Unit 4: Reproductive Systems, Human Variation, Fertilization
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIOL 1003
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
sex determination (environment)
some aspect of the environment influences which traits develop
sex determination (genetic)
chromosomes determine sex
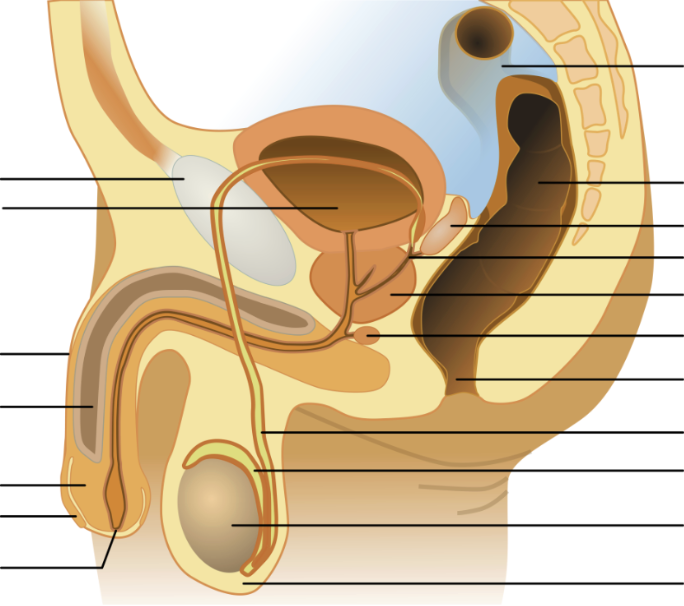
testis (sperm production)
house seminiferous tubules (where sperm are made)
specialized cells (Leydig cells) produce testosterone
scrotum (sperm production)
pouch of skin that holds the testes
expands/contracts to regulate temperature
seminiferous tubules (sperm production)
structures within the testes that are the actual sites of sperm production
epididymis (sperm production)
rubbery device which sits astride the testes
sperm mature and are stored prior to ejaculation
seminal vesicles (semen production)
produce alkaline fluid that can neutralize acidity of the vagina
fluid contains fructose and nutrients to provide energy for the sperm
bulbourethral (cowper’s) glands (semen production)
provide a mucus-rich alkaline fluid that lubricates and neutralizes the inside of the urethra (leftover urine) for easier passage of sperm
prostate gland (semen production)
organ which wraps around urethra and provides muscular contractions to propel semen during ejaculation
block urine flow from bladder during ejaculation
provides enzymes and zinc that aid in sperm mobility
vas (ductus) deferens (transport)
muscles that line the vas deferens contract to propel semen during ejaculation
ejaculatory ducts (transport)
ducts formed by the joining of vas deferens with the duct from the seminal vesicle, empties into urethra
penis (transport)
the organ encircles the urethra as the urethra exists the abdomen
changes from flaccid to effect
urethra (transport)
the tube that runs from the bladder through the penis through which urine and semen exit the body
order sperm travels…
seminiferous tubules
epididymis
vas deferens
ejaculatory duct (then)
urethra
penis
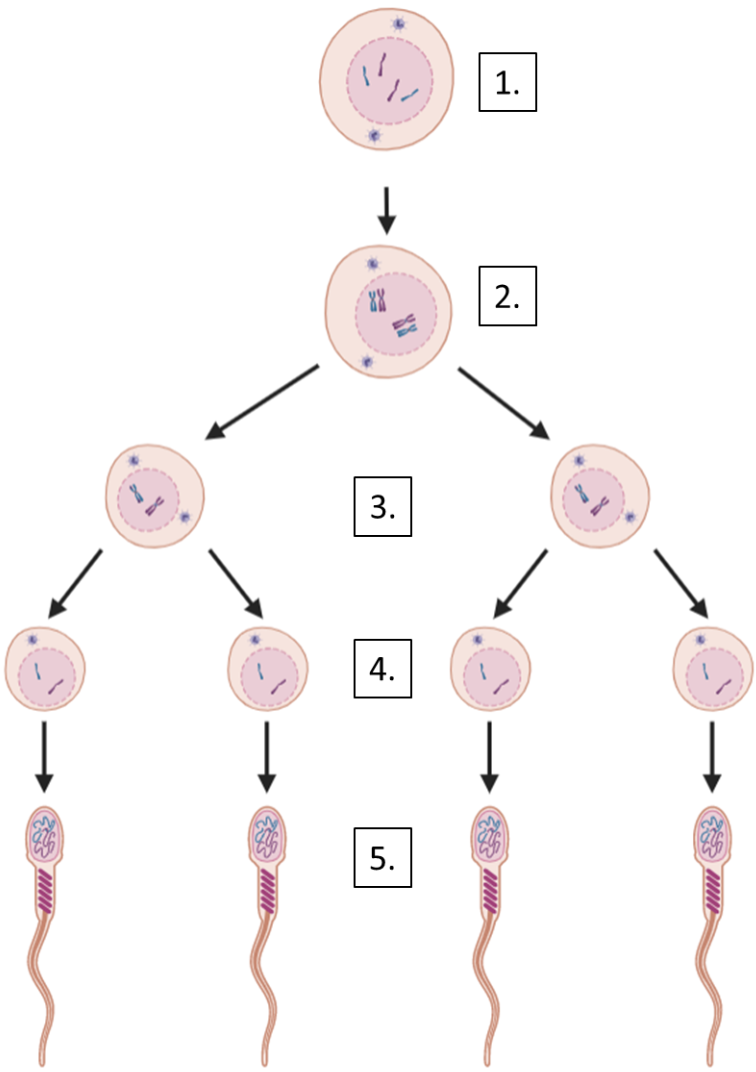
diploid, 4 un-replicated
~S phase
diploid, 4 replicated
~Meiosis 1
haploid, 2 replicated
~Meiosis 2
haploid, 2 un-replicated
~Maturation
haploid, 2 un-replicated
all human fetuses start with the same beginning reproductive organs…
gonad (testes or ovaries)
tubes (female duct or male duct)
urogenital sinus
what develops male reproductive structures?
SRY gene present on the Y chromosome
Sertoli cells lead female structures to degrade
Leydig cells migrate into the gonad and produce testosterone → further development of male structures
negative feedback
the effect of an action decreases the subsequent action
hypothalamus - male
secretes GnRH
pituitary - male
responds to GnRH by releasing LH and FSH
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) - male
targets Leydig cells (in seminiferous tubules) to secrete testosterone
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) - male
targets Sertoli cells (in seminiferous tubules) to stimulate spermatogenesis
testosterone - male
inhibits hypothalamus
inhibits secretion of GnRH
makes pituitary less responsive to GnRH
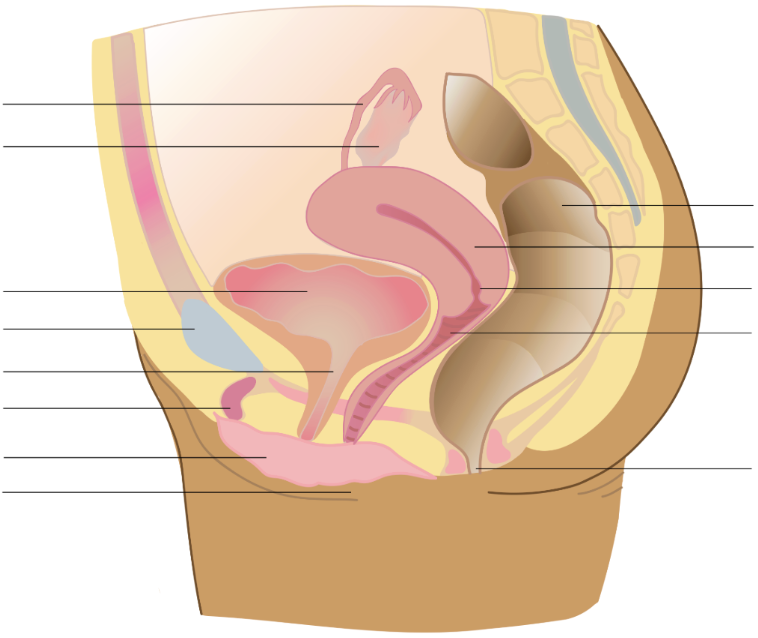
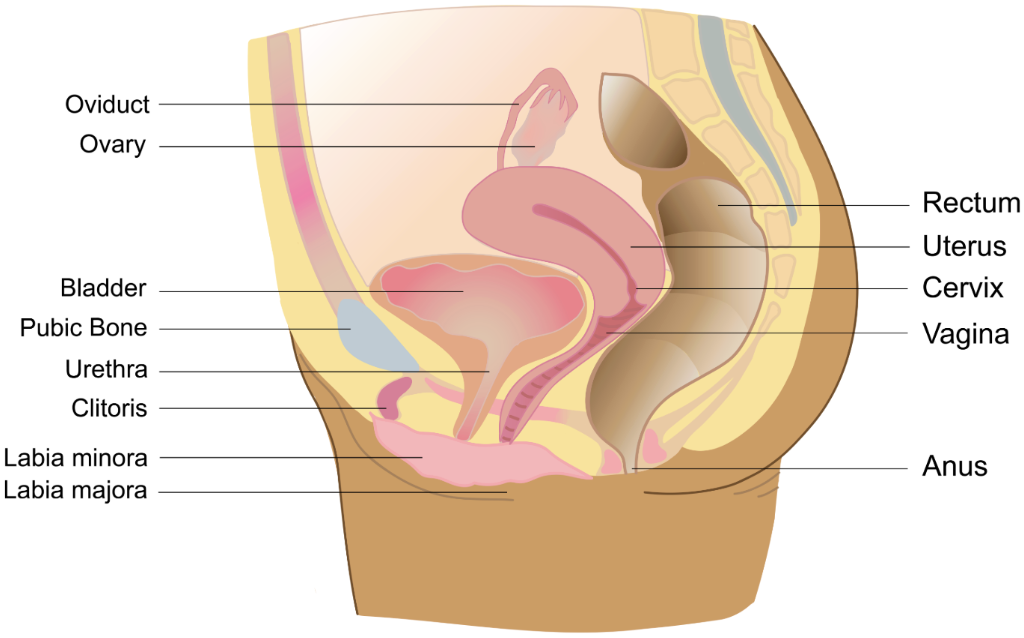
ovary (egg production)
site of egg production
if fertilized…site is corpus luteum
produces hormones (estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone)
corpus luteum (egg production)
sit of egg maturation within the ovary
after ovulation, produces progesterone to maintain a possible pregnancy
uterus (egg production)
muscle-lined, triangular organ where fertilized egg implants and develops
organ develops a thick blood lining and sheds on a monthly cycle
vagina (transport)
expandable structure that serves as the opening of the female reproductive tract
point of sperm entry and exit of unfertilized eggs, menstrual discharge, and babies
cervix (transport)
the opening between the vagina and uterus
size of opening varies
oviducts (fallopian tubes)
ducts transport mature eggs from the ovary toward the uterus
place of fertilization
vulva
exterior parts surrounding the vagina
labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, urethra
clitoris
a sensitive nerve-rich organ
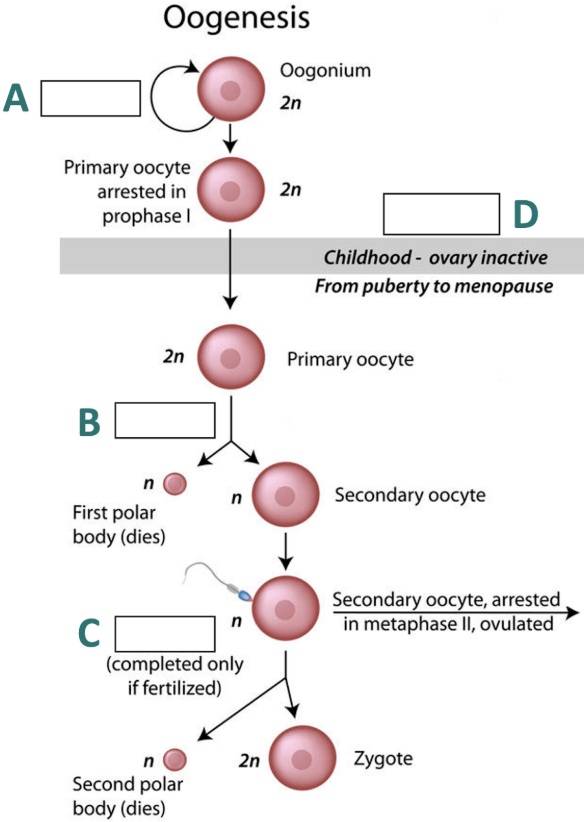
A = mitosis
B = meiosis 1
C = meiosis 2
D = before birth
positive feedback
the effect of an action increases the subsequent action
hypothalamus - female
secretes GnRH
pituitary - female
responds to GnRH by releasing LH and FSH
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) - female
targets follicle cells and corpus luteum
stimulates follicle cells to produce estrogen (1-12)
stimulates follicle growth and ovulation (12-14)
stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone & estrogen (15-28)
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) - female
targets follicle cells
stimulates follicles to produce estrogen and grow (oogenesis), ovulation
Follicular Phase (1-12)
negative feedback : high E = low GnRH
- low GnRH → low LH + FSH → low estrogen
low estrogen leads to endometrium shedding
follicle cells begin growing
Ovulation (12-14)
menstruation complete → endometrium thickens
follicles mature in ovary
positive feedback : high E = high GnRH
- high GnRH → high LH + FSH → high estrogen + progesterone → ovulation
rupture releases an oocyte → oocyte travels into oviducts and completes meiosis
Luteal Phase (15-28)
negative feedback : high E + P = low GnRH
- low GnRH → low LH + FSH → estrogen + progesterone begin to fall at end of phase
if oocyte not fertilized…
corpus luteum degrades → drop of progesterone → triggers menstruation and follicular phase
if oocyte fertilized…
oocyte completes meiosis 2, forming a zygote and polar body
zygote travels through oviduct, completes several cell divisions (blastocyst)
blastocyst implants uterine lining → produces HGG → signals corpus luteum to produce progesterone
high progesterone → inhibits shedding of uterine lining so pregnancy is maintained
all internal structures begin with…
2 biopotential gonads
2 sets of ducts (mullerian or wolfifan)
a fetus will develop female structures unless…
the SRY gene is present (typically on Y chromosome)
SRY translated and transcribed into TDF protein
TDF (testes-determining factor)
prevents transcription of ovary-promoting genes
turns ON transcription of testes-promoting genes
Sertoli cells secrete a hormone causing degradation of female structures
Leydig cells secrete testosterone which promote male structures development
intersex
having characteristics that don’t fit binary notion (male or female) reproductive systems
*1-2 people per 100 people
gender identity
an internal sense of being male, female, neither, or some combination of both.
cisgender
people whose gender matches the sex they were assigned at birth
transgender
people whose gender does not match the sex they were assigned at birth
nonbinary
a person whose gender identity is a combination of or goes beyond the gender binary of woman and man
gender dysphoria
a feeling of distress that can happen when a person's gender identity differs from their sex assigned at birth or from their sex-related physical characteristics