Word Parts of the Nervous System
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what does the sensory system do
collects data from one’s surroundings and sends information to the brain by wires (aka nerves)
peripheral nervous system
nerves that send and receive signals from the brain
central nervous system
the brain and spinal cord
what is the largest portion of the brain
cerebrum
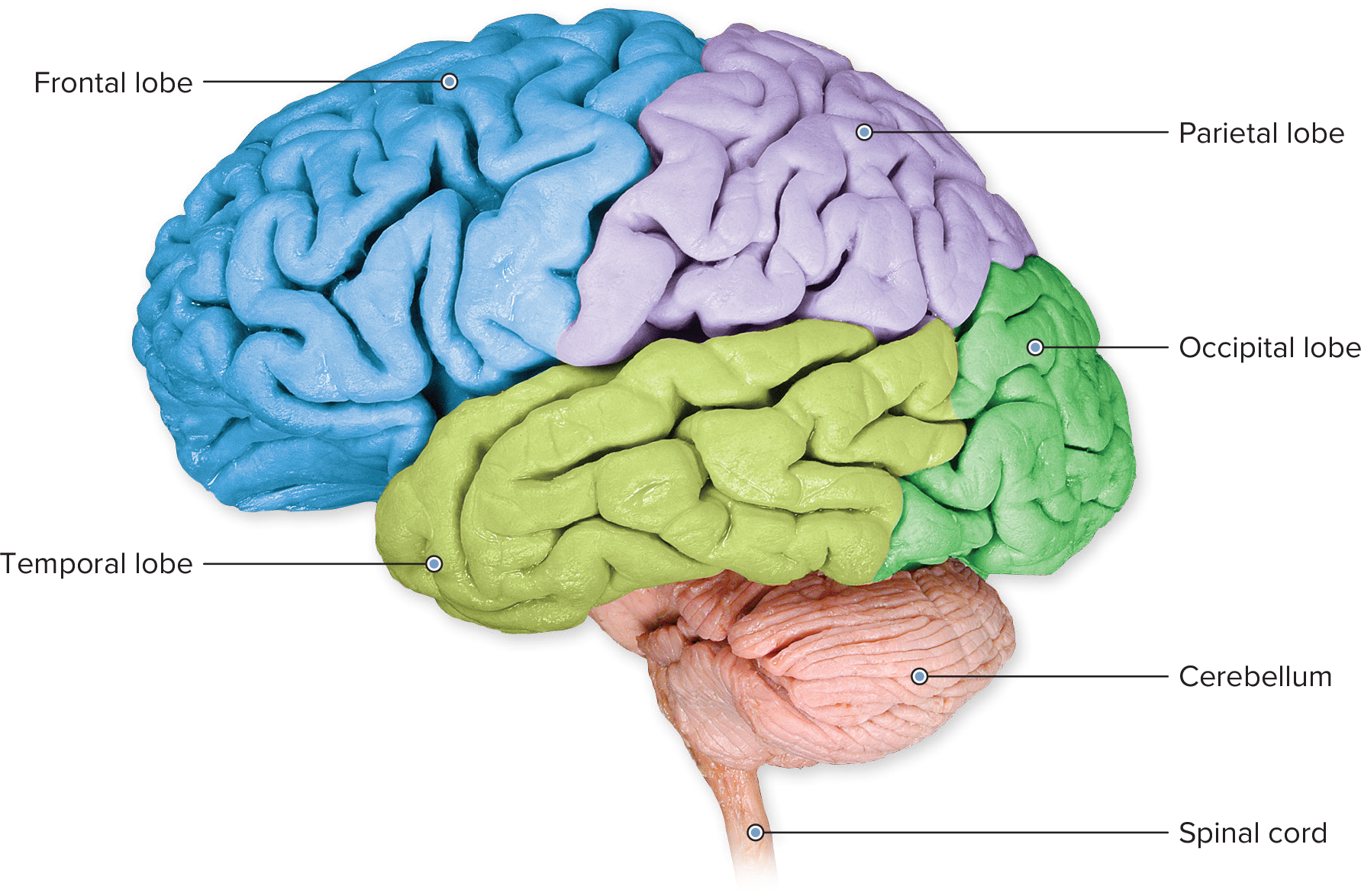
where and does the cerebellum do
under the cerebrum that controls things like coordination of movement
what is meninges
protective membrane to protect the central nervous system
what is the dura
the tough outer layer
cerebr/o - cerebrophathy
encephal/o - encephalitis
notes: encephalo root comes from en (inside) and cephalus (head), literally “the stuff inside the head”
brain
cerebell/o - cerebellar
cerebellum
notes: the word cerebrum plus diminutive suffix, it means “little brain,” referring to the region of the brain that controls voluntary movements and looks somewhat like a mini version of the whole brain
lob/o - lobotomy
lobe
notes: lobes are smaller subdivisions of any organ
cephal/o - microcephaly
head
crani/o - craniometer
head, skull
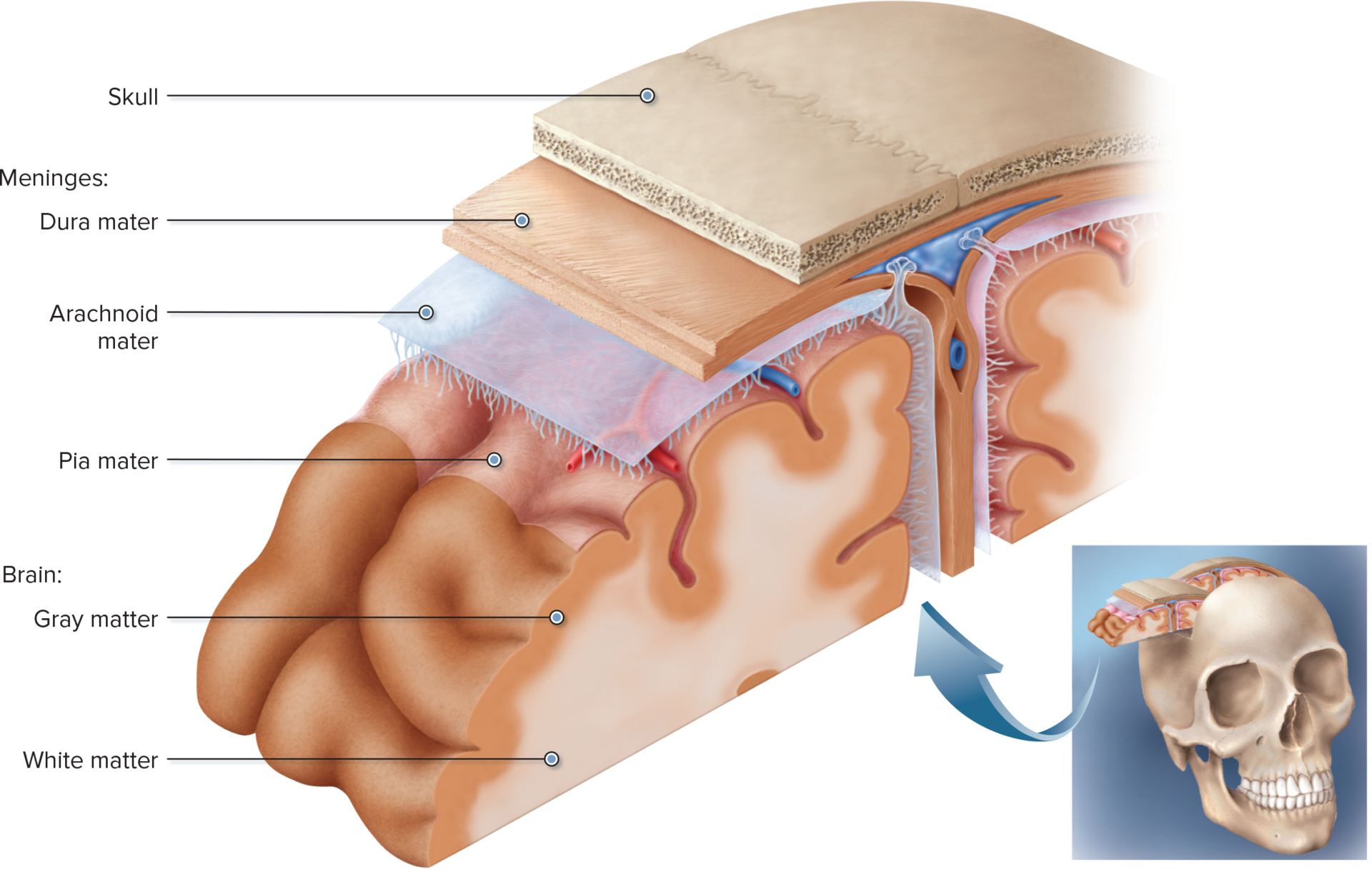
mening/o - meningitis
meningi/o - meningophathy
meninges (membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord)
dur/o - epidural
dura (tough outer membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord)
neur/o - neuralgia
notes: neuron comes from a Greek word meaning “tendon” or “string” because they thought neurons looked like string
nerve
gangli/o - ganglion
notes: according to Galen, ganglion means “knot” and could refer to anything gathered up into a ball
nerve bundle
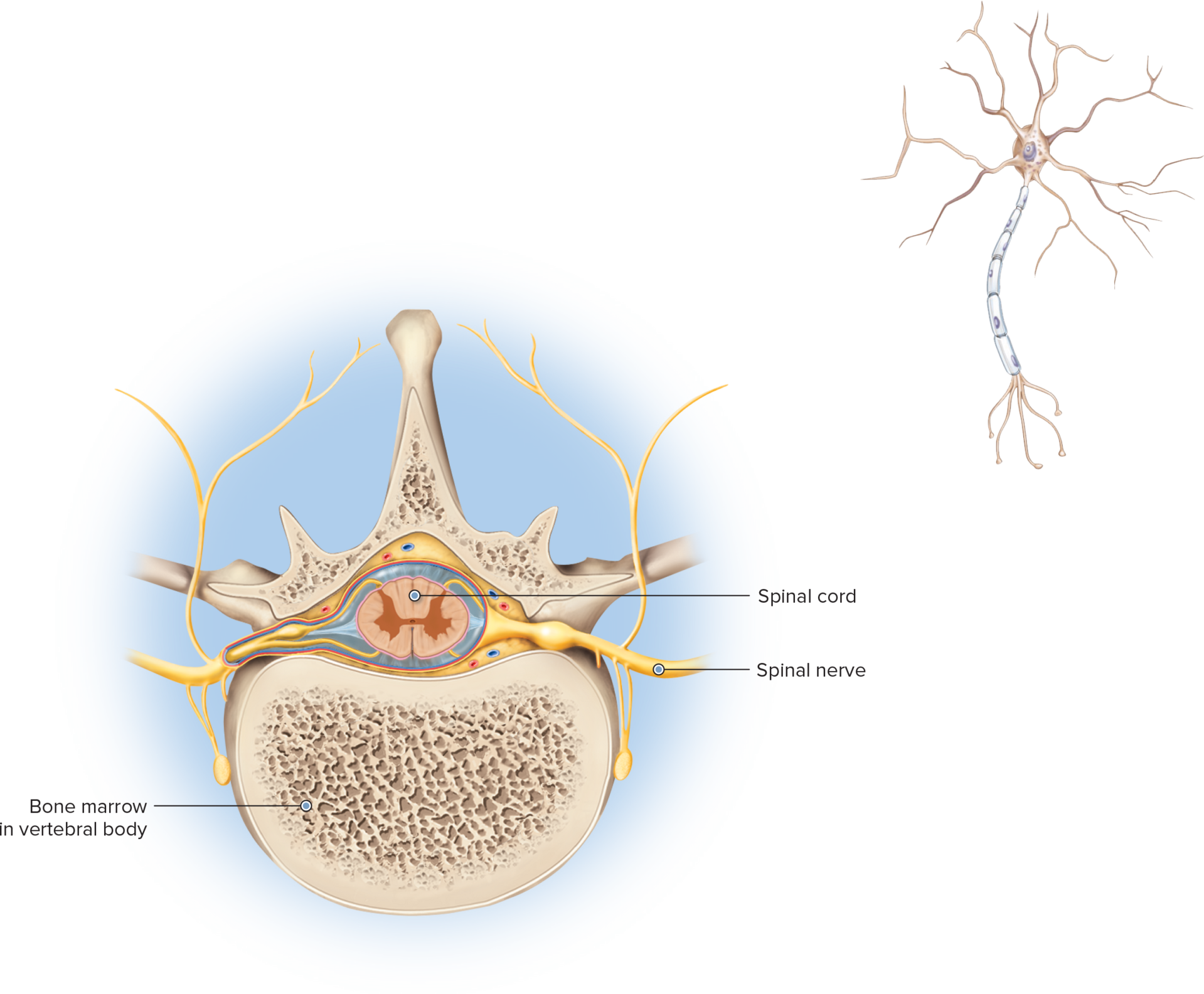
myel/o - myelitis
notes: the notes come from the Greek word “the innermost part” and refers to the bone marrow and spinal cord
spinal cord, bone marrow
what does neurology focus on
actions
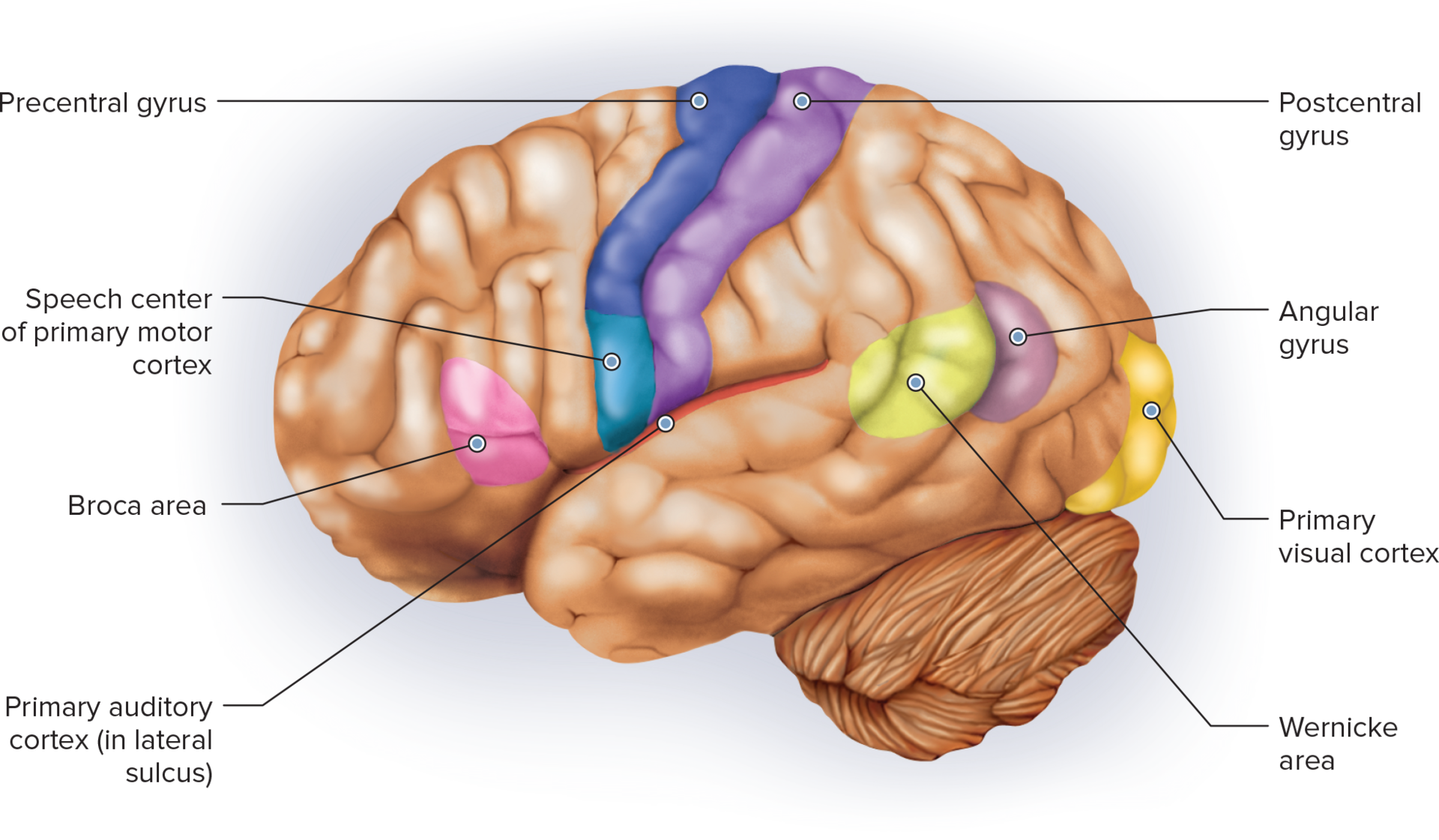
what does psychiatry and psychology study
study of human perceptions, emotions, and behavior
esthesi/o - anesthesia
feeling, sensation
phas/o - aphasia
speech
phren/o - phrenetic
psych/o - psychology
notes: phren/o, comes from Greek, can also refer to the diaphragm
mind
somn/o - somnography
somn/i - insomnia
hypn/o - hypnosis
sleep
gnosi/o - agnosia
know
-mania — pyromania
excessive desire
-phobia — photophobia
excessive fear or sensitivity
-paresis — hemiparesis
notes: paresis comes from the Greek word “to let go” or “to slacken”
slight or partial paralysis
ton/o - dystonia
muscle tone, tension, pressure
tax/o - ataxia
arrangement, order, coordination
-plegia — quadriplegia
notes: plegia comes from the Greek word “to strike”
paralysis
-asthenia — myasthenia
weakness