1.3 - Refraction & Lenses - Theory
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Refraction
The bending of a wave as it passes at an angle from one medium to another.

Laws of Refraction
1) The incident ray, the refracted ray, and normal all lie in the same plane.
2) The angle of incidence and the angle of refraction are related by snells law (n = index of refraction)
n = sini / sinr
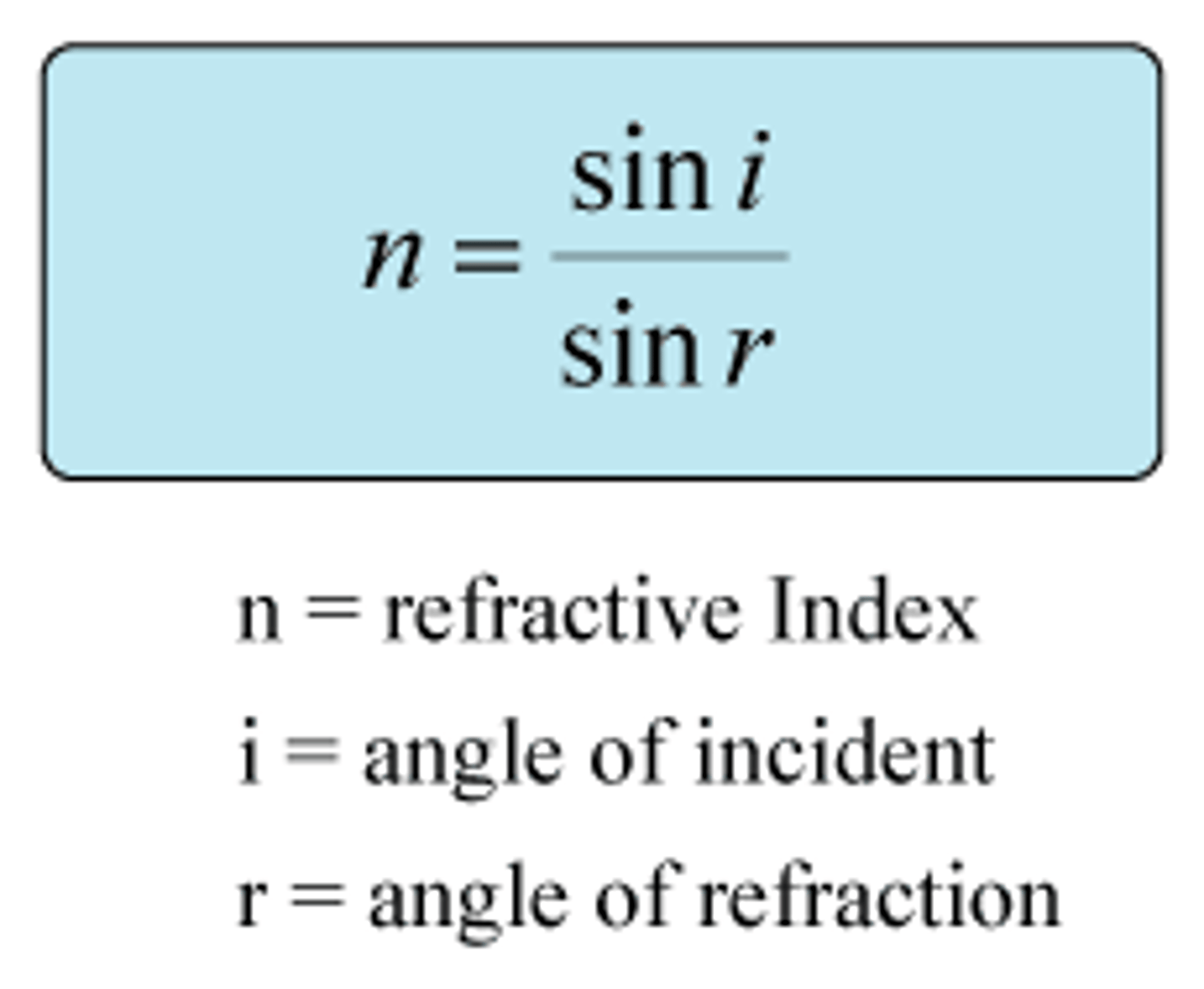
Refractive Index Equation for light (using incident and refracted angles)
n = sin i / sin r (where i is the less dense medium)
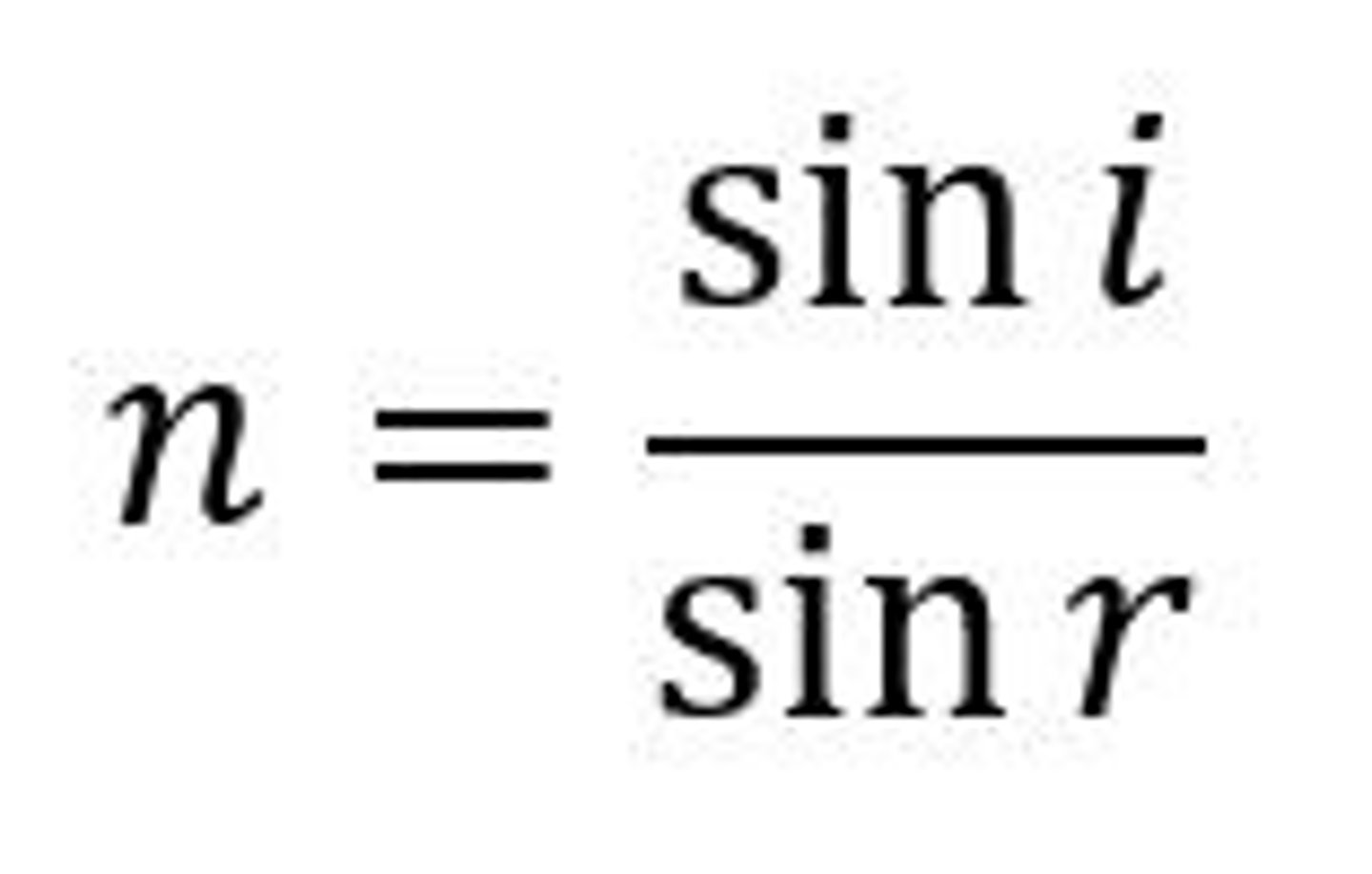
Refractive Index Equation for light (using wavelengths)
n = wavelength less dense / wavelength more dense
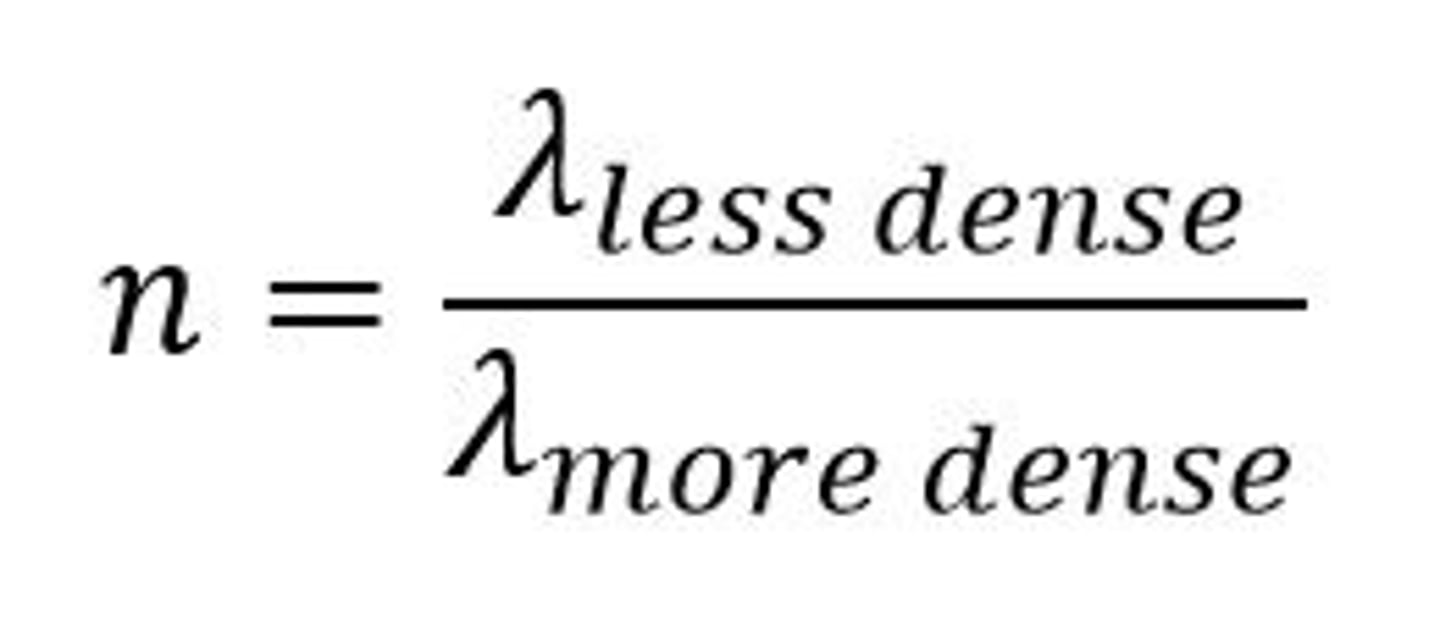
Refractive Index Equation for light (using velocities)
n = v less dense / v more dense
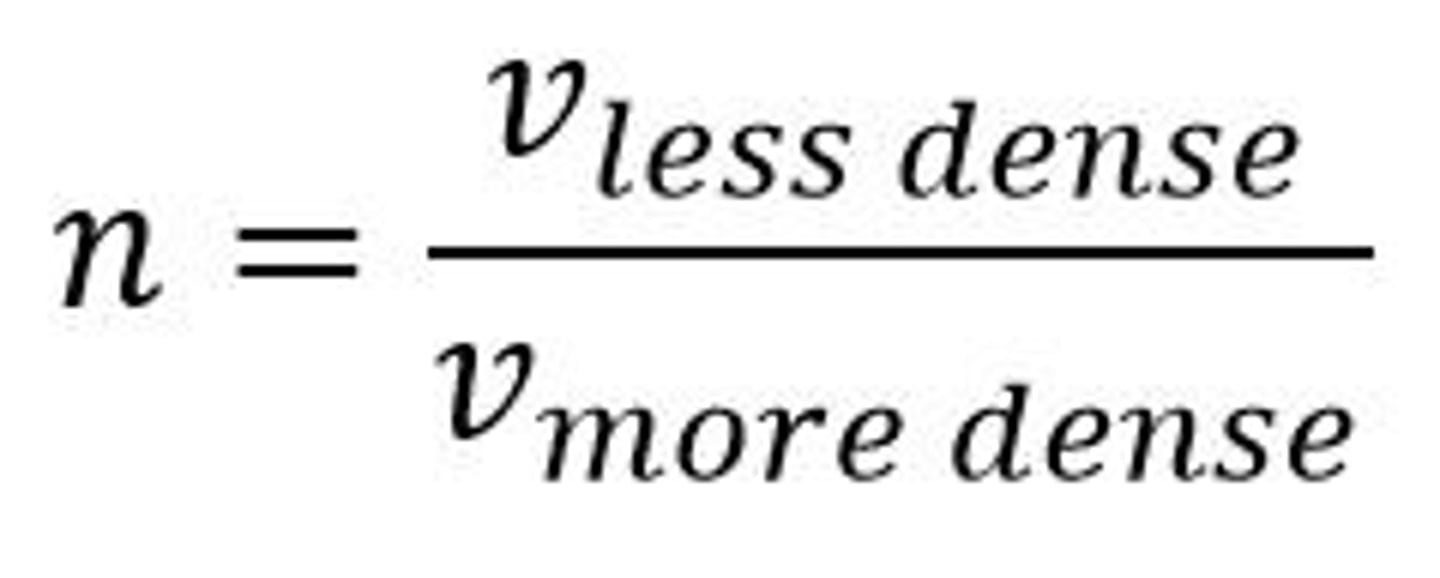
Refractive Index Equation (using depth)
n = real depth / apparent depth

Refractive Index Equation (All equations for general use)
n2/n1 = sin i / sin r = c/v = c1/ c2 = 1/sinC
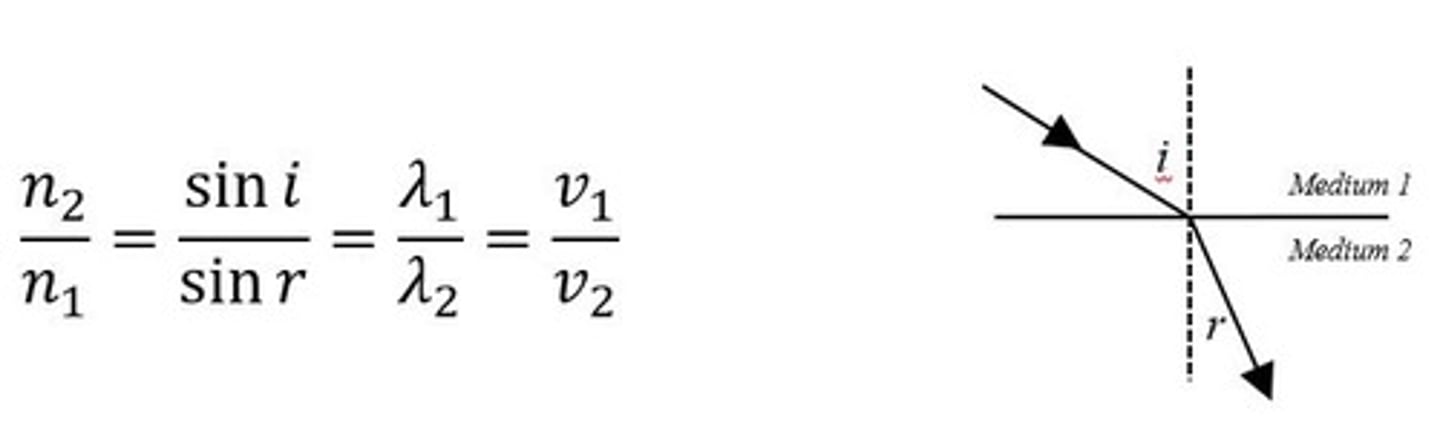
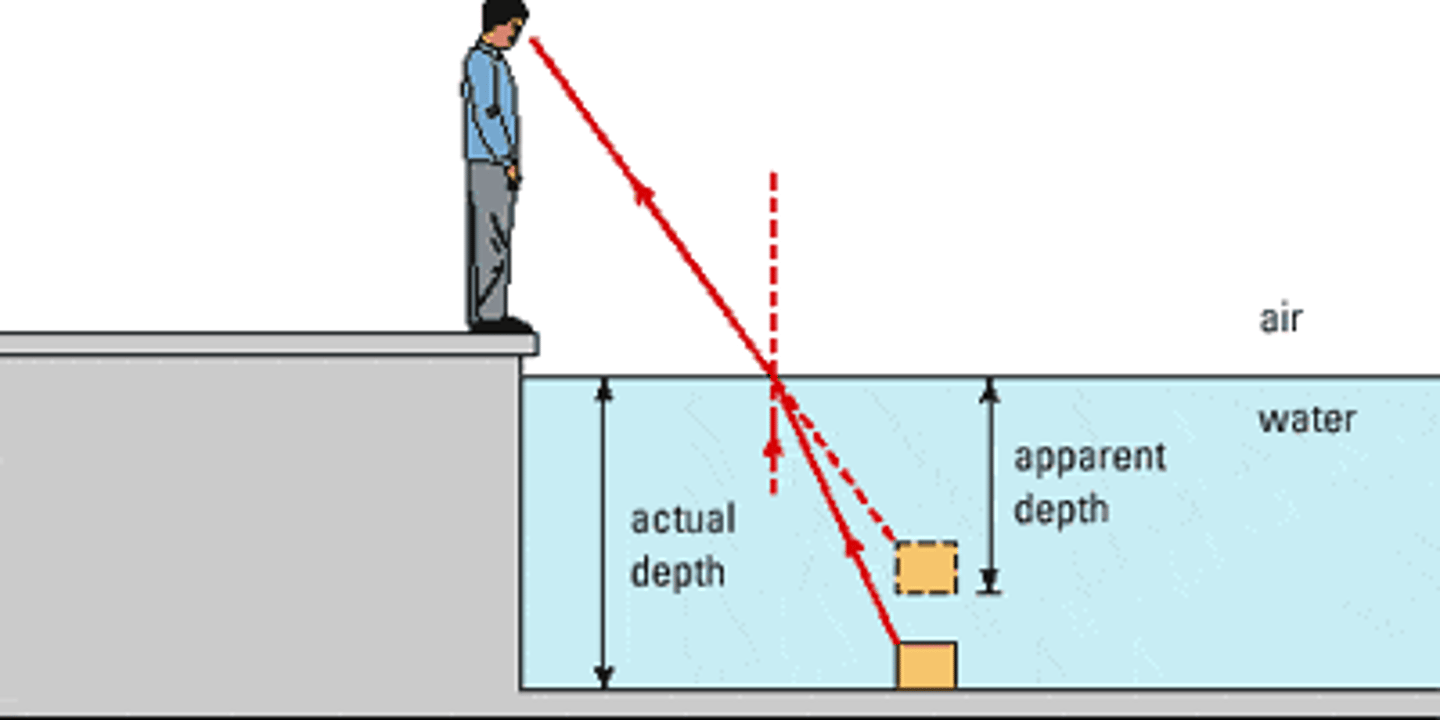
Why does an object appear shallower in water than at their actual depth?
Light rays get bent away from the normal as they go from water into the air. The observer thinks the emergent ray (and image) are higher than the actual object.
Critical Angle
When travelling from a more dense medium to a less dense medium, it is the angle of incidence that produces an angle of refraction of 90 degrees
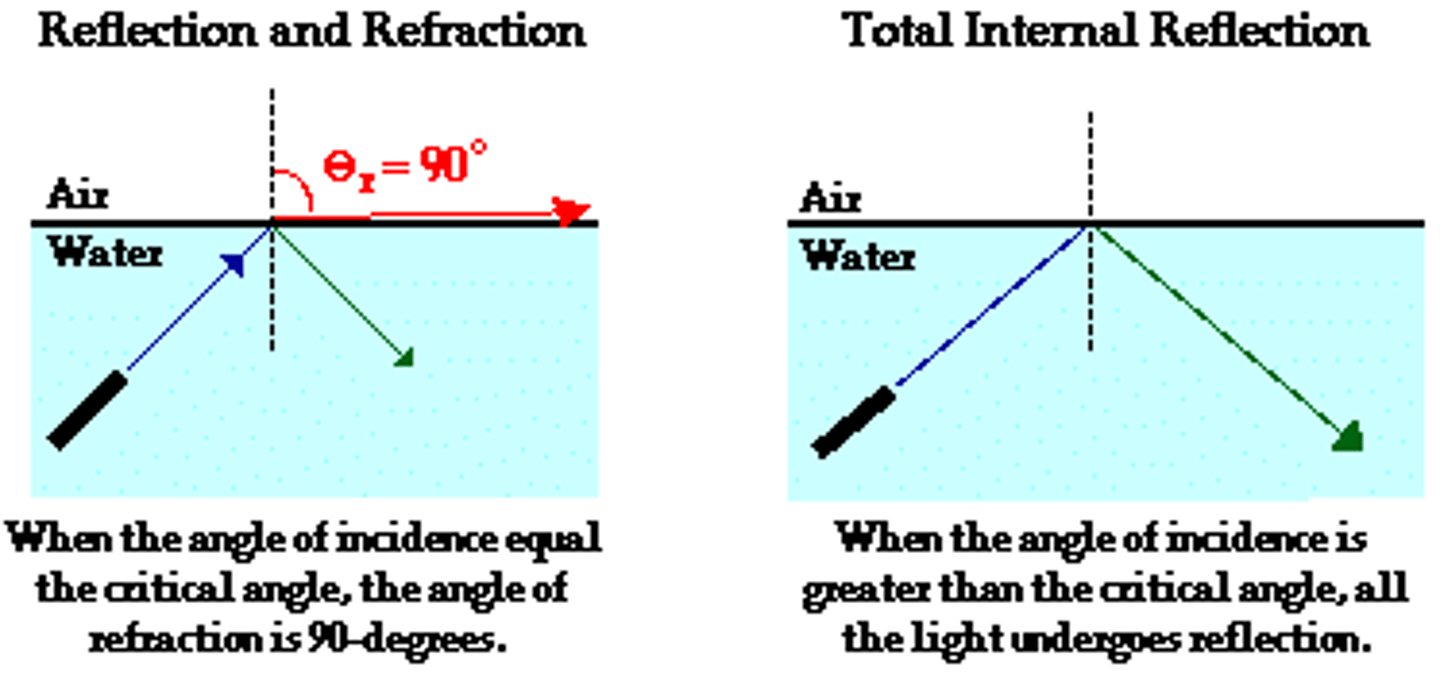
Critical angle equation
n = 1/sin C
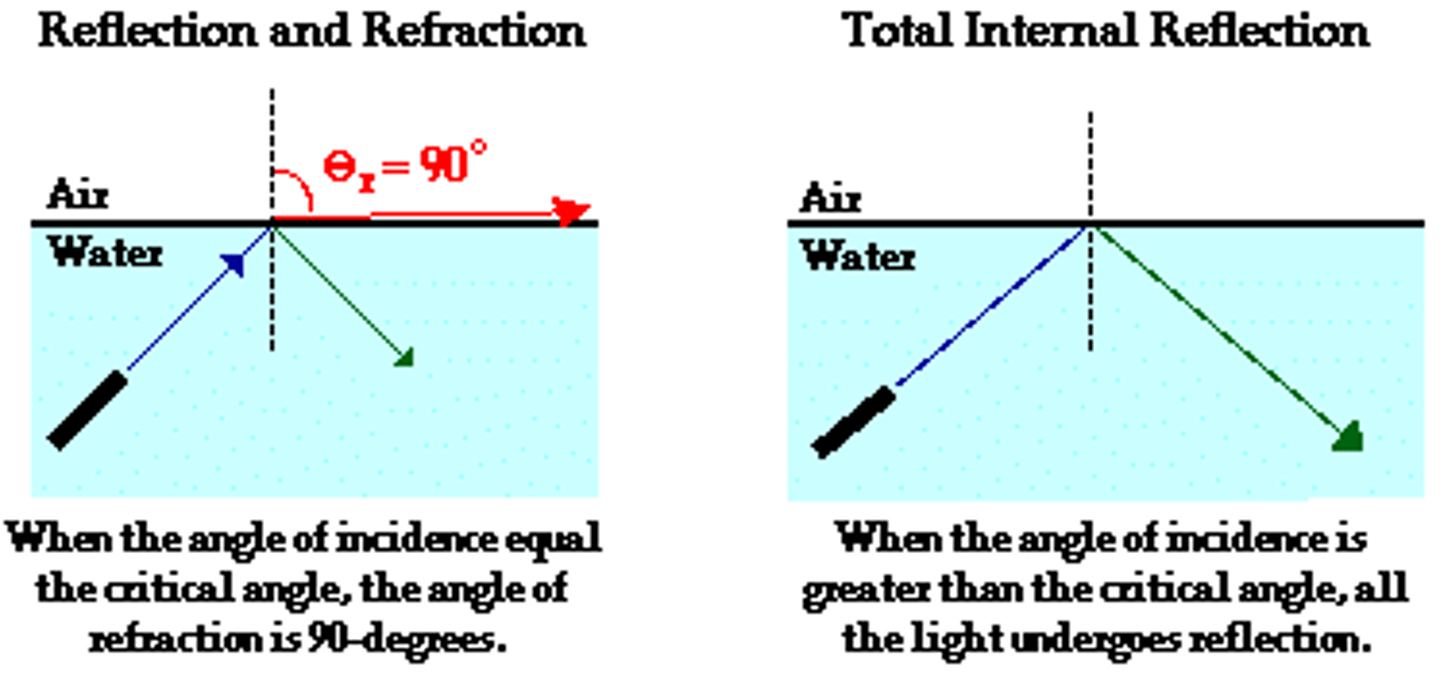
Total Internal Reflection
The complete reflection that takes place within a substance when the angle of incidence of light striking the surface boundary is greater than the critical angle
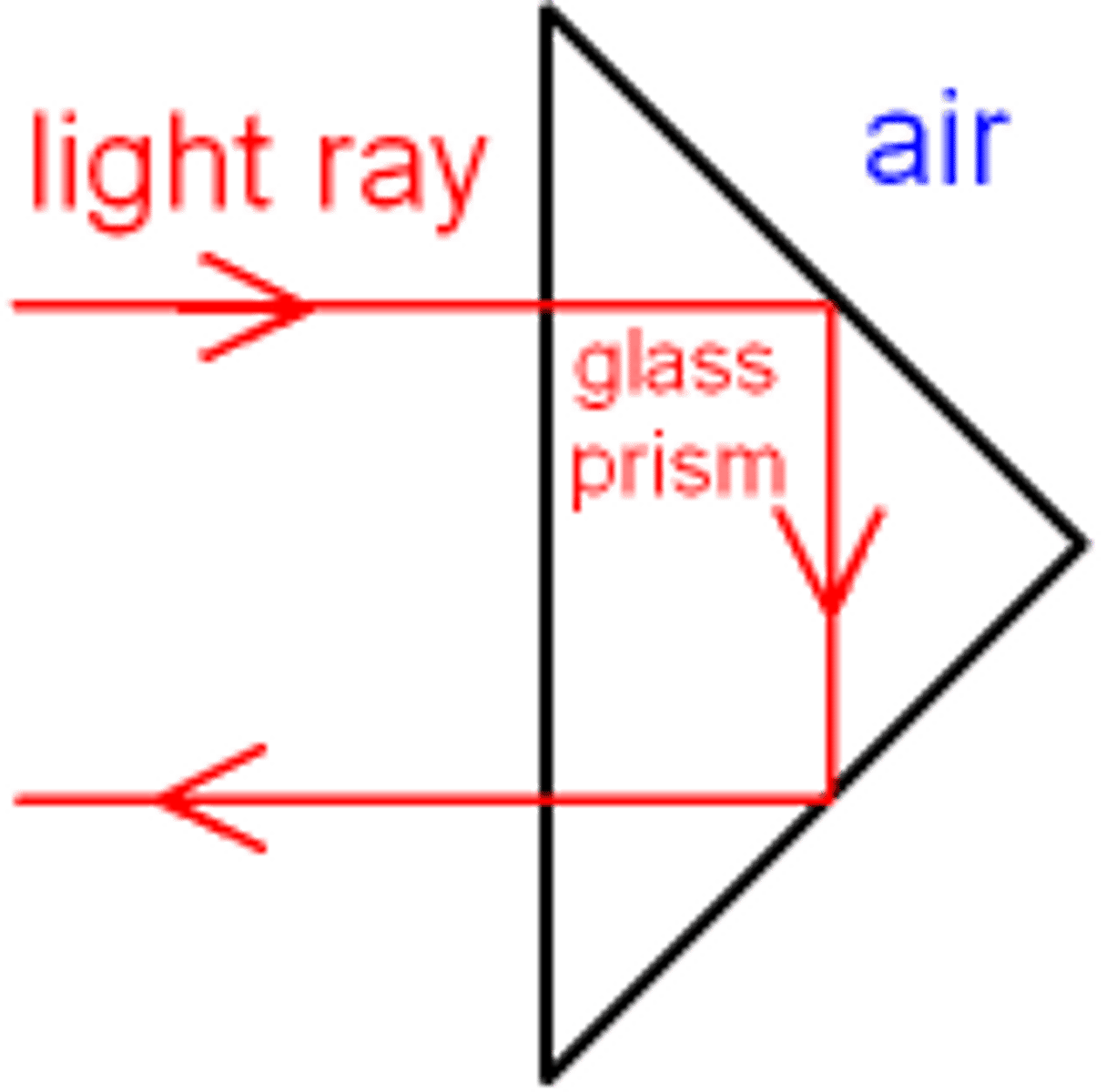
How can a prism act as a reflector?
By total internal reflection. The incident light strikes the back of the prism at an angle greater than the critical angle. This in turn reflects again off the other surface, reflecting the light out entirely.
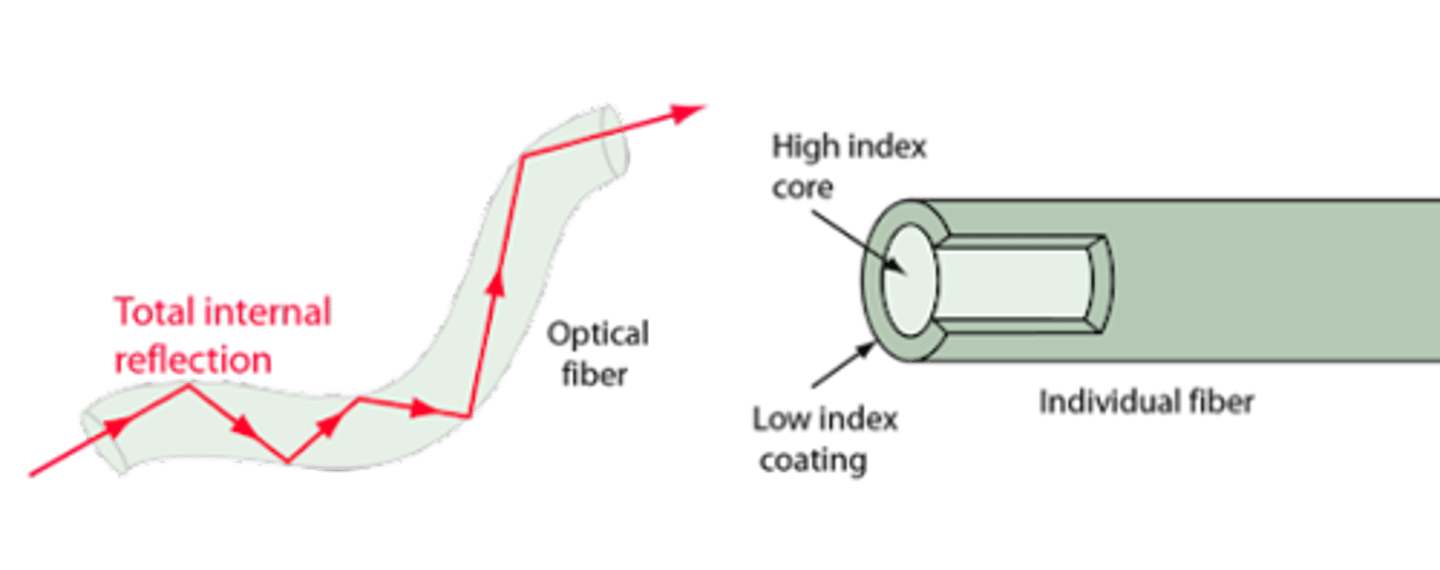
How do optical fibers transmit light?
A high index inner core.
A low index outer cladding.
The light strikes the boundary between the two mediums at an angle greater than the critical angle. This results in total internal reflection. This repeats down the optical fiber.
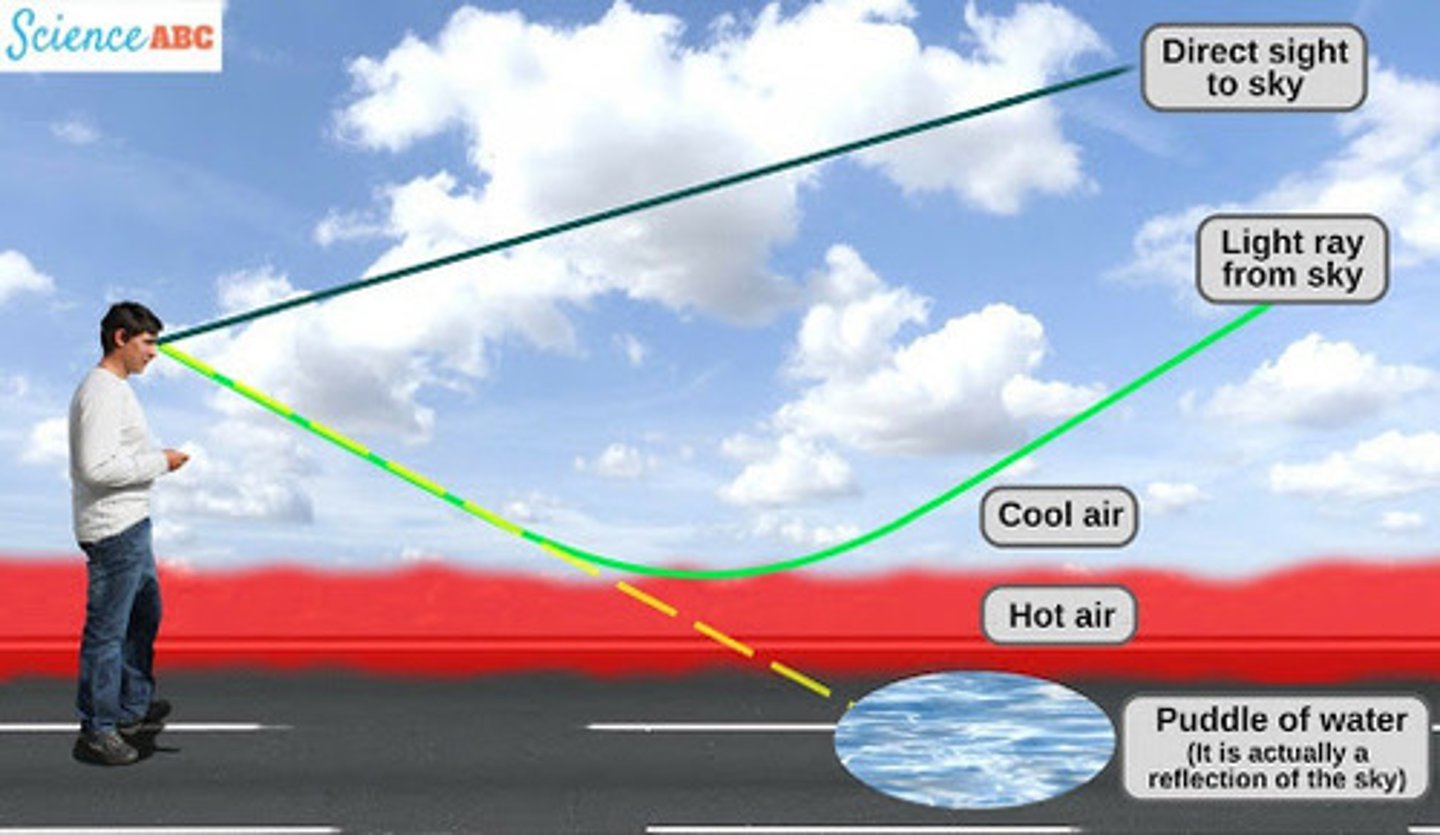
How are mirages formed?
Hot air sits directly above a hot surface (e.g. road/desert)
The air up higher is cooler and more dense.
Light is travelling from a more dense medium (cool air) to a less dense medium (warm air). It refracts away from the normal.
This happens continuously until it eventually gets totally internally reflected.
The observer see's a reflection of the sky (but thinks it's a puddle)
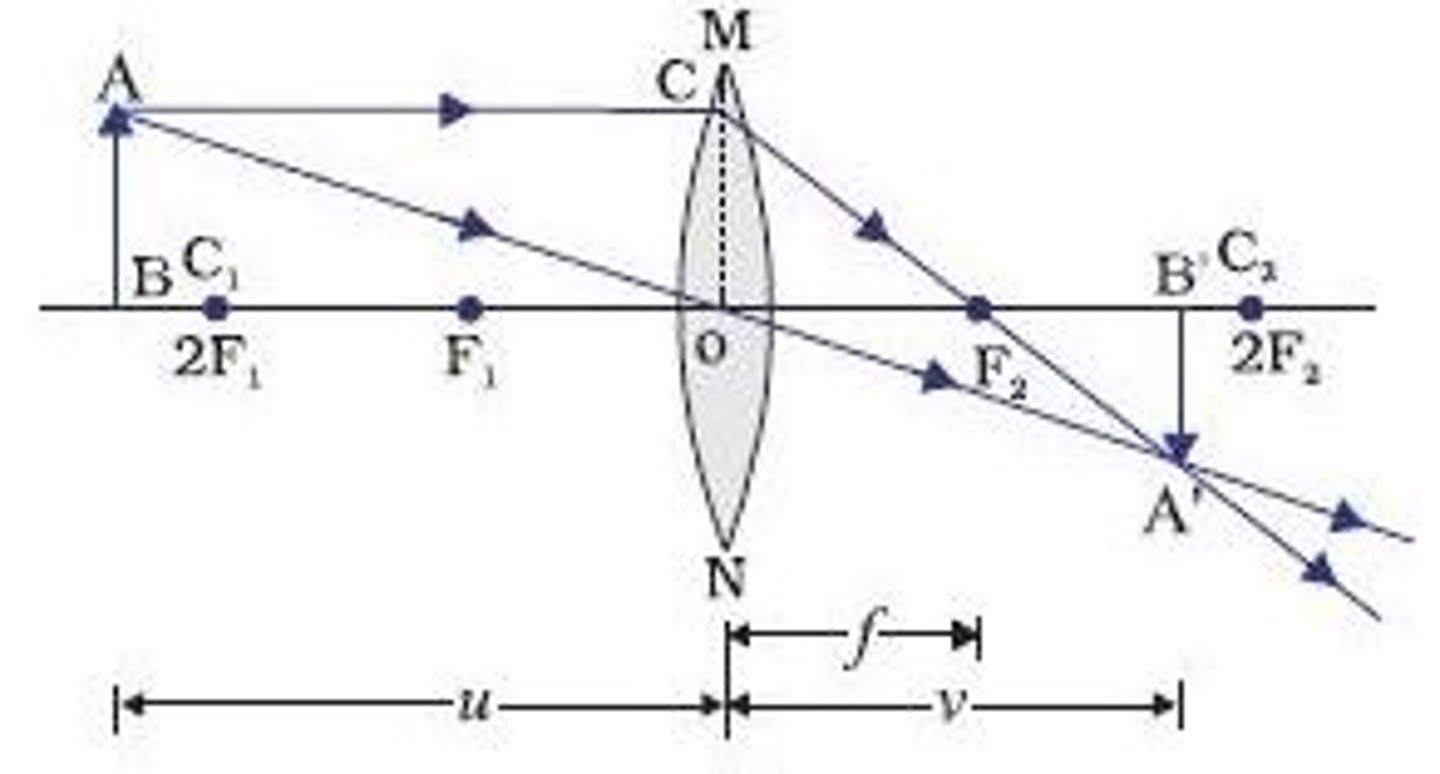
Convex Lens - object beyond 2F (Diagram & Nature of Image)
L - Between F and 2F
O - Inverted
S - Diminished
T - Real
Convex Lens - object on 2F (Diagram & Nature of Image)
L - on 2F
O - Inverted
S - Same size
T - Real
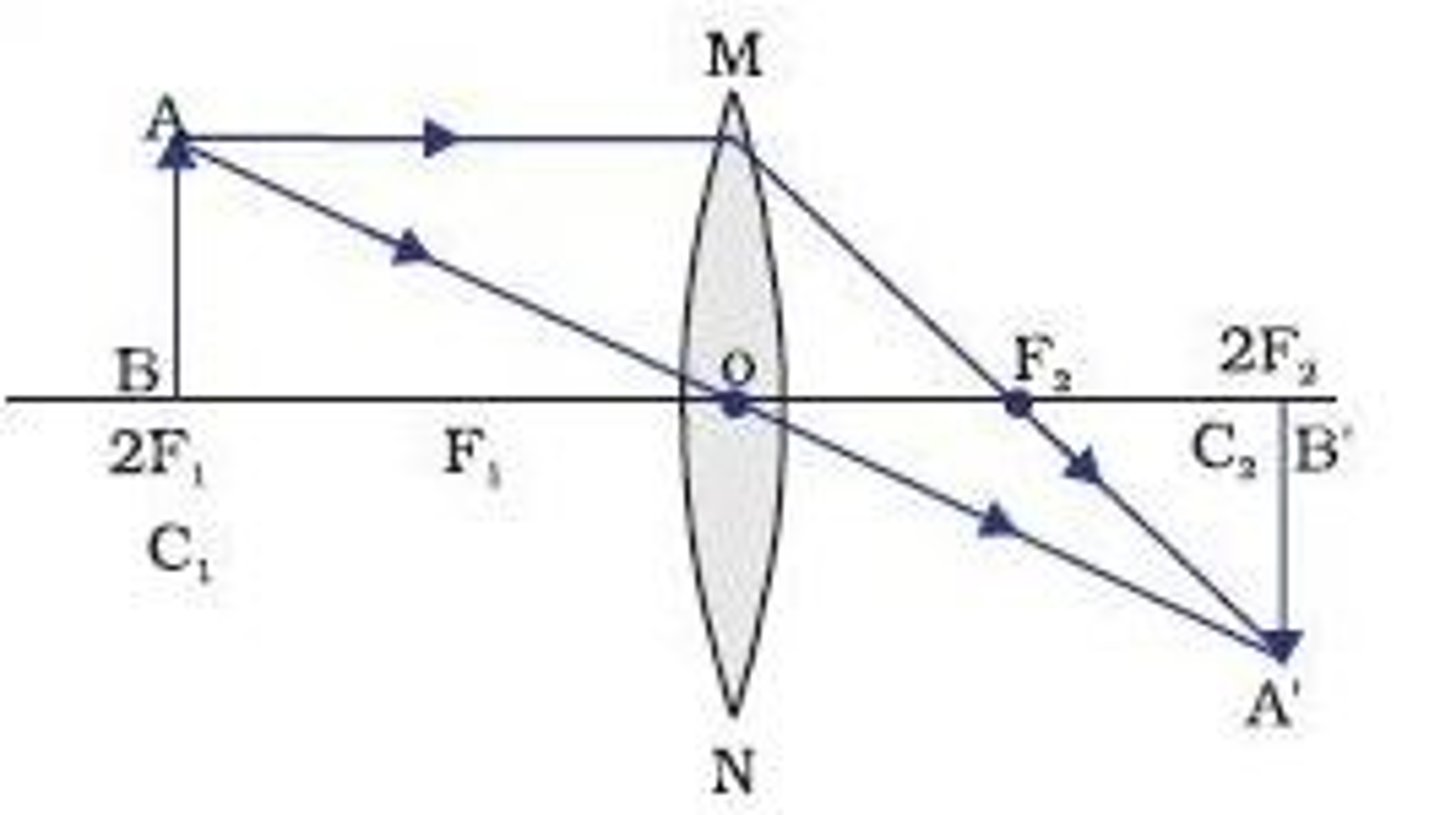
Convex Lens - object between F and 2F (Diagram & Nature of Image)
L - beyond 2F
O - Inverted
S - Magnified
T - Real
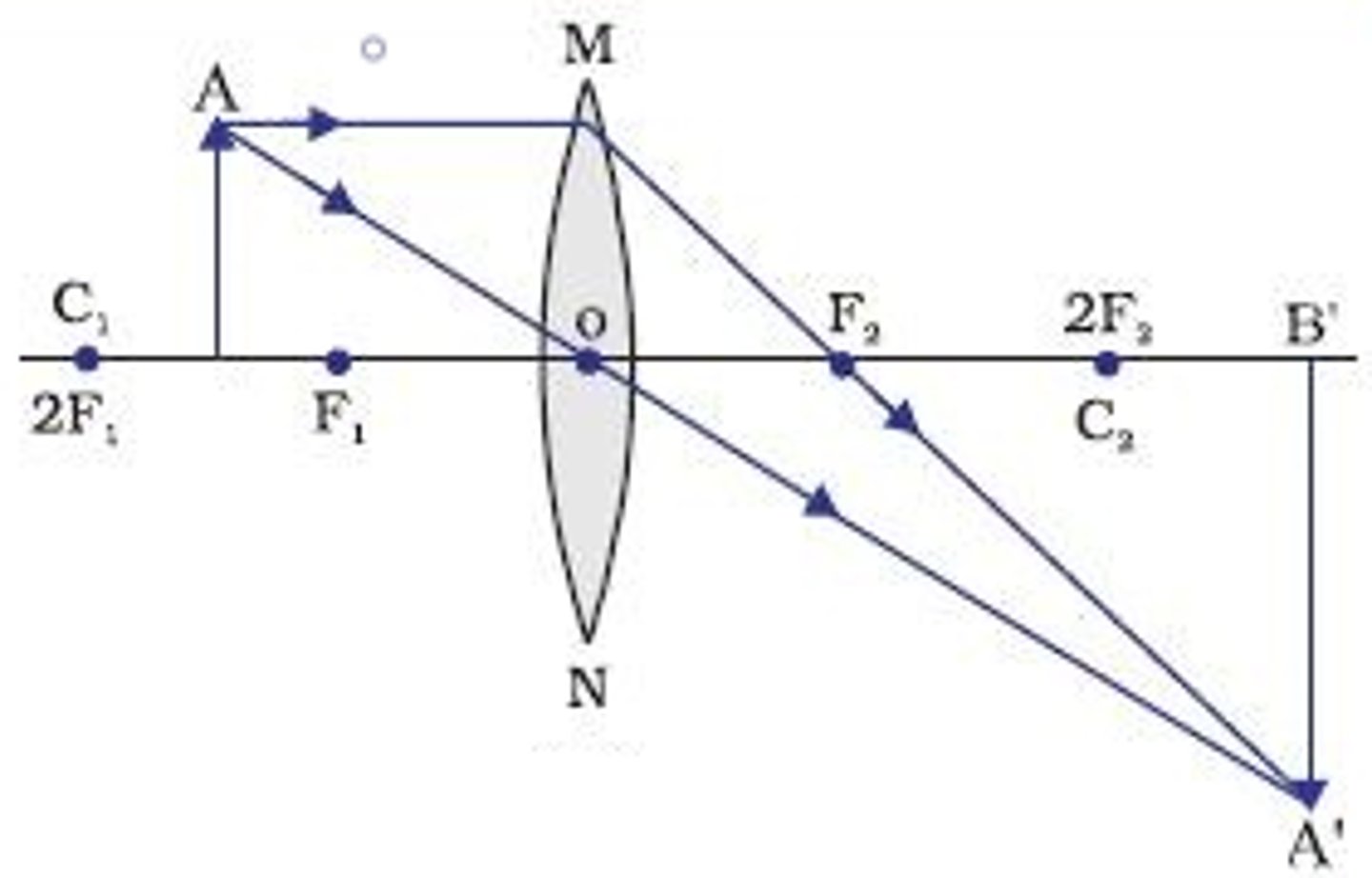
Convex Lens - object on F (Diagram & Nature of Image)
No image formed.
Rays parallel and do not meet.
Blurry.
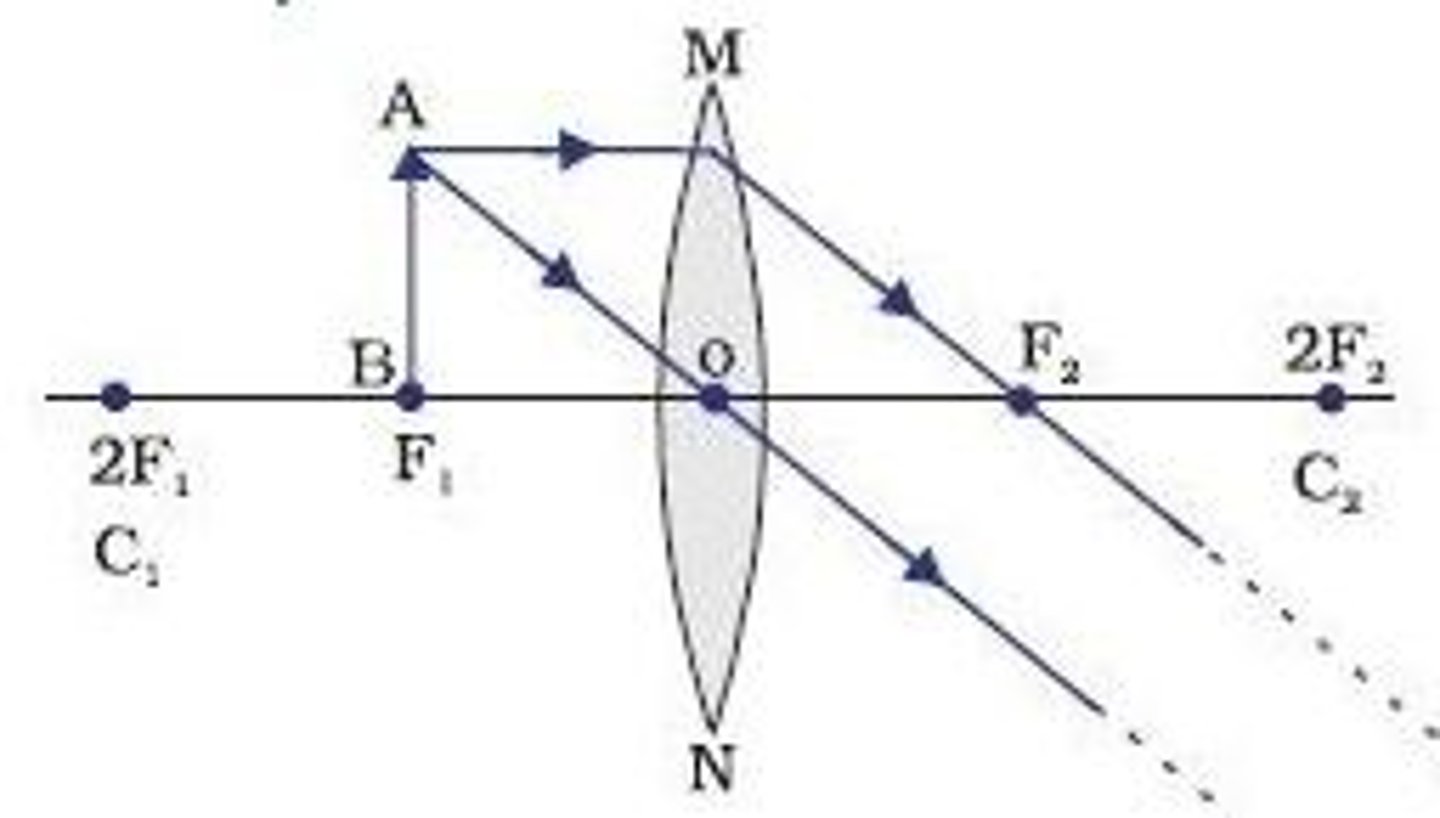
Convex Lens - object between F and mirror (Diagram & Nature of Image)
L - behind object
O - Erect/Upright
S - Magnified
T - Virtual
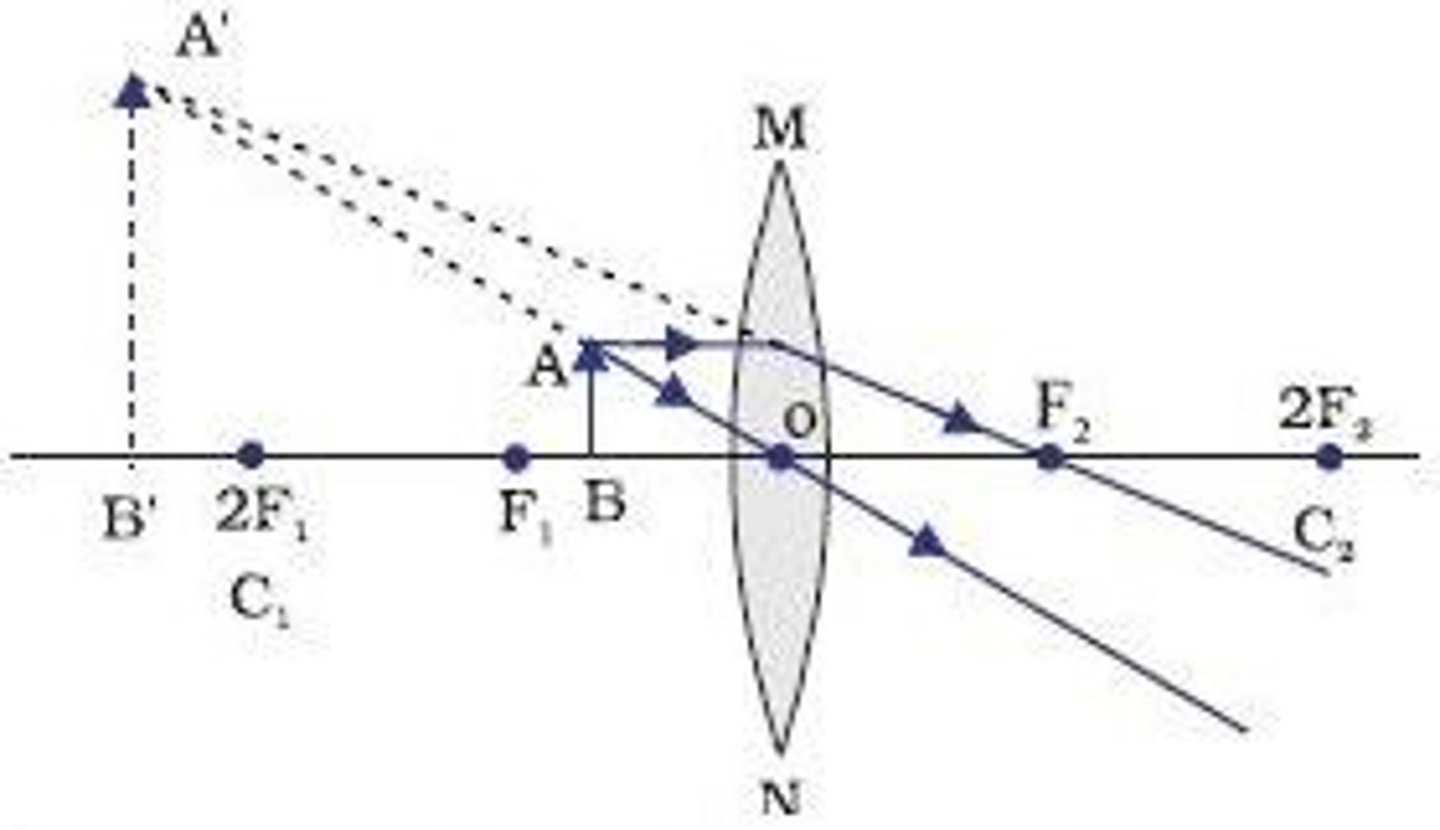
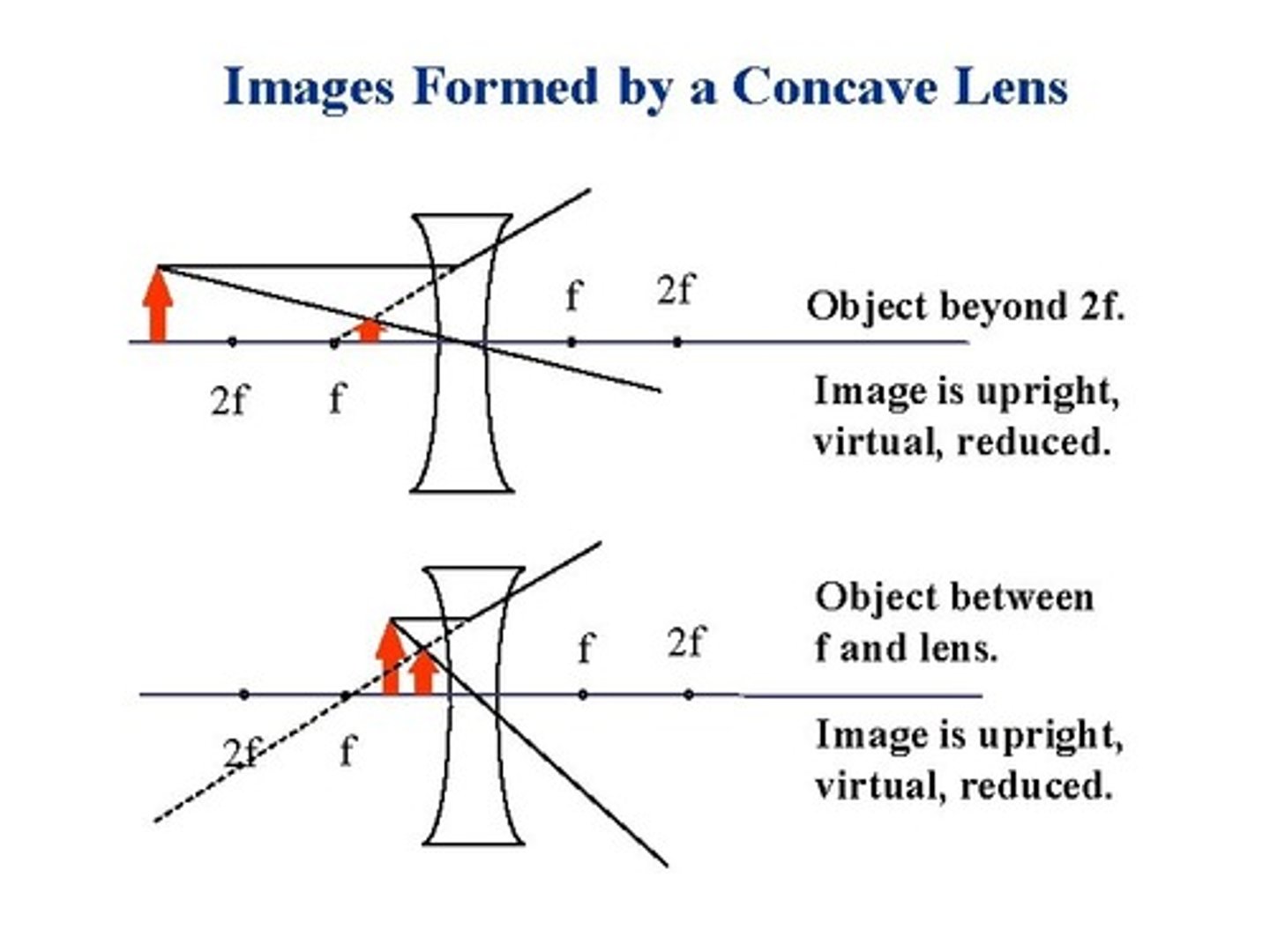
Concave Lens (Diagram & Nature of Image)
L - Between object and lens
O - Erect/Upright
S - Diminished
T - Virtual
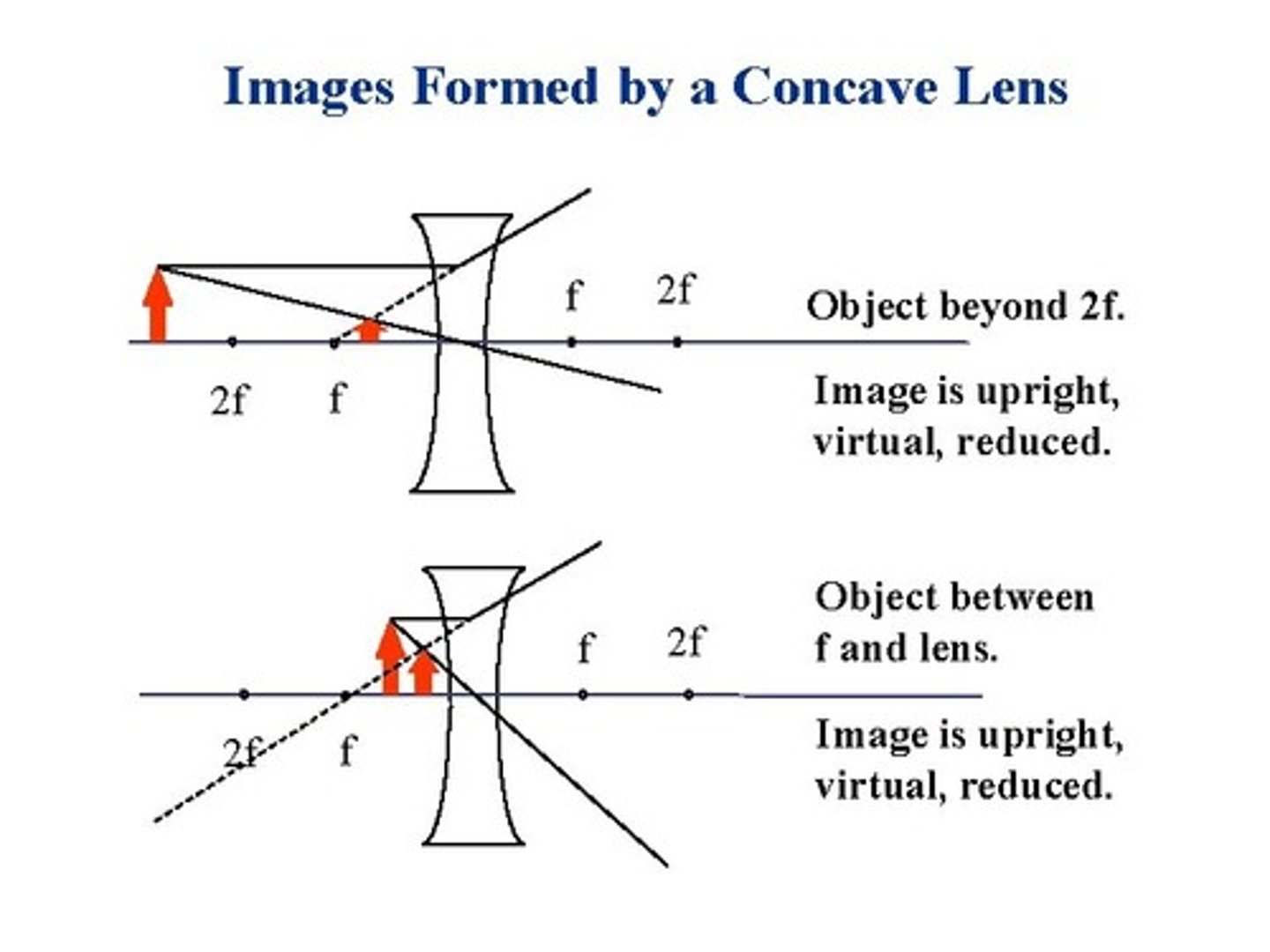
Why would a concave lens not be appropriate as a magnifying glass?
Image is always diminished.
Lens Equation
1/f = 1/u + 1/v
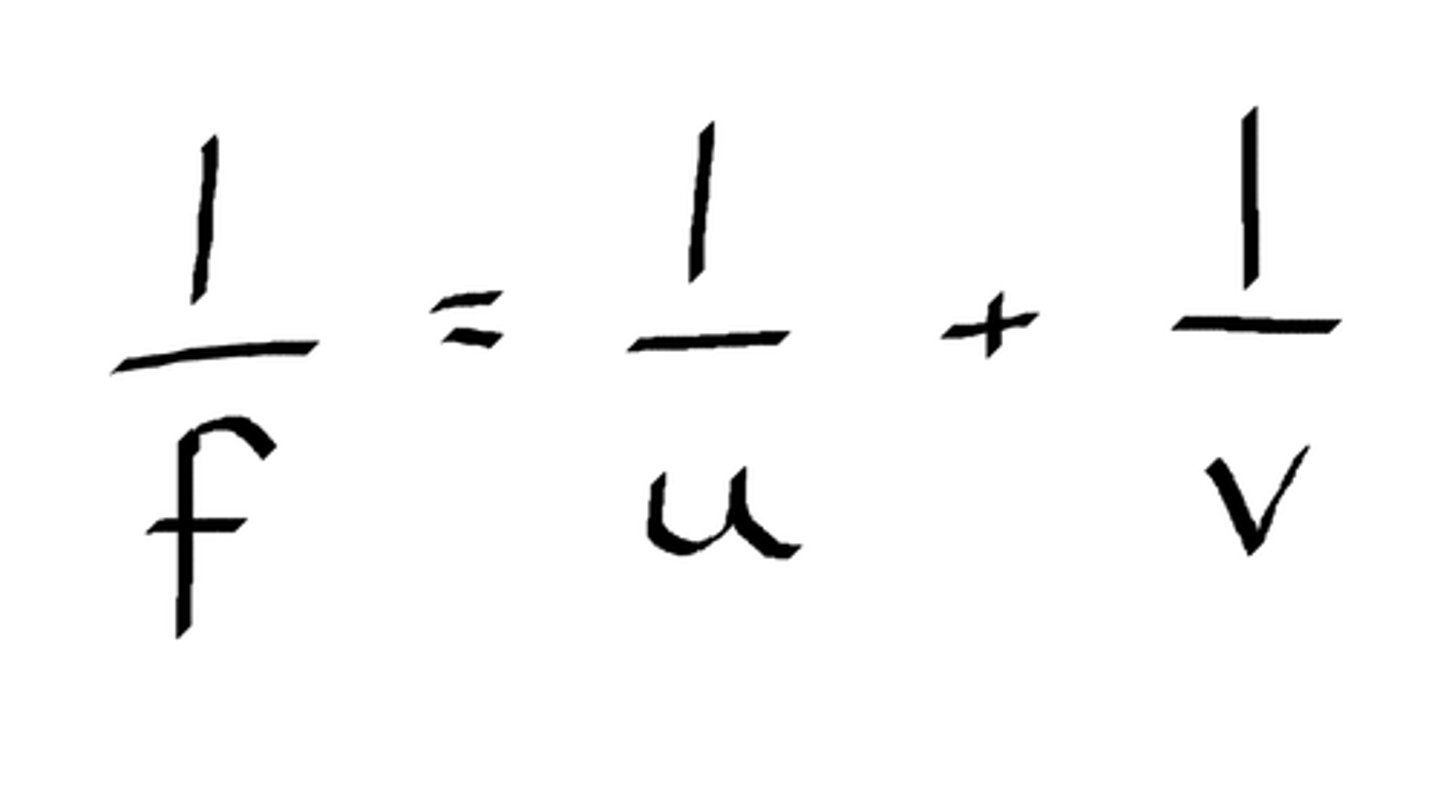
Magnification Equation
m = v / u
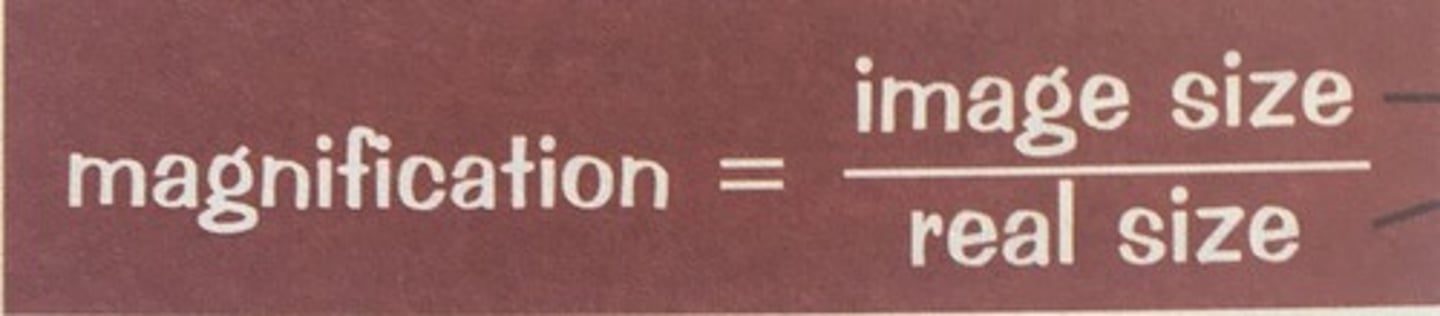
Sign convention for Lens Equations
converging mirror: f is +
diverging mirror: f is -
Real image: v is +
Virtual image: v is -
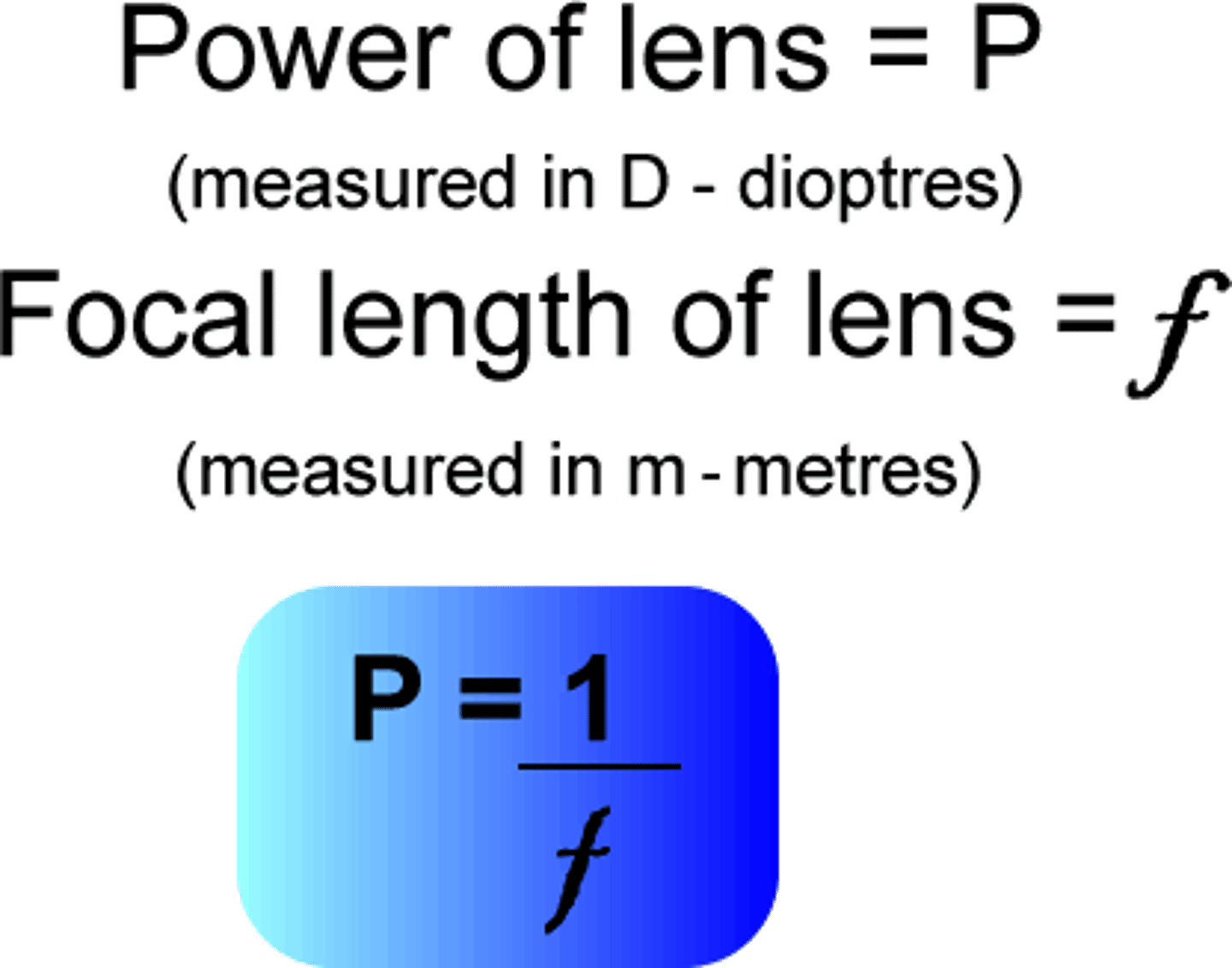
Power of a Lens Equation
P = 1/f
Power of lenses in a series
P = P1 + P2 + P3...
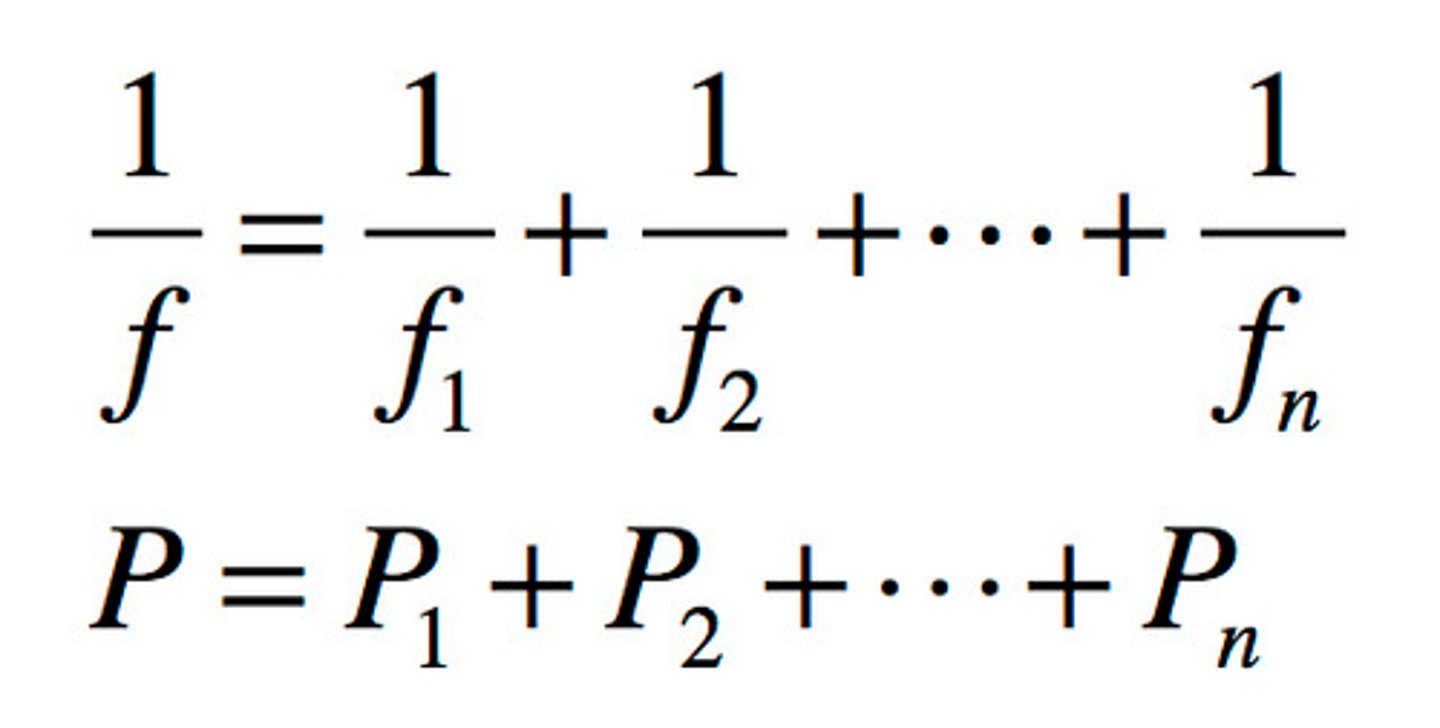
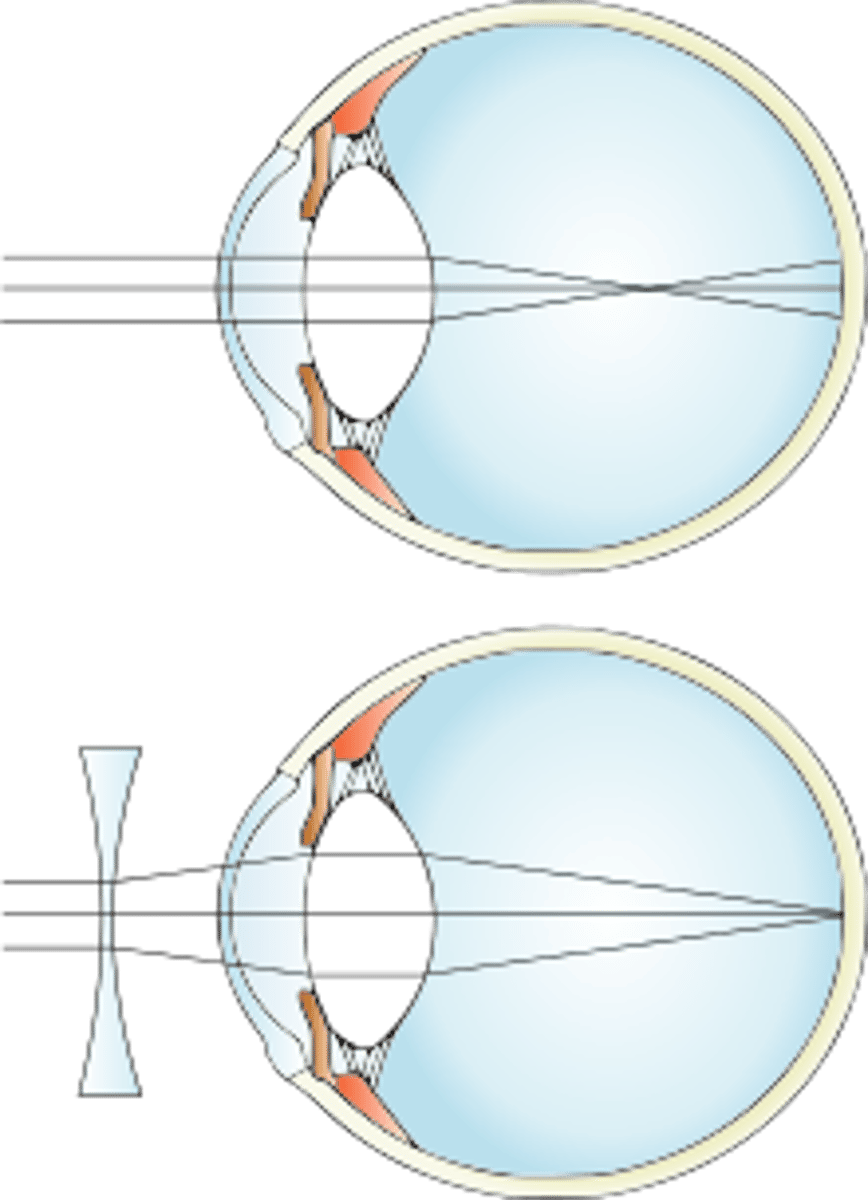
What is the technical name for shortsightedness?
Myopia
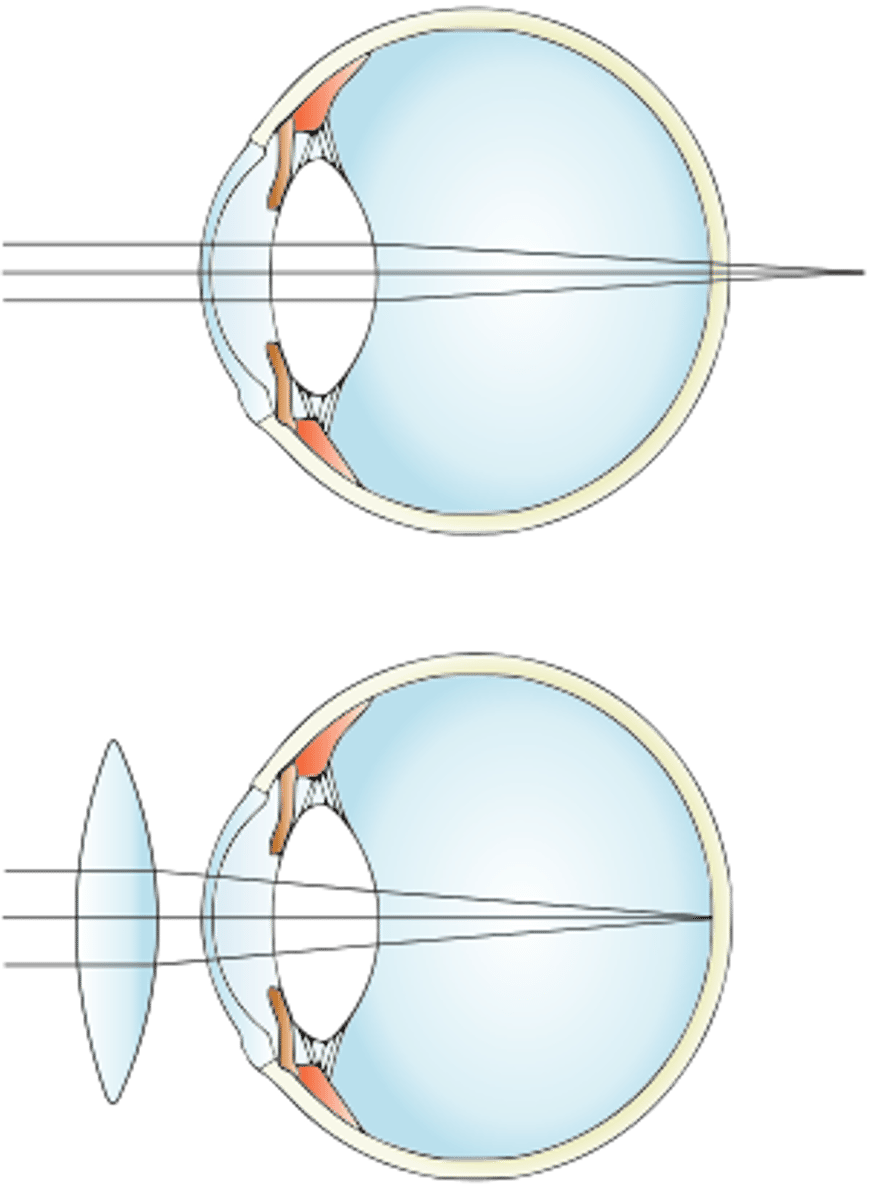
What is the technical name for long-sightedness?
Hypermetropia
How do you correct shortsightedness?
A concave lens (or diverging lens)
How do you correct long-sightedness?
A convex lens (or converging lens)
What is the pupil in the eye?
A small opening in the center of the eye which allows light in to hit the retina.
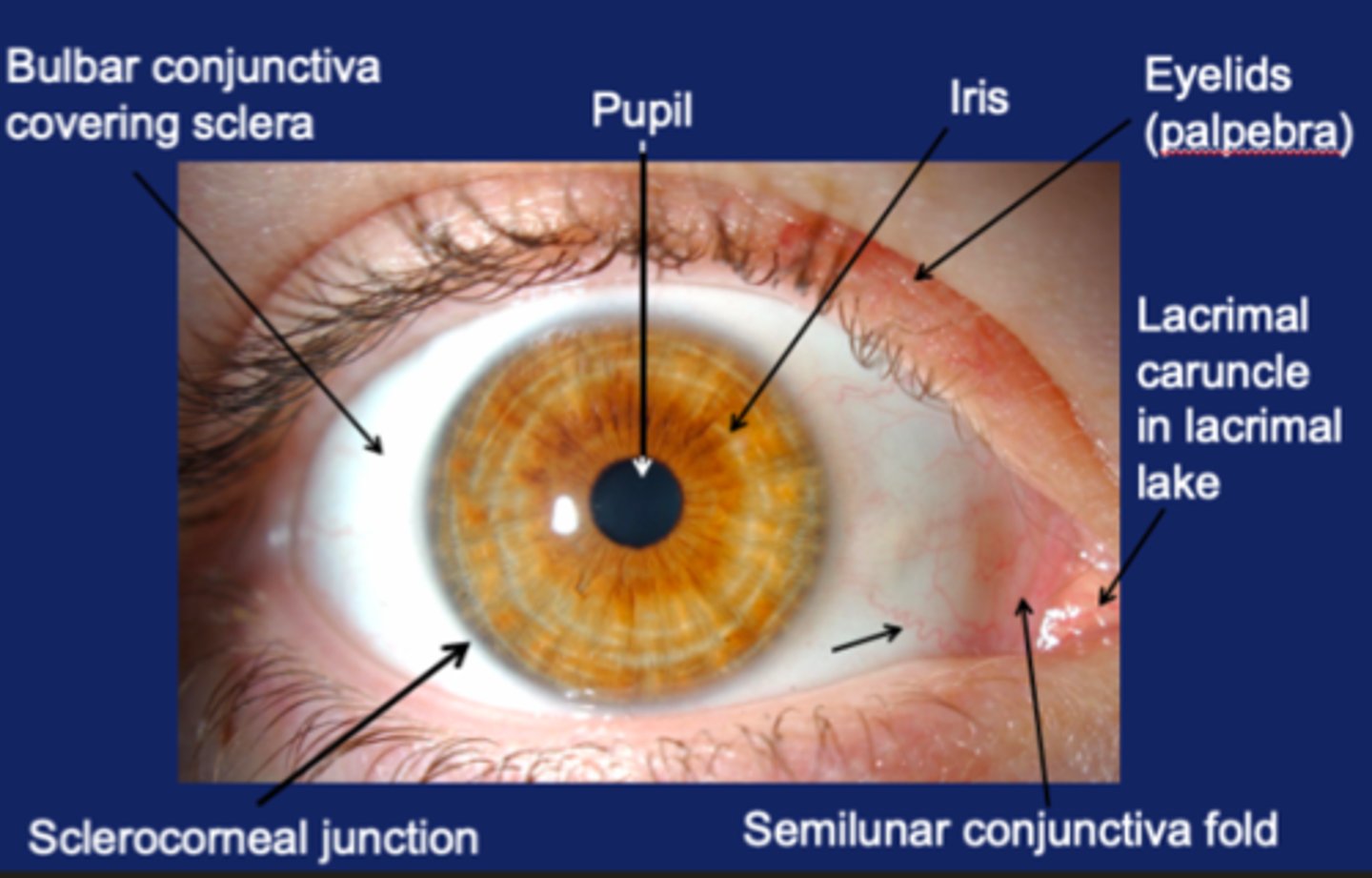
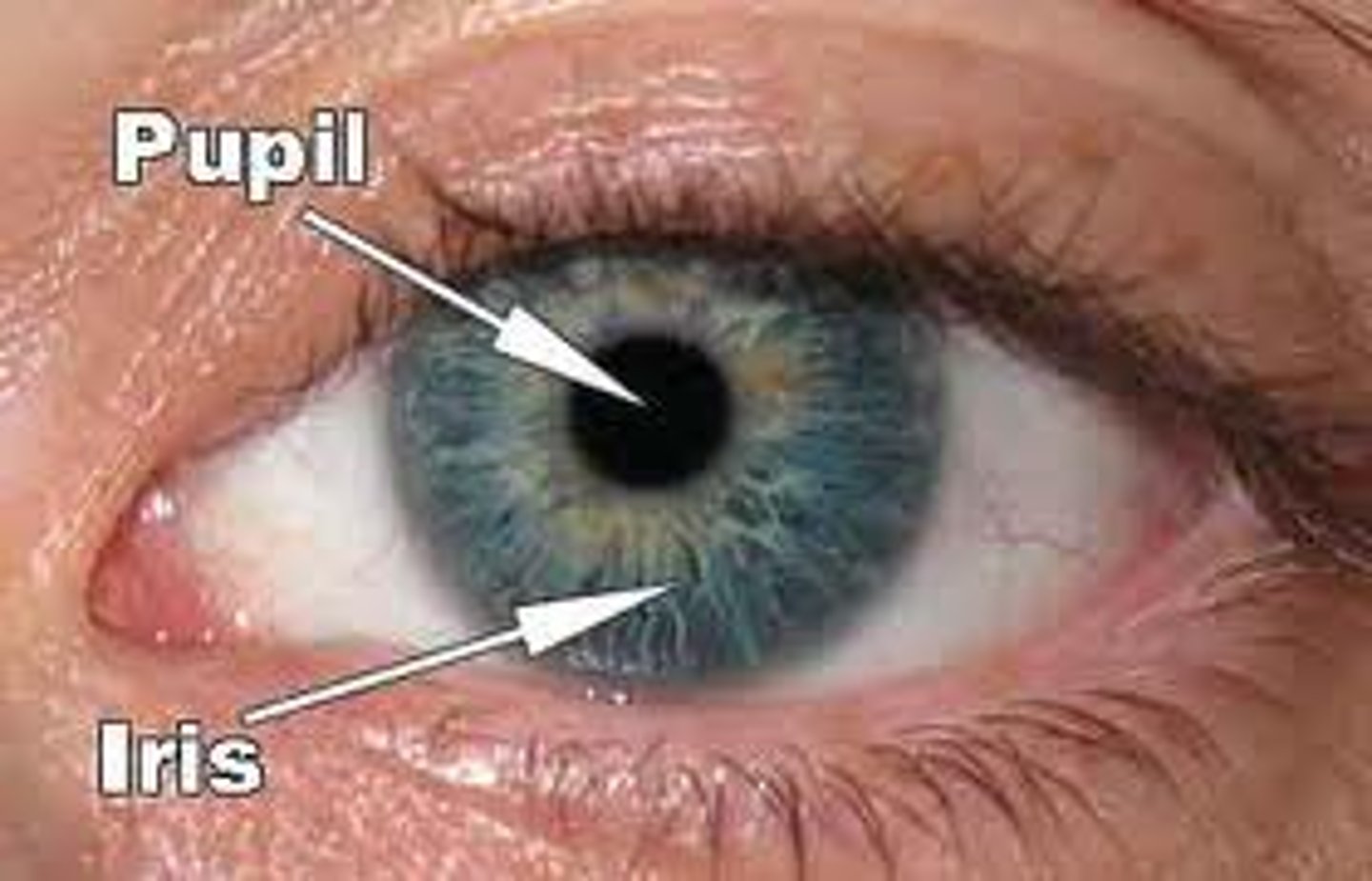
What is the iris of the eye?
Is the colored portion of the eye that dilates or constricts the pupil in response to light. It controls the amount of light entering the eye.
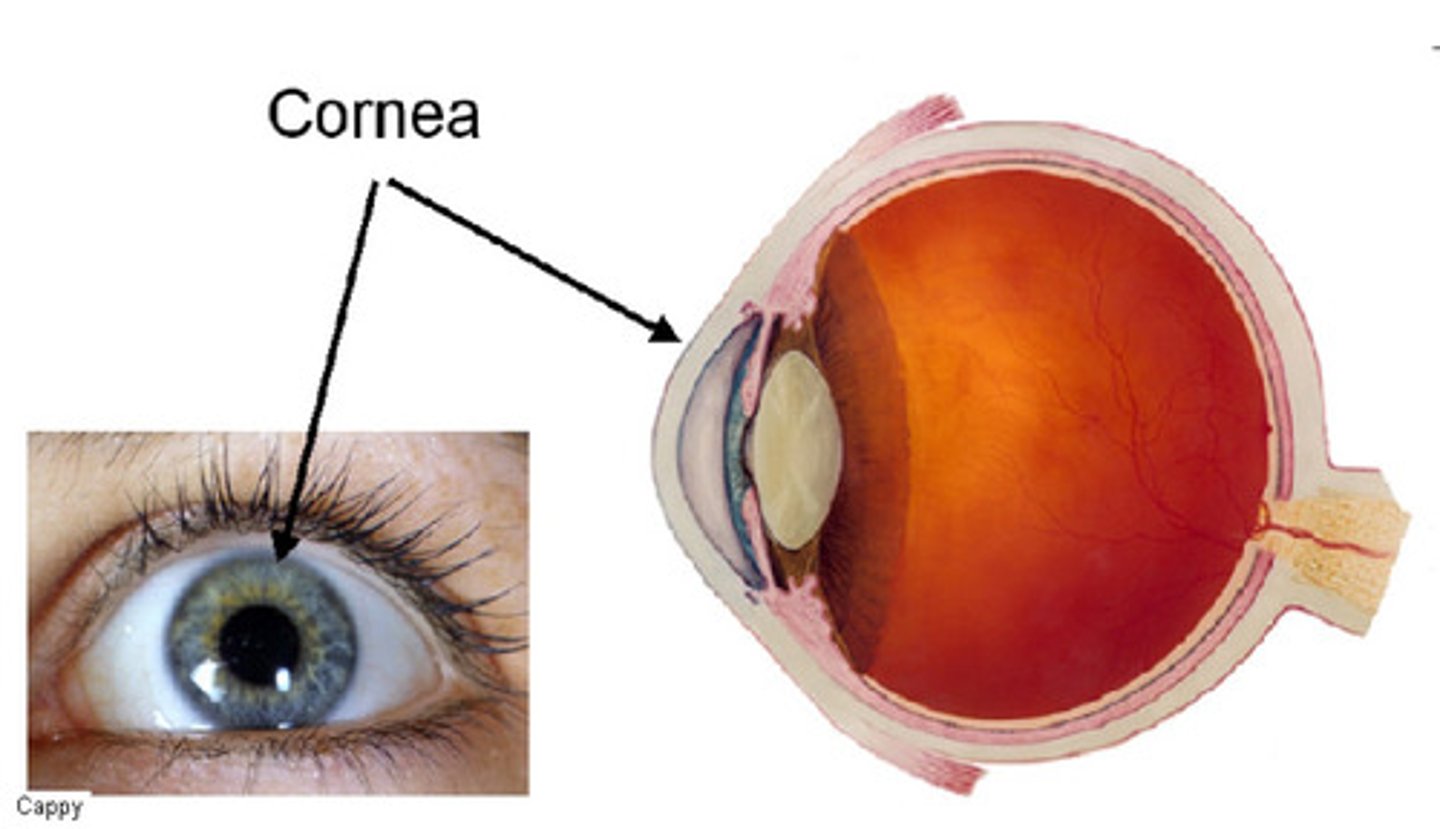
What is the function of the cornea?
Refracts light as it enters the eye.
What is the function of the sclerotic coat?
A firm fibrous membrane that maintains the shape of the eye as an approximately globe shape.
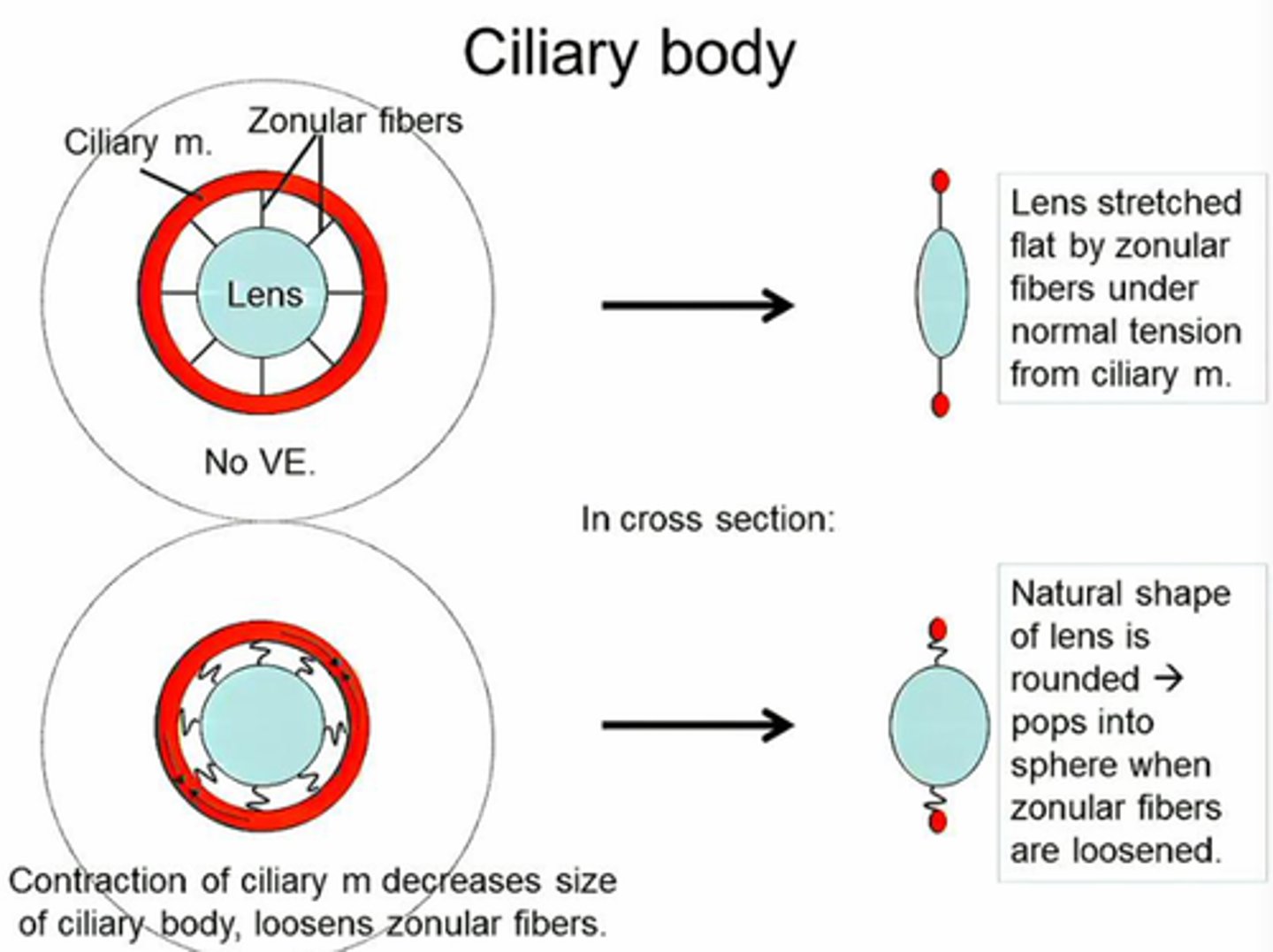
What do the ciliary muscles do?
Change the shape of the lens.
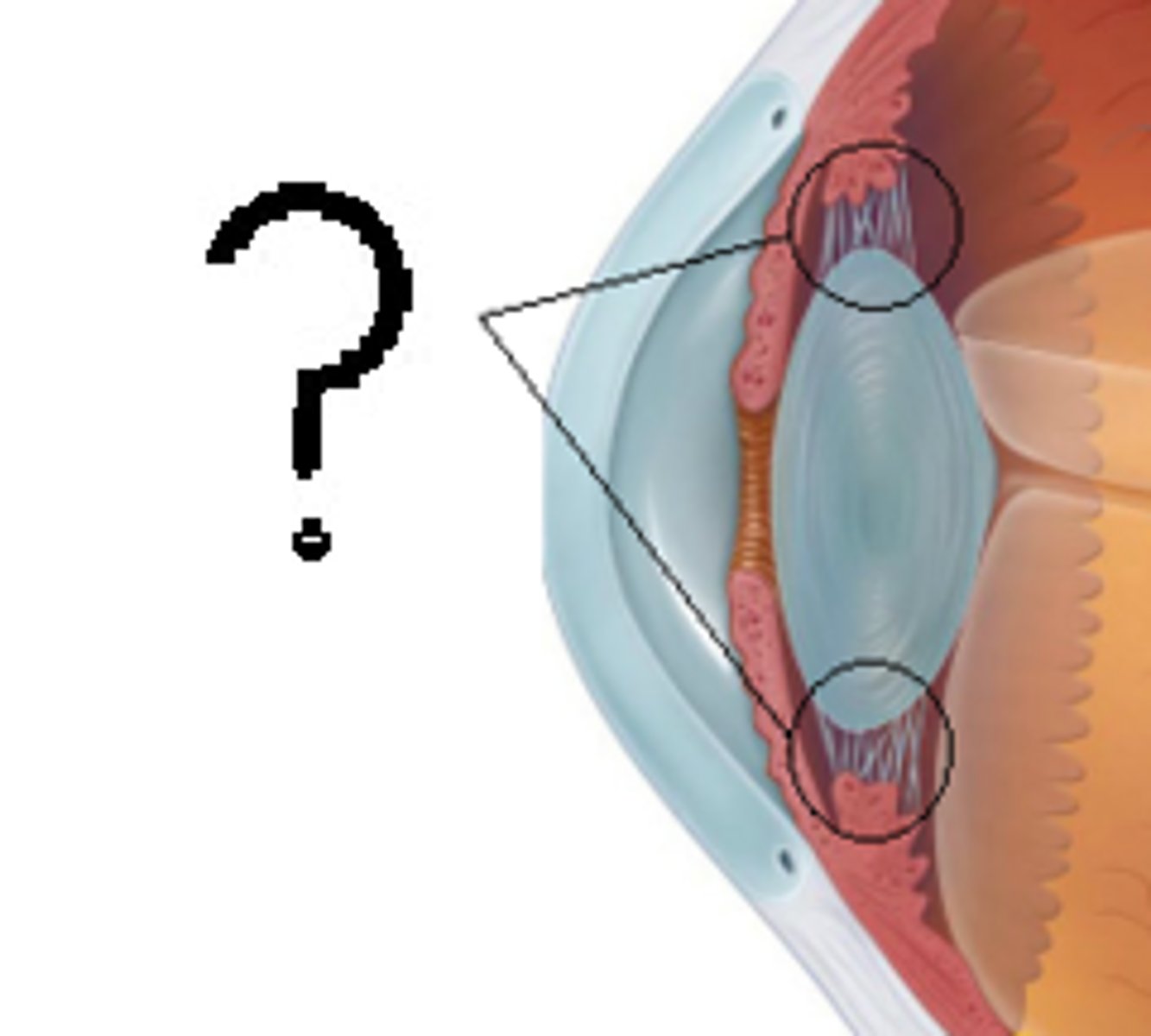
What is accommodation of the eye?
The process of changing the shape of the lens to focus on near or distant objects.
Draw a diagram of the eye.
n/a
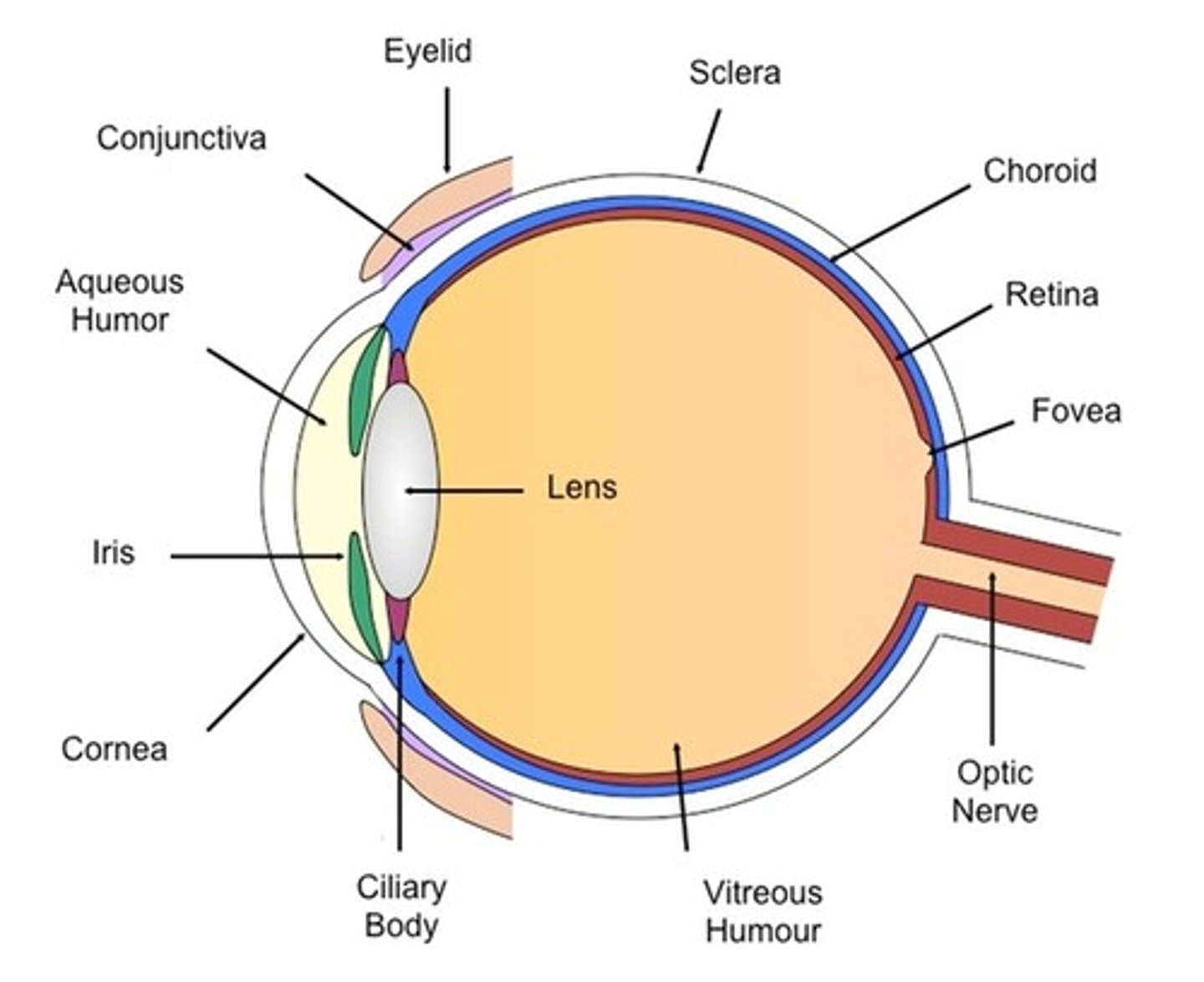
What does the optic nerve do?
Carries impulses from the receptors to the brain
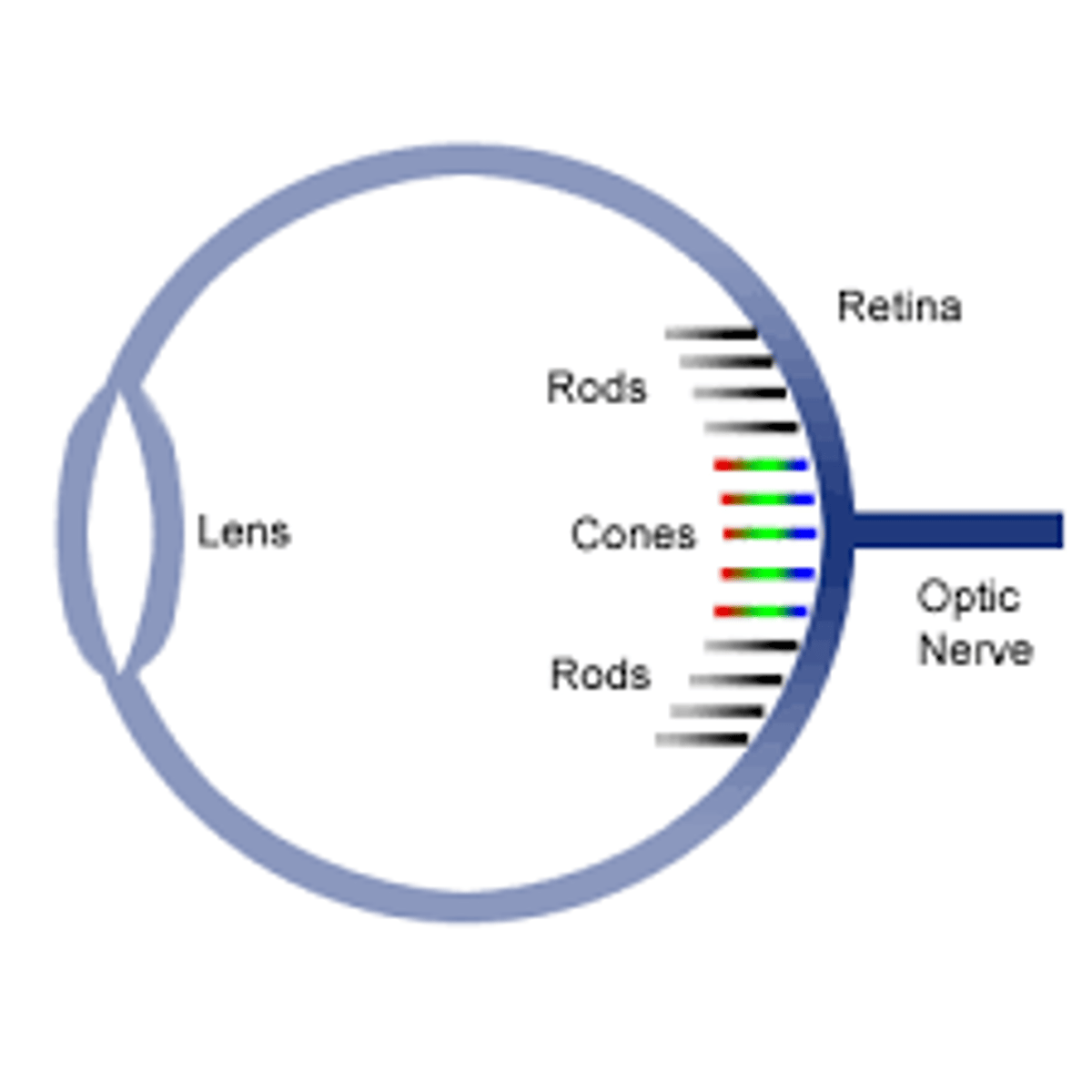
What does the retina contain?
Photoreceptors (rods and cones)
Precautions when determining the focal length of a convex lens (4)
approximate value was found to ensure the object was placed outside the focal point
image position determined when a sharp focused image is formed on the screen
measure all distances to the centre of the lens
avoid parallax error
Precaution when finding refractive index using Snell’s Law
Avoid small angles of incidence as the angle of refraction will always be smaller. Smaller angles means greater percentage error.
Avoid parallax error
drawing a graph is more accurate than individual calculations as outliers can be identified and slope gives weighted mean