3.7 Homeostasis and the Kidney
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Define homeostasis
The process of maintaining the body in a state of dynamic equilibrium - a constant internal state despite changes in the external environment
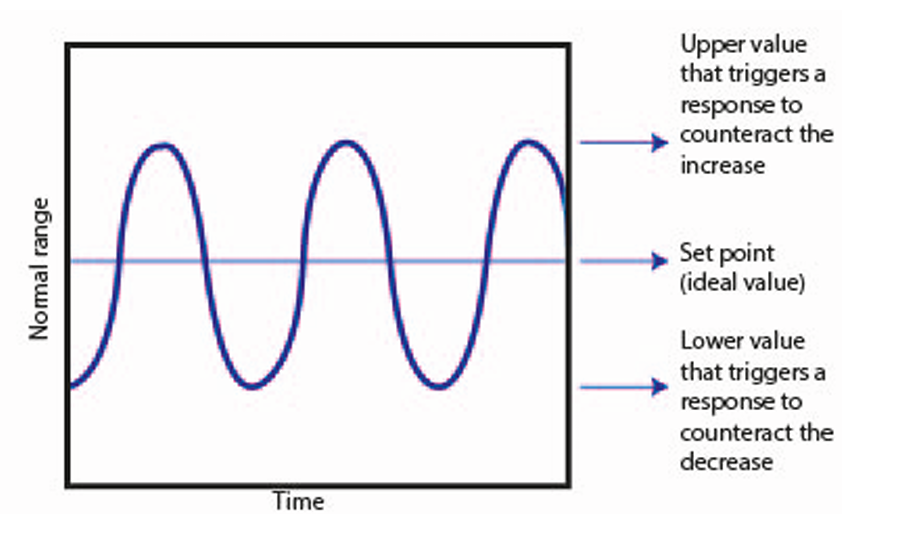
Define negative feedback
A change in a system produces a second change, which reverses the first change
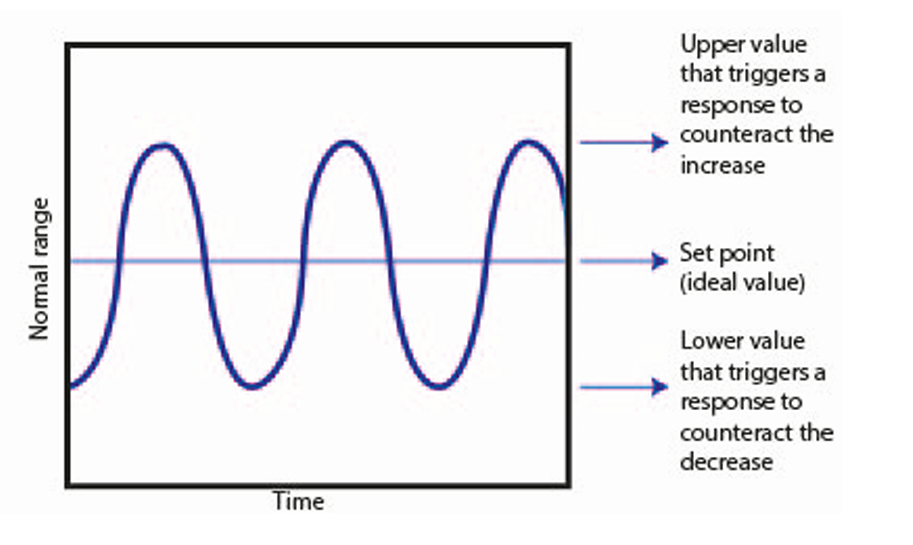
Define set point
The norm at which the system operates
State the series of stages in negative feedback
A receptor detects the level of the factor and its deviation from the set point
The receptor sends instructions to a co-ordinator
The co-ordinator communicates with one or more effectors which make responses that are corrective procedures
The factor returns to normal
Define positive feedback
In which an effector increases a change
What are the two main functions of the urinary system
Osmoregulation
Excretion
Define excretion
The removal of nitrogenous metabolic waste from the body
Define osmoregulation
The mechanism by which the balance of water and dissolved solutes in the plasma is regulated
Describe the production of urea
Protein is digested into amino acids
Excess amino acids are deaminated
Amino group is converted to ammonia and then to urea
Contents of blood from the aorta to renal arteries
Oxygenated
High level of urea
Contents of blood from renal veins to vena cava
Deoxygenated
Lower level of urea
State the three main regions to the mammalian kidney
Cortex, medulla and renal pelvis
Where do the renal arteries divide into arterioles
Cortex
Where is the site of osmoregulation
medulla
Where is the origin of the ureter
renal pelvis
Structures in the cortex
-Glomerulus
-Proximal Convoluted Tubule
-Distal Convoluted Tubule
Structures in the medulla
Collecting duct
Loop of Henle
Advantages of ammonia
Little energy needed to produce it
Highly soluble
Disadvantages of ammonia
Highly toxic in concentrated solution
Needs a very high volume of water for its excretion
Advantages of Urea
Less toxic than ammonia
Less water needed for its excretion
Disadvantages of Urea
More energy needed to produce urea than ammonia
Advantages of uric acid
Very low toxicity
Low solubility
Low volume of water needed for its excretion
Disadvantages of uric acid
High energy required to produce uric acid
Habitats that require ammonia as a nitrogenous waste
water
Habitats that require urea as a nitrogenous waste
terrestrial in conditions with adequate water supply
Habitats that require uric acid as a nitrogenous waste
Terrestrial in arid conditions
Define ultrafiltration
Filtration under high pressure
How does the blood arriving in the capillaries of the glomerulus from the afferent arteriole high pressure
-The afferent arteriole ha a wider diameter than the efferent arteriole
The heart's contraction
What are the three layers separating the blood entering the glomerulus from the inside of the Bowman's capsule
The wall of the capillary
The basement membrane
Podocytes
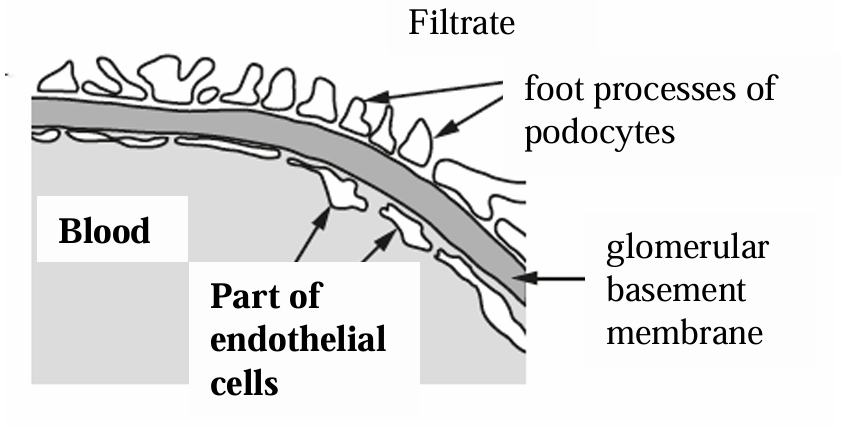
Describe the wall of the capillary
A single layer of endothelium cells with pores called fenestrations
Describe basement membrane
An extracellular layer of proteins, mainly collagen and glycoproteins
Describe podocytes
Squamous epithelial cells
Explain the role of the basement membrane
act as a selective barrier
Explain the role of podocytes
Pedicels wrap around a capillary pulling the podocyte closer to the basement membrane
Name the gaps between pedicles
filtration slits
How is the efficiency of filtration increased
Feet of podocytes increase surface area for filtration
The short distance between the podocytes and the capillary
Channels between the feet of the podocytes increase the concentration gradient between the tissue fluid
What is in the glomerular filtrate
water, glucose, salts, urea, amino acids
Describe the net filtration pressure
Hydrostatic pressure of the plasma is high
Osmotic pressure of the plasma is lower than that of the filtrate due to the presence of plasma proteins
Fluid pressure in the Bowman's capsule increases as the volume increases
Where does selective reabsorption mostly take place
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
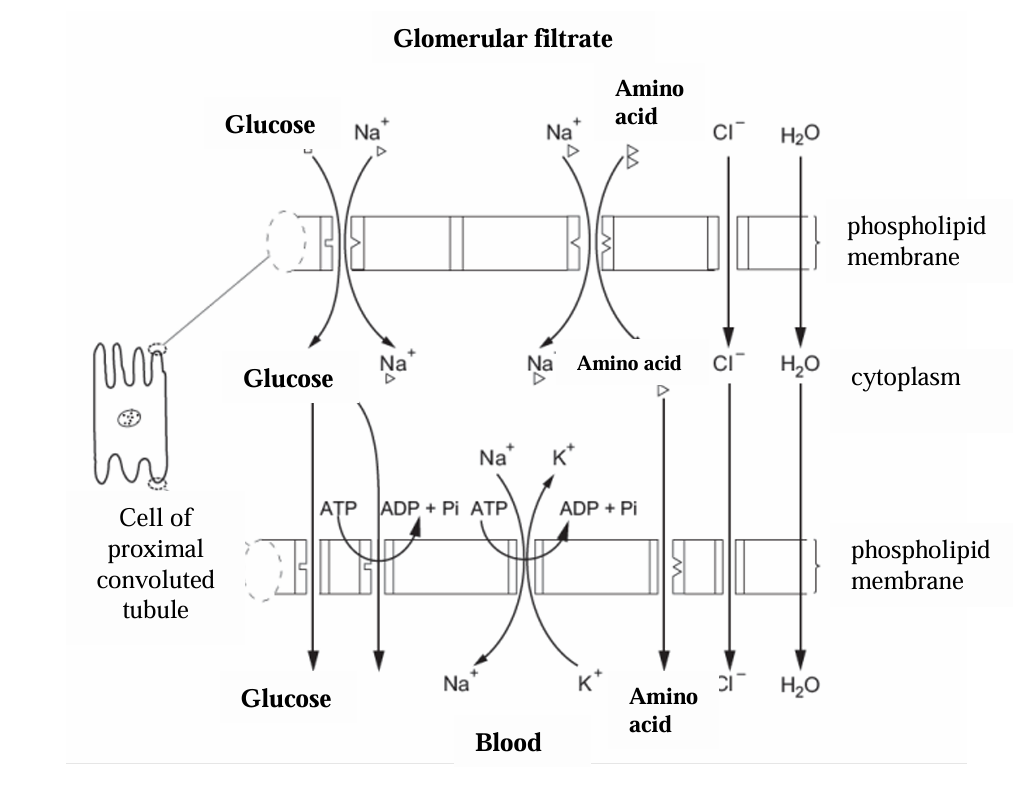
State how the PCT is suited to selective reabsorption
A large surface area because it is long
Microvilli on cuboidal epithelial cells
Basal channels
Many mitochondria
Close association with capillaries
Large amount of RER and golgi body
Why does the PCT have many mitochondria
Provide ATP for active transport
How much glucose and amino acids are reabsorbed in PCT
ALL
Why does PCT have microvilli
Increase surface area
Why are the capillaries in closes contact with PCT
Reduce diffusion distance
Constant blood flow increases concentration gradient
Why does the PCT have basal channels
Increases surface area
Concentration increases in channels so increases concentration gradient
Why does the PCT have a large amount of RER and golgi bodies
Production of proteins for facilitated diffusion and active transport
How is water reabsorbed in the PCT
By osmosis from a high water potential gradient in the filtrate to a lower water potential in the cytoplasm of PCT cells. Water then moves into the tissue fluid and then the blood
How are glucose and amino acids reabsorbed
Co-transport
Glucose or amino acid and two Na+ ions bind to a carrier protein in the cuboidal epithelium cell membrane
They enter the cell by facilitated diffusion
Na+ ions are pumped into the capillary reducing their concentration in the epithelial cell below that of the lumen.
More Na+ enters the cell bringing in glucose or an amino acid molecule
Glucose or amino acid enters the capillary by facilitated diffusion
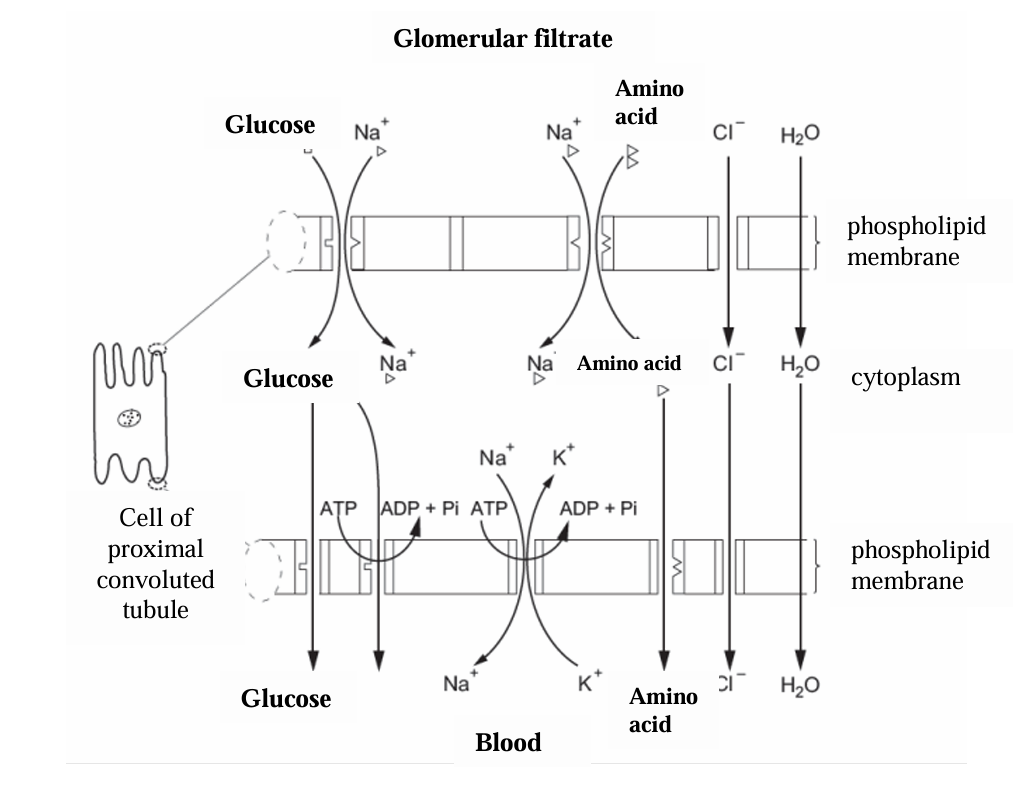
Why is Co-transport of glucose called secondary active transport
it is not using energy from ATP directly but uses energy from the electrochemical gradient of Na+ ions from the lumen into the cell which was generated by the active transport of Na+ into the capillary
How are chloride ions reabsorbed in the PCT
They follow the sodium ions down an electrochemical gradient
What happens to the water potential as the filtrate travels along the PCT and why
it increases because ions and polar substances are reabsorbed into the blood
Why does the sodium ion concentration stay the same throughout the PCT
it is reabsorbed at the same rate as water
Why does concentration of urea increase in the PCT
It is not reabsorbed
Volume of filtrate decreases
State the permeability of the descending limb
Permeable to water
State what happens to the water in the descending limb
Leaves the filtrate into the tissue fluid of the medulla by osmosis and then it moves to the vasa recta
State what Na+ and Cl- do in the descending limb
diffuse into the descending limb from the medulla
When is the filtrate at its most concentrated in the loop of Henle
at the bottom of the hairpin
State the permeability of the ascending limb to water
Impermeable
How is the low water potential in the medulla maintained
sodium and chloride ions are actively transported out of the filtrate in the tubule to the tissue fluid in the medulla
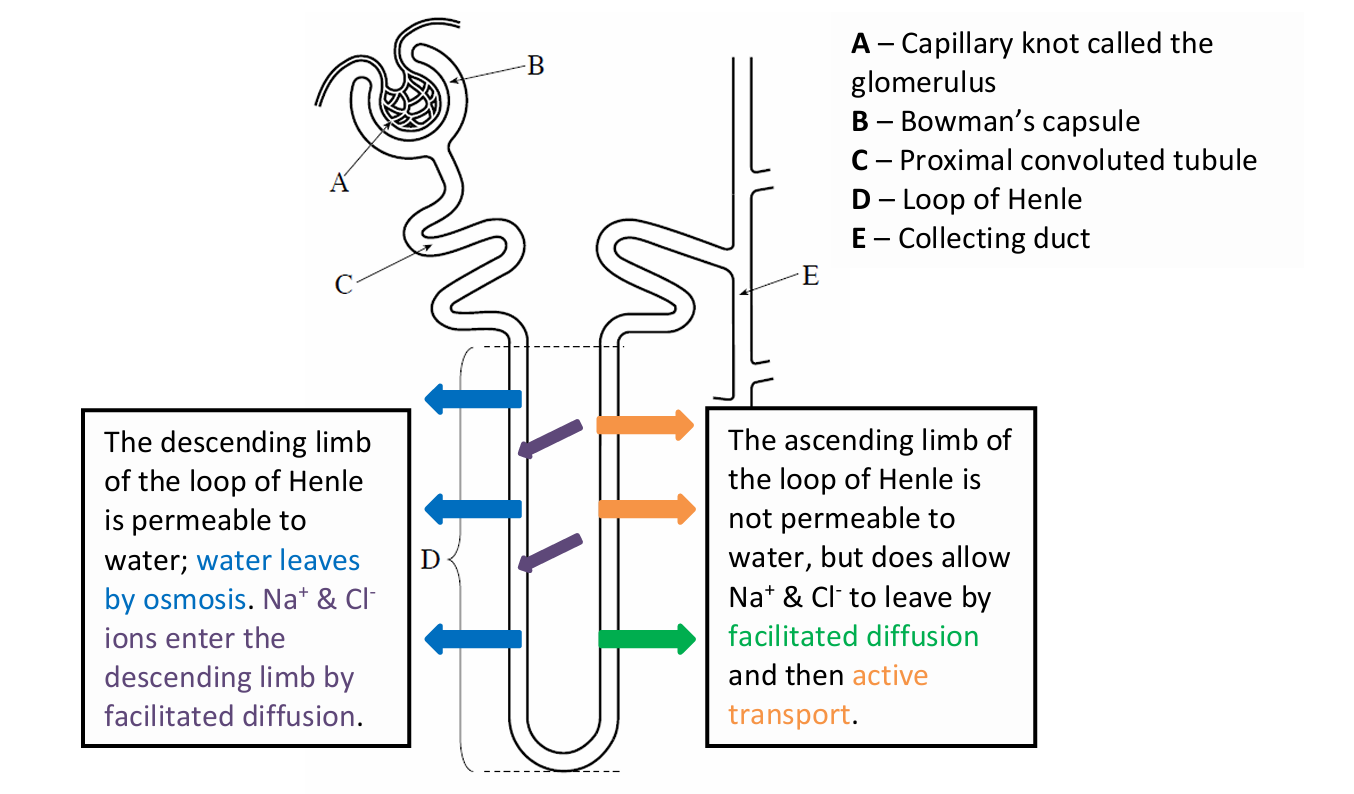
What is the mechanism in the loop of Henle called
Counter-current multiplier
What does the vasa recta act as in water reabsorption
Counter current exchanger
What does a longer loop of Henle cause
more ions can be pumped into the medulla. This lowers the water potential of the medulla allowing more water to be reabsorbed into the bloodstream by osmosis
Describe the steps of osmoregulation when there is an increase in the water potential of the blood
Detector/ receptor - Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect higher water potential of the blood and send a nervous impulse to the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland
Coordinator - Posterior lobe of the pituary gland releases less ADH into the blood.
Effector -Permeability of collecting duct and distal convuluted tubule to water decreases
Describe the steps of osmoregulation when there is a decreases in water potential of blood
Detector - Osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus detect low water potential of the blood and send a nervous impulse to the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland
Coordinator - Posterior lobe of the pituitary gland releases more ADH into the blood.
Effector - Permeability of collecting duct and distal convuluted tubule to water increases
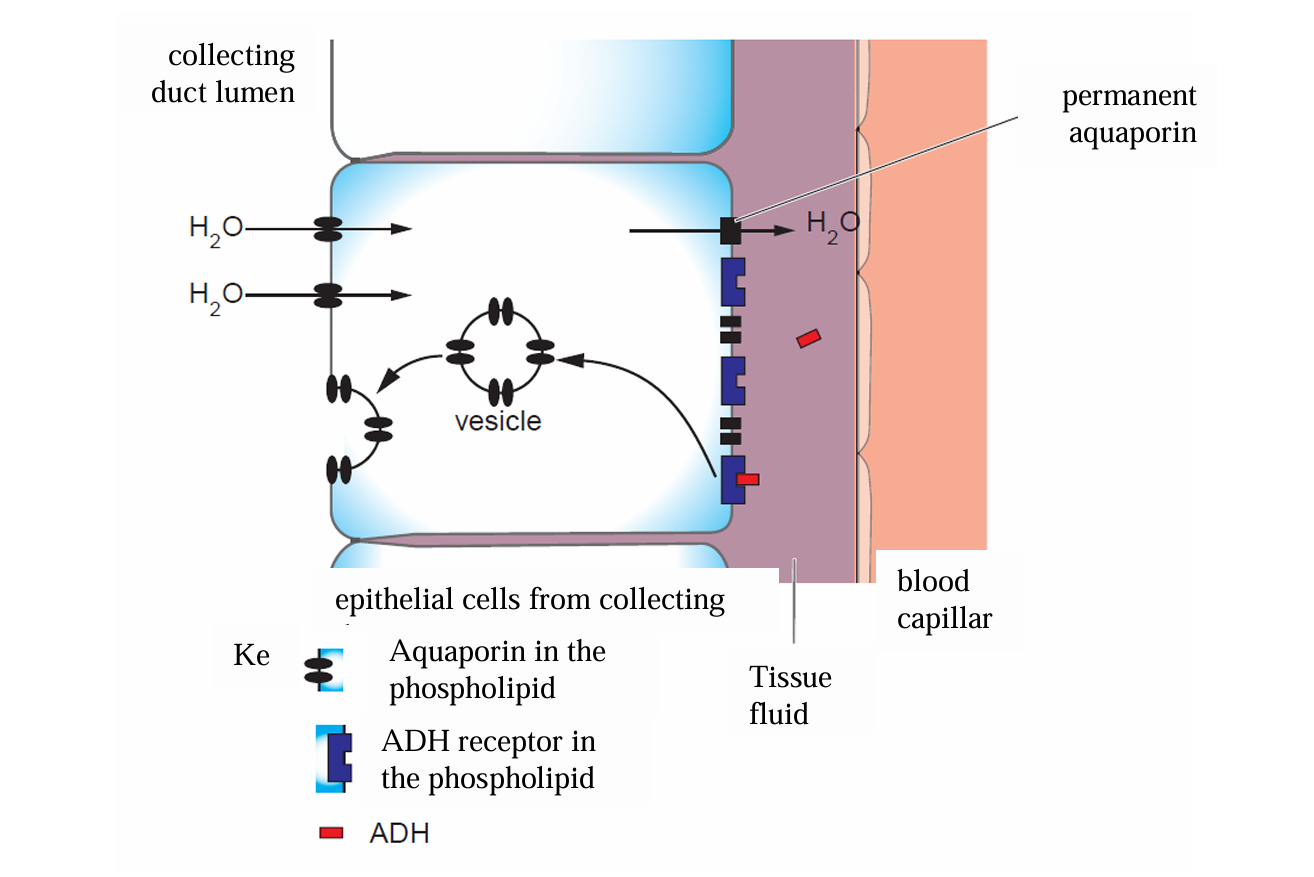
State the result of less ADH being released
Fewer aquaporins are inserted into the membrane of cells in the collecting duct
Less water is reabsorbed from the collecting duct and distal convoluted tubule
Larger volume of less concentrated urine produced
State the result of more ADH being released
More aquaporins are inserted into the membrane of cells in the collecting duct
More water is reabsorbed from the collecting duct and distal convoluted tubule
Smaller volume of more concentrated urine produced
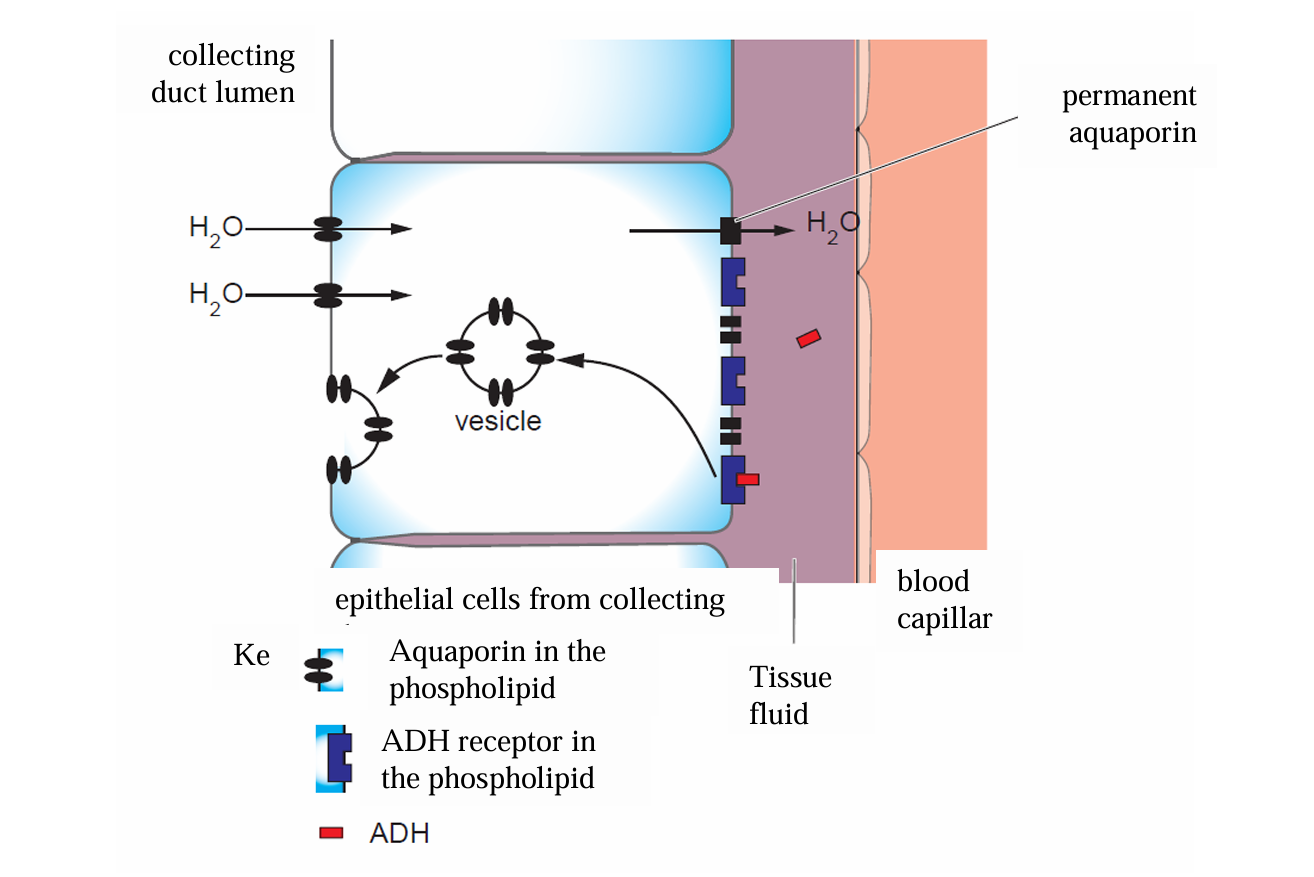
Where does ADH bind to
receptors on the membrane
What can a fall in water potential be caused by
Reduced water intake
Sweating
Intake of large amount of salts
Another name for ADH
vasopressin
What does ADH stand for
antidiuretic hormone
State common causes for kidney failure
diabetes
high blood pressure
autoimmune disease
infection
crushing injuries
Problem with a high protein diet
increased urea levels which can be converted into uric acid, this can crystalise and form kidney stones which can tear and damage tissues
Problem of high blood pressure
excessive filtration by the glomeruli and loss of nutrients
Leads to damage to the glomerulus which if severe can lead to cells and plasma proteins being lost in the urine
Define haemodialysis
using a dialysis machine to remove excess water, urea and ions from the plasma
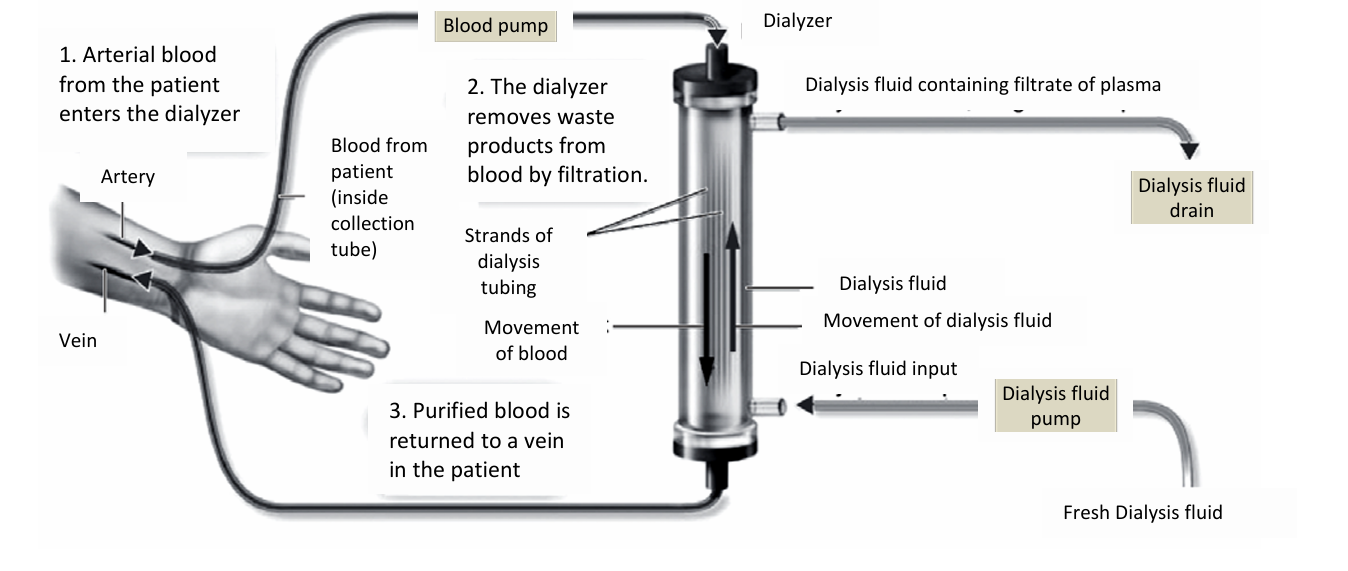
Define peritoneal dialysis
uses selectively permeable membranes in the body to remove excess water, urea and ions from the plasma
Advantages of haemodialysis
Effective removal of waste products
Care given by trained professionals
Rapid correction of electrolyte imbalances
Treatment usually occurs only three times a week
Disadvantages of haemodialysis
Vascular access surgery required
Schedule inflexibility
Must travel to centre 3 times a week
Risk of bacteraemia
Cramping with unltrafiltration
Advantages of peritoneal dialysis
Schedule flexibility
Few risks of dialysis associated cramps
clinic visits limited to 1 - 2x a month
No need for vascular access
Disadvantages of peritoneal dialysis
Permanent external catheter
Risk of peritonitis
Must store dialysis equipment at home
Need for self monitoring care
Where there is complete failure of the kidneys what is the treatment
Kidney transplant
What can result in a rejection to a transplanted kidney
differences in blood groups and in the antigens on the surface of cells
Advantages of living donor
Shorter waiting time
Less risk of rejection
Lasts longer
Donor makes informed decision
Disadvantages of living donor
Pressure on potential donors
Donor only has one kidney
Risk to donor and recipient from surgery
Advantages of deceased donor
Feel healthier
Have more energy
Be able to work and travel
Deceased donors not harmed in surgery
Disadvantages of deceased donor
Long waiting times
Pain following surgery
Could reject kidney
Need to take immunosuppressive drugs for the rest of your life
Increased risk of infection
Lasts less time
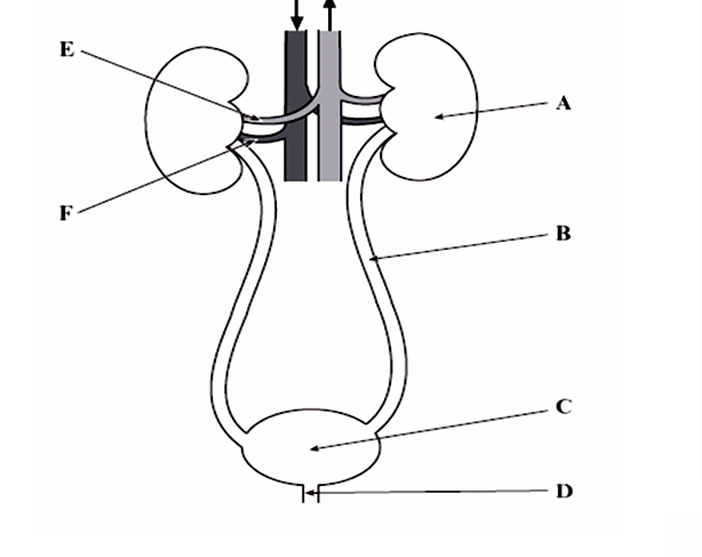
A – Kidney
B – Ureter (transports urine to the bladder)
C – Bladder (stores urine)
D – Urethra (carries urine out of the body)
E – Renal vein (blood returns to the general circulation)
F – Renal artery (blood enters the kidney)
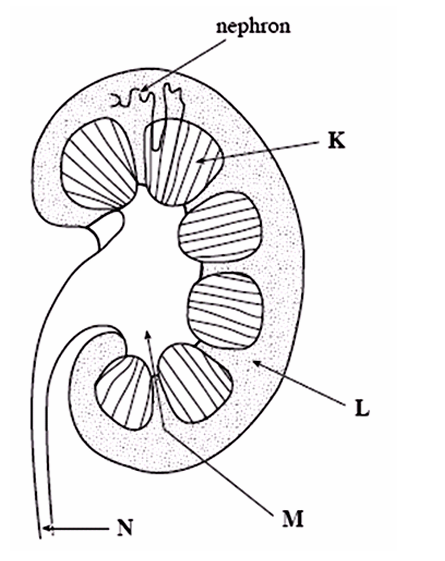
K – Medulla (reabsorption of water occurs here)
L – Cortex (ultrafiltration and selective reabsorption occurs in this region)
M – Pelvis (empties urine into the ureter)
N – Ureter (transports urine to the bladder)