physical development
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
developmental debates
stability vs change
nature vs nurture
continuity vs discontinuity
stability
a person’s personality traits during infancy will stay the same throughout their lifespan
change
our personalities are modified by events in our lifespan and our interactions with our families, schools, and friends
nature
the genetically inherited traits impact our personality traits, intelligence, and preferences more than the environment
nurture
the environment children are raised in is more impactful on development
continuity
development is a continuous journey; changes are gradual and not abrupt
discontinuity
human development happens in stages and the changes are abrupt
teratogens
substance or factor that can cause a birth defect
ex. alcohol
maternal illness
as soon as the embryo starts to receive nutrients from the mother through the placenta, it becomes vulnerable to maternal diseases
critical periods
times during which some environmental factors can have an impact on the development of certain parts of an infant
ex. limb development critical period is 3-8 weeks
genetic mutations
missing, mutated, or extra chromosomes can cause genetic disorders
ex. cystic fibrosis, sickle-cell anemia, Tay-Sachs, Down syndrome, Turner syndrome
hormonal factors
chemical messengers produced during pregnancy that regulate physical development and can influence prenatal growth and psychological development
environmental factors
external conditions and influences during pregnancy, such as nutrition, stress, exposure to substances, that affect prenatal development
adverse childhood experiences (ACEs)
potentially traumatic events that occur in childhood (0-17 years)
ex. violence, abuse, neglect
sociocultural differences exist in what is considered an ACE and how they affect outcomes people may experience
fine motor coordination
the development of precise, controlled movements using small muscles, usually in the hands and fingers
ex. grasping
gross motor coordination
the development of controlled movements using large muscle groups that allow children from perform activities like crawling, walking, and running
synaptic pruning
like weeding a garden, but with neural connections
getting rid of unused neural connections
reflex
innate involuntary behavior patterns
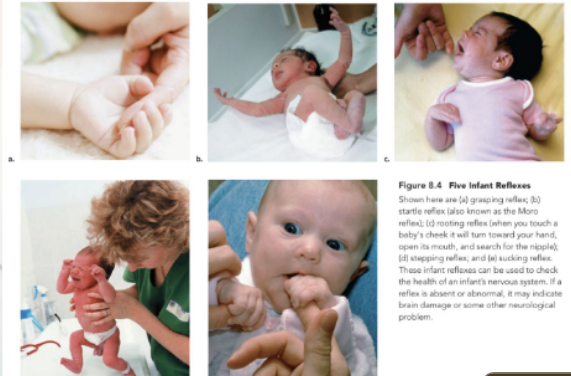
infant reflexes
grasping reflect, startle reflex, rooting reflex, stepping reflex, sucking reflex
visual cliff apparatus
glass covered table with the illusion of a cliff that babies were placed onto
they were hesitant to cross, meaning they had depth perception
adolescent growth spurt
a period of rapid physical growth that occurs during adolescence, characterized by significant increases in height and weight
puberty
reproductive ability develops
primary and secondary sex characteristics are developed
primary sex characteristics
physical characteristics directly involved in reproduction, including the reproductive organs
secondary sex characteristics
physical traits that distinguish males from females, but are not directly involved in reproduction
ex. facial hair
menarche
first time a female experiences her menstrual period (age 10-16)
spermarche
male equivalent of a menarche - growing facial hair, deepening of the voice
adulthood
spans most of the lifespan
leveling off and varying decline in reproductive ability, mobility, flexibility, reaction time, visual and auditory sensory activity
menopause
the biological process in adulthood marked by the cessation of reproductive ability