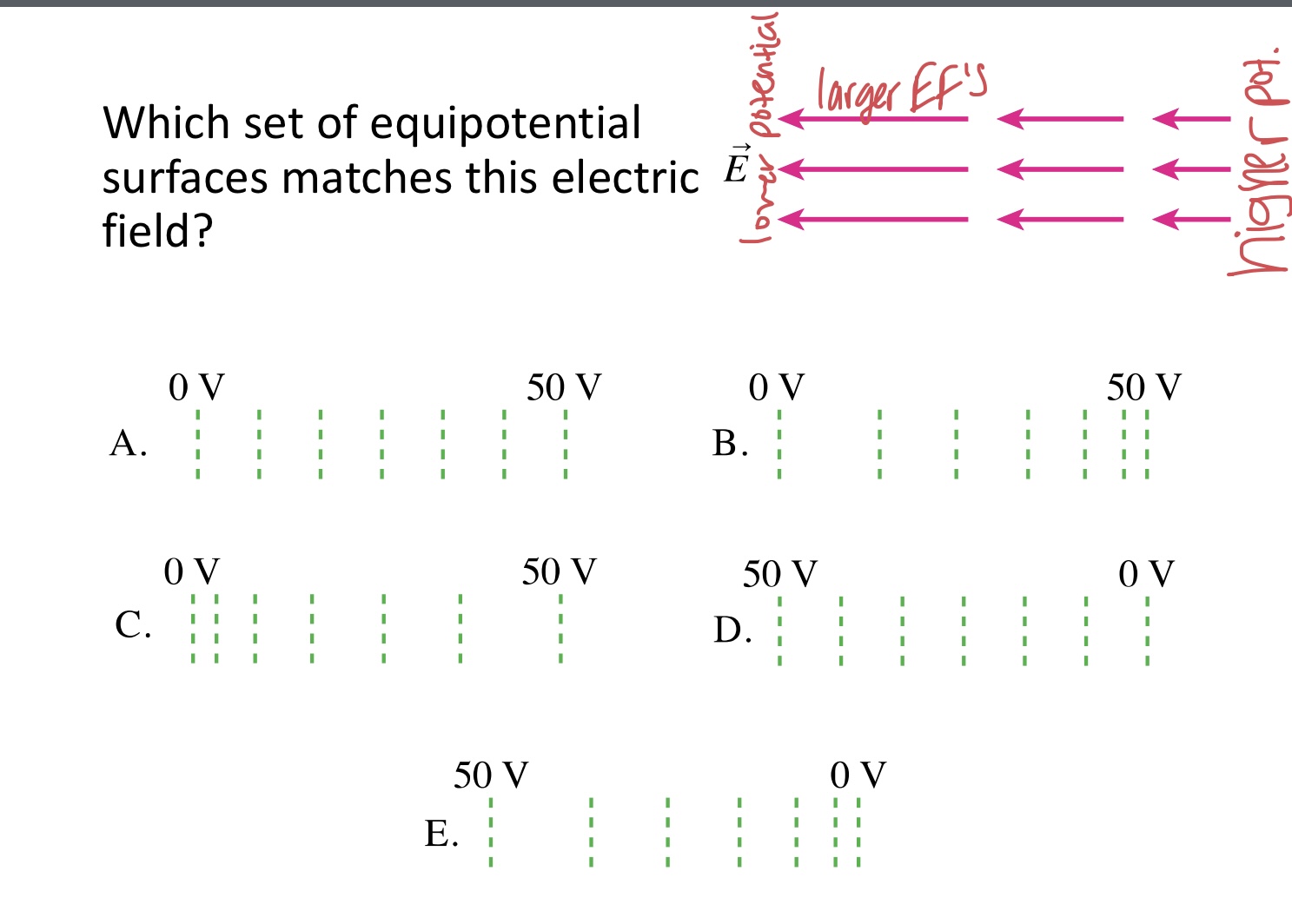
Which set of equipotential surfaces matches this electric field?
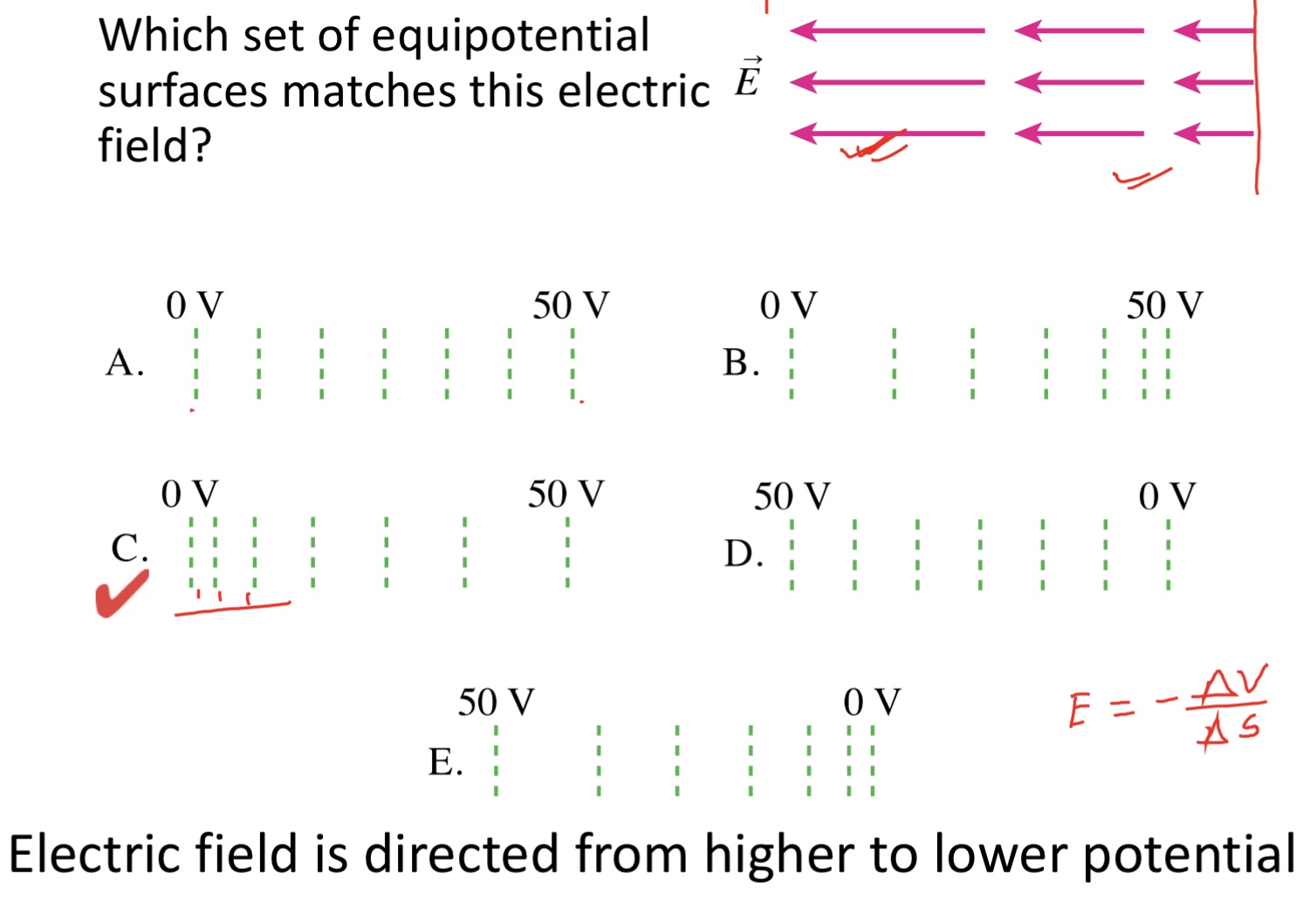

E. All three would require the same amount of work

D. II > I > III
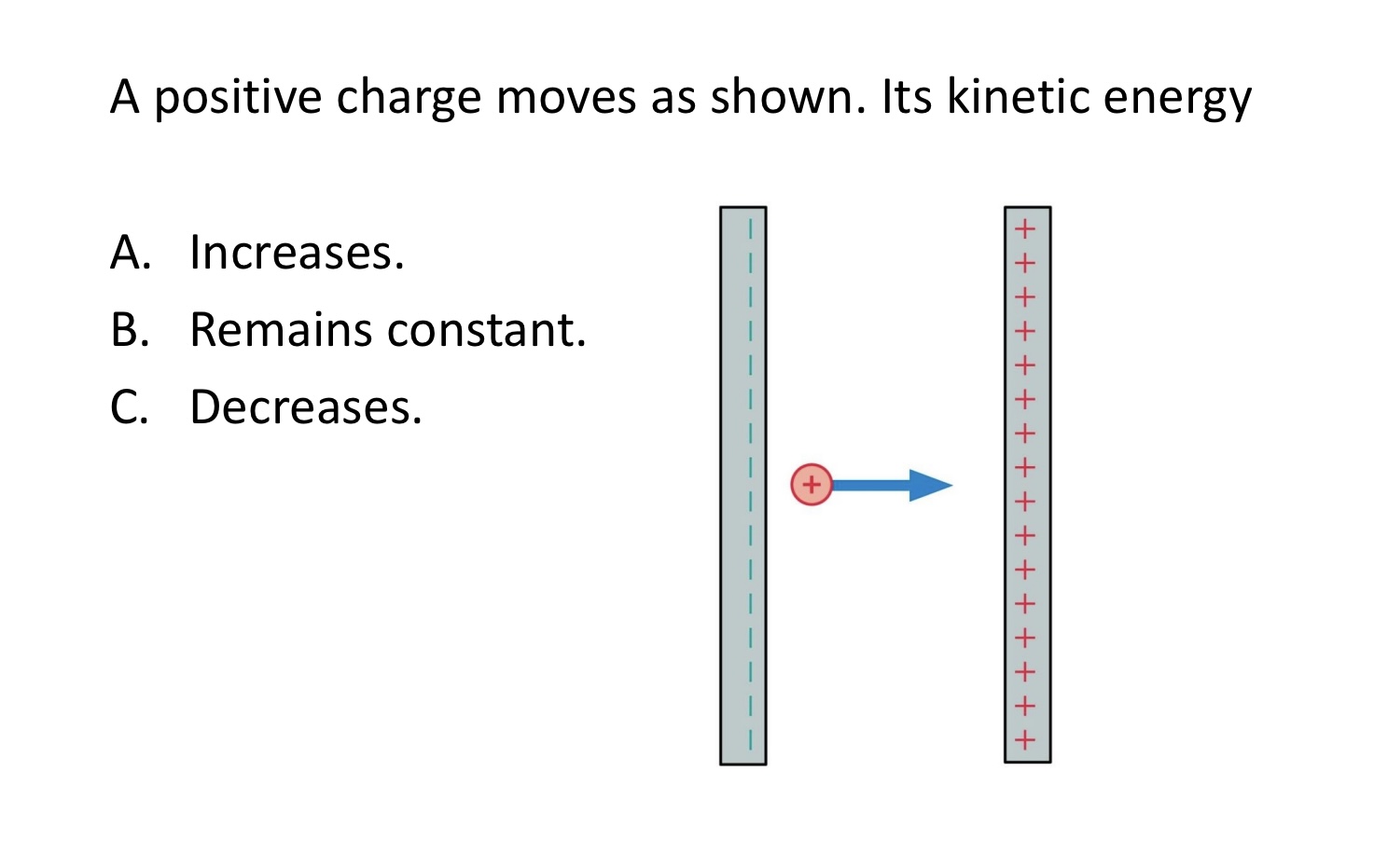
A positive charge moves as shown. Its kinetic energy:
A. Increases.
B. Remains constant.
C. Decreases.
C. Decreases
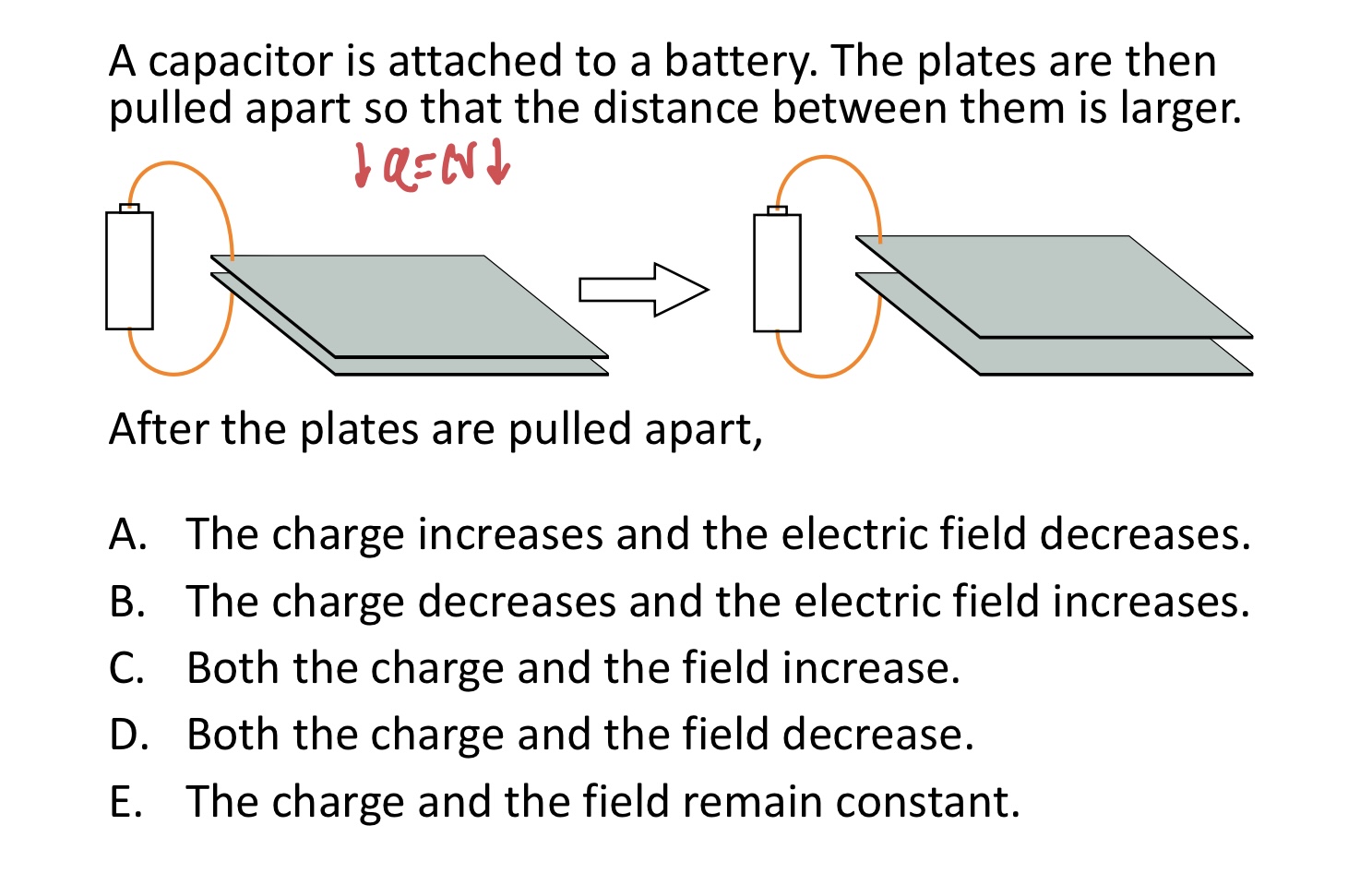
A capacitor has a charge Q. The plates are then pulled apart so that the distance between them is larger.
After the plates are pulled apart,
A. The charge increases and the electric field decreases.
B. The charge decreases and the electric field increases.
C. Both the charge and the field increase.
D. Both the charge and the field decrease.
E. The charge and the field remain constant.
D. Both the charge and field will decrease

Which of the following combinations of capacitors has the highest capacitance?
B
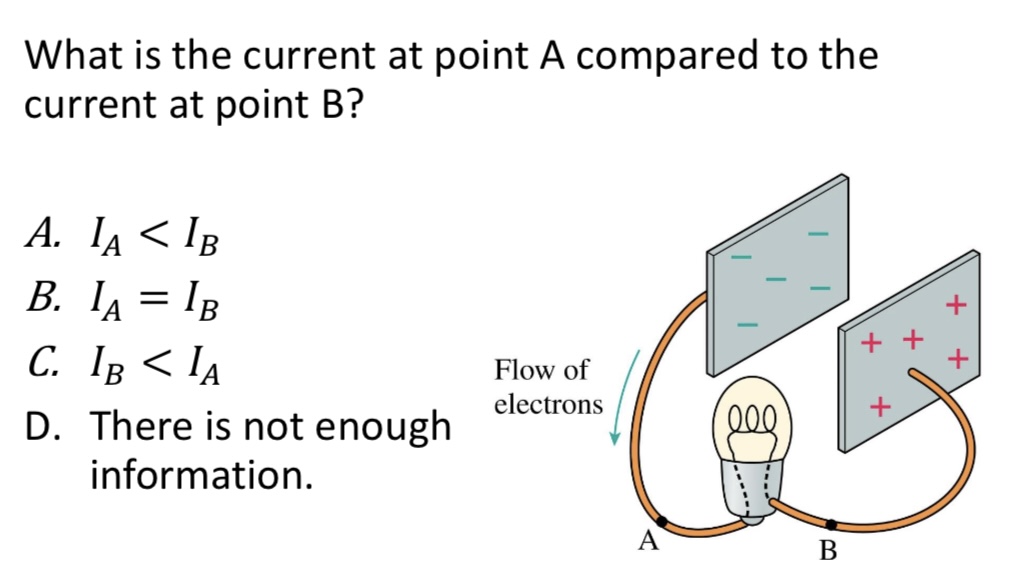
What is the current at point A compared to the current at point B?
A. 𝐼𝐴 < 𝐼𝐵
B. 𝐼𝐴 = 𝐼𝐵
C. 𝐼𝐵 < 𝐼𝐴
D. There is not enough information.
B. 𝐼𝐴 = 𝐼𝐵

A battery is connected to a wire and creates a current in the wire. Which of the following changes would increase the current?
A. Increasing the length of the wire
B. Keeping the wire the same length, but making it thicker
C. Using a battery with a lower emf (Voltage)
D. Making the wire into a coil, but keeping its
dimensions the same
E. Changing the wire material from copper to
nichrome
B. Keeping the wire the same length, but making it thicker

Wire 2 is twice the length and twice the diameter of wire 1. What is the ratio 𝑅2/𝑅1 of their resistances?
A. 1/4
B. 1/2
C. 1
D. 2
E. 4
B. 1/2

Which has a larger resistance, a 60 W lightbulb or a 100 W lightbulb?
A. The 60 W bulb
B. The 100 W bulb
C. Their resistances are the same.
D. There’s not enough information to tell.
A. The 60W bulb
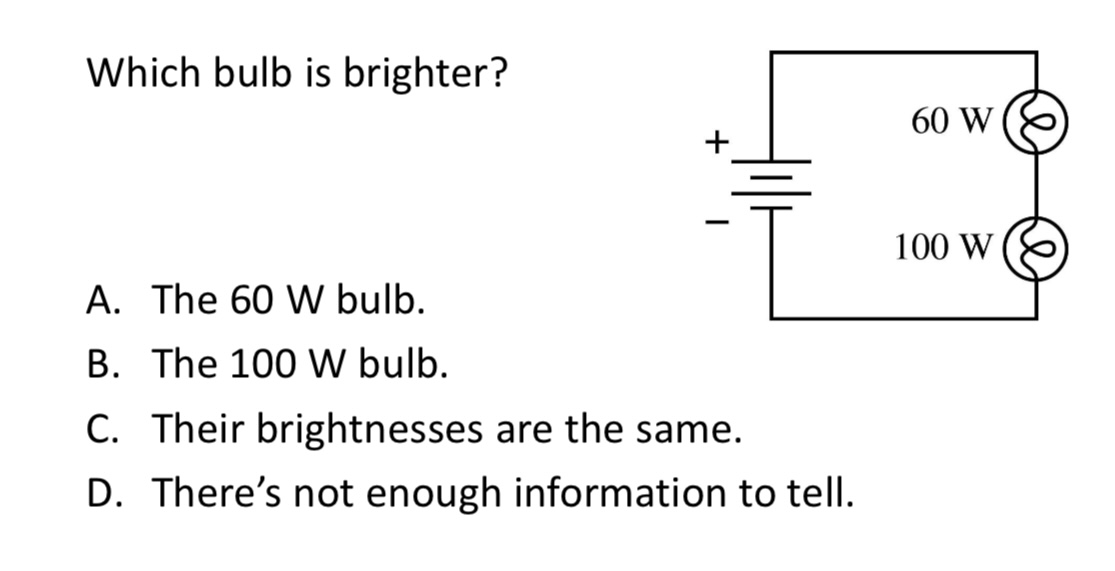
Which bulb is brighter?
A. The 60 W bulb.
B. The 100 W bulb.
C. Their brightnesses are the same.
D. There’s not enough information to tell.
A. The 60W bulb
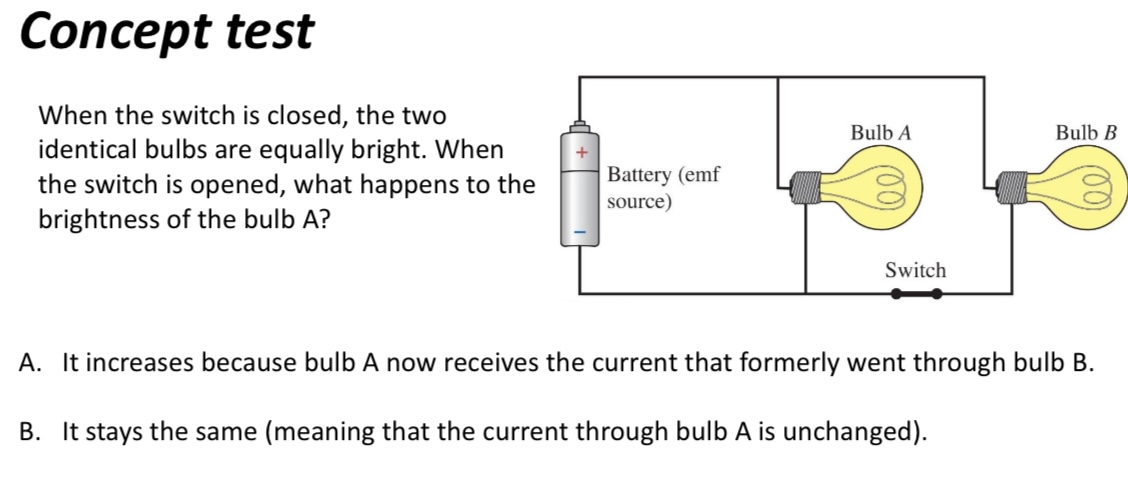
When the switch is closed, the two identical bulbs are equally bright. When the switch is opened, what happens to the brightness of the bulb A?
A. It increases because bulb A now receives the current that formerly went through bulb B.
B. It stays the same (meaning that the current through bulb A is unchanged).
B. It stays the same (meaning that the current through bulb A is unchanged).
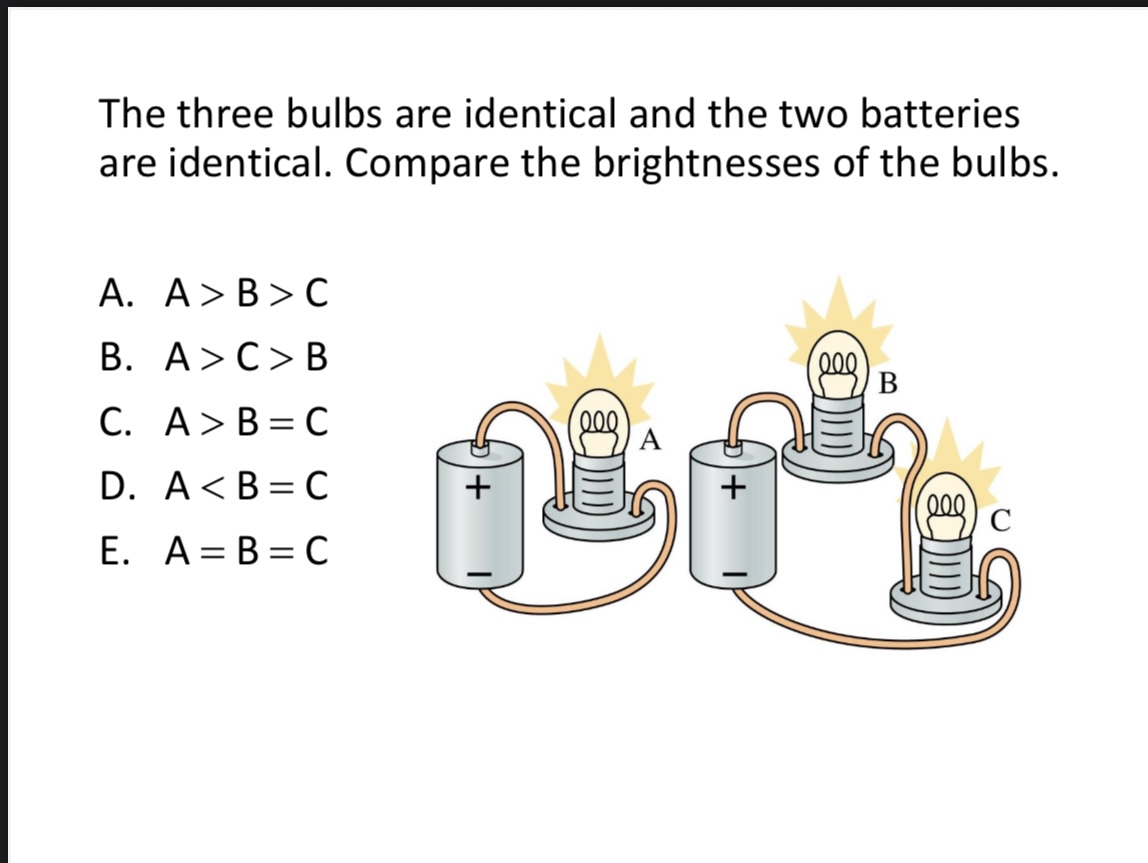
The three bulbs are identical and the two batteries are identical. Compare the brightnesses of the bulbs.
A. A > B > C
B. A > C = B
C. A > B = C
D. A < B = C
E. A = B = C
C. A > B = C
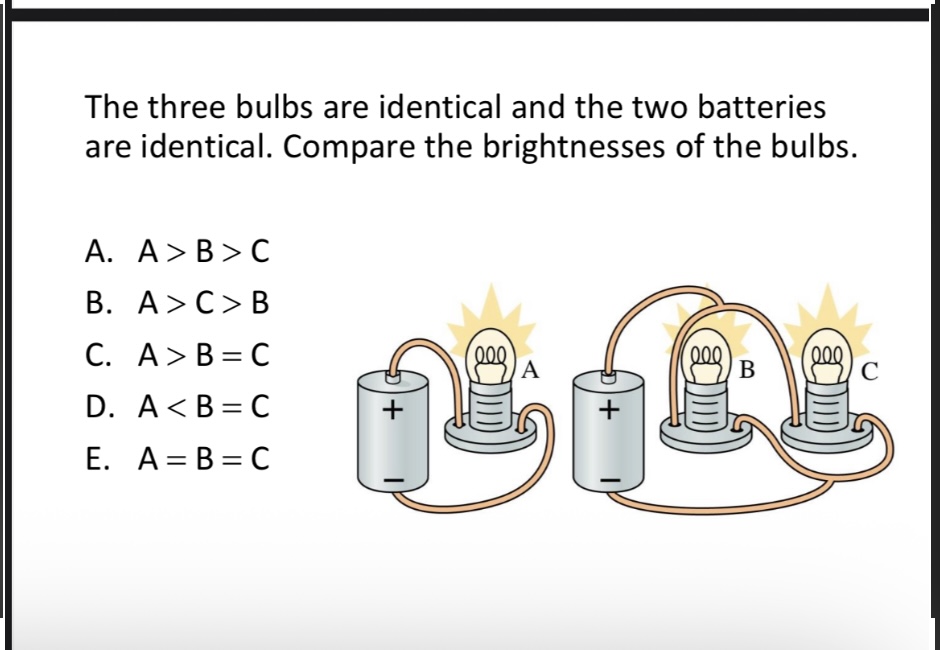
The three bulbs are identical and the two batteries are identical. Compare the brightnesses of the bulbs.
A. A > B > C
B. A > C > B
C. A > B = C
D. A < B = C
E. A = B = C
E. A = B = C
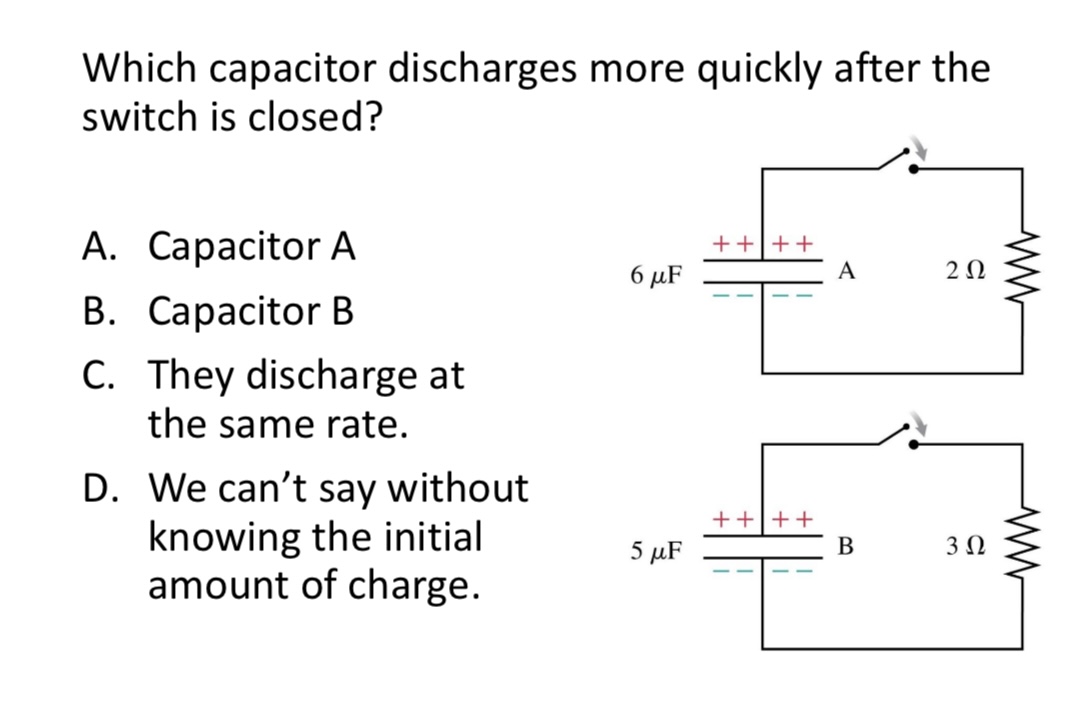
Which capacitor discharges more quickly after the switch is closed?
A. Capacitor A
B. Capacitor B
C. They discharge at the same rate.
D. We can’t say without knowing the initial amount of charge.
A. Capacitor A
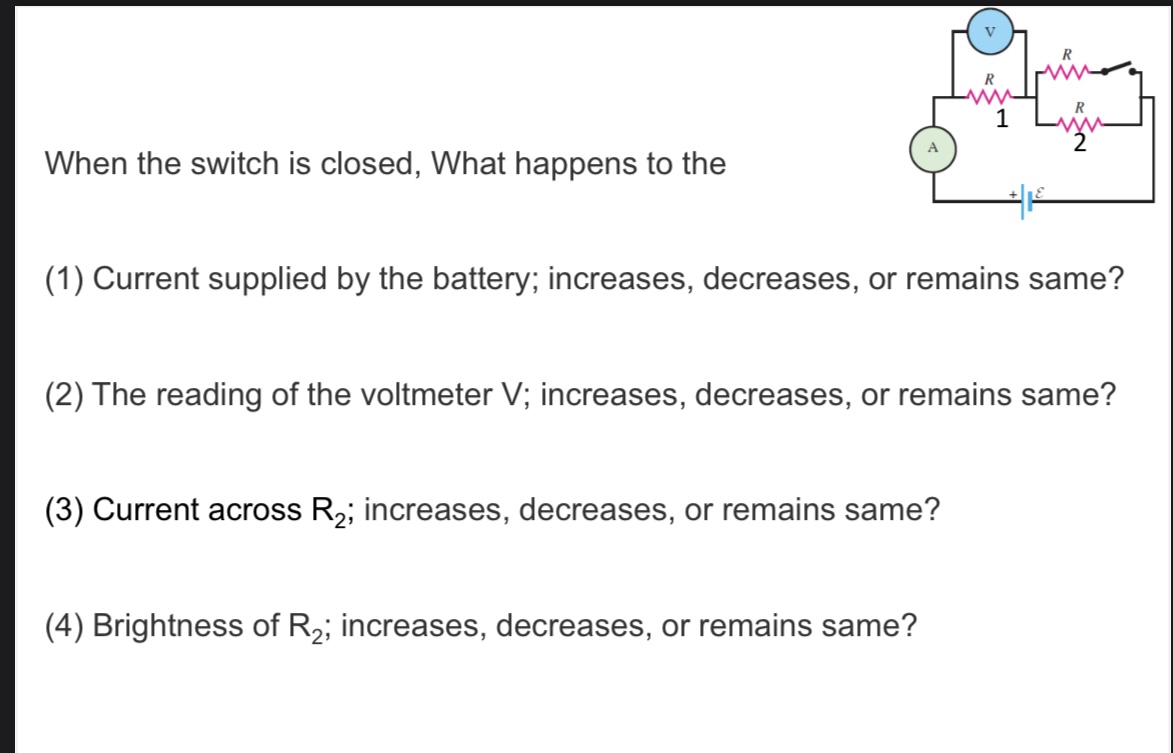
When the switch is closed, What happens to the
(1) Current supplied by the battery; increases, decreases, or remains same?
(2) The reading of the voltmeter V; increases, decreases, or remains same?
(3) Current across R2; increases, decreases, or remains same?
(4) Brightness of R2; increases, decreases, or remains same?
Increases because resistance of the circuit decreases
Increases because Ohm’s law V=IR
Decreases because current is divided into two paths
Decreases because power dissipated decreases. P=I2R
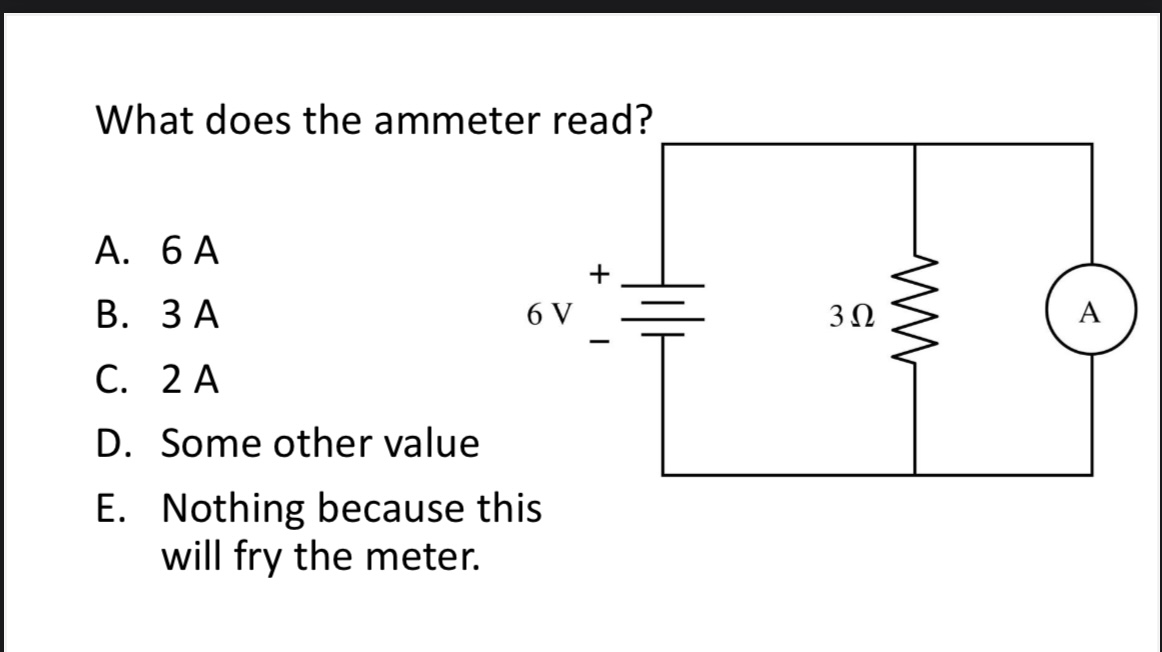
What does the ammeter read?
A. 6 A
B. 3 A
C. 2 A
D. Some other value
E. Nothing because this will fry the meter.
E. Nothing because this will fry the meter.