Module 34 - Skeletal Muscle Gross Anatomy Pt.2
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Function of arm muscles
Attach the arm to the thorax (thoracic cage)
3 Main arm muscles
Pectoralis major
Latissimus dorsi
Deltoid
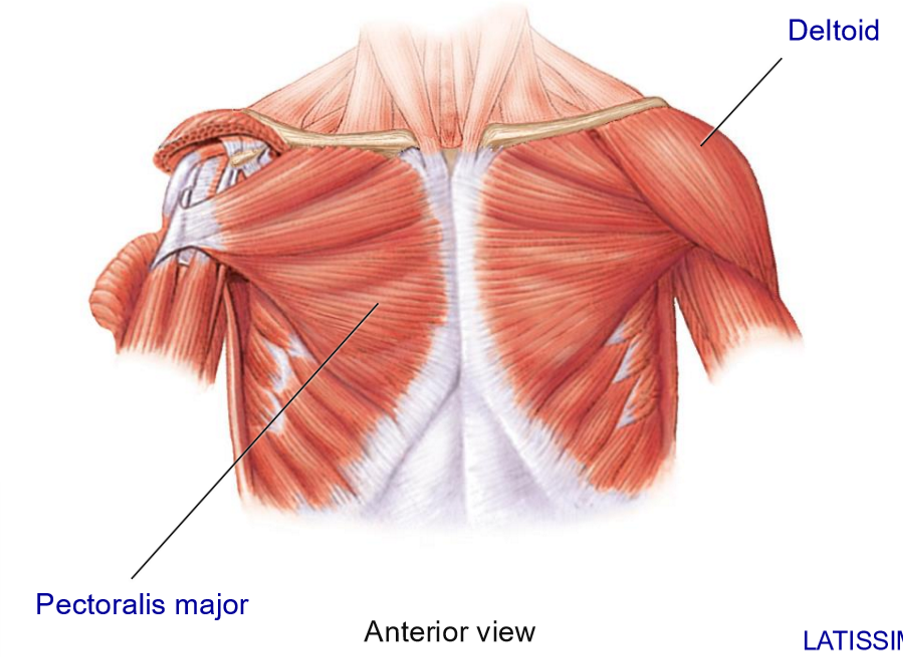
Pectoralis Major - Structure + Movements
Structure: anterior muscle
Fan-shaped, broad origin on thoracic cage
Insertion on the lateral side of the humerus, wrapping from the front
Movements (of the arm): flexion, adduction, medial rotation
Assists with extension if the arm is already flexed
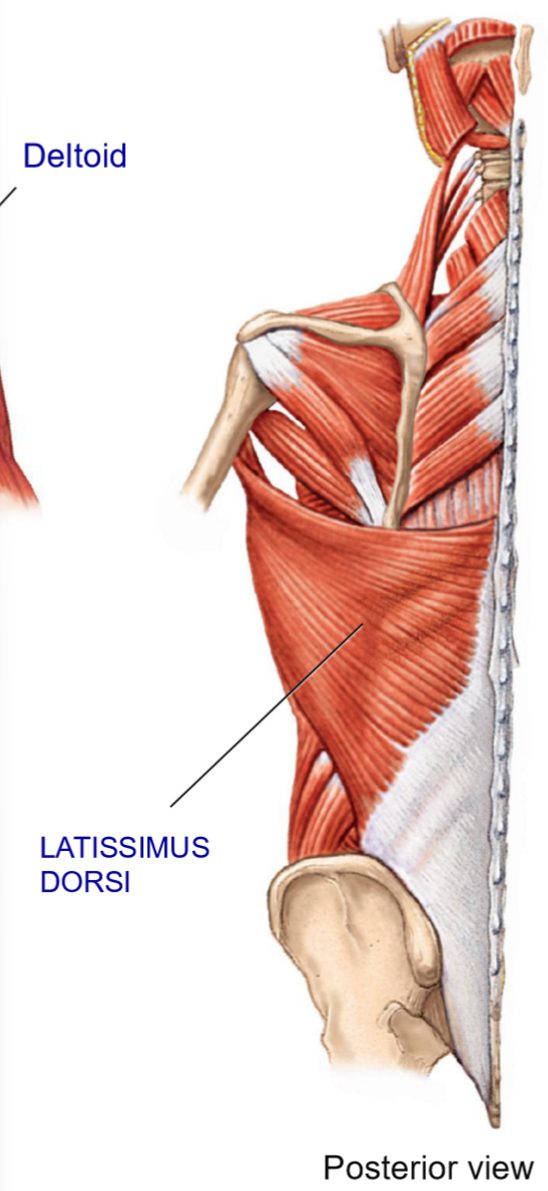
Lats - Structure + Movements
Structure: large posterior muscle
Broad origin down the vertebral column
Passes under the axillary region to insert on anteiror humerus
Movements: extension (prime mover), adduction, medial rotation
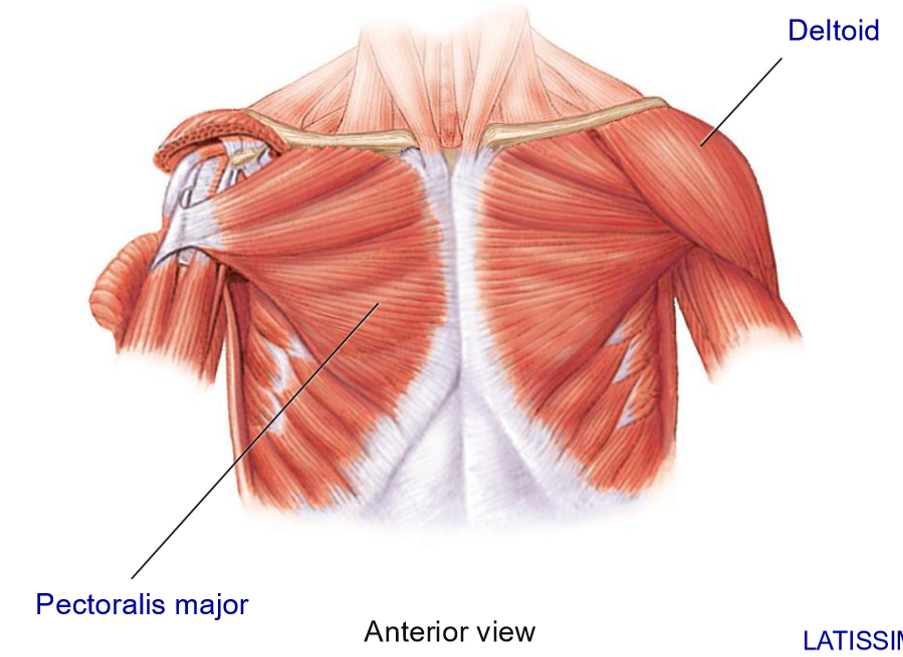
Deltoid - Structure + Movements
Structure: triangular muscle that forms a cap over the shoulder joint
Broad origins on scapula + clavicle and inserts on lateral humerus
Movements: abduction, flexion/extension, medial/lateral rotation
Name the rotator cuff muscles
SITS
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Subscapularis
Main functions + Movements of the rotator cuff
Hold the head of the humerus in the glenoid cavity
Form a cap over proximal humerus
Enable abduction, adduction, and rotation
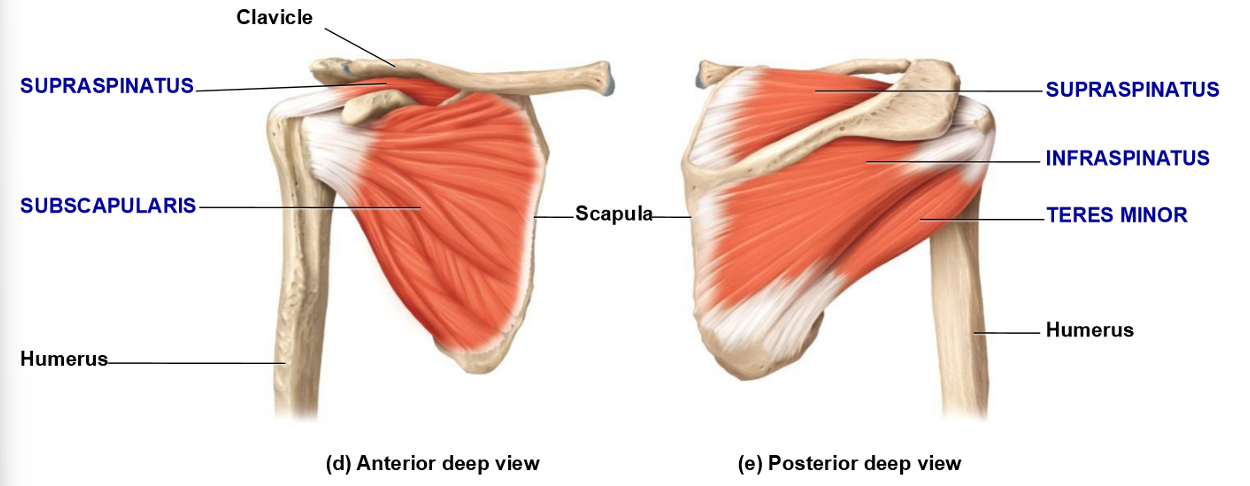
Infraspinatus – Location, Insertion, Movement
• (Muscle belly) Located in infraspinous fossa
• Inserts on lateral humerus
• Movement: lateral rotation
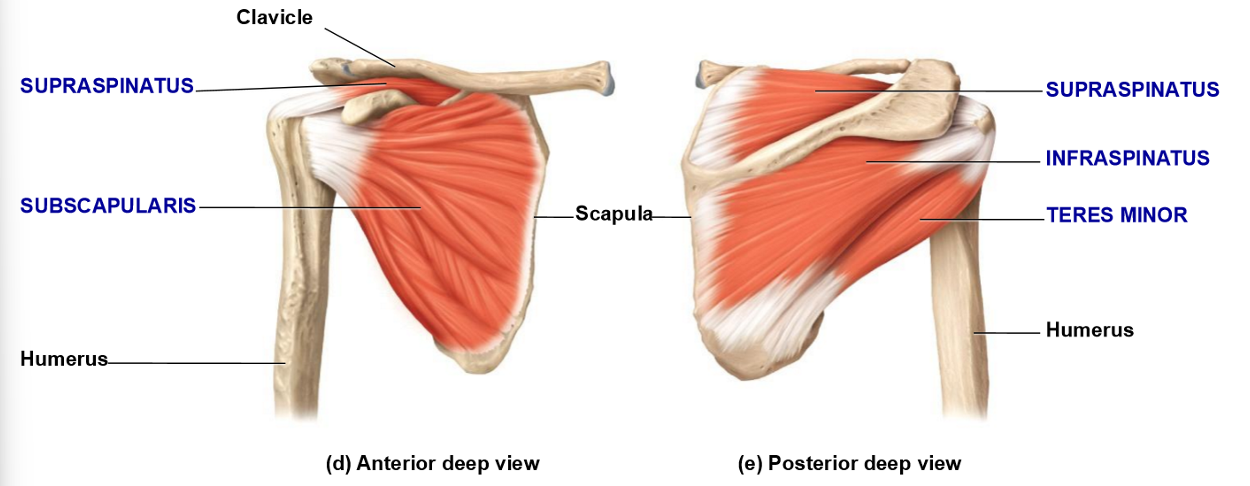
Subscapularis – Location, Insertion, Movement
• Located in subscapular fossa (anterior side
• Inserts on anterior humerus
• Movement: medial rotation
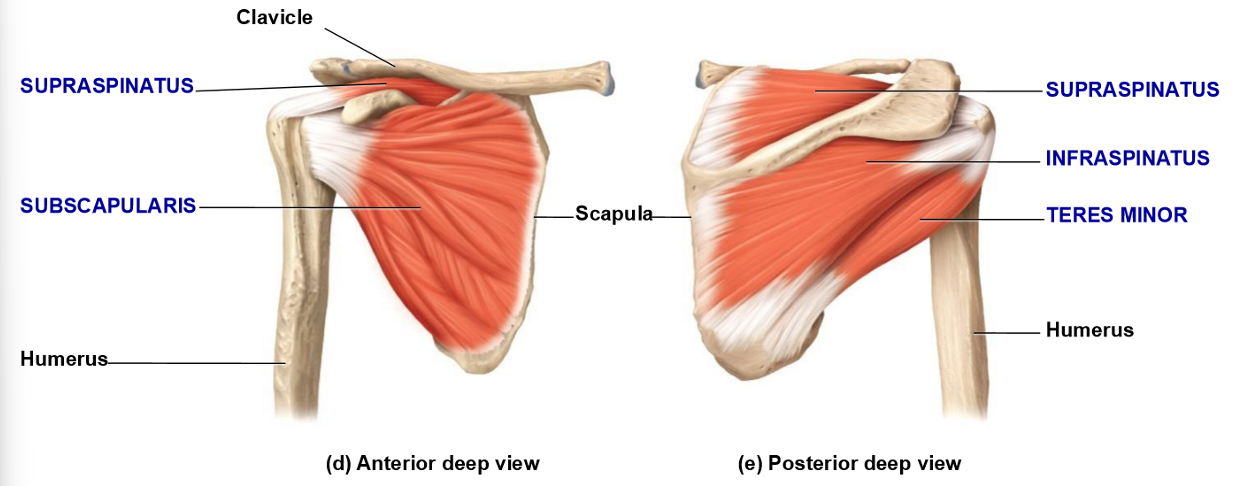
Supraspinatus – Location, Insertion, Movement
• (Muscle belly) Located in supraspinous fossa
• Inserts on superior humerus (greater tubercle)
• Movement: abduction
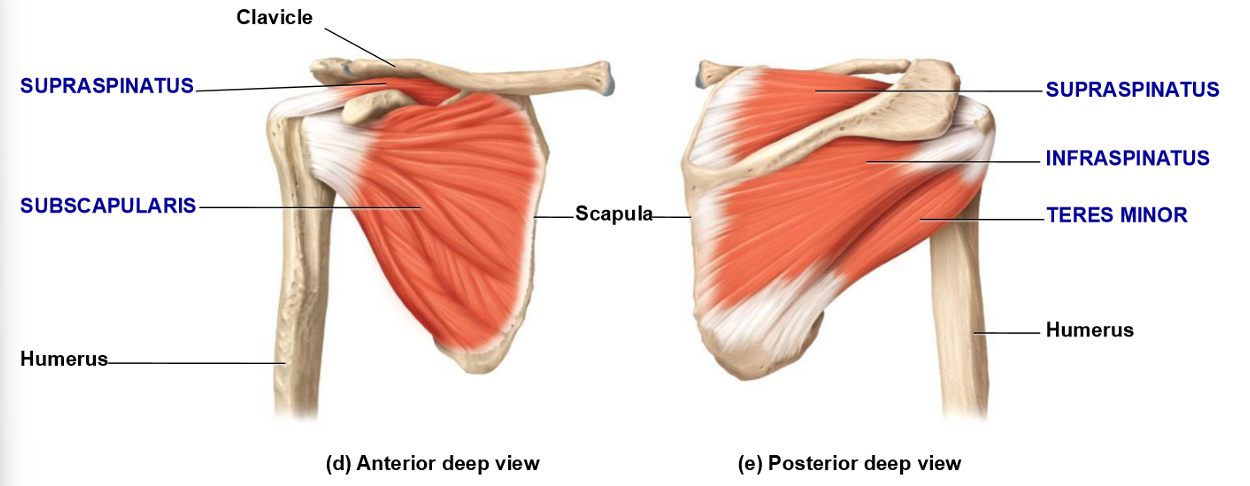
Teres Minor – Location, Insertion, Movements
• Small, rounded muscle bellt below infraspinatus
• Inserts on greater tubercle
• Movements:
– Adduction
– Lateral rotation
– Assists with extension
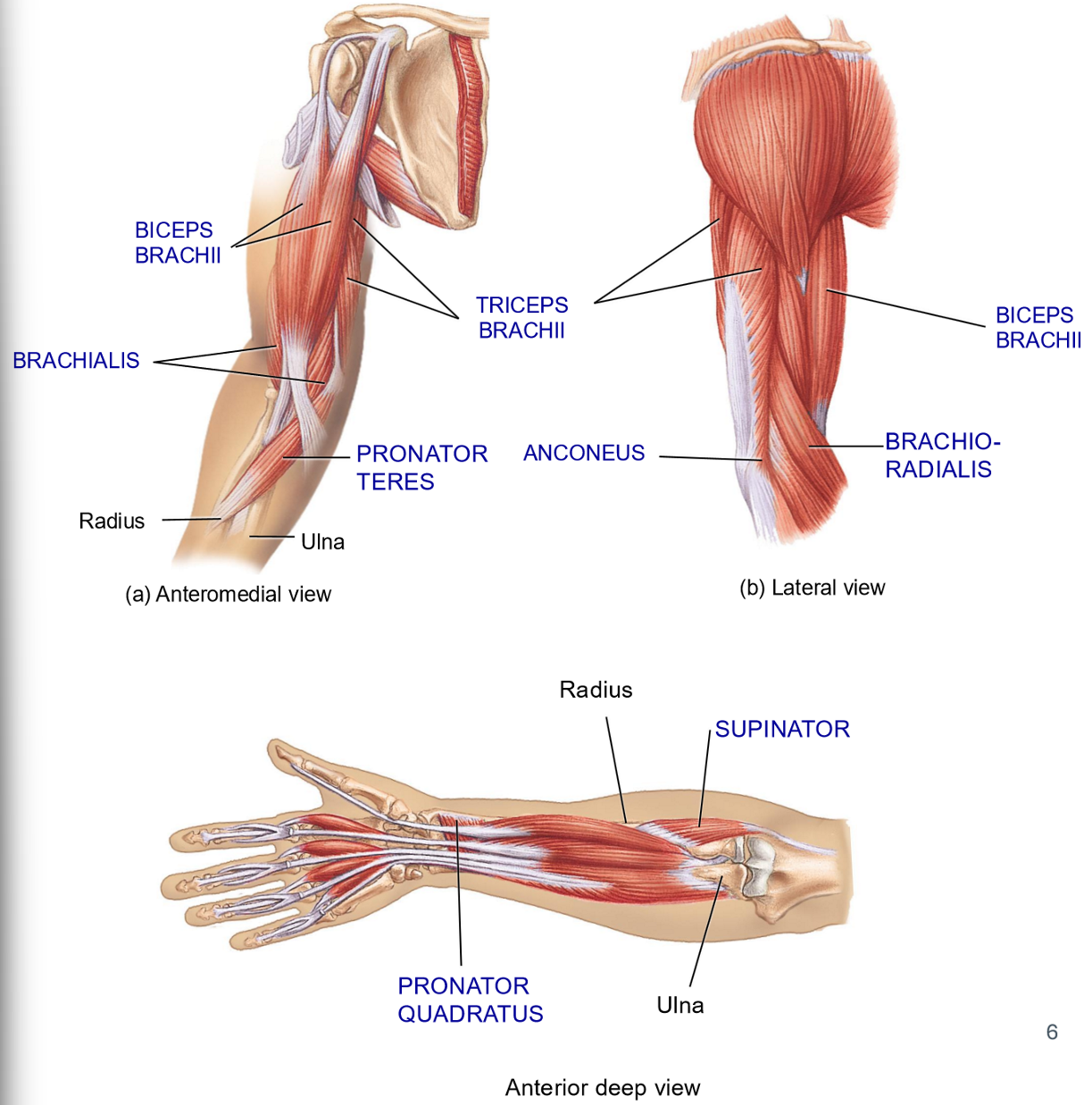
Forearm Extensors Muscles - Structure + Movement
Triceps brachii – posterior humerus
3 heads
inserts on olecranon process of ulna
extends forearm
Anconeus – small posterior muscle extending from distal humerus to olecranon/ulna
Assists extension
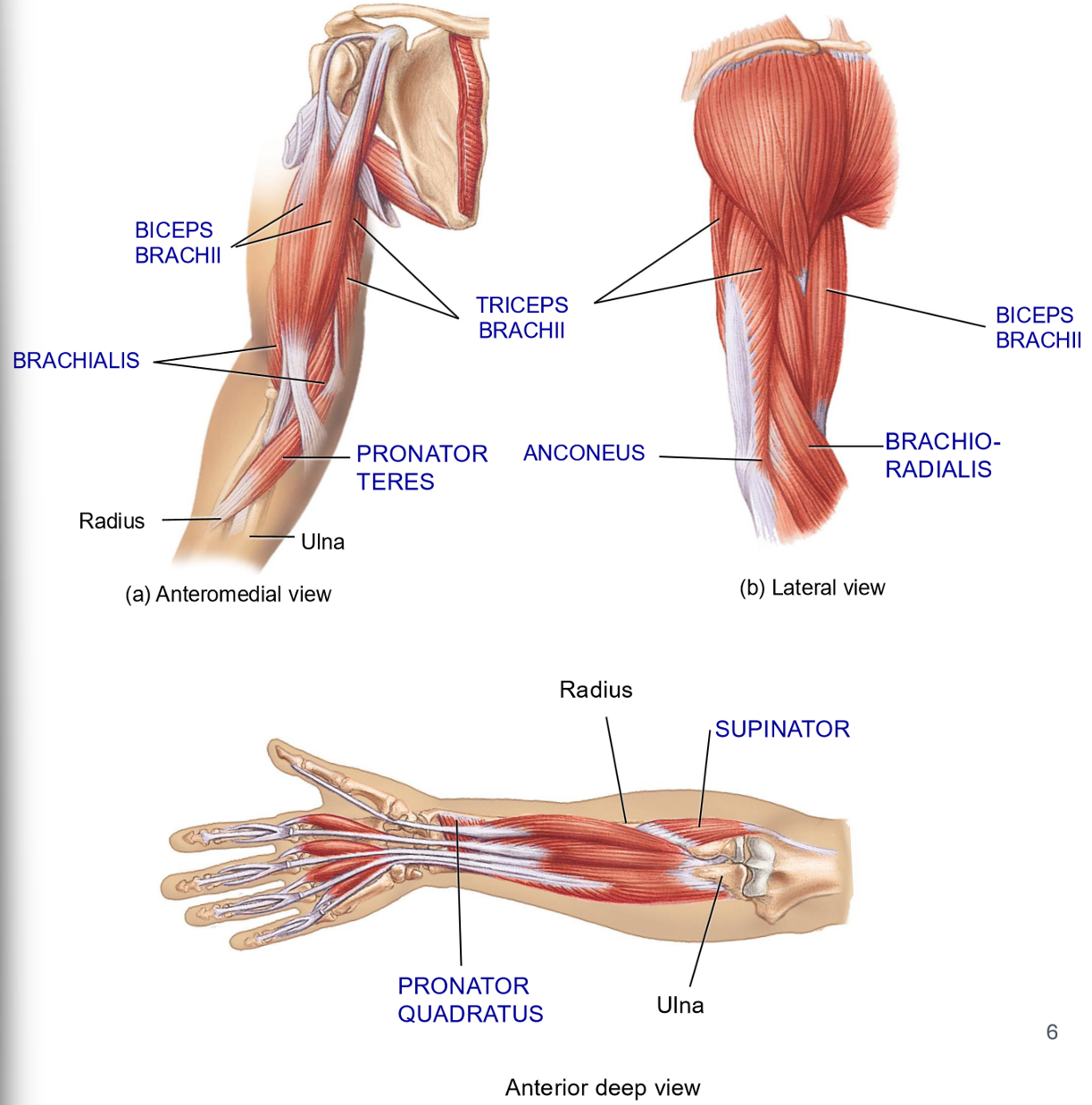
Name the 3 Forearm Flexors
Biceps Brachii
Brachioradialis
Brachilais
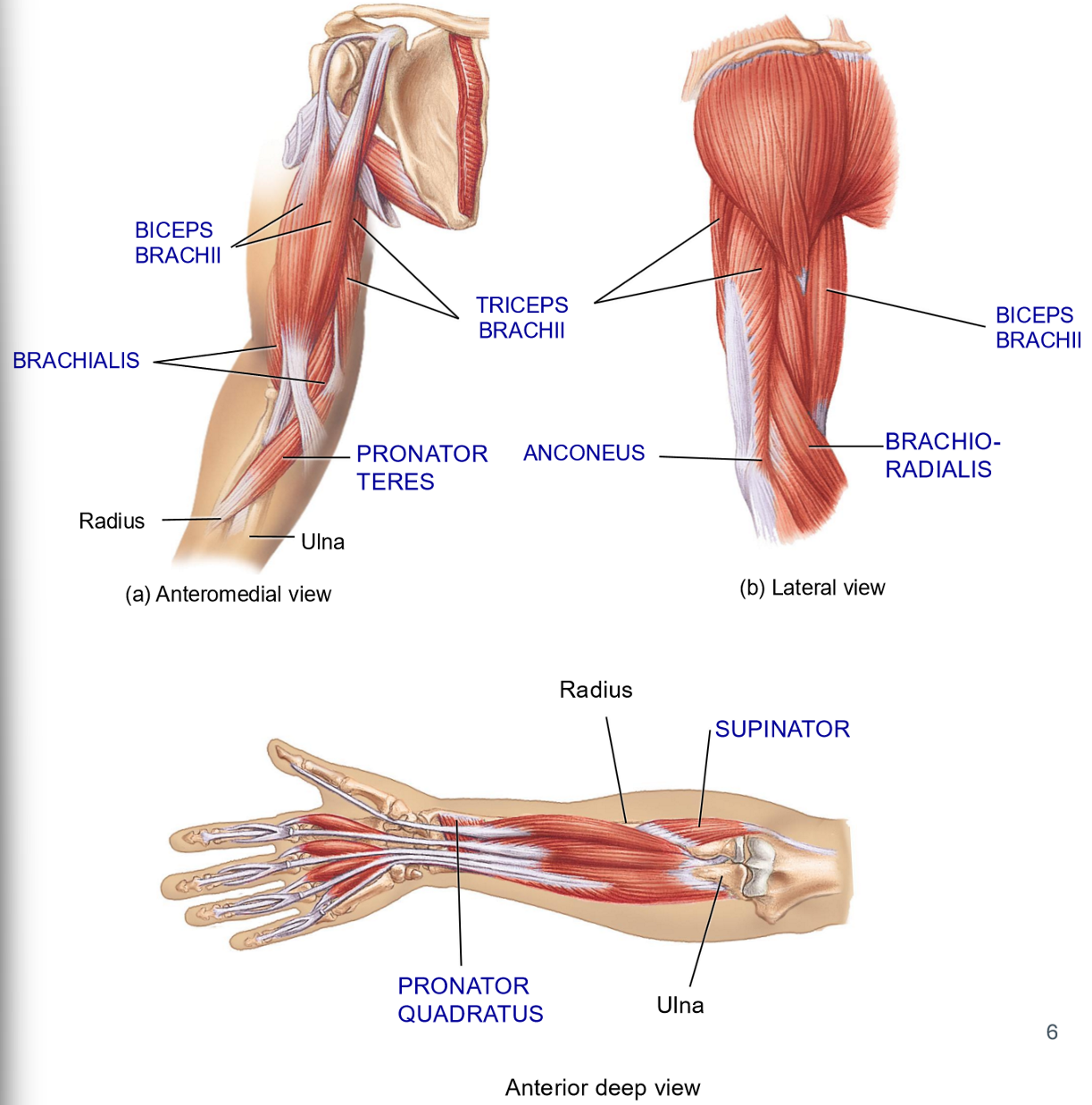
Biceps - Structure + Functions
Structure:
2-headed muscle on anterior humerus
Origins on scapula + Inserts on radius
Movements: flexion + supination
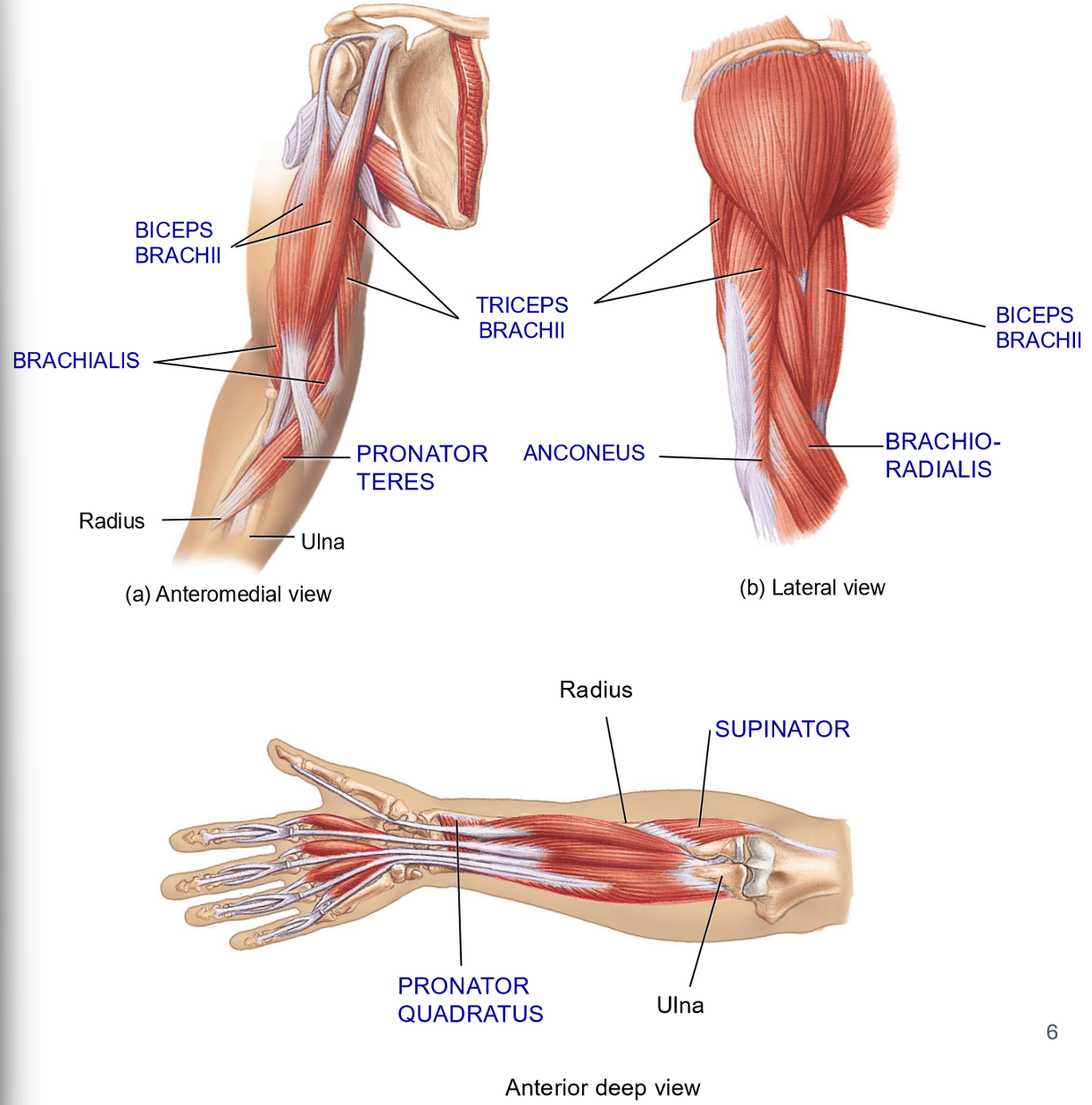
Brachioradialis - Structure + Movement
Structure: most of muscle belly in the forearm
Originates in distal humerus + inserts on radius
Movement: Flexion
Brachialis - Structure + Movement
Structure: Deep to biceps
Originates on mid humerus + Inserts on ulna
Movement: Flexion
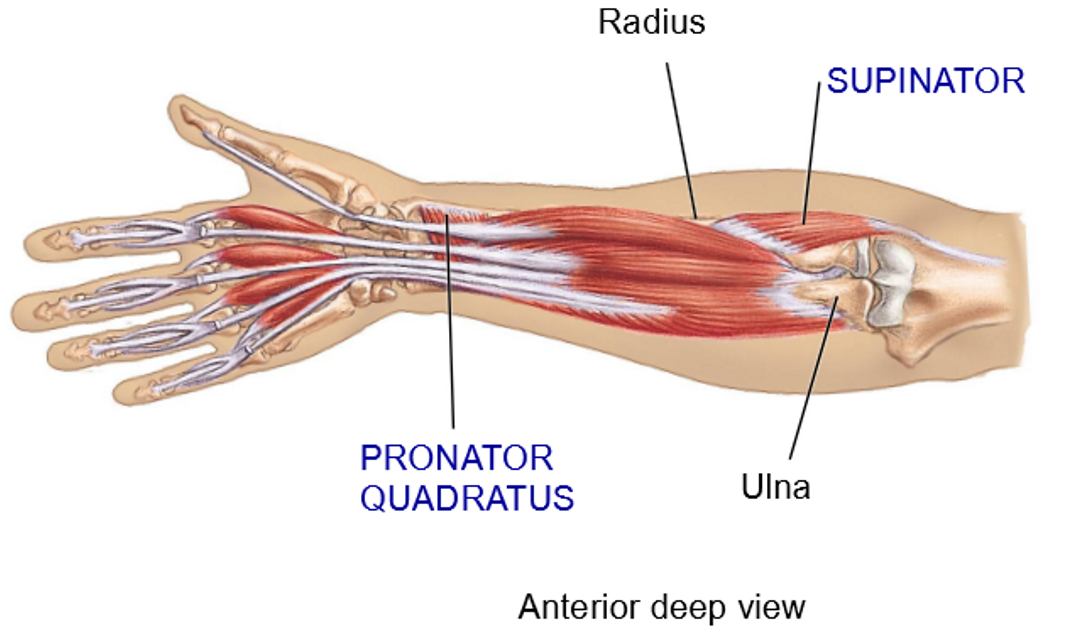
Muscles involved in Supination - Structure + Movement
Biceps
Supinator: posterior, deep muscle, extends from ulna/humerus to radius
Movement: supination
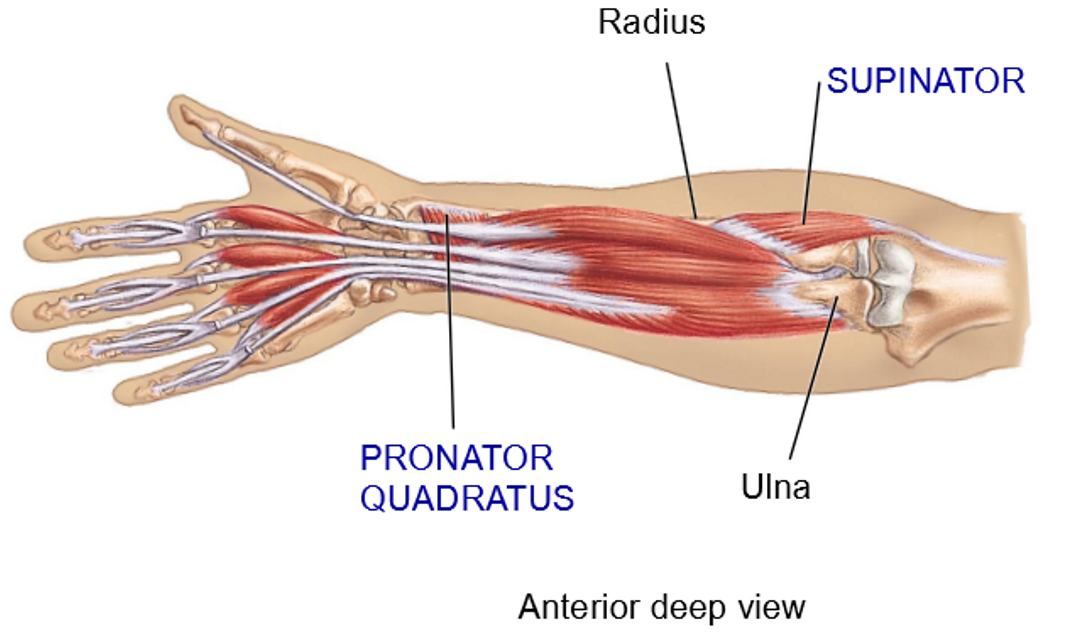
2 muscles involved in Pronation - Structure
Pronator quadratus: anterior distal side, between ulna and radius
Pronatetor teres: anterior side, running opposite to supinator
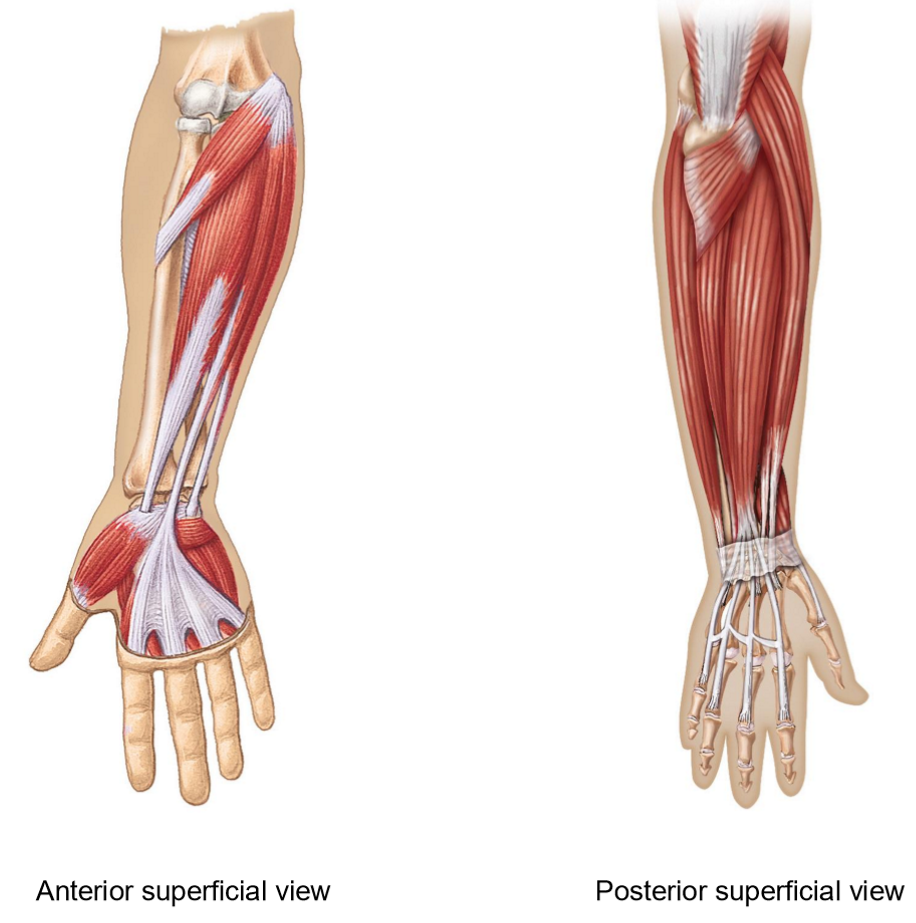
Extrinsic Muscles of the Hand + Features
• Muscles with at least 1 origin outside the hand
• Muscle bellies are in the forearm (not hand)
• Long tendons extend into the hand and fingers
• Purpose: preserve manual dexterity
Movements of the anterior forearm muscles
Flexion of wrist, hand + fingers
Abduction + Adduction of wrist
Tendones travel to the distal phalanges
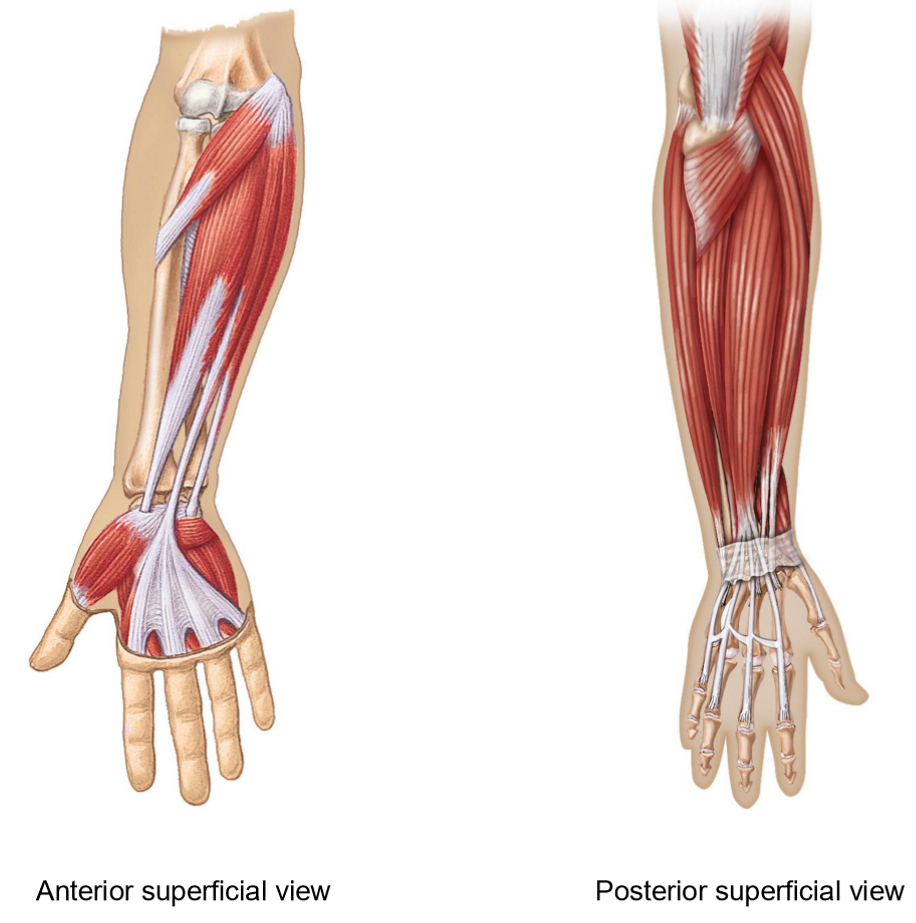
Movements of Posterior Forearm Muscles
Uses long tendons to move
Extension of wrist, hand and fingers
Abduction
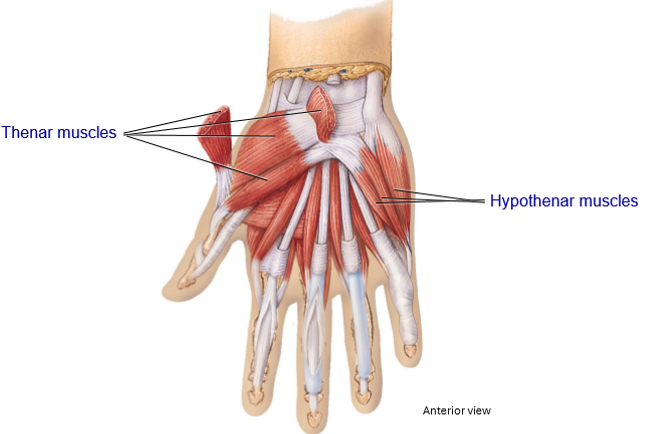
Intrinsic Muscles of the hand + Features/Movements
Muscles that originate + insert in the hand
Smaller muscle bellies
Overall movements: adduction, abduction, opposition, reposition
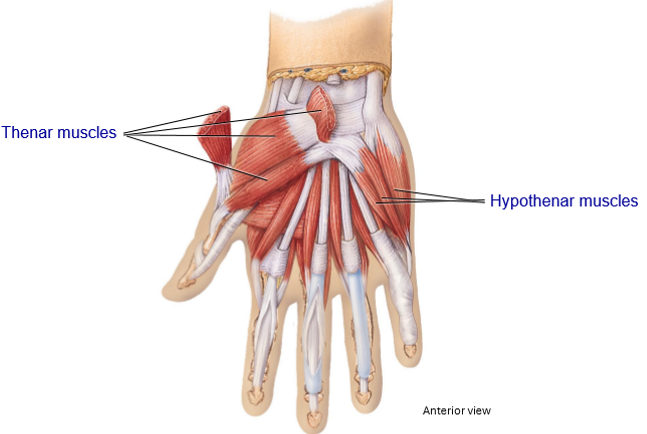
2 intrinsic muscle of the hand + Their movements
Thenar Muscles
Located on the thumb side (fleshy part of thumb)
Movement: Opposition
Hypothenar Muscles
Located on pinky side
Movement: Assist in opposition, adduction, abduction
Where do the thigh muscles originate and insert?
Originate: Coxa (hip)
Insert: Femur
Hip flexors are found on which side (anterior/posterior)?
Anterior
What muscles make up the hip flexors? + Movement
• Iliacus + Psoas Major = Iliopsoas
• Located on anterior side of hip
• Share common tendon of insertion on proximal femur
• Movement: flexion of thigh
What composes the posterolateral muscles of the thigh? + Movements
Gluteals
Tensor Fasciae Latae
Movements: Extension and abduction of thigh, flexion + stabilize femur
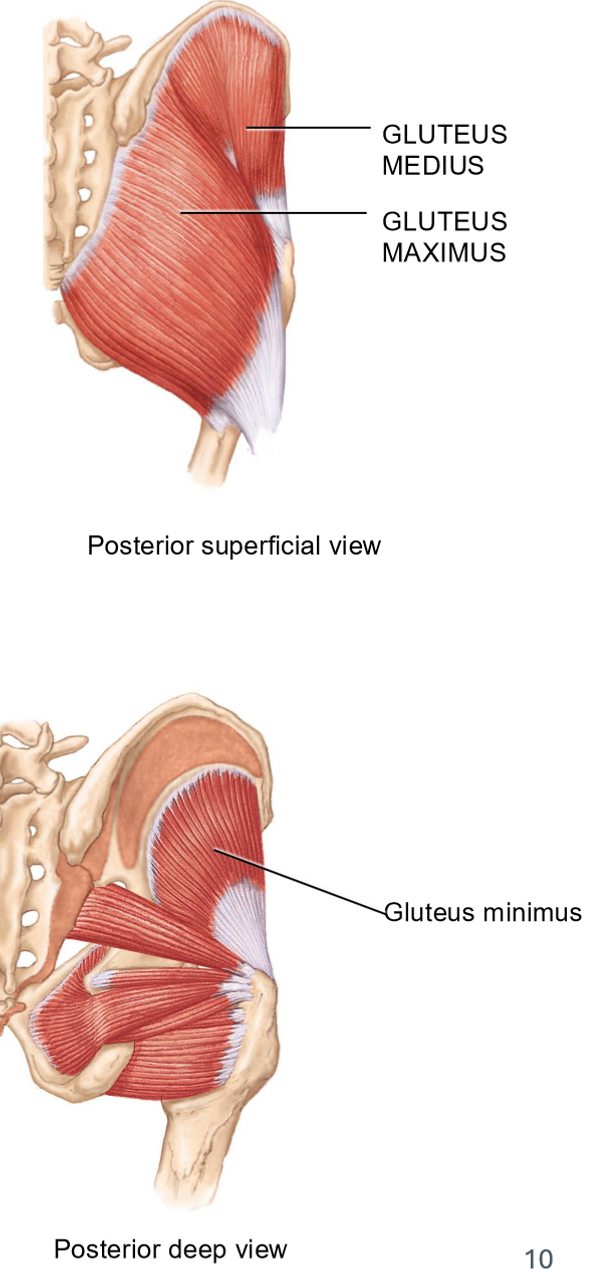
Gluteal muscles (3) + Movements
All on the posterior/lateral side
Gluteus Maximus: most superficial + largest
Movements: extension, abduction, lateral rotation
Gluteus Medius: deep to maximus
Movements: abduction
Glueteus Minimus: deepest gluteal muscle
Movements: Abduction
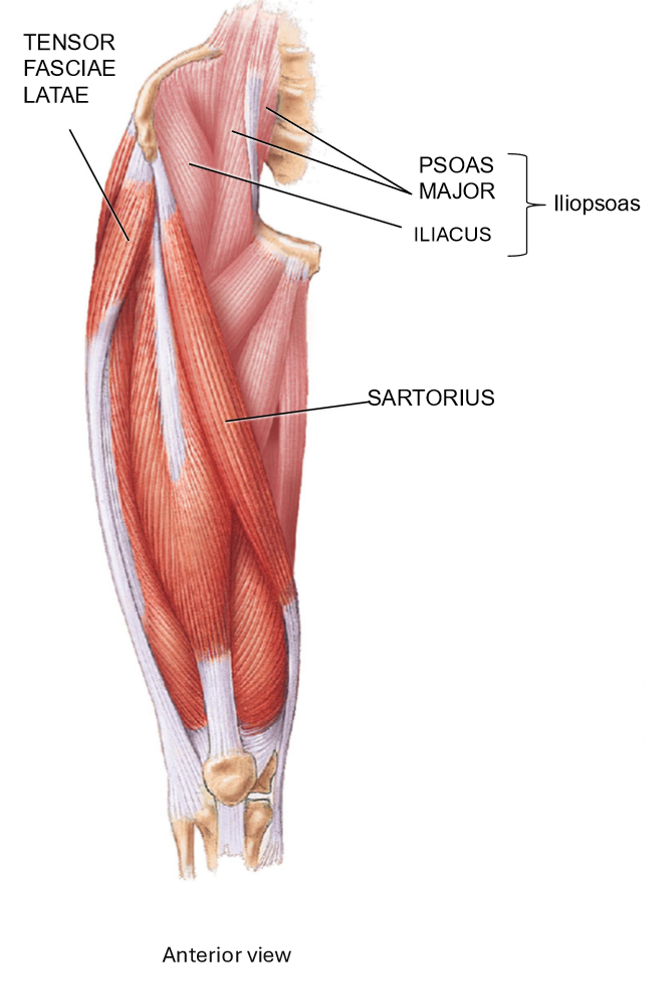
Tensor Fasciae Latae - Structure & Movements
Structure: small muscle belly with long tendon, crosses the knee
Originates on lateral thigh > crosses hip + knee joint > inserts onto leg bones
Movement: flexion, abduction, stabilizes femu when standing
Deep Thigh Rotators – Function
Responsible for lateral rotation of thigh
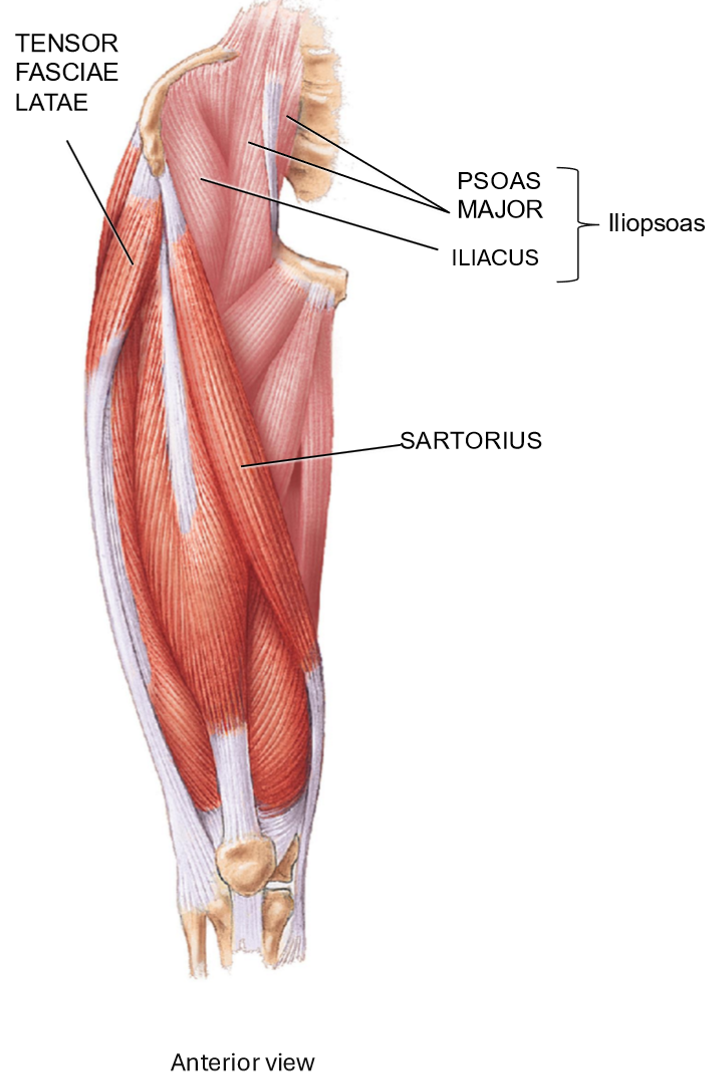
Sartorius - Structure + Function
Part of muscles that move the leg + thigh muscles
Structure: Runs lateral → medial across thigh
Function: cross-legged position
When contracting:
– Hip flexion
– Lateral rotation of thigh
– Knee flexion
Medial Thigh Muscles - Structure + Movement
Part of muscles that move the leg + thigh muscles
Structure: Run from hip → medial femur
Movement: adduction of thigh
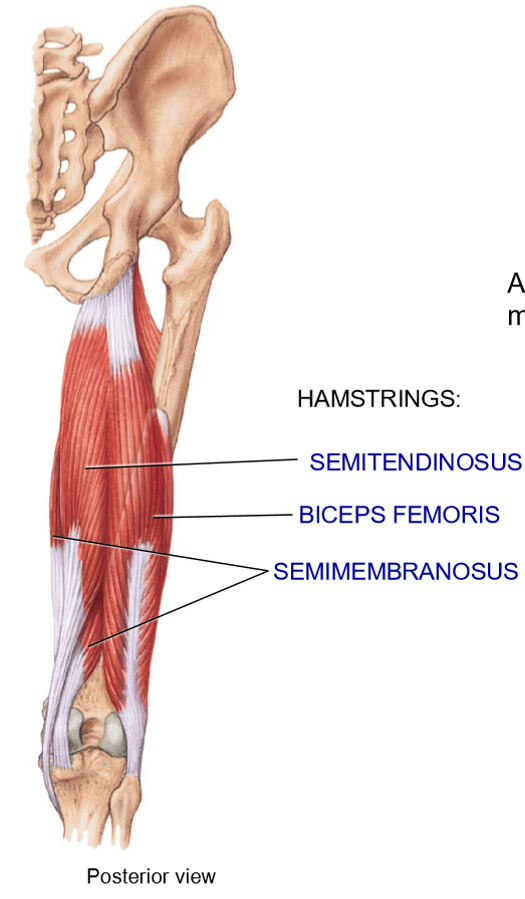
Name the muscles that move the leg
Hamstrings: posterior of thigh
Biceps femoris: lateral and superificial
Semitendinosus: Medial superficial
Semimembranosus: deep
What movements do the hamstrings produce?
Flexion of knee
Extension of hip
Biceps femoris performs lateral rotation of leg
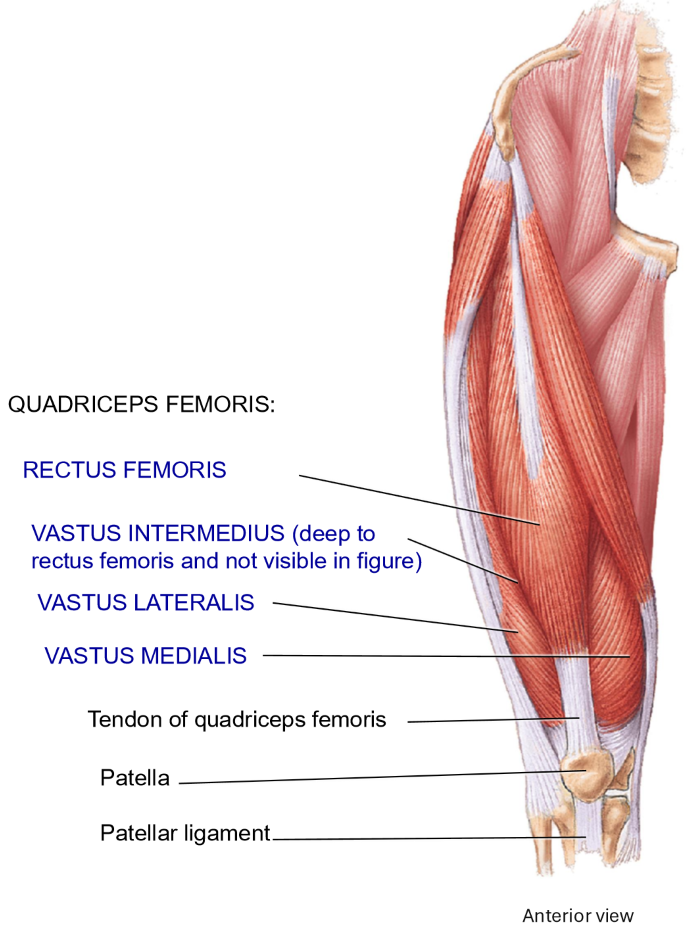
Leg extensors at the knee: Quadriceps femoris - Muscles + Structure + Movement
Anterior surface of thigh
Rectuc femoris: also does hip flexion
Originates at the hip
Vastus intermedius
Originates on femur
Vastus medialis
Originates on femur
Vastus lateralis
Originates on femur
Movement: Extension of the leg at the knee
All 4 quads muscles (leg extensors) joint into the…
Patellar tendon, covering the patella
Inserts on and around patella
Then continues as the patellar ligament
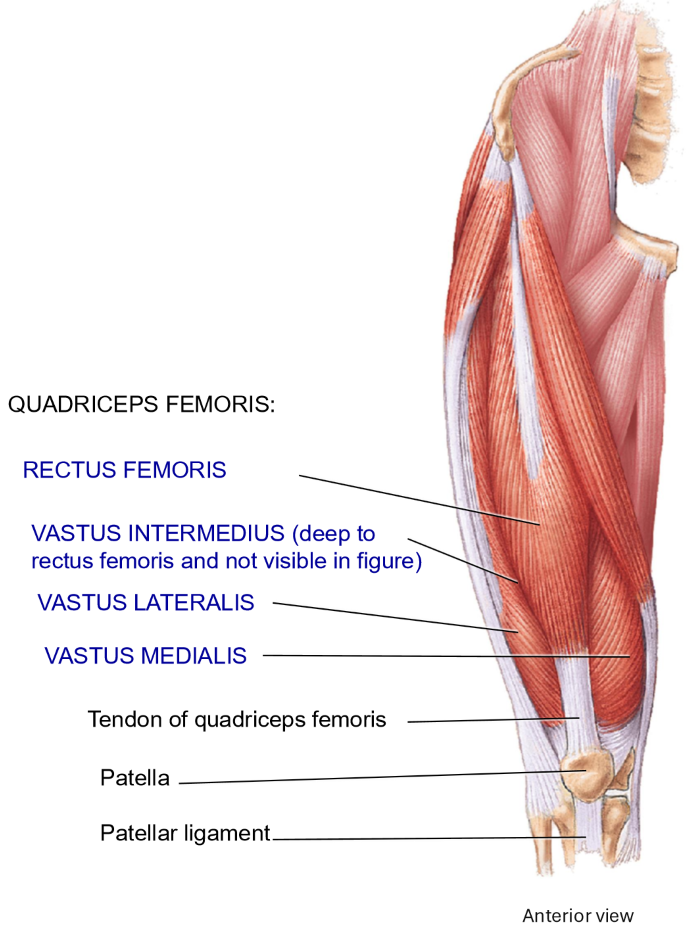
Where does the patellar ligament insert?
Tibial tuberosity
So it extends from the patella to the tibial tuberosity
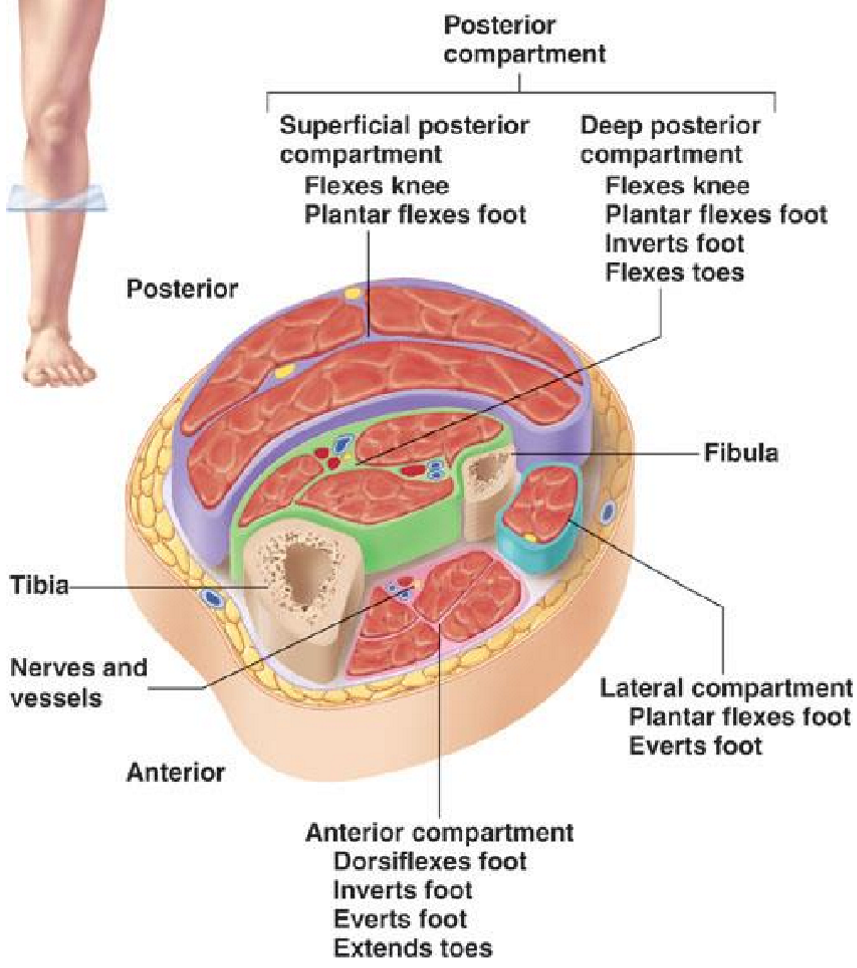
Name the 3 compartments of the leg
Anterior compartment
Lateral compartment
Posterior compartment: contains
superficial muscles
Deep muscles
Anterior compartment - Muscles + Movements
Muscle: extensors
Movements: dosriflexion, eversion, inversion of foot + extension of toes
Lateral compartment - Movement
Plantar flexion
Eversion
Posterior compartment - Muscles + Movement
Largest compartment, with superificial + deep groups
3 Superificial Muscles: their fascia merge into calcaneal tendon (achilles tendon)
Gastrocnemius: 2 heads, most superficial
Soleus: deep to gastrocnemius
Plantaris: small, high muscle (extends from heel-ish to back of knee ish)
Movement: plantar flexion
Deep muscles:
Movement: plantar flexion, inversion, flexion of toes
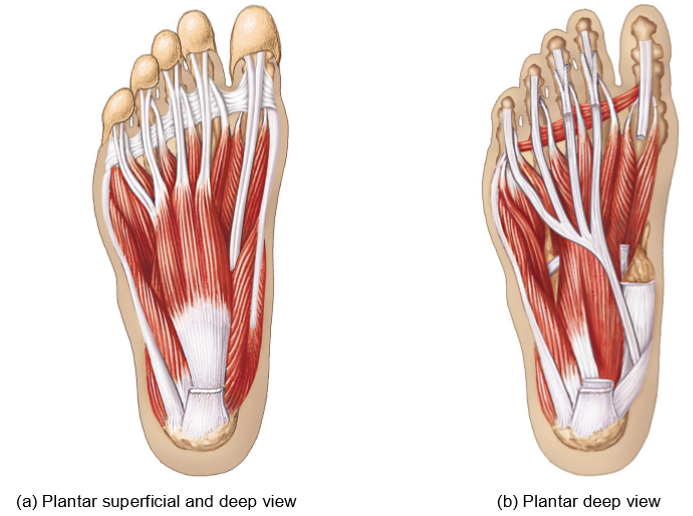
Extrinsic muscles of the foot - Structure + Movement + Function
Structure: Long muscle bellies in the leg with long tendons (reaching the toes)
Originates + inserts within the foot
Movement: flexion, extension, abduction, adduction of toes
Function: support the body’s weight, creat arches of foot, help with locomotion