General Chemistry Midterm: Chapter E-5.4
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
124 Terms
Compounds
When more than one element combines, they form this. (an element mixture)
SI Units
Based on the metric system.
Length
What is the unit “meter” used to measure?
Mass
What is the unit “Kilogram” used to measure?
Time
What is the unit “Second” used to measure?
Amount of Substance
What is the unit “Mole” used to measure?
Round it to the right number of Significant figures.
What can be done in order to make the number more precise?
mL or cm³
What units can Volume be written as?
The principal quantum number
What is the n symbolizes?
It symbolizes the angular number and tells us whether it is a s, p or d orbital.
What does the l symbolize and what does it tell us?
You find the number of radial nodes by looking at where the graph touches the x-axis.
How do you find the number of radial nodes?
They go from a high energy state to a low energy state.
How do electron configurations work?
When an electron goes from a high to a low energy state.
What is an Emission in an energy state change?
Going from a lower energy state to a higher energy state
What is an Absorption in an energy state change?
When electrons are unpaired and attracted to an external magnetic field.
What is a paramagnetic electron configuration?
Yes
Do electrons get ejected when there is more energy?
No
Do electrons get ejected when there is a low frequency?
It is the inverse of energy - if there is a lower wavelength there is a higher energy
What is wavelength’s relationship to energy?
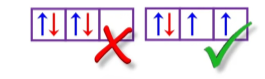
Pauli Exclusion Principle
When 2 electrons in the same species cannot have all four quantum numbers be equivalent. (Arrows cannot be equivalent in a s or p subshell)
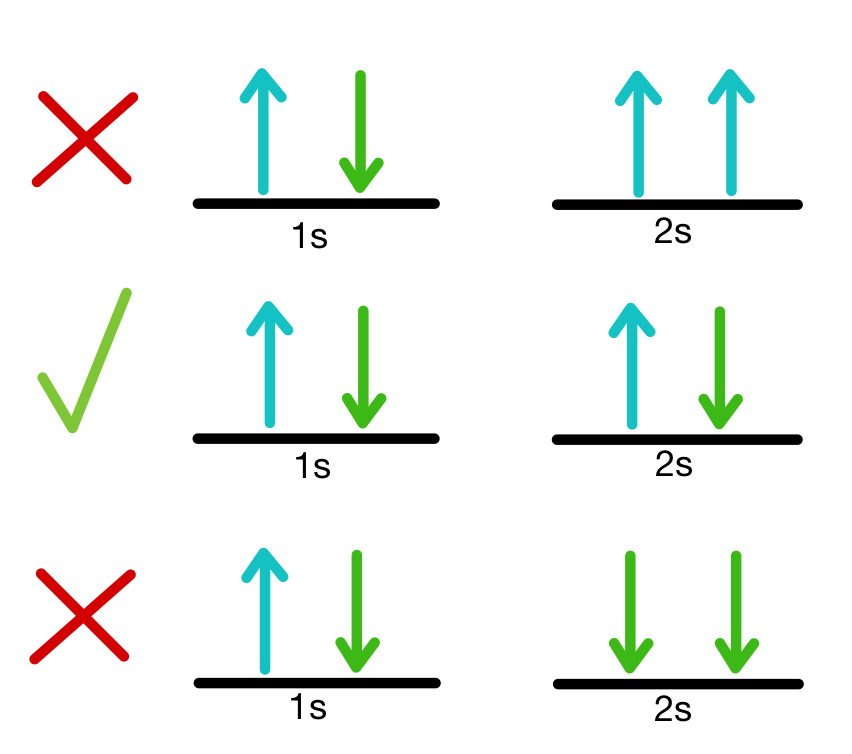
Hund’s Rule
every orbital in a subshell is singly occupied with one electron before any one orbital is doubly occupied, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals have the same spin.
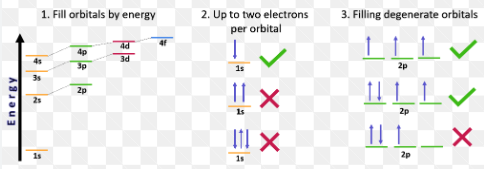
Aufbau Principle
This means that you have to start from the lowest energy state to the highest energy state.
Boron's size and high nuclear charge cause it to behave differently than other elements- Plus Boron’s 2s orbital is filled so their orbitals are more stable
Why is there an anomaly in the Boron and Beryllium element?
Nitrogen’s orbital is filled- making it more stable while Oxygen has half filled orbitals, causing electron electron replusion.
Why is there an anomaly in the Oxygen and Nitrogen element?
They want to lose electrons.
What are metal’s valence electrons like?
They want to get more stable.
What are nonmetal’s valence electrons like?
2+
What are the charges for Zn and Cd?
Cu, Ag, Au, Cr, and Mo
What are the elements that have abnormal electron configurations?
They lower it.
What does chemical bonding do to the potential energy of the atoms or ions that are bound together?
Covalent Bonding
When elements (nonmetals) share electrons.
Ionic Bonds
When metals and nonmetals transfer electrons.
More energy is released.
What happens in all chemical bonds?
It would be Polar Covalent
If the distance in a dipole moment is long, what does that mean for the bond? (Along with electronegativity difference)
Releasing energy
What does exothermic mean?
Energy entering
What does endothermic mean?
Pauling electronegativity
This is based on each element bonding to other elements. (bond strength, bond weakening, etc.)
Si-H and C-H
What are the 2 bonds that are NONPOLAR COVALENT
H₂, N₂, O₂, F₂, Cl₂, Br₂, I₂
What are the 7 diatomic molecules?
nanometers
What are the units used in wavelength?
Joules (sometimes eV if they ask for it)
What are the units used for Eₚₕₒₜₒₙ?
The bond strength weakens.
If the bond length increases, what happens to the bond strength?
It gets stronger.
If the bond length decreases, what happens to the bond strength?
They have high nuclear charge yet are low in energy.
What is a characteristic of a core electron?
they have low nuclear charge but they are high in energy.
What is a characteristic of valence electron?
Ionic Bonds
A bond formed between a metal and a nonmetal where electrons are not equally shared and they are transformed from one atom to another.
Covalent Bonds
Bonds formed between 2 nonmetals where valence electrons are shared between one another.
Chemical bond
The force that holds atoms together in a compound.
They lower the potential energy of the charged particles that compose atoms.
Why do chemical bonds form?
The one with the lowest potential energy.
What compound would be the most stable one?
Mono-
What is the Greek prefix for 1?
Di-
What is the Greek prefix for 2?
Tri-
What is the Greek prefix for 3?
Tetra
What is the Greek prefix for 4?
Penta
What is the Greek Prefix for 5?
Hexa-
What is the Greek Prefix for 6?
Hepta
What is the Greek Prefix for 7?
Octa
What is the Greek Prefix for 8?
Nona
What is the Greek Prefix for 9?
Deca
What is the Greek Prefix for 10?
Transition Metals
What type of metals will have Roman numbers in front of their name?
Acetate
CH₃COO⁻
Carbonate
CO₃²⁻
Bicarbonate ( hydrogen carbonate )
HCO₃⁻
Nitrate
NO₃⁻
Nitrite
NO₂⁻
Sulfate
SO₄²⁻
Sulfite
SO₃²⁻
Phosphate
PO₄³⁻
Hydrogen Phosphate
HPO₄²⁻
Dihydrogen Phosphate
H₂PO₄⁻
Oxalate
C₂O₄²⁻
Cyanide
CN⁻
Chromate
CrO₄²⁻
Dichromate
Cr₂O₇²⁻
Permangnate
MnO₄⁻
Peroxide
O₂²⁻
Azide
N₃⁻
Per- -ate
XO₄⁻
-ate
XO₃⁻
-ite
XO₂⁻
Hypo- -ite
XO⁻
Ammonium
NH₄⁺
Hydroxide
OH⁻
Hydronium
H₃O⁺
Pb (Lead) and Sn (Tin)
Which 2 elements would need Roman numerals in front of their compound names?
Chromium
Electron Configuration: [Ar] 3d5 4s1
Copper
Electron Configuration: [Ar] 3d10 4s1
Niobium
Electron Configuration: [Kr] 4d4 5s1
Molybdenum
[Kr] 4d5 5s1
Ruthenium
Electron Configuration: [Kr] 4d7 5s1
Rhodium
Electron Configuration: [Kr] 4d8 5s1
Palladium
Electron Configuration: [Kr] 4d10 5s0
Silver
Electron Configuration: [Kr] 4d10 5s1
Lanthanum
Electron Configuration: [Xe] 5d1 6s2
Actinium
Electron Configuration: [Rn] 6d1 7s2
Thorium
Electron Configuration: [Rn] 6d1 7s2
The ones within the same group and the same valence electrons.
What 2 elements would be more similar?
9.11E-31
What is the mass of an electron?
-1.602E-19 (e) 1.602E-19 (p)
What is the charge for either an electron or a proton?
3.336E-30
What unit would be used to convert dipole length?
4s
Which energy state is lower in this case: 4s or 4p?